Low MXene Loading of Epoxy Composite with Enhanced Hydrothermal Resistance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiments
2.1. Materials
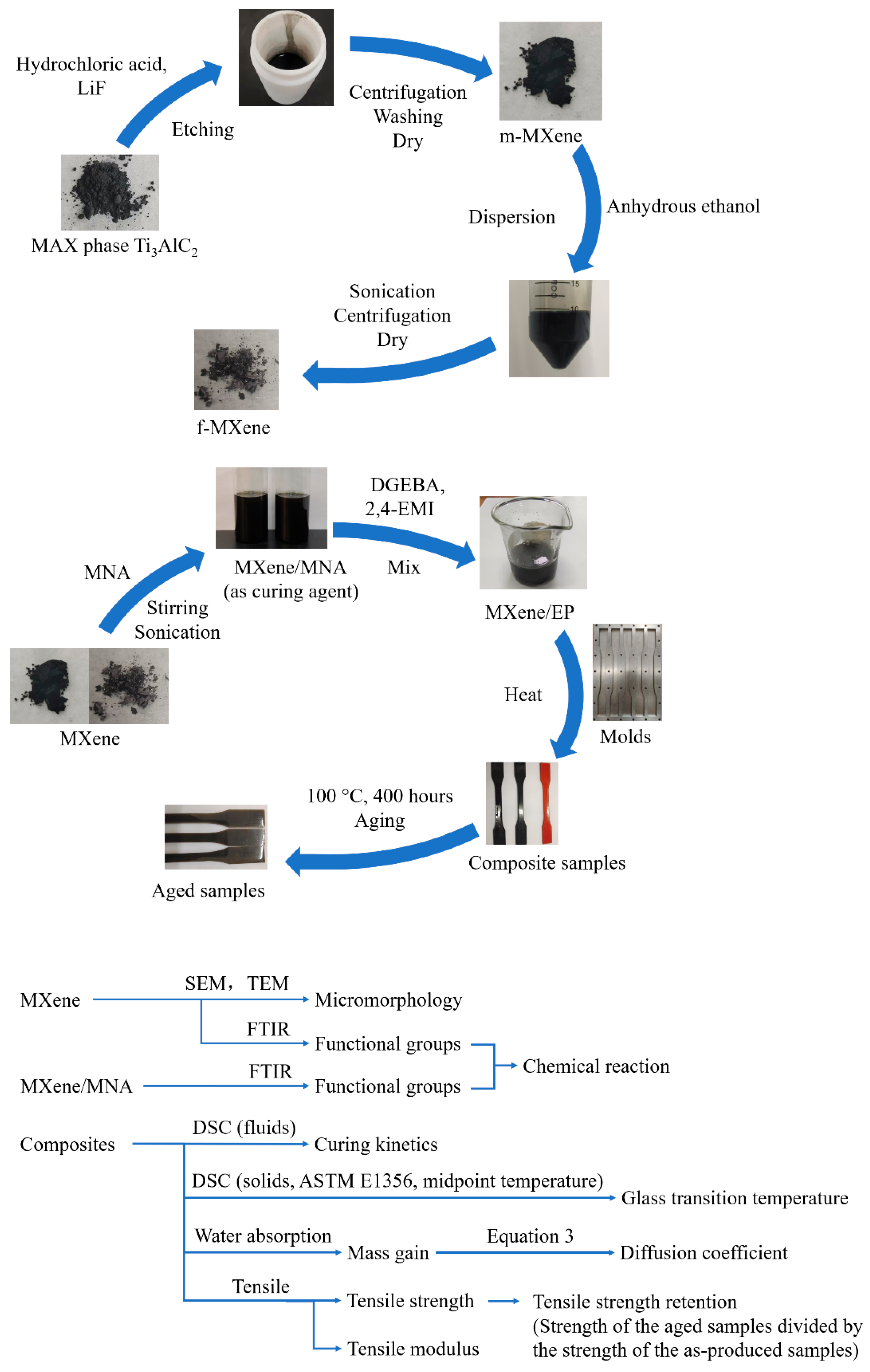
2.2. Preparation of MXene
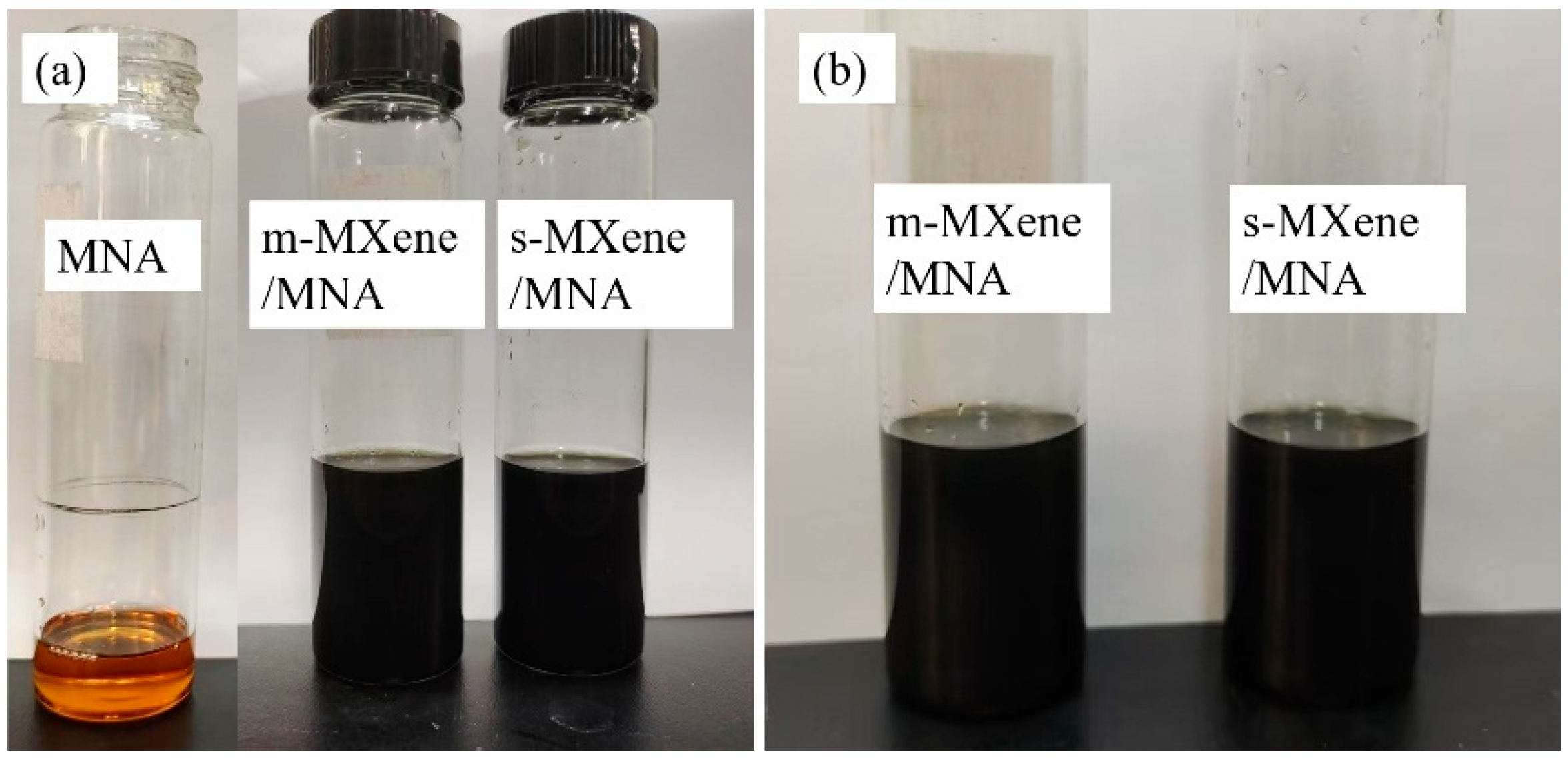
2.3. Preparation of MXene/EP Composites
2.4. Aging
2.5. Characterization
2.5.1. Tensile
2.5.2. Microstructure
2.5.3. Water Absorption
2.5.4. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy
2.5.5. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Micromorphology
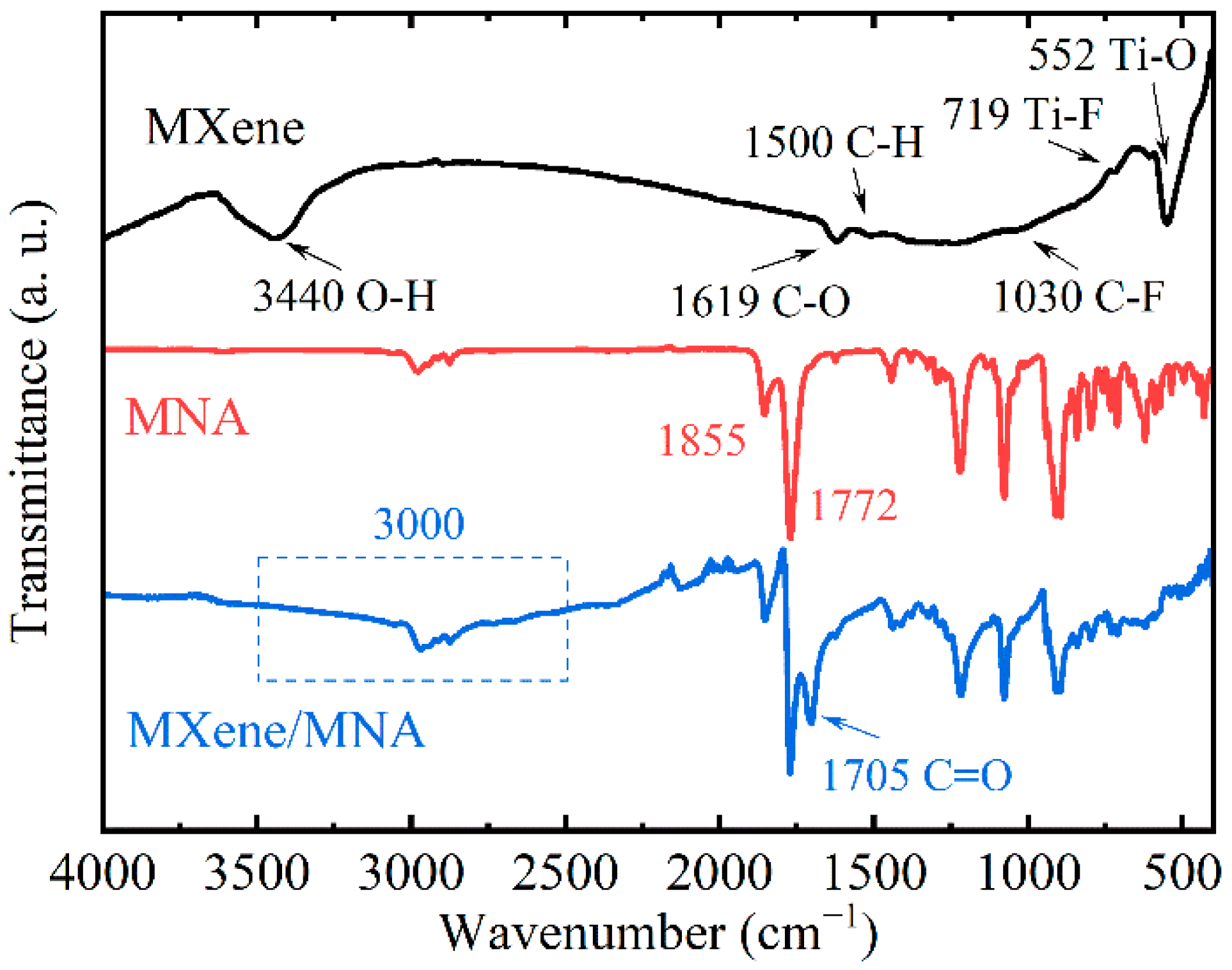
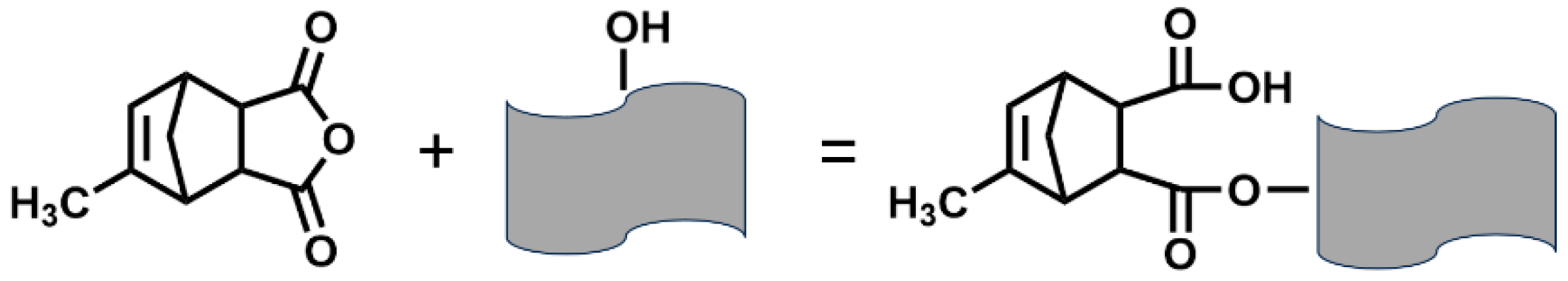
3.2. Functional Group Analysis
3.3. Curing Kinetics
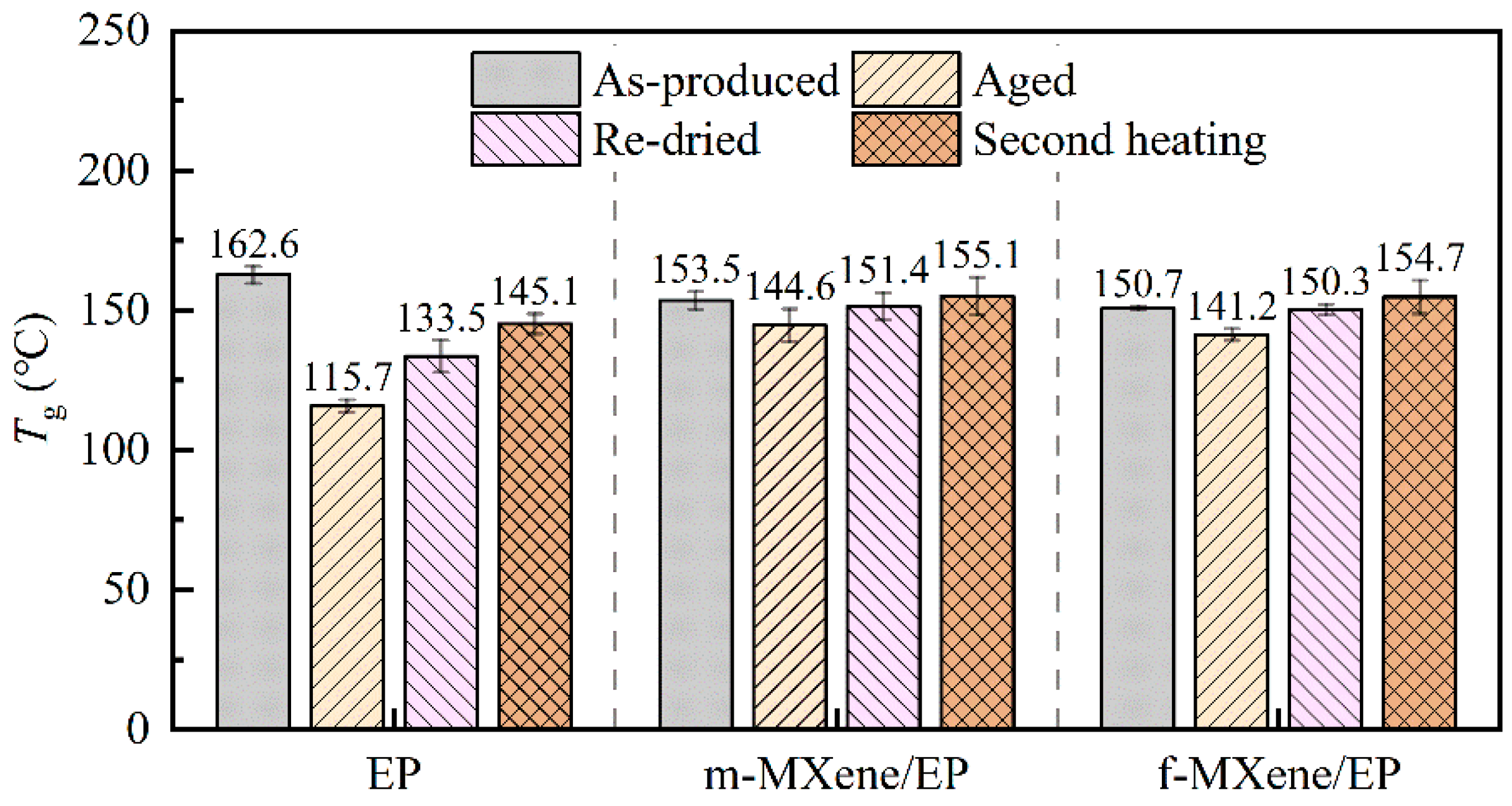
3.4. Glass Transition Temperature
3.5. Water Absorption
3.6. Tensile Properties’ Evolution
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Henry Lee, K.N. Handbook of Epoxy Resins; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Aung, H.H.; Du, B. Curing Regime-Modulating Insulation Performance of Anhydride-Cured Epoxy Resin: A Review. Molecules 2023, 28, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, F.-L.; Li, X.; Park, S.-J. Synthesis and application of epoxy resins: A review. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 29, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apicella, A.; Nicolais, L.; de Cataldis, C. Characterization of the morphological fine structure of commercial thermosetting resins through hygrothermal experiments. In Characterization of Polymers in the Solid State I: Part A: NMR and Other Spectroscopic Methods Part B: Mechanical Methods; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1985; pp. 189–207. [Google Scholar]
- Moy, P.; Karasz, F.E. Epoxy-water interactions. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1980, 20, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Lucas, J.P. Hygrothermal effects of epoxy resin. Part I: The nature of water in epoxy. Polymer 1999, 40, 5505–5512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Xu, X.; Ji, J.; Yang, Y.; Shen, J.; Ye, M. The hygrothermal aging process and mechanism of the novolac epoxy resin. Compos. Part B Eng. 2016, 107, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevalier, M.; Dantras, E.; Tonon, C.; Guigue, P.; Lacabanne, C.; Puig, C.; Durin, C. Correlation between sub-T relaxation processes and mechanical behavior for different hydrothermal ageing conditions in epoxy assemblies. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 115, 1208–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillet, C.; Tamssaouet, F.; Hassoune-Rhabbour, B.; Tchalla, T.; Nassiet, V. Parameters Influencing Moisture Diffusion in Epoxy-Based Materials during Hygrothermal Ageing-A Review by Statistical Analysis. Polymers 2022, 14, 2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewimille, B.; Bunsell, A.R. Accelerated ageing of a glass fibre-reinforced epoxy resin in water. Composites 1983, 14, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odegard, G.M.; Bandyopadhyay, A. Physical aging of epoxy polymers and their composites. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2011, 49, 1695–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, I.B.C.M.; van der Meer, F.P.; Raijmaekers, S.; Lahuerta, F.; Nijssen, R.P.L.; Sluys, L.J. Numerical/experimental study of the monotonic and cyclic viscoelastic/viscoplastic/fracture behavior of an epoxy resin. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2019, 168, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starkova, O.; Chandrasekaran, S.; Prado, L.A.S.A.; Tölle, F.; Mülhaupt, R.; Schulte, K. Hydrothermally resistant thermally reduced graphene oxide and multi-wall carbon nanotube based epoxy nanocomposites. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2013, 98, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starkova, O.; Gaidukovs, S.; Platnieks, O.; Barkane, A.; Garkusina, K.; Palitis, E.; Grase, L. Water absorption and hydrothermal ageing of epoxy adhesives reinforced with amino-functionalized graphene oxide nanoparticles. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2021, 191, 109670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaskova-Kuzmina, T.; Aniskevich, A.; Papanicolaou, G.; Portan, D.; Zotti, A.; Borriello, A.; Zarrelli, M. Hydrothermal Aging of an Epoxy Resin Filled with Carbon Nanofillers. Polymers 2020, 12, 1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaskova-Kuzmina, T.; Aniskevich, A.; Sevcenko, J.; Borriello, A.; Zarrelli, M. Cyclic Moisture Sorption and its Effects on the Thermomechanical Properties of Epoxy and Epoxy/MWCNT Nanocomposite. Polymers 2019, 11, 1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prolongo, S.G.; Jiménez-Suárez, A.; Moriche, R.; Ureña, A. Influence of Thickness and Lateral Size of Graphene Nanoplatelets on Water Uptake in Epoxy/Graphene Nanocomposites. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naguib, M.; Kurtoglu, M.; Presser, V.; Lu, J.; Niu, J.; Heon, M.; Hultman, L.; Gogotsi, Y.; Barsoum, M.W. Two-Dimensional Nanocrystals Produced by Exfoliation of Ti3AlC2. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 4248–4253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Zhou, D.; Yang, J.; Zhou, S.; Wang, H.; Yuan, X.; Liang, J.; Li, X.; Chen, Y.; Li, H. 2D single- and few-layered MXenes: Synthesis, applications and perspectives. J. Mater. Chem. A 2022, 10, 13651–13672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, N.; Kushwaha, A.; Kumar, M. Two-dimensional MXenes: Recent emerging applications. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 25172–25193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimenez, R.; Serrano, B.; San-Miguel, V.; Cabanelas, J.C. Recent Advances in MXene/Epoxy Composites: Trends and Prospects. Polymers 2022, 14, 1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Liu, S.; Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Liu, C.; Shen, C. Advances in multifunctional flexible MXene-based stress sensors. J. Mater. Chem. C 2024, 12, 7845–7861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Liu, C.; Cheng, H.; Jiang, C.; Zhou, B.; Huang, M.; Liu, C.; Feng, Y. Recent progress of Ti3C2Tx MXene-based layered films for electromagnetic interference shielding. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2025, 223, 131–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, C.; Zehra, S.; Aslam, R.; Aslam, J.; Quraishi, M.A.; Mobin, M. MXenes as Emerging 2D Materials for Anticorrosive Application: Challenges and Opportunities. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 9, 2200579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, M.S.; Sokol, M.; Palmese, G.R.; Barsoum, M.W. Water Transport and Thermomechanical Properties of Ti3C2Tz MXene Epoxy Nanocomposites. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 39143–39149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Ying, G.; Wen, D.; Zhang, K.; Hu, C.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wang, X.; Wang, C. Aqueous solution-processed MXene (Ti3C2Tx) for non-hydrophilic epoxy resin-based composites with enhanced mechanical and physical properties. Mater. Des. 2021, 197, 109276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janjua, A.A.; Younas, M.; Ilyas, R.A.; Shyha, I.; Faisal, N.H.; Inam, F.; Saharudin, M.S. Optimizing DMF Utilization for Improved MXene Dispersions in Epoxy Nanocomposites. J. Compos. Sci. 2024, 8, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, R.; Zhao, J.; Lv, N.; Fu, A.; Yin, C.; Song, C.; Chao, M. Curing and Molecular Dynamics Simulation of MXene/Phenolic Epoxy Composites with Different Amine Curing Agent Systems. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wazalwar, R.; Tripathi, M.; Raichur, A.M. Curing Behavior and Mechanical Properties of Tetra-Functional Epoxy Reinforced with Polyethyleneimine-Functionalized MXene. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2022, 4, 2573–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sliozberg, Y.; Andzelm, J.; Hatter, C.B.; Anasori, B.; Gogotsi, Y.; Hall, A. Interface binding and mechanical properties of MXene-epoxy nanocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2020, 192, 108124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, D.-Y.; Guo, F.-L.; Hou, W.-D.; Long, J.-F.; Li, Y.-Q.; Fu, S.-Y. Cryogenic mechanical properties and liquid oxygen compatibility of MXene/epoxy nanocomposites. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2024, 7, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourhashem, S.; Seif, A.; Zhou, Z.; Ji, X.; Sgroi, M.F.; Duan, J.; Rashidi, A.; Ci, X.; Lu, H.; Mirzaee, M.; et al. Theoretical and experimental investigations about the role of MXene nanosheets covered with ZnO quantum dots on barrier resistance of epoxy coatings. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 111869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Zhou, M.; Yu, H. Interfacial combination of Ti3C2Tx MXene with waterborne epoxy anticorrosive coating. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 572, 150894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Chao, M.; Li, L.; Luo, C.; Chen, X.; Yan, L. Silane-Modified MXene Nanosheets for Improved Anticorrosive Properties of Epoxy Coatings: A Combined Experimental and Computational Study. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2024, 7, 20509–20522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D638-22; Standard Test Method for Tensile Properties of Plastics. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2022.
- Parker, T.; Zhang, D.; Bugallo, D.; Shevchuk, K.; Downes, M.; Valurouthu, G.; Inman, A.; Chacon, B.; Zhang, T.; Shuck, C.E.; et al. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectral Library of MXenes. Chem. Mater. 2024, 36, 8437–8446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delor-Jestin, F.; Drouin, D.; Cheval, P.Y.; Lacoste, J. Thermal and photochemical ageing of epoxy resin—Influence of curing agents. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2006, 91, 1247–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Q.; Chen, Q.; Gu, W.; Wang, R.; Gu, X.; Liu, J.; Sun, T.; Chen, Y.; Sun, J.; Zhang, S. The study of curing behavior and thermo-mechanical properties of epoxy adhesives with different anhydrides. Polymer 2024, 307, 127342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Jiang, W.; Hu, B.; Liang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Kang, J.; Cao, Y.; Xiang, M. Effects of graphene oxide size on curing kinetics of epoxy resin. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 29215–29226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, M.; Wang, K.; Lu, H.; Yang, Y.; Nutt, S. Covalent polymer functionalization of graphene nanosheets and mechanical properties of composites. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 7098–7105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, K.; Lv, S.; Zhou, Y.; Ma, X.; Tang, J. Synergistic Effect of Graphene Oxide and OH-MWCNTs on the Cure Kinetics of an Epoxy-Anhydride System. Mater. Trans. 2019, 60, 616–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kissinger, H.E. Reaction Kinetics in Differential Thermal Analysis. Anal. Chem. 1957, 29, 1702–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putz, K.W.; Palmeri, M.J.; Cohn, R.B.; Andrews, R.; Brinson, L.C. Effect of Cross-Link Density on Interphase Creation in Polymer Nanocomposites. Macromolecules 2008, 41, 6752–6756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jojibabu, P.; Ram, G.D.J.; Deshpande, A.P.; Bakshi, S.R. Effect of carbon nano-filler addition on the degradation of epoxy adhesive joints subjected to hygrothermal aging. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2017, 140, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Koh, K.L.; Lu, J.; Yang, L.; Phua, S.; Kong, J.; Chen, Z.; Lu, X. Simultaneous catalyzing and reinforcing effects of imidazole-functionalized graphene in anhydride-cured epoxies. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 18395–18402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Hu, X.; Jiang, Q.; Sun, Z.; Wang, P.; Qiu, Y.; Liu, W. Influence of graphene oxide with different oxidation levels on the properties of epoxy composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2018, 161, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.S.; Jeon, I.Y.; Ahn, S.N.; Kwon, Y.D.; Baek, J.B. Edge-functionalized graphene-like platelets as a co-curing agent and a nanoscale additive to epoxy resin. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 7337–7342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balguri, P.K.; Samuel, D.G.H.; Thumu, U. A review on mechanical properties of epoxy nanocomposites. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 44, 346–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Liu, S.P.; Liu, R.T.; Geng, C.J.; Hu, Z.D. Preparation and Characterization of Hydrophilic Wetting-Modified Polyamide Fibers. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2020, 2020, 8475497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoramishad, H.; Hamed, B.; Kordzangeneh, D. The deleterious effect of cyclic hygrothermal aging on nanocomposite adhesives. J. Adhes. 2022, 98, 507–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasi, J.M.; Helman, I.D.; Pisani, W.A.; Klimek-McDonald, D.R.; Chinkanjanarot, S.; Miskioglu, I.; King, J.A.; Odegard, G.M. Accelerated hydrothermal aging of cycloaliphatic epoxy/graphene nanoparticle composites. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2016, 133, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jing, M.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, S.; Li, M.; Chen, F.; Ma, Y.; Sun, B. Low MXene Loading of Epoxy Composite with Enhanced Hydrothermal Resistance. Polymers 2025, 17, 1229. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17091229
Jing M, Zhang S, Zhang S, Li M, Chen F, Ma Y, Sun B. Low MXene Loading of Epoxy Composite with Enhanced Hydrothermal Resistance. Polymers. 2025; 17(9):1229. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17091229
Chicago/Turabian StyleJing, Mengke, Shujie Zhang, Sichang Zhang, Mingzhou Li, Fan Chen, Yuchen Ma, and Bo Sun. 2025. "Low MXene Loading of Epoxy Composite with Enhanced Hydrothermal Resistance" Polymers 17, no. 9: 1229. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17091229
APA StyleJing, M., Zhang, S., Zhang, S., Li, M., Chen, F., Ma, Y., & Sun, B. (2025). Low MXene Loading of Epoxy Composite with Enhanced Hydrothermal Resistance. Polymers, 17(9), 1229. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17091229






