The Effect of Antibiotic Treatment on the Bacterial Community of the Brown Planthopper and Its Correlation with Rice Virulence
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
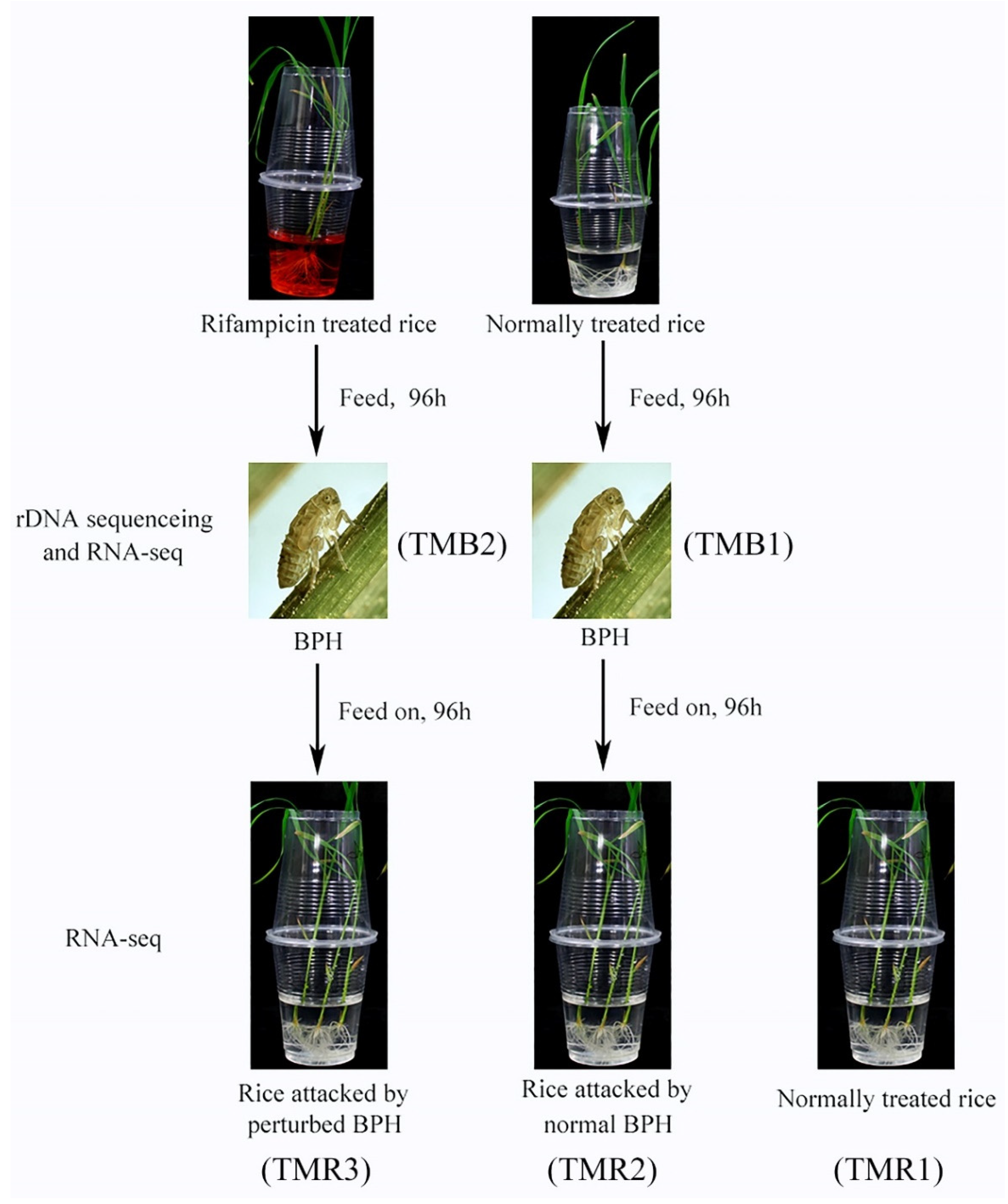
2.1. Acquisition of Biological Samples
2.2. Cultivation of Rice and Rearing of BPH
2.3. Perturbation of Bacterial Communities of BPH
2.4. 16S rRNA Sequencing of Bacterial Communities of Treated/Untreated BPH
2.5. RNA-Seq of BPH Feeding on Rifampicin-Treated and Untreated Rice
2.6. RNA-Seq of Rice Fed on by Treated/Untreated BPH
2.7. Analysis of 16S rRNA Sequencing Data
2.8. Analysis of BPH RNA-Seq Data
2.9. Analysis of Rice RNA-Seq Data
3. Results
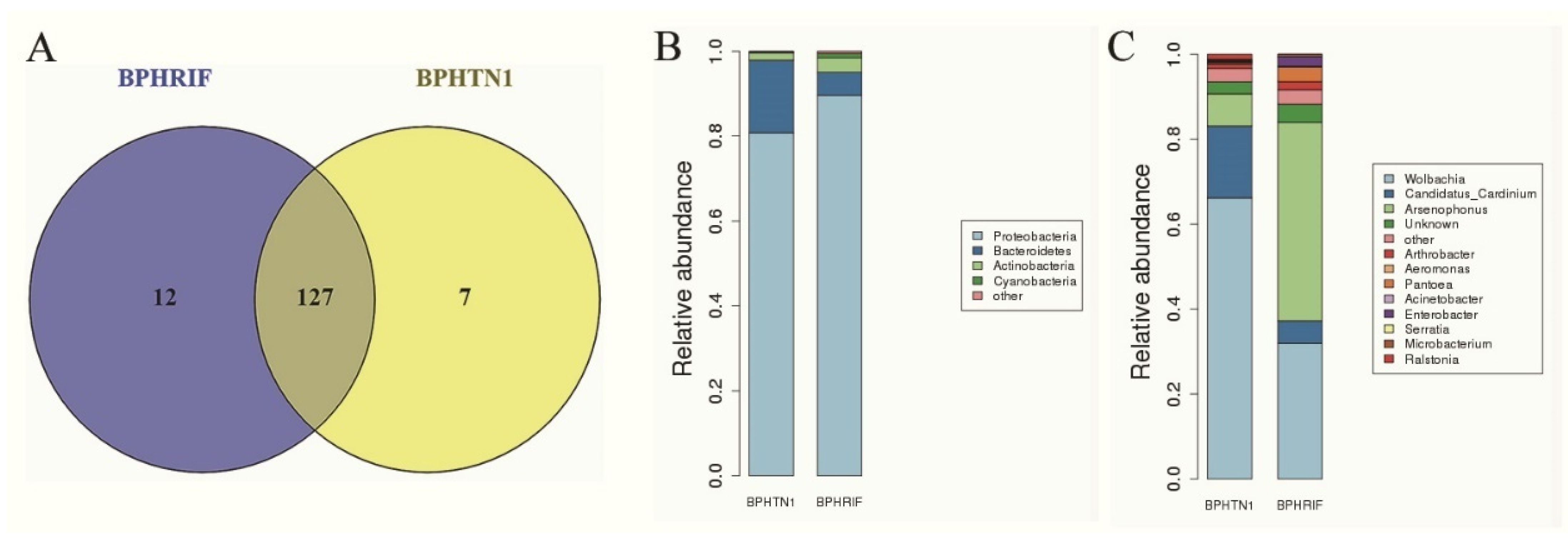
3.1. Change in Bacterial Communities after Feeding Antibiotic-Treated Rice
3.2. Change in BP Transcriptome after Feeding Rifampicin-Treated Rice
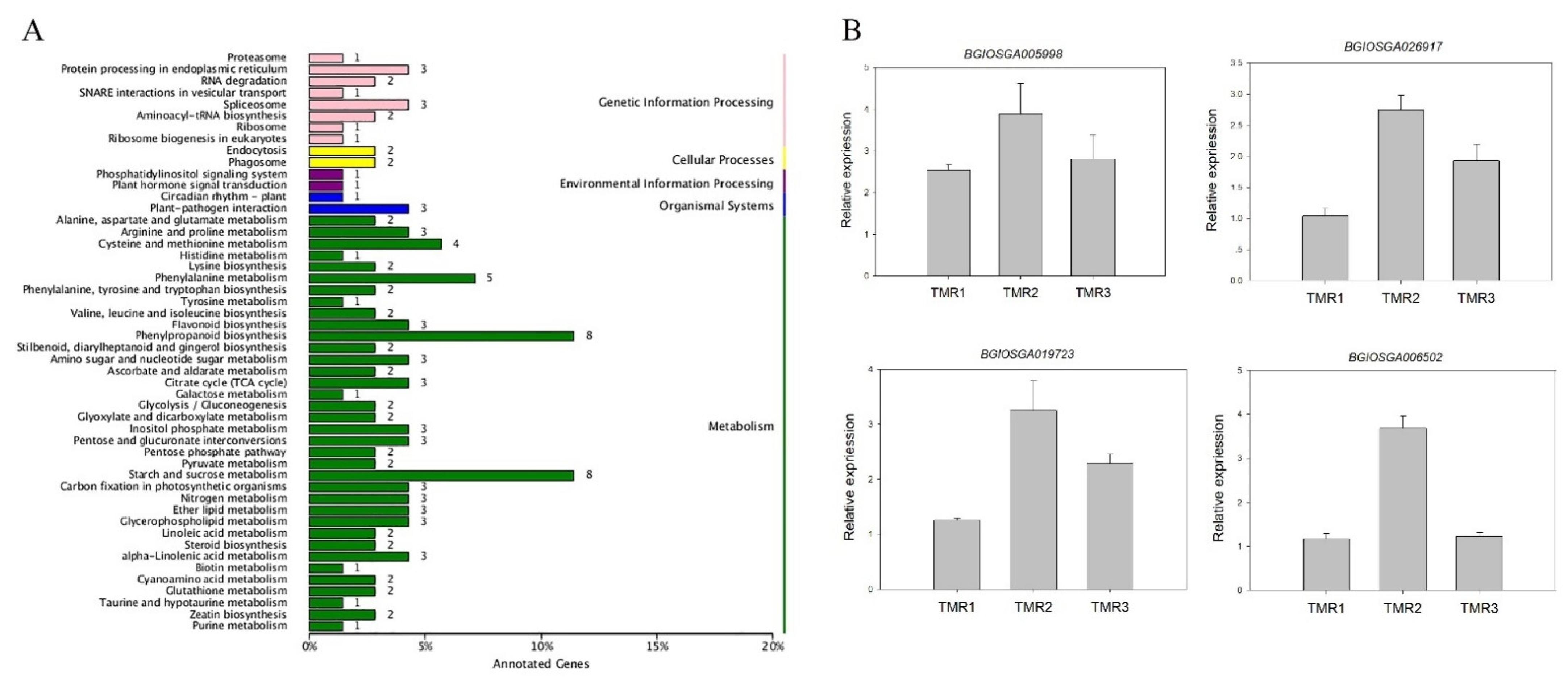
3.3. Change in the Transcriptome of Rice after Being Fed by Perturbed BPH
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Backus, E.A.; Serrano, M.S.; Ranger, C.M. Mechanisms of hopperburn: A review of insect taxonomy, behavior, and physiology. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2005, 50, 125–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.C.; Liu, Z.D.; Huang, C.; Lu, M.H.; Liu, J.; Yang, Q.P. Statistics and analysis of crop yield losses caused by main diseases and insect pests in recent 10 years. Plant Prot. 2016, 42, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.Y.; Wang, X.L.; Yuan, H.Y.; Chen, R.Z.; Zhu, L.L.; He, R.F.; He, G.C. Responses of two contrasting genotypes of rice to brown planthopper. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2008, 21, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabauatan, P.Q.; Cabunagan, R.C.; Choi, I.R. Rice viruses transmitted by the brown planthopper Nilaparvata lugens Stål. In Planthoppers: New Threats to the Sustainability of Intensive Rice Production Systems in Asia, 1st ed.; Heong, K.L., Hardy, B., Eds.; International Rice Research Institute: Los Baños, Philippines, 2009; pp. 357–368. [Google Scholar]
- Nakashima, N.; Noda, H. Nonpathogenic Nilaparvata lugens reovirus is transmitted to the brown planthopper through rice plant. Virology 1995, 207, 303–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.P.; Bari, M.N.; Haque, S.S.; Kabir, M.M.M.; Afrin, S.; Nowrin, F.; Islam, M.S.; Landis, D.A. Establishing next-generation pest control services in rice fields: Eco-agriculture. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Pray, C.; Rozelle, S. Enhancing the crops to feed the poor. Nature 2002, 418, 678–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christou, P.; Capell, T.; Kohli, A.; Gatehouse, J.A.; Gatehouse, A.M.R. Recent developments and future prospects in insect pest control in transgenic crops. Trends Plant Sci. 2006, 11, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.; Zhang, W.L.; Liu, B.F.; Hu, J.; Wei, Z.; Shi, Z.Y.; He, R.F.; Zhu, L.L.; Chen, R.Z.; Han, B.; et al. Identification and characterization of Bph14, a gene conferring resistance to brown planthopper in rice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 22163–22168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.Q.; Wu, H.; Chen, H.; Liu, Y.L.; He, J.; Kang, H.Y.; Sun, Z.G.; Pan, G.; Wang, Q.; Hu, J.L.; et al. A gene cluster encoding lectin receptor kinases confers broad-spectrum and durable insect resistance in rice. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2014, 33, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, W.T.; Du, B.; Shangguan, X.X.; Zhao, Y.; Pan, Y.F.; Zhu, L.L.; He, Y.Q.; He, G.C. BAC and RNA sequencing reveal the brown planthopper resistance gene BPH15 in a recombination cold spot that mediates a unique defense mechanism. BMC Genet. 2014, 15, 674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, Y.; Hattori, M.; Yoshioka, H.; Yoshioka, M.; Takahashi, A.; Wu, J.; Sentoku, N.; Yasui, H. Map-based cloning and characterization of a brown planthopper resistance gene BPH26 from Oryza sativa L. ssp. indica cultivar ADR52. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Cao, L.M.; Zhang, Y.X.; Cao, C.X.; Liu, F.; Huang, F.K.; Qiu, Y.F.; Li, R.B.; Lou, X.J. Map-based cloning and characterization of BPH29, a B3 domain-containing recessive gene conferring brown planthopper resistance in rice. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 6035–6045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.; Kim, S.R.; Kim, Y.H.; Suh, J.P.; Park, H.M.; Sreenivasulu, N.; Misra, G.; Kim, S.M.; Hechanova, S.L.; Kim, H.; et al. Map-based cloning and characterization of the BPH18 gene from wild rice conferring resistance to brown planthopper (BPH) insect pest. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.S.; Gao, F.Y.; Wu, X.T.; Lu, X.J.; Zeng, L.H.; Lv, J.Q.; Su, X.W.; Luo, H.; Ren, G.J. Bph32, a novel gene encoding an unknown SCR domain-containing protein, confers resistance against the brown planthopper in rice. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Huang, J.; Wang, Z.Z.; Jing, S.L.; Wang, Y.; Ouyang, Y.D.; Cai, B.D.; Xin, X.F.; Liu, X.; Zhang, C.X.; et al. Allelic diversity in an NLR gene BPH9 enables rice to combat planthopper variation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 12850–12855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.P.; Xu, C.X.; Wu, D.; Zhao, Y.; Qiu, Y.F.; Wang, X.X.; Ouyang, Y.D.; Cai, B.D.; Liu, X.; Jing, S.L.; et al. Bph6 encodes an exocyst-localized protein and confers broad resistance to planthoppers in rice. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.; Chen, R.Z.; Guo, J.P.; He, G.C. Current understanding of the genomic, genetic, and molecular control of insect resistance in rice. Mol. Breeding 2020, 40, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.H.; Bernal, C.C.; Tan, J.; Horgan, F.G.; Fitzgerald, M.A. Planthopper “adaptation” to resistant rice varieties: Changes in amino acid composition over time. J. Insect Physiol. 2011, 57, 1375–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jena, K.K.; Kim, S.M. Current status of brown planthopper (BPH) resistance and genetics. Rice 2010, 3, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, P. Biology of bacteriocyte-associated endosymbionts of plant sap-sucking insects. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2005, 59, 155–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.H.; Yu, N.; Xu, X.X.; Liu, Z.W. Community structure, dispersal ability and functional profiling of microbiome existing in fat body and ovary of the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens. Insect Sci. 2019, 26, 683–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wari, D.; Kabir, A.M.; Mujiono, K.; Hojo, Y.; Shinya, T.; Tani, A.; Nakatani, H.; Galis, I. Honeydew-associated microbes elicit defense responses against brown planthopper in rice. J. Exp. Bot. 2019, 70, 1683–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shentu, X.P.; Xiao, Y.; Song, Y.; Cao, Z.Y.; Fan, J.X.; Yu, X.P. Comparative analysis of the diversity of the microbial communities between non-fertilized and fertilized eggs of brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens Stål. Insects 2020, 11, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, C.X.; Yu, L.L.; Fan, H.W.; Wang, Z.; Xu, H.J.; Xi, Y.; Zhu, Z.R.; Zhou, W.W.; et al. Genomes of the rice pest brown planthopper and its endosymbionts reveal complex complementary contributions for host adaptation. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, A.E. The microbial dimension in insect nutritional ecology. Funct. Ecol. 2009, 23, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, P.J.; Yang, L.; Wang, W.X.; Fan, J.M.; Fu, Q.; Li, G.Q. Constructing the major biosynthesis pathways for amino acids in the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens Stål (Hemiptera: Delphacidae), based on the transcriptome data. Insect Mol. Biol. 2014, 23, 152–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrater, J.B.; Naredo, A.I.; Almazan, M.L.P.; de Jong, P.W.; Dicke, M.; Horgan, F.G. Varied responses by yeast-like symbionts during virulence adaptation in a monophagous phloem-feeding insect. Arthropod-Plant Interact. 2015, 9, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.X.; Yu, X.P.; Chen, J.M.; Zheng, X.S.; Xu, H.X.; Zhang, J.F.; Chen, L.Z. Dynamics of yeast-like symbiote and its relationship with the virulence of brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens Stål, to Resistant Rice Varieties. J. Asia Pac. Entomol. 2004, 7, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.; Lv, L.; Jing, S.L.; Zhu, L.L.; He, G.C. Bacterial symbionts of the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens (Homoptera: Delphacidae). Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 1740–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.X.; Zheng, X.S.; Yang, Y.J.; Tian, J.C.; Fu, Q.; Ye, G.Y.; Lu, Z.X. Changes in endosymbiotic bacteria of brown planthoppers during the process of adaptation to different resistant rice varieties. Environ. Entomol. 2015, 44, 582–587. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.X.; Zhu, T.H.; Lai, F.X.; Fu, Q. Diversity and infection frequency of symbiotic bacteria in different populations of the rice brown planthopper in China. J. Entomol. Sci. 2015, 50, 47–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrater, J.B.; Horgan, F.G. Does Nilaparvata lugens gain tolerance to rice resistance genes through conspecifics at shared feeding sites? Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2016, 160, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horgan, F.G.; Srinivasan, T.S.; Crisol-Martínez, E.; Almazan, M.L.; Ramal, A.F.; Oliva, R.; Quibod, I.L.; Bernal, C.C. Microbiome responses during virulence adaptation by a phloem-feeding insect to resistant near-isogenic rice lines. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 9, 11911–11929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magoč, T.; Salzberg, S.L. FLASH: Fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C.; Haas, B.J.; Clemente, J.C.; Quince, C.; Knight, R. UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2194–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Garrity, G.M.; Tiedje, J.M.; Cole, J.R. Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5261–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590-6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schloss, P.D.; Westcott, S.L.; Ryabin, T.; Hall, J.R.; Hartmann, M.; Hollister, E.B.; Lesniewski, R.A.; Oakley, B.B.; Parks, D.H.; Robinson, C.J.; et al. Introducing mothur: Open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 7537–7541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, J.R.; Chai, B.; Farris, R.J.; Wang, Q.; Kulam, S.A.; McGarrell, D.M.; Garrity, G.M.; Tiedje, J.M. The Ribosomal Database Project (RDP-II): Sequences and tools for high-throughput rRNA analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, D294–D296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Pertea, G.; Trapnell, C.; Pimentel, H.; Kelley, R.; Salzberg, S.L. TopHat2: Accurate alignment of transcriptomes in the presence of insertions, deletions and gene fusions. Genome Biol. 2013, 14, R36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trapnell, C.; Williams, B.; Pertea, G.; Mortazavi, A.; Kwan, G.; Van Baren, M.J.; Salzberg, S.L.; Wold, B.J.; Pachter, L. Transcript assembly and quantification by RNA-Seq reveals unannotated transcripts and isoform switching during cell differentiation. Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 511–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.L.; Wang, T.Z.; Zhu, H.F.; Pan, H.B.; Yu, X.P. Diversity and dynamics of microbial communities in brown planthopper at different developmental stages revealed by high-throughput amplicon sequencing. Insect Sci. 2020, 27, 883–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, A.E. Multiorganismal insects: Diversity and function of resident microorganisms. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2015, 60, 17–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, T.P.; Zhou, C.Y.; Zhao, D.S.; Zhu, Y.X.; Bing, X.L.; Huang, H.J.; Hong, X.Y. Antibiotic exposure perturbs the bacterial community in the small brown planthopper Laodelphax striatellus. Insect Sci. 2019, 27, 895–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Shi, J.T.; Xiong, Z.Z.; Shentu, X.P.; Yu, X.P. Three antimicrobials alter gut microbial communities and causing different mortality of brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens Stål. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2021, 174, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.T.; Song, Y.; Shentu, X.P.; Yu, X.P. Antimicrobials affect the fat body microbiome and increase the brown planthopper mortality. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 644897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosokawa, T.; Koga, R.; Kikuchi, Y.; Meng, X.Y.; Fukatsu, T. Wolbachia as a bacteriocyte-associated nutritional mutualist. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 769–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weintraub, P.G.; Beanland, L. Insect vectors of phytoplasmas. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2006, 51, 91–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heck, M. Insect transmission of plant pathogens: A systems biology perspective. mSystems 2018, 3, e00168-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.Z.; Singh, A.; Kaithakottil, G.G.; Mathers, T.C.; Gravino, M.; Mugford, S.T.; van Oosterhout, C.; Swarbreck, D.; Hogenhout, S.A. An aphid RNA transcript migrates systemically within plants and is a virulence factor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 12763–12771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacchi, L.; Genchi, M.; Clementi, E.; Bigliardi, E.; Avanzati, A.M.; Pajoro, M.; Negri, I.; Marzorati, M.; Gonella, E.; Alma, A.; et al. Multiple symbiosis in the leafhopper Scaphoideus titanus (Hemiptera: Cicadellidae): Details of transovarial transmission of Cardinium sp. and yeast-like endosymbionts. Tissue Cell 2008, 40, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonella, E.; Crotti, E.; Rizzi, A.; Mandrioli, M.; Favia, G.; Daffonchio, D.; Alma, A. Horizontal transmission of the symbiotic bacterium Asaia sp. in the leafhopper Scaphoideus titanus Ball (Hemiptera: Cicadellidae). BMC Biol. 2012, 12, S4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marina, B.; Maggie, L.; Murad, G. Transovarial transmission of Rickettsia spp. and organ-specific infection of the whitefly Bemisia tabaci. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 5565–5574. [Google Scholar]
- Pavlidi, N.; Vontas, J.; Van Leeuwen, T. The role of glutathione S-transferases (GSTs) in insecticide resistance in crop pests and disease vectors. Curr. Opin. Insect. Sci. 2018, 27, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, J.Y.; Chen, X.J.; Zhang, C.Y. Transcriptome-based identification and characterization of genes responding to imidacloprid in Myzus persicae. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Y.; Xu, W.Y.; Zhou, W.W.; Lu, D.D.; Shang, H.W.; Zhu, Z.R. Effects of water stressed rice on the brown planthopper transcriptome. J. Plant. Prot. 2017, 44, 973–981. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, X.Y.; Zhu, L.L.; He, G.C. Towards understanding of molecular interactions between rice and the brown planthopper. Mol. Plant. 2013, 6, 621–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.J.; Zhang, C.X.; Hong, X.Y. How does saliva function in planthopper–host interactions? Arch. Insect Biochem. 2019, 100, e21537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, T. Phenylpropanoid biosynthesis. Mol. Plant. 2010, 3, 2–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Liu, Y.Q.; Yuan, D.Y.; Duan, M.J.; Liu, Y.L.; Shen, S.J.; Yang, C.Y.; Qiu, Z.Y.; Liu, D.M.; Wen, P.Z.; et al. An R2R3 MYB transcription factor confers brown planthopper resistance by regulating the phenylalanine ammonia-lyase pathway in rice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2020, 117, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Luo, T.; Wang, W.W.; Cao, T.T.; Li, R.; Lou, Y.G. Silencing OsSLR1 enhances the resistance of rice to the brown planthopper Nilaparvata lugens. Plant. Cell Environ. 2017, 40, 2147–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jan, R.; Khan, M.A.; Asaf, S.; Lee, I.J.; Kim, K.M. Overexpression of OsF3H modulates WBPH stress by alteration of phenylpropanoid pathway at a transcriptomic and metabolomic level in Oryza sativa. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Cheah, B.H.; Fang, Y.F.; Kuang, Y.H.; Lin, S.C.; Liao, C.T.; Huang, S.H.; Lin, Y.F.; Chuang, W.P. Transcriptomics identifies key defense mechanisms in rice resistant to both leaf-feeding and phloem feeding herbivores. BMC Plant. Biol. 2021, 21, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Samples | Raw Reads | Clean Reads | GC Content | % ≥ Q30 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TMB1-1 | 42,986,218 | 42,049,682 | 44.56 | 93.91 |
| TMB1-2 | 44,165,642 | 43,209,258 | 44.54 | 93.76 |
| TMB1-3 | 47,541,582 | 46,680,550 | 43.72 | 93.73 |
| TMB2-1 | 45,485,624 | 44,656,850 | 43.55 | 93.67 |
| TMB2-2 | 44,521,806 | 43,586,560 | 44.12 | 93.79 |
| TMB2-3 | 46,011,104 | 45,052,222 | 44.25 | 93.77 |
| TMR1-1 | 45,073,386 | 44,379,244 | 54.97 | 93.56 |
| TMR1-2 | 45,142,932 | 44,365,444 | 54.39 | 93.26 |
| TMR1-3 | 45,295,128 | 44,536,280 | 53.79 | 93.21 |
| TMR2-1 | 45,913,532 | 44,847,806 | 52.56 | 93.00 |
| TMR2-2 | 82,922,232 | 81,738,152 | 46.86 | 93.02 |
| TMR2-3 | 80,85,2316 | 79,583,178 | 49.48 | 93.75 |
| TMR3-1 | 81,61,2046 | 80,658,880 | 48.45 | 93.50 |
| TMR3-2 | 81,958,948 | 80,806,938 | 47.85 | 93.22 |
| TMR3-3 | 86,133,980 | 85,114,310 | 49.46 | 93.70 |
| GO Category | TMR1 vs. TMR2 | TMR1 vs. TMR3 | TMR2 vs. TMR3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Biological Process | methylerythritol 4-phosphate pathway | methylerythritol 4-phosphate pathway | oxidation-reduction process |
| pentose-phosphate shunt | pentose-phosphate shunt | tRNA methylation | |
| photosystem II assembly | photosystem II assembly | lipid metabolic process | |
| regulation of transcription, DNA-templated | |||
| basipetal auxin transport | |||
| (1->3)- β-D-glucan biosynthetic process | |||
| Molecular Function | chlorophyll binding | chlorophyll binding | chromatin binding |
| peroxidase activity | |||
| ATP binding |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, X.; Chen, L.; Zhou, H.; Tang, M. The Effect of Antibiotic Treatment on the Bacterial Community of the Brown Planthopper and Its Correlation with Rice Virulence. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2327. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11112327
Xu X, Chen L, Zhou H, Tang M. The Effect of Antibiotic Treatment on the Bacterial Community of the Brown Planthopper and Its Correlation with Rice Virulence. Agronomy. 2021; 11(11):2327. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11112327
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Xiaorong, Liang Chen, Hantao Zhou, and Ming Tang. 2021. "The Effect of Antibiotic Treatment on the Bacterial Community of the Brown Planthopper and Its Correlation with Rice Virulence" Agronomy 11, no. 11: 2327. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11112327
APA StyleXu, X., Chen, L., Zhou, H., & Tang, M. (2021). The Effect of Antibiotic Treatment on the Bacterial Community of the Brown Planthopper and Its Correlation with Rice Virulence. Agronomy, 11(11), 2327. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11112327






