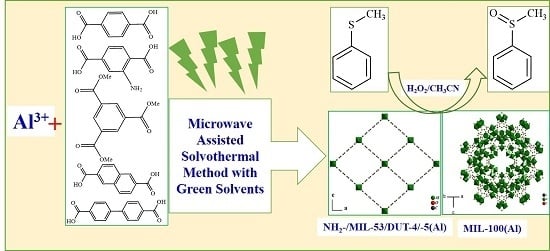
Microwave-Assisted Synthesis of Nanoporous Aluminum-Based Coordination Polymers as Catalysts for Selective Sulfoxidation Reaction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials and Methods
2.2. Synthetic Procedure for Al-MOFs
2.2.1. MW Synthesis of DUT-4
2.2.2. MW Synthesis of DUT-5
2.2.3. MW Synthesis of MIL-53
2.2.4. MW Synthesis of NH2-MIL-53
2.2.5. MW Synthesis of MIL-100
2.3. Catalytic Experiment
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis
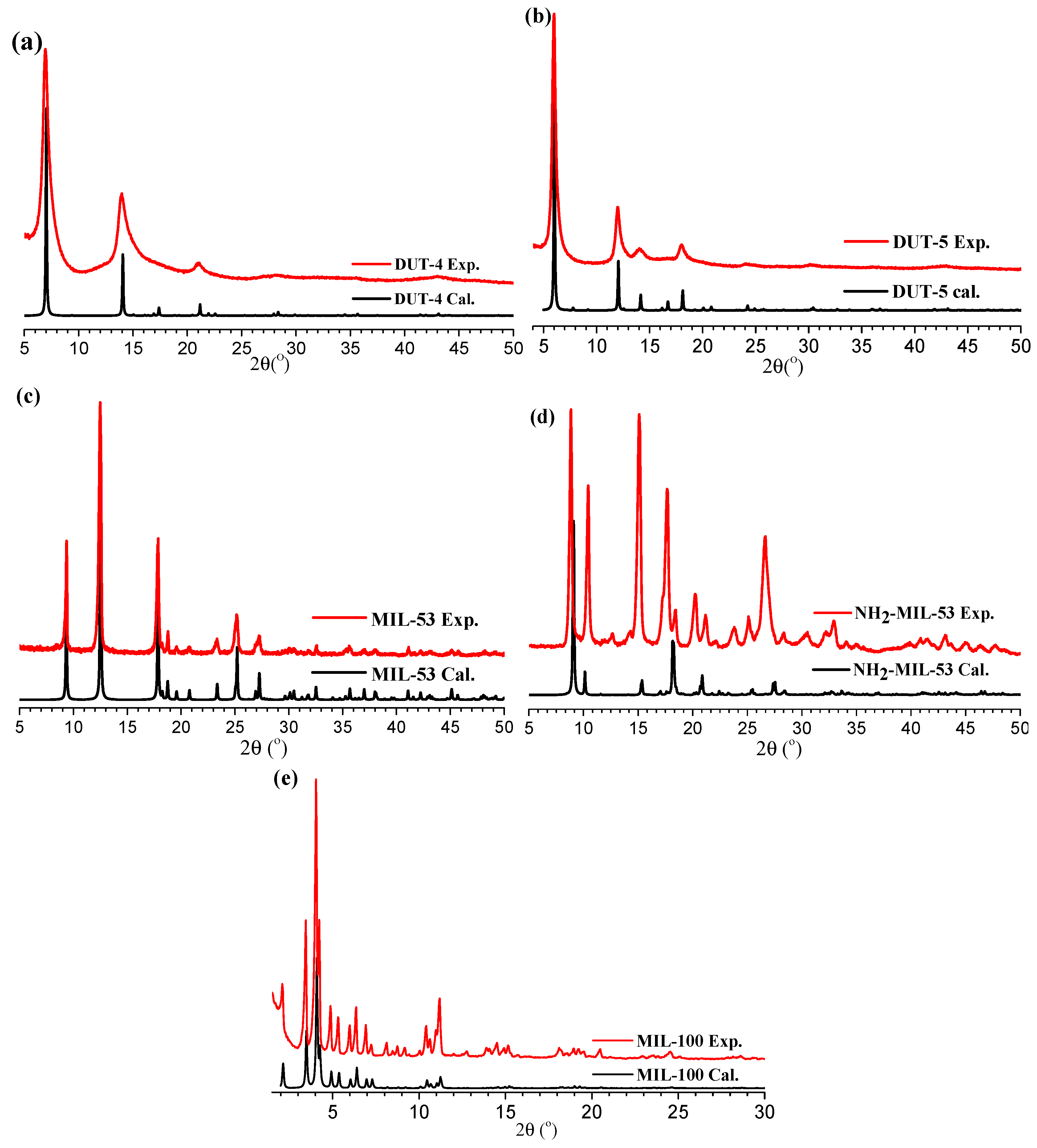
3.2. Characterization
3.3. Nitrogen Gas Sorption Properties
3.4. Catalytic Activity of Synthesized MOFs in Sulfoxidation Reaction
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Senkovska, I.; Hoffmann, F.; Fröba, M.; Getzschmann, J.; Böhlmann, W.; Kaskel, S. New highly porous aluminium based metal-organic frameworks: Al(OH)(ndc) (ndc = 2,6-naphthalene dicarboxylate) and Al(OH)(bpdc) (bpdc = 4,4′-biphenyl dicarboxylate). Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2009, 122, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loiseau, T.; Serre, C.; Huguenard, C.; Fink, G.; Taulelle, F.; Henry, M.; Bataille, T.; Ferey, G. A Rationale for the Large Breathing of the Porous Aluminum Terephthalate (MIL-53) Upon Hydration. Chem. Eur. J. 2004, 10, 1373–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Kim, W.Y.; Ahn, W.S. Amine-functionalized MIL-53 (Al) for CO2/N2 separation: Effect of textural properties. Fuel 2012, 102, 574–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkringer, C.; Popov, D.; Loiseau, T.; Ferrey, G.; Burghammer, M.; Riekel, C.; Haouas, M.; Taulelle, F. Synthesis, single-crystal X-ray microdiffraction, and NMR characterizations of the giant pore metal-organic framework aluminum trimesate MIL-100. Chem. Mater. 2005, 21, 5695–5697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, F.; Zou, X.; Yu, G.; Zhao, N.; Fan, S.; Zhu, G. Environmentally friendly synthesis of highly hydrophobic and stable MIL-53 MOF nanomaterials. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 7430–7432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stock, N. Metal-organic frameworks: Aluminium-based frameworks. In Encyclopedia of Inorganic and Bioinorganic Chemistry; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Trung, T.K.; Trens, P.; Tanchoux, N.; Bourrelly, S.; Llewellyn, P.L.; Loera-Serna, S.; Serre, C.; Loiseau, T.; Fajula, F.; Ferey, G. Hydrocarbon adsorption in the flexible metal organic frameworks MIL-53 (Al, Cr). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 16926–16932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lohe, M.R.; Gedrich, K.; Freudenberg, T.; Kockrick, E.; Dellmann, T.; Kaskel, S. Heating and separation using nanomagnet-functionalized metal-organic frameworks. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 3075–3077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, M.; Guan, Q.; Li, W. Controllable Assembly of Al-MIL-100 via an Inducing Occupied Effect and Its Selective Adsorption Activity. Cryst. Growth Des. 2016, 16, 3639–3646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, S.-H.; Chien, C.-H.; Lai, Y.-L.; Yang, C.-C.; Lee, J.-J.; Senthil Raja, D.; Lin, C.-H. A mesoporous aluminium metal-organic framework with 3 nm open pores. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 324–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.-L.; Lo, S.-H.; Singco, B.; Yang, C.-C.; Huang, H.-Y.; Lin, C.-H. Novel trypsin-FITC@ MOF bioreactor efficiently catalyzes protein digestion. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 928–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, Y.-H.; Fu, C.-P.; Liu, W.-L.; Lin, C.-H.; Huang, H.-Y.; Ma, S. Nanoporous Carbons Derived from Metal-Organic Frameworks as Novel Matrices for Surface-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Mass Spectrometry. Small 2016, 12, 2057–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senthil Raja, D.; Chang, I.-H.; Jiang, Y.-C.; Chen, H.-T.; Lin, C.-H. Enhanced gas sorption properties of a new sulfone functionalized aluminum metal-organic framework: Synthesis, characterization, and DFT studies. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2015, 216, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, S.-H.; Senthil Raja, D.; Chen, C.-W.; Kang, Y.-H.; Chen, J.-J.; Lin, C.-H. Waste polyethylene terephthalate (PET) materials as sustainable precursors for the synthesis of nanoporous MOFs, MIL-47, MIL-53 (Cr, Al, Ga) and MIL-101 (Cr). Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 9565–9573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stock, N.; Biswas, S. Synthesis of metal-organic frameworks (MOFs): Routes to various MOF topologies, morphologies, and composites. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 933–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, N.A.; Jhung, S.H. Synthesis of metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) with microwave or ultrasound: Rapid reaction, phase-selectivity, and size reduction. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2015, 285, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kappe, C.O. Controlled microwave heating in modern organic synthesis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 6250–6284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klinowski, J.; Paz, F.A.A.; Silva, P.; Rocha, J. Microwave-assisted synthesis of metal-organic frameworks. Dalton Trans. 2011, 40, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.-S.; Son, W.-J.; Kim, J.; Ahn, W.-S. Metal-organic framework MOF-5 prepared by microwave heating: Factors to be considered. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2008, 116, 727–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, Y.-K.; Hundal, G.; Jang, I.T.; Hwang, Y.K.; Jun, C.-H.; Chang, J.-S. Microwave synthesis of hybrid inorganic-organic materials including porous Cu3(BTC)2 from Cu(II)-trimesate mixture. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2009, 119, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taddei, M.; Dau, P.V.; Cohen, S.M.; Ranocchiari, M.; van Bokhoven, J.A.; Costantino, F.; Sabatini, S.; Vivani, R. Efficient microwave assisted synthesis of metal-organic framework UiO-66: Optimization and scale up. Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 14019–14026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, C.-T.; Lin, W.-C.; Lo, S.-H.; Kao, C.-C.; Lin, C.-H.; Yang, C.-C. Microwave synthesis and gas sorption of calcium and strontium metal-organic frameworks with high thermal stability. CrystEngComm 2012, 14, 1219–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, B.S.; Burgess, K. Metal-catalyzed epoxidations of alkenes with hydrogen peroxide. Chem. Rev. 2003, 103, 2457–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaabani, A.; Rezayan, A.H. Silica sulfuric acid promoted selective oxidation of sulfides to sulfoxides or sulfones in the presence of aqueous H2O2. Catal. Commun. 2007, 8, 1112–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Chen, X.; Yang, Z.; Du, X.; Liu, Y.; Cui, Y. Chiral microporous Ti (salan)-based metal-organic frameworks for asymmetric sulfoxidation. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 7120–7122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, M.-H.; Yang, X.-L.; Zou, C.; Wu, C.-D. A SnIV-porphyrin-based metal-organic framework for the selective photo-oxygenation of phenol and sulphides. Inorg. Chem. 2011, 50, 5318–5320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Chen, L.; Cui, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L.; Su, C.-Y. Applications of metal-organic frameworks in heterogeneous supramolecular catalysis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 6011–6061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jhung, S.H.; Jin, T.; Hwang, Y.K.; Chang, J.-S. Microwave effect in the fast synthesis of microporous materials: which stage between nucleation and crystal growth is accelerated by microwave irradiation? Chem. Eur. J. 2007, 13, 4410–4417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sing, K.D.; Everett, D.H.; Haul, R.; Moscou, L.; Pierotti, R.; Rouquerol, J.; Siemieniewska, T. Commission on colloid and surface chemistry including catalysis. Pure Appl. Chem. 1985, 57, 603–619. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, K.; Kubo, K.; Iida, K.; Otani, K.-I.; Murase, T.; Yanamoto, D.; Shiro, M. Asymmetric Catalytic Sulfoxidation with H2O2 using Chiral Copper Metal-Organic Framework Crystals. Asian J. Org. Chem. 2013, 2, 1055–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
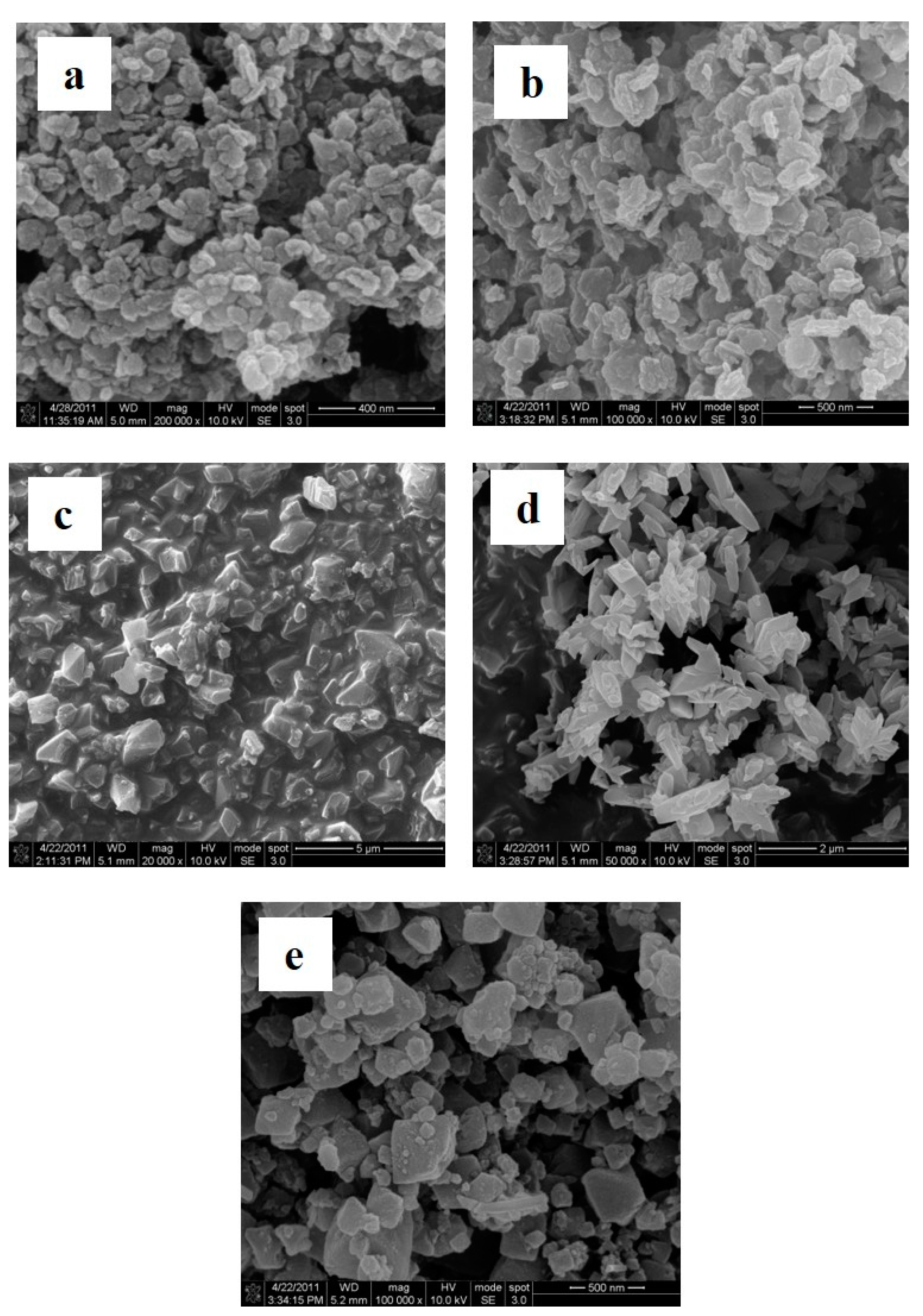



| S. No. | Al-MOF | Dispersion Medium | Particle Size (nm) (MW/CE) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | DUT-4 | Water | 340/816 |
| 2. | DUT-5 | Water | 278/1528 |
| 3. | MIL-53 | Water | 390/806 |
| 4. | NH2-MIL-53 | Water | 477/1607 |
| 5. | MIL-100 | Water | 592/2407 |
| Al-MOF | Reaction Cond. Temp./Time | Pore Size (Å) | Pore Volume (cm3/g) | Surface Area (m2·g−1) (BET/Langmuir) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DUT-4 | 120 °C/24 h | 8.5 | 0.68 | 1308/1996 | [1] |
| 120 °C/52 min | 10.2, 15.6 | 0.75 | 1184/1340 | CW | |
| DUT-5 | 120 °C/24 h | 11.1 | 0.81 | 1613/2335 | [1] |
| 120 °C/83 min | 12.4 | 0.83 | 1157/1305 | CW | |
| MIL-53 | 220 °C/72 h | 8.5 | 0.68 | 1181/1590 | [2] |
| 200 °C/46 min | 11.3 | 0.73 | 1403/1511 | CW | |
| NH2-MIL-53 | 130 °C/48-144 h | - | 0.48 | 811/- | [3] |
| 200 °C/46 min | 8.8, 13.8 | 1.0 | 865/1013 | CW | |
| MIL-100 | 210 °C/72 h | - | 0.82 | 2152/2919 | [4] |
| 200 °C/83 min | 8.6, 11.8, 20.0 | 0.85 | 1701/1967 | CW |
| Entry | Catalyst | Conversion % a | % Selectivity of Sulfoxide for 72 h a | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 24 h | 48 h | 72 h | |||
| 1 | DUT-4 | 55 | 88 | 94 b | 98.8 |
| 2 | DUT-5 | 49 | 83 | 94 b | 98.2 |
| 3 | MIL-53 | 59 | 80 | 97 | >99 |
| 4 | NH2-MIL-53 | 38 | 81 | 86 | >99 |
| 5 | MIL-100 | 54 | 81 | 90 | >99 |
| 6 | - | 7 | 9 | 13 | - |
| Entry | Catalyst | Conversion % a | % Selectivity of Sulfoxide for 7 h a | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 h | 4 h | 5 h | 6 h | 7 h | |||
| 1 | DUT-4 | 78 | 86 | 92 | 92 b | 98 b | 97.7 |
| 2 | DUT-5 | 83 b | 92 b | 93 b | 94 b | 95 b | 95.5 |
| 3 | MIL-53 | 75 | 87 | 87 | 95 | 99 | >99 |
| 4 | NH2-MIL-53 | 76 | 86 | 90 | 94 | 96 | >99 |
| 5 | MIL-100 | 87 | 94 | 95 b | 95 b | 99 b | 99 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vinu, M.; Lin, W.-C.; Senthil Raja, D.; Han, J.-L.; Lin, C.-H. Microwave-Assisted Synthesis of Nanoporous Aluminum-Based Coordination Polymers as Catalysts for Selective Sulfoxidation Reaction. Polymers 2017, 9, 498. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9100498
Vinu M, Lin W-C, Senthil Raja D, Han J-L, Lin C-H. Microwave-Assisted Synthesis of Nanoporous Aluminum-Based Coordination Polymers as Catalysts for Selective Sulfoxidation Reaction. Polymers. 2017; 9(10):498. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9100498
Chicago/Turabian StyleVinu, Madhan, Wei-Cheng Lin, Duraisamy Senthil Raja, Jeng-Liang Han, and Chia-Her Lin. 2017. "Microwave-Assisted Synthesis of Nanoporous Aluminum-Based Coordination Polymers as Catalysts for Selective Sulfoxidation Reaction" Polymers 9, no. 10: 498. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9100498
APA StyleVinu, M., Lin, W.-C., Senthil Raja, D., Han, J.-L., & Lin, C.-H. (2017). Microwave-Assisted Synthesis of Nanoporous Aluminum-Based Coordination Polymers as Catalysts for Selective Sulfoxidation Reaction. Polymers, 9(10), 498. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9100498