The Effect of Salt on the Complex Coacervation of Vinyl Polyelectrolytes
Abstract
:1. Introduction

2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Polyelectrolyte Complexes
2.3. Turbidity Measurements
2.4. Visual Characterization of Complexes
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Effect of pH on Coacervate Stoichiometry

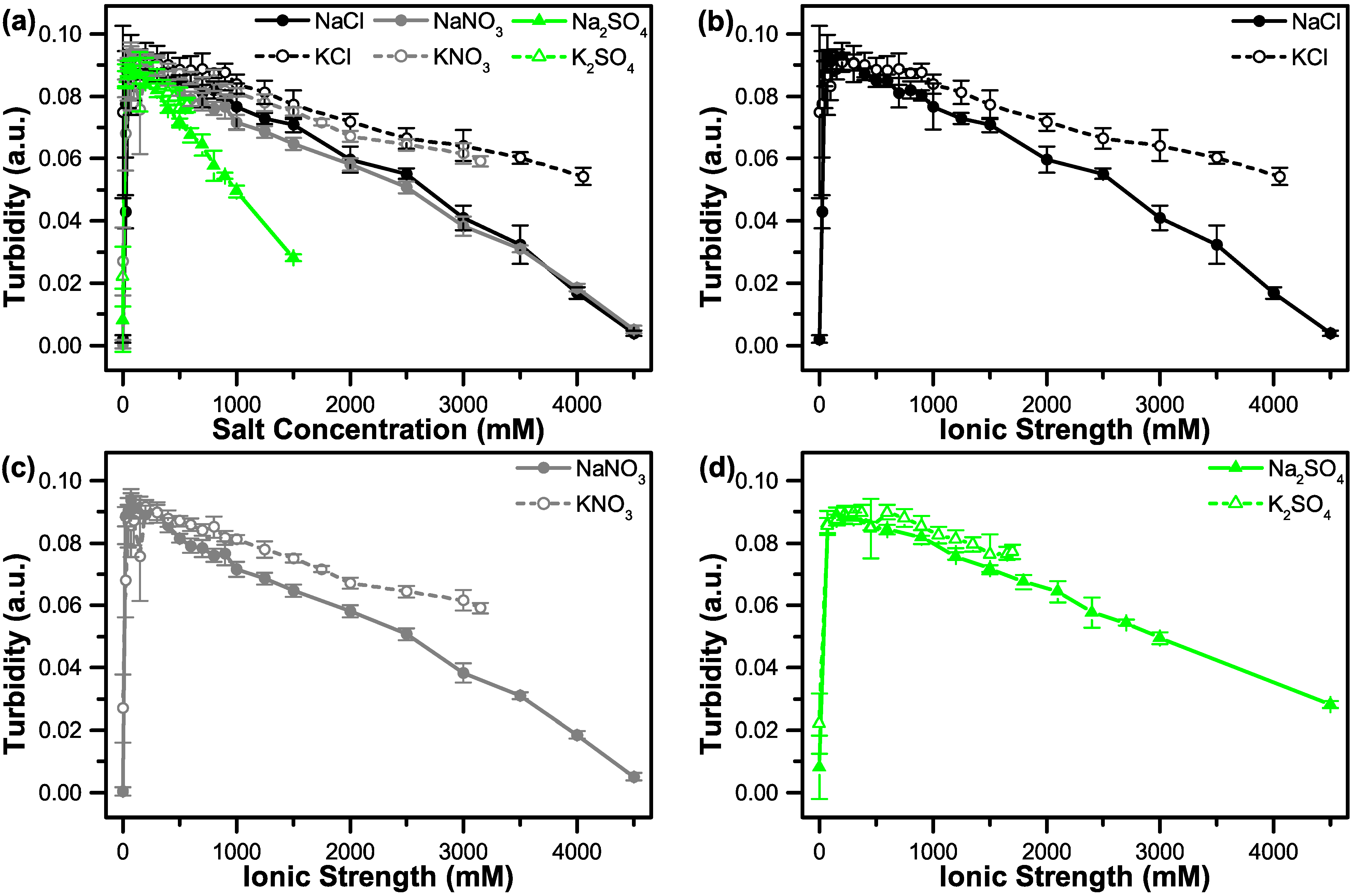
3.2. The Effect of Salt on Coacervate Formation




3.3. The Effect of pH on Coacervate Salt Stability


4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Spruijt, E.; Westphal, A.H.; Borst, J.W.; Cohen Stuart, M.A.; van der Gucht, J. Binodal compositions of polyelectrolyte complexes. Macromolecules 2010, 43, 6476–6484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Gucht, J.; Spruijt, E.; Lemmers, M.; Cohen Stuart, M.A. Polyelectrolyte complexes: Bulk phases and colloidal systems. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 361, 407–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biesheuvel, P.M.; Cohen Stuart, M.A. Electrostatic free energy of weakly charged macromolecules in solution and intermacromolecular complexes consisting of oppositely charged polymers. Langmuir 2004, 20, 2785–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priftis, D.; Tirrell, M. Phase behaviour and complex coacervation of aqueous polypeptide solutions. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 9396–9405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priftis, D.; Megley, K.; Laugel, N.; Tirrell, M. Complex coacervation of poly (ethylene-imine)/polypeptide aqueous solutions: Thermodynamic and rheological characterization. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 398, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priftis, D.; Laugel, N.; Tirrell, M. Thermodynamic characterization of polypeptide complex coacervation. Langmuir 2012, 28, 15947–15957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pergushov, D.V.; Müller, A.H.E.; Schacher, F.H. Micellar interpolyelectrolyte complexes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 6888–6901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priftis, D.; Farina, R.; Tirrell, M. Interfacial energy of polypeptide complex coacervates measured via capillary adhesion. Langmuir 2012, 28, 8721–8729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chollakup, R.; Smitthipong, W.; Eisenbach, C.D.; Tirrell, M. Phase behavior and coacervation of aqueous poly(acrylic acid)–poly(allylamine) solutions. Macromolecules 2010, 43, 2518–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chollakup, R.; Beck, J.B.; Dirnberger, K.; Tirrell, M.; Eisenbach, C.D. Polyelectrolyte molecular weight and salt effects on the phase behavior and coacervation of aqueous solutions of poly(acrylic acid) sodium salt and poly(allylamine) hydrochloride. Macromolecules 2013, 46, 2376–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priftis, D.; Xia, X.; Margossian, K.O.; Perry, S.L.; Leon, L.; Qin, J.; de Pablo, J.J.; Tirrell, M. Ternary, tunable polyelectrolyte complex fluids driven by complex coacervation. Macromolecules 2014, 47, 3076–3085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Priftis, D.; Farina, R.; Perry, S.L.; Leon, L.; Whitmer, J.K.; Hoffman, K.Q.; Tirrell, M.; de Pablo, J.J. Interfacial tension of polyelectrolyte complex coacervate phases. ACS Macro Lett. 2014, 3, 565–568. [Google Scholar]
- Kayitmazer, A.B.; Strand, S.P.; Tribet, C.; Jaeger, W.; Dubin, P.L. Effect of polyelectrolyte structure on protein−polyelectrolyte coacervates: Coacervates of bovine serum albumin with poly(diallyldimethylammonium chloride) versus chitosan. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 3568–3577. [Google Scholar]
- Kayitmazer, A.B.; Seeman, D.; Minsky, B.B.; Dubin, P.L.; Xu, Y. Protein–polyelectrolyte interactions. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 2553–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jewell, C.M.; Lynn, D.M. Multilayered polyelectrolyte assemblies as platforms for the delivery of DNA and other nucleic acid-based therapeutics. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2008, 60, 979–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jewell, C.M.; Lynn, D.M. Surface-mediated delivery of DNA: Cationic polymers take charge. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 13, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, H.; Gao, J.; Chen, C.-W.; Huard, J.; Wang, Y. Injectable fibroblast growth factor-2 coacervate for persistent angiogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 13444–13449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittella, F.; Kataoka, K. Polymeric micelles for siRNA delivery. In Advances in Delivery Science and Technology; Howard, K.A., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2012; pp. 161–184. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, D.S.; Waite, J.H.; Tirrell, M. Promotion of osteoblast proliferation on complex coacervation-based hyaluronic acid—Recombinant mussel adhesive protein coatings on titanium. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 1080–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, P.T. Form and function in multilayer assembly: New applications at the nanoscale. Adv. Mater. 2004, 16, 1271–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laugel, N.; Betscha, C.; Winterhalter, M.; Voegel, J.C.; Schaaf, P.; Ball, V. Relationship between the growth regime of polyelectrolyte multilayers and the polyanion/polycation complexation enthalpy. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 19443–19449. [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt, C.; Turgeon, S.L. Protein/polysaccharide complexes and coacervates in food systems. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 167, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, R.J.; Wang, C.S.; Shao, H. Complex coacervates as a foundation for synthetic underwater adhesives. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 167, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.; Moon, D.; Kim, H.J.; Seo, J.H.; Kang, I.S.; Cha, H.J. Interfacial tension of complex coacervated mussel adhesive protein according to the Hofmeister series. Langmuir 2014, 30, 1108–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.; Choi, Y.S.; Kang, D.G.; Song, Y.H.; Cha, H.J. The adhesive properties of coacervated recombinant hybrid mussel adhesive proteins. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 3715–3722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, D.S.; Zeng, H.; Srivastava, A.; Krogstad, D.V.; Tirrell, M.; Israelachvili, J.N.; Waite, J.H. Viscosity and interfacial properties in a mussel-inspired adhesive coacervate. Soft Matter 2010, 6, 3232–3236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, D.S.; Zeng, H.; Lu, Q.; Israelachvili, J.; Waite, J.H. Adhesion mechanism in a DOPA-deficient foot protein from green mussels. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 5640–5648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulton, A.B. How crowded is the cytoplasm? Cell 1982, 30, 345–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, S.B.; Trach, S.O. Estimation of macromolecule concentrations and excluded volume effects for the cytoplasm of Escherichia coli. J. Mol. Biol. 1991, 222, 599–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minton, A.P. Excluded volume as a determinant of macromolecular structure and reactivity. Biopolymers 1981, 20, 2093–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrbka, L.; Vondrášek, J.; Jagoda-Cwiklik, B.; Vácha, R.; Jungwirth, P. Quantification and rationalization of the higher affinity of sodium over potassium to protein surfaces. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 15440–15444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nic, M.; Jirat, J.; Kosata, B. IUPAC Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 2nd ed.; McNaught, A.D., Wilkinson, A., Eds.; Blackwell Scientific Publications: Oxford, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Spruijt, E.; Sprakel, J.; Cohen Stuart, M.A.; van der Gucht, J. Interfacial tension between a complex coacervate phase and its coexisting aqueous phase. Soft Matter 2010, 6, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spruijt, E.; Cohen Stuart, M.A.; van der Gucht, J. Linear viscoelasticity of polyelectrolyte complex coacervates. Macromolecules 2013, 46, 1633–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Kruif, C.G.; Weinbreck, F.; de Vries, R. Complex coacervation of proteins and anionic polysaccharides. Curr. Opin. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2004, 9, 340–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, D.J. Practical analysis of complex coacervate systems. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1990, 140, 227–238. [Google Scholar]
- Castelnovo, M.; Joanny, J.F. Complexation between oppositely charged polyelectrolytes: Beyond the random phase approximation. Eur. Phys. J. E Soft Matter Biol. Phys. 2001, 6, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, Z.; Muthukumar, M. Entropy and enthalpy of polyelectrolyte complexation: Langevin dynamics simulations. J. Chem. Phys. 2006, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dautzenberg, H.; Kriz, J. Response of polyelectrolyte complexes to subsequent addition of salts with different cations. Langmuir 2003, 19, 5204–5211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tainaka, K.-I. Effect of counterions on complex coacervation. Biopolymers 1980, 19, 1289–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucur, C.B.; Sui, Z.; Schlenoff, J.B. Ideal mixing in polyelectrolyte complexes and multilayers: Entropy driven assembly. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 13690–13691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anema, S.G.; de Kruif, C.G.K. Co-acervates of lactoferrin and caseins. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 4471–4478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anema, S.G.; de Kruif, C.G.K. Coacervates of lysozyme and β-casein. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 398, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overbeek, J.T.G.; Voorn, M.J. Phase separation in polyelectrolyte solutions. Theory of complex coacervation. J. Cell. Comp. Physiol. 1957, 49, 7–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinbreck, F.; de Vries, R.; Schrooyen, P.; de Kruif, C.G. Complex coacervation of whey proteins and gum arabic. Biomacromolecules 2003, 4, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krogstad, D.V.; Lynd, N.A.; Choi, S.-H.; Spruell, J.M.; Hawker, C.J.; Kramer, E.J.; Tirrell, M.V. Effects of polymer and salt concentration on the structure and properties of triblock copolymer coacervate hydrogels. Macromolecules 2013, 46, 1512–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spruijt, E.; Leermakers, F.A.M.; Fokkink, R.; Schweins, R.; van Well, A.A.; Cohen Stuart, M.A.; van der Gucht, J. structure and dynamics of polyelectrolyte complex coacervates studied by scattering of neutrons, X-rays, and light. Macromolecules 2013, 46, 4596–4605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dautzenberg, H.; Karibyants, N. Polyelectrolyte complex formation in highly aggregating systems. Effect of salt: Response to subsequent addition of NaCl. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 1999, 200, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindhoud, S.; de Vries, R.; Schweins, R.; Cohen Stuart, M.A.; Norde, W. Salt-induced release of lipase from polyelectrolyte complex micelles. Soft Matter 2009, 5, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindhoud, S.; Voorhaar, L.; de Vries, R.; Schweins, R.; Stuart, M.A.C.; Norde, W. Salt-induced disintegration of lysozyme-containing polyelectrolyte complex micelles. Langmuir 2009, 25, 11425–11430. [Google Scholar]
- Voets, I.K.; de Keizer, A.; Stuart, M.A.C. Complex coacervate core micelles. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 147–148, 300–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overbeek, J.T.G.; Bungenberg de Jong, H.G. Sols of Macromolecular Colloids with Electrolytic Nature. In Colloid Science; Kruyt, H., Ed.; Elsevier Publishing Company: New York, NY, USA, 1949; pp. 184–231. [Google Scholar]
- Weinbreck, F.; Nieuwenhuijse, H.; Robijn, G.W.; de Kruif, C.G. Complexation of whey proteins with carrageenan. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 3550–3555. [Google Scholar]
- Kunz, W.; Lo Nostro, P.; Ninham, B.W. The present state of affairs with Hofmeister effects. Curr. Opin. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2004, 9, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Cremer, P.S. Interactions between macromolecules and ions: The Hofmeister series. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2006, 10, 658–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagliazucchi, M.; Olvera de la Cruz, M.; Szleifer, I. Self-organization of grafted polyelectrolyte layers via the coupling of chemical equilibrium and physical interactions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2010, 107, 5300–5305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlsson, F.; Linse, P.; Malmsten, M. Monte Carlo simulations of polyelectrolyte−protein complexation. J. Phys. Chem. B 2001, 105, 9040–9049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, R.G. Hard and soft acids and bases. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1963, 85, 3533–3539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, R.G. Hard and soft acids and bases, HSAB, part I: Fundamental principles. J. Chem. Educ. 1968, 45, 581–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmeister, F. Zur Lehre von der Wirkung der Salze. Archiv f. experiment. Pathol. u. Pharmakol. 1888, 25, 1–30. (In German) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, K.D. Ion hydration: Implications for cellular function, polyelectrolytes, and protein crystallization. Biophys. Chem. 2006, 119, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, K.D. Charge density-dependent strength of hydration and biological structure. Biophys. J. 1997, 72, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, K.D. Ions from the Hofmeister series and osmolytes: Effects on proteins in solution and in the crystallization process. Methods 2004, 34, 300–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiriukhin, M.Y.; Collins, K.D. Dynamic hydration numbers for biologically important ions. Biophys. Chem. 2002, 99, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacace, M.G.; Landau, E.M.; Ramsden, J.J. The Hofmeister series: Salt and solvent effects on interfacial phenomena. Q. Rev. Biophys. 1997, 30, 241–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Perry, S.L.; Li, Y.; Priftis, D.; Leon, L.; Tirrell, M. The Effect of Salt on the Complex Coacervation of Vinyl Polyelectrolytes. Polymers 2014, 6, 1756-1772. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym6061756
Perry SL, Li Y, Priftis D, Leon L, Tirrell M. The Effect of Salt on the Complex Coacervation of Vinyl Polyelectrolytes. Polymers. 2014; 6(6):1756-1772. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym6061756
Chicago/Turabian StylePerry, Sarah L., Yue Li, Dimitrios Priftis, Lorraine Leon, and Matthew Tirrell. 2014. "The Effect of Salt on the Complex Coacervation of Vinyl Polyelectrolytes" Polymers 6, no. 6: 1756-1772. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym6061756
APA StylePerry, S. L., Li, Y., Priftis, D., Leon, L., & Tirrell, M. (2014). The Effect of Salt on the Complex Coacervation of Vinyl Polyelectrolytes. Polymers, 6(6), 1756-1772. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym6061756





