Structure of Amphiphilic Terpolymer Raspberry Vesicles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Analytical Methodologies
3.1. Thermodynamic Integration for Free Energies
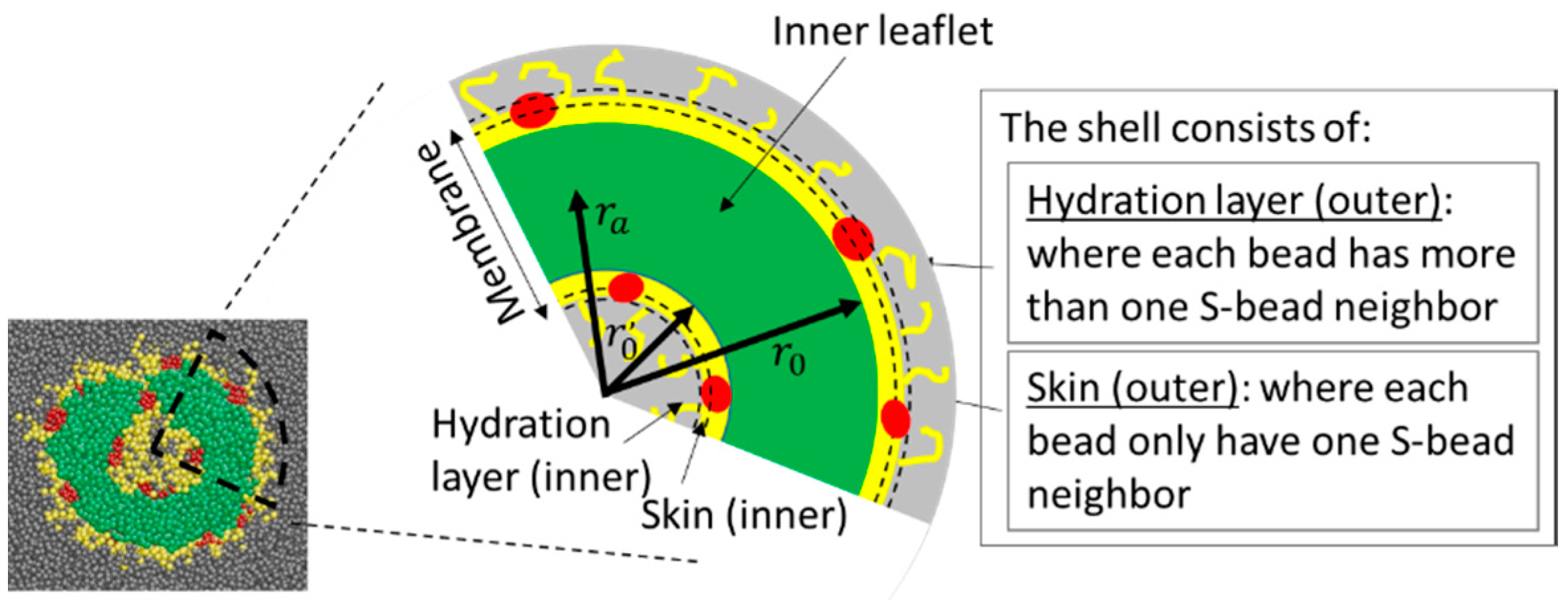
3.2. Skin Characterisations
4. Results and Discussion
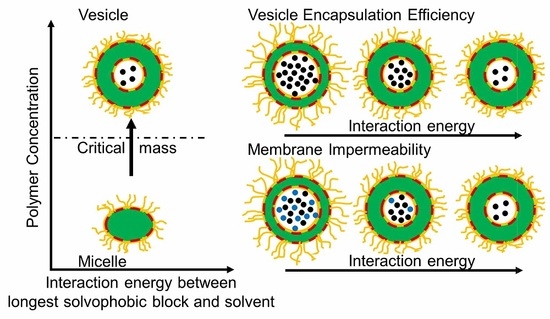
4.1. General Descriptions of Equilibrium Aggregate Structures
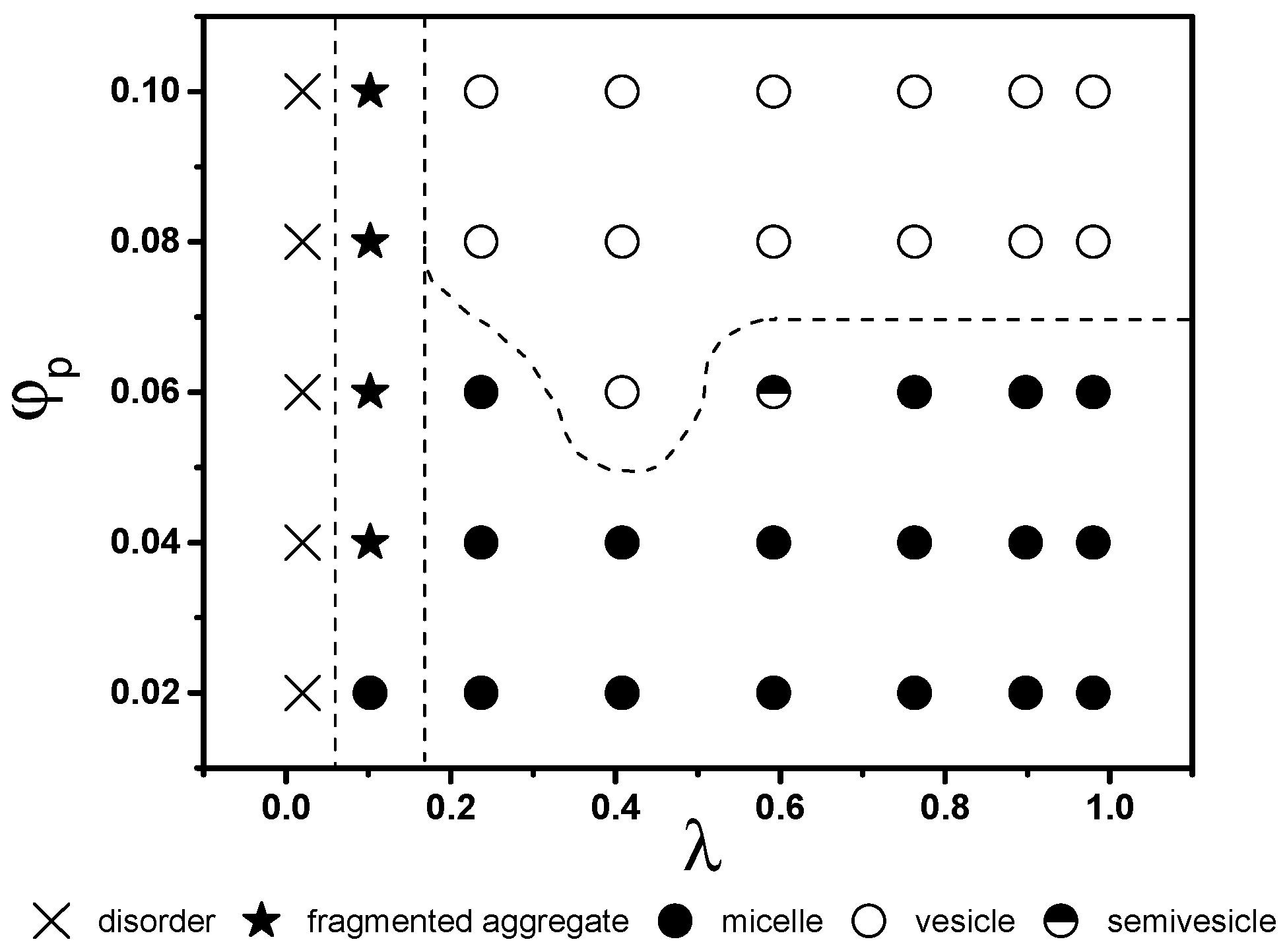
4.2. State Diagram
4.3. Free Energy
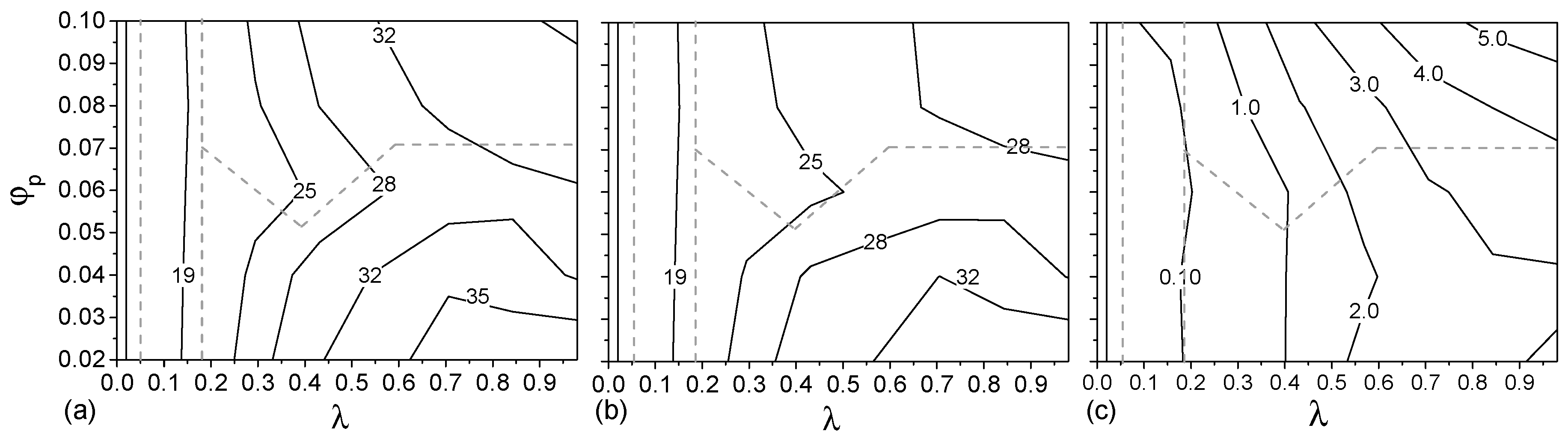
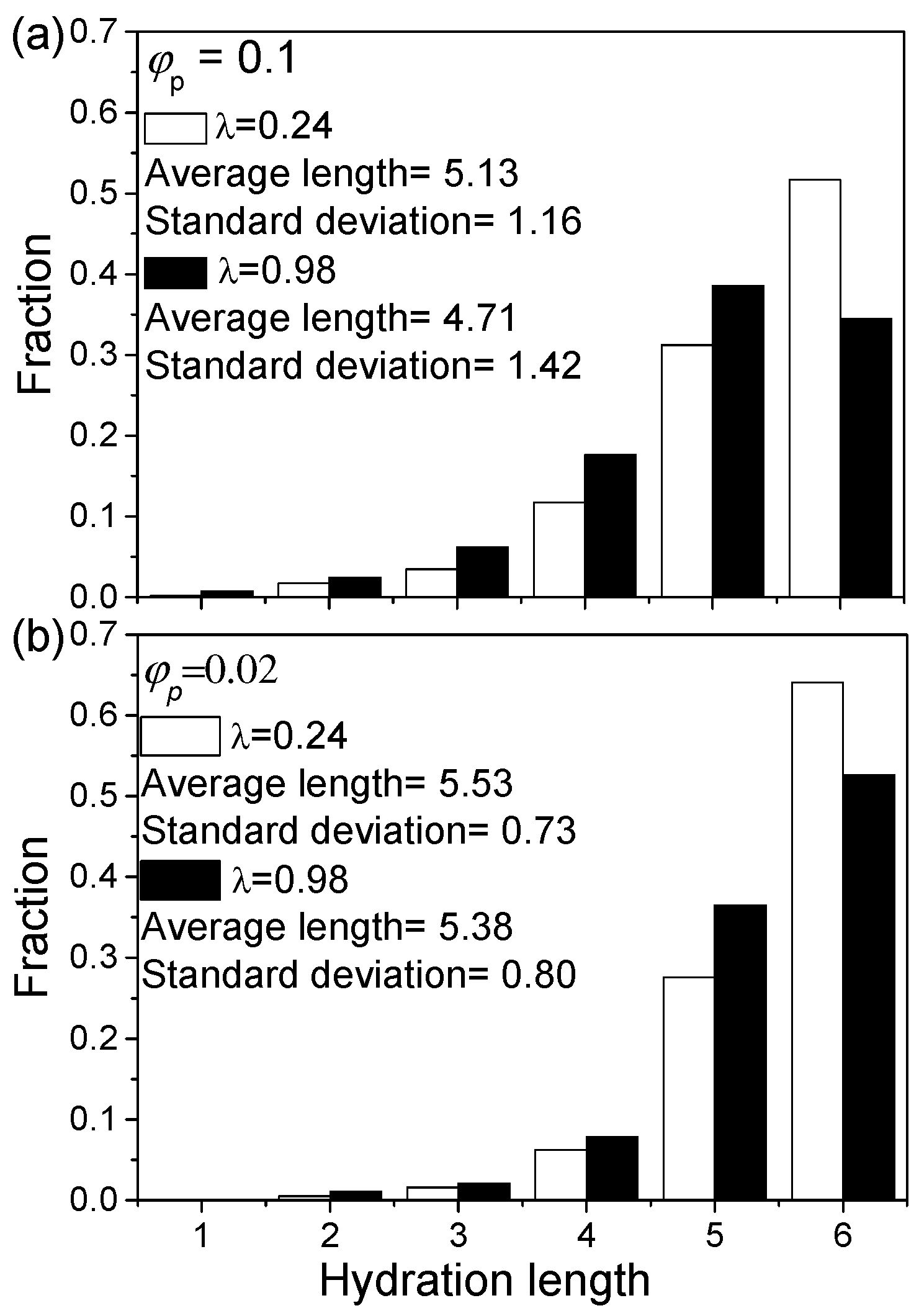
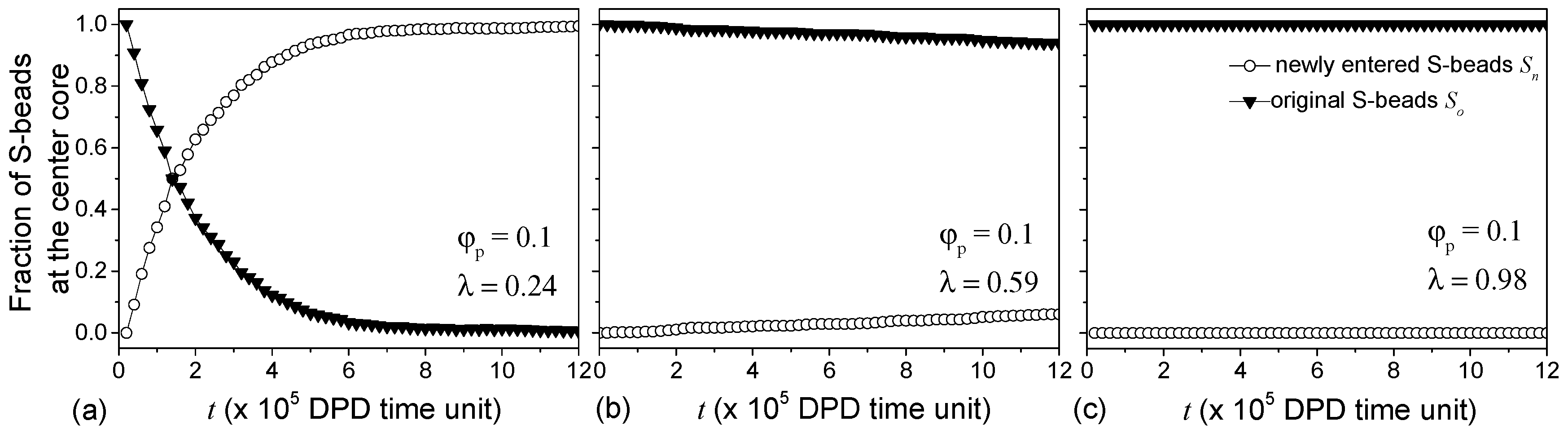
4.4. Morphology of Clusters
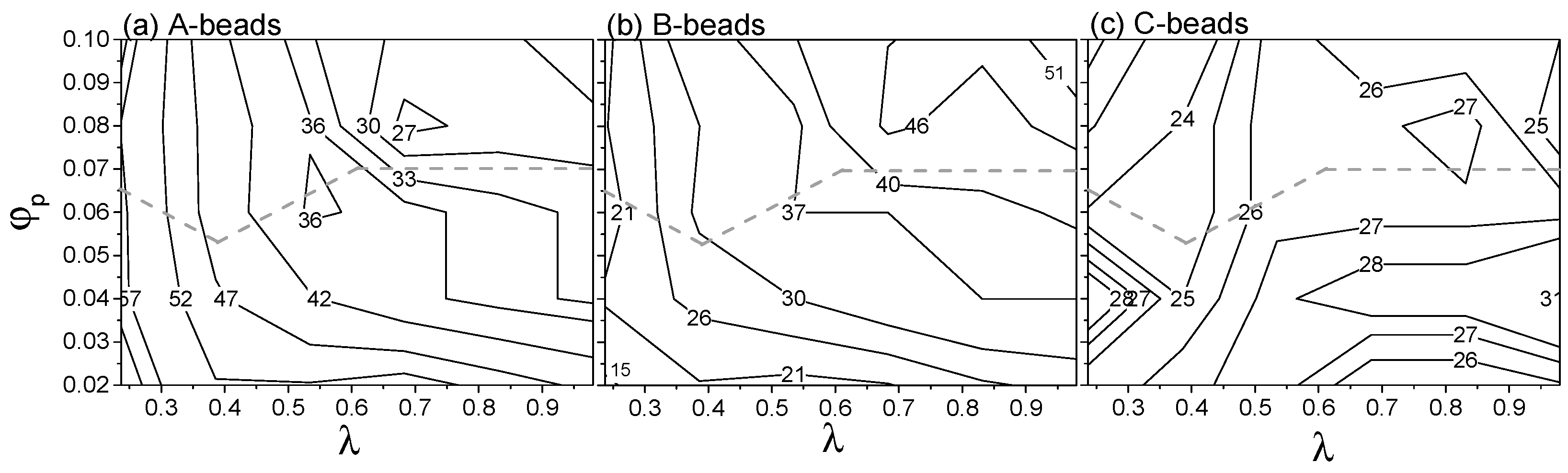
4.5. Properties of Shells of Aggregates
4.5.1. Skin Morphology
4.5.2. Interaction with Solvent and Aggregates
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Petty, H.R. Molecular Biology of Membranes: Structure and Function; Plenum: New York, NY, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Eisenberg, A. Multiple morphologies of “crew-cut” aggregates of polystyrene-b-poly (acrylic acid) block copolymers. Science 1995, 268, 1728–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Discher, D.E.; Eisenberg, A. Polymer vesicles. Science 2002, 297, 967–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, L.; Eisenberg, A. Thermodynamic size control of block copolymer vesicles in solution. Langmuir 2001, 17, 6804–6811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardes, A.T. Computer simulations of spontaneous vesicle formation. Langmuir 1996, 12, 5763–5767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, H.; Takasu, M. Self-assembly of amphiphiles into vesicles: A Brownian dynamics simulation. Phys. Rev. E 2001, 64, 041913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonietti, M.; Förster, S. Vesicles and liposomes: A self-assembly principle beyond lipids. Adv. Mater. 2003, 15, 1323–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Hillmyer, M.A.; Lodge, T.P. Laterally nanostructured vesicles, polygonal bilayer sheets, and segmented wormlike micelles. Nano Lett. 2006, 6, 1245–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, L.; He, J.; Chen, Y.; Kakuchi, T. Synthesis of ABB′ and ABC star copolymers via a combination of NMRP and ROP reactions. Polym. Chem. 2016, 7, 3599–3607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Yan, D. Supramolecular Self-Assembly of Giant Polymer Vesicles with Controlled Sizes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 4896–4899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.-Y.; Wang, J. Temperature-induced morphological change of ABC 3-miktoarm star terpolymer assemblies in aqueous solution. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2011, 85, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, W.; Li, B.; Jin, Q.; Ding, D.; Shi, A.-C. Helical vesicles, segmented semivesicles, and noncircular bilayer sheets from solution-state self-assembly of ABC miktoarm star terpolymers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 8503–8512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, S.-H.; Tsao, H.-K.; Sheng, Y.-J. Morphologies of multicompartment micelles formed by triblock copolymers. J. Chem. Phys. 2006, 125, 194903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.W.; Li, X.; Tang, P.; Yang, Y. Self-assembly of amphiphilic ABC star triblock copolymers and their blends with AB diblock copolymers in solution: Self-consistent field theory simulations. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 1552–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Xu, R.; Wang, Z.; He, X. Kinetics of multicompartment micelle formation by self-assembly of ABC miktoarm star terpolymer in dilute solution. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 11462–11470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, C.; Panagiotopoulos, A.Z.; Verso, F.L.; Likos, C.N. Customizing wormlike mesoscale structures via self-assembly of amphiphilic star polymers. Soft Matter 2015, 11, 3530–3535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Zhao, L.; Qian, H.-J.; Lu, Z.-Y. Coarse-grained simulation study on the self-assembly of miktoarm star-like block copolymers in various solvent conditions. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 2245–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, L.; Liu, Y.; Hou, Y.; Song, W.; Wang, Y. Self-assembly and micelle-to-vesicle transition from star triblock ABC copolymers based on a cyclodextrin core. Polym. Chem. 2016, 7, 3406–3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Nese, A.; Matyjaszewski, K. Thermoresponsive star triblock copolymers by combination of ROP and ATRP: From micelles to hydrogels. J. Polym. Sci. Part A: Polym. Chem. 2011, 49, 1942–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsen, M.W. Effect of architecture on the phase behavior of AB-type block copolymer melts. Macromolecules 2012, 45, 2161–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-I.; Liao, C.-H.; Lodge, T.P. Multicompartment micelles from A 2-star-(B-alt-C) block terpolymers in selective solvents. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 5638–5647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Ma, Z.; Ding, Z.; Li, R.K. Kinetics of Laterally Nanostructured Vesicle Formation by Self-Assembly of Miktoarm Star Terpolymers in Aqueous Solution. Langmuir 2013, 29, 12811–12817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Hillmyer, M.A.; Lodge, T.P. Morphologies of multicompartment micelles formed by ABC miktoarm star terpolymers. Langmuir 2006, 22, 9409–9417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.; Xia, H.; Zhou, Y.; Xue, X.; Luo, S. Dissipative particle dynamics simulations of the morphologies and dynamics of linear ABC triblock copolymers in solutions. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 58024–58031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoogerbrugge, P.; Koelman, J. Simulating microscopic hydrodynamic phenomena with dissipative particle dynamics. Europhys. Lett. 1992, 19, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groot, R.D.; Rabone, K. Mesoscopic simulation of cell membrane damage, morphology change and rupture by nonionic surfactants. Biophys. J. 2001, 81, 725–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groot, R.D.; Warren, P.B. Dissipative particle dynamics: Bridging the gap between atomistic and mesoscopic simulation. J. Chem. Phys. 1997, 107, 4423–4435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Jiang, T.; Lin, J.; Cai, C. Toroid formation through self-assembly of graft copolymer and homopolymer mixtures: Experimental studies and dissipative particle dynamics simulations. Langmuir 2013, 29, 8417–8426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espanol, P.; Warren, P. Statistical mechanics of dissipative particle dynamics. Europhys. Lett. 1995, 30, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobling, T.I.; Ikkala, O.; Groschel, A.H.; Muller, A.H. Controlling Multicompartment Morphologies Using Solvent Conditions and Chemical Modification. ACS Macro Lett. 2016, 5, 1044–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawabata, Y.; Ichiguchi, K.; Ando, T.; Kato, T. Vesicle formations at critical vesicle concentration in a polyoxyethylene type nonionic surfactant system. Colloids Surf. A: Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2014, 462, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, M.; Xia, G.; Wang, R.; Xie, D. Controlling the self-assembly pathways of amphiphilic block copolymers into vesicles. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 7865–7874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Schmid, F. Spontaneous formation of complex micelles from a homogeneous solution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 100, 137802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Schmid, F. Dynamics of spontaneous vesicle formation in dilute solutions of amphiphilic diblock copolymers. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 2654–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Jang, S.; Kon Kim, J. Morphology and microphase separation of star copolymers. J. Polym. Sci. Part B: Polym. Phys. 2015, 53, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.I.; Yang, L.F.; Lin, C.H.; Yu, H.T. A Comparison of Y-, H-, and π-shaped Diblock Copolymers via Dissipative Particle Dynamics. Macromol. Theory Simul. 2008, 17, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.-P.; Sun, L.-Z.; Wang, C.; Luo, M.-B. Monte Carlo simulation on polymer translocation in crowded environment. J. Chem. Phys. 2011, 135, 174901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, C.M. Polymer Coatings—Concepts of Solvent Evaporation Phenomena. Ind. Eng. Chem. Prod. Res. Dev. 1970, 9, 282–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Type of Beads | B | A | C | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| B | 25.0 | |||
| A | 38.5 | 25.0 | ||
| C | 89.4 | 78.0 | 25.0 | |
| S | 26.0 | 97.9 | 125.0 | 25.0 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, Y.; Di Mare, L.; Li, R.K.Y.; Wong, J.S.S. Structure of Amphiphilic Terpolymer Raspberry Vesicles. Polymers 2017, 9, 275. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9070275
Guo Y, Di Mare L, Li RKY, Wong JSS. Structure of Amphiphilic Terpolymer Raspberry Vesicles. Polymers. 2017; 9(7):275. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9070275
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Yingying, Luca Di Mare, Robert K. Y. Li, and Janet S. S. Wong. 2017. "Structure of Amphiphilic Terpolymer Raspberry Vesicles" Polymers 9, no. 7: 275. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9070275
APA StyleGuo, Y., Di Mare, L., Li, R. K. Y., & Wong, J. S. S. (2017). Structure of Amphiphilic Terpolymer Raspberry Vesicles. Polymers, 9(7), 275. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9070275