Voltage Effect in Holograms of Polyvinyl Alcohol with FeCl3
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Preparation of Aqueous Solutions
| Component | Chemical formula | Purity (%) | Molecular weight (g/mol) | Solution weight (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Poly(vinyl alcohol) | (C2H4O) x | 95.0 | 30,000 | 7 |
| Iron (III) chloride | FeCl3 | 98.0 | 126.75 | 10 |
| ID (S1%:S2%) | pH (a.u.) | Refractive index (a.u.) |
|---|---|---|
| A = (10:1) | 2.64 | 1.494 |
| B = (10:1.5) | 2.47 | 1.504 |
| C = (10:2) | 2.33 | 1.520 |
| D = (10:2.5) | 2.25 | 1.530 |
| E = (10:3) | 2.23 | 1.540 |
| F = (10:5) | 2.16 | 1.545 |
2.2. Preparation of Samples
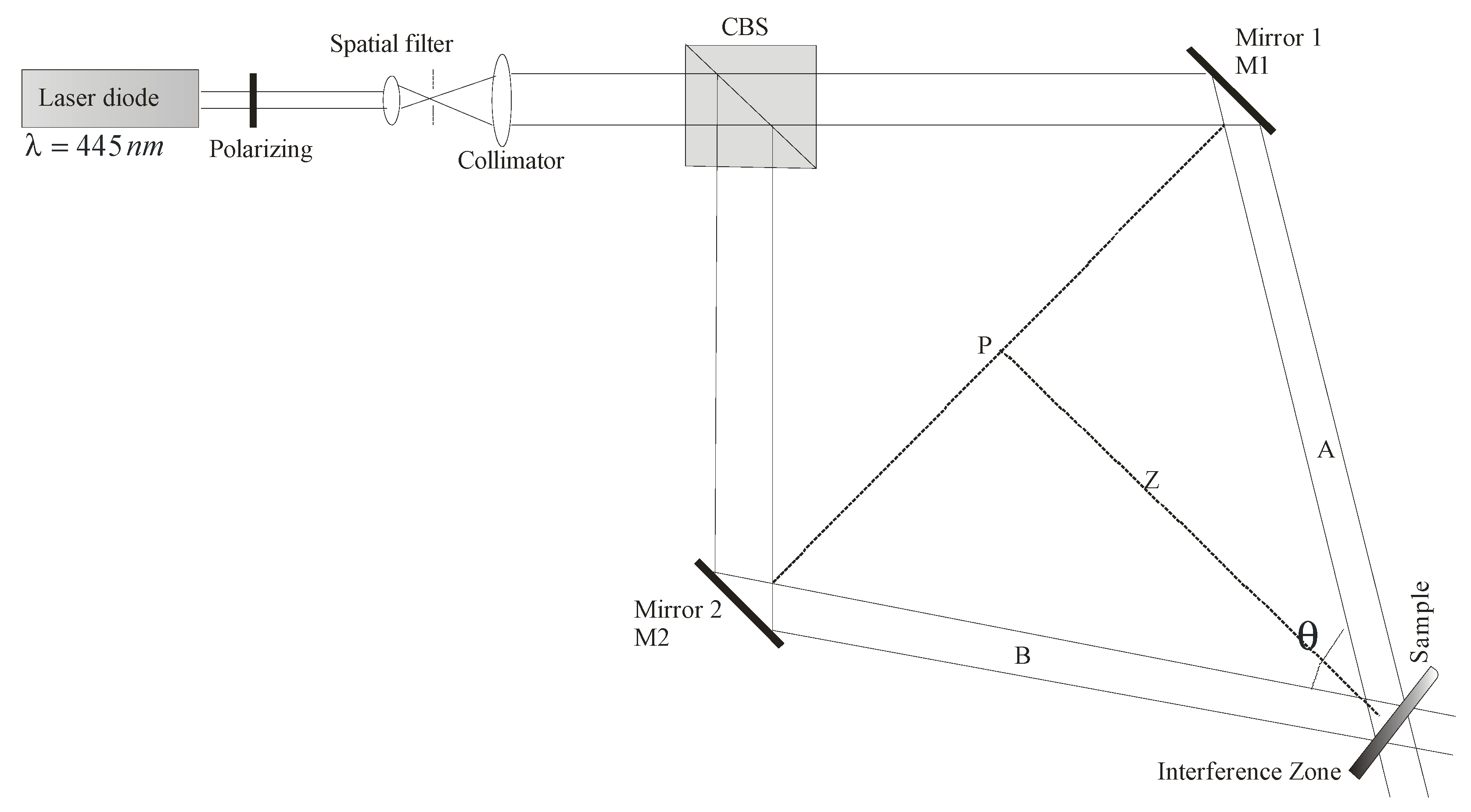
2.3. Holographic Recording
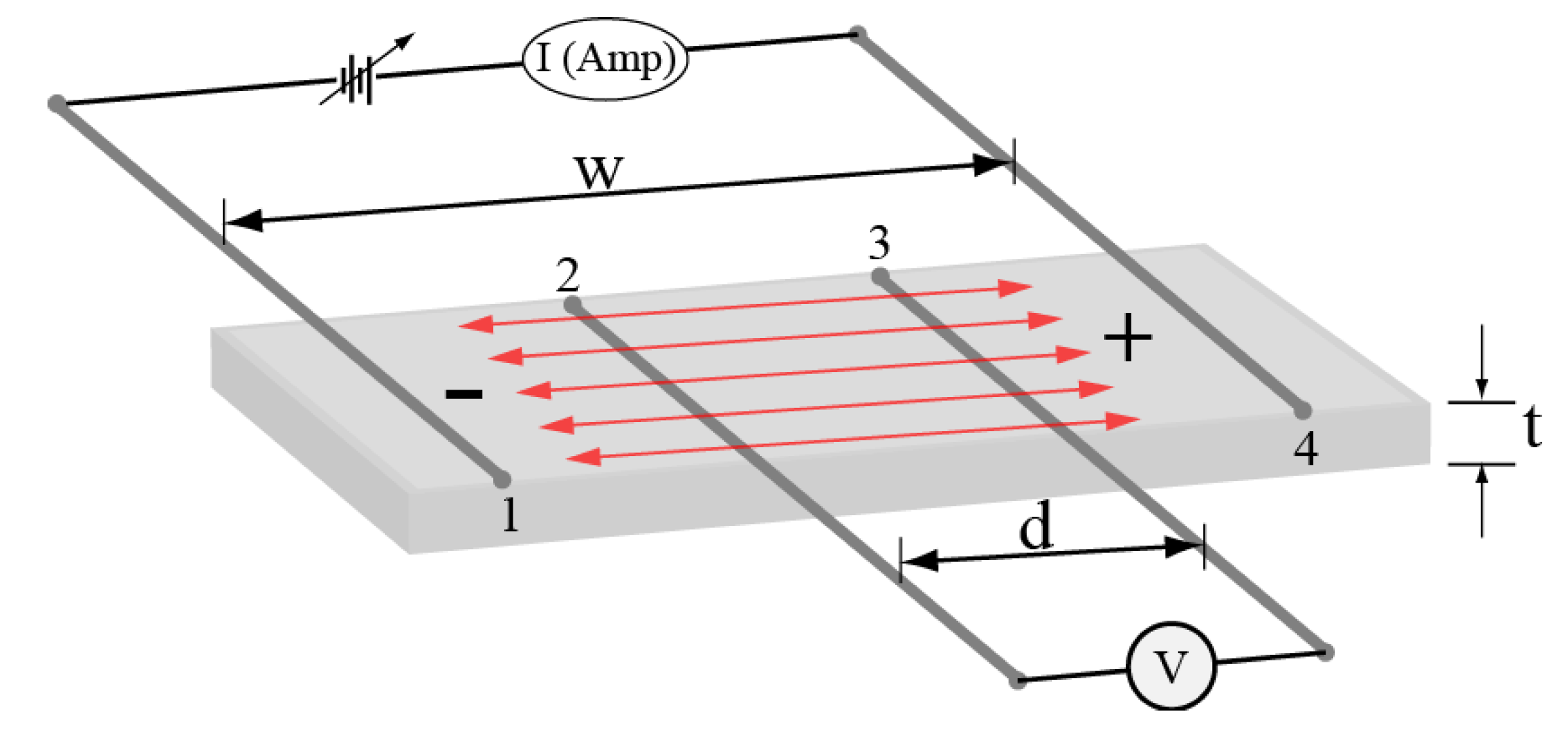
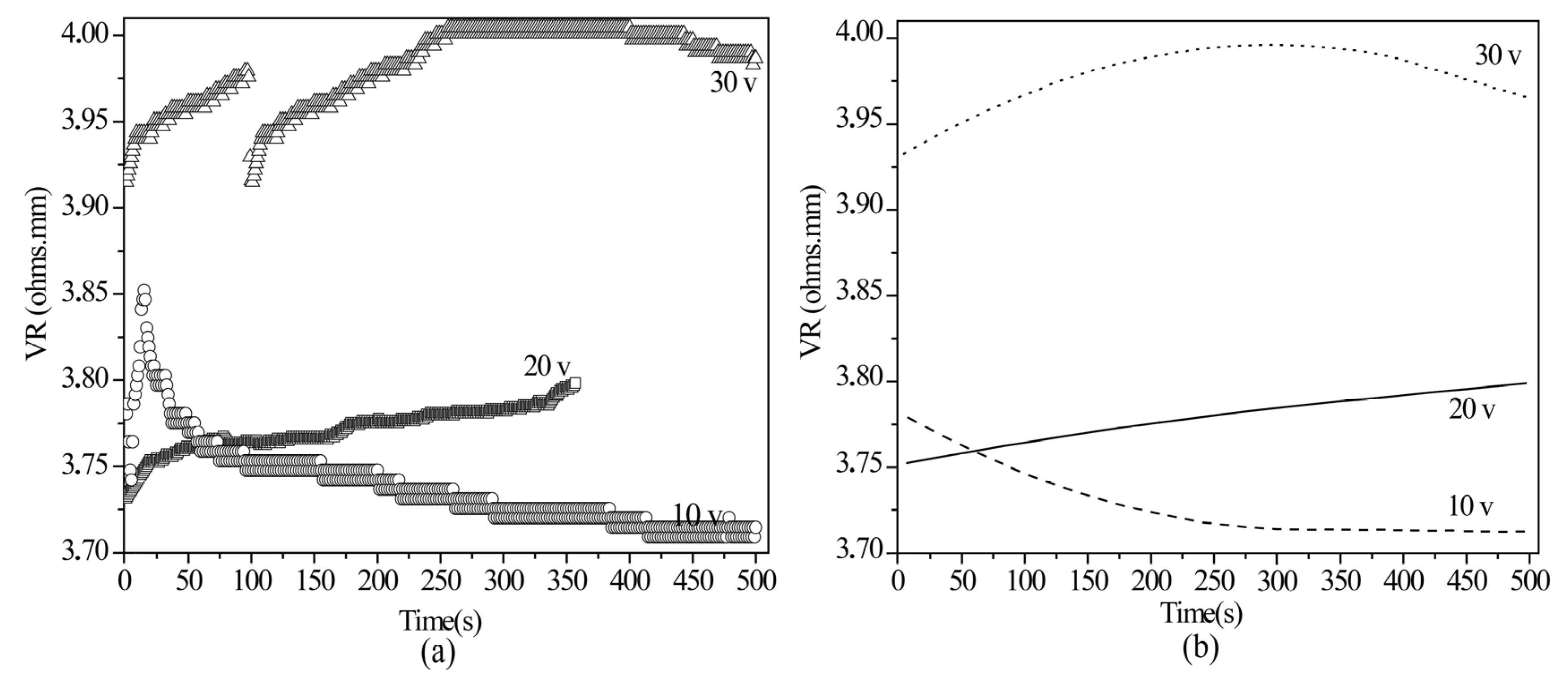
2.4. Volume Resistivity by Four-Point Technique
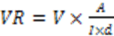
2.5. Electrodes Arrangement of Copper (+) and Ferrite (−) for Holographic Grating Recording
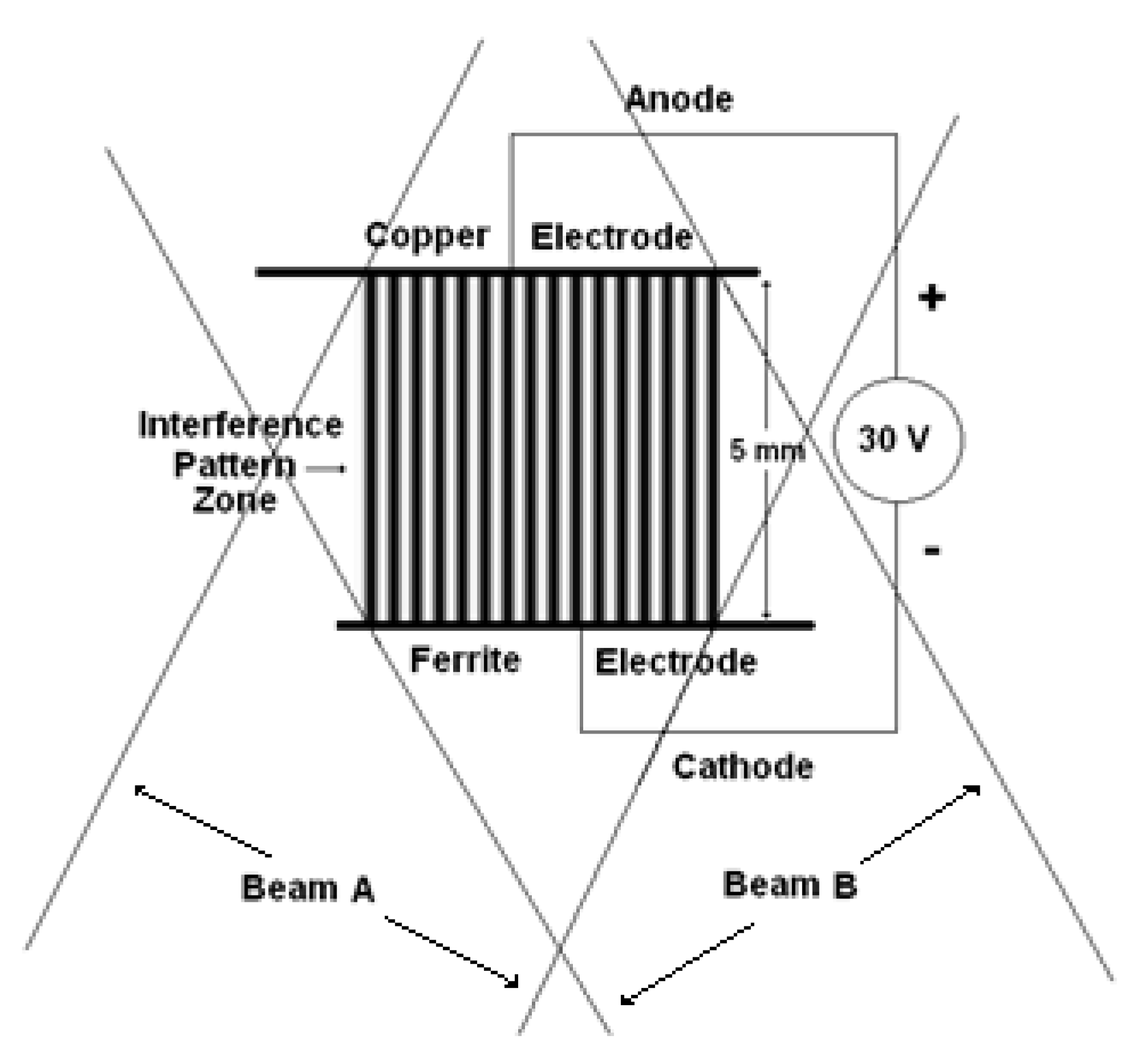
3. Results and Discussion
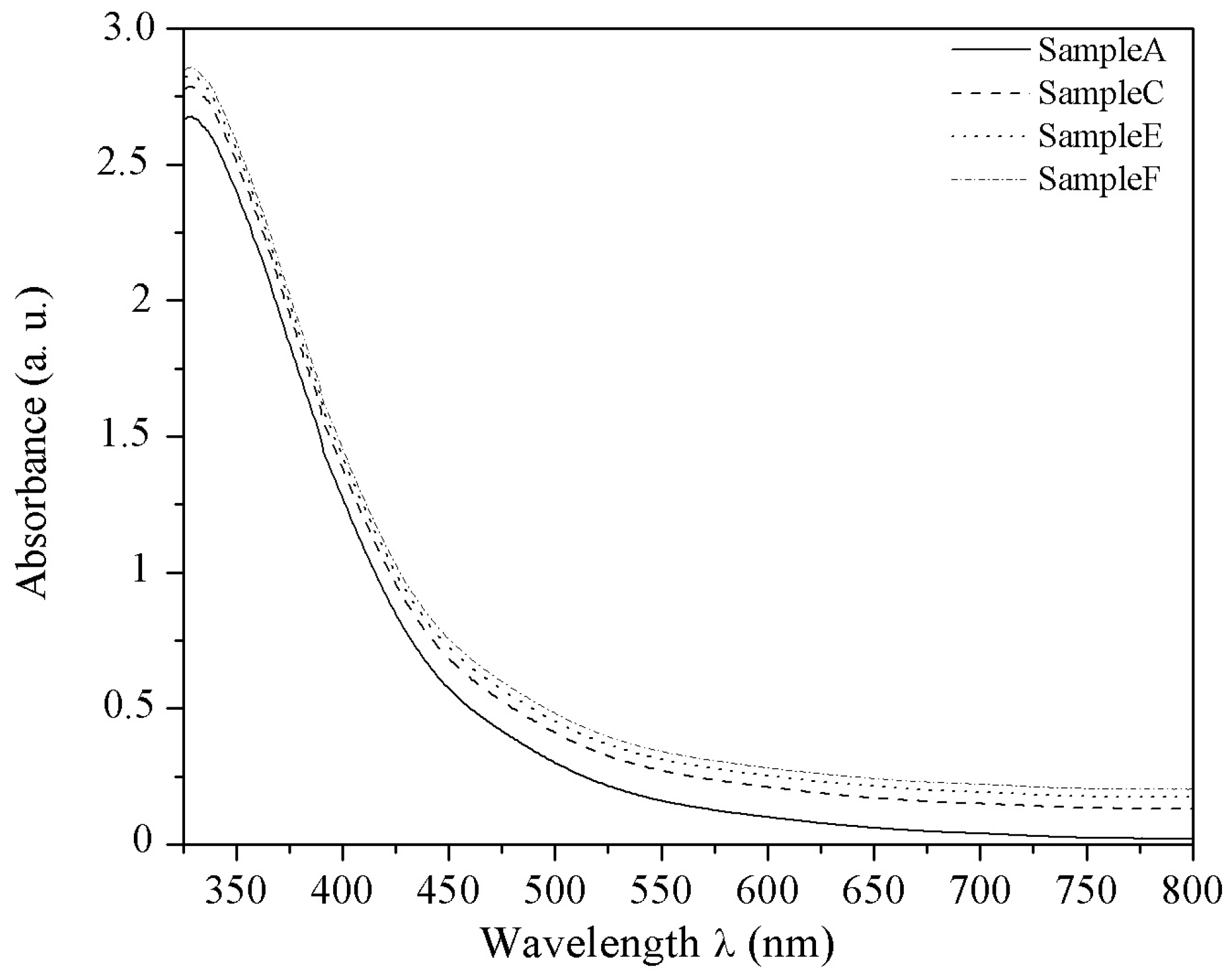
3.1. Experimental Results
Holographic Recording vs. FeCl3 Concentration
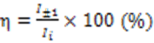
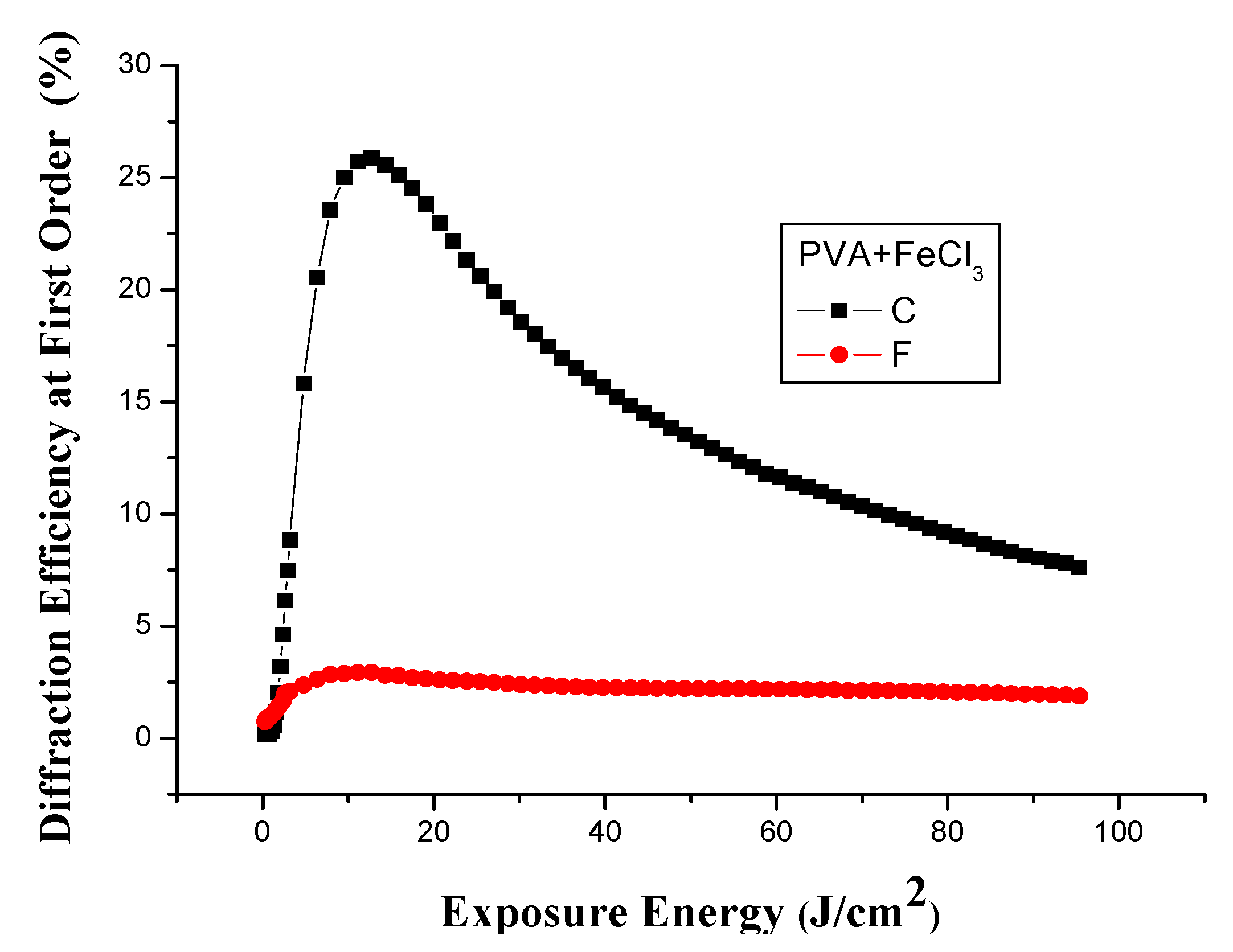
3.2. Spatial Frequency
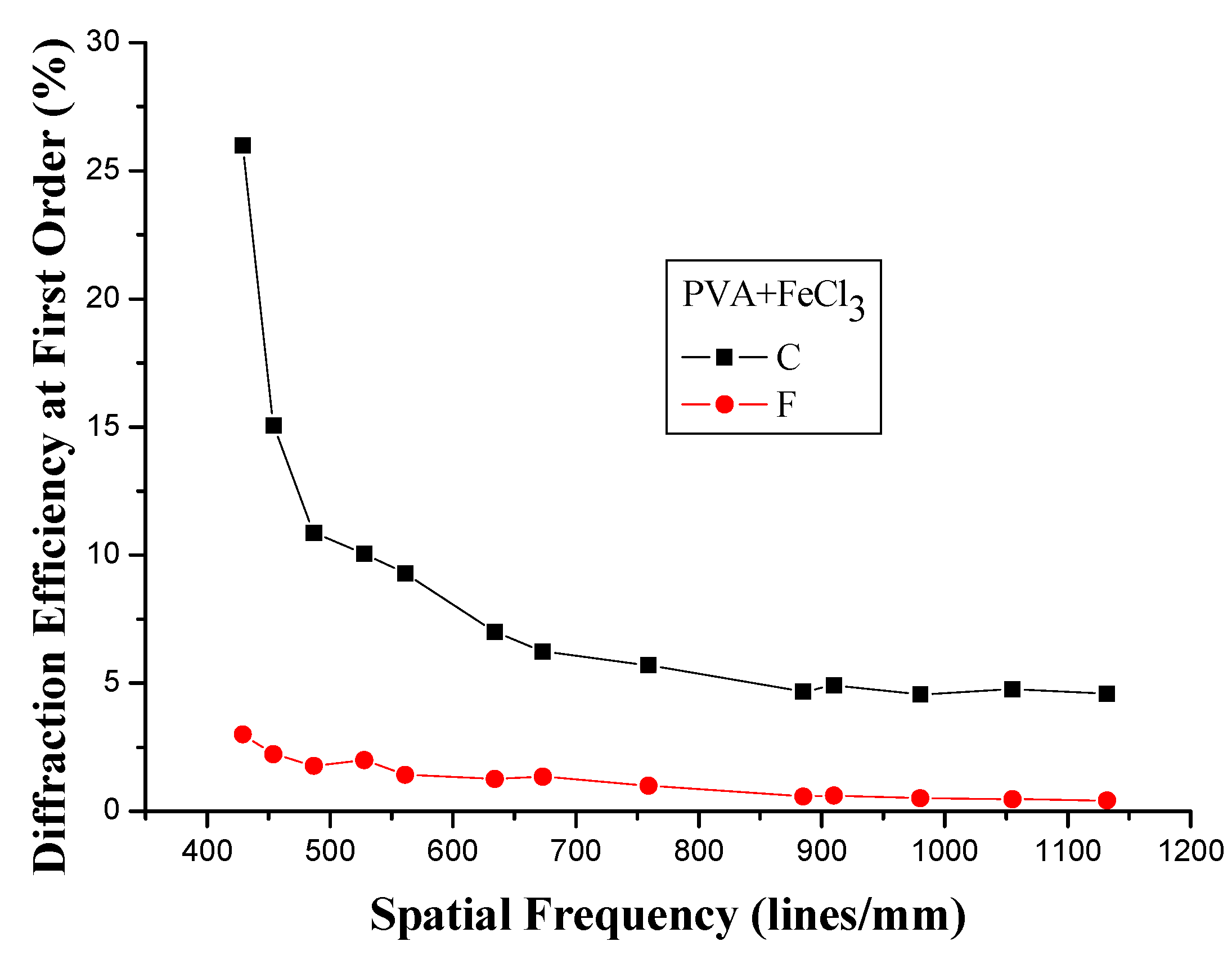
3.3. Holographic Recording at Different Thicknesses
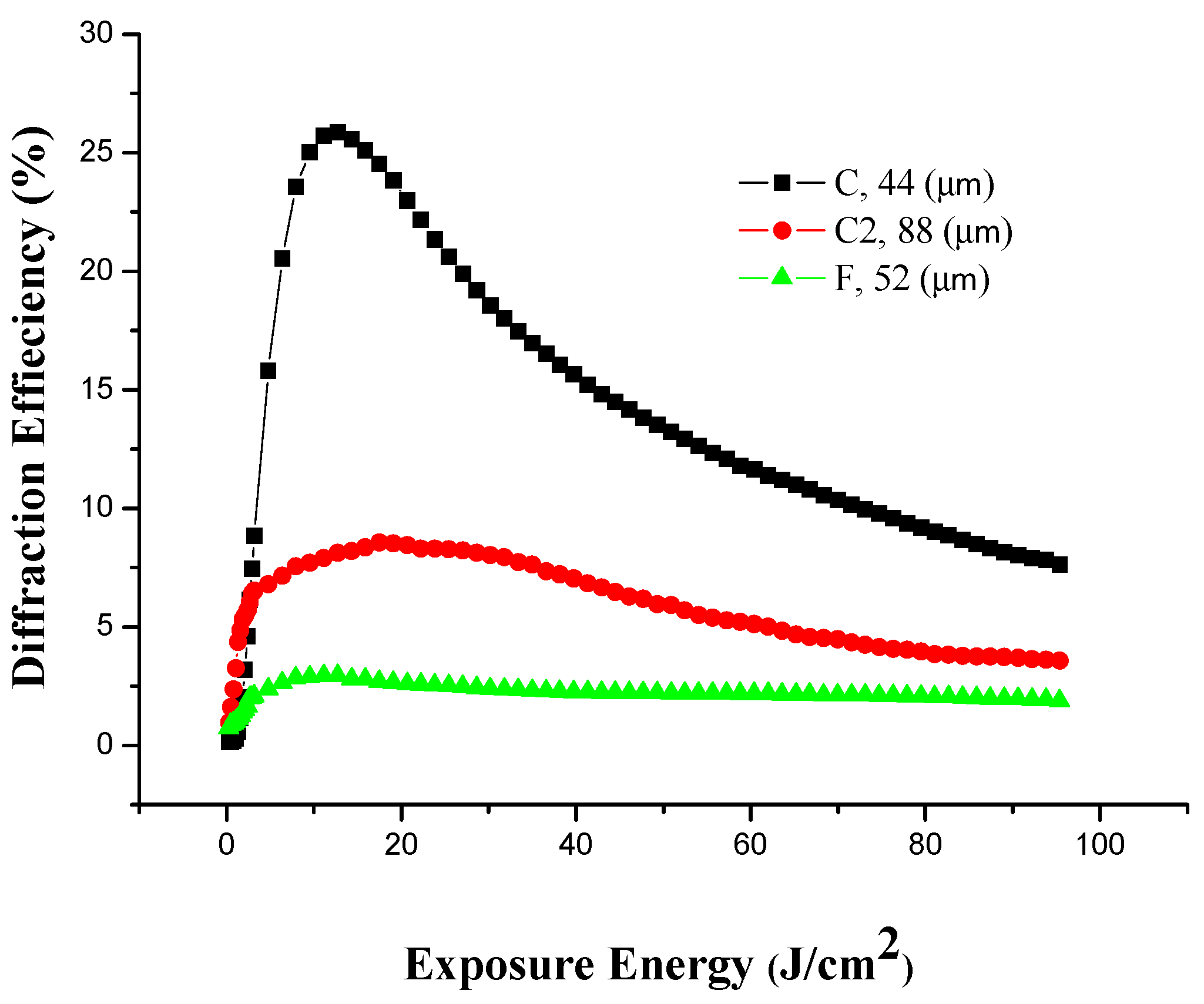
| Concentration | Amounts poured into 25 cm2 area (mL ± 0.1mL) | Thickness (µm ± 1 µm) | Exposure time (min ± 1 s) | Maximum efficiency of first order (% ± 0.5%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10:2 (Sample C) | 1 | 44 | 4 | 26 |
| 10:2 (Sample C2) | 2 | 88 | 4 | 8.6 |
| 10:5 (Sample F) | 1 | 52 | 4 | 3 |
| 10:5 (Sample F2) | 2 | 103 | 4 | – |
3.4. Conductive Characteristics of the Samples
3.4.1. Impedance and Conductivity Measurements of Photosensitive Material
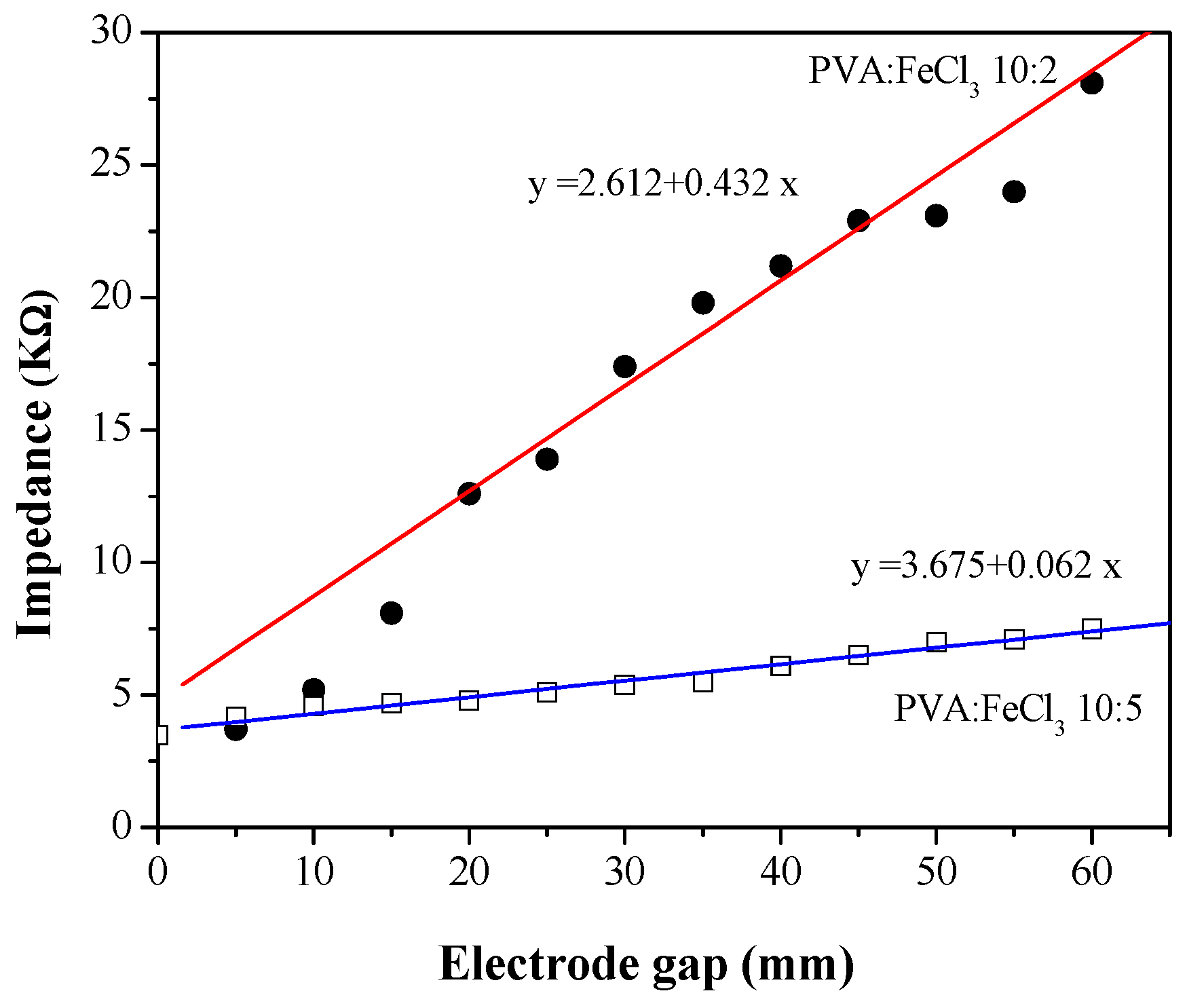
3.4.2. Volume Resistivity by Four-Point Technique
3.5. Effect of Voltage on Holographic Recording
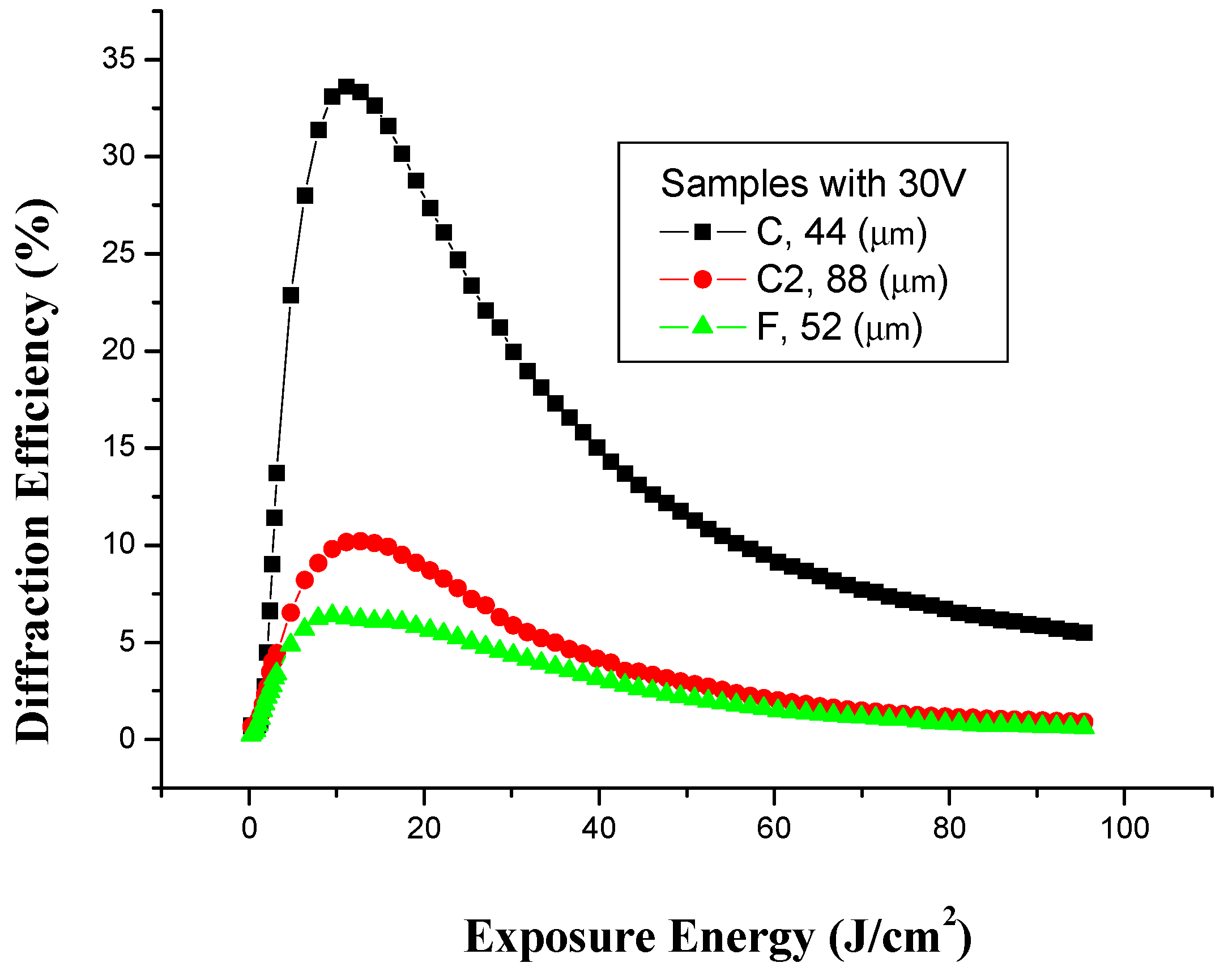
| Concentration | Thickness (µm ± 1µm) | Voltage in the registration process ferrite (−), copper (+) (V ± 0.1V) | Exposure time (min ± 1 s) | Maximum diffraction efficiency to first order (% ± 0.5%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C 10:2 | 44 | 30V | 3.5 | 34.2 |
| C2 10:2 | 88 | 30V | 4 | 10.2 |
| F 10:5 | 52 | 30V | 3 | 6.4 |
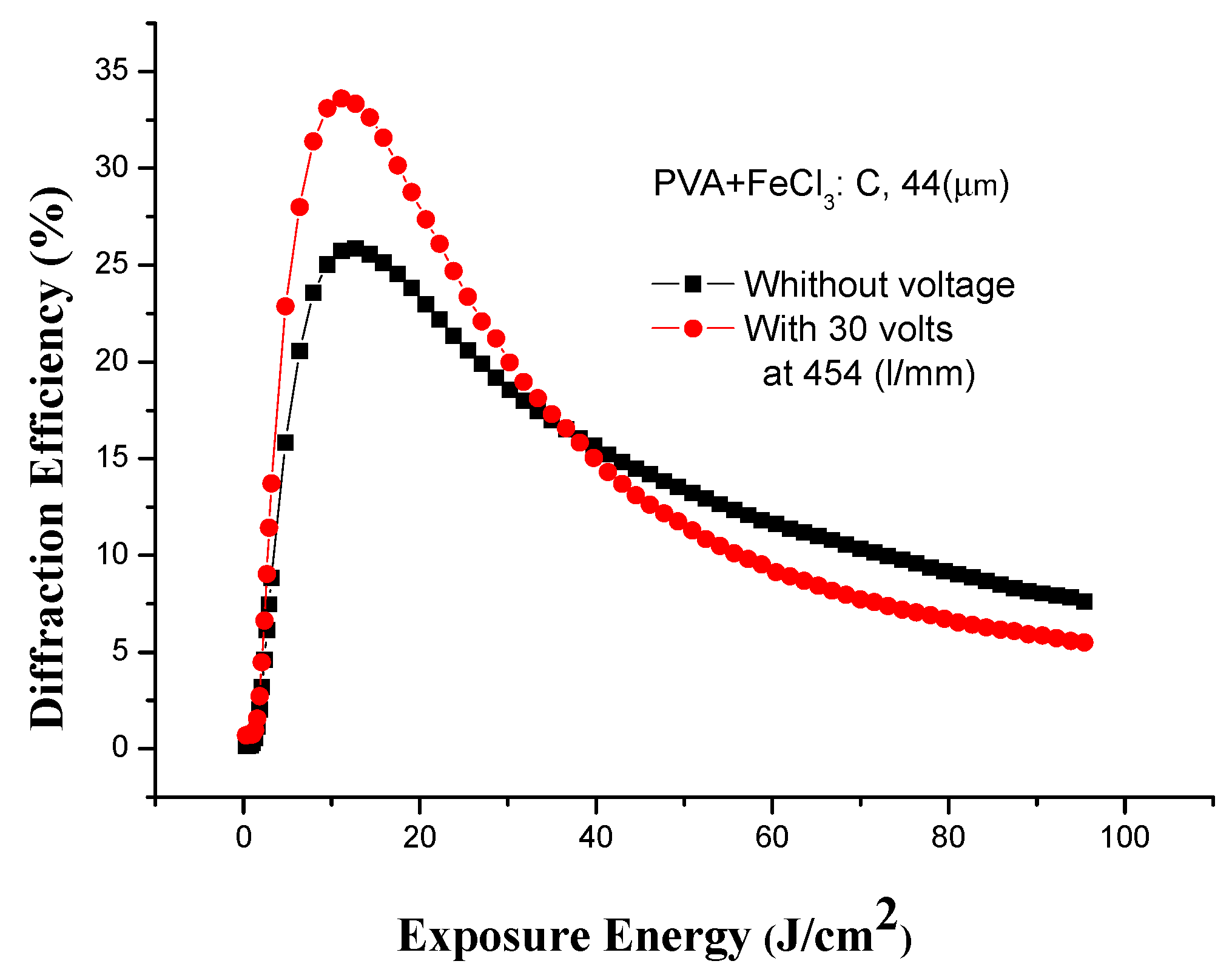
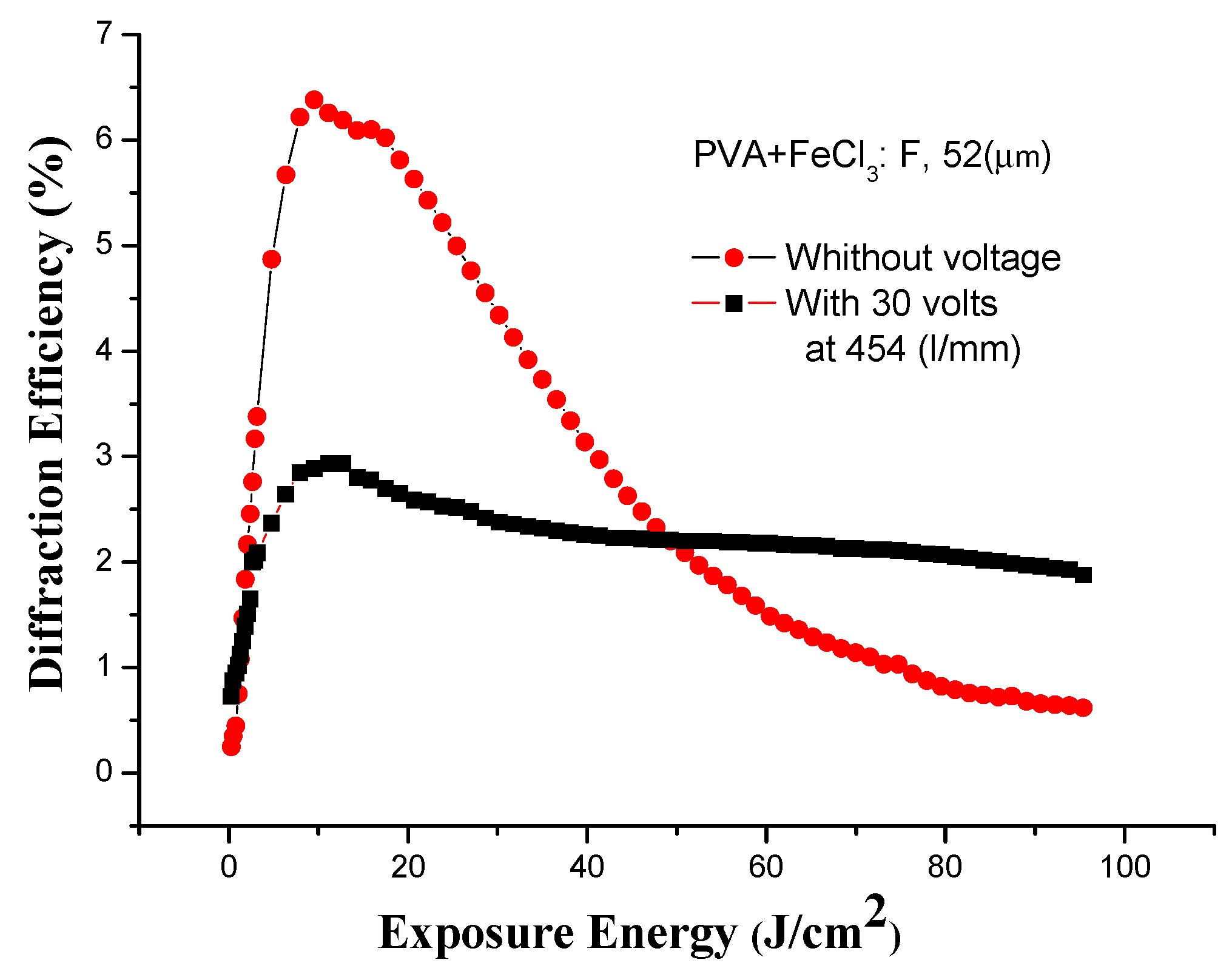
3.5.1. Diffraction Pattern
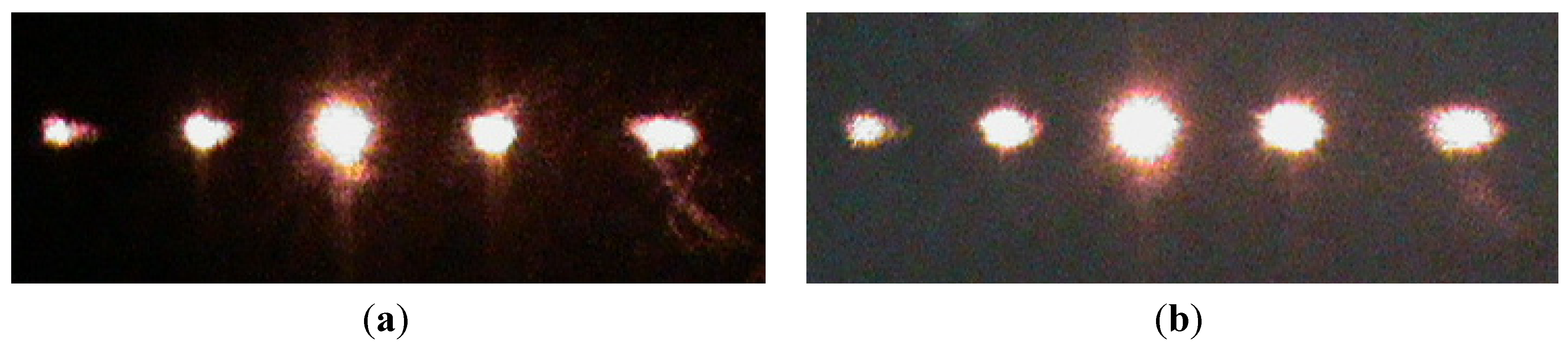

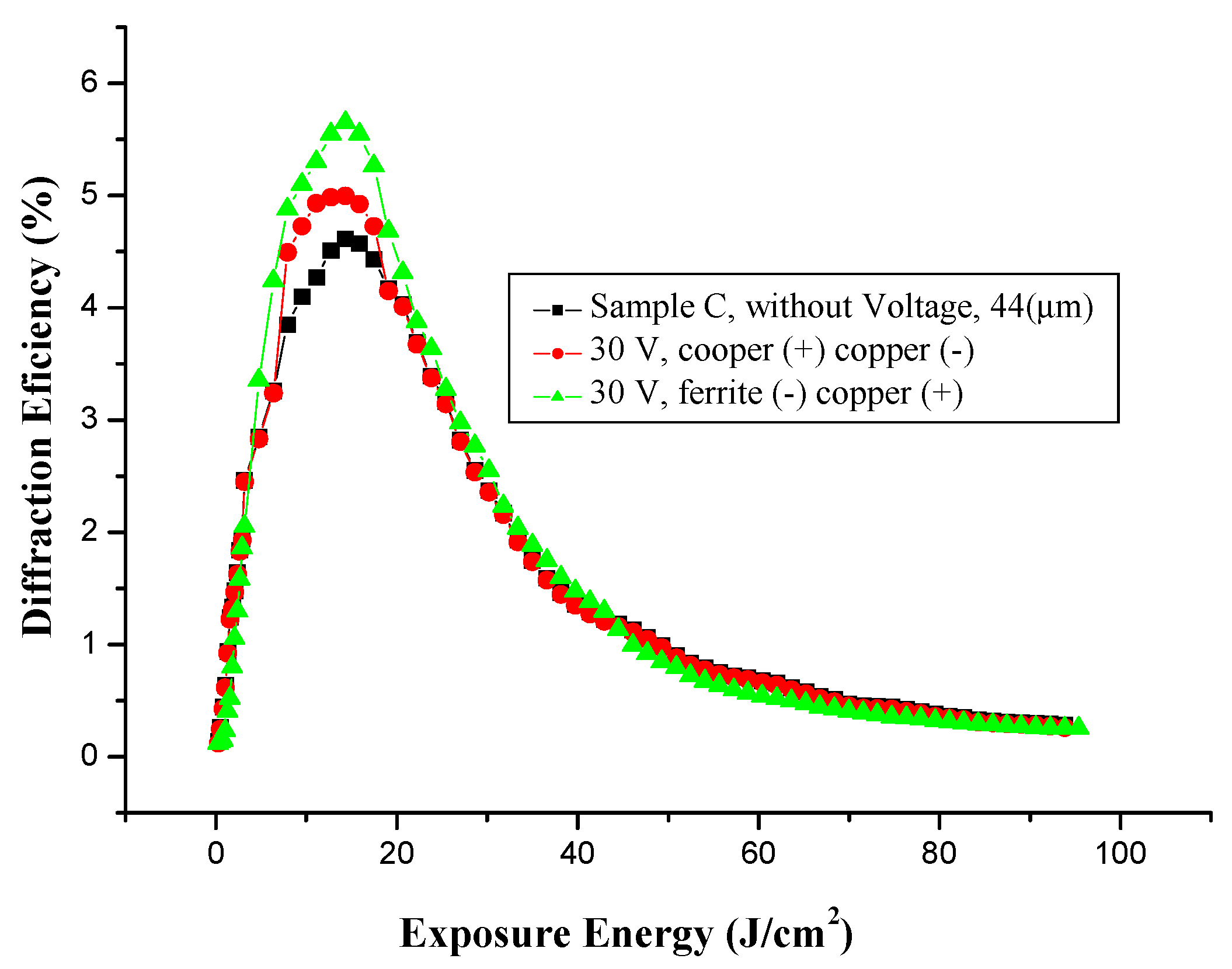
3.5.2. Effect of Voltage on Holographic Recording with Copper Electrodes
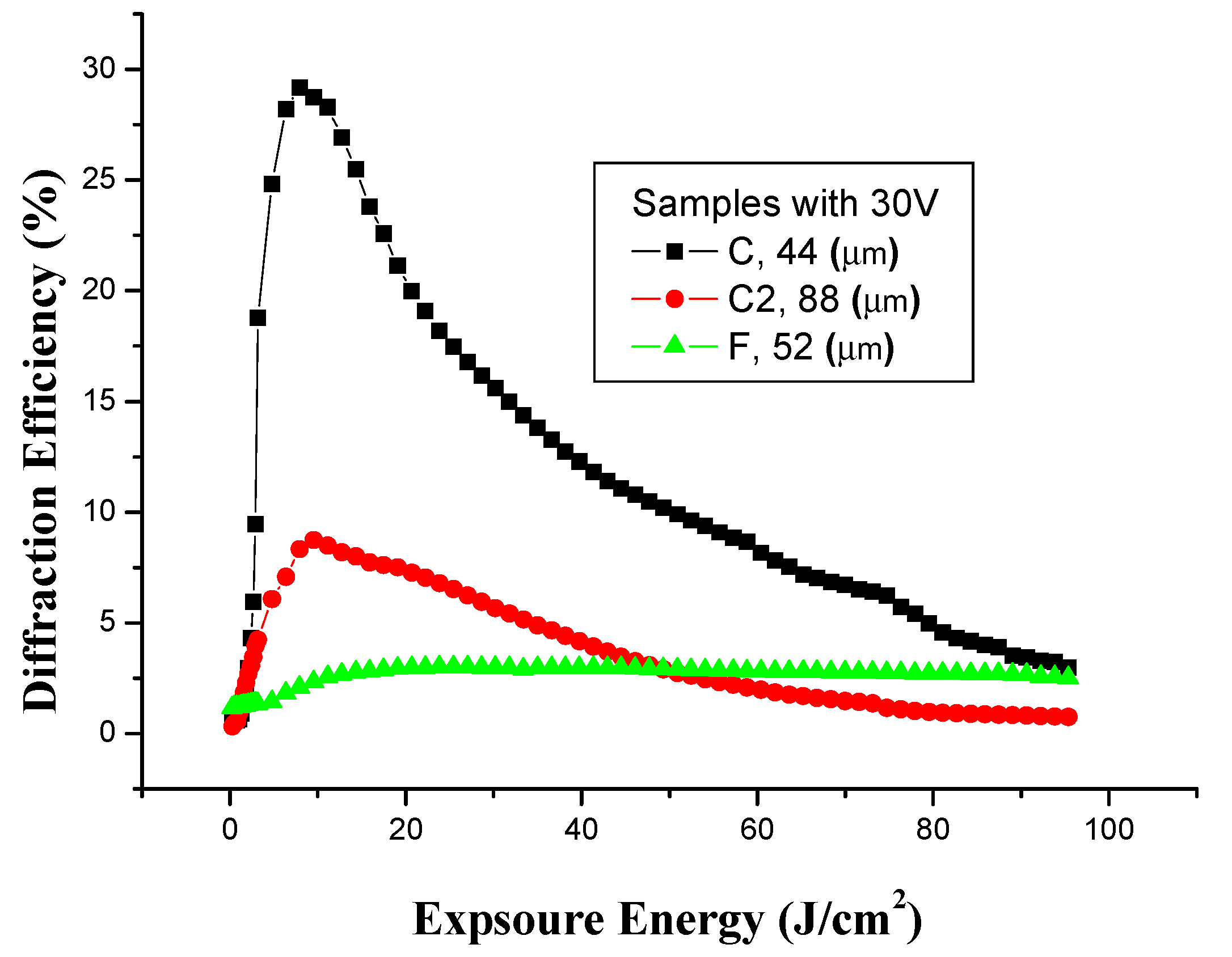
| Concentration | Thickness (µm ± 1µm) | Voltage in the registration process copper (−), copper (+) (V ± 0.1 V) | Exposure time (min ± 1 s) | Maximum diffraction efficiency to first order (% ± 0.5%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C 10:2 | 44 | 30 V | 2.5 | 29.2 |
| C2 10:2 | 88 | 30 V | 3 | 8.7 |
| F 10:5 | 52 | 30 V | 7.5 | 3 |
3.5.3. Effect of Voltage on Holographic Register for High Frequency, with Different Electrodes
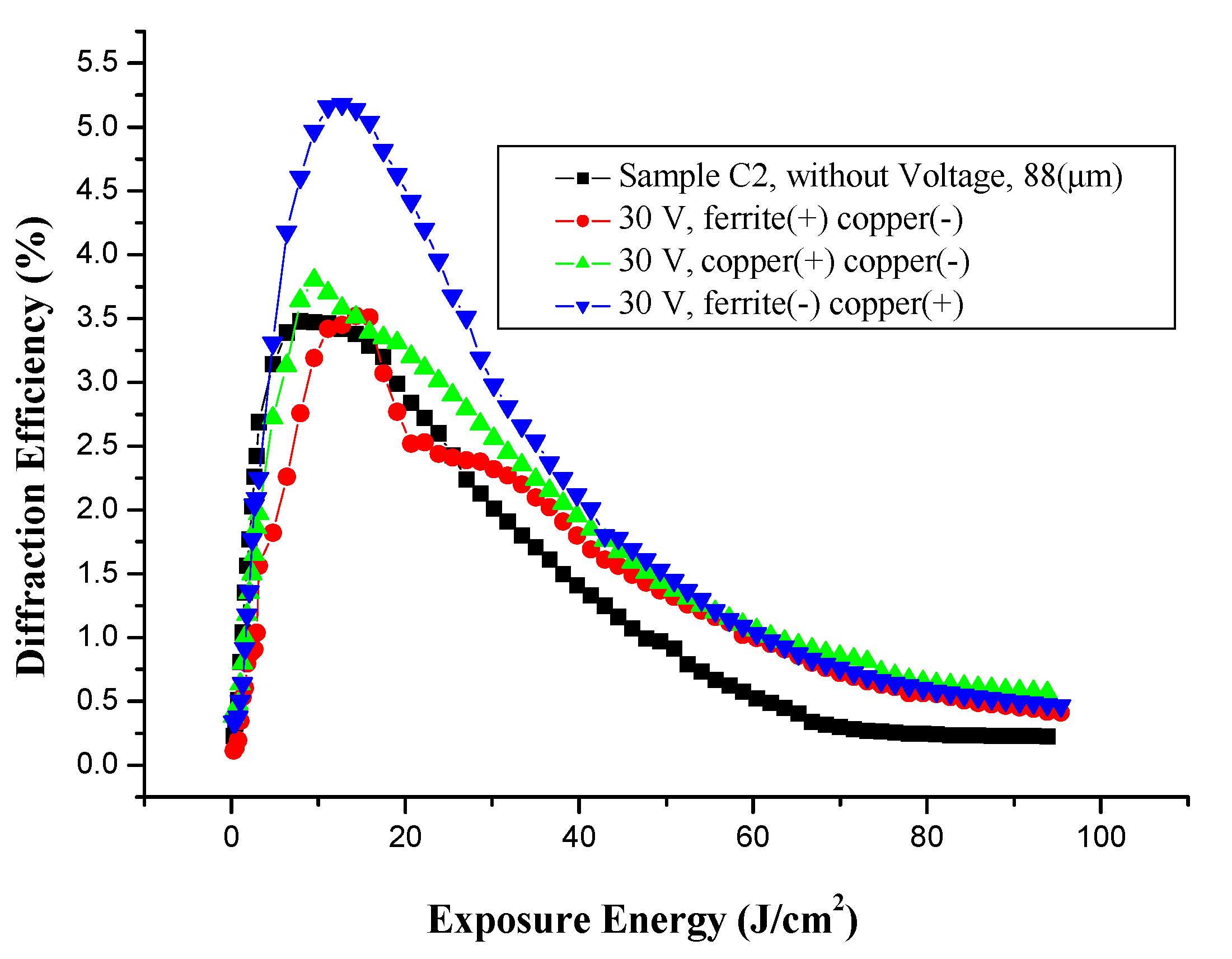
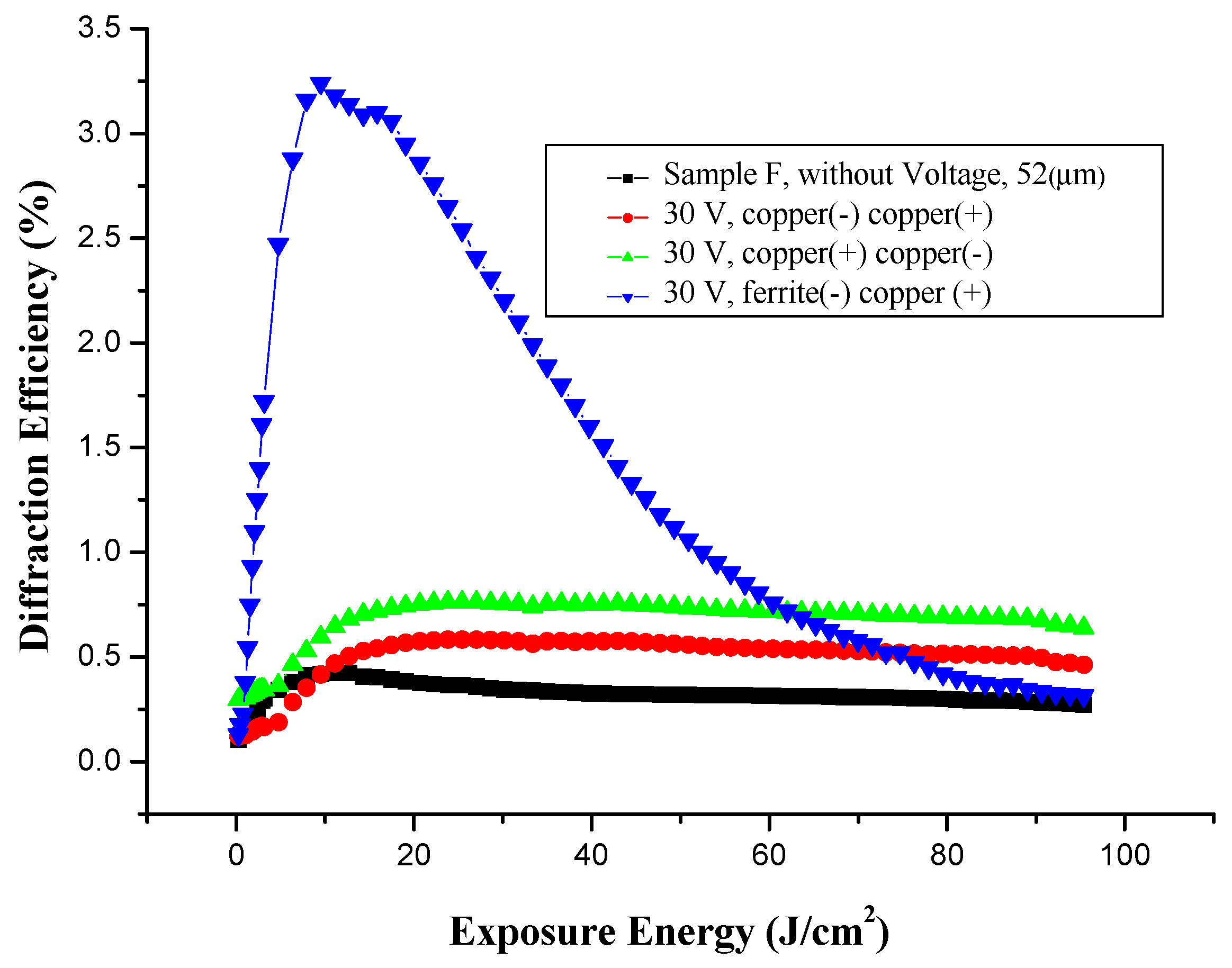
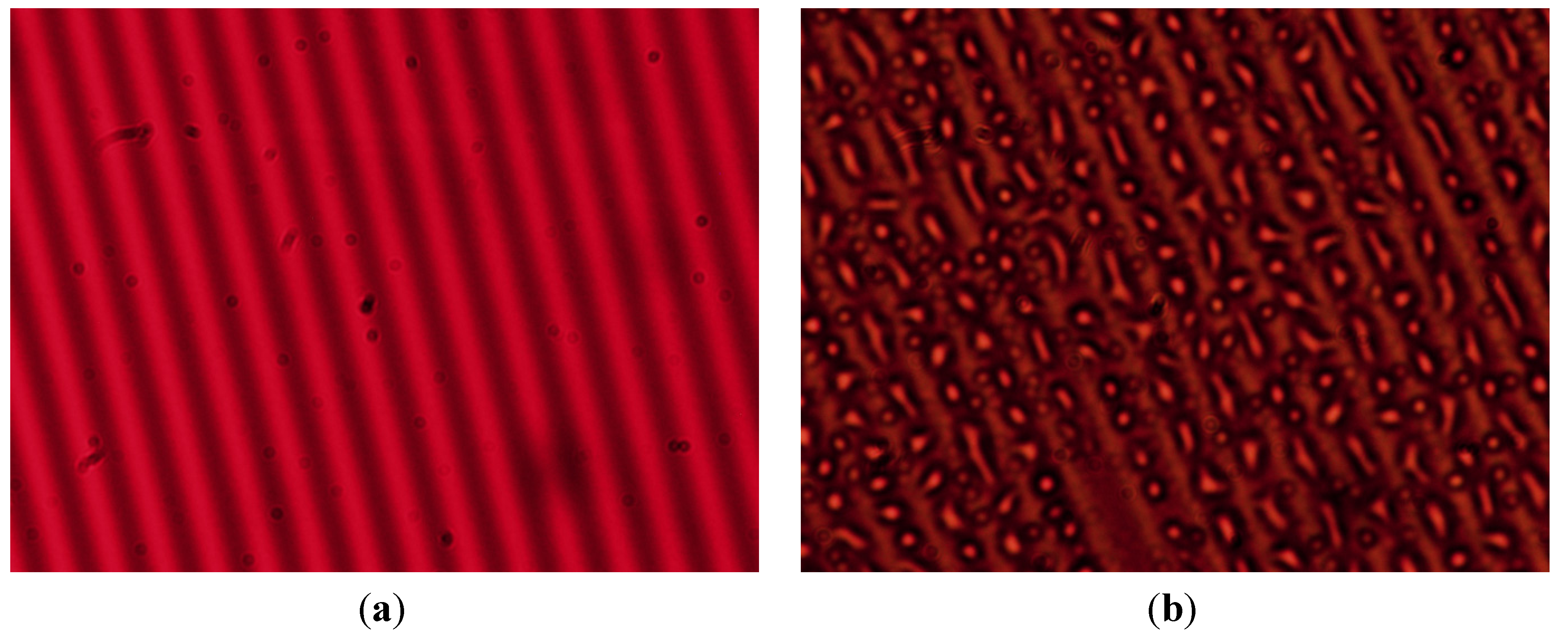
3.5.4. Microstructure of Gratings
3.6. Discussion
3.6.1. Hypothesis Mechanism for Holographic Recording and Voltage Effect
3.6.2. Diagram Chemical Reactions

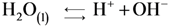
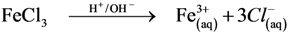

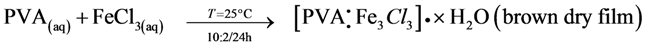
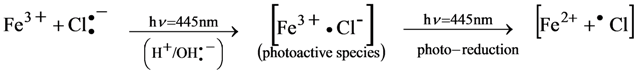
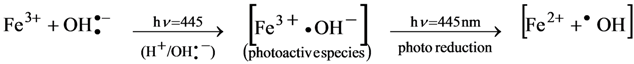
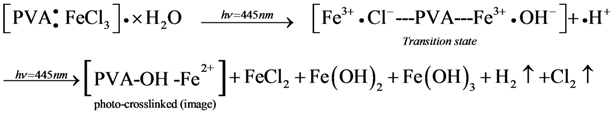
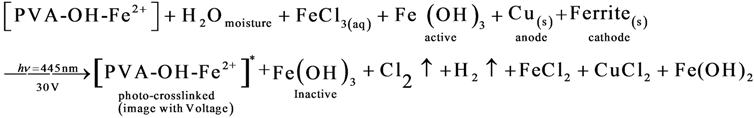
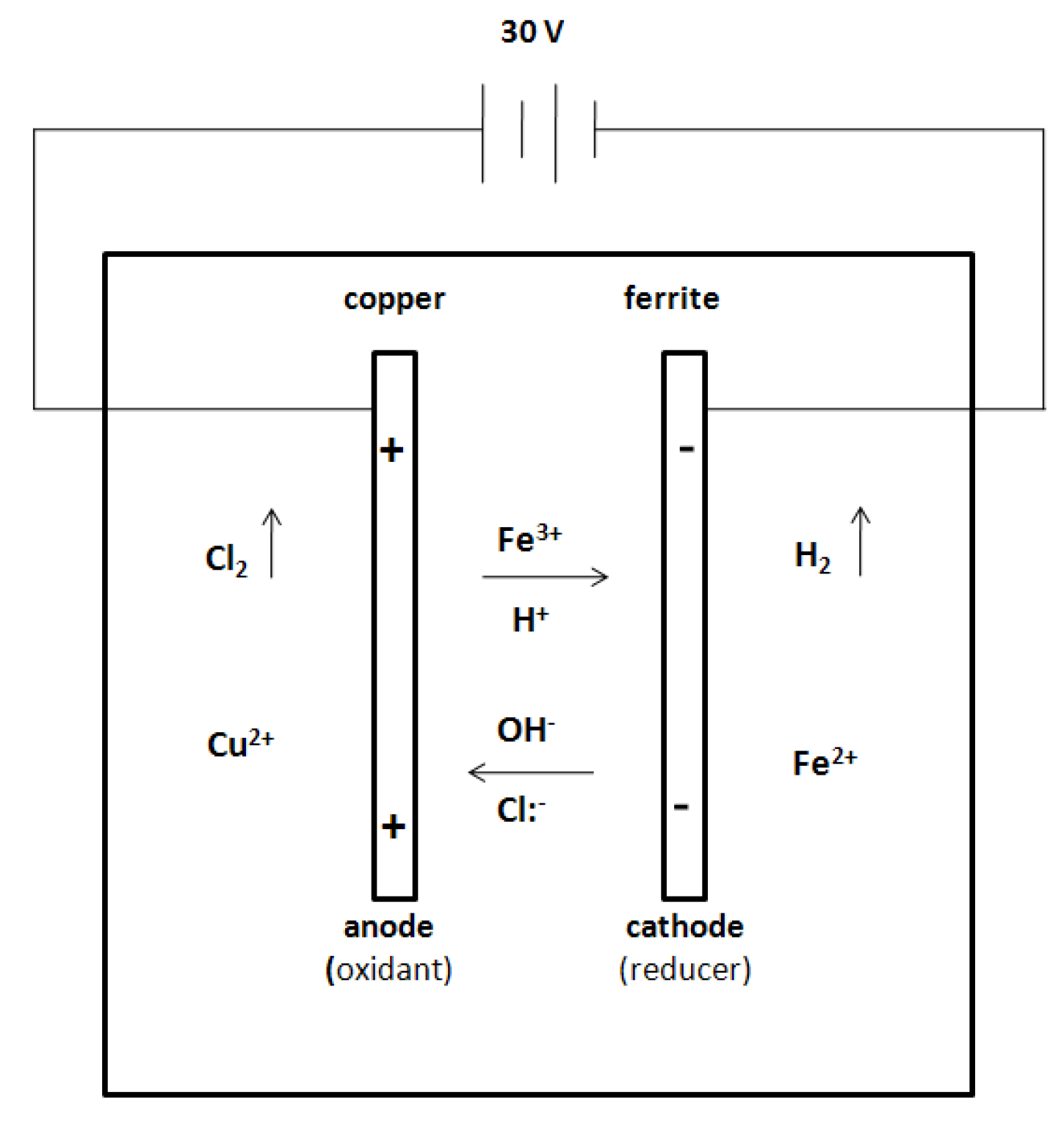
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- John, B.M.; Joseph, R.; Sreekumar, K.; Sudha-Kartha, C. Copper doped methylene blue sensitized poly(vinyl alcohol)-acrylamide films for stable diffraction efficiency. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2006, 45, 8686–8690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramitha, V. A New Metal Ion Doped Panchromatic Photopolymer for Holographic Applications. Ph.D. Thesis, Cochin University of Science and Technology, Cochin, India, November 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Pramitha, V.; Nimmi, K.P.; Subramanyan, N.V.; Joseph, R.; Sreekumar, K.; Sudha Kartha, C. Silver-doped photopolymer media for holographic recording. Appl. Opt. 2009, 48, 2255–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solymar, L.; Cooke, D.J. Volume Holography and Volume Gratings; Academic Press: London, UK, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Finch, A. Polyvinyl Alcohol Developments; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Nachtrieb, N.H. Conduction in fused salts and salt-metal solutions. Ann. Rev. Phys. Chem. 1980, 31, 131–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patachia, S.; Rinja, M.; Isac, L. Some methods for doping poly (vinyl alcohol) hydrogels [PVA-HG]. Rom. J. Phys. 2006, 51, 253–262. [Google Scholar]
- Gaafar, S.A.; Abd El-Kader, F.H.; Rizk, M.S. Changes in the structure of poly (vinyl alcohol)-CrCI composites irradiated by low level fast neutron doses. Phys. Scr. 1994, 49, 366–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDiarmid, A.G. Nobel Lecture: Synthetic metals: A novel role for organic polymers. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2001, 73, 701–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valsangiacom, M.S.; Bulinski, M.; Iova, I.; Schinteie, G.; Kuncser, C.; Filoti, G.; Bejan, D. Optical and electronic proprieties of mixed Fe-Sn doped PVA. Rom. Rep. Phys. 2003, 55, 283–286. [Google Scholar]
- Sakhno, O.V.; Goldenberg, L.M.; Stumpe, J.; Smirnova, T.N. Surface modified ZrO2 and TiO2 nanoparticles embedded in organic photopolymers for highly effective and UV-stable volume holograms. Nanotechnology 2007, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamil, M.; Ahmad, F.; Rhee, J.T.; Jeon, Y.J. Nanoparticle-doped polymer-dispersed liquid crystal display. Curr. Sci. 2011, 101, 1544–1552. [Google Scholar]
- Juhl, A.T.; Busbee, J.D.; Koval, J.J.; Natarajan, L.V.; Tondiglia, V.P.; Vaia, R.A.; Bunning, T.J.; Braun, P.V. Holographically directed assembly of polymer nanocomposites. Acsnano 2010, 4, 5953–5961. [Google Scholar]
- Ostrowski, A.M.; Naydenova, I.; Toal, V. Light-induced redistribution of Si-MFI zeolite nanoparticles in acrylamide-based photopolymer holographic gratings. J. Opt. A Pure Appl. Opt. 2009, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X. Photopolymerizable Metal Nanoparticle-/Semiconductor Quantum Dot-Polymer Nanocomposite Materials for Nonlinear Optics. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Electro-Communications Tokyo, Tokyo, Japan, March 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Yovcheva, T.; Naydenova, I.; Sainov, S.; Toal, V.; Mintova, S. Holographic recording in corona charged acrylamide-based MFI-zeolite photopolymer. J. Nonlinear Opt. Phys. Mater. 2011, 20, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Cao, L.; Yi, Y.; He, Q.; Jin, G. Plasmon-active mixed gratings in volume holographic polymeric nanocomposites. In Proceedings of Photonic Fiber and Crystal Devices: Advances in Materials and Innovations in Device Applications VII, San Diego, CA, USA, 25 August 2013.
- Budkevich, B.A.; Polikanin, A.M.; Pilipovich, V.A.; Petrochenko, N.Ya. Amplitude-phase hologram recording on FeCl3–PVA films. J. Appl. Spectrosc. 1989, 50, 621–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manivannan, G.; Changkakoti, R.; Lessard, R.A. Cr (VI)- and Fe (III)-doped polymer systems as real-time holographic recording materials. Opt. Eng. 1993, 32, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulinski, M.; Kuncser, V.; Plapcianu, C.; Krautwald, S.; Franke, H.; Rotaru, P.; Filoti, G. Optical and electric properties of polyvinyl alcohol doped with pairs of mixed valence metal ions. Rom. Rep. Phys. 2003, 5, 283–286. [Google Scholar]
- Olivares-Pérez, A.; Hernández-Garay, M.P.; Fuentes-Tapia, I.; Ibarra-Torres, J.C. Holograms in polyvinyl alcohol photosensitized with CuCl2 (2H2O). Opt. Eng. 2011, 50, 065801:1–065801:6. [Google Scholar]
- Hernández-Garay, M.P.; Olivares-Pérez, A.; Fuentes-Tapia, I. Characterization and evolution of electro-optical properties from holograms replication on polymer (PVA) with salts (FeCl3). In Proceedings of 5th International Workshop on Information Optics (WIO’06), Toledo, Spain, 5–7 June 2006; pp. 446–454.
- Skoog, D.A.; West, D.M.; Holler, F.J.; Crouch, S.R. Fundamentals of Analytical Chemistry; Thomson-Brooks/Cole: London, UK, 2004; pp. 500–560. [Google Scholar]
- Basolo, F.; Johnson, R. Química de los Compuestos de Coordinación; (in Spanish). Reverté: Barcelona, Spain, 1978; pp. 81–100. [Google Scholar]
- Hamzah, H.M.; Saion, E.; Kassim, A.; Yousuf Hussain, M.; Shahrim Mustafa, I.; Ahmad Ali Omer, M. Temperature dependence of AC electrical conductivity of PVA-PPy-FeCl3 composite polymer films. Malays. Polym. J. 2008, 3, 24–31. [Google Scholar]
- Van Renesse, R.L. Photopolymers in holography. Opt. Laser Technol. 1972, 4, 24–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sio, L.; Veltri, A.; Tedesco, A.; Caputo, R.; Umeton, C.; Sukhov, A.V. Characterization of an active control system for holographic setup stabilization. Appl. Opt. 2008, 47, 1363–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frejlich, J.; Cescato, L.; Mendes, G.F. Analysis of an active stabilization system for a holographic setup. Appl. Opt. 1988, 10, 1967–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Society for Testing and Materials. Standard Test Methods for D-C Resistance or Conductance of Moderately Conductive Materials; ASTM D4496-04; American Society for Testing and Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Hariharan, P. Basics of Holography; Cambridge University Press: London, UK, 2002; pp. 15–24. [Google Scholar]
- Kogelnik, H. Coupled wave theory for thick hologram gratings. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1969, 48, 2909–2947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawansi, A.; El-Khodary, A.; Abdelnaby, M.M. A study of the physical properties of FeCl3 filled PVA. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2005, 5, 572–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontanilla-Urdaneta, R.C.; Olivares-Pérez, A.; Fuentes-Tapia, I.; Ríos-Velasco, M.A. Analysis of voltage effect on holographic gratings by modulation transfer function. Appl. Opt. 2011, 50, 1827–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korneev, N.; Flores Ramirez, O.; Bertram, R.P.; Benter, N.; Soergel, E.; Buse, K.; Hagen, R.; Kostromine, S.G. Pyroelectric properties of electrically poled photoaddressable polymers. J. Appl. Phys. 2002, 92, 1500–1503. [Google Scholar]
- Kyritsis, A.; Pissis, P.; Gómez, R.J.L.; Monleón, P.M. Dielectric relaxation spectroscopy in PHEA hydrogels. J. Non Cryst. Solids 1994, 2, 1041–1046. [Google Scholar]
- Ricciardi, R.; Auriemma, F.; de Rosa, C.; Lauprêtre, F. X ray diffacction analysis of poly(vinyl alcohol) hydrogels, obtained by freezing and thawing techniques. Macromolecules 2004, 37, 1921–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willcox, P.J. Microesturcture of poly(vinyl alcohol) hydrogels produced by freeze/thaw cycling. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 1999, 37, 3438–3454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentín, J.L.; López, D.; Hernández, R.; Mijangos, C.; Saalwächter, K. Structure of poly(vinyl alcohol) cryo-hydrogels as studied by proton low-field NMR spectroscopy. Macromolecules 2009, 42, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, C.M.; Peppas, N. Structure and morphology of freeze/thawed PVA hydrogels. Macromlecules 2000, 33, 2472–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, R.; Rao, K.J. Electrical conductivity studies of poly (ethylene oxide) poly (vinylalcohol) blends. Solid State Ionics. 1998, 106, 113–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awadhia, A.; Patel, S.K.; Agrawal, S.L. Dielectric investigation in PVA based gel electrolytes. Prog. Cryst. Growth Charact. Mater. 2006, 52, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trieu, H.H.; Qutubuddin, S. Polyvinyl alcohol hydrogels I. Microscopic structure by freeze-etching and critical point drying technique. Colloid Polym. Sci. 1994, 272, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.P.; Gupta, P.N. Study of dielectric relaxation in polymer electrolytes. Eur. Polym. J. 1998, 34, 1023–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Londoño, M.E.; Jaramillo, J.M. Dielectric behavior of poly(vinyl alcohol) hydrogels preparing by freezing/thawing technique. Revista EIA 2011, 165, 132–137. [Google Scholar]
- The Chemistry of Ferric Chloride. Available online: http://www.artmondo.net/printworks/articles/ferric.htm (accessed on 7 March 2014).
- Sherman, D.M. Electronic structures of Fe3+ coordination sites in iron oxides: Applications to spectra, bonding and magnetism. Phys. Chem. Miner. 1985, 12, 161–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherman, D.M. Molecular orbital (SCF-X-SW) theory of Fe2+-Mn3+, Mn2+-Fe3+ and Fe3+-Mn3+ charge transfer and magnetic exchange interactions in oxides and silicates. Am. Mineral. 1990, 75, 256–261. [Google Scholar]
- Sherman, D.M.; Waite, T.D. Electronic spectra of Fe3+ oxides and oxide hydroxides in the near-IR to near-UV. Am. Mineral. 1985, 70, 1262–1269. [Google Scholar]
- Hudson, R.J.; Covault, D.T.; Morel, F.M. Investigations of iron coordination and redox reactions in seawater using 59Fe radiometry and ion-pair solvent extraction of amphiphilic iron complexes. Mar. Chem. 1992, 38, 209–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, D.H.; Sykes, K.W. Ionic association and reaction rates. Part I. A spectrophotometric study of the hydrolysis of iron (III). J. Chem. Soc. 1960, 1960, 3626–3633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balt, S.; Verwey, A.M.A. Electronicspectra and ligandfieldparameters in chloroaquoiron (III) complexes. Spectrochim. Mol. Spectrosc. 1967, 23, 2069–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heistand, R.N.; Clearfield, A. The effect of specific swamping electrolyte supon the formation constant of the monochloro iron (III) complex. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1963, 85, 2566–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, R.J.; Sylva, R.N. Spectrophotometric investigation of iron (III) hydrolysis in light and heavy water at 25 °C. J. lnorg. Nucl. Chem. 1975, 37, 779–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverman, J.; Dodson, R.W. The exchange reaction between the two oxidation states of iron in acid solution. J. Phys. Chem. 1952, 56, 846–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schugar, H.J. The structure of iron (III) in aqueous solution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1967, 89, 3712–3720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faust, B.C.; Hoigne, J. Photolysis of Fe (III)-hydroxy complexes as sources of OH radicals in clouds, fog and rain. Atmos. Environ. Part A Gen. Top. 1990, 24, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherman, D.M. Electronic structures of iron(III) and manganese(IV) (hydr)oxide minerals: Thermodynamics of photochemical reductive dissolution in aquatic environments. Geochim. et Cosmochim. Acta. 2005, 69, 3249–3255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collienne, R.J. Photoreduction of iron in the epilimn ion of acidic lakes. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1983, 28, 83–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mc Knight, D.M.; Kimball, B.A.; Bencala, K.E. Iron photoreduction and oxidation in an acidic mountain stream. Science 1988, 240, 637–640. [Google Scholar]
- Turner, R.C.; Kathleen, E.M. The ultraviolet absorption spectra of the ferric ion and its first hydrolysis product in aqueous solutions. Can. J. Chem. 1957, 35, 1002–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, M.G.; Santappa, M.; Uri, N. Photoinitiated free radical polymerization of vinyl compounds in aqueous solution. J. Polym. Sci. 1951, 7, 243–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; Nansheng, D. Photochemistry of hydrolytic iron (III) species and photoinduced degradation of organic compounds. Chemosphere 2000, 41, 1137–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, H.G.; Uri, N. Oxidation of aromatic compounds in aqueous solution by free radicals produced by photo-excited electron transfer in iron complexes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1953, 75, 2754–2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, A.R.; Ghosh, P.; Chadha, S.C.; Palit, S.R. End group studies in poly (methyl methacrylate) initiated by redox systems containing reducing sulfoxy compounds in aqueous media. Die Makromol. Chem. 1966, 97, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, F.; David, P.G. Photoredox chemistry of iron(llI) chloride and iron(llI) perchlorate in aqueous media. A comparative study. J. Phys. Chem. 1976, 80, 579–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadtochenko, V.A.; Kiwi, J. Photolysis of FeOH2+ and FeCl2+ in aqueous solution. Photodissociation kinetics and quantum yields. Inorg. Chem. 1998, 37, 5233–5238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balzani, V.; Carassiti, V. Photochemistry of Coordination Compounds; Academic Press: London, UK, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Horvath, O.; Stevenson, K. Charge-Transfer Photochemistry of Coordination Compounds; VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Hasinoff Brian, B. The kinetic activation volumes for the binding of chloride to iron(III), studied by means of a high pressure laser temperatura jump apparatus. Can. J. Chem. 1976, 54, 1820–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, R.; Kester, D.J. Ultraviolet spectroscopic study of ferric hydroxide complexation. J. Solut. Chem. 1978, 7, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, R.; Kester, D.J. Ultraviolet spectroscopic study of ferric equilibria at high chloride concentrations. J. Solut. Chem. 1981, 10, 51–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polikanin, A.M.; Budkevich, B.A. Photochemical processes in the iron (III) chloride-dye-binder system. J. Appl. Spectrosc. 1993, 59, 699–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oster, G.K.; Oster, G. Photoreduction of metal ions by visible light. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1959, 81, 5543–5545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toshima, N.; Hara, S. Direct synthesis of conducting polymers from simple monomers. Prog. Polym. Sci. 1995, 20, 155–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirakawa, H.; Louis, E.J.; Diarmid, A.G.; Chiang, A.G.; Heeger, A.J. Synthesis of electrically conducting organic polymers: Halogen derivatives of polyacetylene, (CH)x. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1977, 474, 578–580. [Google Scholar]
- Dutta, P.; Biswas, S.; Ghosh, M.; De, S.K.; Chatterjee, S. The DC and AC conductivity of polyaniline–polyalcohol blends. Synth. Met. 2000, 122, 455–461. [Google Scholar]
- Kukhtarev, N.V.; Markov, V.B.; Odulov, S.G.; Soskin, M.S.; Vinetskii, V.L. Holographic storage in electrooptic crystals. Ferroelectrics 1978, 22, 949–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, H.P.; dos Santos, M.V.P.; dos Santos, C.G.; de Melo, C.P. Preparation and electrical and dielectric characterization of PVA/PPY blends. Mater. Charact. 2003, 50, 223–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Olivares-Pérez, A.; Hernández-Garay, M.P.; Toxqui-López, S.; Fuentes-Tapia, I.; Ordóez-Padilla, M.J. Voltage Effect in Holograms of Polyvinyl Alcohol with FeCl3. Polymers 2014, 6, 899-925. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym6030899
Olivares-Pérez A, Hernández-Garay MP, Toxqui-López S, Fuentes-Tapia I, Ordóez-Padilla MJ. Voltage Effect in Holograms of Polyvinyl Alcohol with FeCl3. Polymers. 2014; 6(3):899-925. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym6030899
Chicago/Turabian StyleOlivares-Pérez, Arturo, Mary Paz Hernández-Garay, Santa Toxqui-López, Israel Fuentes-Tapia, and Manuel Jorge Ordóez-Padilla. 2014. "Voltage Effect in Holograms of Polyvinyl Alcohol with FeCl3" Polymers 6, no. 3: 899-925. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym6030899
APA StyleOlivares-Pérez, A., Hernández-Garay, M. P., Toxqui-López, S., Fuentes-Tapia, I., & Ordóez-Padilla, M. J. (2014). Voltage Effect in Holograms of Polyvinyl Alcohol with FeCl3. Polymers, 6(3), 899-925. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym6030899




