The Analysis of Partial Sequences of the Flavonone 3 Hydroxylase Gene in Lupinus mutabilis Reveals Differential Expression of Two Paralogues Potentially Related to Seed Coat Colour
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
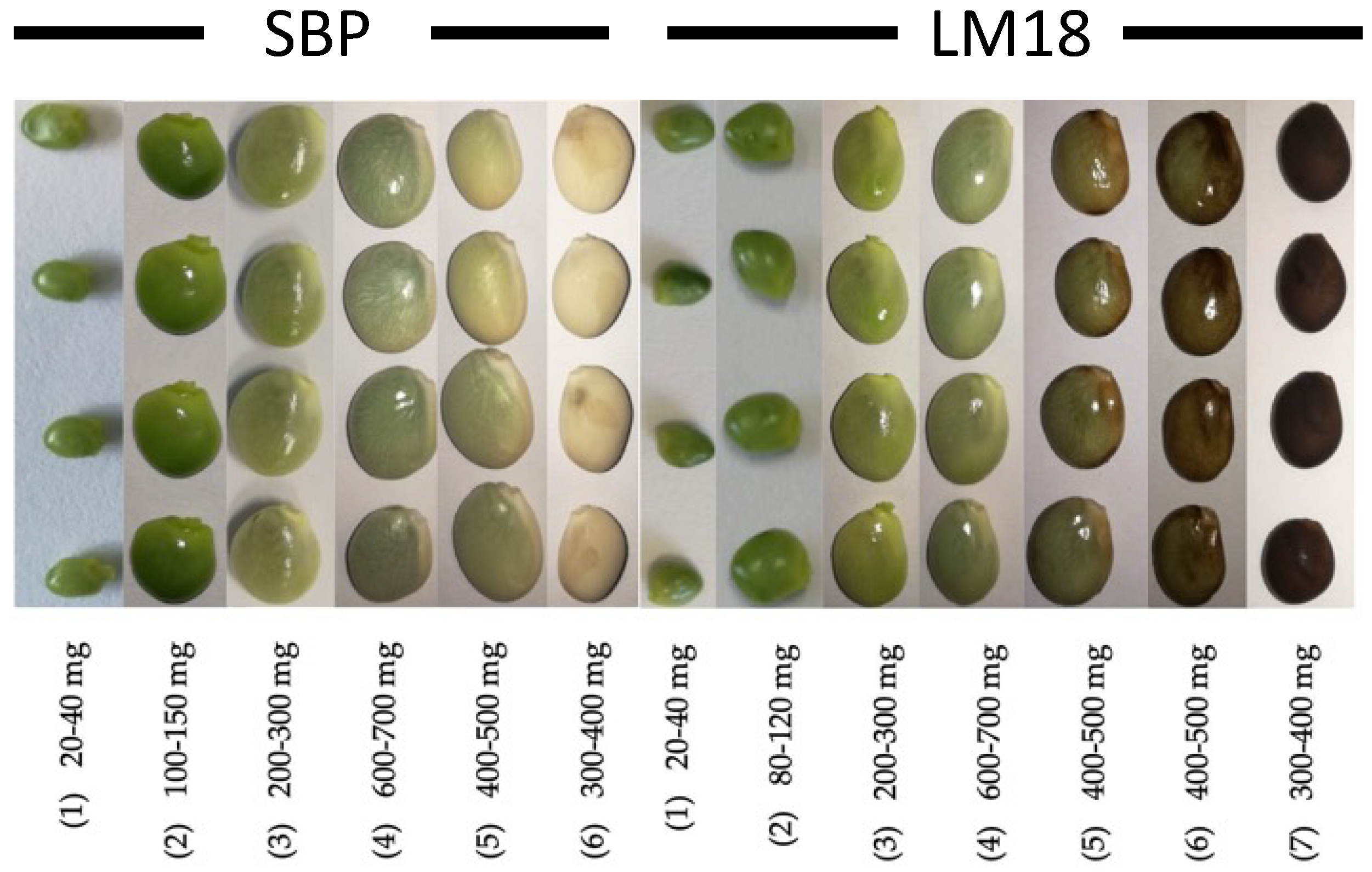
2.1. Plant Material
2.2. Gene Analysis
2.3. Transcription Analysis
2.3.1. Reference Genes
2.3.2. Quantitative Reverse-Transcription PCR
3. Results
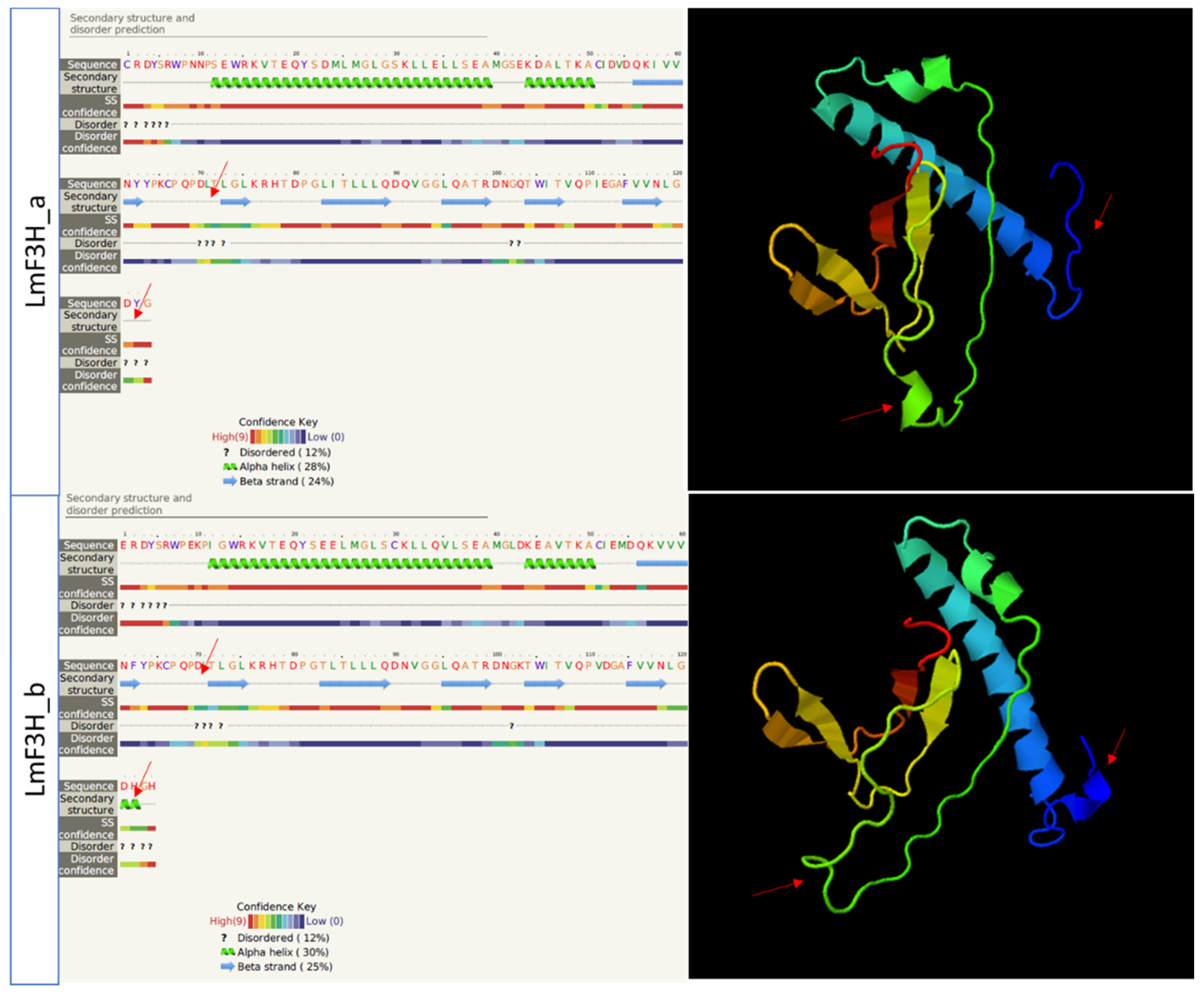
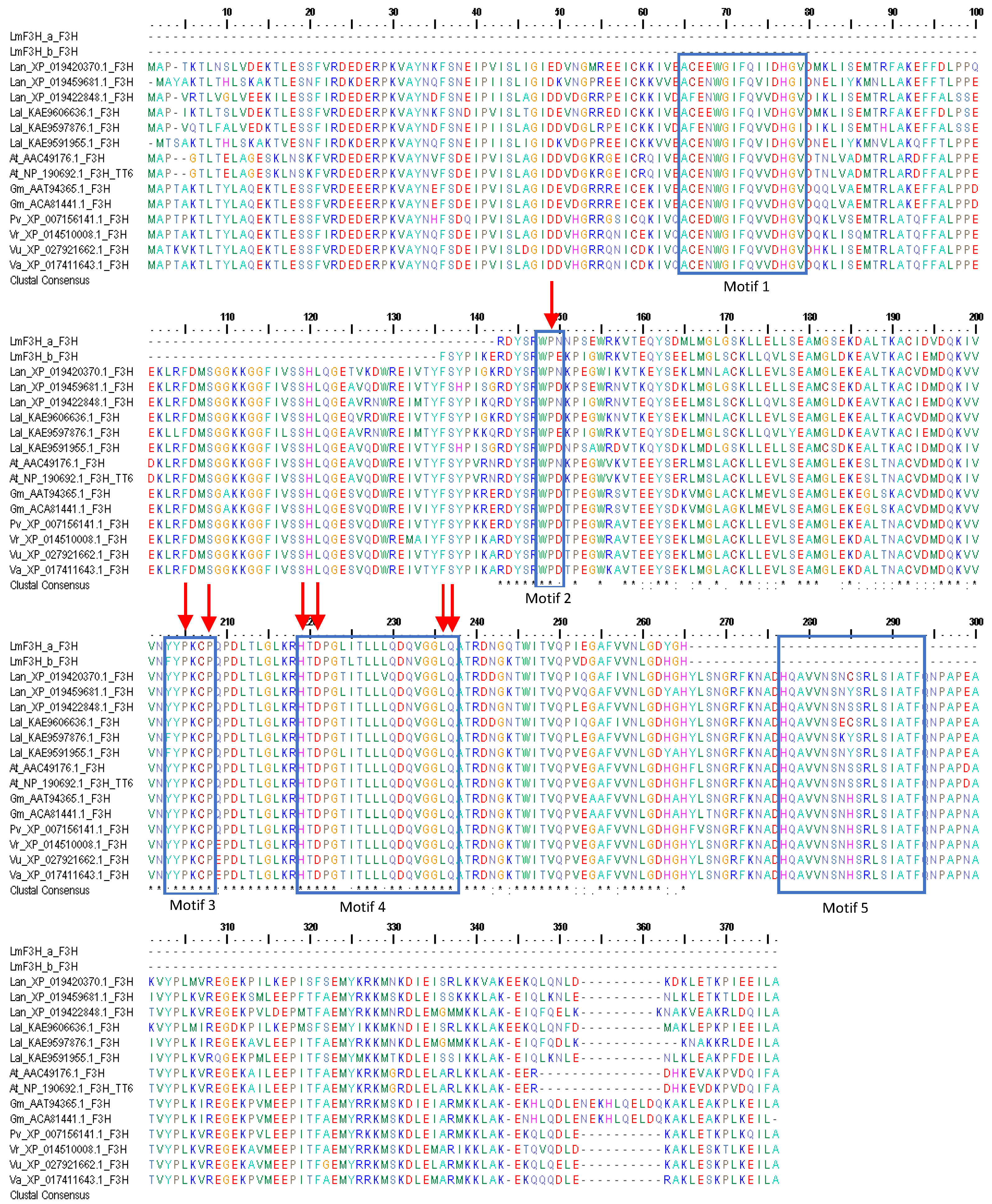
3.1. DNA Sequences Analysis
3.2. Gene Expression Analysis
3.2.1. Selection and Validation of Reference Genes
3.2.2. Expression Profiles of LmF3h_a and LmF3h_b
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lepiniec, L.; Debeaujon, I.; Routaboul, J.M.; Baudry, A.; Pourcel, L.; Nesi, N.; Caboche, M. Genetics and biochemistry of seed flavonoids. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2006, 57, 405–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunetti, C.; Di Ferdinando, M.; Fini, A.; Pollastri, S.; Tattini, M. Flavonoids as antioxidants and developmental regulators: Relative significance in plants and humans. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 3540–3555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, N.U.; Park, J.; Jung, H.J.; Yoonkang Hur, Y.; Nou, S.-I. Anthocyanin biosynthesis for cold and freezing stress tolerance and desirable colour in Brassica rapa. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2015, 15, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panche, A.; Diwan, A.; Chandra, S. Flavonoids: An overview. J. Nutr. Sci. 2016, 5, e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarial, R.; Thakur, S.; Sakinah, M.; Zularisam, A.W.; Sharad, A.; Kanwar, S.S.; Singh, L. Potent anticancer antioxidant and antibacterial activities of isolated flavonoids from Asplenium nidus. J. King Saud Univ.-Sci. 2018, 30, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaakola, L.; Määttä, K.; Pirttilä, A.M.; Törrönen, R.; Kärenlampi, S.; Hohtola, A. Expression of genes involved in anthocyanin biosynthesis in relation to anthocyanin, proanthocyanidin, and flavonol levels during bilberry fruit development. Plant Physiol. 2002, 130, 729–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, N.; Cheng, F.; Wu, J.; Liu, B.; Zheng, S.N.; Liang, J.L.; Wang, X.W. Anthocyanin biosynthetic genes in Brassica rapa. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grotewold, E. The genetics and biochemistry of floral pigments. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2006, 57, 761–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quattrocchio, F.; Wing, J.F.; Leppen, H.T.C.; Mol, J.N.M.; Koes, R.E. Regulatory genes controlling anthocyanin pigmentation are functionally conserved among plant species and have distinct sets of target genes. Plant Cell 1993, 5, 1497–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirley, B. Flavonoid biosynthesis. A colorful model for genetics biochemistry cell biology and biotechnology. Plant Physiol. 2001, 126, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Huang, K.; Liu, Y.; Jiao, T.; Ma, G.; Qian, Y.; Wang, P.; Dai, X.; Gao, L.; Xia, T. Functional Analysis of Two Flavanone-3-Hydroxylase Genes from Camellia sinensis: A Critical Role in Flavonoid Accumulation. Genes 2017, 8, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charrier, B.; Coronado, C.; Kondorosi, A.; Ratet, P. Molecular characterization and expression of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) flavanone-3-hydroxylase and dihydroflavonol-4-reductase encoding genes. Plant Mol. Biol. 1995, 29, 773–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cotting, R.M.; Hosfîeld, G.L. Flavanone 3-Hydroxylase: A Candidate Gene Product for the P Color Gene. USDA Pub. 2005, 48, 38–39. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, X.; Martens, S.; Chen, M.; Li, D.; Dong, J.; Tao, W. Cloning and characterization of a functional flavanone-3-hydroxylase gene from Medicago truncatula. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2009, 37, 3283–3289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Wang, J.; Chu, S.; Yan, H.; Yu, D. Diversifying Selection on Flavanone 3- Hydroxylase and Isoflavone Synthase Genes in Cultivated Soybean and Its Wild Progenitors. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- McClean, P.E.; Lee, R.K.; Otto, C.; Gepts, P.; Bassett, M.J. Molecular and phenotypic mapping of genes controlling seed coat pattern and colour in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). J. Hered. 2002, 93, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, H.; Borisjuk, L.; Wobus, U. Molecular physiology of legume seed development. Ann. Rev. Plant Biol. 2005, 56, 253–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellaloui, N. Soybean seed phenol lignin and isoflavones partitioning as affected by seed node position and genotype differences. Food Nutr. Sci. 2012, 3, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Todd, J.J.; Vodkin, L.O. Pigmented soybean (Glycine max) seed coats accumulate proanthocyanidins during development. Plant Physiol. 1993, 102, 663–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devic, M.; Guilleminot, J.; Debeaujon, I.; Bechtold, N.; Bensaude, E.; Koornneef, M.; Pelletier, G.; Delseny, M. The BANYULS gene encodes a DFR-like protein and is a marker of early seed coat development. Plant J. 1999, 19, 387–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debeaujon, I.; Peeters, A.J.M.; Léon-Kloosterziel, K.M.; Koornneef, M. The TRANSPARENT TESTA12 gene of Arabidopsis encodes a multidrug secondary transporter–like protein required for flavonoid sequestration in vacuoles of the seed coat endothelium. Plant Cell 2001, 13, 853–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, R.; Min, C.W.; Kim, S.W.; Wang, Y.; Agrawal, G.K.; Rakwal, R.; Kim, G.S.; Won Lee, W.B.; Ko, J.M.; Baek, I.Y.; et al. Comparative investigation of seed coats of brown- versus yellow-colored soybean seeds using an integrated proteomics and metabolomics approach. Proteomics 2014, 15, 1706–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dwivedi, S.L.; Upadhyaya, H.D.; Chung, M.I.; Vita, P.; García-Lara, L.S.; Guajardo-Flores, D.; Gutiérrez-Uribe, J.A.; Serna-Saldívar, S.O.; Rajakumar, G.; Sahrawat, K.L.; et al. Exploiting Phenylpropanoid Derivatives to Enhance the Nutraceutical Values of Cereals and Legumes. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atchinson, G.W.; Nevado, B.; Eastwood, R.J.; Contreras-Ortiz, N.; Reynel, C.; Madriñán, S.; Filatov, D.A.; Hughes, C.E. Lost crops of the Incas: Origins of domestication of the Andean pulse crop tarwi Lupinus mutabilis. Am. J. Bot. 2016, 103, 1592–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvajal-Larenas, F.E.; Linnemann, A.R.; Nout, M.J.R.; Koziol, M.; Van Boekel, M.A.J.S. Lupinus mutabilis: Composition uses toxicology and debittering. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 56, 1454–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, J.M.N.; Talhinhas, P.; Sousa, R.B. Yield and seed chemical composition of Lupinus mutabilis in Portugal. Rev. Ciênc. Agrár. 2016, 39, 518–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulisano, A.; Alves, S.; Neves-Martins, J.; Trindade, L. Genetics and breeding of Lupinus mutabilis: An emerging protein crop. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilengue, N.; Alves, S.; Talhinhas, P.; Neves-Martins, J. Genetic and genomic diversity in a tarwi (Lupinus mutabilis Sweet) germplasm collection and adaptability to Mediterranean climate conditions. Agronomy 2020, 10, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talhinhas, P.; Baroncelli, R.; Le Floch, G. Anthracnose of lupins caused by Colletotrichum lupini: A recent disease and a successful worldwide pathogen. J. Plant Pathol. 2016, 98, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talhinhas, P.; Neves-Martins, J.; Oliveira, H. Evaluation of anthracnose resistance in Lupinus spp. germplasm. Rev. Ciênc. Agrár. 2016, 39, 550–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilengue, N.; Neves-Martins, J.; Talhinhas, P. Response to anthracnose in a tarwi (Lupinus mutabilis) collection is influenced by anthocyanin pigmentation. Plants 2020, 9, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Statler, G.D. Resistance of bean plants to Fusarium solani f. sp. phaseoli. Plant Dis. Rep. 1970, 54, 698–699. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, H.B.; Burns, R.E. Relationship between tannin content of sorghum grain and preharvest seed molding. Agron. J. 1973, 65, 957–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stasz, T.E.; Harman, G.E.; Marx, G.A. Time and Site of Infection of Resistant and Susceptible Germinating Pea Seeds by Pythium ultimum. Phytopathology 1980, 70, 730–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, F.M.A.; Rengifo, J.; Redden, R.J.; Basford, K.E.; Beebe, S.E. Association Between Seed Coat Polyphenolics (Tannins) and Disease Resistance in Common Bean. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2003, 58, 285–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, A.; Oliveira, J.; Saúde, F.; Mota, J.; Ferreira, R.B. Proteins in Soy Might Have a Higher Role in Cancer Prevention than Previously Expected: Soybean Protein Fractions Are More Effective MMP-9 Inhibitors Than Non-Protein Fractions, Even in Cooked Seeds. Nutrients 2017, 9, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, B.J.; Yuan, S.H.; Chang, S.K. Comparative analyses of phenolic composition, antioxidant capacity, and color of cool season legumes and other selected food legumes. Food Sci. 2007, 72, S167–S177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, C.W. Health Effects of Soy Protein and Isoflavones in Humans. J. Nutr. 2008, 138, 1244S–1249S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang., R.F.; Zhang, F.X.; Zang, M.W.; Wei, Z.C.; Yang, C.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, X.J.; Deng, Y.Y.; Chi, J.W. Phenolic Composition and Antioxidant Activity in Seed Coats of 60 Chinese Black Soybean (Glycine max L. Merr.) Varieties. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 5935–5944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segev, A.; Badani, H.; Kapulnik, Y.; Shomerand, I.; Oren-Shamir, M.; Galili, S. Determination of phenolic compounds, flavonoids, and antioxidant activity colored chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). J. Food Sci. 2010, 75, S115–S119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariza-Nieto, M.; Blair, M.W.; Welch, R.M.; Glahn, R.P. Screening of bioavailability patterns in eight bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) genotypes using the Caco-2 cell in vitro model. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 7950–7956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blair, M.W.; Izquierdo, P.; Astudillo, C.; Grusak, M.A. A legume biofortification quandary: Variability and genetic control of seed coat micronutrient accumulation in common beans. Front. Plant Sci. 2013, 4, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishili, F.J.; Fulton, J.; Shehu, M.; Kushwaha, S.; Marfo, K.; Jamal, M.; Kergna, A.; De Borer, J.L. Consumer preferences for quality characteristics along the cowpea value chain in Nigeria Ghana and Mali. Agribusiness 2009, 25, 16–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kläsener, G.R.; Ribeiro, N.D.; Casagrande, C.R.; Arns, F.D. Consumer preference and the technological and nutritional quality of different bean colours. Acta Sci. Agron. 2020, 42, e43689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, V.; Ruchi, V.; Gayathri, R.; Bai, M.R.; Shobana, S.; Anjana, R.M.; Unnikrishnan, R.; Sudha, V. Hurdles in Brown Rice Consumption. In Brown Rice; Manickavasagan, A., Santhakumar, C., Venkatachalapathy, N., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland; New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 255–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassett, M.J. Genetics of Seed Coat Color and Pattern in Common Bean. In Plant Breeding Reviews; Janick, J., Ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2007; Volume 28, pp. 239–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillman, J.D.; Tetlow, A.; Lee, J.D.; Shannon, J.G.; Bilyeu, K. Loss-of-function mutations affecting a specific Glycine max R2R3 MYB transcription factor result in brown hilum and brown seed coats. BMC Plant Biol. 2011, 11, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.; Jeong, N.; Moon, J.K.; Lee, Y.H.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, H.M.; Hwang, C.H.; Back, K.; Palmer, R.G.; Jeong, S.C. Genetic analysis of genes controlling natural variation of seed coat and flower colors in soybean. J. Hered. 2010, 101, 757–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ubayasena, L.; Vijayan, P.; Bett, K.E.; Gray, G.R.; Küster, H.; Warkentin, T.D. Gene expression profiles of seed coats and bio-chemical properties of seed coats and cotyledons of two field pea (Pisum sativum) cultivars contrasting in green cotyledon bleaching resistance. Euphytica 2015, 193, 49–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IBPGR. Lupin Descriptors; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Hane, J.K.; Ming, Y.; Kamphuis, L.G.; Nelson, M.N.; Carg, G.; Atkins, C.A.; Bayer, P.E.; Bravo, A.; Bringans, S.; Cannon, S.; et al. Comprehensive draft genome sequence for lupin (Lupinus angustifolius) an emerging health food: Insights into plant–microbe interactions and legume evolution. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2016, 15, 318–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, L.; Mezulis, S.; Yates, C.; Wass, M.; Sternberg, M. The Phyre2 web portal for protein modeling, prediction and analysis. Nat. Protoc. 2015, 10, 845–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabala, G.; Vodkin, L.O. Methylation Affects Transposition and Splicing of a Large CACTA Transposon from a MYB Transcription Factor Regulating Anthocyanin Synthase Genes in Soybean Seed coats. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, A.; Cabral, A.; Fino, J.; Azinheira, H.G.; Loureiro, A.; Talhinhas, P.; Pires, A.S.; Várzea, V.; Moncada, P.; Oliveira, H.; et al. Comparative validation of conventional and RNA-seq data-derived reference genes for qPCR expression studies of Colletotrichum kahawae. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0150651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, C.M.; Jost, R.; Erskine, W.; Nelson, M.N. Identifying Stable Reference Genes for RT-qPCR Normalisation in Gene Expression Studies of Narrow-Leafed Lupin (Lupinus angustifolius L.). PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0148300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kroc, M.; Koczyk, G.; Kamel, K.A.; Czepiel, K.; Fedorowicz-Strońska, O.; Krajewski, P.; Kosińska, J.; Podkowiński, J.; Wilczura, P.; Święcicki, W. Transcriptome-derived investigation of biosynthesis of quinolizidine alkaloids in narrow-leafed lupin (Lupinus angustifolius L.) highlights candidate genes linked to iucundus locus. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, F.; Xiao, P.; Chen, D.; Xu, L.; Zhang, B. miRDeepFinder: A miRNA analysis tool for deep sequencing of plant small RNAs. Plant Mol. Biol. 2012, 80, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfaffl, M.W.; Tichopad, A.; Prgomet, C.; Neuvians, T.P. Determination of stable housekeeping genes differentially regulated target genes and sample integrity: BestKeeper-excel-based tool using pair-wise correlations. Biotechnol. Lett. 2004, 26, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandesompele, J.; De Preter, K.; Pattyn, F.; Poppe, B.; Van Roy, N.; De Paepe, A.; Speleman, F. Accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome Biol. 2002, 3, research0034.1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, C.L.; Jensen, J.L.; Orntoft, T.F. Normalization of real-time quantitative reverse transcription-PCR data: A model-based variance estimation approach to identify genes suited for normalization applied to bladder and colon cancer data sets. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 5245–5250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellemans, J.; Mortier, G.; De Paepe, A.; Speleman, F.; Vandesompele, J. qBase relative quantification framework and software for management and automated analysis of real-time quantitative PCR data. Genome Biol. 2007, 8, R19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silver, N.; Best, S.; Jiang, J.; Thein, S.L. Selection of housekeeping genes for genes expression studies in human reticulocytes using real time PCR. BMC Mol. Biol. 2006, 7, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfaffl, M.W. A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT–PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruijter, J.M.; Ramakers, C.; Hoogaars, W.M.; Karlen, Y.; Bakker, O.; Van den Hoff, M.J.; Moorman, A.F. Amplification efficiency: Linking baseline and bias in the analysis of quantitative PCR data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wisman, E.; Hartmann, U.; Sagasser, M.; Baumann, E.; Palme, K.; Hahlbrock, K.; Saedler, H.; Weisshaar, B. Knock-out mutants from an En-1 mutagenized Arabidopsis thaliana population generate phenylpropanoid biosynthesis phenotypes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 12432–12437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, S.; Tian, N.; Long, J.; Chen, Y.; Qin, Y.; Feng, J.; Xiao, W.; Liu, S. Molecular cloning and characterization of a flavanone 3-Hydroxylase gene from Artemisia annua L. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 105, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himi, E.; Maekawa, M.; Noda, K. Differential Expression of Three Flavanone 3-Hydroxylase Genes in Grains and Coleoptiles of Wheat. Intern. J. Plant Genom. 2011, 2011, 369460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, Y.; Higeta, D.; Suzuki, A.; Yoshida, H.; Ozeki, Y. Excision of Transposable Elements from the Chalcone Isomerase and Dihydroflavonol 4-Reductase Genes May Contribute to the Variegation of the Yellow-Flowered Carnation (Dianthus caryophyllus). Plant Cell Physiol. 2002, 43, 578–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishihara, M.; Yamada, E.; Saito, M.; Fujita, K.; Takahashi, H.; Nakatsuka, T. Molecular characterization of mutations in white-flowered torenia plants. BMC Plant Biol. 2014, 14, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LPWG. Legume phylogeny and classification in the 21st century: Progress, prospects and lessons for other species–rich clades. Taxon 2013, 62, 217–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavin, M.; Herendeen, P.S.; Wojciechowski, M.F. Evolutionary rates analysis of Leguminosae implicates a rapid diversification of lineages during the tertiary. Syst. Biol. 2005, 54, 575–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirley, B.W.; Kubasek, W.L.; Storz, G.; Bruggemann, E.; Koornneef, M.; Ausubel, F.M.; Goodman, H.M. Analysis of Arabidopsis mutants deficient in flavonoid biosynthesis. Plant J. 1995, 8, 659–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koornneef, M. Mutations affecting the testa colour in Arabidopsis. Inf. Serv. 1990, 27, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Park, K.I.; Nitasaka, E.; Hoshino, A. Anthocyanin mutants of Japanese and common morning glories exhibit normal proanthocyanidin accumulation in seed coats. Plant Biotechnol. 2018, 35, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, L.; Li, B.; Pandey, M.K.; Wu, Y.; Lei, Y.; Yan, L.; Dai, X.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, J.; Wei, G.; et al. Transcriptome Analysis of a New Peanut Seed Coat Mutant for the Physiological Regulatory Mechanism Involved in Seed Coat Cracking and Pigmentation. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Himi, E.; Noda, K. Red grain colour gene (R) of wheat is a Myb-type transcription factor. Euphytica 2005, 143, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Tang, F.; Huang, Y.; Xu, F.; Chen, Y.; Tong, C.; Chen, H.; Bao, J. Analysis of Genotype×Environment interactions for polyphenols and antioxidant capacity of rice by association mapping. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 5361–5368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akond, A.S.M.G.M.; Khandaker, L.; Berthold, J.; Gates, L.; Peters, K.; Delong, H.; Hossain, K. Anthocyanin total polyphenols and antioxidant activity of common bean. Am. J. Food Technol. 2011, 6, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostini-Costa, T.S.; Teodoro, A.F.P.; Alves, R.B.N.; Braga, L.R.; Ribeiro, I.F.; Silva, J.P.; Quintana, L.G.; Burle, M.L. Total phenolics flavonoids tannins and antioxidant activity of lima beans conserved in a Brazilian genebank. Ciênc. Rural 2015, 45, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Reference Gene | Primer Name and Direction | Primer Sequence | Tm 1 (°C) | Size (bp) | Eff 2 | Eff 2 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ubiquitin C (Ubc) | LangUBC-F | 5′ CTGACAGCCCACTGAATTGTGA 3′ | 60.8 | 108.0 | 1.952 | 0.930 |
| LangUBC-R | 5′ TCTTGGGCATAGCAGCAAGC 3′ | 61.0 | ||||
| Helicase (Hel) | LangHEL-F | 5′ TTGTACGAGGTCGGTGCTCT 3′ | 60.9 | 127.0 | 1.947 | 0.927 |
| LangHEL-R | 5′ ACAAGCAACCAAATATTGCACCATA 3′ | 60.0 | ||||
| Alcohol dehydrogenase class-3 (Adh3) | LangADH3-F | 5′ AGCACACAGCGTAGGCATC 3′ | 58.0 | 91.0 | 1.957 | 0.932 |
| LangADH3-R | 5′ AGTTGATGAGTACATAACCCACA 3′ | 58.0 | ||||
| ATP synthase (ATPsyn) | LangATPsyn-F | 5′ AGTATGCTGTTCCTGTTCGTCA 3′ | 59.0 | 145 | -- | -- |
| LangATPsyn-R | 5′ ATGGTGATCTTCTCCTTCTTTAG 3′ | 59.0 | ||||
| Alpha tubulin (αTub) | LangTUBA-F | 5′ CGGGTTAGAAAGTTGGCGGA 3′ | 58.0 | 101 | 1.944 | 0.926 |
| LangTUBA-R | 5′ CAACAAGAGAGATCCCAAACC 3′ | 58.0 |
| Gene of Interest | Primer Name and Direction | Primer Sequence | Tm 1 (°C) | Size (bp) | Eff 2 | Eff (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F3h_a | LmutF3h_a-F | 5′ GGAACTATTATCAGAAGCAATGGG 3′ | 60.0 | 120 | 1.988 | 0.947 |
| LmutF3h_a-R | 5′ AAGTGTAAGATCAGGTTGAGGG 3′ | 60.0 | ||||
| F3h_b | LmutF3h_a-F | 5′ TACCCTAAATGTCCACAACCTG 3′ | 60.0 | 129 | 1.926 | 0.917 |
| LmutF3h_a-R | 5′ TCCAAGTCTTTCCATTATCCCT 3′ | 60.0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guilengue, N.; Azinheira, H.G.; Alves, S.; Neves-Martins, J.; Talhinhas, P.; Morais-Cecílio, L. The Analysis of Partial Sequences of the Flavonone 3 Hydroxylase Gene in Lupinus mutabilis Reveals Differential Expression of Two Paralogues Potentially Related to Seed Coat Colour. Agronomy 2022, 12, 450. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12020450
Guilengue N, Azinheira HG, Alves S, Neves-Martins J, Talhinhas P, Morais-Cecílio L. The Analysis of Partial Sequences of the Flavonone 3 Hydroxylase Gene in Lupinus mutabilis Reveals Differential Expression of Two Paralogues Potentially Related to Seed Coat Colour. Agronomy. 2022; 12(2):450. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12020450
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuilengue, Norberto, Helena G. Azinheira, Sofia Alves, João Neves-Martins, Pedro Talhinhas, and Leonor Morais-Cecílio. 2022. "The Analysis of Partial Sequences of the Flavonone 3 Hydroxylase Gene in Lupinus mutabilis Reveals Differential Expression of Two Paralogues Potentially Related to Seed Coat Colour" Agronomy 12, no. 2: 450. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12020450
APA StyleGuilengue, N., Azinheira, H. G., Alves, S., Neves-Martins, J., Talhinhas, P., & Morais-Cecílio, L. (2022). The Analysis of Partial Sequences of the Flavonone 3 Hydroxylase Gene in Lupinus mutabilis Reveals Differential Expression of Two Paralogues Potentially Related to Seed Coat Colour. Agronomy, 12(2), 450. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12020450








