Effects of Organic and Inorganic Fertilization on Soil Organic Carbon and Enzymatic Activities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Soil Sampling and Chemical Analysis
2.4. Calculations and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Different Fertilization Treatments on Soil Enzymatic Activity
3.2. Effects of Different Fertilization Treatments on SOC Fractions and CPMI
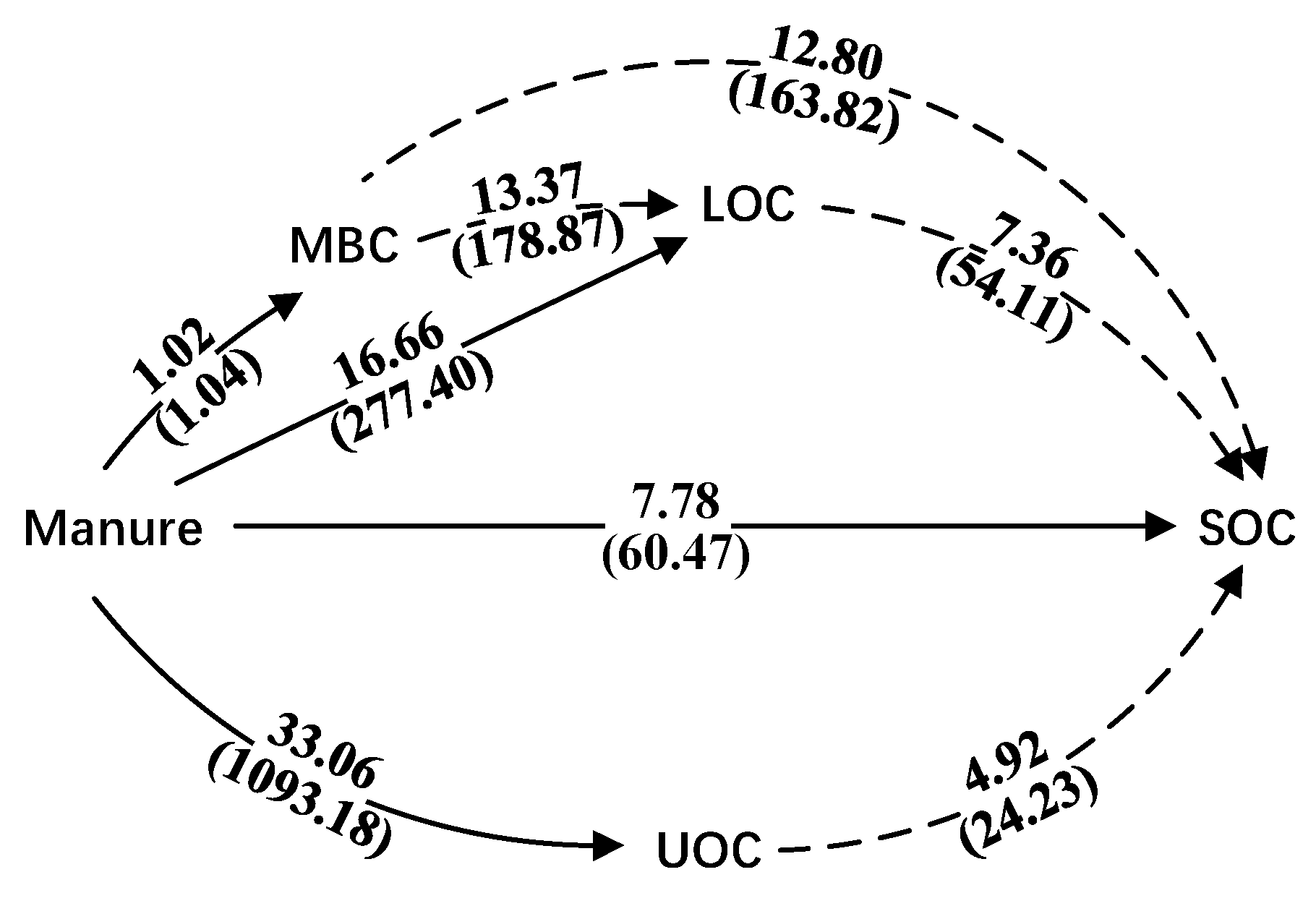
3.3. Effects of Interaction of Chemical Fertilizer and Organic Manure on SOC Fractions
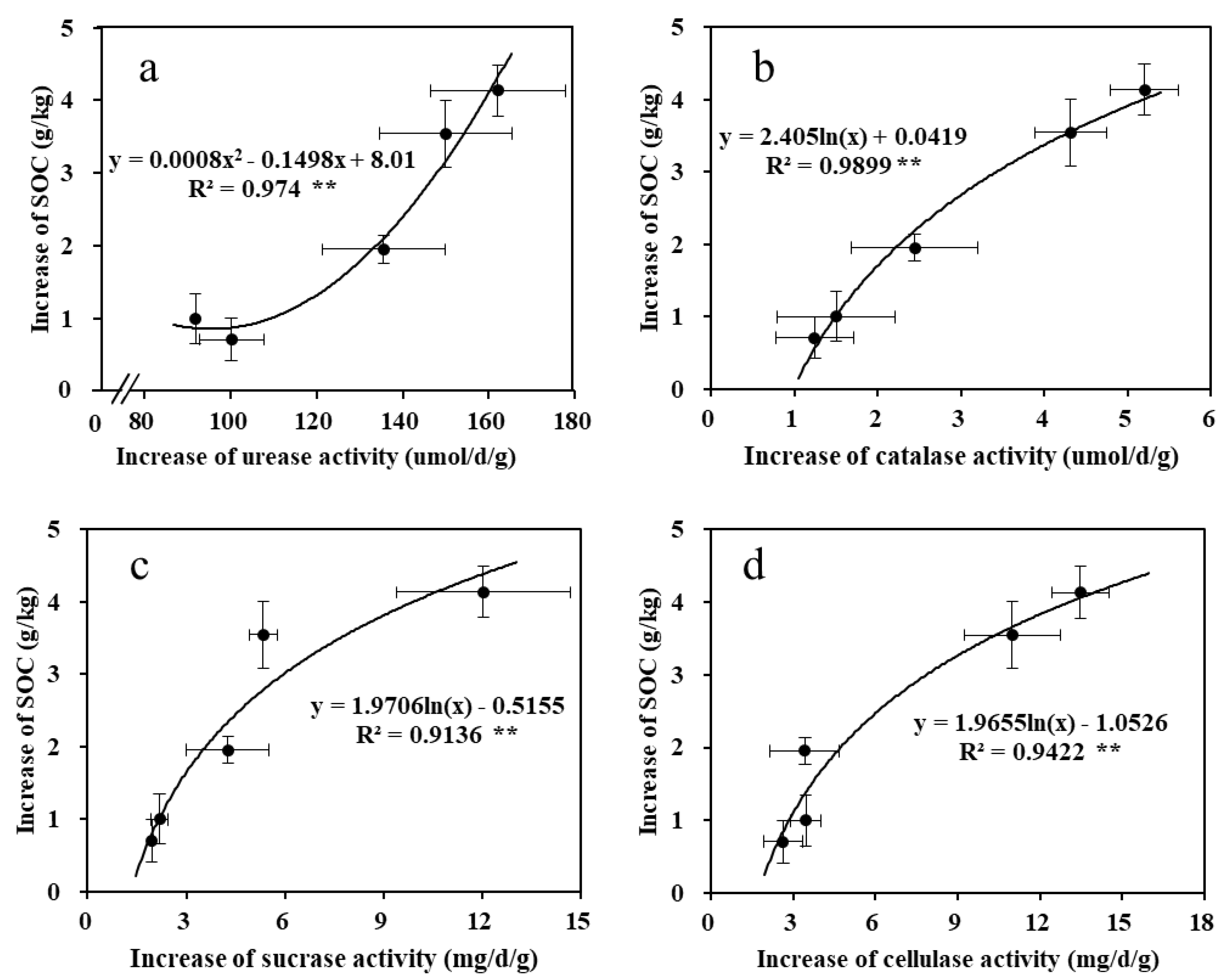
3.4. Linear Relationship between Organic Manure Application and SOC Increase
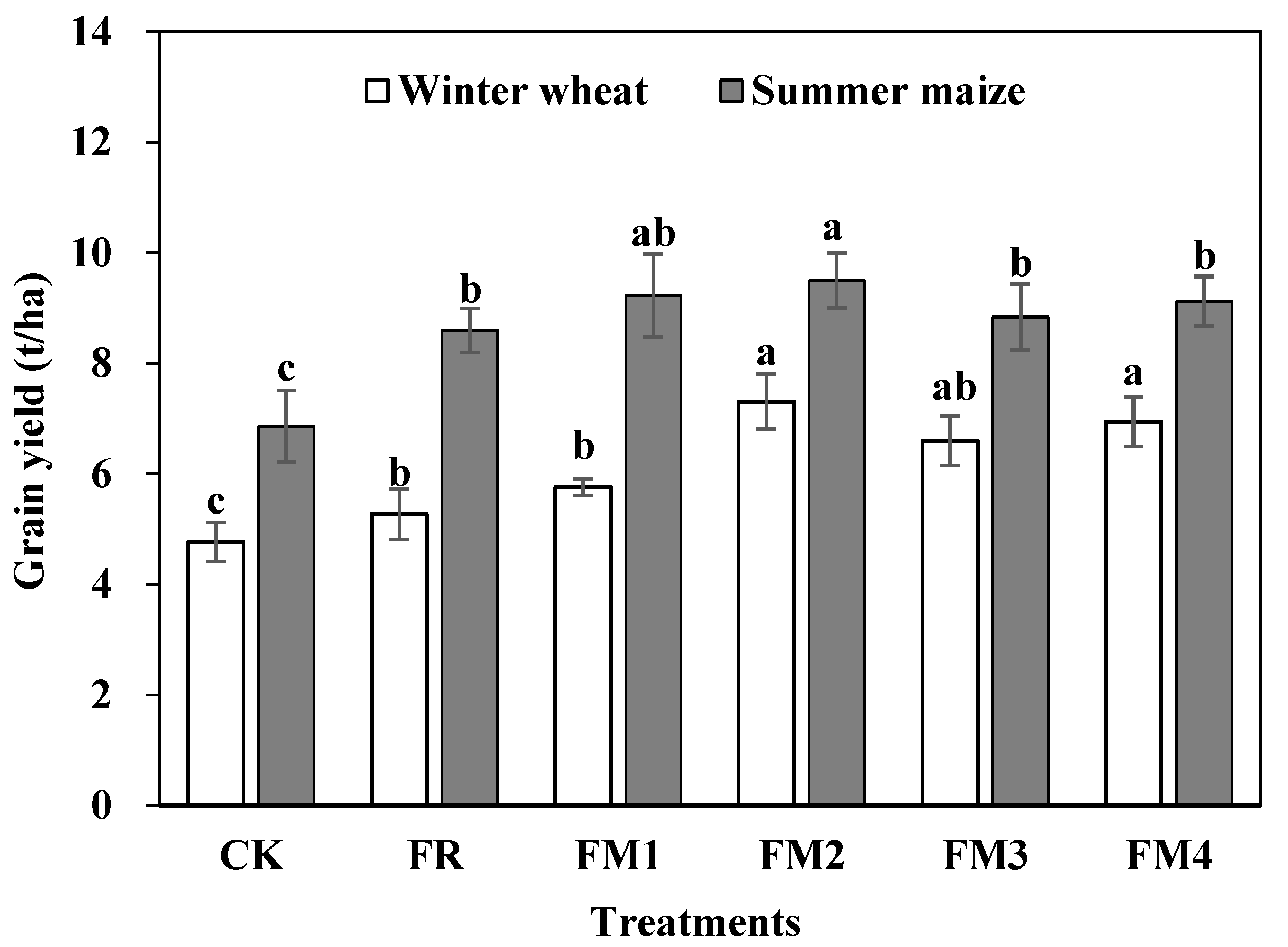
3.5. Crop Yields of Different Treatments
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO. FAOSTAT Database—Agriculture Production; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Cui, Z.; Chen, X.; Ju, X.; Shen, J.; Chen, Q.; Liu, X.; Zhang, W.; Mi, G.; Fan, M.; et al. Integrated nutrient management for food security and environmental quality in China. Adv. Agron. 2012, 116, 1–40. [Google Scholar]
- Bijay, S.; Sapkota, T.B. The effects of adequate and excessive application of mineral fertilizers on the soil. In Reference Module in Earth Systems and Environmental Sciences; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Q.; Liu, T.; Ding, H.; Guo, L.; Li, C.; Jiang, Y.; Cao, C. Application rates of nitrogen fertilizers change the pattern of soil organic carbon fractions in a rice-wheat rotation system in China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2022, 338, 108081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Xia, H.; Jiang, C.; Riaz, M.; Yang, L.; Chen, Y.; Fan, X.; Xia, X. 14 year applications of chemical fertilizers and crop straw effects on soil labile organic carbon fractions, enzyme activities and microbial community in rice-wheat rotation of middle China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 841, 156608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ye, C.; Su, Y.; Peng, W.; Lu, R.; Liu, Y.; Huang, H.; He, X.; Yang, M.; Zhu, S. Soil Acidification caused by excessive application of nitrogen fertilizer aggravates soil-borne diseases: Evidence from literature review and field trials. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2022, 340, 108176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, J.; Kleber, M. The contentious nature of soil organic matter. Nature 2015, 528, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, G.; Kurothe, R. Effect of farmyard manure and fertilizer application on crop yield, runoff and soil erosion and soil organic carbon under rainfed pearl millet (Pennisetum glaucum). Indian J. Agric. Sci. 2014, 84, 816–823. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, D.; Cheng, H.; Ren, L.; Jin, X.; Fang, W.; Yan, D.; Li, Y.; Wang, Q.; Cao, A. Organic fertilizers activate soil enzyme activities and promote the recovery of soil beneficial microorganisms after dazomet fumigation. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 309, 114666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Zhang, Y.; Bei, S.; Li, X.; Reinsch, S.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, J. Contrasting impacts of manure and inorganic fertilizer applications for nine years on soil organic carbon and its labile fractions in bulk soil and soil aggregates. Catena 2020, 194, 104739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyamasoka-Magonziwa, B.; Vanek, S.J.; Ojiem, J.O.; Fonte, S.J. Examining the contributions of maize shoots, roots, and manure to stable soil organic carbon pools in tropical smallholder farming soils. Geoderma 2022, 425, 116049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkinson, D.S.; Rayner, J.H. The turnover of soil organic matter in some of the Rothamsted classical experiments. Soil Sci. 2006, 171, S130–S137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palm, C.A.; Myers, R.J.; Nandwa, S.M. Combined use of organic and inorganic nutrient sources for soil fertility maintenance and replenishment. In Replenishing Soil Fertility in Africa; SSSA Special Publication; SSSA and ASA: Madison, WI, USA, 1997; Volume 51, pp. 193–217. [Google Scholar]
- Balezentiene, L.; Klimas, E. Effect of organic and mineral fertilizers and land management on soil enzyme activities. Agron. Res. 2009, 52, 191–197. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Q.; Chen, H.; Gong, Y.; Yang, H.; Fan, M.; Kuzyakov, Y. Effects of 15 years of manure and mineral fertilizers on enzyme activities in particle-size fractions in a North China Plain soil. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2014, 60, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R. The Chemical Analysis of Agricultural Soil; China Agriculture Science and Technique Press: Beijing, China, 1999; pp. 107–109, 231–233. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Loginow, W.; Wisniewski, W.; Gonet, S.S.; Ciescinska, B. Fractionation of organic carbon based on susceptibility to oxidation. Pol. J. Soil Sci. 1987, 20, 47–52. [Google Scholar]
- Bhatt, G.M. Significance of path coefficient analysis in determining the nature of character association. Euphytica 1973, 22, 338–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, G.; Lefroy, R.; Lisle, L. Soil carbon fractions based on their degree of oxidation, and the development of a carbon management index for agricultural systems. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 1995, 46, 1459–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo, C.; Merino, A.; Osorio-Hernández, V.; Etchevers, J.D.; Figueroa, B.; Limon-Ortega, A.; Aguirre, E. Physical and chemical processes determining soil organic matter dynamics in a managed vertisol in a tropical dryland area. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 194, 104348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhao, M.; Yan, Z.; Yang, Y.; Niklas, K.J.; Huang, H.; Donko Mipam, T.; He, X.; Hu, H.; Joseph Wright, S. Global patterns and predictors of soil microbial biomass carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus in terrestrial ecosystems. Catena 2022, 211, 106037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Han, X.; Li, L.; Zou, W.; Ren, J.; Li, G. Distribution of organic carbon and humic acids in aggregates of Mollisol as affected by amendments with different rates of organic manure plus mineral fertilizer. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2016, 22, 1586–1594. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Totsche, K.U.; Amelung, W.; Gerzabek, M.H.; Guggenberger, G.; Klumpp, E.; Knief, C.; Lehndorff, E.; Mikutta, R.; Peth, S.; Prechtel, A.; et al. Microaggregates in soils. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2018, 181, 104–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, E.-H.; Chung, R.-S.; Tsai, Y.-H. Effect of different application rates of organic fertilizer on soil enzyme activity and microbial population. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2007, 53, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Z.; Lehmann, J.; Van Zwieten, L.; Joseph, S.; Archanjo, B.S.; Cowie, B.; Thomsen, L.; Tobin, M.J.; Vongsvivut, J.; Klein, A.; et al. Probing the nature of soil organic matter. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 52, 4072–4093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Kästner, M.; Joergensen, R.G. Microbial necromass on the rise: The growing focus on its role in soil organic matter development. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 150, 108000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Tian, Z.; Lu, Y.; Ren, T.; Peng, X. Determination of soil bulk density dynamic in a Vertisol during wetting and drying cycles using combined soil water content and thermal property sensors. Geoderma 2022, 428, 116149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, S.; Dheri, G.S.; Brar, B.S. Long-term effects of NPK fertilizers and organic manures on carbon stabilization and management index under rice-wheat cropping system. Soil Tillage Res. 2017, 166, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Y.; Xu, M.; Wang, W.; Sun, X.; Liang, C. Soil organic carbon fractions and management index after 20 yr. of manure and fertilizer application for greenhouse vegetables. Soil Use Manag. 2011, 27, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, M.S.; Hazra, K.K.; Ghosh, P.K.; Praharaj, C.S.; Kumar, N. Long-term effect of pulses and nutrient management on soil carbon sequestration in Indo-Gangetic plains of India. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2013, 93, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.K.; Park, H.J.; Cha, S.J.; Kwon, S.J.; Park, J.H. Effect of pyroligneous acid on soil urease, amidase, and nitrogen use efficiency by Chinese cabbage (Brassica campestris var. Pekinensis). Environ. Pollut. 2021, 291, 118132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Xie, Z.; Li, X.; He, Z.H.; Peng, X.X. Association-dissociation of glycolate oxidase with catalase in rice: A potential switch to modulate intracellular H2O2 levels. Mol. Plant 2016, 9, 737–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, F.; Yuan, Y.; Fan, H.; Liu, W.; Liu, Y. Effects of elevated nitrogen deposition on soil organic carbon mineralization and soil enzyme activities in a Chinese fir plantation. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2012, 32, 517. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Adame, M.F.; Chen, C. Resource stoichiometry, vegetation type and enzymatic activity control wetlands soil organic carbon in the Herbert River catchment, North-east Queensland. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 296, 113183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jie, X.; Yang, L.; Zhou, C.; Yang, X. Effect of long-term fertilization on the contents of combined formation of humus in the protected cultivation. Chin. J. Soil Sci. 2009, 40, 805–808. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Liang, C.; Du, L.; Chen, X.; Li, J. Effects of long-term localized fertilization on soil humus combining form in sheltered vegetable field. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2006, 17, 831–834. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]



| Total Nitrogen (g/kg) | Total Phosphorus (g/kg) | Total Potassium (g/kg) | Available Phosphorus (mg/kg) | Available Potassium (mg/kg) | Sand (%) | Silt (%) | Clay (%) | SOC (g/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.57 | 0.76 | 21.20 | 33.06 | 125.60 | 45.60 | 40.70 | 13.70 | 5.92 |
| Treatment | Organic Manure a (t/ha) | Chemical Fertilizer b (kg/ha) | Chemical Fertilizer c (kg/ha) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | P2O5 | K2O | N | P2O5 | K2O | ||
| CK | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| FR | 0 | 225 | 90 | 90 | 240.00 | 90.00 | 90.00 |
| FM1 | 2.11 | 180 | 47.55 | 51.45 | 240.00 | 90.00 | 90.00 |
| FM2 | 4.21 | 135 | 5.25 | 12.9 | 240.00 | 90.00 | 90.00 |
| FM3 | 6.32 | 90 | 0 | 0 | 240.00 | 52.80 | 64.35 |
| FM4 | 8.42 | 45 | 0 | 0 | 240.00 | 10.50 | 25.80 |
| Treatment | SOC (g/kg) | LOC (g/kg) | UOC (g/kg) | CPI | L | LI | CPMI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 8.61 ± 0.23 d | 1.17 ± 0.65 e | 7.44 ± 0.65 a,b | 1.00 ± 0.03 e | 0.17 ± 0.10 d | 1.00 ± 0.00 e | 100.00 ± 0.00 e |
| FR | 9.32 ± 0.29 c | 2.19 ± 0.14 d | 7.13 ± 0.29 b | 1.08 ± 0.03 d | 0.31 ± 0.03 c | 1.86 ± 0.20 d | 200.55 ± 14.81 d |
| FM1 | 9.67 ± 0.35 c | 2.41 ± 0.02 d | 7.26 ± 0.67 b | 1.12 ± 0.04 d | 0.34 ± 0.02 c | 2.04 ± 0.16 c,d | 244.47 ± 53.69 d |
| FM2 | 10.56 ± 0.19 b | 3.09 ± 0.33 c | 7.48 ± 0.33 a,b | 1.23 ± 0.02 c | 0.42 ± 0.06 b,c | 2.39 ± 0.42 c | 308.87 ± 43.94 c |
| FM3 | 12.15 ± 0.46 a | 4.17 ± 0.23 b | 7.98 ± 0.27 a,b | 1.41 ± 0.05 b | 0.52 ± 0.01 b | 3.11 ± 0.04 b | 444.32 ± 11.74 b |
| FM4 | 13.10 ± 0.35 a | 4.86 ± 0.28 a | 8.24 ± 0.63 a | 1.52 ± 0.04 a | 0.64 ± 0.10 a | 3.86 ± 0.19 a | 587.12 ± 30.69 a |
| Treatment | MBC (mg/kg) | MBN (mg/kg) | MBC/MBN | qMB (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 33.86 ± 4.1 d | 23.96 ± 1.05 e | 1.41 ± 0.11 d | 0.39 ± 0.07 c |
| FR | 75.51 ± 4.57 c | 28.79 ± 1.16 d | 2.62 ± 0.11 c | 0.81 ± 0.03 b |
| FM1 | 83.96 ± 2.67 c | 31.89 ± 0.44 c | 2.63 ± 0.12 c | 0.87 ± 0.04 a,b |
| FM2 | 93.23 ± 1.67 b | 32.63 ± 1.48 b | 2.86 ± 0.08 b | 0.88 ± 0.02 a |
| FM3 | 98.62 ± 5.65 a,b | 35.1 ± 1.25 a | 2.81 ± 0.03 b | 0.82 ± 0.03 b |
| FM4 | 103.69 ± 7.35 a | 34.25 ± 0.76 a | 3.03 ± 0.05 a | 0.77 ± 0.02 b |
| Treatment | COM (%) | IFM (g/kg) | IFMC (%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SOC | LOC | UOC | SOC | LOC | UOC | SOC | LOC | UOC | |
| CK | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / |
| FR | 7.62 | 46.59 | −4.35 | / | / | / | / | / | / |
| FM1 | 10.39 | 51.93 | −2.43 | 0.29 | 0.24 | 0.13 | 3.01 | 10.00 | 1.84 |
| FM2 | 18.49 | 62.08 | 0.51 | 1.24 | 0.89 | 0.35 | 11.77 | 29.00 | 4.65 |
| FM3 | 29.15 | 71.95 | 6.79 | 2.83 | 1.98 | 0.85 | 23.31 | 47.48 | 10.68 |
| FM4 | 34.25 | 75.91 | 9.68 | 3.78 | 2.67 | 1.11 | 28.83 | 54.91 | 13.45 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, C.; Zhao, Z.; Li, F.; Zhang, J. Effects of Organic and Inorganic Fertilization on Soil Organic Carbon and Enzymatic Activities. Agronomy 2022, 12, 3125. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12123125
Zhang C, Zhao Z, Li F, Zhang J. Effects of Organic and Inorganic Fertilization on Soil Organic Carbon and Enzymatic Activities. Agronomy. 2022; 12(12):3125. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12123125
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Congzhi, Zhanhui Zhao, Fang Li, and Jiabao Zhang. 2022. "Effects of Organic and Inorganic Fertilization on Soil Organic Carbon and Enzymatic Activities" Agronomy 12, no. 12: 3125. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12123125
APA StyleZhang, C., Zhao, Z., Li, F., & Zhang, J. (2022). Effects of Organic and Inorganic Fertilization on Soil Organic Carbon and Enzymatic Activities. Agronomy, 12(12), 3125. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12123125







