1. Introduction
Dry adhesion is the result of multiple attractive forces, including short-range intermolecular forces such as van der Waals’ and longer range electrostatic forces, which occur between contacting materials. The total force generated between contacting materials is therefore directly related to the amount of area in intimate contact, as well as the chemical makeup of the mating surfaces. Substantial investments in the study and development of dry adhesives have been made in recent years, spurred in large part by the discovery of the exceptional adhesive capabilities of gecko lizards [
1]. The majority of this work has focused on the study of fibrillar, or “hairy”, dry adhesives; natural examples such as the gecko [
2,
3,
4,
5,
6], or the development and characterization of artificial systems meant to mimic those found naturally [
7,
8,
9,
10].
A compliant adhesive surface facilitates the creation of large adhesive contact area during initial contact (bonding). During loading, excessive compliance in the adhesive system may cause inadequate load sharing between contact points, leaving the interface susceptible to peeling failure. Therefore, strong adhesion is generated by an adhesive surface that maximizes compliance normal to the mating surface during bonding, while also minimizing compliance in the direction of loading. Fibrillar structures are one possible solution to this problem; the slender fibrillar structures maximize compliance at the microscale to generate a large contact area, while the underlying structure supplies adequate rigidity to suppress peeling. Fibrillar adhesives are particularly effective when adhering to microscopically rough, irregular surfaces due to the extreme compliance of the fibers and their inherent contact splitting nature [
6]. In addition, careful design of the fibers can allow for a large ratio of maximum adhesion to minimum adhesion, often termed adhesion “reversibility”, which is typically highly desirable for dry adhesive systems and is essential for locomotion-based applications [
8]. It is therefore unfortunate that the large scale application of artificial fibrillar dry adhesives faces multiple significant challenges, most notably high fabrication costs and limited durability.
Alternative dry adhesive systems have been successfully developed using the same general principles of compliance control. A prime example is the creation of thin composite polymer/fabric sheets, soft and flexible normal to the surface but relatively inextensible parallel to the surface, which generate a very strong adhesion in shear while remaining easily detachable by manually peeling at the edges [
11]. To create an adhesive that is strong when loaded normally to the surface, the general concept to generate a strong bond is the same but the optimal means to achieve it must be different since the directions of bonding and loading are now the same. If the adhesive can be cycled between a compliant configuration during bonding to a rigid configuration during loading, then the problem will have been at least partially solved. This is the strategy employed by various researchers using phase-changing [
12] or smart materials, such as thermosensitive shape memory polymers (SMPs) [
7,
13,
14,
15].
Phase-changing materials may be used as a bulk layer behind an adhesive membrane. Bonding is performed while the phase-changing material is melted; thus, the adhesive has the compliance of the thin membrane to generate large contact area, but once solidified in this deformed shape the compliance is decreased dramatically thus ensuring strong peel resistance. SMPs are a class of material that can perform a similar function, though without undergoing phase change [
16,
17,
18]. An SMP has a cross-linking network that sets its permanent shape, determined during its initial curing stage. At a particular temperature, the SMP undergoes a thermal transition enabling short-range molecular motion. Above this temperature, the polymer becomes more compliant, and any deformation applied may be subsequently fixed or “frozen” in place by cooling the SMP below its thermal transition temperature while maintaining its deformed, or “temporary”, shape. The SMP will maintain this temporary shape until again heated above its transition temperature, at which point it will return to its original permanent shape. Epoxy-based SMPs are particularly attractive as a structural layer in adhesive systems owing to their excellent thermal and mechanical properties, as well as their relative ease of processing [
17]. Epoxy-based SMPs have a thermal transition defined by their glass transition temperature (
Tg).
Intelligent use of either phase-changing or SMP materials in a dry adhesive system has been shown to effectively increase maximum adhesion and improve adhesive reversibility, both with and without the aid of supplementary fibrillar structures. Though a phase-changing material approach necessitates the addition of an adhesive barrier membrane to qualify as a dry adhesive, the performance advantages have been shown using SMP as a bulk adhesive material both with [
7,
14] and without [
13] the addition of a “sticky” adhesive material layer. Elimination of this additional layer is advantageous from both manufacturability and durability standpoints. An obvious drawback to the use of thermosensitive functional materials is the necessity of a heat source to cycle between compliant and rigid states. An external heat source constitutes additional equipment cost and reduced flexibility of operation for the adhesive system, making the bonding process more complex and adding thermal mass thus slowing the thermal response time of the functional material with a given power input. In contrast, an internally conductive material would allow the functional material to also act as the heat source by passing current through it. In this work, we demonstrate an epoxy-based SMP dry adhesive system doped with electrically conductive carbon black (CB) to enable internal joule heating, bypassing the operational requirement of a secondary heat source. Our approach additionally enables adhesion to non-flat surfaces, which has not been previously demonstrated with SMP adhesive systems to our knowledge.
3. Results and Discussion
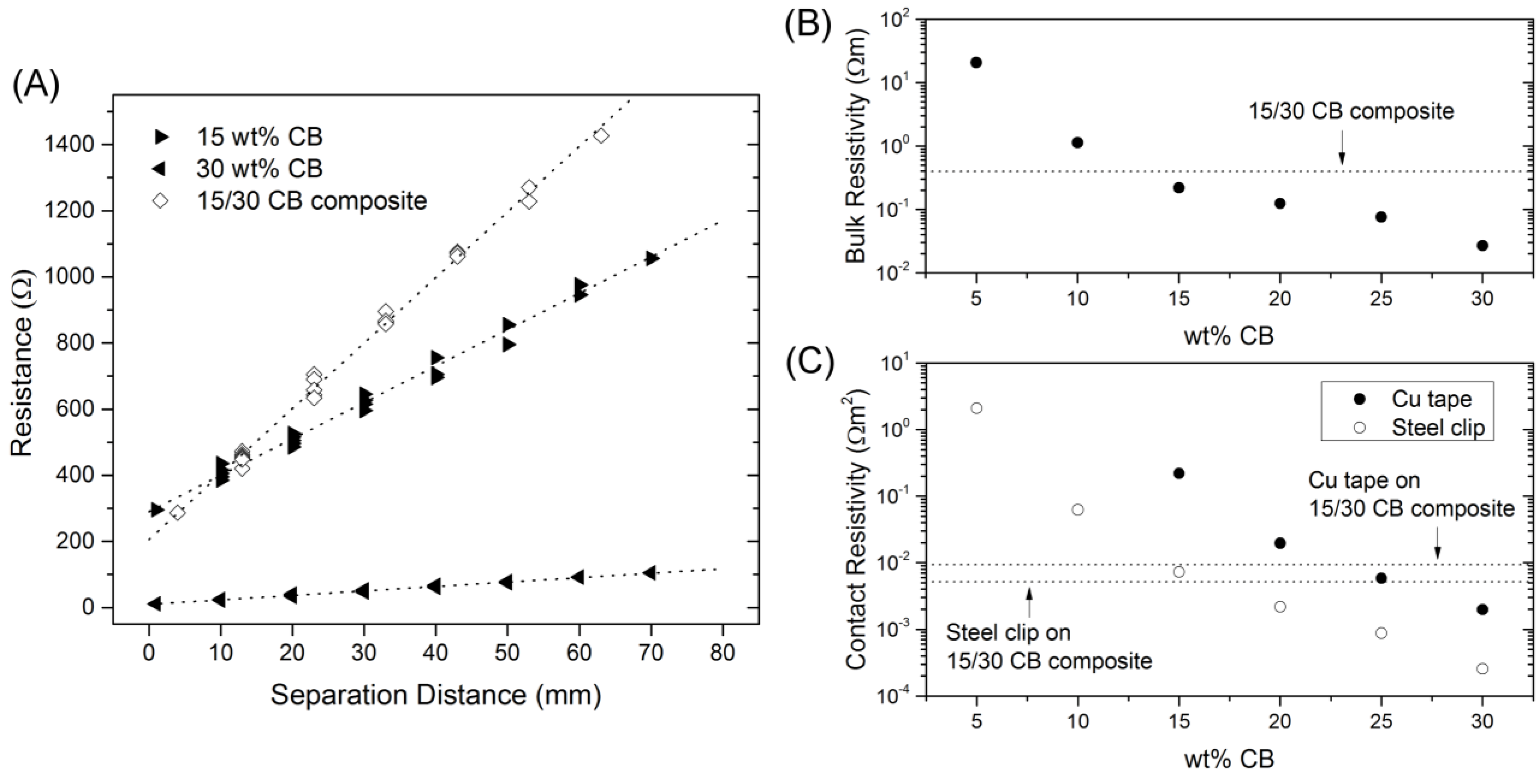
Examples of TLM curves for CB/SMP blends of 15 and 30 wt% CB are shown in
Figure 2A for samples with a 20 mm
2 cross section, with contact pads that are 50 mm
2 in area. The 15/30 CB composite curve will be addressed later. Above 20 wt% CB, the CB/SMP blends become thick, even clumpy, prior to curing and tend to form significant cracks at free surfaces while curing. It has been documented previously for other CB/polymer blends that tensile strength is expected to decrease with increasing CB loading [
21], most likely due to internal and surface cracks. Measurements terminate at 30 wt% CB due to the practical challenge of manufacturing and handling continuous bars above this CB concentration. Bulk and contact resistivities are calculated based upon least-squares regression line of the TLM data, together with the sample and contact pad geometries. A greater slope to the regression line indicates a larger bulk resistivity, while a greater
y-intercept indicates a larger contact resistance. Performing the similar measurements for several CB/SMP blends provides bulk and contact resistivities as a function of CB wt% in
Figure 2B,C, respectively. The calculation of contact resistivity includes the contribution from bulk resistance beneath the contact pad, and so these values can be considered somewhat conservatively high, though the contribution is not large for the homogeneous samples. As should be expected, both bulk and surface resistivities are inversely proportional to the concentration of CB. Contact resistance decreases more steeply with increasing CB concentration than the bulk resistance, as shown in
Table 1 where the ratio of bulk to contact resistivities are calculated for each CB/SMP blend tested.
To evenly heat a slender strip of CB/SMP, most of the power input should be dissipated within the bulk of the material. Therefore, it is desirable to have a large bulk resistivity in comparison to the contact resistivity to the Cu tape. From
Table 1, it is clear that this ratio increases with CB loading, and so a higher CB loading is expected to provide better heating performance. As previously described, continuous sheets with high CB loading above 20 wt% become prone to crack formation and lose the mechanical durability necessary for a flexible, reusable adhesive.
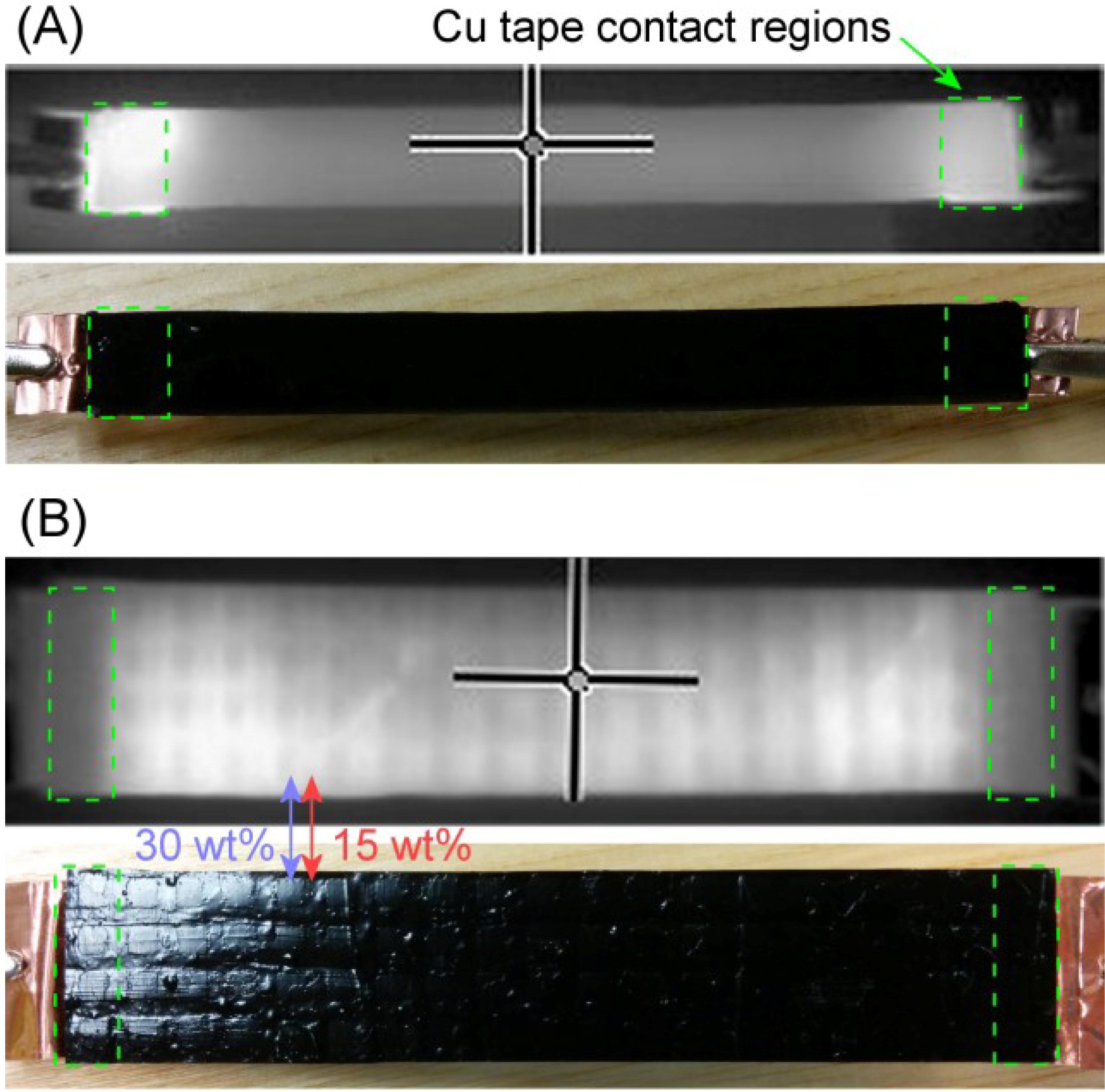
Figure 3A shows infrared (IR) and optical images of a 15 wt% CB/SMP blend experiencing internal joule heating through Cu tape attached to the ends of its opposite face. The hot spots directly beneath the Cu tape contact regions clearly indicate poor heating performance, with the majority of power dissipation occurring at the SMP–Cu tape interface. The tape adhesive layer thins and loses contact well before the bulk of the CB/SMP strip reaches its
Tg, as is required for its use as an adhesive.
Figure 2.
(A) TLM data gathered using the steel clip method for homogeneous 15 and 30 wt% CB/shape memory polymer (SMP) blends, and the 15/30 CB composite design. Linear curve fits used to calculate effective bulk and contact resistivities are shown. The 15/30 CB composite has a relatively high effective bulk resistivity (B) and a relatively low effective contact resistance (C), shifting the power dissipation into the bulk of the material for more even heating when using Cu tape.
Figure 2.
(A) TLM data gathered using the steel clip method for homogeneous 15 and 30 wt% CB/shape memory polymer (SMP) blends, and the 15/30 CB composite design. Linear curve fits used to calculate effective bulk and contact resistivities are shown. The 15/30 CB composite has a relatively high effective bulk resistivity (B) and a relatively low effective contact resistance (C), shifting the power dissipation into the bulk of the material for more even heating when using Cu tape.
Table 1.
Ratio between the experimentally determined bulk and surface resistivities as a function of wt% carbon black (CB).
Table 1.
Ratio between the experimentally determined bulk and surface resistivities as a function of wt% carbon black (CB).
| wt% CB | Bulk to Surface Resistivity Ratio (m−1) |
|---|
| Cu Tape | Steel Clip |
|---|
| 5 | – | 10 |
| 10 | – | 18 |
| 15 | 1 | 30 |
| 20 | 6 | 57 |
| 25 | 13 | 86 |
| 30 | 14 | 105 |
| 15/30 | 42 | 76 |
Reduced contact resistance may be achieved by introducing small integrated contact pads within the moderately doped (15 wt%) bulk CB/SMP made of more highly doped (30 wt%) CB/SMP. An initial goal of the project was to create sheets of adhesive which may be cut arbitrarily to form usable strips of varying size and orientation. Therefore, the 30 wt% contact pads are molded as small (3.5 × 3.5 mm), separate islands set into the surface of a bulk sheet of 15 wt% composite CB/SMP, referred to as the filler. The finished product will be referred to as 15/30 CB composite. This design allows power to flow relatively unimpeded through the interface between the 30 wt% CB/SMP and Cu tape to be dissipated as heat within the connecting 15 wt% CB/SMP material. Thermal performance is shown in
Figure 3B to be far superior to the homogeneous strip shown in
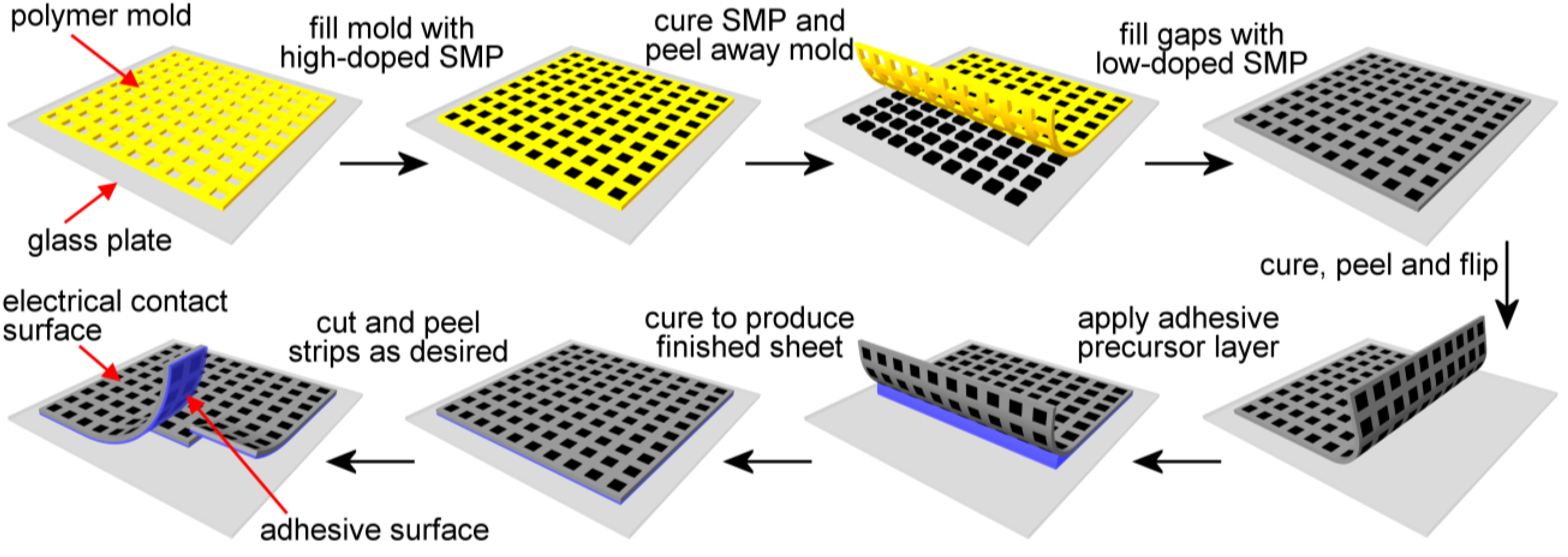
Figure 3A, enabling consistent heating without threatening the integrity of the Cu tape contact. The fabrication method is described in
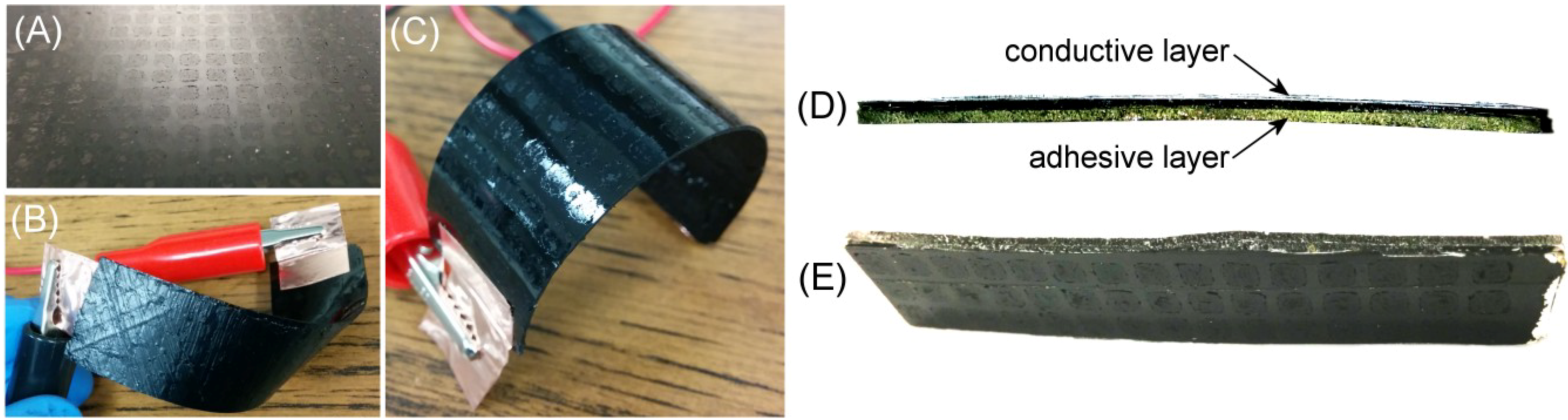
Figure 4, where an additional “adhesive layer”, in this case consisting of non-doped SMP, has been added to give added bending strength, increased surface compliance (described later) and a smoother surface finish. The finished sheet may be cut arbitrarily to create adhesive strips with one electrically conductive side, and one adhesive side. The entire sheet consists of an SMP functional material, as depicted in
Figure 5.
Figure 3.
(A) Infrared and visible spectrum images of a homogeneous strip of 15 wt% CB doped SMP with applied voltage, showing excessive power dissipation at the tape contact regions; and (B) Similar images of a composite strip with 30 wt% islands and 15 wt% filler, showing the power dissipation now occurs mostly between the tape contact regions, within the more resistive filler material.
Figure 3.
(A) Infrared and visible spectrum images of a homogeneous strip of 15 wt% CB doped SMP with applied voltage, showing excessive power dissipation at the tape contact regions; and (B) Similar images of a composite strip with 30 wt% islands and 15 wt% filler, showing the power dissipation now occurs mostly between the tape contact regions, within the more resistive filler material.
Figure 4.
The fabrication method for the composite SMP conductive layer is shown.
Figure 4.
The fabrication method for the composite SMP conductive layer is shown.
Figure 5.
(A) A composite carbon-doped SMP sheet with 30 wt% islands and 15 wt% filler; (B) A strip of the sheet is heated above its Tg by internal joule heating and deformed; (C) The material’s shape fixing property allows the strip to maintain its deformed shape when cooled; and (D) An adhesive layer comprised of non-doped SMP is applied to the conductive composite, viewed from the side and (E) the conductive face.
Figure 5.
(A) A composite carbon-doped SMP sheet with 30 wt% islands and 15 wt% filler; (B) A strip of the sheet is heated above its Tg by internal joule heating and deformed; (C) The material’s shape fixing property allows the strip to maintain its deformed shape when cooled; and (D) An adhesive layer comprised of non-doped SMP is applied to the conductive composite, viewed from the side and (E) the conductive face.
The electrical properties of the 15/30 CB composite strips are characterized for comparison to the homogeneous CB/SMP values in
Figure 2. The contact resistance measured for the composite strips using the steel clip method is much closer to the 15 wt% CB value than expected, most likely because contact pressure from the alligator clip is applied unevenly, more heavily weighted towards the edge of our samples which consist of the 15 wt% CB/SMP material. Surprisingly, the bulk resistivity is also increased compared with the homogeneous 15 wt% CB/SMP samples. This is most likely explained by the existence of an additional interfacial resistance between the 15 and 30 wt% CB/SMP components within the composite. It was observed that air bubbles were easily trapped within the CB/SMP mixtures during mixing and resulted in small internal voids after curing. It is likely these bubbles are especially prevalent at the interfaces between the composite components, resulting in an increased resistance to current flow. The ratio of bulk to surface resistivities is compared to the homogeneous blends in
Table 1, indicating a significantly increased ratio particularly in the case of the Cu tape contact, which as previously stated is a desirable quality for bulk heating.
Treating the 15/30 CB composite as a repeating pattern of parallel and sequential resistors, a rough estimate of the expected effective bulk resistivity may be calculated using the homogeneous CB/SMP data. Likewise, an effective contact resistivity may be estimated from the homogeneous data. These calculated estimates are provided in
Table 2 along with the corresponding experimentally determined values. The calculated values assume simple, 1D current flow, and so it is unsurprising that the experimental values are greater. The significant increase over the calculated values again indicates additional interfacial resistances within the composite material, which would affect the data used to calculate contact resistivity as well as the bulk resistivity.
Table 2.
Comparison of experimentally determined 15/30 CB composite resistivities to estimates calculated from homogeneous test data.
Table 2.
Comparison of experimentally determined 15/30 CB composite resistivities to estimates calculated from homogeneous test data.
| Material Property | Calculated | Experimental |
|---|
| Bulk Resistivity (Ωm) | 0.089 | 0.396 |
| Contact Resistivity (Ωm2) | 0.0040 | 0.0094 |
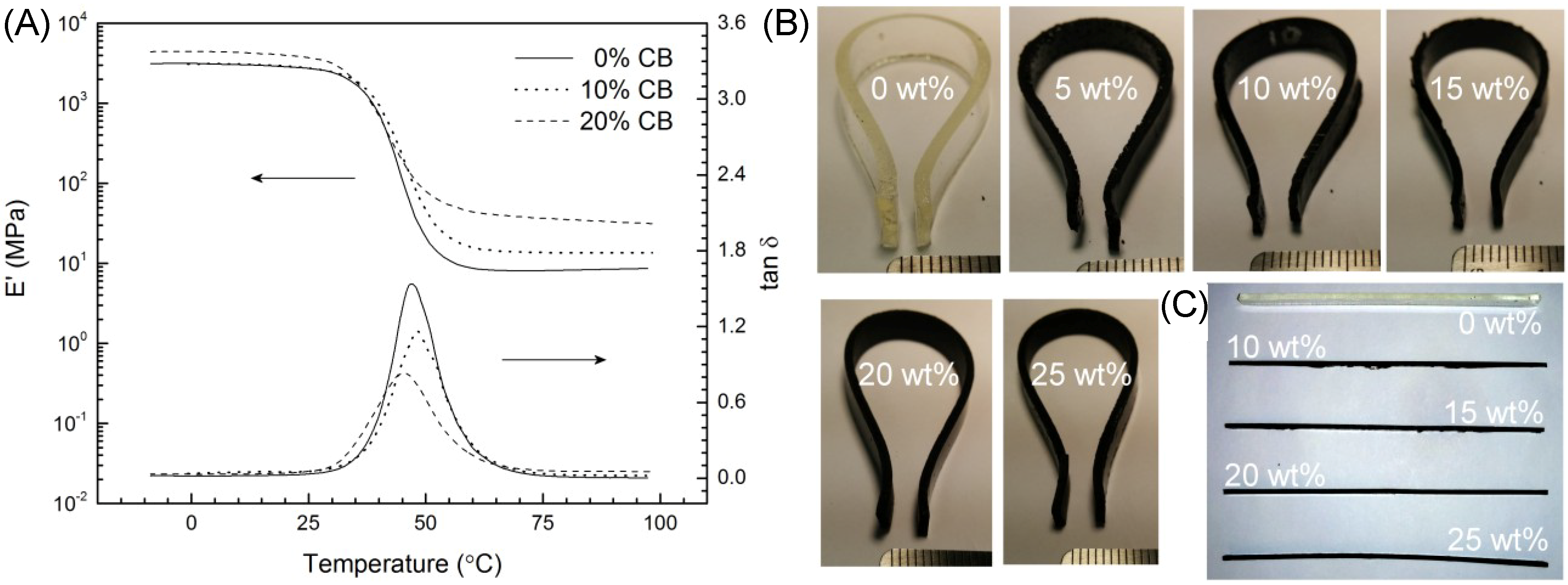
In addition to conferring electrical conductivity, adding CB to polymers is known to affect mechanical properties. Specifically, an increase in storage modulus and hardness are to be expected [
21,
22]. Dynamic mechanical analysis measurements of 10 and 20 wt% CB/SMP blends are compared with a non-doped control sample in
Figure 6A. Storage modulus (
E') is shown to generally increase with increasing CB loading, particularly when above the material’s
Tg around 40 °C. Since the increase in compliance above
Tg is a fundamental feature for the operation of our adhesive, this increase in
E' above
Tg is a negative consequence of the added CB. However, the addition of a non-doped SMP layer as the adhesive interface as shown in
Figure 4 negates this potential problem. The tan δ curves provide additional assurance that the
Tg undergoes only slight variation due to the addition of CB into the SMP. Comparing the non-doped SMP curves to those reported in Reference [
19] shows essentially identical results. The final property of significant interest is whether the shape fixity and recovery of the non-doped SMP is maintained with added CB. Several initially-straight bars of varying CB/SMP blends are shown in
Figure 6B, bent and fixed into a horse-shoe shape with a loaded separation of ~1.5 mm. Upon unloading, this gap changes only a trivial amount up to a CB loading of 25 wt%, the highest loading tested, indicating that CB loading does not significantly impact the SMPs excellent shape fixity. Upon reheating,
Figure 6C indicates similarly excellent shape recovery of each tested sample, with only perhaps a slight bend remaining in the 25 wt% CB/SMP.
Figure 6.
(A) Dynamic mechanical analysis (DMA) curves for various levels of CB-doped SMP. The SMP (B) shape-fixing and (C) shape-recovery properties are minimally affected by carbon doping, demonstrated using initially-straight material strips.
Figure 6.
(A) Dynamic mechanical analysis (DMA) curves for various levels of CB-doped SMP. The SMP (B) shape-fixing and (C) shape-recovery properties are minimally affected by carbon doping, demonstrated using initially-straight material strips.
The SMP formulation used for our dry adhesive system has been previously shown to demonstrate excellent adhesive performance to smooth glass surfaces [
13]. In that work, test samples with interfacial areas of 0.32 cm
2 were externally heated and required preload of about 40 N/cm
2 during bonding to generate a maximum adhesion of approximately 200 N/cm
2. To compare our CB/SMP dry adhesive with the previous results, adhesive tests were performed using similar preload for 55 × 5 mm strips (2.75 cm
2), heated by 2 W of internal joule heating using a 60 V power source. The CB/SMP test strips were fabricated in a U-shape with smooth, flat glass as the test substrate. The resulting adhesion averaged approximately 30 N/cm
2. The reduction in adhesion strength as compared to the previous work is most likely primarily due to thermal contraction increasing interfacial stresses as lateral dimensions of the adhesive increase. Over the usual range of bonding temperatures the CB/SMP adhesive expands and contracts on the order of 1% due its large thermal expansion coefficient on the order of 200 µm/mK [
13]. It was observed during loading that failure of the SMP-substrate interface occurs suddenly, analogous to brittle fracture. The role of thermal contraction is further indicated by the occurrence of spontaneous fracture in large samples (cm scale) even in the absence of load if the difference between bonding temperature and ambient temperature is too great. For this reason, interface temperatures were limited to 75 °C, compared with the previous work which used a standard of 90 °C for bonding temperature. It is a general trend that adhesion for the selected SMP increases with temperature; therefore, reduced bonding temperature is likely a secondary cause for the lower-than-expected adhesion. Surface patterning to promote crack trapping would likely alleviate the issue of catastrophic failure due to localized interfacial stresses. The stresses may be further reduced by adding a less-rigid layer as the adhesive interface in place of the SMP. As the bulk SMP contracts, the more compliant surface material would deform more easily to reduce the buildup of interfacial stresses.
The adhesive performance of our finished CB/SMP composite adhesive is demonstrated in
Figure 7 on curved surfaces. First, a CB/SMP strip 15 mm wide by 65 mm long is heated using a 70 V power supply with Cu tape forming the electrical contacts on opposing ends. The now-compliant strip is pressed using finger pressure to a 4.25 inch diameter clean glass cylinder, covering a 70° arc. The pressure is maintained as the power supply is turned off, resulting in a strong, rigid bond. A 10 lb weight is supported by the strip, indicating an adhesive strength in excess of 4.6 N/cm
2. It is believed that the reduction in adhesion compared with the flat CB/SMP strip tests is due largely to the greatly reduced preload applied during bonding. It was observed after bonding that some areas were not in proper contact after cooling, partly from trapped air pockets and partly from thermal contraction as explained above. Testing the adhesion of the strip necessitated choosing a pick point; in this case, the weight was applied to the center of the strip, creating an additional localized concentration of stress on the interface thus reducing the apparent adhesion. This was likewise the case for the concave-surface demonstration, for which a 25 mm wide by 45 mm long CB/SMP strip was bonded using finger pressure to the inside of a watch glass. This configuration yielded a failure strength exceeding 5.9 N/cm
2; again, less than the result from the smaller and higher-preload flat strip tests. Surface patterns designed to promote crack trapping could also effectively alleviate the issues of air entrapment by creating pathways for the air to escape during bonding. Increased preload during bonding or the use of a softer and/or stickier adhesive layer in place of or in addition to the non-doped SMP would also be expected to increase performance by helping to reduce thermally-induced interfacial stresses and reducing the necessary preload to ensure proper surface contact. As a final demonstration in
Figure 7E, a composite SMP adhesive is gently removed from the glass by heating and peeling, thus achieving the desired adhesive reversibility.
A brief collection of representative conventional, or “wet”, and dry adhesive strengths are given in
Table 3. Fibrillar adhesives are typically tested in shear, since this is also typically their direction of maximum strength and reversibility. It is stressed that wet adhesives are fundamentally different than dry adhesives, and should not be treated as a competitor to dry adhesive systems. A dry adhesive bond is by nature a temporary one, whereas the use of wet adhesives is usually intended as a permanent bond between two surfaces. Both the uses for the methods of action of each are very different.
Figure 7.
(A) An adhesive strip is internally heated and bonded to a curved glass surface covering a 70° arc (B); (C) The bonded strip supports a 10 lb weight; (D) A bonded strip supports 15 lbs on a concave glass surface, shown in greater detail in (E); and (F) Heating the bonded strip allows for easy peel removal.
Figure 7.
(A) An adhesive strip is internally heated and bonded to a curved glass surface covering a 70° arc (B); (C) The bonded strip supports a 10 lb weight; (D) A bonded strip supports 15 lbs on a concave glass surface, shown in greater detail in (E); and (F) Heating the bonded strip allows for easy peel removal.
Table 3.
Conventional “wet” adhesive and representative fibrillar dry adhesive strength for comparison to the adhesive described in this work.
Table 3.
Conventional “wet” adhesive and representative fibrillar dry adhesive strength for comparison to the adhesive described in this work.
| Classification | Adhesive | Adhesive Strength (N/cm2) | Substrate (s) | Reference |
|---|
| Wet (permanent, requires cure time) | Mussel adhesive extracts | 10–300 | Skin to skin | [24] |
| Cyanoacrylates (super glue) | 1500 | Steel to Al | Master Bond (MB) Series data sheets |
| 210 | Steel to butyl |
| 3 M Epoxy 2216 B/A | 1170–1320 (shear) | Steel to steel | 3 M technical data sheet |
| 900 (shear) | Plastic to plastic |
| LOCTITE epoxy E-120HP | 2300 (shear) | Glass to glass | LOCTITE technical data sheet |
| 150 (shear) | Acrylic to acrylic |
| Dry (reusable, reversible, no cure time) | Carbon nanotube fibers | 3–150 (shear) | Glass/plastic | [8] |
| Polymer fibers | 0.2–15 (shear) |
| Gekko gecko | 10 (shear) | Acetate sheet | [5] |
| SMP (<cm) | 200 | Glass | [13] |
| SMP (>cm) | 5–30 | Glass | This work |