Abstract
Novel bio-based aliphatic copolyesters, poly(lactic acid-co-10-hydroxy decanoate) (P(LA-co-HDA), PLH), were successfully synthesized from lactic acid (LA) and 10-hydroxycapric acid (HDA) by a thermal polycondensation process, in the presence of p-toluenesulfonic acid (p-TSA) and SnCl2·2H2O as co-catalyst. The copolymer structure was characterized by Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) and proton nuclear magnetic resonance (1H NMR). The weight average molecular weights (Mw) of PLH, from gel permeation chromatography (GPC) measurements, were controlled from 18,500 to 37,900 by changing the molar ratios of LA and HDA. Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) results showed that PLH had excellent thermal stability, and the decomposition temperature at the maximum rate was above 280 °C. The glass transition temperature (Tg) and melting temperature (Tm) of PLH decreased continuously with increasing the HDA composition by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) measurements. PLH showed high ductility, and the breaking elongation increased significantly by the increment of the HDA composition. Moreover, the PLH copolymer could degrade in buffer solution. The cell adhesion results showed that PLH had good biocompatibility with NIH/3T3 cells. The bio-based PLH copolymers have potential applications as thermoplastics, elastomers or impact modifiers in the biomedical, industrial and agricultural fields.
1. Introduction
Because of increasing worldwide concern about the shortage of nonrenewable petroleum resources, bio-based monomers and natural polymers that are made from renewable resources have attracted much attention in the past few decades [1,2,3,4,5]. Moreover, most of the bio-based polymers, such as poly(lactic acid) (PLA), poly(ε-caprolactone) (PCL) and poly(hydroxybutyrate) (PHB), are biodegradable [6,7], which can be applied in the industrial and agricultural fields [8]. Moreover, these polymers are also biocompatible materials, which are of great utility in the application of neural, myocardial and bone tissue engineering [9,10,11,12]. Recently, many studies on the synthesis, properties and degradability of biodegradable polymers have been reported on the basis of various bio-based monomers. Miller et al. [13] developed several thermoplastic materials, poly(alkylene 4-hydroxybenzoates), poly(alkylene vanillates) and poly(alkylene syringates), with good thermal properties, the monomers of which are derived from lignin. Mecking’s group selected isomerized alkoxycarbonylation of fatty acids with long-chain linear monomers containing a C19–C23 alkyl chain length to prepare fully renewable polyester by polycondensation [14]. Barrett and his members had prepared several photocurable polyesters based on different polyols and itaconic acids from photoactive renewable monomers [15].
Poly(lactic acid) (PLA) is a biodegradable aliphatic polyester derived from 100% renewable resources, such as corn and sugar beets, gaining much interest in recent years [16,17,18,19,20,21]. PLA has primarily been used as biomedical materials and biodegradable plastic materials, because of its excellent biocompatibility, biodegradability and suitable physicochemical properties [22,23,24]. However, PLA is a rather brittle biomaterial to be used as a glassy plastic and showed thermal degradation over its thermal temperature, which would not be suitable for further applications in the biomedical, industrial and agricultural fields. One of the most effective methods for enhancing the thermal and mechanical properties of PLA is copolymerization of LA with other monomers or polymers for reducing its crystallization and enhancing its flexibility. Recently, ricinoleic acid [20], glycolic acid [25], hydrocinnamic acid [26], polyethylene glycol [27] and poly(ε-caprolactone) [28] have been employed to prepare a series of PLA copolymers. The thermal, strength and degradable properties of these PLA copolymers could be rather improved. However, the ductility of the copolymer still needs to be enhanced for increasing the scope of application.
10-Hydroxycapric acid (HDA) is a kind of bio-based monomer from castor oil with a flexible long linear chain [29]. At present, there has been no study on the polymerization of HDA or on introducing it into polymer chains. The thermal stability and ductility of bio-based polyester could be generally increased by introducing flexible soft segments into the polymer chain and forming a random chain microstructure to alternate with hard crystalline blocks [30]. Accordingly, the HDA chain might improve the properties of the PLA copolymer. Therefore, in this paper, the synthesis and characterization of bio-based copolymers, poly(lactic acid-co-10-hydroxy decanoate) (P(LA-co-HDA), PLH) composed of LA and HDA, were described, and the degradation, thermal and mechanical properties, especially the ductility of PLH, were investigated in detail. Moreover, the biocompatibility of PLH was also evaluated by means of an MTT assay and cell staining.
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
l-Lactic acid (LA, 90%, l(+)-enantiomers) was purchased from Aladdin Industrial Corporation and used after distillation. 10-Hydroxydecanoic acid (HDA, 99%, Tan Yun Chemicals, Yingkou, China) was purified by recrystallization in methanol. Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium (DMEM), fetal bovine serum (FBS) and penicillin-streptomycin (P/S) were purchased from Gibco (Shanghai, China). NIH/3T3 cells were purchased from Biomedical Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China. Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), fluorescein diacetate (FDA) and 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-thiazolyl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) were purchased from Amersco, Shanghai, China). Tin(II) dichloride dehydrate (SnCl2·2H2O, 98%), p-toluenesulfonic acid (p-TSA, 99%), chloroform and methanol were purchased from Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd. (Beijing, China) and used as received.
2.2. Synthesis of Poly(lactic acid-co-hydroxy decanoate)
PLH copolymers with various molar ratios were synthesized from LA and HDA with various molar ratios by a two-step melt polycondensation procedures, shown in Scheme 1. The typical synthesis proceeded as follows: LA (1.802 g, 20 mmol), HDA (0.377 g, 2 mmol) and 0.4 wt% co-catalyst (weight of catalyst/initial weight of monomer) composed of p-TSA and SnCl2·2H2O with a molar ratio of p-TSA/SnCl2·2H2O = 1/1 (the same in all experiments, except for other explains) were added into the reactor. The mixture was then kept at 80 °C for about 1 h through nitrogen until the solution became homogeneous. The reaction system was further heated to 140 °C for an additional 10 h and then kept for 18 h in a vacuum atmosphere of 200–500 Pa at 170 °C. Once the polymerization finished, the reaction mixture was cooled to room temperature and resulted in a solid. PLH was finally purified by being dissolved in CHCl3 and precipitated in an excess of methanol three times and then dried under vacuum.
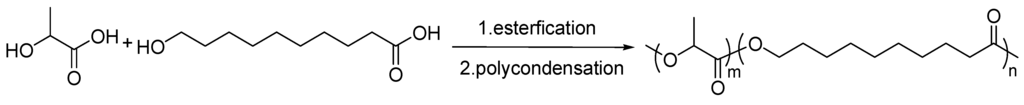
Scheme 1.
Synthesis of poly(lactic acid-co-10-hydroxy decanoate) (PLH) via a two-step polymerization of l-lactic acid (LA) and 10-hydroxycapric acid (HDA).
For the preparation of PHDA (poly(10-hydroxy decanoate)) and PLA, the mixture of HDA (LA) and 0.4 wt% co-catalyst was stirred for about 3 h at 100 °C through nitrogen until the solution became homogeneous. The reaction system was further heated to 150 °C for an additional 10 h and then kept for 18 h in a vacuum atmosphere at 220 °C (200 °C for PLA). The final products were obtained by dissolving in CHCl3 and precipitated in an excess of methanol three times, then dried under vacuum.
2.3. Characterization
Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (Nicolet iS50 FTIR, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) was performed by casting samples in dichloromethane onto NaCl plates. Proton nuclear magnetic resonance (1H NMR) analysis was recorded on a BUKER400 AVANCEIII spectrometer with deuterated chloroform (CDCl3) as the solvent and an internal tetramethylsilane (TMS) as the reference standard. Number-average molecular weight (Mn), weight-average molecular weight (Mw) and polydispersity index (PDI) were measured by gel permeation chromatography (GPC, Waters 1515, Waters, Milford, MA, USA) using mono-dispersed polystyrene as the standards. The copolymers were eluted with tetrahydrofuran (THF) through a linear Styragel HR2 column (Waters, 7.8 mm ° 300 mm) at a flow rate of 1 mL/min. Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) was conducted under nitrogen using a heat/cool/heat cycle at a heating rate of 10 °C/min on a PE Instruments DSC8000 with an aluminum pan (PE, Waltham, MA, USA). Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) was performed with a TGA 1100SF apparatus from Mettler Toledo International Trading Co., Ltd. (METTLER, Greifensee, Switzerland). Instruments were heated at a rate of 10 °C/min under a flow of nitrogen (50 mL/min) from 25 to 650 °C. The decomposition temperature (Td) value was calculated from the onset of decomposition using the peak from the first derivative of the weight loss to identify the maximum slope. A dynamic time sweep test was performed on a rheometer (DHR-2, TA Co., Ltd., New Castle, DE, USA) with a plate diameter of 25 mm and a gap inferior to 1 mm, to verify the thermal stability of PLA, PHDA and PLH copolymers at a lower angular frequency in a linear regime. The heated chamber was continuously purged with nitrogen to avoid thermal degradation. A tensile test was conducted by using a Kaiqiang WDT-10 testing machine (Kaiqiangli Co., Ltd., Shenzhen, China) in triplicate at an elongation speed of 10 mm/min. The contact angle of the copolymer sheet was measured using an OCA 15EC (Dataphysics Co., Ltd., Filderstadt, Germany) with ultra-pure water droplets. The average value was obtained by placing several drops on the sheet surface. The surface morphology of the PLH film after immersion in phosphate buffered saline as a function of time was observed by an S-4800 scanning electron microscope (SEM, Hitachi Limited, Tokyo, Japan) operating at 15 kV. All of the samples were sputter-coated with gold to minimize sample charging.
2.4. Hydrolytic Degradation of PLH
The degradation of the as-synthesized PLH copolymer was studied in phosphate buffers at pH 7.4 and phosphate buffered saline (PBS) at pH 10.2. The PLH film panels (20 mm × 20 mm in size, approximately) were punched out from a sheet of polymer made by compression molding. These films were suspended in an excess of buffer. The samples were kept at 37 °C in a water-bath shaker (Shanghai Joyn Electronic Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China). The buffer solution was replaced at every time point to maintain the pH value as constant. The degradation behavior was determined by the weight loss of the samples. All experiments were repeated in triplicate.
2.5. Cell Adhesion of PLH
The PLH films were sterilized by 75% ethanol and dried at room temperature. Then, the PLH films were placed into a plastic dish with a 3.5-cm diameter (3 × 104 cells/well) in a complete DMEM (with 10% fetal bovine serum and penicillin-streptomycin supplemented) suspension in a 5% CO2 incubator at 37 °C for 24 h. Finally, the NIH/3T3 cells were stained with FDA, which could cleave into a green fluorescent product by metabolically-active cells. The density of the cells that adhered to each scaffold was measured from randomly selected views of each film, which was observed at 100-fold magnification by a fluorescent microscope (Nikon 80i, Tokyo, Japan).
2.6. MTT Assay
NIH/3T3 cells were cultured onto a 96-well plate (3 × 104 cells/well) in complete DMEM (with 10% fetal bovine serum and penicillin-streptomycin supplemented) in a humidified atmosphere of 5% CO2 at 37 °C. After 24 h, the growth medium was replaced with 100 mL of complete DMEM culture medium. Five holes were set for every sample. The cells treated with the same amount of PBS were used as a control group and incubated for another 24 h. The cell viability was assayed by adding 20 μL of MTT (Amersco) PBS solution (2 mg/mL). After incubation at 37 °C for another 4 h, the formed crystals were dissolved in 150 mL of DMSO and then recorded at 595 nm with a reference wavelength of 570 nm on a 96-well plate Elisa microplate reader (Infinite M200 Pro, Tecan, Männedorf, Switzerland). All measurements were taken in triplicate. A glass coverslip was used as the control. The percent of cell viability was calculated from the ratio of the mean absorbance of the sample to the mean absorbance of the control.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Structural Characterization and Molecular Weight
LA and HDA could be polymerized by polycondensation in the presence of co-catalyst of p-TSA and SnCl2·2H2O [31], and the polymerization mechanism is shown in Scheme S1. The structure of the obtained PLH copolymer was characterized by FTIR (Figure S1) and 1H NMR (Figure 1, PLH (LA/HAD = 9/1)). The strong peak at 1758 cm−1 assigned to the absorption of the ester group in PLH. The chemical shifts at δ 5.18 and 1.58 are ascribed to the protons of the C(O)CH and CHCH3 groups in LA units. Peaks appearing at δ 4.13, 2.37, 1.57 and 1.30 are assigned to the OCH2, C(O)CH2, C(O)CH2CH2 and CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2 groups in HDA repeating units, respectively. These results indicated the successful preparation of the PLH copolymer.
By calculation of the peak areas of δ 5.18 and 4.13, the molar ratios of LA to HDA could be obtained, and the results are listed in Table 1. The molar ratios of LA to HDA were 9.3/1, 7.8/1, 7.0/1, 6.3/1, 6.1/1 and 5.0/1. Thus, the PLH samples with different compositions were abbreviated as PLH9.3, PLH7.8, PLH7.0, PLH6.3, PLH6.1 and PLH5.0, respectively.
The molecular weights of the PLH copolymers, PLA and PHDA homopolymers were confirmed by GPC. As listed in Table 1, Mn is ranged from 11,000 to 36,000 g/mol and Mw is at 18,000~68,000 g/mol with relatively narrow polydispersity (PDI) at 1.6~1.9. These results meant that the molecular weights of the PLH copolymer could be controlled by adjusting the molar ratio of LA to HDA. Moreover, the contact angles of the copolymers were increasing with an increase in HDA content (Figure S2). Since the hydrophobicity (135° ± 1°) of PHDA, the hydrophobicity of the PLH copolymers increased by the insertion of HDA in PLA.
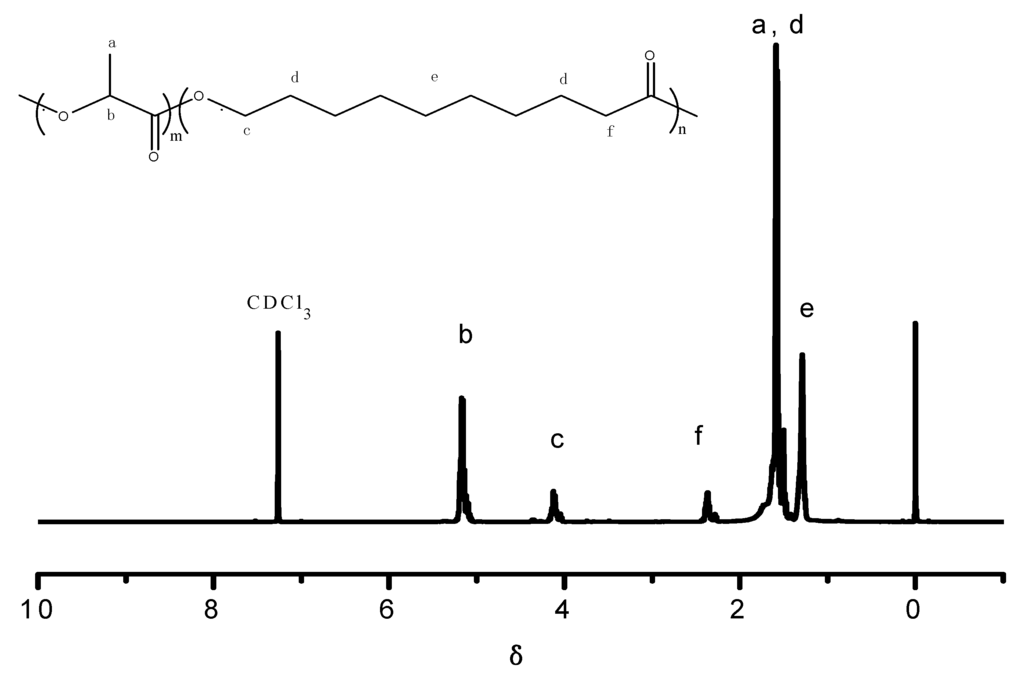
Figure 1.
1H NMR spectrum of PLH.

Table 1.
Compositions and molecular weights of the PLH copolymers, PLA and PHDA homopolymers. PDI, polydispersity. PLH9.3, PLH composition with molar ratios of LA to HDA of 9.3/1.
| Sample | nL-LA/nHDA a | nL-LA/nHDA b | Mn (×10-4) c | Mw (×10-4) c | PDI c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PLA | / | / | 1.75 | 2.81 | 1.61 |
| PLH9.3 | 12/1 | 9.3/1 | 1.15 | 1.85 | 1.61 |
| PLH7.8 | 11/1 | 7.8/1 | 1.48 | 2.44 | 1.65 |
| PLH7.0 | 10/1 | 7.0/1 | 2.18 | 3.79 | 1.74 |
| PLH6.3 | 9/1 | 6.3/1 | 1.82 | 3.20 | 1.76 |
| PLH6.1 | 8/1 | 6.1/1 | 1.51 | 2.48 | 1.64 |
| PLH5.0 | 7/1 | 5.0/1 | 1.17 | 2.01 | 1.72 |
| PHDA | / | / | 3.59 | 6.81 | 1.90 |
a In-feed molar ratio; b molar ratio calculated from 1H NMR spectrum; c molecular weight (Mn, Mw and Mw/Mn) determined by GPC measurement using THF as the eluent; / is pure polymer.
3.2. Thermal Transition Behavior
Random copolymers generally have their thermal and elastic properties as a function of composition between those of the neat homopolymers. DSC measurements had been performed to investigate the effect of the composition on the thermal property of PLH. The melting temperatures (Tm) of the PLH copolymers and PLA and PHDA homopolymers were obtained from the first heating scans, and the glass transition temperatures (Tg) were obtained from the second heating scans. All of the results are shown in Figure 2, and the thermal transition data are summarized in Table 2.

Table 2.
Thermal properties of the PLH copolymers.
| Sample | Tg (°C) a | Tm (°C) a | Td,5% (°C) b | Td,max (°C) b | Tensile Strength (MPa) c | Tensile Modulus (Mpa) c | εb (%) c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PLA | 71.0 | 158.4 | 230 | 272 | / | / | / |
| PLH9.3 | 26.2 | 110.5 | 237 | 280 | / | / | / |
| PLH7.8 | 21.5 | 106.4 | 244 | 285 | 27.3 | 1631 | 7 |
| PLH7.0 | 19.2 | 95.0 | 253 | 288 | 20.7 | 633 | 15 |
| PLH6.3 | 18.7 | 93.3 | 257 | 290 | 5.7 | 70 | 155 |
| PLH6.1 | 18.1 | 93.0 | 259 | 293 | 3.6 | 66 | 475 |
| PLH5.0 | 11.8 | 66.4 | 262 | 295 | 1.5 | 28 | 600 |
| PHDA | / | 80.2 | 387 | 428 | / | / | / |
a Tg and Tm results from DSC measurements; b Td,5% and Td,max results from TGA measurements; c mechanical properties; /, without a measurement due to brittleness.
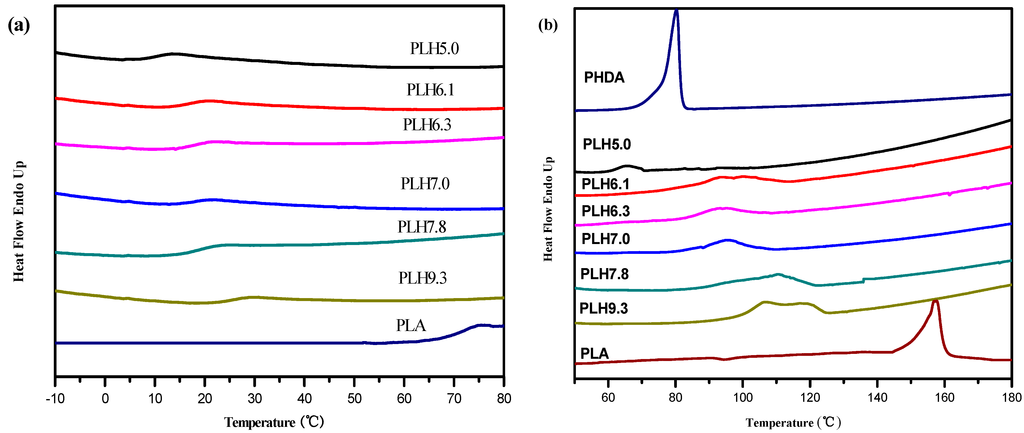
Figure 2.
DSC curves of the PLH copolymers: (a) Tg from the second heating scan and (b) Tm from the first heating scan.
As Figure 2a,b shows, all of the calorimetric curves of PLH with various compositions showed one Tg and one Tm. It can be seen that the thermal transition behavior of PLH strongly depends on the LA and HDA compositions. Tg and Tm of the PLH copolymers shifted to lower temperatures with increasing the HDA composition, due to the long alkyl chain length of HDA. Such a behavior is typical for random copolymers, which form a single amorphous phase without micro- or nano-scale separation.
3.3. Thermal Stability
TGA curves of the PLH copolymers are shown in Figure 3. The decomposition temperature at 5% weight loss (Td,5%) and the decomposition temperature at the maximum rate (Td,max) are listed in Table 2.
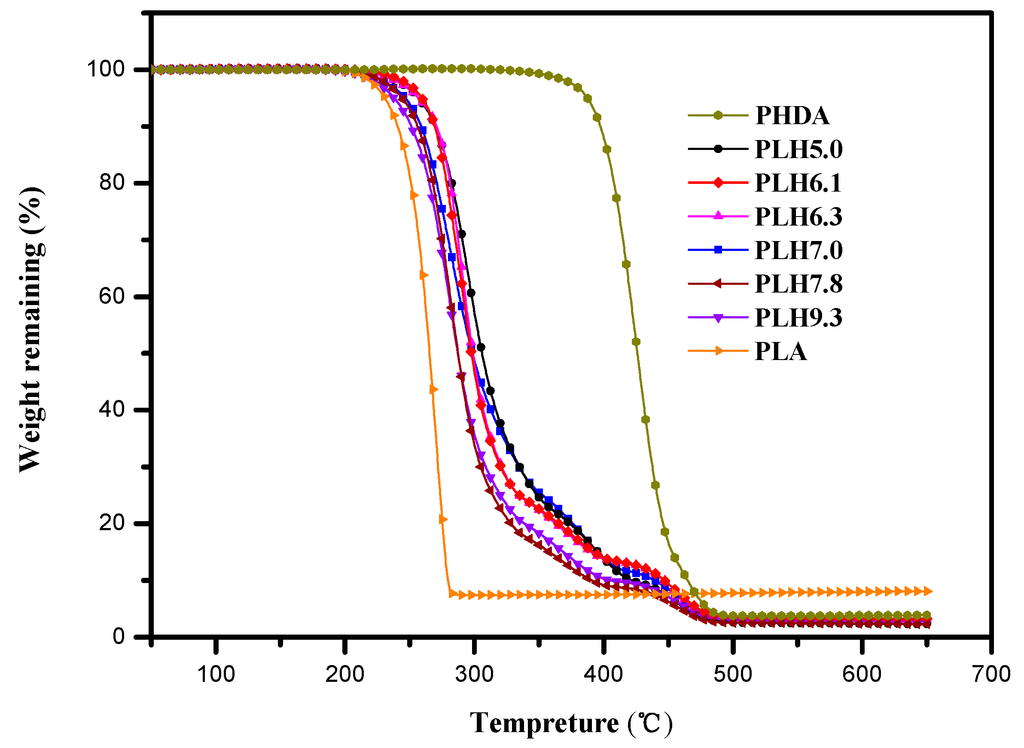
Figure 3.
TGA curves of the PLH copolymers under N2 at a heating rate of 10 °C/min.
Weight loss does not take place for all synthesized polymers before 190 °C under N2 atmosphere. Td,5% and Td,max of PLH copolyesters are 237–262 °C and 280–295 °C, respectively. These results indicated that PLH had a higher decomposition temperature and excellent thermal stability, possibly due to the introduction of HDA units increasing the thermal stability. From Figure 3, the TGA curves of the PLH copolymer showed a three-stage processing thermal degradation. The maximum recorded at the first decomposition stage occurred at 280–295 °C and shifted to a higher temperature with increasing the amount of had, and this stage formed 74–85 wt% of the weight loss. Following, a second decomposition was at 340 °C, and a third decomposition was at 420 °C. From the TGA curves of PLA and PHDA, it was obviously observed that the thermal stability of PHDA was much higher than PLA. Since there were three kinds of molecular chains existing in PLH, including LA, LA-HDA and HDA units, the first decomposition stage of PLH might belong to the LA unit, and the second and third decomposition stages were assigned to the LA-HDA and HDA units, respectively. Therefore, the higher thermal stability of the PLH copolymers could contribute to the long and flexible chain of the HDA units in the PLA chains. Moreover, the melting temperature of the PLH copolymers decreased depending on the composition of HDA, and a wider range of temperatures between melting and decomposition exists, resulting in a more comfortable melting processing.
The thermal stability of the PLH copolymer was further investigated by a rheological method at 180 °C, and the results are shown in Figure 4. For PLA, there was a reduction in viscosity over time. The decrease in viscosity generally corresponds to a loss in molecular weight [32,33]. Accordingly, this viscosity decrement of PLA suggested possible thermal degradation occurring during thermal processing, because of unzipping and chain scission reactions. Interestingly, significant increases in viscosity over time for the PLH copolymers were observed, and the higher HDA composition showed higher viscosity over time. These results indicated that there was almost no (or very little) breaking down of the inter-/intra-molecular forces in the PLH copolymers. HDA with a long and soft chain might induce the chains to become entangled with each other, reducing the thermal degradation of the PLH copolymers. Accordingly, the PLH copolymers showed high thermal stability.
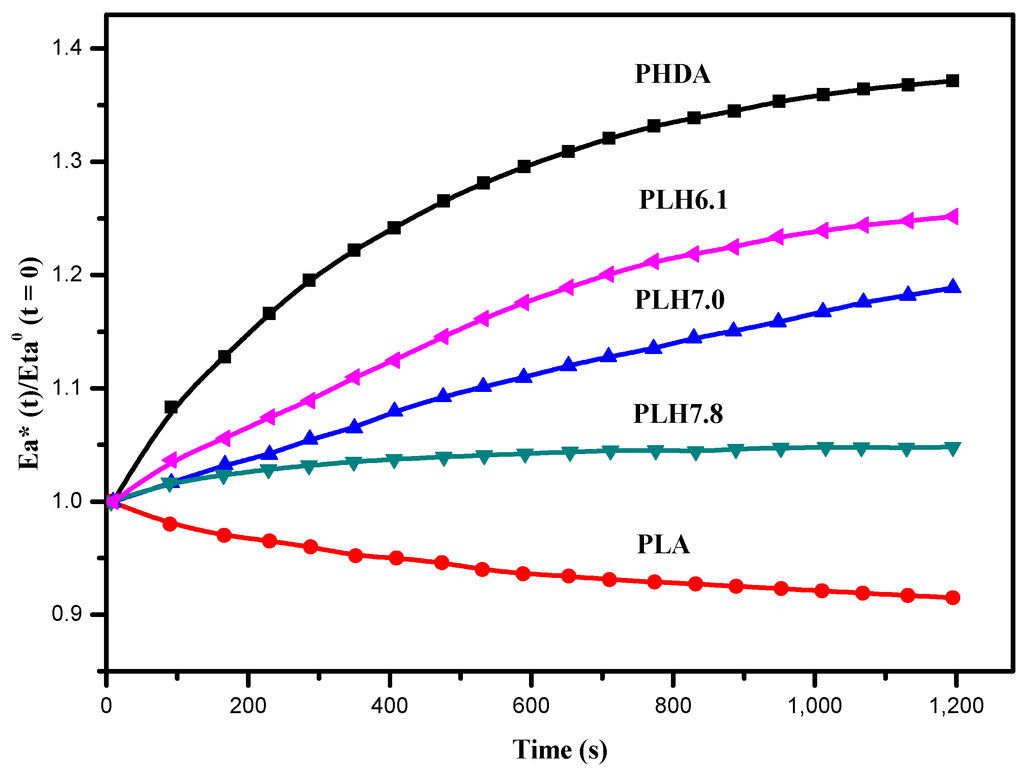
Figure 4.
Eta*(t)/Eta0 (t = 0) evolution versus time for the PLH copolymers at 180 °C.
3.4. Mechanical Properties
The tensile strength (E), tensile modulus (σb) and elongation at break (εb) of the PLH copolymers are illustrated in Table 2, which was calculated from Figure S3. Mechanical tests of PLA, PLH9.3 and PHDA cannot be carried out, because of their brittle properties. With increasing the composition of HDA in PLH copolymers, the elongation at break increased significantly. When nLA/nHDA was 5.0/1, the elongation reached 640%, which was higher than the other reported copolymers, such as the elongation at break of the modified PLLA by TFC being 12.9% [20], penta-block copolymers (penta-sb-PLA) being 470% [34], poly(l-lactic acid) and poly(butylene carbonate) (PLA-b-PBC) being 430% [35] and poly(l-lactic acid)-block-poly(butylene succinate-co-butylene adipate) (PLLA-b-P(BS-co-BA) being 503% [36]. This result suggested that the PLH copolymers had high ductility. On the opposite side, the tensile strength decreased from 27.3 to 1.5 MPa, and the tensile modulus decreased from 1631 to 28 MPa. These results indicated that the mechanical properties of PLH decreased with the increment of HDA. Therefore, the mechanical properties of PLH could be controlled to a suitable level by adjusting the HDA composition.
3.5. Hydrolytic Degradation
The degradation property is very important for bio-based polymers. Thus, the hydrolytic degradation of the cured PLH films was monitored in basic (pH 10.2) and neutral pH phosphate buffers (pH 7.4). The buffers were used in excess to avoid auto-catalysis and to maintain a stable pH environment. The degradation behavior was detected by the weight loss during the hydrolysis, as shown in Figure 5. In the first period of degradation for 25 days, the weight loss was similar both in pH 10.2 and 7.4. After 25 days, the weight loss was slight greater in the basic phosphate buffer solution, and about a 19% mass loss was observed after being degraded for 40 days, while the weight loss was 16% in PBS.
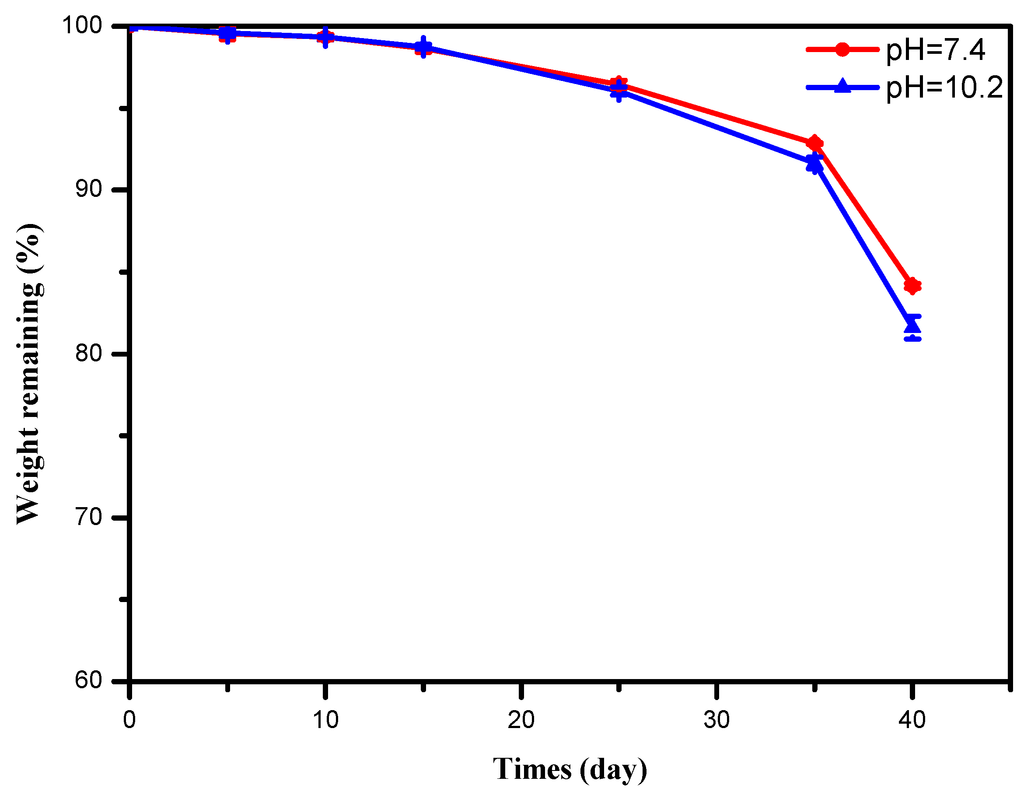
Figure 5.
Remaining weight of PLH7.0 with degradation time in basic pH 10.2 and PBS pH 7.4.
The results of molecular weight measurements of the PLH7.0 copolymers are presented in Figure 6. The average molecular weight (Mn) of PLH7.0 decreased gradually with the degradation time, especially for PLH7.0 degraded in pH 10.2, decreasing to approximately 0.5 ° 104 by 40 days. These results suggested that the PLH copolymer could degrade in basic and neutral buffer solutions, and the weight and molecular weight decreased with degradation time. As the molecular weight of PLH7.0 decreased quickly and the PLH films became very brittle or broken, thus, the mechanical properties of the PLH films after degradation could not be tested.
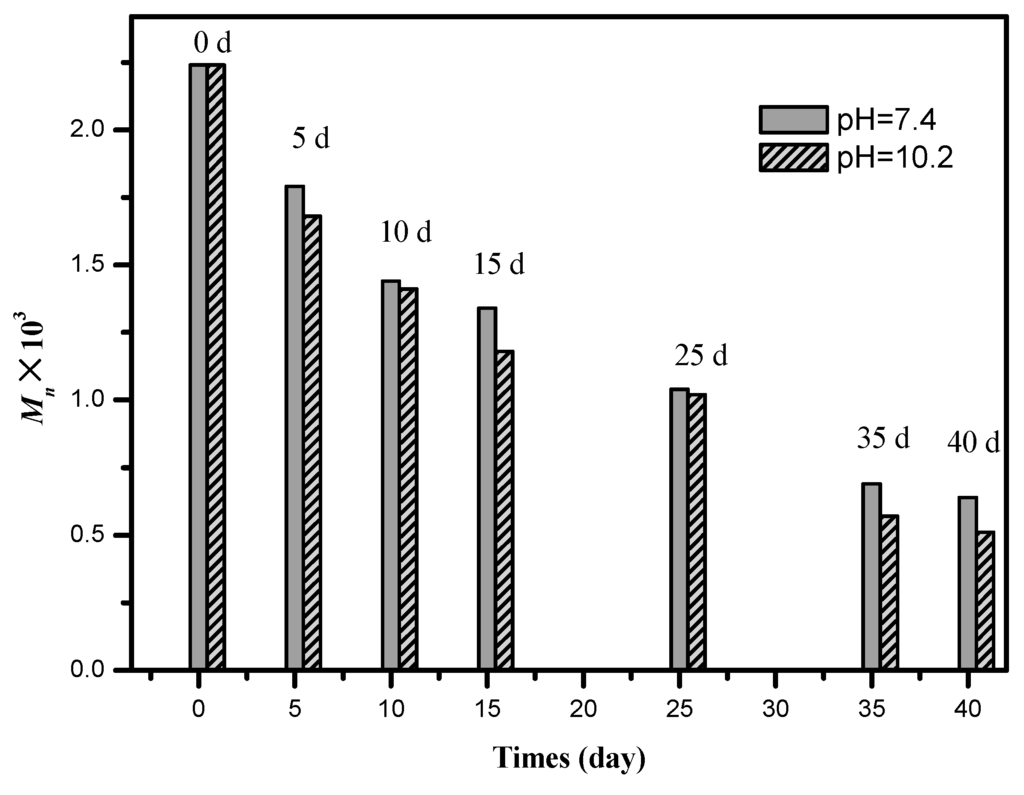
Figure 6.
Molecular weight of PLH7.0 in different pH phosphate butter solutions with degradation time.
The chemical structure of the PLH7.0 after degradation was also confirmed by FTIR and 1H NMR, as shown in the Supplementary Information, Figures S4 and S5. In Figure S4b, a new peak at 1614 cm−1 appeared after degradation for 40 days, which was assigned to the carboxylic acid group, while the stretching vibration of carbonyl groups at 1757 cm−1 still existed. Moreover, a broad band at 3400–3600 cm−1 was observed after degradation, which could be ascribed to the vibration of the hydroxyl and carboxyl groups. In the 1H NMR spectrum (Figure S5b), there was a new signal characteristic peak at around δ 3.6, arising from CH2OH end groups. These results indicated that the hydrolytic degradation was due to the simple hydrolysis of the ester bonds to form hydroxyl and carboxyl end groups.
The surface morphology of the PLH copolymer after degradation was observed by SEM. The SEM images of the PLH7.0 films before and after incubation in basic and neutral pH phosphate buffers are shown in Figure 7. In the basic phosphate buffer, the surface morphology slightly changed after degradation for 15 days and became rough with some micro-holes after 35 days. In pH 7.4, a rough surface morphology of PLH appeared after 35 days. These results suggested the degradation in the basic condition was faster, which was in accord with the results of Figure 5 and Figure 6.
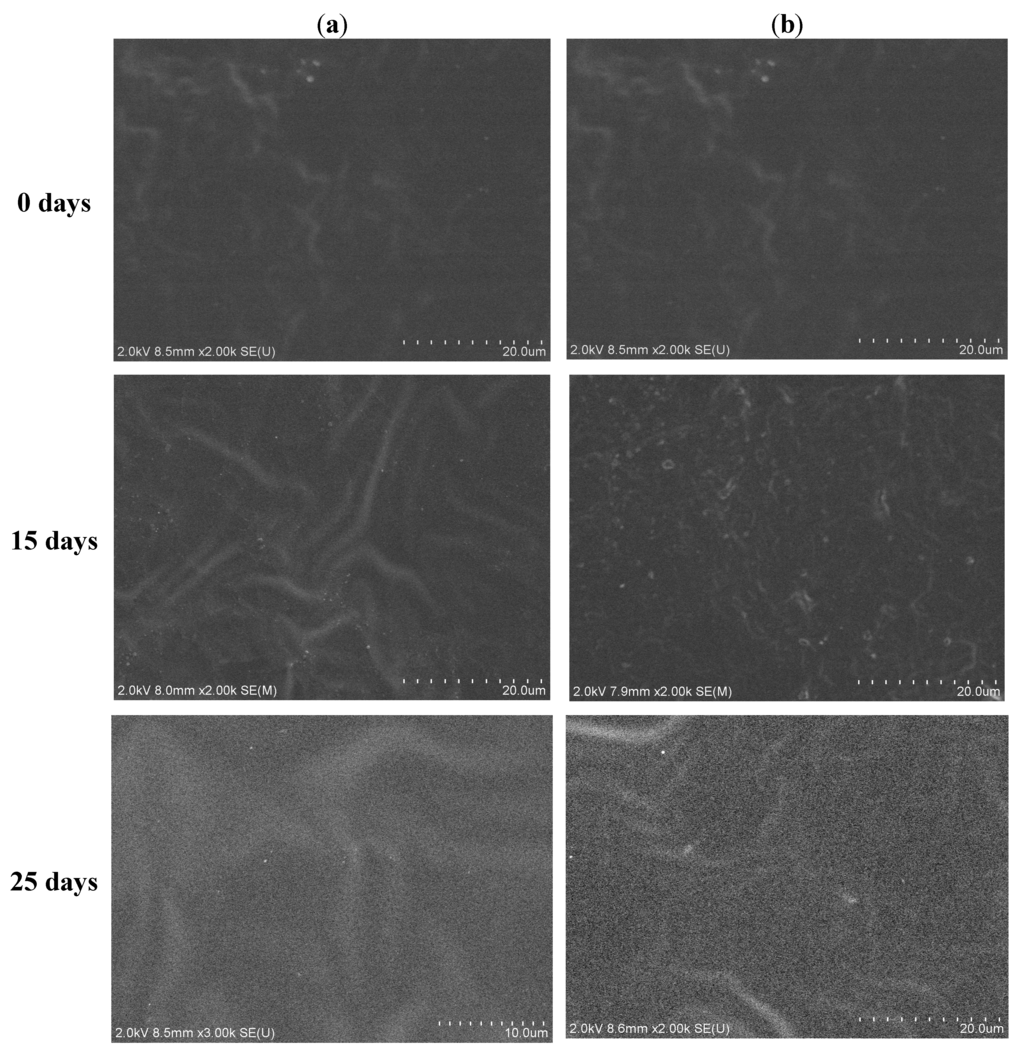
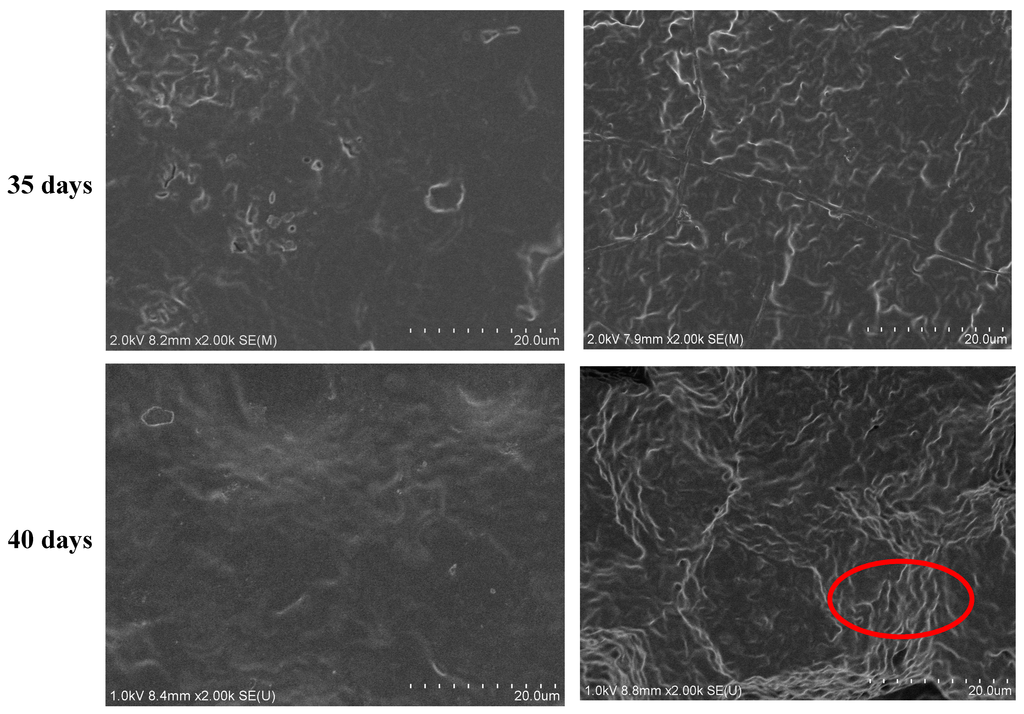
Figure 7.
SEM images for the surface morphology of PLH after degradation in different phosphate butter solutions with different times: (a) pH 7.4 and (b) pH 10.2.
3.6. Biocompatibility
The biocompatibility of PLH was estimated using NIH/3T3 cells as the model cells by the MTT assay method. Since only live cells have enzymes that can reduce the MTT reagent, the MTT assay gives an estimate of the number of metabolically-active cells when the MTT reagent is oxidized by oxidoreductases in mitochondria to form purple formazan crystals. These formazan crystals are water insoluble, but can dissolve in DMSO. Then, the absorbance was measured subsequently after being incubated in DMSO for 4 h. The obtained absorbance values are directly proportional to the number of metabolically-active cells, and the results are shown in Figure 8. The cell viabilities for PLA and PHDA were about 62% and 80%. The cell viabilities for PLH increased with the increment of the HDA amounts in PLH and reached 92% for PLH6.3. These results indicated that the PLH copolymers had low cell toxicity and had better biocompatibility than pure PLA.
Moreover, the morphology of the cell growth was also observed by fluorescence microscopy. Figure 9 shows the NIH/3T3 cell adhesion on the PLA, PLH and PHDA polymers. It is clear that NIH/3T3 cells adhered well to and proliferated on the PLH copolymers. By comparison with neat PLA membranes, the amounts of cells grown on the PLH copolymers were greater after 24 h of proliferation, indicating the good cell compatibility of the PLH copolymers.
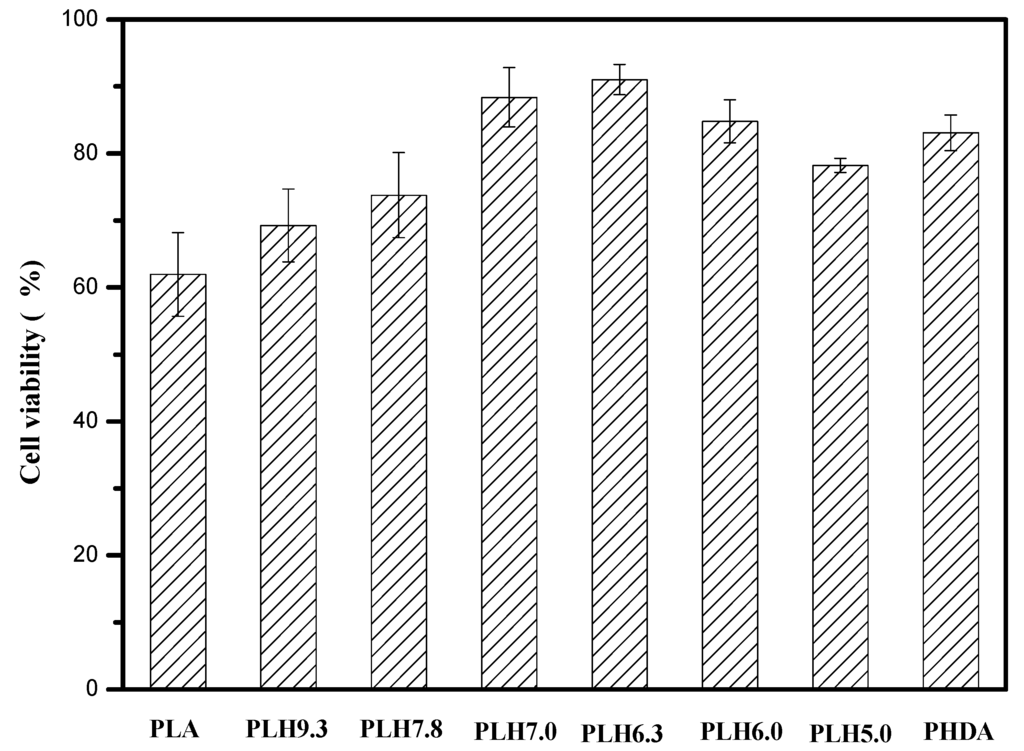
Figure 8.
Cell viability of the PLH copolymers after incubation with NIH/3T3 cells for 24 h.
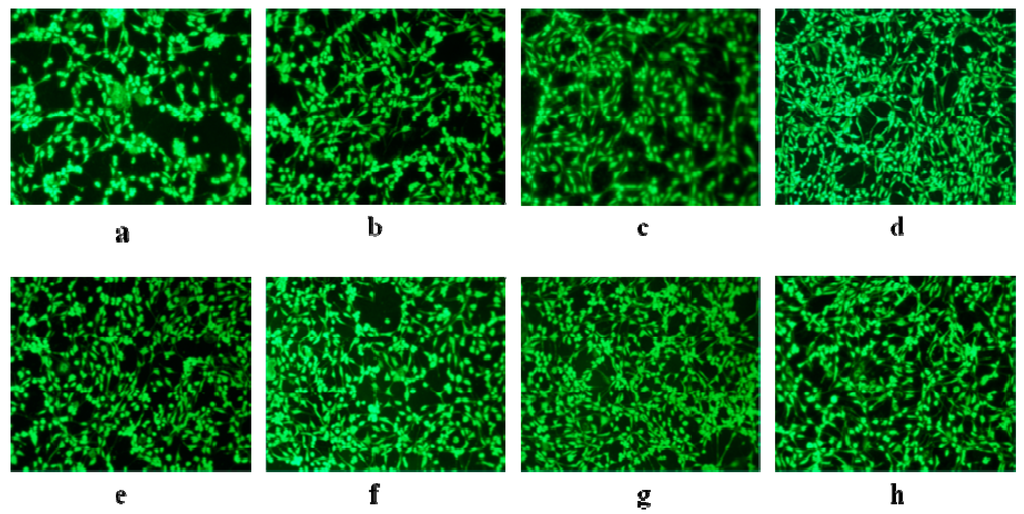
Figure 9.
Fluorescent microscopy images of NIH/3T3 cells grown on PLH polymers. (a) PLA; (b) PLH9.3; (c) PLH7.8; (d) PLH7.0; (e) PLH6.3; (f) PLH6.1; (g) PLH5.0; and (h) PHDA.
4. Conclusions
Novel aliphatic random copolymers, PLH, were successfully synthesized from LA and HDA via a polycondensation process using p-TSA and SnCl2·2H2O as co-catalyst. The molecular weight and composition of the PLH copolymers could be adjusted by changing the molar ratio of LA and HDA. Tg and Tm of PLH decreased continuously with increasing of the HDA composition in the copolymers. The PLH copolymer also showed excellent thermal stability before 237 °C (Td,5%). The elongation at break increased significantly with HDA in the copolymers, while the tensile modulus and strength showed just the opposite result. The novel bio-based PLH copolymer has tunable properties, possessing a good tensile modulus (28~1631 MPa) and strength (1.5~27.3 MPa) compared to nearly amorphous polymers possessing low Tg and very high elongation (~640%). Moreover, the PLH copolymer has biodegradable and biocompatible properties. Therefore, it has potential applications in the biomedical, industrial and agriculture fields.
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary materials can be accessed at: http://www.mdpi.com/2073-4360/7/03/0468/s1.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51173072 and 21341009), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (JUSRP51408B) and the Enterprise University Research Prospective Program, Jiangsu Province (No. BY2012057).
Author Contributions
Mingqing Chen designed the experiment, Jinting Hua and Li Zhang performed the experiment, Dongjian Shi analyzed the data of all experiment. Dongjian Shi, Jinting Hua and Mingqing Chen wrote the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Coombs, J.; Hall, K. Chemicals and polymers from biomass. Renew. Energy 1998, 15, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozell, J.J. Feedstocks for the future-biorefinery production of chemicals from renewable carbon. CLEAN Soil Air Water 2008, 36, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolau, B.J.; Perera, M.A.D.N.; Brachova, L.; Shanks, B. Platform biochemicals for a biorenewable chemical industry. Plant J. 2008, 54, 536–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schreck, K.M.; Hillmyer, M.A. Block copolymers and melt blends of polylactide with Nodax™ microbial polyesters: Preparation and mechanical properties. J. Biotechnol. 2007, 132, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Beilen, J.B.; Poirier, Y. Production of renewable polymers from crop plants. Plant J. 2008, 54, 684–701. [Google Scholar]
- Albertsson, A.C.; Varma, I.K. Aliphatic polyesters: Synthesis, properties and applications. In Degradable Aliphatic Polyesters; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2002; pp. 1–40. [Google Scholar]
- Drumright, R.E.; Gruber, P.R.; Henton, D.E. Polylactic acid technology. Adv. Mater. 2000, 12, 1841–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandini, A. Polymers from renewable resources: A challenge for the future of macromolecular materials. Macromolecules 2008, 41, 9491–9504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoichet, M.S. Polymer scaffolds for biomaterials applications. Macromolecules 2009, 43, 581–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stout, D.A.; Basu, B.; Webster, T.J. Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid): Carbon nanofiber composites for myocardial tissue engineering applications. Acta Biomater. 2011, 7, 3101–3112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripathi, G.; Basu, B. A porous hydroxyapatite scaffold for bone tissue engineering: Physico-mechanical and biological evaluations. Ceram. Int. 2012, 38, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, G.; Basu, B. Injection-molded high-density polyethylene-hydroxyapatite-aluminum oxide hybrid composites for hard-tissue replacement: Mechanical, biological, and protein adsorption behavior. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 124, 2133–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mialon, L.; Vanderhenst, R.; Pemba, A.G.; Miller, S.A. Polyalkylenehydroxybenzoates (PAHBs): Biorenewable aromatic/aliphatic polyesters from lignin. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2011, 32, 1386–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trzaskowski, J.; Quinzler, D.; Bährle, C.; Mecking, S. Aliphatic long-chain C20 polyesters from olefin metathesis. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2011, 32, 1352–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, D.G.; Merkel, T.J.; Christopher, L.J.; Yousaf, M.N. One-step syntheses of photocurable polyesters based on a renewable resource. Macromolecules 2010, 43, 9660–9667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edlund, U.; Källrot, M.; Albertsson, A.C. Single-step covalent functionalization of polylactide surfaces. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 8865–8871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slivniak, R.; Domb, A.J. Lactic acid and ricinoleic acid based copolyesters. Macromolecules 2005, 38, 5545–5553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, C.Q.; Yang, K.; Ji, P.; Yu, M.H. Synthesis and characterization of poly(l-lactic acid)-poly(ε-caprolactone) multiblock copolymers by melt polycondensation. J. Polym. Sci. A 2004, 42, 5045–5053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanamaker, C.L.; O’Leary, L.E.; Lynd, N.A.; Hillmyer, M.A.; Tolman, W.B. Renewable-resource thermoplastic elastomers based on polylactide and polymenthide. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 3634–3640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.X.; Kim, H.S.; Shim, J.H.; Yoon, J.S. Role of epoxy groups on clay surface in the improvement of morphology of poly(l-lactide)/clay composites. Macromolecules 2005, 38, 3738–3744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meaurio, E.; Zuza, E.; Sarasua, J.R. Miscibility and specific interactions in blends of poly(l-lactide) with poly(vinylphenol). Macromolecules 2005, 38, 1207–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garlotta, D. A literature review of poly(lactic acid). J. Polym. Environ. 2001, 9, 63–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouvel, C.; Dubois, P.; Dellacherie, E.; Six, J.L. Controlled synthesis of amphiphilic biodegradable polylactide-grafted dextran copolymers. J. Polym. Sci. Part A 2004, 42, 2577–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, M.H. High molecular weight polylactic acid polymers. In Biopolymers from Renewable Resources; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1998; pp. 367–411. [Google Scholar]
- Ikada, Y.; Tsuji, H. Biodegradable polyesters for medical and ecological applications. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2000, 21, 117–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.P.; Li, J.H.; Chen, M.Q.; Ren, J.J.; Ni, Z.B.; Liu, X.Y. Synthesis and characterization of biodegradable polyester P(DHCA-co-LA). Acta Polym. Sin. 2010, 3, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Li, S.M.; Ghzaoui, A.E.; Nouailhas, H.; Zhuo, R.X. Synthesis and gelation properties of PEG-PLA-PEG triblock copolymers obtained by coupling monohydroxylated PEG-PLA with adipoyl chloride. Langmuir 2007, 23, 2778–2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, O.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, Y.M.; Kim, Y.H. Synthesis and characterization of poly(l-lactide)–poly(ε-caprolactone) multiblock copolymers. Macromolecules 2003, 36, 5585–5592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranganathan, S.; Kumar, R.; Maniktala, V. On the mechanism and synthetic applications of the thermal and alkaline degradation of c-18 castor oil. Tetrahedron 1984, 40, 1167–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernándeza, J.; Etxeberriab, A.; Ugartemendiaa, J.M.; Petiscoa, S.; Sarasua, J.R. Effects of chain microstructures on mechanical behavior and aging of a poly(l-lactide-co-ε-caprolactone) biomedical thermoplastic elastomer. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2012, 12, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, S., II; Lee, C.W.; Miyamoto, M.; Kimura, Y. Melt polycondensation of l-lactic acid with Sn(II) catalysts activated by various proton acids: A direct manufacturing route to high molecular weight poly(l-lactic acid). J. Polym. Sci. Part A 2000, 38, 1673–1679. [Google Scholar]
- Mallet, B.; Lamnawar, K.; Maazouz, A. Improvement of blown film extrusion of poly(lactic acid): Structure–processing–properties relationships. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2014, 54, 840–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Itry, R.; Lamnawar, K.; Maazouz, A. Improvement of thermal stability, rheological and mechanical properties of PLA, PBAT and their blends by reactive extrusion with functionalized epoxy. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2012, 97, 1898–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirata, M.; Masutani, K.; Kimura, Y. Synthesis of ABCBA penta stereoblock polylactide copolymers by two-step ring-opening polymerization of l-and d-lactides with poly(3-methyl-1,5-pentylene succinate) as macroinitiator (C): Development of flexible stereocomplexed polylactide materials. Biomacromolecules 2013, 14, 2154–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zheng, L.C.; Li, C.C.; Zhu, W.X.; Zhang, D.; Guan, G.H.; Xiao, Y.N. Synthesis and properties of biodegradable multiblock poly (ester-carbonate) comprising of poly(l-lactic acid) and poly(butylene carbonate) with hexamethylene diisocyanate as chain-extender. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 131, 39158:1–39158:9. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, X.Q.; Wu, B.S.; Wu, L.B.; Hu, J.J.; Bu, Z.Y.; Li, B.G. Poly(l-lactic acid)-block-poly(butylene succinate-co-butylene adipate) multiblock copolymers: From synthesis to thermo-mechanical properties. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 3550–3558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).