Abstract
Potato is an important food crop worldwide and is grown in a large number of countries. As such, the crop is under disease pressures and the need for selecting disease resistance genes during breeding programs is essential. Of particular importance within Australia and other parts of the world is the potyvirus, Potato virus Y (PVY). In this paper, three commonly used PVY resistance markers, M45, RYSC3 and M6, were evaluated using existing genomic resources and phenotypic data from the Australian potato breeding program to identify a region where the PVY resistance gene, Ryadg may reside. A region of Chromosome XI was investigated, and a cluster of disease resistance genes was identified that the resistance gene Ryadg is suspected to reside within. Protein characterization was also performed on the putative resistant gene. A specific variant that had complete association with the resistance gene was identified and a single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) assay was designed to avoid dissociation of marker and gene in future breeding programs. This SNP marker (SNP37279) was validated as a Kompetitive Allele-specific PCR (KASP) genotyping assay and was found to perform more accurately than all previously used markers for detecting Ryadg.
1. Introduction
Potato (Solanum tuberosum) is the fourth most important food crop globally with production exceeding 350 million tonnes per annum [1]. This is mainly due to its climate adaptability, large yield and high nutritional value [2]. The risk of disease to potato production in such an extensively grown crop is significant and has wide-reaching implications. Potato is a monoculture crop, making many of the pests and pathogens of high economic importance. Data collected from 19 regions worldwide in 2001–2003 estimated that the potential losses in potatoes from insect pests, pathogens and viruses is 44.9% [3].
Susceptibility to viral diseases is particularly high despite years of breeding. A recurring impediment to potato production is Potato virus Y (Family Potyviridae, genus Potyvirus, PVY), a ssRNA virus that is transmitted in a non-persistent manner via aphids and mechanically spread through germination of infected plant material. PVY has been reported to cause 10–80% yield losses in potato, depending on the virus strain and if co-infections are occurring with other viruses [4]. It has been designated the fifth most economically important plant virus [3] and is the most important virus worldwide infecting potato [5]. Within Australia, PVY has been detected in all states but is successfully controlled in Western Australia and Tasmania. Detection of potato infecting viruses through seed certification schemes has assisted in minimising the rate of infection in field. Despite these efforts, PVY is now being more routinely observed, and several strains have now been detected in the field [3,6]. Of most importance is PVYNTN, inducing symptoms such as leaf and stem necrosis, leaf-drop, stunting and necrosis of the tuber.
Due to the easy transmission of PVY by aphid vectors, infected plant material and mechanical means, attempts of control using chemical-based treatments are often not practical or cost-effective. In addition, symptoms of PVY infection can be strain specific and certain cultivars do not exhibit symptoms when infected [5]. A more appealing method for control of viral diseases is through breeding and the delivery of resistant cultivars [7]. Resistant cultivars can produce harvestable yield without the need for additional inputs or management requirements. However, producing new resistant cultivars can be a long process as phenotypic recurrent selection can take 10–12 years to produce a new variety with the desired trait [8,9,10,11]. The use of molecular tools such as marker-assisted selection (MAS) to assist breeding efforts can reduce this timeframe through easier and earlier screening and allow more informed decisions through reduced phenotypic errors [12,13].
Introgression of PVY resistance genes into commercial germplasm from the wild relatives Solanum tuberosum subsp. andigena and S. stoloniferum has provided a robust source of resistance [7,14,15]. These introgressions provide the resistance genes Ryadg and Rysto that confer resistance to all strains of PVY [16,17]. Within the Australian potato germplasm, that has a strong European and North American heritage, but which is also well adapted to local conditions, Ryadg is the most prominent resistance source [5,18,19,20]. In addition, the majority of resistance genes are under simple genetic control where the simplex state provides the trait. Thus, the identification of parents with higher genetic dosage is more valuable for breeding programs to increase desired allele transmission to progeny [9,21,22].
Virus resistance traits are typically selected in conjunction with other specific aims of breeding programs. Selection of resistant parents can be assisted by using marker-based genotyping in conjunction with phenotyping. This combinatorial approach is of benefit as there are known asymptomatic cultivars when infected with PVY, such as Shepody, that would not be detected using phenotyping alone [5]. Several markers have been developed to select for cultivars containing Ryadg, these include the sequence-characterized amplified region (SCAR) marker RYSC3 [22] and converted amplified fragment length polymorphism (AFLP) marker M45 [23], that have been primarily used to genotype the Australian collection. Slater et al. [24,25] performed genotyping using both markers and found 10/74 cultivars were incorrectly genotyped as susceptible to PVY using the RYSC3 marker, while M45 delivered superior accuracy with only cv. Emma genotyping as resistant using both markers yet is phenotypically classified as susceptible to PVY. Low association between RYSC3 marker alleles and Ryadg mediated resistance was also reported by Dalla Rizza et al. [26] and Herrera et al. [27]. To this effect, use of the RYSC3 marker has been replaced by alternative markers such as M45 and M6 [23,27]. There is currently no formal evidence in the literature to suggest that the M6 marker incorrectly genotypes any samples, however, it has only recently been reported and has not been subjected to close scrutiny or evaluation.
Recently, efforts have been made to improve the genomic resources available for the auto-tetraploid potato to the community for the improvement of potato breeding. This has resulted in the first draft of the 840 Mb potato genome, identification of c. 40,000 genes, estimated breeding values for desirable market traits and the identification of large cohorts of sequence variants [28,29,30,31]. These resources allow for the mining of diagnostic markers for specific traits, such as disease resistance and for the application of more traditional breeding tools, such as marker assisted selection (MAS) or the identification of SNP markers for use in genomic selection. Both methods of genomic assisted breeding would deliver benefits to the potato industry through new improved cultivars that are more disease resistant.
The marker systems currently in place for the selection of PVY resistant germplasm are ineffective due to the breakdown of association between the markers and the PVY resistant trait [25]. In this paper we will show that M6 will likely fall into the same category as other previously reported markers, resulting in no predictive diagnostic markers available that are 100% accurate for Ryadg. In addition, screening for these markers is not compatible or effective for high-throughput (HTP) multiplexed screening methods and is not able to be integrated into more complex genomic selection systems where multiple complex traits can be selected for simultaneously. With the genomic resources now available, the application of genetic mapping to find causal markers with more precision than classical biparental maps has been enabled. The aims of this paper are to use existing genomic resources and genotypic data from the Australian potato cultivar collection [24,25,31] to investigate the position of the Ryadg gene on Chromosome XI and develop a diagnostic SNP marker system for the reliable detection of the resistance allele for implementation in potato varietal improvement.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material and Sampling
The germplasm collection used for the SNP discovery portion of this study was as described in Caruana et al. [31]. A SNP validation panel of 80 cultivars with the majority having known Ryadg phenotypes was assembled. Cultivars from the germplasm collection were used to perform crosses under glasshouse conditions. Two populations (Lady Christl × La Ratte and Lady Claire × Friar consisting of 93 and 45 individuals, respectively) were developed to validate the developed molecular markers. Crosses were chosen on the basis that one cultivar (Lady Christl and Friar) contained the PVY resistance gene, Ryadg [25]. Seeds from the crosses were collected and grown to seedlings and all plants available from each cross sampled for DNA screening at 4 weeks.
2.2. Phenotyping
The parental material used in this study [31] had been previously screened for virus resistance [24,25]. Briefly the samples as well as known resistant and susceptible cultivars were grown in 150 mm pots in standard potting mix under glasshouse conditions. Three replicates for each cultivar and a control were inoculated with PVYNTN at the sixth leaf stage. Leaves from infected plants were ground in chilled 0.05 M phosphate inoculation buffer at a 1:5 dilution of leaf material to buffer. Two leaves of each plant were dusted with carborundum powder then lightly rubbed with the PVYNTN inoculum. At 21 days post infection, visual symptoms were noted, and new growth was sampled to test for virus infection. Samples were tested for PVY using a double antibody sandwich ELISA technique [24,25].
2.3. DNA Extractions
The germplasm collection and F1 progeny were sampled for DNA extraction. In all cases the sixth leaf was sampled for an automated 96 well format DNA extraction. Tissue was lysed after being frozen at −80 °C using a Tissuelyser II Mixer Mill (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany). DNA was extracted using a MagJET Plant Genomic DNA Kit (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) on a KingFisher Flex 96 (Thermo Scientific) and then stored at −20 °C.
2.4. Bioinformatic Data Analysis
The underlying DNA sequence of markers M45, M6 and RYSC3 were compared to the potato reference genome sequence using BLASTn using the Spud DB blast function (http://solanaceae.plantbiology.msu.edu/blast.shtml, accessed on 19 August 2020).
All 2 × 150 base, paired-end RNA sequencing data was taken from the previously published study of Caruana et al. [31]. Briefly, c. 3 million reads from leaf tissue of 181 potato cultivars were generated and SNP variants were identified using a pipeline that entailed the following. Initial sequence data fastq files were processed through a custom perl script for quality trimming and then adapters were removed using cutadapt v1.9 [32]. The trimmed sequence data were aligned to the Solanum tuberosum Group Phureja DM1-3 Assembly Version 3 DM pseudomolecule (v4.03) assembly [28,33] using the Spliced Transcripts Alignment to a Reference (STAR) software v2.5.3a, with default settings [34]. The alignments were converted to bam files and were initially processed with using Picard v2.1.0 to mark and remove duplicate reads (http://broadinstitute.github.io/picard). Base-score recalibration and variant calling was performed using the HaplotypeCaller function of The Genome Analysis Toolkit (GATK, [35]) under the following parameters; quality of mapped read >30; base quality >20; more than five reads covering the base in every genotype; more than four reads covering the alternate base (relative to the reference used) in at least one genotype; a minimum alternate allele fraction of 0.4. SNP calls (minimum two alternate bases at dp 5 to call heterozygote sample) and genotype assignment (AAAA, AAAB, AABB, ABBB or BBBB). All of these parameters needed to be met for a SNP to be called.
Due to the low occurrence of the Ryadg gene in the population used, initial filtering parameters were removed to include SNPs of minor allele frequency in the population. A region of Chromosome XI was delimited with existing markers RySC3 and M45. SNPs of interest were obtained by identifying unique genotypes matching only the known resistant cultivars that fell within the delimited region. Correlation of the SNP and virus resistance phenotypes was possible through the generation of marker–trait association proportions enabling the identification of associated alleles and nucleotide bases.
2.5. KASP Assay
Kompetitive Allele-specific PCR (KASP) assays were designed for one SNP in haplotypic configuration with the putative Ryadg gene. For each SNP, two forward allele specific primers and one reverse primer were developed using Sequencher 5.0 (Genecodes, Ann Arbor, MI, USA; Table 1). The developed primers were tested on a panel of 80 cultivars where the presence or absence of the Ryadg gene for the majority of samples was known as well as 138 segregating progeny from two crosses (Lady Christl × La Ratte and Lady Claire × Friar) where the presence or absence was unknown but would be present. KASP genotyping assays were performed in a total volume of 5 μL containing 0.07 μL of primer mix (containing 12 μL of each allele specific forward primer and 30 μm of reverse primer), 2.5 μL of KASPTM 2x Master Mix (LGC Genomics, Teddington, UK) and 2.5 μL of normalised genomic DNA (10 ng/μL) according to the manufacturer’s guidelines (LGC Genomics). Assays were run under the following cycling conditions: 94 °C for 15 min; 10 touchdown cycles of 94 °C for 20 s, 61–55 °C for 60 s (dropping 0.6 °C per cycle); 26 cycles of 94 °C for 20 s, 55 °C for 60 s. Detection of fluorescent samples was performed using a FLUOstar Omega microplate reader (BMG Labtech, Ortenberg, Germany) and cluster plot analysis was completed in KlusterCallerTM software (LGC Genomics). Alternatively, both fluorescence detection and cluster plot analysis were performed using CFX Manager (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA).

Table 1.
Kompetitive Allele-specific PCR (KASP) primers for SNP3279 used for detection of Ryadg positive cultivars. 5′ tag not supplied.
2.6. Protein Characterisation
The putative resistant allele of the transcript PGSC0003DMT400043732 was identified through SNP identification and translated into a protein sequence to identify open reading frames using the ExPASy Translate Tool (https://web.expasy.org/translate/, accessed on 23 October 2020). The protein sequence for transcript PGSC0003DMT400043732 was initially characterised using InterProScan (EMBL-EBI; http://www.ebi.ac.uk/interpro/, accessed on 23 October 2020; [36]) for functional analysis, family classification and prediction of domains. A BLASTp of the protein sequence was also performed for identification of significant alignments (NCBI; https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi, accessed on 23 October 2020) and a protein model was developed using I-TASSER [37,38]. Alignment of the two sequences (putative resistant allele vs. susceptible) was performed using Clustal Omega (EMBL-EBI; [39]).
3. Results
The underlying DNA sequence of markers M45, M6 and RYSC3 were compared to the potato reference genome sequence using BLASTn and all identified a specific region on Chromosome XI (Table 2). The maximum region that was delimited by the markers was included in the analysis. This area spanned position 1 to 1,826,346 bp. The region from the start of Chromosome XI to the M45 marker was of most interest (1–1,494,355 bp; Table 2) as M45 has higher predictive ability when compared to RYSC3. The M6 marker was detected within the sequence interval between M45 and RYSC3 and is located closer to the RYSC3 marker than M45 (Table 2).

Table 2.
Genome positions of current Ryadg markers in use based on the reference genome published.
Within the maximum region of 1,826,346 bp, 200 genes were identified by extracting all predicted and known coding sequences from the genome via the general feature format (GFF) file. From the available genotypic data, a total of 35,569 unfiltered SNPs were also putatively located within these genes in the candidate target region. Within the germplasm collection, 6 out of the 181 cultivars used to generate the sequence and SNP data had previously been phenotyped and genotyped as positive for Ryadg [25]. SNPs unique to these six cultivars were extracted by comparing known resistant cultivars (Carlingford, Friar, Galil, Lady Christl, PO3 and Royal Blue) to all susceptible cultivars. From this, only seven SNPs were found to correlate to the PVY resistant phenotype and five of those SNPs were contained within one gene. These five SNPs were located in the gene (PGSC0003DMG402016981; gene model ID PGSC0003DMT400043732), located between 1,407,371 and 1,411,692 bp in the reference genome. A total of four of the five SNPs were identified as triallelic in nature across the germplasm set used (Table 3). The candidate Ryadg gene containing the associated SNPs was annotated as a Bacterial spot disease resistance protein 4 (Figure 1). The candidate gene identified is located within a cluster of disease resistance genes in the reference genome, with 6/8 genes between 1,390,274 and 1,430,902 bp being categorised with a similar annotation and function (Supplementary file 1). A triallelic SNP within the gene at genome position 1,410,649 bp (position 3279 of transcript PGSC0003DMT400043732) was selected for primer design for diagnostic assay development (Table 3).

Table 3.
The SNPs identified in this study that were tested as potential markers for the detection of Ryadg, from left to right, the transcript that they were identified from, the position they reside at within that transcript, the reference base, the alternative base, and the single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) classification.
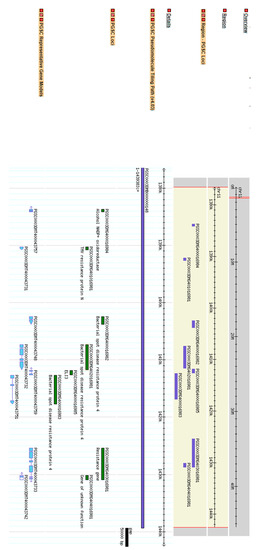
Figure 1.
Screenshot of the SPUD DB genome browser tool (http://solanaceae.plantbiology.msu.edu/cgi-bin/gbrowse/potato/, accessed on 19 August 2020) showing the cluster of resistance genes.
A KASP assay was developed for SNP3279, putatively associated with the Ryadg locus. The assay was screened across a collection of 80 breeding parents for validation of the SNP marker and included known resistant sources (Carlingford, Friar, Galil, Lady Christl, PO3 and Royal Blue) as well as Emma that was known to incorrectly genotype as resistant with the M45 and RySC3 assays but phenotypes as susceptible (Table 4). The data generated by the SNP3279 molecular marker was in complete agreement with the known phenotypic results. All known resistant cultivars genotyped as positive for the resistant source with the M45 marker and also phenotyped as resistant to PVYN. The cv. PO3 was the only known resistant source used in the study that genotyped as resistant using both the RySC3 and the M45 marker (Table 4). The assay also agreed with the M45 marker data, with the exception that the cultivar Emma genotypes correctly as susceptible with the SNP3279 assay. In addition, SNP3279 genotyped a further four cultivars as containing the resistant allele (Granola, Suvi, Foxton and Maranca). The complete set of results of phenotyping and genotyping for the collection of breeding parents are presented in Supplementary File 2.

Table 4.
Cultivars identified that have exhibited a dissociation event between a marker and Ryadg. From left to right; the cultivar being evaluated; the result for RySC3 where a “-” indicates a negative result and “+” indicates a positive; the result for M45 where a “-” indicates a negative result and “+” indicates a positive; the result for SNP3279 where a “-” indicates a negative result and “+” indicates a positive; the phenotypic result from being challenged with PVYN; the resistance classification pulled from the European potato databases (SASA, IPK, NIVAP), if no classification was present, the classification of parents of the cultivars was provided. Validation of KASP SNP marker was performed using parental material positive for Ryadg and Emma, negative for Ryadg.
The SNP3279 marker was also evaluated on novel progeny resulting from the crosses Lady Christl × La Ratte and Lady Claire × Friar in an attempt to identify allele dosage as well as validate the molecular marker in novel segregating germplasm. From the Lady Christl × La Ratte cross, 93 progeny were evaluated. In total, 38/93 progeny were genotyped as resistant while the remaining 55/93 progeny were genotyped as susceptible. The observed segregation ratio was 1:1.4 and a Chi2 analysis yielded a nonsignificant result for deviation away from a 1:1 ratio. A total of 45 progeny from the Lady Claire x Friar cross were also evaluated. From this cross, 16/45 were genotyped as resistant while the remaining 29/45 were genotyped as susceptible. The observed segregation ratio was 1:1.8 and a Chi2 analysis also yielded a nonsignificant result for deviation away from a 1:1 ratio. In the case of both crosses, the resistant parents Lady Christl and Friar appear to follow simplex dosage based on the observed segregation ratio of 1:1 in the offspring, indicative of simplex by nuliplex.
Protein Characterisation
The putative resistant allele of the transcript PGSC0003DMT400043732 that has the potential to be the introgressed gene Ryadg, was translated into a protein sequence to identify open reading frames using the Translate Tool (ExPASy). The protein sequence for transcript PGSC0003DMT400043732 was initially characterised using Interpro Scan (EMBL-EBI) for functional analysis, family classification and prediction of domains. The main matches included toll/interleukin-1 receptor homology (TIR) domain superfamily, P-loop containing nucleoside triphosphate hydrolase, winged helix DNA-binding domain superfamily, leucine-rich repeat (LRR) domain superfamily, helical domain of apoptotic protease-activating factors, disease resistance protein signatures and other uncharacterised leucine-rich repeating domains. A BLASTp of the translated protein sequence was also performed for identification of significant alignments. A Tobacco mosaic virus (TMV) resistance protein (Accession number Q40392.1) produced the most significant alignment to transcript PGSC0003DMT400043732 with 95% query coverage and an E value of 0. An alignment of the two protein sequences (Clustal Omega) representing resistant and susceptible cultivars revealed three amino acid changes at positions 1016, 1059 and 1060 and which are downstream of the LRR region.
4. Discussion
Advancements in genotyping technologies have removed the need for anonymous marker systems and molecular marker assays have coalesced to SNP variants and markers. This standardisation has significant benefits including the ability to transfer assays across platforms (target capture assays, SNP chips, genome sequencing) as well as the scalability to simultaneously screen for multiple genetic traits using a wide spectrum of multiplexing strategies. For applications in genomic selection (GS), routine genotyping using SNPs that are causal variants for traits will improve the selection power of the markers. The ability to rapidly develop and resolve GS issues relating to historic molecular marker assays has now been enabled in potato through the delivery of the reference genomic sequence along with large collections of known sequence variants [28,29,30,31,33].
Despite the introduction of GS and its initial development in potato, the application of marker assisted selection on simple traits, in some circumstances can still be of value and can be a cost-effective solution. For species like potato with complex genetic inheritance, marker assisted selection is still an important tool to increase selection accuracy of specific genotypes and ultimately reduce the time required to deliver new cultivars. For the most beneficial long-lived potato cultivar, robust forms of disease resistance are of most value, if the mechanism of resistance is durable. As potato has a wide range of traits that have to meet stringent production needs, initial selection of key traits that are under simple genetic control could remove unwanted genotypes from the breeding process prior to more costly genome-wide genotyping and GS.
This study aimed to exemplify and utilise the benefits of existing genetic and genomic resources in potato, through combining SNP genotypic data with the reference genome sequence for the development of new improved diagnostic markers linked to Ryadg. The identification of SNP markers in a high throughput genotyping assay like KASP can validate such markers in a rapid cost-effective manner. The M45 and RYSC3 markers are the most commonly used molecular markers for detection of the PVY resistance gene, Ryadg, and have been effective to some degree in selecting PVY resistant germplasm. However, errors have occurred in typing germplasm and these errors in genotyping are primarily due to the distance between the diagnostic marker and PVY resistance gene. This was exemplified with cv. Emma which contains both the M45 and RySC3 marker but is susceptible to PVY infection. The three PVY resistance markers (M45, M6 and RYSC3) were identified on Chromosome XI at positions 1,494,355, 1,708,102 and 1,826,029, respectively. M6 is a more recently described marker for PVY resistance [27] and has not been screened against a large population of phenotypes. Given that this marker is located on Chromosome XI in-between M45 and RYSC3 and both of these markers have lost linkages with Ryadg [25], it is unlikely that the M6 assay will be more robust.
The presence and location of the Ryadg gene is a result of a historic introgression from S. tuberosum ssp. Andigena [40,41]. The region of Chromosome XI that this gene is located on is expected to contain novel variation and haplotypes compared to the more conventional potato genome because of this introgression event. As the reference genome was derived from a S. tuberosum Phureja clone, it is also expected that the reference sequence does not contain the Ryadg gene. Due to the location of the M45 and RYSC3 markers towards the end of Chromosome XI and the increase in linkage breakages with RYSC3 and the PVY resistance trait as demonstrated by cvs. Carlingford, Friar, Galil, Lady Christl, and Royal Blue, it was surmised that the actual Ryadg gene was upstream of both markers. In addition, the cv. Emma genotyped as resistant with both markers, whilst phenotyping as susceptible [24,25], indicating that the break in linkage had occurred between these markers and the Ryadg gene.
A list of genes in the region has been supplied that were available on PGSC (Supplementary File 1). To shorten this list, SNPs unique to resistant cultivars in the delimited region were extracted and positioned on the genome. Five SNPs between 1,407,371 and 1,411,692 bp were found in a “Bacterial spot resistance gene” (PGSC0003DMG402016981; gene model ID PGSC0003DMT400043732), which was located close to the M45 marker. This gene showed typical R gene qualities such as leucine-rich repeats and nucleotide binding sites [42,43,44] while also residing in a large cluster of disease resistance genes. Out of the five SNPs located within the resistance gene, four were triallelic, suggesting the gene was highly variable or has arisen from a highly divergent haplotype or is the result of a local gene duplication in a specific lineage that is not present within the reference genome. Presence absence variation has been well documented for disease resistance in plants [45]. As the Ryadg has resulted from a wild relative introgression into the potato genome, it is also possible that the cluster of introgressed genes could contain a large cohort of genes that act together and strongly affect disease resistance within the plant. It is suggested that any gene that is present within this cluster could potentially be Ryadg but SNP3279 is likely to hold a strong association due to the effect an introgressed cluster has. Wild introgressions in other plant species as well as specific examples in potato have observed reduced recombination rates within introgressed genetic fragments due to highly divergent genetic sequences and other characteristics [46,47,48,49]. As a result, a genetic marker within the introgressed region is likely to hold association with the trait as a diagnostic assay in a robust manner whilst not necessarily having to be the causative variant. In order to unambiguously determine the Ryadg gene and identify the exact genes that were introgressed, functional genomic knockout studies are required.
KASP technology was chosen to attempt to evaluate SNP copy number to provide allele dosage of the resistant allele for parental material. Allele dosage counts are valuable to potato breeding as the autotetraploid nature of the potato generates complex patterns of inheritance that can dictate the required size of a population that has to be screened to remove unwanted plants [12]. The KASP assay described here can successfully distinguish between nulliplex and simplex accurately, however, higher dosage levels have not knowingly been evaluated and would require further evaluation. Segregation of Ryadg was attempted in unknown populations, however, despite the size of the populations being limiting, segregation and allele dosage was confirmed making it possible to accurately designate allele dosage to parental cultivars.
The newly designed KASP assay for the putatively associated Ryadg variant, SNP3279, accurately genotyped the parent cultivars that did or did not contain the PVY resistance gene, Ryadg, as well as amending cultivars that had been previously genotyped incorrectly due to recombination events between M45 and Ryadg (Table 4). As the SNP used for the primer design is triallelic, the marker assay developed was specifically targeted to identify the base associated with the resistance allele, while also assaying one of the other two possible nucleotides. As the assay technology only works in a biallelic nature there is the possibility that some cultivars would genotype with a missing allele and may appear as missing data, whilst being accurately genotyped. While the SNP3279 marker accurately repeated the genotyping results for known resistant cultivars, there were new cultivars (Foxton, Maranca, Suvi and Granola) that putatively had resistance based on the presence of SNP3279 but that had not been phenotyped previously. Although these cultivars had not been previously phenotyped, they had been assigned susceptible through genotyping with the historic markers and so represent a potential mislabelled source of PVY resistance. Upon examining these cultivar pedigrees, most had been rated as resistant or were developed with known resistant parents (Table 4). It is likely that these genotyping errors are due to recombination events occurring between the previously used markers and the Ryadg gene as is the case with cv. Emma. In the case of cv. Granola for example, its heritage has included breeding lines known to carry Ryadg in its development and cv. Granola has been reported to contain varying levels of resistance to PVY (Table 4).
Protein characterisation of transcript PGSC0003DMT400043732 showed classic disease resistance protein components when characterised through Interpro Scan (EMBL-EBI). Of most interest was: the identification of Toll/Interleukin receptors known to mediate cell death and disease resistance pathways across all kingdoms [50]; a P-loop containing nucleoside triphosphate hydrolase where reactions catalysed by enzymes cause hydrolysis of bound nucleotide triphosphates (NTPs) [51]; a winged helix DNA-binding domain superfamily responsible for DNA recognition through contact [52]; a leucine-rich repeat (LRR) domain superfamily responsible for detection of pathogens. The majority of currently identified disease resistance genes in plants contain nucleotide binding (NB) and LRR domains [53] and through in silica characterisation in this study it appears that the gene encoded from transcript PGSC0003DMT400043732 falls in this group. The protein sequences of the resistant and susceptible cultivars showed 99.73% identity with three amino acid changes at positions 1016, 1059 and 1060 of this transcript. At these positions the resistant transcript contains Arginine (Arg), Glutamic Acid (Glu) and Alanine (Ala) whereas the susceptible transcript contains Glutamine (Gln) and Aspartic Acid (Asp). The amino acid changes at positions 1016 and 1059 are considered to be minor with a strong similarity between the substituted AAs. The most extreme change seen is at position 1060 where Ala (a nonpolar/aliphatic amino acid) is replaced with Asp (a polar negative amino acid).
5. Conclusions
The aim of this study was to incorporate the genomic resources that have been developed for Solanum species with large genotypic and variant datasets with historic phenotypic records, to identify genes directly associated with PVY resistance. By combining these new and established resources, this study demonstrates the utility of applied genomics in potatoes to further enhance precision breeding. We identified a gene showing strong characteristics similar to known viral resistance genes and developed a simple diagnostic assay to screen unknown samples that accurately detect its presence in potato germplasm. However, using a haploid reference genome, significant differences between this and the wild introgressed fragment are likely to be present. To further characterise the region containing Ryadg, long read DNA sequencing would unequivocally define the gene content of the targeted region, enabling detailed gene knockout studies for absolute clarity. Alternatively, extensive use of the marker in an applied breeding setting, where the marker would undergo a robust evaluation, could confirm the predictive diagnostic nature of the marker or identify limitations that would indicate a need for further studies.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/agronomy11050832/s1, Supplementary File 1: A list of potential candidate genes that may include Ryadg. Supplementary File 2: The complete set of historic results of phenotyping and genotyping for the collection of breeding parents in the Australian germplasm collection.
Author Contributions
Conceptualisation, B.M.C., N.O.I.C., B.C.R., A.T.S., and F.C.; methodology, B.M.C.; formal analysis, B.M.C.; data curation, B.M.C.; writing—original draft preparation, B.M.C. and N.O.I.C; writing—review and editing, B.M.C., N.O.I.C and B.C.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Victorian Department of Jobs, Precincts and Regions. Brittney Caruana was the recipient of an Australian Postgraduate Award.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the Victorian Department of Jobs Precincts and Regions and La Trobe University who supported this work.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- FAOSTAT. Statistical Database Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Oerke, E.C. Crop losses to pests. J. Agric. Sci. 2006, 144, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kehoe, M.A.; Jones, R.A.C. Improving Potato virus Y strain nomenclature: Lessons from comparing isolates obtained over a 73-year period. Plant Pathol. 2016, 65, 322–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffries, C. Technical Guidelines for the Safe Movement of Germplasm. No19 Potato; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1998; Volume 177. [Google Scholar]
- Nolte, P.; Whitworth, J.L.; Thornton, M.K.; McIntosh, C.S. Effect of seedborne Potato virus Y on performance of Russet Burbank, Russet Norkotah, and Shepody potato. Plant Dis. 2004, 88, 248–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Rodriguez, M.; Chikh-Ali, M.; Johnson, S.B.; Gray, S.; Malseed, N.; Crump, N.S.; Karasev, A.V. The recombinant Potato Virus Y (PVY) strain, PVYNTN, identified in potato fields in Victoria, South Eastern Australia. Plant Dis. 2020, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swiezynski, K. Inheritance of resistance to viruses. Potato Genetics; Scottish Crop Research Institute: Dundee, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Bradshaw, J.; Mackay, G. Breeding Strategies for Clonally Propagated Potatoes; Scottish Crop Research Institute: Dundee, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Gebhardt, C. Bridging the gap between genome analysis and precision breeding in potato. Trends Genet. 2013, 29, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, F.; Lopez-Vizcon, C. Application of molecular marker-assisted selection (MAS) for disease resistance in a practical potato breeding programme. Potato Res. 2012, 55, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindhout, P.; Meijer, D.; Schotte, T.; Hutten, R.C.; Visser, R.G.; van Eck, H.J. Towards F1 hybrid seed potato breeding. Potato Res. 2011, 54, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slater, A.T.; Cogan, N.O.I.; Forster, J.W. Cost Analysis of the application of marker-assisted selection in potato breeding. Mol. Breed. 2013, 32, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hospital, F. Challenges for effective marker-assisted selection in plants. Genetica 2009, 136, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barker, H. Extreme resistance to Potato virus V in clones of Solanum tuberosum that are also resistant to Potato viruses Y and A: Evidence for a Locus Conferring Broad-Spectrum Potyvirus Resistance. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1997, 95, 1258–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hämäläinen, J.H.; Sorri, V.A.; Watanabe, K.N.; Gebhardt, C.; Valkonen, J.P.T. Molecular examination of a chromosome region that controls resistance to Potato Y and a Potyviruses in potato. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1998, 96, 1036–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cockerham, G. Genetical studies on resistance to potato viruses X and Y. Heredity 1970, 25, 309–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebhardt, C.; Bellin, D.; Henselewski, H.; Lehmann, W.; Schwarzfischer, J.; Valkonen, J.P.T. Marker-assisted combination of major genes for pathogen resistance in potato. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2006, 112, 1458–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valkonen, J.P.T.; Wiegmann, K.; Hämäläinen, J.H.; Marczewski, W.; Watanabe, K.N. Evidence for utility of the same PCR-based markers for selection of extreme resistance to Potato virus Y controlled by Rysto of Solanum stoloniferum derived from different sources. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2008, 152, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottoman, R.J.; Hane, D.C.; Brown, C.R.; Yilma, S.; James, S.R.; Mosley, A.R.; Crosslin, J.M.; Vales, M.I. Validation and implementation of marker-assisted selection (MAS) for PVY resistance (Ryadg gene) in a tetraploid potato breeding program. Am. J. Potato Res. 2009, 86, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, H.; Hunnius, W. Potato Breeding: Problems and Perspectives; V.P. Parey: Berlin, Germany, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Mendoza, H.A.; Mihovilovich, E.J.; Saguma, E. Identification of triplex (YYYy) potato virus y (PVY) immune progenitors derived from Solanum tuberosum ssp.andigena. Am. Potato J. 1996, 73, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasai, K.; Morikawa, Y.; Sorri, V.A.; Valkonen, J.; Gebhardt, C.; Watanabe, K.N. Development of SCAR markers to the PVY resistance gene Ryadg based on a common feature of plant disease resistance genes. Genome 2000, 43, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brigneti, G.; Garcia-Mas, J.; Baulcombe, D.C. Molecular mapping of the Potato virus Y resistance gene Rysto in potato. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1997, 94, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slater, A.T. Molecular and Quantitative Genetic Studies for Potato Germplasm Enhancement. Ph.D. Thesis, La Trobe University, Bundoora, Australia, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Slater, A.T.; Schultz, L.; Lombardi, M.; Rodoni, B.C.; Bottcher, C.; Cogan, N.O.I.; Forster, J.W. Screening for resistance to PVY in Australian potato germplasm. Genes 2020, 11, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalla Rizza, M.; Vilaró, F.L.; Torres, D.G.; Maeso, D. Detection of PVY extreme resistance genes in potato germplasm from the Uruguayan breeding program. Am. J. Potato Res. 2006, 83, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Rosario Herrera, M.; Vidalon, L.J.; Montenegro, J.D.; Riccio, C.; Guzman, F.; Bartolini, I.; Ghislain, M. Molecular and genetic characterization of the Ryadg locus on chromosome XI from Andigena potatoes conferring extreme resistance to Potato virus Y. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2018, 131, 1925–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Potato Genome Sequencing Consortium. Genome sequence and analysis of the tuber crop potato. Nature 2011, 475, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uitdewilligen, J.G.A.M.L.; Wolters, A.-M.A.; D’hoop, B.B.; Borm, T.J.A.; Visser, R.G.F.; van Eck, H.J. A next-generation sequencing method for genotyping-by-sequencing of highly heterozygous autotetraploid potato. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vos, P.G.; Uitdewilligen, J.G.A.M.L.; Voorrips, R.E.; Visser, R.G.F.; van Eck, H.J. Development and analysis of a 20K SNP array for potato (Solanum tuberosum): An insight into the breeding history. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2015, 128, 2387–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caruana, B.M.; Pembleton, L.W.; Constable, F.; Rodoni, B.; Slater, A.T.; Cogan, N.O.I. Validation of genotyping by sequencing using transcriptomics for diversity and application of genomic selection in tetraploid potato. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet J. 2011, 17, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.K.; Bolser, D.; de Boer, J.; Sønderkær, M.; Amoros, W.; Carboni, M.F.; D’Ambrosio, J.M.; de la Cruz, G.; Di Genova, A.; Douches, D.S.; et al. Construction of reference chromosome-scale pseudomolecules for potato: Integrating the potato genome with genetic and physical maps. G3 GenesGenomesGenetics 2013, 3, 2031–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobin, A.; Davis, C.A.; Schlesinger, F.; Drenkow, J.; Zaleski, C.; Jha, S.; Batut, P.; Chaisson, M.; Gingeras, T.R. STAR: Ultrafast universal RNA-seq aligner. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, A.; Hanna, M.; Banks, E.; Sivachenko, A.; Cibulskis, K.; Kernytsky, A.; Garimella, K.; Altshuler, D.; Gabriel, S.; Daly, M.; et al. The genome analysis toolkit: A mapreduce framework for analyzing next-generation dna sequencing data. Genome Res. 2010, 20, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, A.L.; Attwood, T.K.; Babbitt, P.C.; Blum, M.; Bork, P.; Bridge, A.; Brown, S.D.; Chang, H.-Y.; El-Gebali, S.; Fraser, M.I.; et al. InterPro in 2019: Improving coverage, classification and access to protein sequence annotations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D351–D360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Freddolino, P.L.; Zhang, Y. COFACTOR: Improved protein function prediction by combining structure, sequence and protein–protein interaction information. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, W291–W299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, Y. I-TASSER Server: New development for protein structure and function predictions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W174–W181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sievers, F.; Wilm, A.; Dineen, D.; Gibson, T.J.; Karplus, K.; Li, W.; Lopez, R.; McWilliam, H.; Remmert, M.; Söding, J.; et al. Fast, Scalable generation of high-quality protein multiple sequence alignments using Clustal Omega. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2011, 7, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munoz, F.J.; Plaisted, R.L.; Thurston, H.D. Resistance to Potato virus Y in Solanum tuberosum spp. Andigena. Am. Potato J. 1975, 52, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvez, R.; Brown, C.R. Inheritance of Extreme resistance to PVY derived from Solanum tuberosum ssp. Andigena. Am. Potato J. 1980, 57, 476–477. [Google Scholar]
- Bent, A.F.; Kunkel, B.N.; Dahlbeck, D.; Brown, K.L.; Schmidt, R.; Giraudat, J.; Leung, J.; Staskawicz, B.J. RPS2 of Arabidopsis thaliana: A leucine-rich repeat class of plant disease resistance genes. Science 1994, 265, 1856–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitham, S.; Dinesh-Kumar, S.P.; Choi, D.; Hehl, R.; Corr, C.; Baker, B. The product of the Tobacco mosaic virus resistance gene N: Similarity to toll and the interleukin-1 receptor. Cell 1994, 78, 1101–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mindrinos, M.; Katagiri, F.; Yu, G.-L.; Ausubel, F.M. The A. Thaliana disease resistance gene RPS2 encodes a protein containing a nucleotide-binding site and leucine-rich repeats. Cell 1994, 78, 1089–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barragan, A.C.; Weigel, D. Plant NLR Diversity: The known unknowns of pan-NLRomes. Plant Cell 2020, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganal, M.W.; Tanksley, S.D. Recombination around the Tm2a and Mi resistance genes in different crosses of Lycopersicon peruvianum. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1996, 92, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, F.; Wing, R.A.; Wise, R.P. Genome dynamics and evolution of the Mla (powdery mildew) resistance locus in barley. Plant Cell 2002, 14, 1903–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkers-Tomczak, A.; Bakker, E.; de Boer, J.; van der Vossen, E.; Achenbach, U.; Golas, T.; Suryaningrat, S.; Smant, G.; Bakker, J.; Goverse, A. Comparative sequence analysis of the potato cyst nematode resistance locus H1 reveals a major lack of co-linearity between three haplotypes in potato (Solanum tuberosum ssp.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2011, 122, 595–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultz, L.; Cogan, N.O.I.; McLean, K.; Dale, M.F.B.; Bryan, G.J.; Forster, J.W.; Slater, A.T. Evaluation and implementation of a potential diagnostic molecular marker for H1-Conferred potato cyst nematode resistance in potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). Plant Breed. 2012, 131, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayless, A.M.; Nishimura, M.T. Enzymatic functions for toll/interleukin-1 receptor domain proteins in the plant immune system. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leipe, D.D.; Koonin, E.V.; Aravind, L. STAND, a class of p-loop NTPases including animal and plant regulators of programmed cell death: Multiple, complex domain architectures, unusual phyletic patterns, and evolution by horizontal gene transfer. J. Mol. Biol. 2004, 343, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajiwala, K.S.; Burley, S.K. Winged helix proteins. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2000, 10, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tameling, W.I.L.; Takken, F.L.W. Resistance proteins: Scouts of the plant innate immune system. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2008, 121, 243–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).