Quantification of Biologically Fixed Nitrogen by White Lupin (Lupins albus L.) and Its Subsequent Uptake by Winter Wheat Using the 15N Isotope Dilution Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description
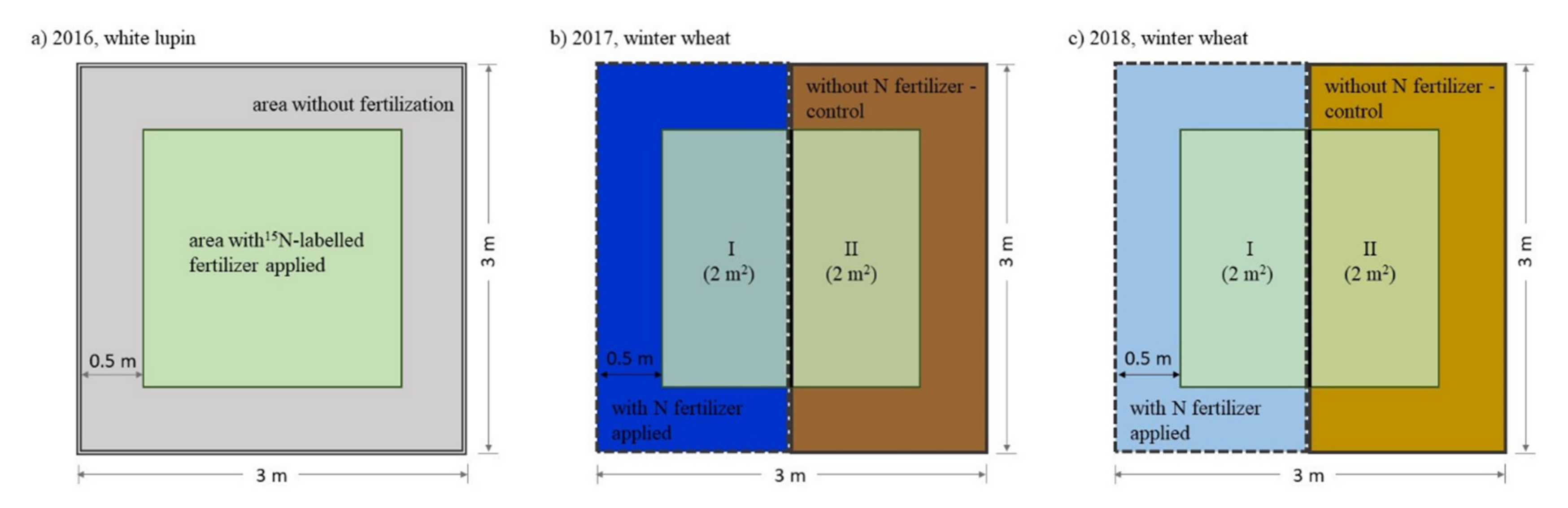
2.2. Experiment Design and Agronomic Management
2.3. Chemical and Isotopic Analysis
2.4. Calculations
- (1)
- %N derived from atmosphere
- (2)
- Amount of N fixed by white lupin from atmosphere (kg ha−1)
- (3)
- % N derived from fertilizer
- (4)
- Amount of N derived from fertilizer (kg ha−1)
- (5)
- % N derived from soil
- (6)
- Coefficient of N-utilization (N-use efficiency) from fertilizer
- (7)
- % N in the winter wheat from white lupin residue
- (8)
- % N derived from residue
- (9)
- Amount of N derived from residue (kg ha−1) = (% NdfR in wheat × TN in winter wheat/N in residues kg ha−1) × 100
- (10)
- Coefficient of nitrogen utilization by winter wheat from crop residue of white lupin (%) =
- (11)
- Total amount of 15N in biomass of lupin and winter wheat (kg ha−1)
- (12)
- % of 15N uptake = (15N kg ha−1 in plant/15N kg ha−1 in fertilizer) × 100.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Preissel, S.; Reckling, M.; Schläfke, N.; Zander, P. Magnitude and farm-economic value of grain pre-crop benefits in Europe. A review. Field Crops Res. 2015, 175, 64–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Księżak, J.; Staniak, M.; Bojarszczuk, J. The regional differentiation of legumes cropping area in Poland between 2001 and 2007. Pol. J. Agron. 2009, 1, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sujak, A.; Kotlarz, A.; Strobel, W. Compositional and nutritional evaluation of several lupin seeds. Food Chem. 2006, 98, 711–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annicchiarico, P.; Harzic, N.; Carroni, A.M. Adaptation, diversity, and exploitation of global white lupin (Lupinus albus L.) landrace genetic resources. Field Crops Res. 2010, 119, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, M.M.; Stoddard, F.L.; Anniechiarico, P.; Prias, J.; Martinez-Villaluenga, C.; Sussmann, D.; Duranti, M.; Seger, A.; Zander, P.K.; Pueyo, J.J. The future of lupine as a protein crop in Europe. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynes, R.J.; Martin, J.R.J.; Goh, K.M. Nitrogen fixation, accumulation of soil nitrogen and nitrogen balance for some field-grown legumes crops. Field Crops Res. 1993, 35, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, J.; McNeill, A.M.; Unkovick, M.J.; Fettell, N.A.; Heenan, D.P. Nat nitrogen balances for cool-season grain legume crops and contributions to wheat nitrogen uptake. A review. Aust. J. Exp. Agric. 2001, 41, 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemecek, T.; von Richthofen, J.S.; Dubois, G.; Casta, P.; Charles, R.; Pahl, H. Environmental impacts of introducing grain legumes into European crop rotations. Eur. J. Agron. 2008, 28, 380–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, J.; Buegger, F.; Jensen, F.S.; Schloter, M.; Heβ, J. Estimating N rhizodeposition of grain legumes using a 15N in situ stem labelling method. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2003, 35, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wichern, F.; Eberhardt, E.; Mayer, J.; Joergensen, R.G.; Müller, M. Nitrogen rhizodeposition in agriculture crops: Methods, estimates and future prospects. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2008, 40, 30–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fustec, J.; Lesuffleur, F.; Mahieu, S.; Cliquet, J.B. Nitrogen rhizodeposition of legumes. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2010, 30, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unkovich, M.J.; Pate, J.S. An appraisal of recent field measurements of symbiotic N2 fixation by annual legumes. Field Crops Res. 2003, 65, 211–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peoples, M.B.; Brockwell, J.; Herridge, D.F.; Rochester, I.J.; Alves, J.R.; Urgulaga, S.; Boddey, R.M.; Dakora, F.D.; Battarai, S.; Maskey, S.L.; et al. The contribution of nitrogen-fixing crop legumes to the productivity of agricultural systems. Symbiosis 2009, 48, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carranca, C.; Torres, M.O.; Madeira, M. Underestimated role of legume roots for soil N fertility. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2015, 35, 1095–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Guidelines on Nitrogen Management in Agricultural Systems; IAEA-TCS-29; IAEA: Vienna, Austria, 2008; pp. 62, 134, 150, 182. ISSN 1018-5518.
- Stevenson, F.C.; Walley, F.L.; van Kessel, C. Direct vs. indirect nitrogen-15 approaches to estimate nitrogen contributions from crop residues. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1998, 62, 1327–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hood, R.C.N.; N’goran, K.; Aigner, M.; Hardarson, G. A comparison of direct and indirect 15N isotope techniques for estimating crop N uptake from organic residues. Plant Soil. 1999, 208, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkegaard, J.A.; Christen, O.; Krupinsky, J.; Layzell, D.B. Break crop benefits in temperate wheat production. Field Crops Res. 2008, 107, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkins, C.A.; Smith, P.M. Regulation of pod set and seed development in lupin. In Proceedings of the Regulation of Pod Set and Seed Development in Lupin, Laugarvatn, Iceland, 1 January 2004; pp. 275–278. [Google Scholar]
- Faluyi, M.A.; Zhou, X.M.; Zhang, F.; Leibovitch, S.; Migner, P.; Smith, D.L. Seed quality of sweet white lupin (Lupinus albus) and management practice in eastern Canada. Eur. J. Agron. 2000, 13, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herridge, D.F.; Peoples, M.B.; Bodday, R. Global inputs of biological nitrogen fixation in agricultural systems. Plant Soil. 2008, 311, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pampana, S.; Masoni, A.; Mariotti, M.; Ercoli, L.; Arduini, I. Nitrogen fixation of grain legumes differs in response to nitrogen fertilisation. Experimental Agric. 2018, 54, 66–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montemurro, F. Different nitrogen fertilization sources, soil tillage, and crop rotations in winter wheat: Effect on yield, quality, and nitrogen utilization. J. Plant Nut. 2009, 32, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimizadeh, M.; Kashani, A.; Zare–Feizabadi, A.; Koocheki, A.R.; Nassiri–Mahallati, M. Nitrogen use efficiency of wheat as affected by preceding crop, application rate of nitrogen and crop residues. Aust. J. Crop Sci. 2010, 4, 363–368. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, K.; Goh, K.M. Management practices of antecedent leguminous and non-leguminous crop residues in relation to winter wheat yields, nitrogen uptake, soil nitrogen mineralization and simple nitrogen balance. Eur. J. Agron. 2002, 16, 295–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutkowska, A.; Pikuła, D. Efficacy of 15N—Nitrogen in fertilization of pea mixtures with wheat, barley, and oats. Plant Soil Environ. 2016, 62, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babulicová, M. The influence of fertilization and crop rotation on the winter wheat production. Plant Soil Environ. 2014, 60, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faligowska, A.; Szymańska, G.; Panasiewicz, K.; Szukała, J.; Koziara, W.; Ratajczak, K. The long-term effect of legumes as forecrops on the productivity of rotation (winter rape-winter wheat-winter wheat) with nitrogen fertilization. Plant Soil Environ. 2019, 65, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panasiewicz, K.; Faligowska, A.; Szymańska, G.; Szukała, J.; Ratajczak, K.; Sulewska, H. The effect of various tillage systems on productivity of narrow-leaved lupin-winter wheat-winter triticale-winter barley rotation. Agronomy 2020, 10, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porporato, A.; D’Odorico, P.; Laio, F.; Rodriguez-Iturbe, I. Hydrologic controls on soil carbon and nitrogen cycles. I. Modeling scheme. Adv. Water Res. 2003, 26, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, G.P.; Groffman, P.M. Nitrogen transformations. In Microbiology and Biochemistry Soil, 3rd ed.; Paul, E.A., Ed.; Academic Press: Burlington, VT, USA, 2007; pp. 341–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, D.; Coyle, M.; Skiba, U.; Sutton, M.A.; Cape, J.N.; Reis, S.; Sheppard, L.J.; Jenkins, A.; Grizzetti, B.; Galloway, J.N.; et al. The global nitrogen cycle in the twenty-first century. Phil. Trans. R Soc. B 2013, 368, 20130164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anglade, J.; Billen, G.; Garnier, J. Relationships for estimating N2 fixation in legumes: Incidence for N balance of legume-based cropping systems in Europe. Ecosphere 2015, 6, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Year /Month | Mean Monthly Air Temperature (°C) | x | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D | ||
| 2016 | −1.9 | 3.4 | 3.7 | 8.6 | 15.4 | 18.3 | 18.8 | 17.5 | 16.5 | 8.0 | 2.9 | 1.7 | 9.4 |
| 2017 | −2.2 | 0.4 | 6.2 | 7.3 | 13.7 | 17.4 | 18.0 | 18.9 | 13.3 | 10.6 | 5.1 | 2.6 | 9.3 |
| 2018 | 1.8 | −3.0 | 0.6 | 12.9 | 16.8 | 18.5 | 20.1 | 21.4 | 15.8 | 11.0 | 5.1 | 2.5 | 10.3 |
| 1951–2015 | −1.2 | −0.2 | 3.5 | 8.8 | 14.3 | 17.5 | 19.3 | 18.6 | 13.9 | 9.1 | 3.9 | 0.2 | 15.6 |
| Monthly Rainfall Sum (mm) | ∑ | ||||||||||||
| 2016 | 31.6 | 36.8 | 49.0 | 37.4 | 43.0 | 83.6 | 149 | 40.6 | 5.6 | 105 | 47.8 | 42.6 | 672 |
| 2017 | 17.7 | 18.4 | 45.4 | 40.6 | 56.8 | 68.2 | 168 | 82.0 | 45.6 | 91.8 | 50.0 | 33.8 | 720 |
| 2018 | 44.6 | 5.0 | 22.6 | 36.2 | 17.4 | 25.4 | 70.5 | 11.6 | 44.2 | 24.8 | 11.4 | 46.2 | 360 |
| 1951–2015 | 31.5 | 27.7 | 31.7 | 31.0 | 50.5 | 59.4 | 77.2 | 55.4 | 45.2 | 34.1 | 35.6 | 38.9 | 518 |
| Crop Rotation (Harvest Year) | ||
|---|---|---|
| 2016 | 2017 | 2018 |
| white lupin + spring winter (reference plant) | winter wheat | winter wheat |
| Specification | Seeds/ Grain | Crop Residues | Sum/Mean Weighted * |
|---|---|---|---|
| White lupin | |||
| Yield (t ha−1) | 3.92 | 4.30 | 8.22 |
| Total nitrogen content (%) | 5.34 | 0.79 | 2.95 * |
| Total nitrogen content in biomass (kg ha−1) | 209.3 | 33.9 | 243.2 |
| Atomic-enrichment percentage (at% 15Nexcess) | 1.071 | 0.972 | 1.058 * |
| Nitrogen fixed from atmosphere (kg ha−1) | 93.7 (44.8%) ** | 17.5 (51.7%) ** | 111.2 |
| Nitrogen uptake from (15NH4)2SO4 (kg ha−1) | 11.3 (5.42%) ** | 1.7 (5.01%) ** | 13.0 |
| Nitrogen uptake from the soil (kg ha−1) | 104.2 (49.8%) ** | 15.2 (43.3%) ** | 119.4 |
| Spring wheat (reference plant) | |||
| Yield (t ha−1) | 1.24 | 2.93 | 4.17 |
| Total nitrogen content (%) | 2.30 | 0.65 | 1.14 * |
| Atomic-enrichment percentage (at% 15Nexcess) | 1.940 | 2.014 | 1.956 * |
| Specification | Nitrogen Dose kg ha−1 | Grain | Crop Residues | Sum/Mean Weighted * |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yield (t ha−1) | 0 | 4.31 b | 7.58 b | 11.89 b |
| 100 | 6.31 a | 8.42 a | 14.73 a | |
| Effect of fertilization 100 kg ha−1 N | +2.0 | + 0.8 | +2.8 | |
| Total nitrogen content (%) | 0 | 1.47 b | 0.19 a | 0.65 b, * |
| 100 | 1.89 a | 0.18 a | 0.90 a, * | |
| Nitrogen in winter wheat biomass (kg ha−1) | 0 | 63.3 b | 14.4 a | 77.7 b |
| 100 | 117.4 a | 15.1 a | 132.5 a | |
| Coefficient of nitrogen utilization (%) | 54.1 | 0.7 | 54.8 | |
| Atomic-enrichment percentage (at% 15Nexcess) | 0 | 0.256 a | 0.232 a | 2.240 a, * |
| 100 | 0.149 a | 0.193 a | 0.171 a, * | |
| Nitrogen content in winter wheat derived from white lupin residues (%) | 0 | 26.3 b | 23.8 b | 25.0 b, * |
| 100 | 15.3 a | 19.8 a | 17.6 a, * | |
| Nitrogen in winter wheat derived from white lupin residues (kg ha−1) | 0 | 16.6 b | 3.4 b | 20.0 b |
| 100 | 18.0 a | 3.0 a | 21.0 a | |
| Coefficient of nitrogen utilization by winter wheat from white lupin residues (%) | 0 | 48.9 b | 10.1 b | 59.0 b |
| 100 | 53.1 a | 8.8 a | 61.9 a | |
| Specification | Nitrogen Dose kg ha−1 | Grain | Crop Residues | Sum/Mean Weighted * |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yield (t ha−1) | 0 | 3.10 b | 7.46 b | 10.56 b |
| 100 | 4.20 a | 8.20 a | 12.40 a | |
| Effect of fertilization 100 kg ha−1 N | +1.10 | +0.74 | +1.84 | |
| Total nitrogen content (%) | 0 | 1.71 b | 0.54 b | 0.88 b, * |
| 100 | 1.97 a | 0.78 a | 1.18 a, * | |
| Nitrogen in winter wheat biomass (kg ha−1) | 0 | 53.0 b | 40.2 b | 93.2 b |
| 100 | 82.7 a | 63.9 a | 146.6 a | |
| Coefficient of nitrogen utilization (%) | 29.7 | 23.7 | 53.4 | |
| Atomic-enrichment percentage (at% 15Nexcess) | 0 | 0.080 a | 0.065 a | 0.068 a, * |
| 100 | 0.069 a | 0.052 a | 0.065 a, * | |
| Nitrogen in winter wheat derived from crop residues of white lupin (%) | 0 | 8.23 b | 6.88 b | 6.99 b, * |
| 100 | 7.09 a | 5.34 a | 6.22 a, * | |
| Nitrogen in winter wheat derived from crop residues of white lupin (kg ha−1) | 0 | 4.36 b | 2.76 b | 7.12 b |
| 100 | 5.86 a | 3.41 a | 9.27 a | |
| Coefficient of nitrogen utilization by winter wheat from crop residues of white lupin (%) | 0 | 12.9 b | 8.1 b | 21.0 b |
| 100 | 17.2 a | 10.0 a | 27.2 a | |
| 33.9 kg ha−1 of nitrogen introduced in crop residues of white lupin | ||||
| Specification | Nitrogen Dose kg ha−1 | Grain | Crop Residues | Sum |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total nitrogen uptake by winter wheat in the second and third years of rotation (kg ha−1) | 0 | 20.96 b | 6.18 b | 27.14 b |
| 100 | 23.86 a | 6.40 a | 30.26 a | |
| Coefficient of nitrogen utilization derived by winter wheat from white lupin residues (%) | 0 | 61.8 b | 18.2 b | 80.0 b |
| 100 | 70.3 a | 18.8 a | 89.1 a | |
| Change in nitrogen utilization rate as a result of nitrogen fertilization | +8.5 | +0.6 | +9.1 | |
| Specification | Nitrogen Dose kg ha−1 | Seeds/GRAIN | Crop Residues | Sum | Percentage Share in Relation to the Initial Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amount of isotope 15N in the biomass of white lupin harvested in 2016 (kg ha−1) | 2.241 | 0.329 | 2.570 | 43.4 | |
| Amount of 15N isotope in winter wheat harvested in 2017 (kg ha−1) | 0 | 0.162 b | 0.033 b | 0.195 b | 3.29 |
| 100 | 0.174 a | 0.029 a | 0.203 a | 3.42 | |
| Amount of 15N isotope in winter wheat harvested in 2018 (kg ha−1) | 0 | 0.042 b | 0.026 b | 0.068 b | 1.14 |
| 100 | 0.057 a | 0.033 a | 0.090 a | 1.52 | |
| Sum for dose N: 0 kg ha−1/100 kg ha−1 | 47.83/48.34 | ||||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kalembasa, S.; Szukała, J.; Faligowska, A.; Kalembasa, D.; Symanowicz, B.; Becher, M.; Gebus-Czupyt, B. Quantification of Biologically Fixed Nitrogen by White Lupin (Lupins albus L.) and Its Subsequent Uptake by Winter Wheat Using the 15N Isotope Dilution Method. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1392. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10091392
Kalembasa S, Szukała J, Faligowska A, Kalembasa D, Symanowicz B, Becher M, Gebus-Czupyt B. Quantification of Biologically Fixed Nitrogen by White Lupin (Lupins albus L.) and Its Subsequent Uptake by Winter Wheat Using the 15N Isotope Dilution Method. Agronomy. 2020; 10(9):1392. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10091392
Chicago/Turabian StyleKalembasa, Stanisław, Jerzy Szukała, Agnieszka Faligowska, Dorota Kalembasa, Barbara Symanowicz, Marcin Becher, and Beata Gebus-Czupyt. 2020. "Quantification of Biologically Fixed Nitrogen by White Lupin (Lupins albus L.) and Its Subsequent Uptake by Winter Wheat Using the 15N Isotope Dilution Method" Agronomy 10, no. 9: 1392. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10091392
APA StyleKalembasa, S., Szukała, J., Faligowska, A., Kalembasa, D., Symanowicz, B., Becher, M., & Gebus-Czupyt, B. (2020). Quantification of Biologically Fixed Nitrogen by White Lupin (Lupins albus L.) and Its Subsequent Uptake by Winter Wheat Using the 15N Isotope Dilution Method. Agronomy, 10(9), 1392. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10091392






