Synthesis and Solution Properties of Double Hydrophilic Poly(ethylene oxide)-block-poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline) (PEO-b-PEtOx) Star Block Copolymers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Instruments
2.2. Materials
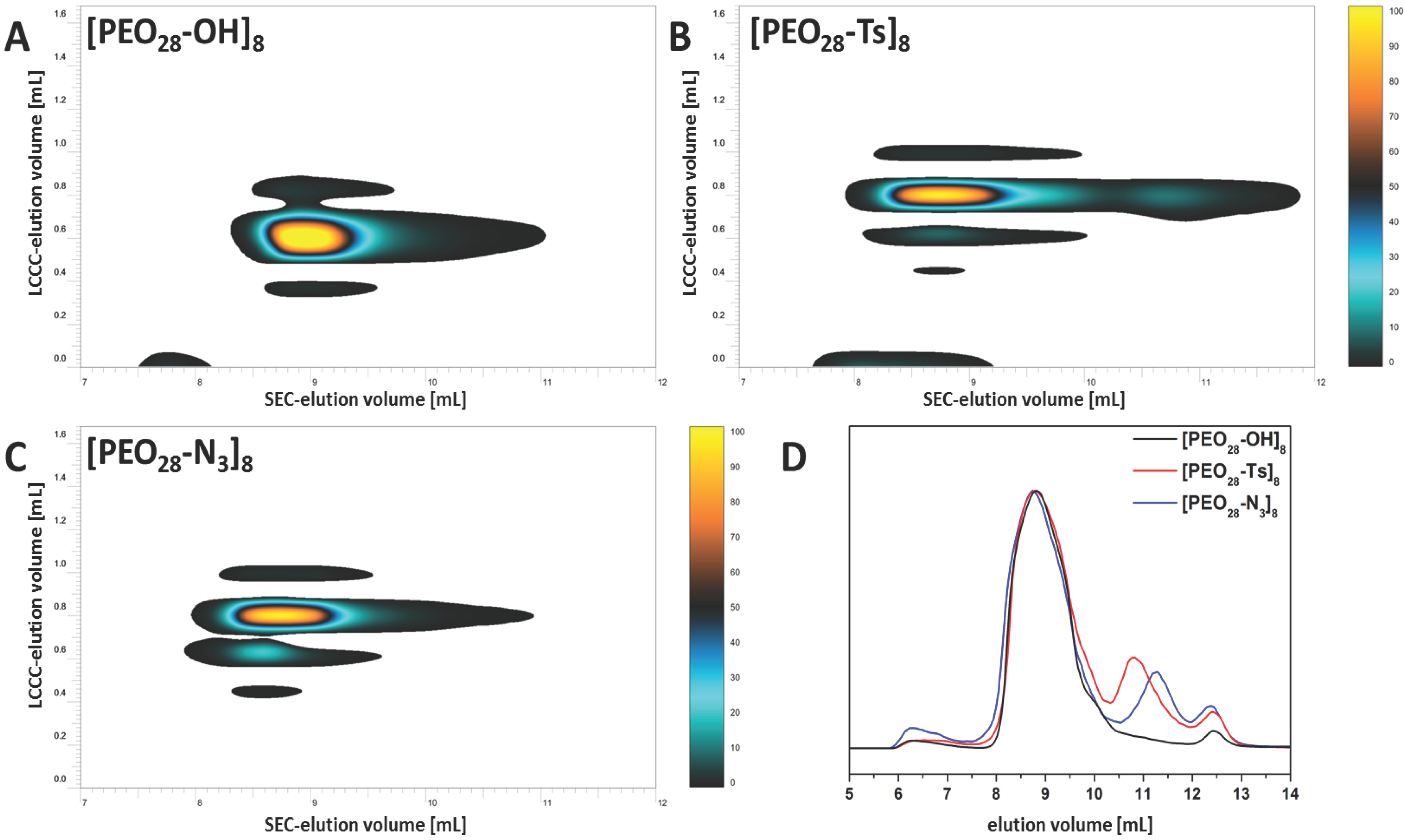
2.2.1. Tosylation of Star-Shaped [PEO28-OH]8
2.2.2. Preparation of Star-Shaped [PEO28-N3]8
2.2.3. Synthesis of Alkyne-Functionalized TB-PEtOxx
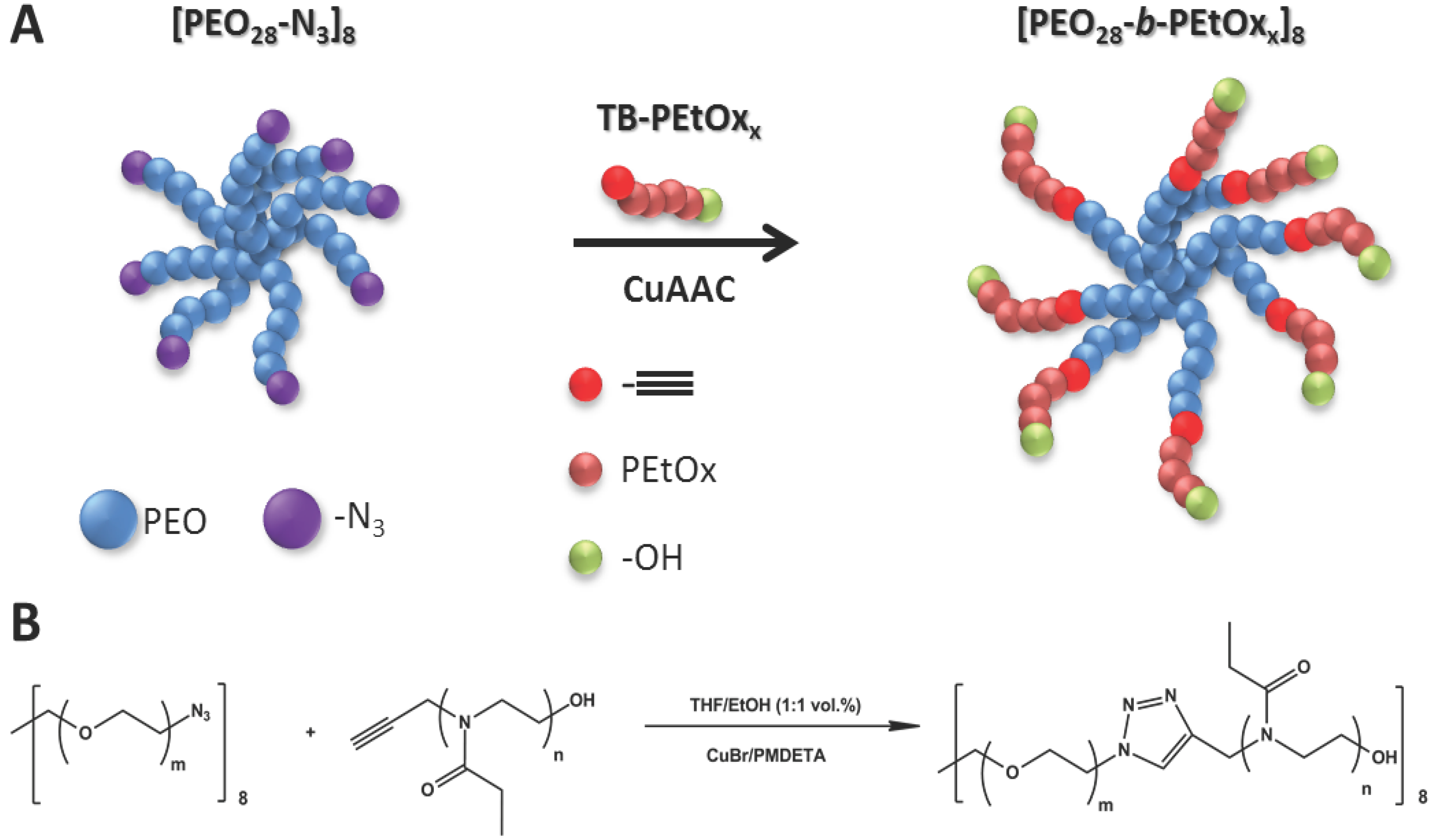
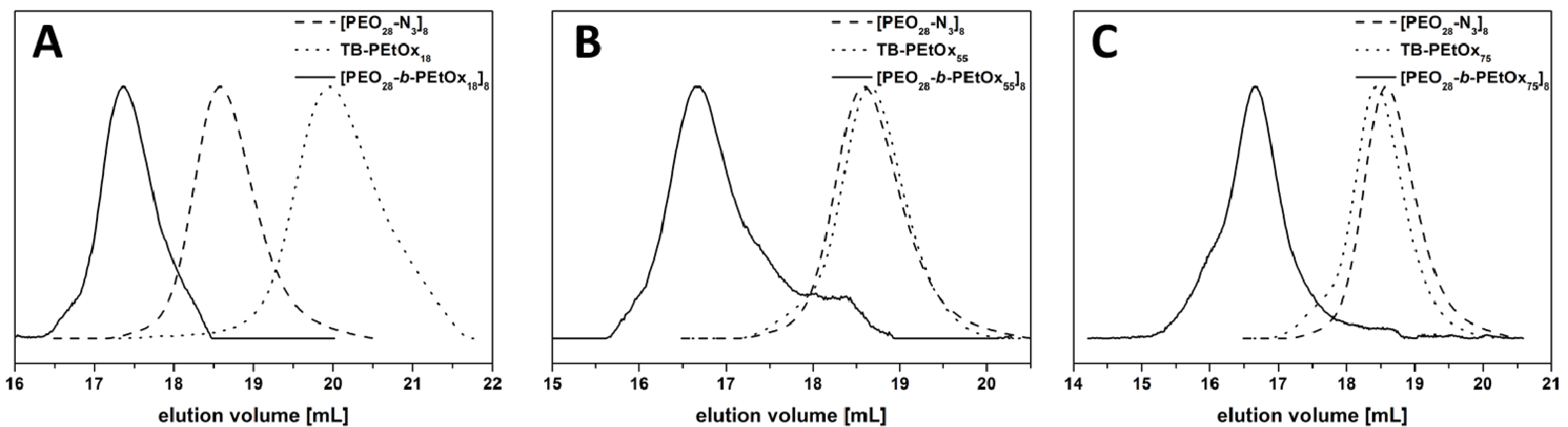
2.2.4. Copper catalyzed Azide-Alkyne Cycloaddition (CuAAC) Click Reaction between [PEO28-N3]8 and TB-PEtOxx
2.2.5. Polymerization of 2-Ethyl-2-oxazoline using a Star-Shaped PEO Macroinitiator
2.2.6. Kinetic Investigation of the Polymerization of 2-Ethyl-2-oxazoline using a Star-Shaped PEO-Macroinitiator
3. Results and Discussion
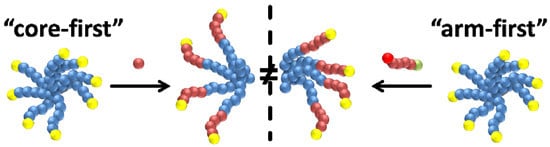
3.1. Star Synthesis via Macromolecular Conjugation (“Arm-First”-Approach)

| Sample | DP a | Mn b [g mol−1] | Mn c [g mol−1] | Ð c | Mp d [g mol−1] | Building Block |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TB-PEtOx18 b,e | 20 | 1800 | 2700 | 1.12 | 1500 | arm in chloroform |
| TB-PEtOx55 b,e | 60 | 5500 | 5600 | 1.09 | 5400 | |
| TB-PEtOx75 b,e | 80 | 7500 | 6700 | 1.10 | 7200 | |
| TB-PEtOx18 e,f | 20 | 1800 | 3900 | 1.18 | – | arm in DMAC |
| TB-PEtOx55 e,e | 60 | 5500 | 9700 | 1.16 | – | |
| TB-PEtOx75 e,e | 80 | 7500 | 12,000 | 1.19 | – | |
| [PEO28-OH]8 b,e | – | 10,000 | 6100 h | 1.07 | 9,900 | star-shaped core |
| [PEO28-Ts]8 b,e | – | 11,000 | 7000 h | 1.04 | – | |
| [PEO28-N3]8 b,e | – | 10,300 | 7000 h | 1.07 | – | |
| [PEO28-N3]8 e,g | – | 10,300 | 12,000 g | 1.15 | – |
| Sample | Mn a [g mol−1] | Ð a | Mn,calc b [g mol−1] | Mw,SLS d [g mol−1] | Approach |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [PEO28-b-PEtOx18]8 c | 22,000 | 1.13 | 22,000 | – | arm-first |
| [PEO28-b-PEtOx55]8 c | 46,000 | 1.18 | 54,000 | – | |
| [PEO28-b-PEtOx75]8 c | 42,000 | 1.14 | 67,000 | – | |
| [PEO28-b-PEtOx16]8 c | 24,000 | 1.24 | 22,000 | – | core-first |
| [PEO28-b-PEtOx50]8 c | 35,000 | 1.15 | 50,000 | 54,000 |
3.2. Star Synthesis via CROP of 2-Ethyl-2-oxazoline Using a Star-Shaped Macroinitiator (“Core-First”-Approach)
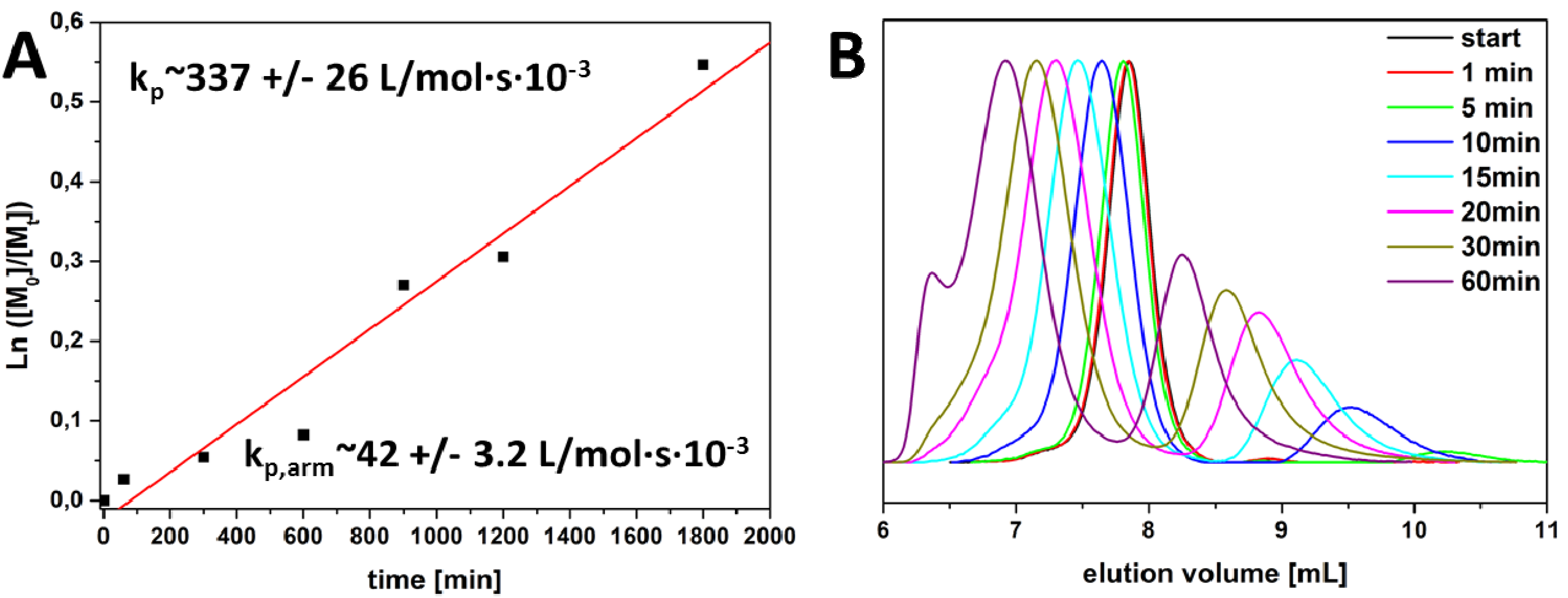
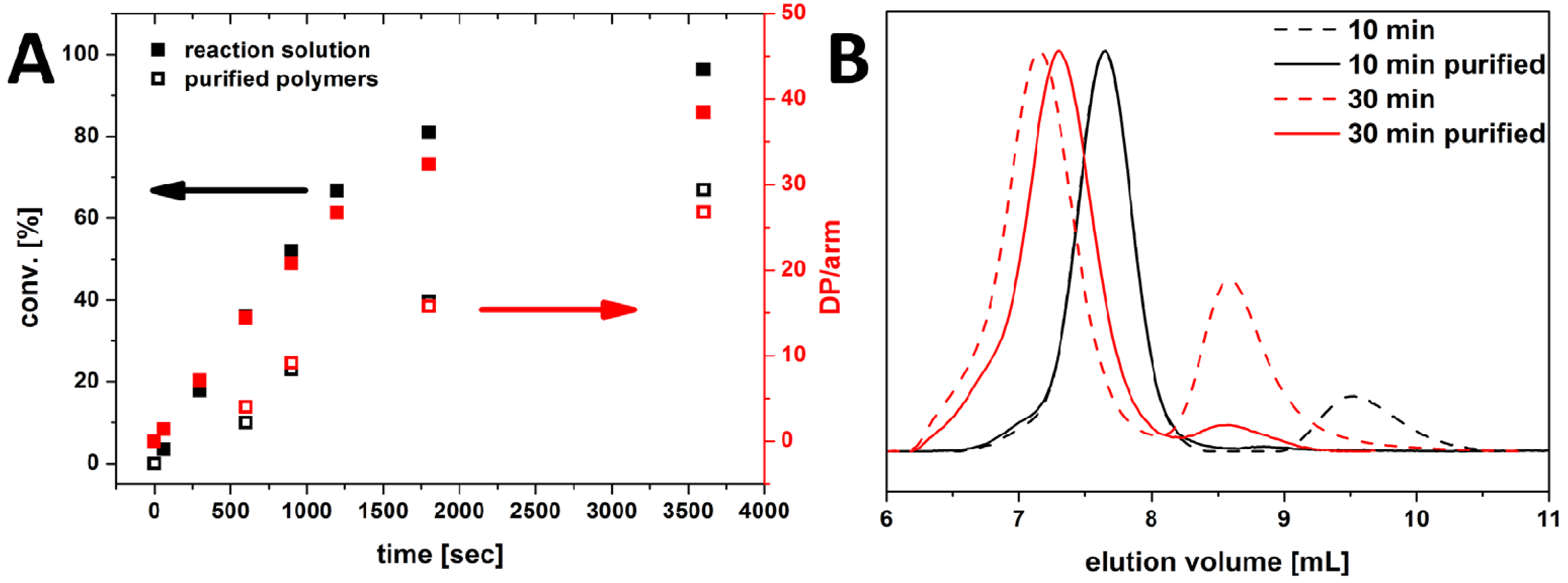
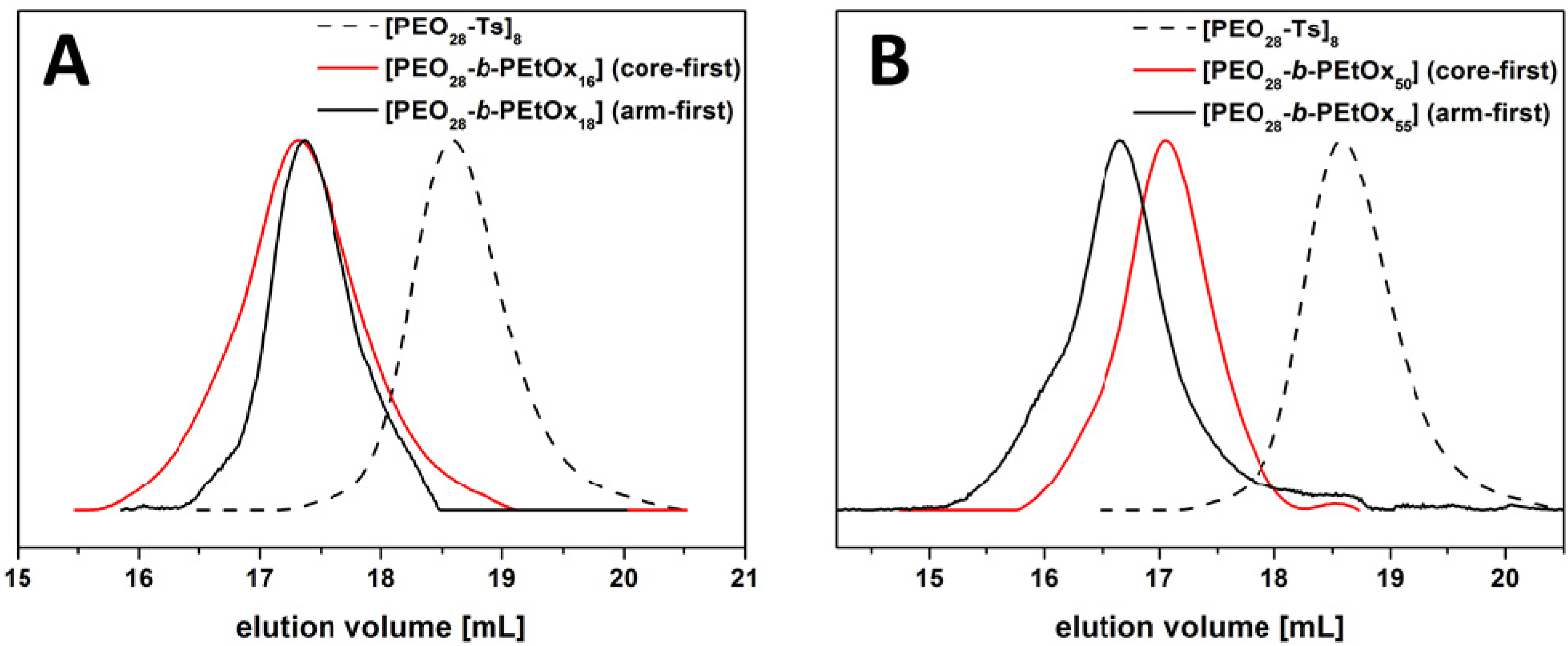
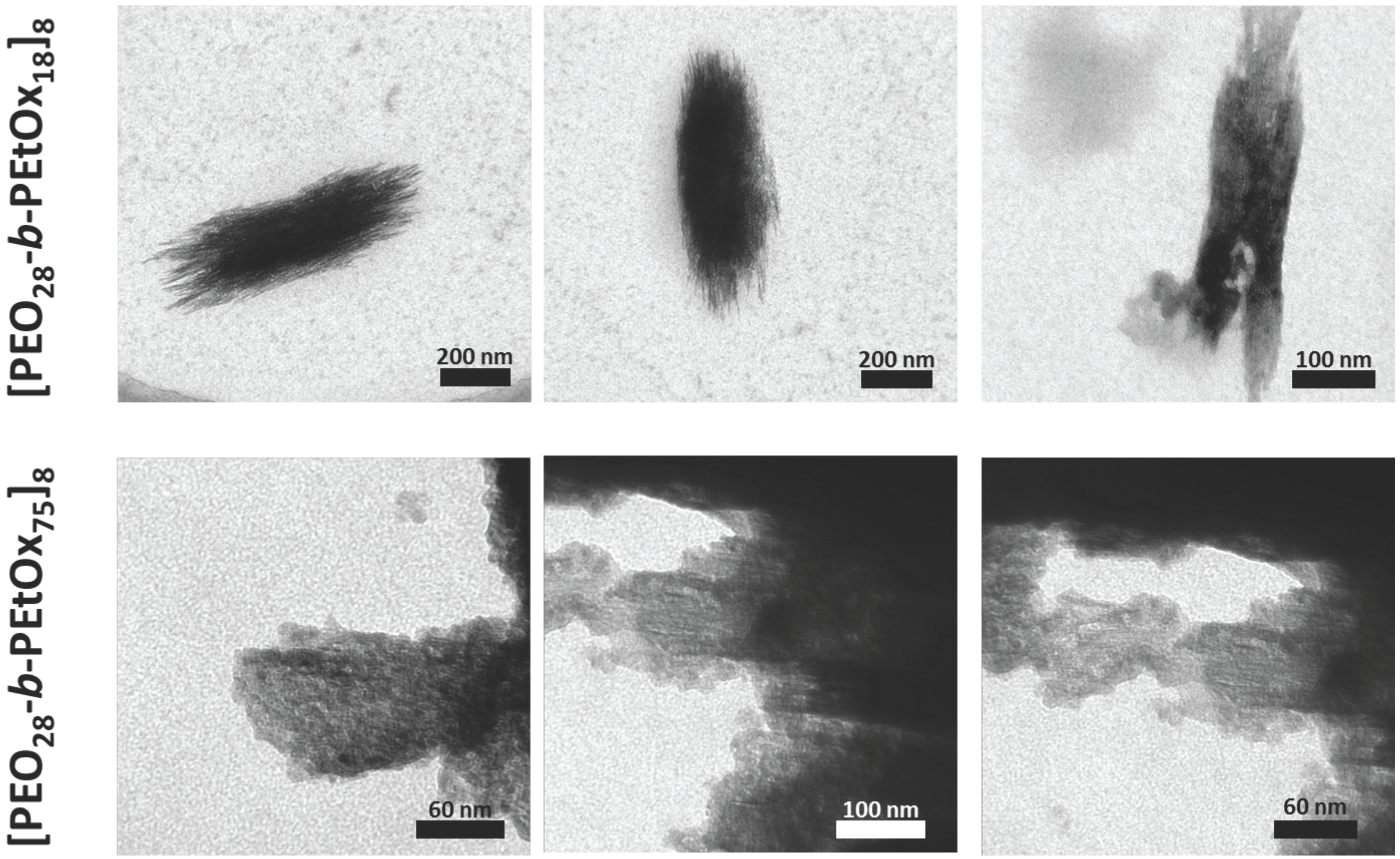
3.3. Study of Star-Shaped [PEO28-b-PEtOxx]8 in Non-Selective Solvents
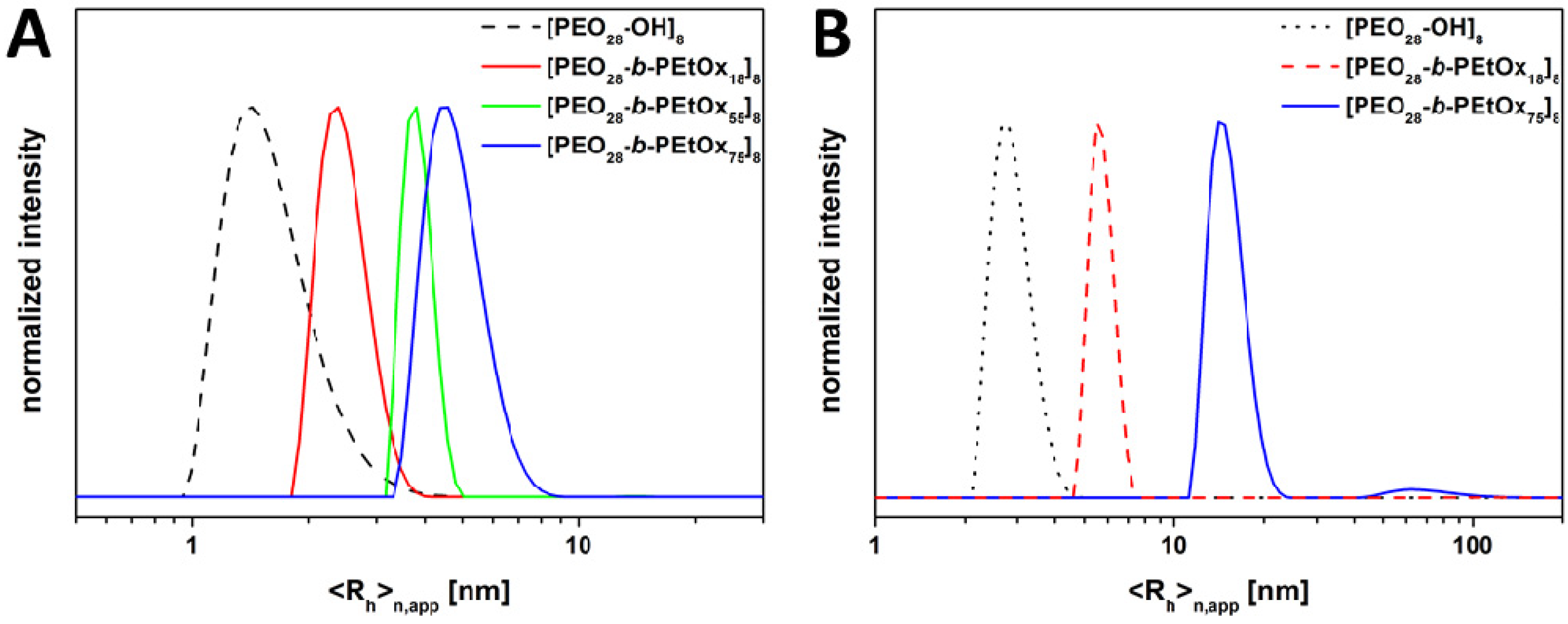
| Sample | approach | <Rh>n,app a [nm] in THF | <Rh>n,app a [nm] in H2O |
|---|---|---|---|
| [PEO28-OH]8 | – | 1.5 | 3 |
| [PEO28-b-PEtOx18]8 | arm | 2.5 | 6 |
| [PEO28-b-PEtOx16]8 | core | 3 | 3 |
| [PEO28-b-PEtOx55]8 | arm | 4 | 9 |
| [PEO28-b-PEtOx50]8 | core | 3 | 3 |
| [PEO28-b-PEtOx75]8 | arm | 5 | 14/62 |
| [PEO28-b-PEtOx18]8 c | arm | – | 92/283 b |
| [PEO28-b-PEtOx75]8 c | arm | – | 72 b |
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barner-Kowollik, C.; Lutz, J.-F.; Perrier, S. New methods of polymer synthesis. Polym. Chem. 2012, 3, 1677–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitsikalis, M.; Pispas, S.; Mays, J.W.; Hadjichristidis, N. Nonlinear Block Copolymer Architectures. In Blockcopolymers–Polyelectrolytes–Biodegradation; Advances in Polymer Science; Springer-Verlag: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1998; Volume 135, pp. 1–137. [Google Scholar]
- Burchard, W. Solution Properties of Branched Macromolecules. Adv. Polym. Sci. 1999, 143, 113–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjichristidis, N.; Pispas, S.; Pitsikalis, M.; Iatrou, H.; Vlahos, C. Asymmetric Star Polymers: Synthesis and Properties. In Branched Polymers I; Advances in Polymer Science; Roovers, J., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1999; Volume 142, pp. 71–127. [Google Scholar]
- Plamper, F.A.; McKee, J.R.; Laukkanen, A.; Nykanen, A.; Walther, A.; Ruokolainen, J.; Aseyev, V.; Tenhu, H. Miktoarm stars of poly(ethylene oxide) and poly(dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate): manipulation of micellization by temperature and light. Soft Matter 2009, 5, 1812–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjichristidis, N.; Pitsikalis, M.; Pispas, S.; Iatrou, H. Polymers with Complex Architecture by Living Anionic Polymerization. Chem. Rev. 2001, 101, 3747–3792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matyjaszewski, K.; Xia, J.H. Atom transfer radical polymerization. Chem. Rev. 2001, 101, 2921–2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moad, G.; Rizzardo, E.; Thang, S.H. Living radical polymerization by the RAFT process. Aust. J. Chem. 2005, 58, 379–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schacher, F.H.; Rupar, P.A.; Manners, I. Functional Block Copolymers: Nanostructured Materials with Emerging Applications. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 7898–7921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Lu, Z.-Y.; Sun, Z.-Y. Self-assembly structures of amphiphilic multiblock copolymer in dilute solution. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 1947–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gröschel, A.H.; Schacher, F.H.; Schmalz, H.; Borisov, O.V.; Zhulina, E.B.; Walther, A.; Müller, A.H.E. Precise hierarchical self-assembly of multicompartment micelles. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riess, G. Micellization of block copolymers. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2003, 28, 1107–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schacher, F.; Walther, A.; Muller, A.H.E. Dynamic Multicompartment-Core Micelles in Aqueous Media. Langmuir 2009, 25, 10962–10969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Förster, S.; Abetz, V.; Müller, A.H.E. Polyelectrolyte Block Copolymer Micelles; Springer Berlin: Heidelberg, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Iatridi, Z.; Tsitsilianis, C. Water-Soluble Stimuli Responsive Star-Shaped Segmented Macromolecules. Polymers 2011, 3, 1911–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schacher, F.H.; Elbert, J.; Patra, S.K.; Mohd Yusoff, S.F.; Winnik, M.A.; Manners, I. Responsive Vesicles from the Self-Assembly of Crystalline-Coil Polyferrocenylsilane-block-Poly(ethylene Oxide) Star-Block Copolymers. Chem. Eur. J. 2012, 18, 517–525. [Google Scholar]
- Schacher, F.H.; Freier, U.; Steiniger, F. Hierarchical self-assembly of star-shaped organometallic crystalline-coil block copolymers in solution. Soft Matter. 2012, 8, 6968–6978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinschulte, A.A.; Schulte, B.; Erberich, M.; Borisov, O.V.; Plamper, F.A. Unimolecular Janus Micelles by Microenvironment-Induced, Internal Complexation. ACS Macro Lett. 2012, 1, 504–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knop, K.; Pavlov, G.M.; Rudolph, T.; Martin, K.; Pretzel, D.; Jahn, B.O.; Scharf, D.H.; Brakhage, A.A.; Makarov, V.; Mollmann, U.; Schacher, F.H.; Schubert, U.S. Amphiphilic star-shaped block copolymers as unimolecular drug delivery systems: investigations using a novel fungicide. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 715–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapienis, G. Star-shaped polymers having PEO arms. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2009, 34, 852–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaglia, F.; Ostacolo, L.; Nese, G.; Canciello, M.; de Rosa, G.; Ungaro, F.; Palumbo, R.; la Rotonda, M.I.; Maglio, G. Micelles based on amphiphilic PCL-PEO triblock and star-shaped diblock copolymers: Potential in drug delivery applications. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2008, 87A, 563–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knop, K.; Hoogenboom, R.; Fischer, D.; Schubert, U.S. Poly(ethylene glycol) in Drug Delivery: Pros and Cons as Well as Potential Alternatives. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 6288–6308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanisch, A.; Schmalz, H.; Müller, A.H.E. A Modular Route for the Synthesis of ABC Miktoarm Star Terpolymers via a New Alkyne-Substituted Diphenylethylene Derivative. Macromolecules 2012, 45, 8300–8309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altintas, O.; Vogt, A.P.; Barner-Kowollik, C.; Tunca, U. Constructing star polymers via modular ligation strategies. Polym. Chem. 2012, 3, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fijten, M.W.M.; Haensch, C.; van Lankvelt, B.M.; Hoogenboom, R.; Schubert, U.S. Clickable poly(2-oxazoline)s as versatile building blocks. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2008, 209, 1887–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjichristidis, N.; Iatrou, H.; Pitsikalis, M.; Pispas, S.; Avgeropoulos, A. Linear and non-linear triblock terpolymers. Synthesis, self-assembly in selective solvents and in bulk. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2005, 30, 725–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempe, K.; Krieg, A.; Becer, C.R.; Schubert, U.S. “Clicking” on/with polymers: A rapidly expanding field for the straightforward preparation of novel macromolecular architectures. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 176–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsitsilianis, C.; Lutz, P.; Graff, S.; Lamps, J.P.; Rempp, P. Core-first synthesis of star polymers with potentially ionogenic branches. Macromolecules 1991, 24, 5897–5902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knischka, R.; Lutz, P.J.; Sunder, A.; Mülhaupt, R.; Frey, H. Functional Poly(ethylene oxide) Multiarm Star Polymers: Core-First Synthesis Using Hyperbranched Polyglycerol Initiators. Macromolecules 2000, 33, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, B.V.K.J.; Rudolph, T.; Hetzer, M.; Ritter, H.; Schacher, F.H.; Barner-Kowollik, C. Supramolecular three-armed star polymers via cyclodextrin host-guest self-assembly. Polym. Chem. 2012, 3, 3139–3145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altintas, O.; Tunca, U.; Barner-Kowollik, C. Star and miktoarm star block (co)polymers via self-assembly of ATRP generated polymer segments featuring Hamilton wedge and cyanuric acid. Polym. Chem. 2011, 2, 1146–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochwimmer, G.; Nuyken, O.; Schubert, U.S. 6,6′-Bisfunctionalized 2,2′-bipyridines as metallo-supramolecular initiators for the living polymerization of oxazolines. Macromol. Rapid Comm. 1998, 19, 309–313. [Google Scholar]
- Altintas, O.; Yankul, B.; Hizal, G.; Tunca, U. One-pot preparation of 3-miktoarm star terpolymers via click [3 + 2] reaction. J. Polym. Sci. A Polym. Chem. 2007, 45, 3588–3598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.A.; Finn, M.G.; Koberstein, J.T.; Turro, N.J. Construction of Linear Polymers, Dendrimers, Networks, and Other Polymeric Architectures by Copper-Catalyzed Azide-Alkyne Cycloaddition “Click” Chemistry. Macromol. Rapid Comm. 2008, 29, 1052–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.H.; Wilson, J.; Chen, W.; Davis, R.M.; Riffle, J.S. A light-scattering study of poly(2-alkyl-2-oxazoline)s: effect of temperature and solvent type. Polymer 1994, 35, 3587–3591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmichael, A.Y.; Caba, B.L.; Huffstetler, P.P.; Davis, R.M.; Riffle, J.S. Synthesis and solution properties of poly(ethylene oxide-b-2-ethyl-2-oxazoline) and poly(ethylene oxide-b-ethyleneimine). Polym. Prepr. 2004, 45, 476–477. [Google Scholar]
- Schlaad, H.; Diehl, C.; Gress, A.; Meyer, M.; Demirel, A.L.; Nur, Y.; Bertin, A. Poly(2-oxazoline)s as Smart Bioinspired Polymers. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2010, 31, 511–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-S.; Kataoka, K. Comprehensive and Accurate Control of Thermosensitivity of Poly(2-alkyl-2-oxazoline)s via Well-Defined Gradient or Random Copolymerization. Macromolecules 2007, 40, 3599–3609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, M.; Lautenschlaeger, C.; Kempe, K.; Tauhardt, L.; Schubert, U.S.; Fischer, D. Poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline) as Alternative for the Stealth Polymer Poly(ethylene glycol): Comparison of in vitro Cytotoxicity and Hemocompatibility. Macromol. Biosci. 2012, 12, 986–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudolph, T.; Kempe, K.; Crotty, S.; Paulus, R.M.; Schubert, U.S.; Krossing, I.; Schacher, F.H. A strong cationic Bronsted acid, [H(OEt2)2][Al{OC(CF3)3}4], as an efficient initiator for the cationic ring-opening polymerization of 2-alkyl-2-oxazolines. Polym. Chem. 2013, 4, 495–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauhardt, L.; Kempe, K.; Knop, K.; Altuntaş, E.; Jäger, M.; Schubert, S.; Fischer, D.; Schubert, U.S. Linear Polyethyleneimine: Optimized Synthesis and Characterization—On the Way to “Pharmagrade” Batches. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2011, 212, 1918–1924. [Google Scholar]
- Einzmann, M.; Binder, W.H. Novel functional initiators for oxazoline polymerization. J. Polym. Sci. A Polym. Chem. 2001, 39, 2821–2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, S.; Uyama, H.; Narita, Y.; Ishiyama, J. Novel multifunctional initiators for polymerization of 2-oxazolines. Macromolecules 1992, 25, 3232–3236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knop, K.; Jahn, B.O.; Hager, M.D.; Crecelius, A.; Gottschaldt, M.; Schubert, U.S. Systematic MALDI-TOF CID Investigation on Different Substituted mPEG 2000. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2010, 211, 677–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Chau, Y. A facile synthesis of branched poly(ethylene glycol) and its heterobifunctional derivatives. Polym. Chem. 2011, 2, 873–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güner, P.T.; Demirel, A.L. Effect of Anions on the Cloud Point Temperature of Aqueous Poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline) Solutions. J. Phys. Chem. B 2012, 116, 14510–14514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christova, D.; Velichkova, R.; Loos, W.; Goethals, E.J.; Prez, F.D. New thermo-responsive polymer materials based on poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline) segments. Polymer 2003, 44, 2255–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, H.C.; Finn, M.G.; Sharpless, K.B. Click Chemistry: Diverse Chemical Function from a Few Good Reactions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2001, 40, 2004–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostovtsev, V.V.; Green, L.G.; Fokin, V.V.; Sharpless, K.B. A Stepwise Huisgen Cycloaddition Process: Copper(I)-Catalyzed Regioselective “Ligation” of Azides and Terminal Alkynes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2002, 114, 2708–2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, F.; Mo, X.; Yang, R.; Wang, Y.; Liang, D. Association of Block Copolymer in Nonselective Solvent. Macromolecules 2009, 42, 5339–5344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, M.I.; Ahmed, H.; Trathnigg, B. Liquid chromatography under critical conditions: practical applications in the analysis of amphiphilic polymers. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 393, 1797–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falkenhagen, J.; Much, H.; Stauf, W.; Müller, A.H.E. Characterization of Block Copolymers by Liquid Adsorption Chromatography at Critical Conditions. 1. Diblock Copolymers. Macromolecules 2000, 33, 3687–3693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Khan, S.; Wang, Y. Retention Behaviors of Block Copolymers in Liquid Chromatography at the Critical Condition. Macromolecules 2005, 38, 7514–7520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharghi, H.; Khalifeh, R.; Doroodmand, M.M. Immobilization of Porphyrinatocopper Nanoparticles onto Activated Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes and a Study of its Catalytic Activity as an Efficient Heterogeneous Catalyst for a Click Approach to the Three-Component Synthesis of 1,2,3-Triazoles in Water. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2009, 351, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegast, G.; Pfannemüller, B. Linear and star-shaped hybrid polymers, 1. A new method for the conversion of hydroxyl end groups of poly(oxyethylene) and other polyols into amino end groups. Makromol. Chem. 1984, 5, 363–371. [Google Scholar]
- Özdemir, C.; Güner, A. Solubility profiles of poly(ethylene glycol)/solvent systems, I: Qualitative comparison of solubility parameter approaches. Eur. Polym. J. 2007, 43, 3068–3093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakashima, K.; Bahadur, P. Aggregation of water-soluble block copolymers in aqueous solutions: Recent trends. Adv. Col. Int. Sci. 2006, 123–126, 75–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casse, O.; Shkilnyy, A.; Linders, J.; Mayer, C.; Häussinger, D.; Völkel, A.; Thünemann, A.F.; Dimova, R.; Cölfen, H.; Meier, W.; Schlaad, H.; Taubert, A. Solution Behavior of Double-Hydrophilic Block Copolymers in Dilute Aqueous Solution. Macromolecules 2012, 45, 4772–4777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambermont-Thijs, H.M.L.; Kuringen, H.P.C.V.; Put, J.P.W.V.D.; Schubert, U.S.; Hoogenboom, R. Temperature Induced Solubility Transitions of Various Poly(2-oxazoline)s in Ethanol-Water Solvent Mixtures. Polymers 2010, 2, 188–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guner, P.T.; Miko, A.; Schweinberger, F.F.; Demirel, A.L. Self-assembled poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline) fibers in aqueous solutions. Polym. Chem. 2012, 3, 322–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Zhang, G.; Zhu, L.; Chen, D.; Jiang, M. Nanoscale tubular and sheetlike superstructures from hierarchical self-assembly of polymeric janus particles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 10171–10174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, K.; Chen, D.; Jiang, M.; Liu, S. Transforming spherical block polyelectrolyte micelles into free-suspending films via DNA complexation-induced structural anisotropy. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 6135–6137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Rudolph, T.; Crotty, S.; Von der Lühe, M.; Pretzel, D.; Schubert, U.S.; Schacher, F.H. Synthesis and Solution Properties of Double Hydrophilic Poly(ethylene oxide)-block-poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline) (PEO-b-PEtOx) Star Block Copolymers. Polymers 2013, 5, 1081-1101. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym5031081
Rudolph T, Crotty S, Von der Lühe M, Pretzel D, Schubert US, Schacher FH. Synthesis and Solution Properties of Double Hydrophilic Poly(ethylene oxide)-block-poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline) (PEO-b-PEtOx) Star Block Copolymers. Polymers. 2013; 5(3):1081-1101. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym5031081
Chicago/Turabian StyleRudolph, Tobias, Sarah Crotty, Moritz Von der Lühe, David Pretzel, Ulrich S. Schubert, and Felix H. Schacher. 2013. "Synthesis and Solution Properties of Double Hydrophilic Poly(ethylene oxide)-block-poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline) (PEO-b-PEtOx) Star Block Copolymers" Polymers 5, no. 3: 1081-1101. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym5031081
APA StyleRudolph, T., Crotty, S., Von der Lühe, M., Pretzel, D., Schubert, U. S., & Schacher, F. H. (2013). Synthesis and Solution Properties of Double Hydrophilic Poly(ethylene oxide)-block-poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline) (PEO-b-PEtOx) Star Block Copolymers. Polymers, 5(3), 1081-1101. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym5031081