Electroosmotic Flow in Mixed Polymer Brush-Grafted Nanochannels
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Simulation Details
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Density Profiles and EOF Velocity
3.2. Transport Properties and Chain Conformation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schoch, R.B.; Han, J.; Renaud, P. Transport phenomena in nanofluidics. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2008, 80, 839–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocquet, L.; Charlaix, E. Nanofluidics, from bulk to interfaces. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 1073–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yameen, B.; Ali, M.; Neumann, R.; Ensinger, W.; Knoll, W.; Azzaroni, O. Synthetic proton-gated ion channels via single solid-state nanochannels modified with responsive polymer brushes. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 2788–2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friebe, A.; Ulbricht, M. Cylindrical pores responding to two different stimuli via surface-initiated atom transfer radical polymerization for synthesis of grafted diblock copolymers. Macromolecules 2009, 42, 1838–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhulina, E.B.; Birshtein, T.M.; Borisov, O.V. Theory of ionizable polymer brushes. Macromolecules 1995, 28, 1491–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csajka, F.S.; Seidel, C. Strongly charged polyelectrolyte brushes: A molecular dynamics study. Macromolecules 2000, 33, 2728–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrillo, J.M.Y.; Dobrynin, A.V. Morphologies of planar polyelectrolyte brushes in a poor solvent: Molecular dynamics simulations and scaling analysis. Langmuir 2009, 25, 13158–13168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akinchina, A.; Shusharina, N.P.; Linse, P. Diblock polyampholytes grafted onto spherical particles: Monte Carlo simulation and lattice mean-field theory. Langmuir 2004, 20, 10351–10360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, L.J.; Man, X.; Han, C.C.; Qiu, D.; Yan, D. Responsive behaviors of diblock polyampholyte brushes within self-consistent field theory. J. Phys. Chem. B 2012, 116, 743–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Q.; You, H. Polyampholyte brushes grafted on the surface of a spherical cavity: Effect of the charged monomer sequence, grafting density, and chain stiffness. Langmuir 2015, 31, 6375–6384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, X.; Guo, W.; Jiang, L. Biomimetic smart nanopores and nanochannels. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 2385–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, R.; Aluru, N.R. Ion concentrations and velocity profiles in nanochannel electroosmotic flows. J. Chem. Phys. 2003, 118, 4692–4701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.M.; Cottin-Bizonne, C.; Ybert, C.; Bocquet, L. Aqueous electrolytes near hydrophobic surfaces: Dynamic effects of ion specificity and hydrodynamic slip. Langmuir 2008, 24, 1442–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezaei, M.; Azimian, A.R.; Semiromi, D.T. The surface charge density effect on the electro-osmotic flow in a nanochannel: A molecular dynamics study. Heat Mass Transf. 2015, 51, 661–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, H.; Mizuno, H.; Kinjo, T.; Washizu, H.; Barrat, J.L. Molecular dynamics simulation of electrokinetic flow of an aqueous electrolyte solution in nanochannels. J. Chem. Phys. 2014, 140, 214701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joly, L.; Ybert, C.; Trizac, E.; Bocquet, L. Liquid friction on charged surfaces: From hydrodynamic slippage to electrokinetics. J. Chem. Phys. 2006, 125, 204716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moshfegh, A.; Jabbarzadeh, A. Fully explicit dissipative particle dynamics simulation of electroosmotic flow in nanochannels. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2016, 20, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doherty, E.A.S.; Berglund, K.D.; Buchholz, B.A.; Kourkine, I.V.; Przybycien, T.M.; Tilton, R.D.; Barron, A.E. Critical factors for high-performance physically adsorbed (dynamic) polymeric wall coatings for capillary electrophoresis of DNA. Electrophoresis 2002, 23, 2766–2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paumier, G.; Sudor, J.; Gue, A.-M.; Vinet, F.; Li, M.; Chabal, Y.J.; Estève, A.; Djafari-Rouhani, M. Nanoscale actuation of electrokinetic flows on thermoreversible surfaces. Electrophoresis 2008, 29, 1245–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Znaleziona, J.; Petr, J.; Knob, R.; Maier, V.; Ševčík, J. Dynamic coating agents in CE. Chromatographia 2008, 67, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteferrante, M.; Melchionna, S.; Marconi, U.; Cretich, M.; Chiari, M.; Sola, L. Electroosmotic flow in polymer-coated slits: A joint experimental/simulation study. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2015, 18, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harden, J.L.; Long, D.; Ajdari, A. Influence of end-grafted polyelectrolytes on electro-osmosis along charged surfaces. Langmuir 2001, 17, 705–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Das, S. Electroosmotic transport in polyelectrolyte-grafted nanochannels with pH-dependent charge density. J. Appl. Phys. 2015, 117, 185304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marconi, U.M.B.; Monteferrante, M.; Melchionna, S. Electro-osmotic flow in coated nanocapillaries: A theoretical investigation. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 25473–25482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Q.; Zuo, C.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y. Modulation of electroosmotic flow by electric field-responsive polyelectrolyte brushes: A molecular dynamics study. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2012, 12, 649–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.; Zuo, C.; Li, L.; Yang, Y.; Li, N. Controlling electroosmotic flow by polymer coating: A dissipative particle dynamics study. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2011, 10, 977–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickey, O.A.; Holm, C.; Harden, J.L.; Slater, G.W. Influence of charged polymer coatings on electro-osmotic flow: molecular dynamics simulations. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 9455–9463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.; Zuo, C.; Li, L.; Ma, Y.; Li, N. Electroosmotic flow in a nanofluidic channel coated with neutral polymers. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2010, 9, 1051–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickey, O.A.; Harden, J.L.; Slater, G.W. Molecular dynamics simulations of optimal dynamic uncharged polymer coatings for quenching electro-osmotic flow. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009, 102, 108304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, R. Control of electroosmotic flow by polymer coating: Effects of the electrical double layer. Langmuir 2006, 22, 7096–7100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, R.; He, P. Modulation of electroosmotic flow by neutral polymers. Langmuir 2007, 23, 5810–5816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tessier, F.; Slater, G.W. Modulation of electroosmotic flow strength with end-grafted polymer chains. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 1250–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, H.; Xia, Z.H.; Zhe, J. Static and dynamic responses of polyelectrolyte brushes under external electric field. Nanotechnology 2009, 20, 195703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Q.; Zuo, C.; Li, L.; Yan, G. Effects of chain stiffness and salt concentration on responses of polyelectrolyte brushes under external electric field. Biomicrofluidics 2011, 5, 044119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, Y.F.; Shendruk, T.N.; Slater, G.W.; Hsiao, P.Y. Structure of polyelectrolyte brushes subject to normal electric fields. Langmuir 2013, 29, 2359–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Q.; Li, L.; Zuo, C.; Huang, F.; Hu, D. Responsive behavior of polyampholyte brushes in electric fields. Model. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 24, 085012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Zhu, L. Mixed polymer brush-grafted particles: A new class of environmentally responsive nanostructured materials. Macromolecules 2009, 42, 9369–9383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Tsouris, V.; Lim, Y.; Mustafa, R.; Choi, J.; Choi, Y.H.; Park, H.-W.; Meron, M.; Lin, B.; Won, Y.-Y. Macroscopic lateral heterogeneity observed in a laterally mobile immiscible mixed polyelectrolyte–neutral polymer brush. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 3771–3782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreer, T.; Muser, M.H.; Binder, K.; Klein, J. Frictional drag mechanisms between polymer-bearing surfaces. Langmuir 2001, 17, 7804–7813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Daivis, P.J. Molecular dynamics study of polymer conformation as a function of concentration and solvent quality. J. Chem. Phys. 2009, 130, 224904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hockney, R.W.; Eastwood, J.W. Computer Simulation Using Particles; Adam Hilger: Bristol, UK, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Groot, R.D. Electrostatic interactions in dissipative particle dynamics–simulation of polyelectrolytes and anionic surfactants. J. Chem. Phys. 2003, 118, 11265–11277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Melchor, M.; Mayoral, E.; Velázquez, M.E.; Alejandre, J. Electrostatic interactions in dissipative particle dynamics using the Ewald sums. J. Chem. Phys. 2006, 125, 224107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, I.C.; Berkowitz, M.L. Ewald summation for systems with slab geometry. J. Chem. Phys. 1999, 111, 3155–3162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plimpton, S. Fast parallel algorithms for short-range molecular dynamics. J. Comput. Phys. 1995, 117, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soddemann, T.; Dunweg, B.; Kremer, K. Dissipative particle dynamics: A useful thermostat for equilibrium and nonequilibrium molecular dynamics simulations. Phys. Rev. E 2003, 68, 046702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moshfegh, A.; Jabbarzadeh, A. Dissipative particle dynamics: Effects of parameterization and thermostating schemes on rheology. Soft Matter 2015, 13, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramin, L.; Jabbarzadeh, A. Effect of compression on self-assembled monolayers: A molecular dynamics study. Model. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2012, 20, 085010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
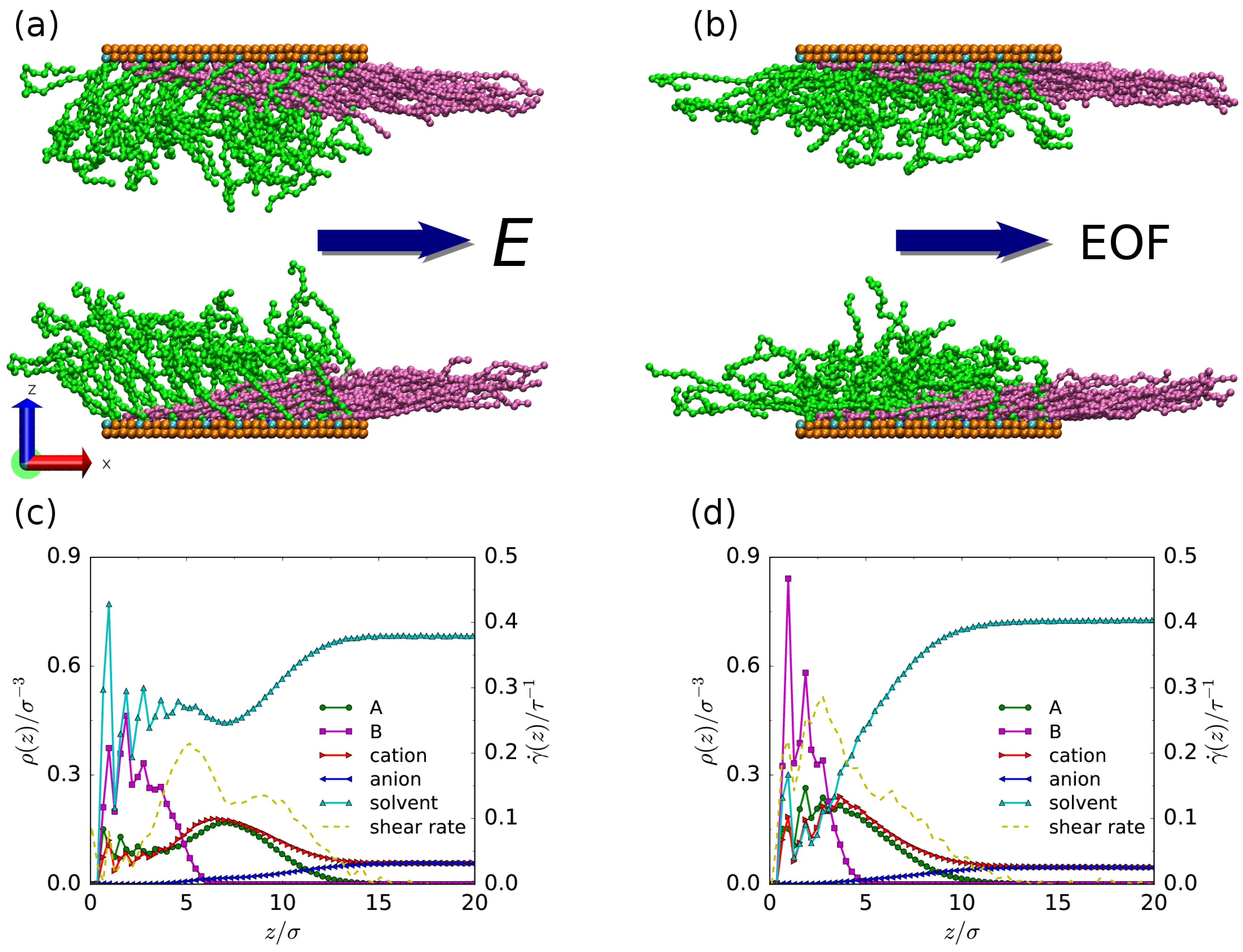
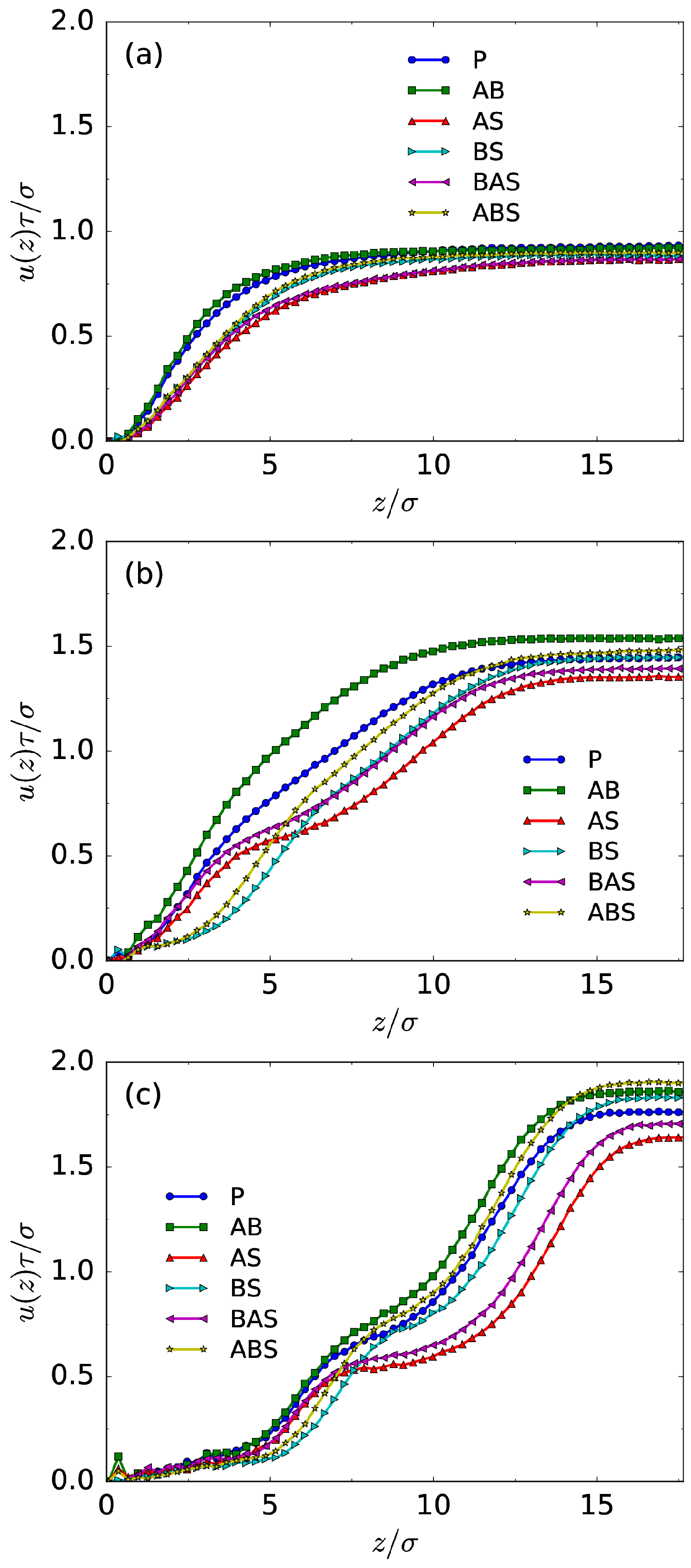
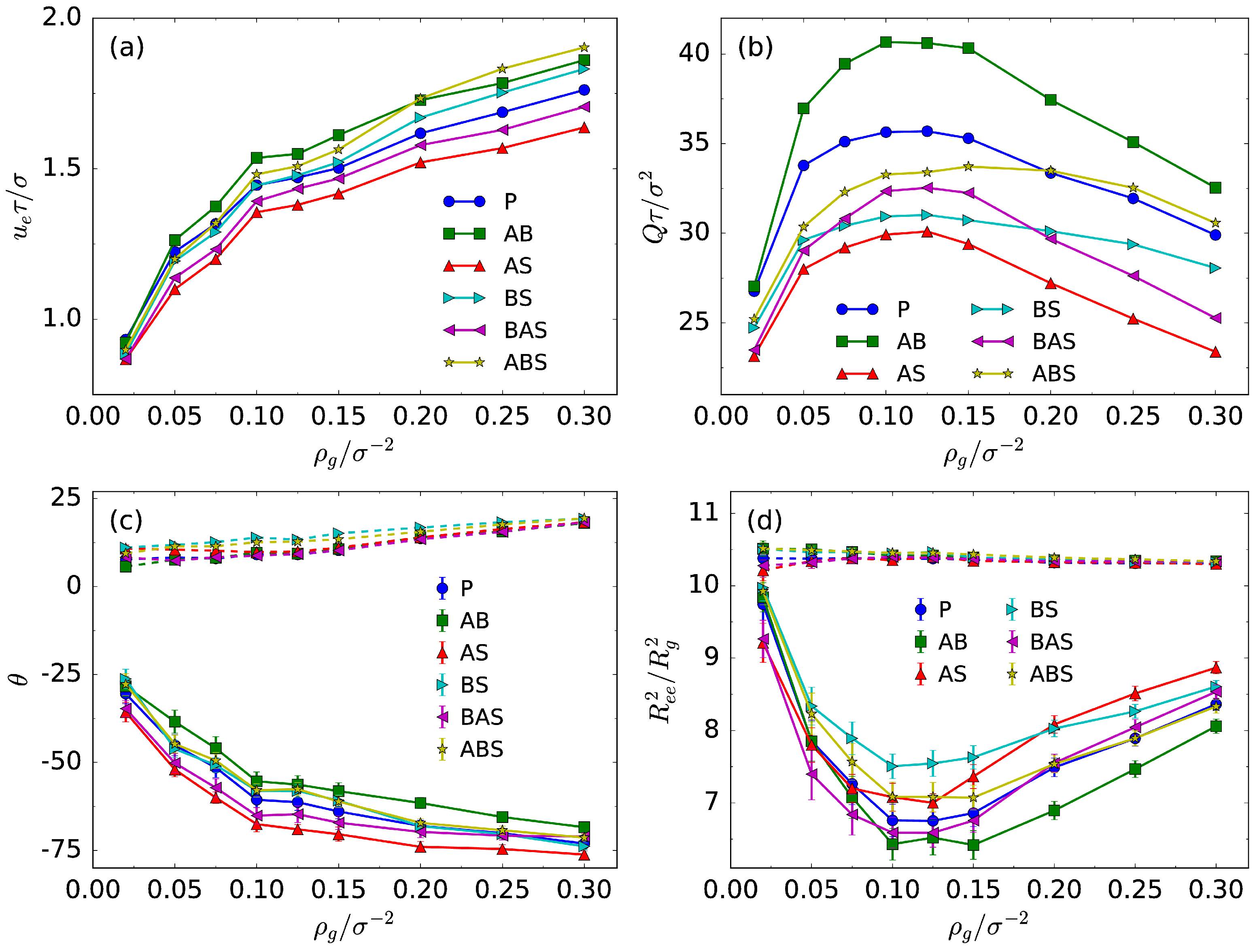
| Solvent case | for A–B | for A–solvent | for B–solvent |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pure repulsion | |||
| A–B attraction | |||
| A–solvent attraction | |||
| B–solvent attraction | |||
| A–B/A–solvent attraction | |||
| B–A/B–solvent attraction |
© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, Q.; You, H. Electroosmotic Flow in Mixed Polymer Brush-Grafted Nanochannels. Polymers 2016, 8, 438. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8120438
Cao Q, You H. Electroosmotic Flow in Mixed Polymer Brush-Grafted Nanochannels. Polymers. 2016; 8(12):438. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8120438
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Qianqian, and Hao You. 2016. "Electroosmotic Flow in Mixed Polymer Brush-Grafted Nanochannels" Polymers 8, no. 12: 438. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8120438
APA StyleCao, Q., & You, H. (2016). Electroosmotic Flow in Mixed Polymer Brush-Grafted Nanochannels. Polymers, 8(12), 438. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8120438






