The Study on the Effect of Waterborne Epoxy Resin Content on the Performance of Styrene–Butadiene Rubber Modified Micro-Surface Mixture
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Emulsified Asphalt
2.1.2. Modifier
2.1.3. Aggregates
2.1.4. Fillert
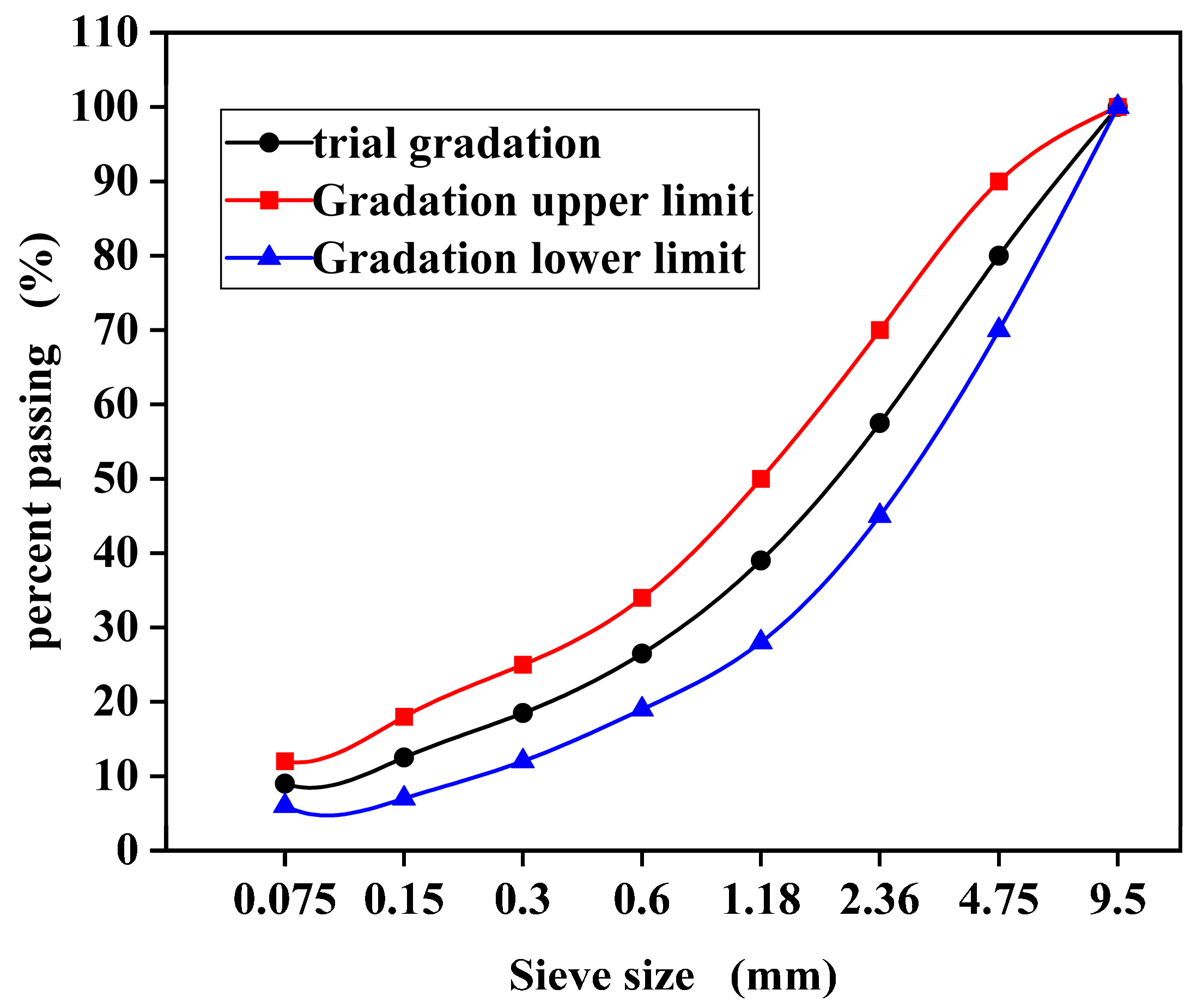
2.2. Gradation
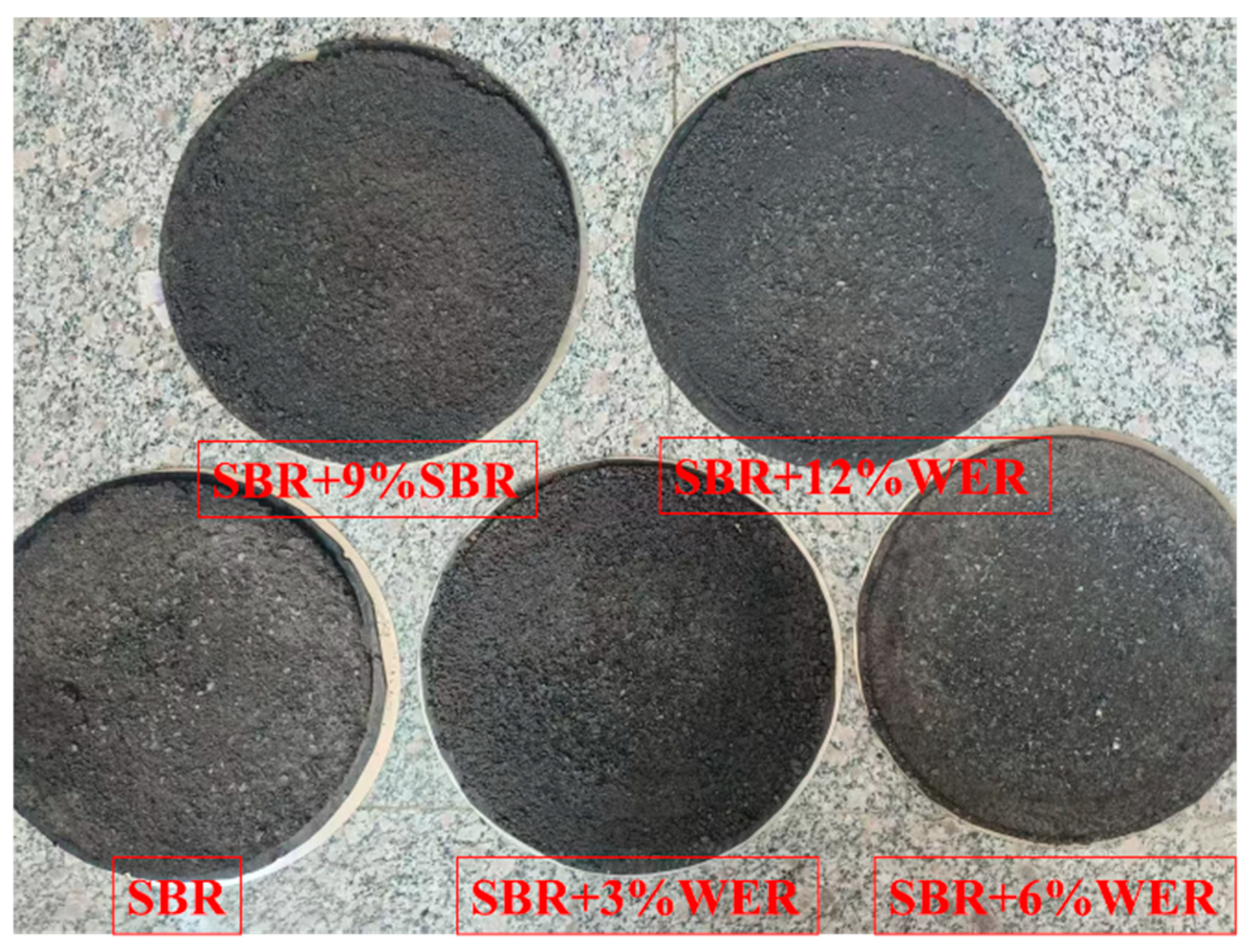
2.3. Experimental Design
2.4. Determination of the Asphalt–Aggregate Ratio of Micro-Surfacing Mixture
| Asphalt–Aggregate Ratio (%) | Dry Material 1 (g) | Water (g) | BC-1 Emulsified Asphalt (g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 6.5 | 106 | 7 | 6.5 |
| 7 | 106 | 7 | 7 |
| 7.5 | 106 | 7 | 7.5 |
| 8 | 106 | 7 | 8 |
| 8.5 | 106 | 7 | 8.5 |
| 9 | 106 | 7 | 9 |
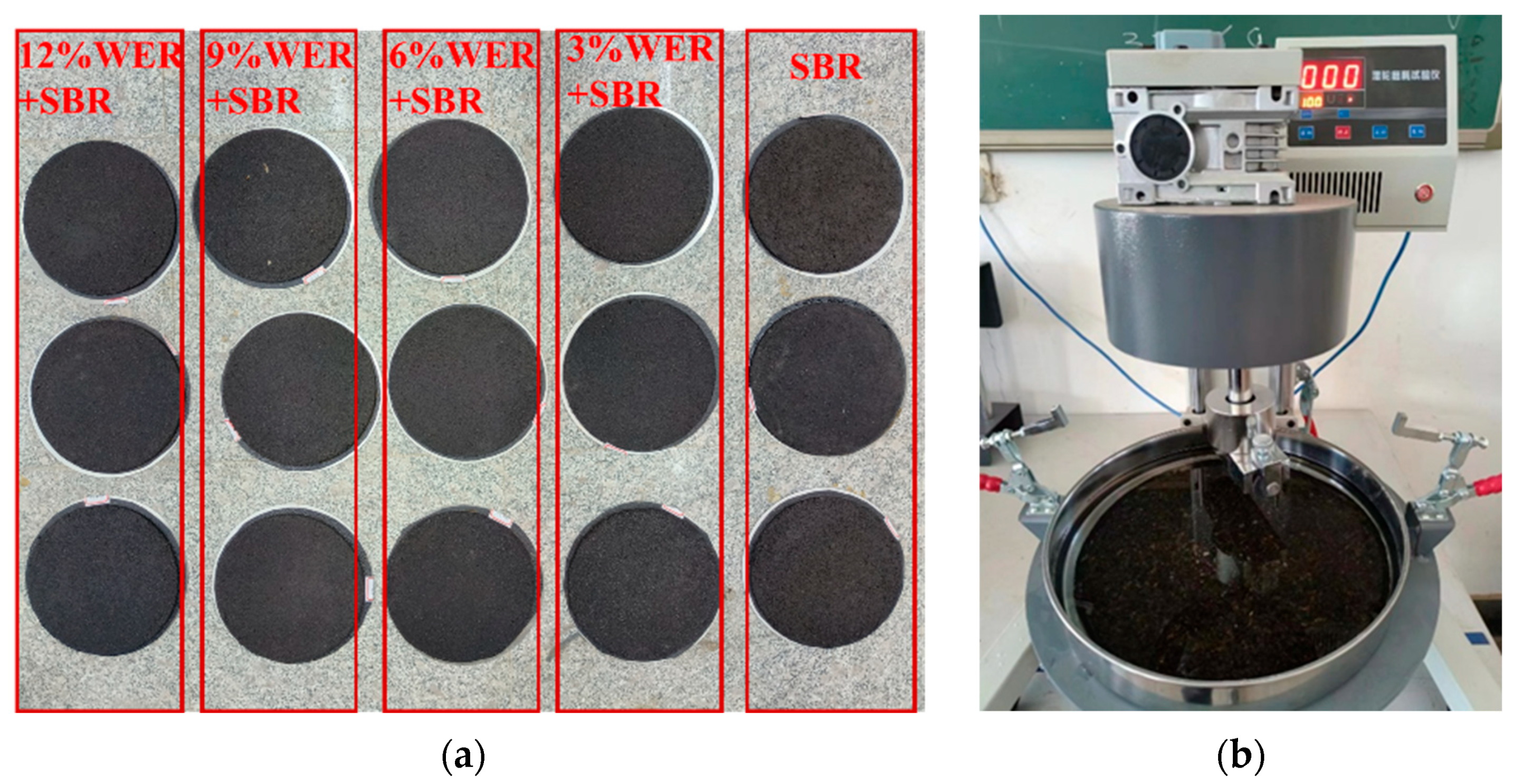
2.5. Wet Wheel Abrasion Test
2.6. Rutting Deformation Test
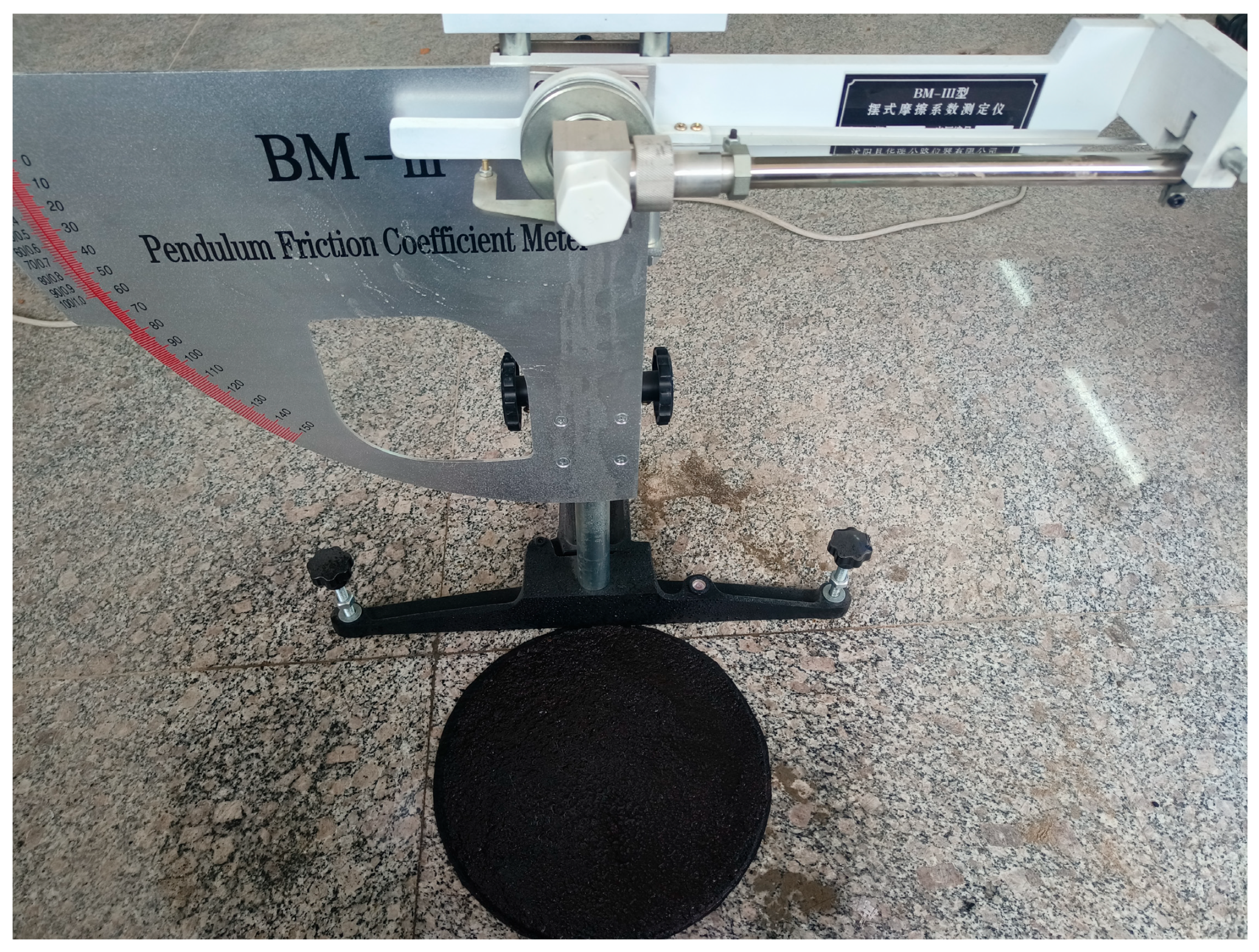
2.7. Anti-Skid Performance Test
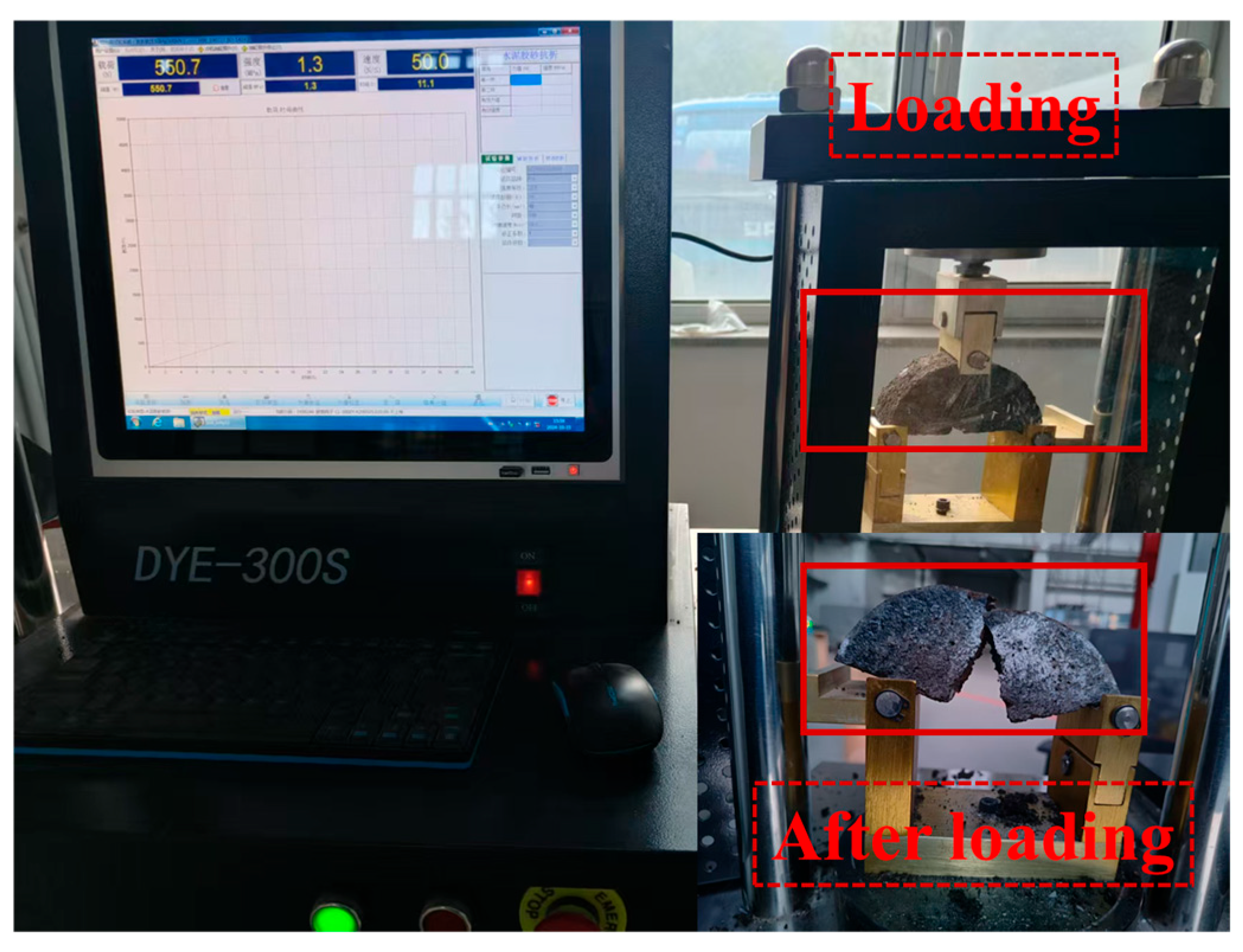
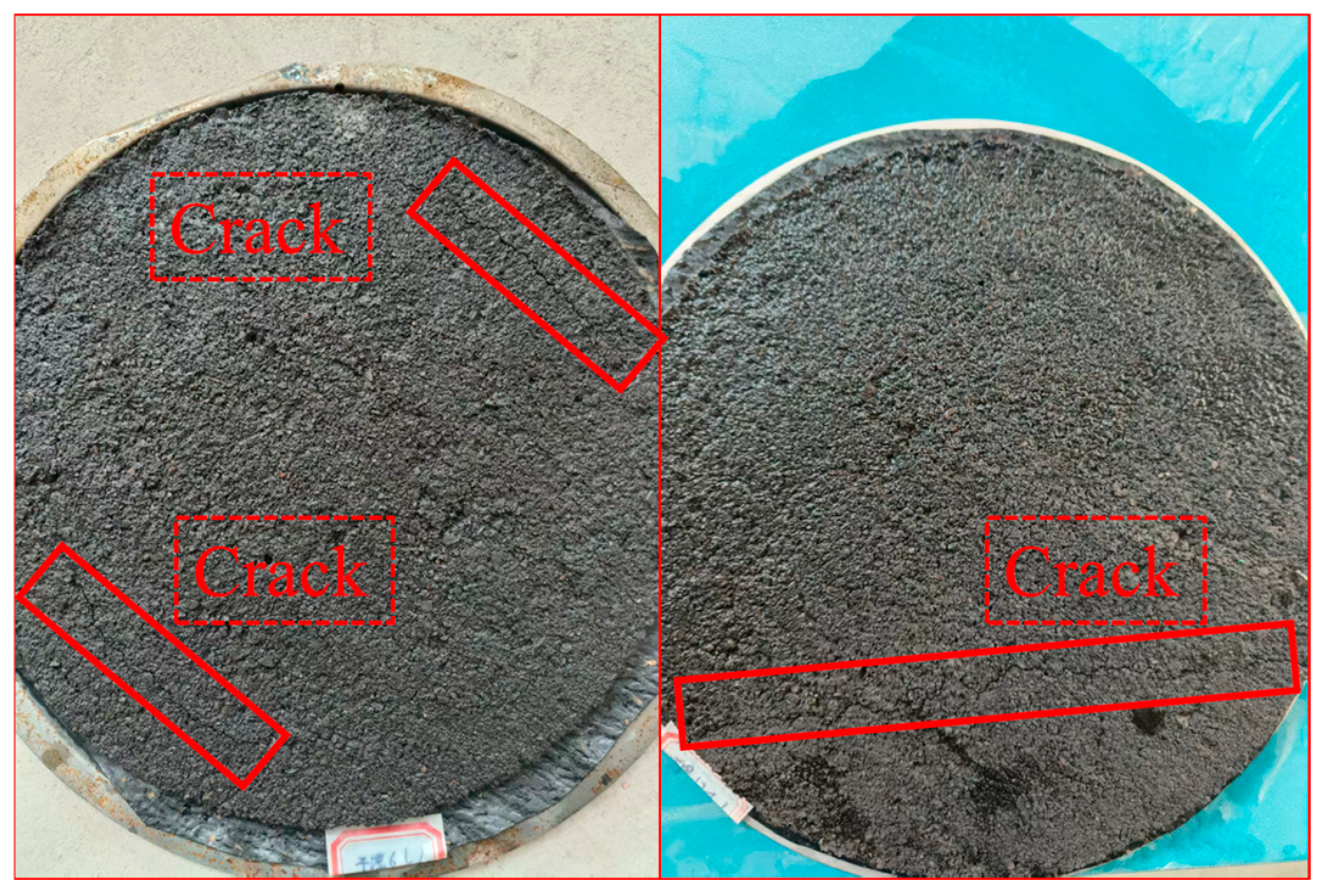
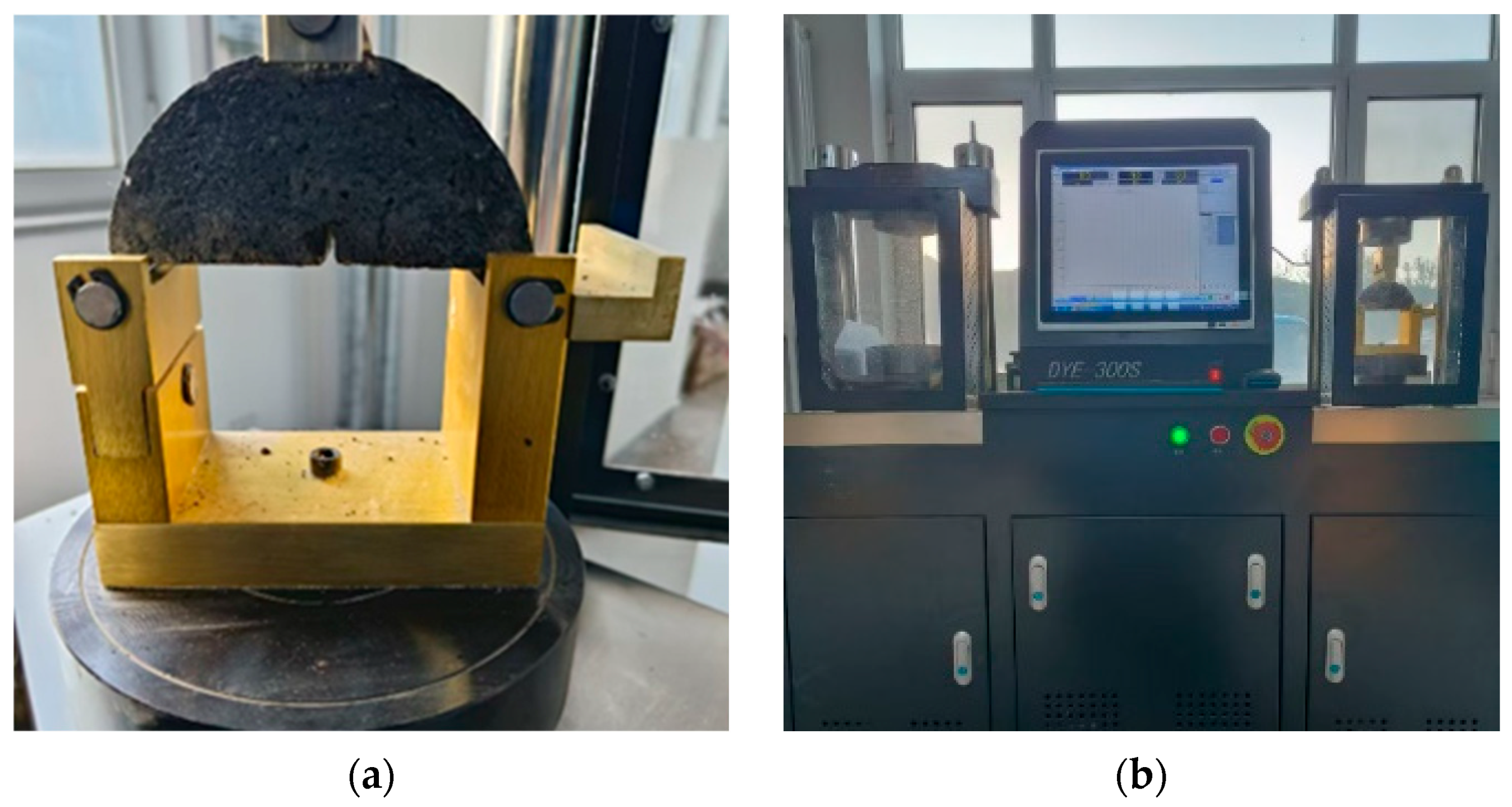
2.8. Semi-Circular Bending Test
2.9. Freeze–Thaw Cycle Test
2.10. Damp–Dry Cycle Test
2.11. Salt Fog Test
2.12. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) Test
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Results of the Asphalt–Aggregate Ratio of the Micro-Surfacing Mixture
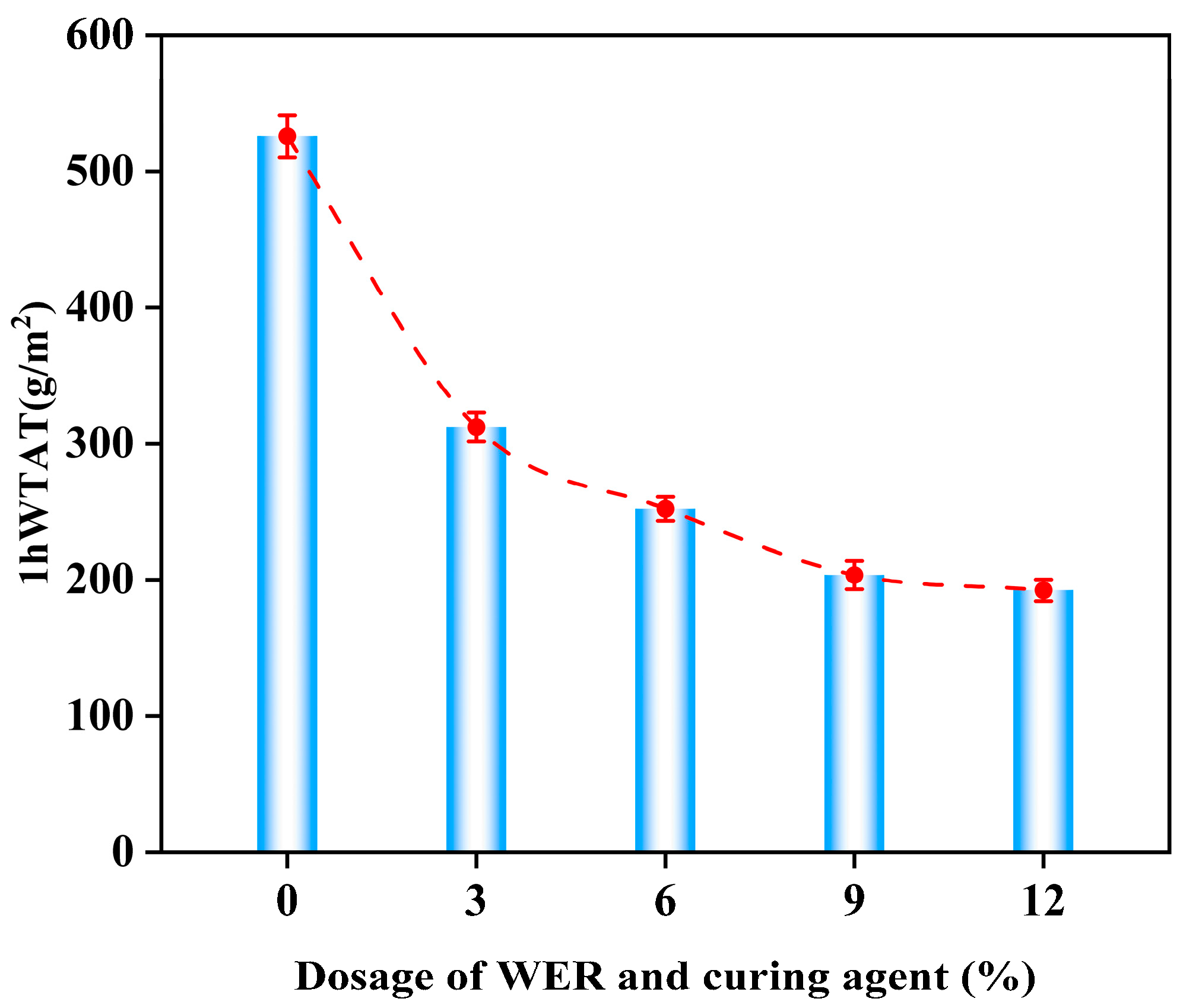
3.2. Wear Resistance Performance
3.3. Water Stability
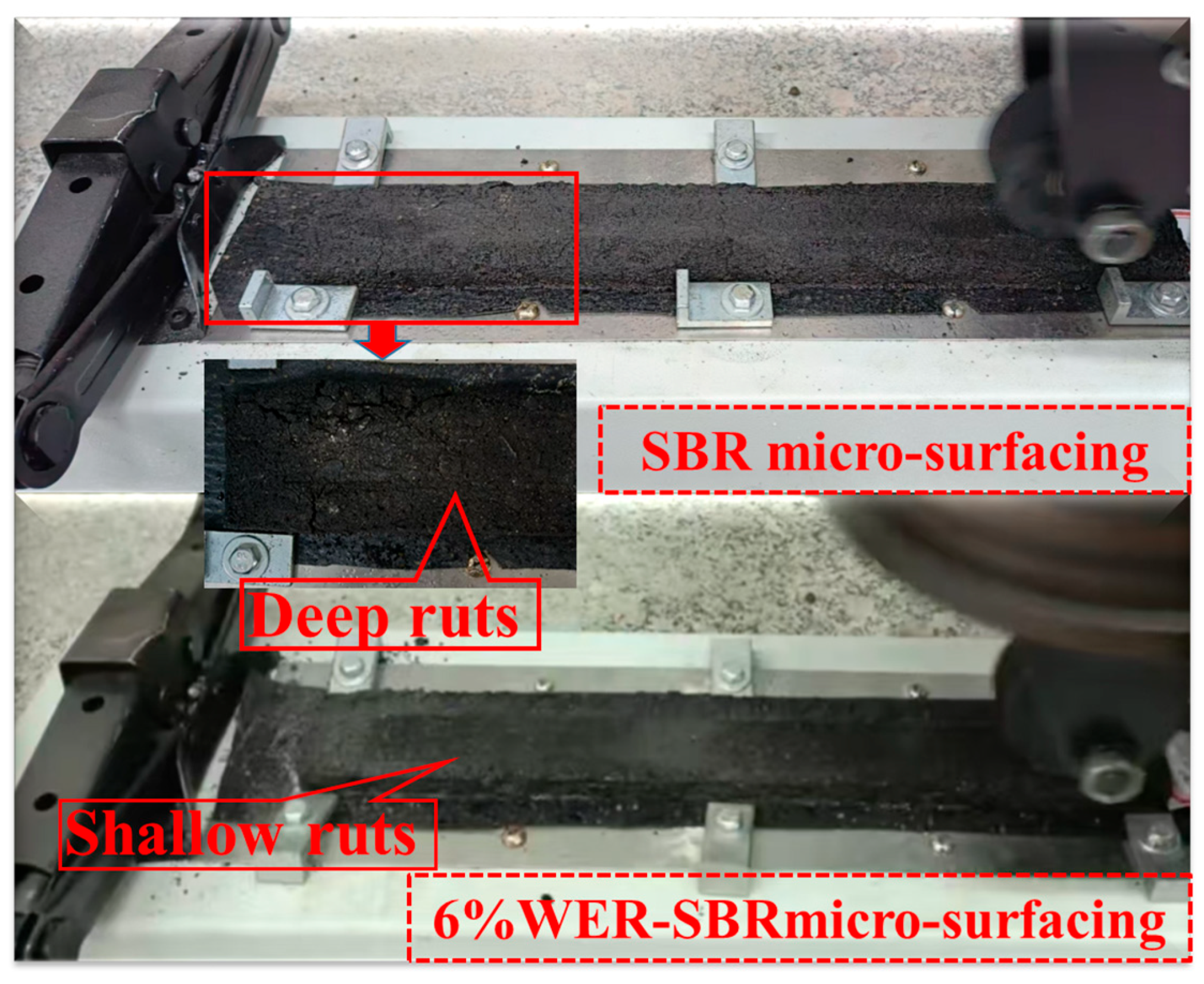
3.4. Rutting Resistance
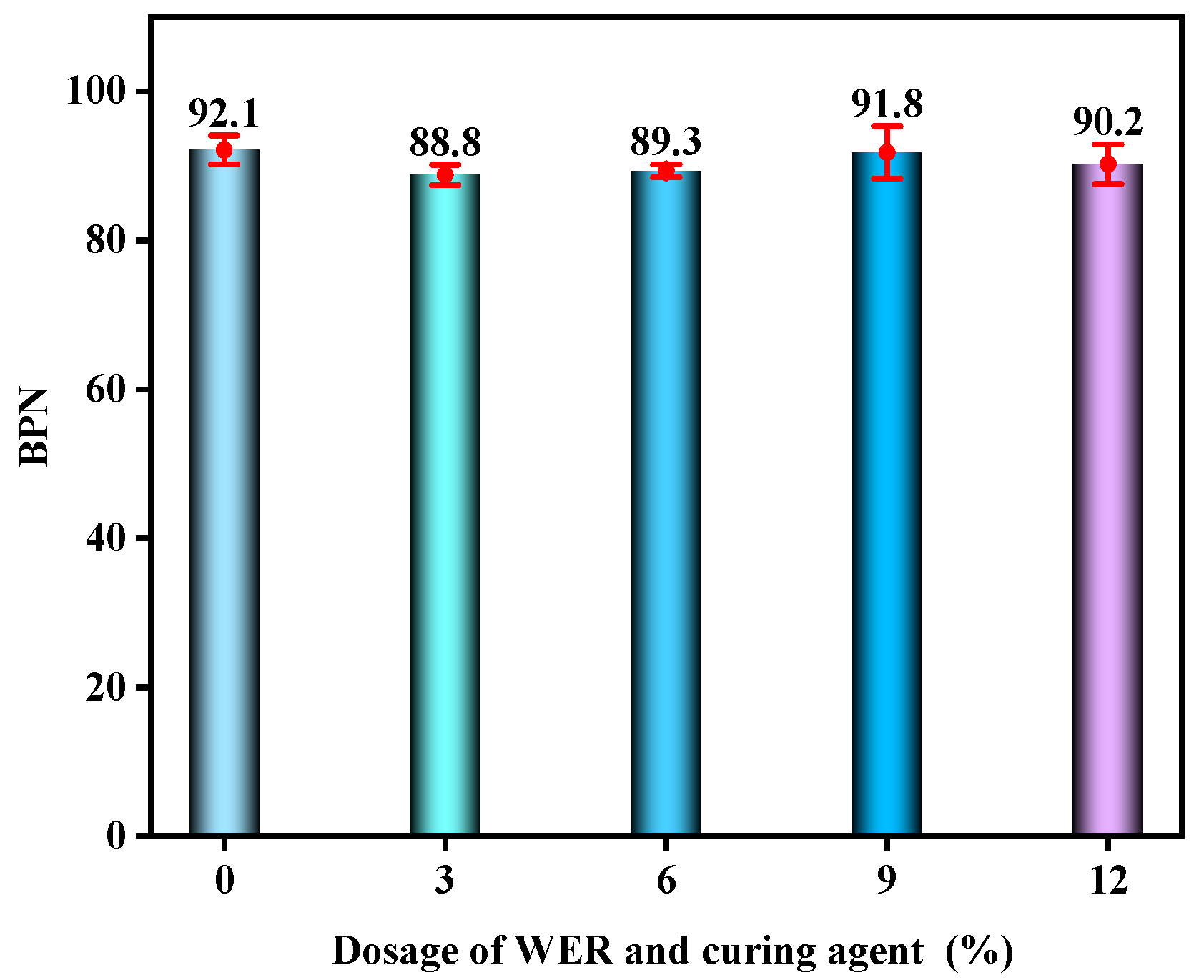
3.5. Skid Resistance
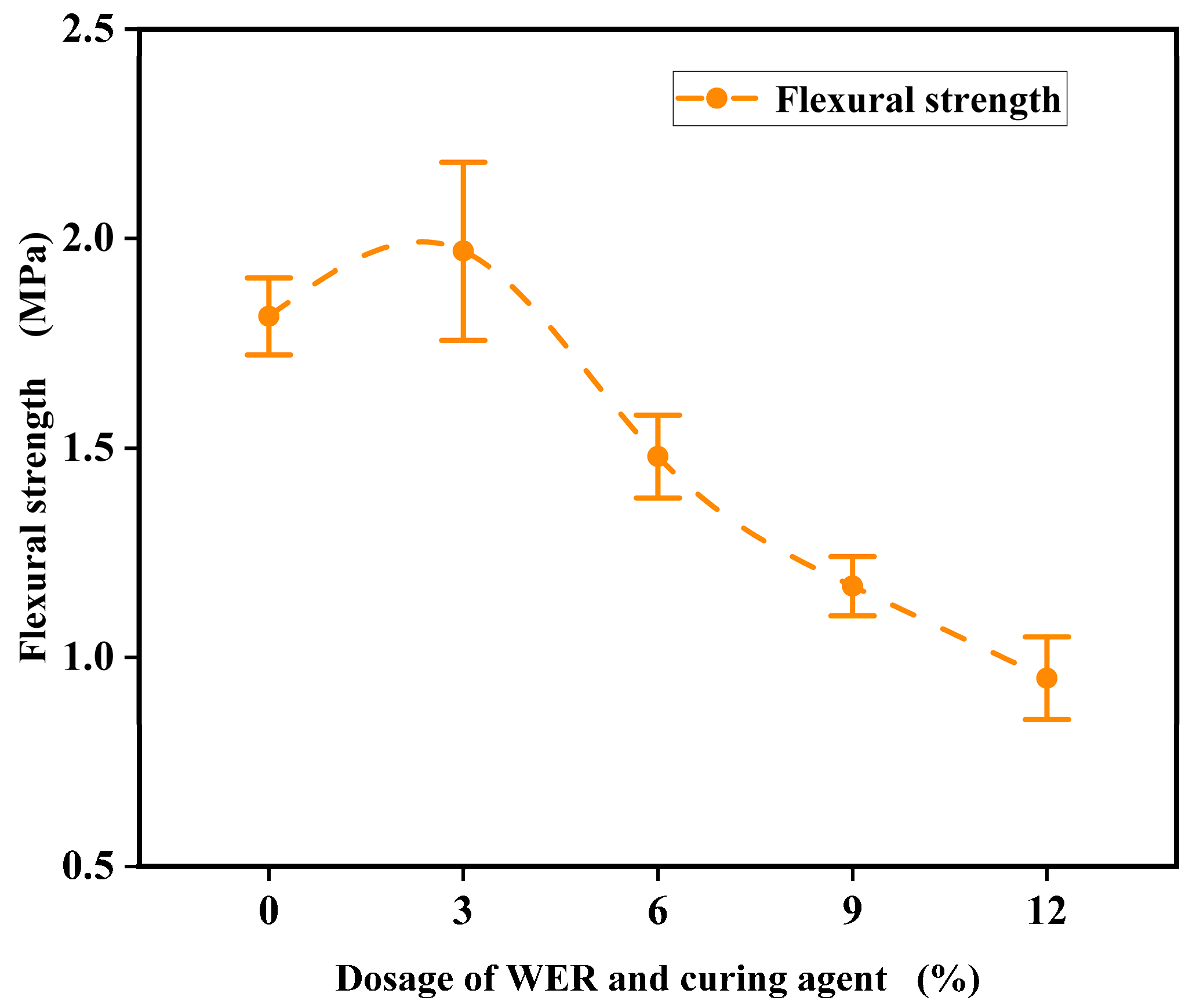
3.6. Low-Temperature Crack Resistance
3.7. Durability Performance
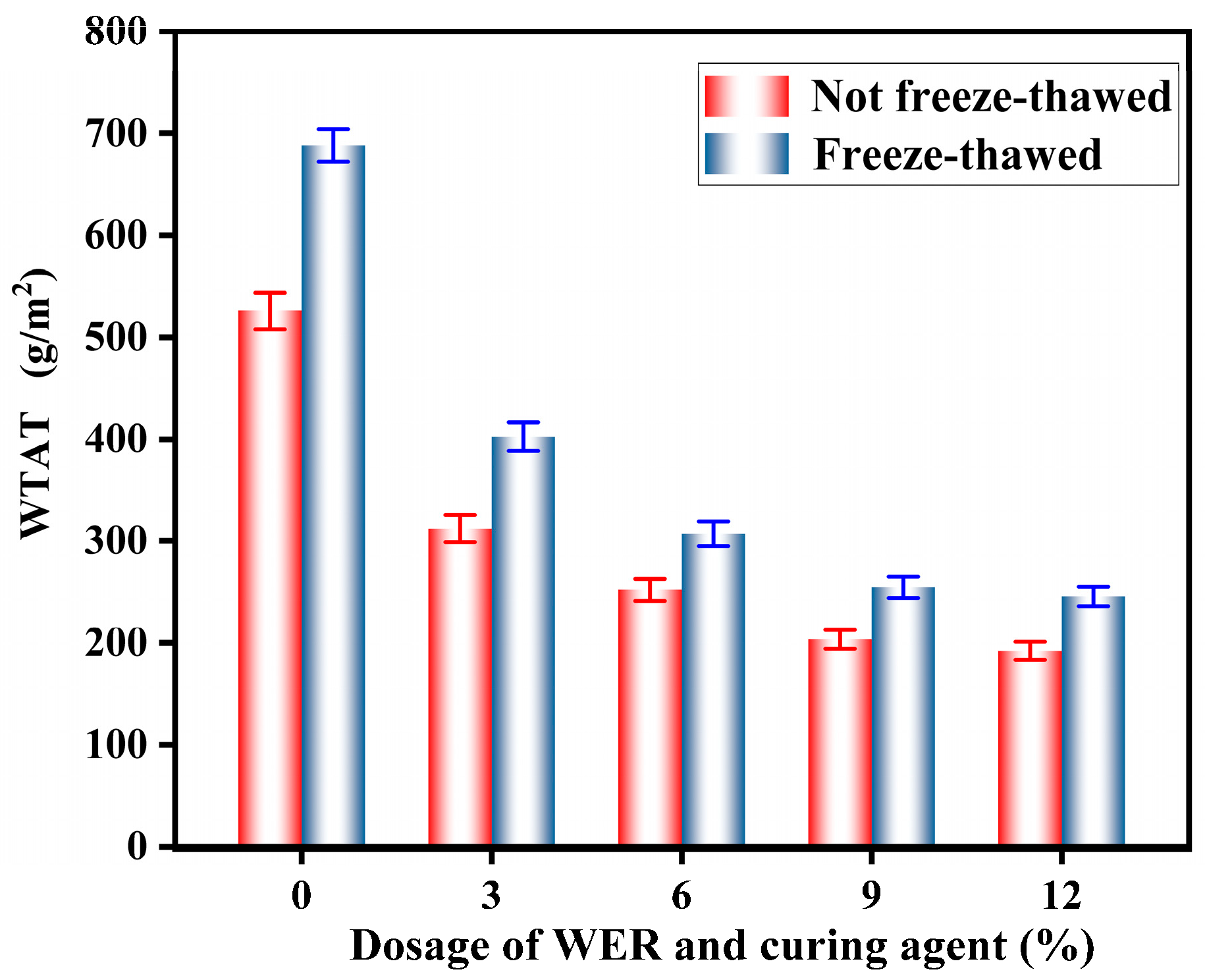
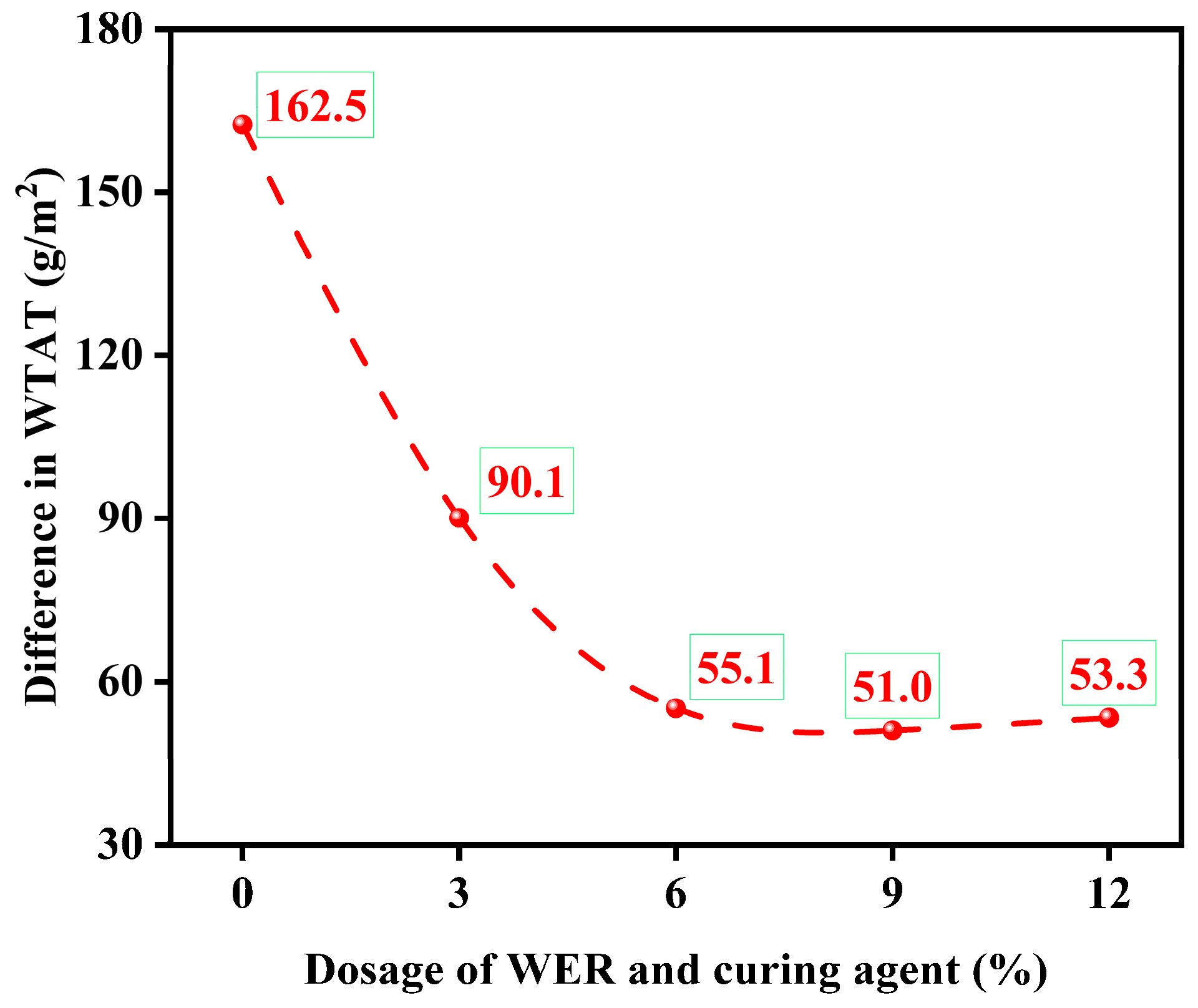
3.7.1. Freeze–Thaw Test Results
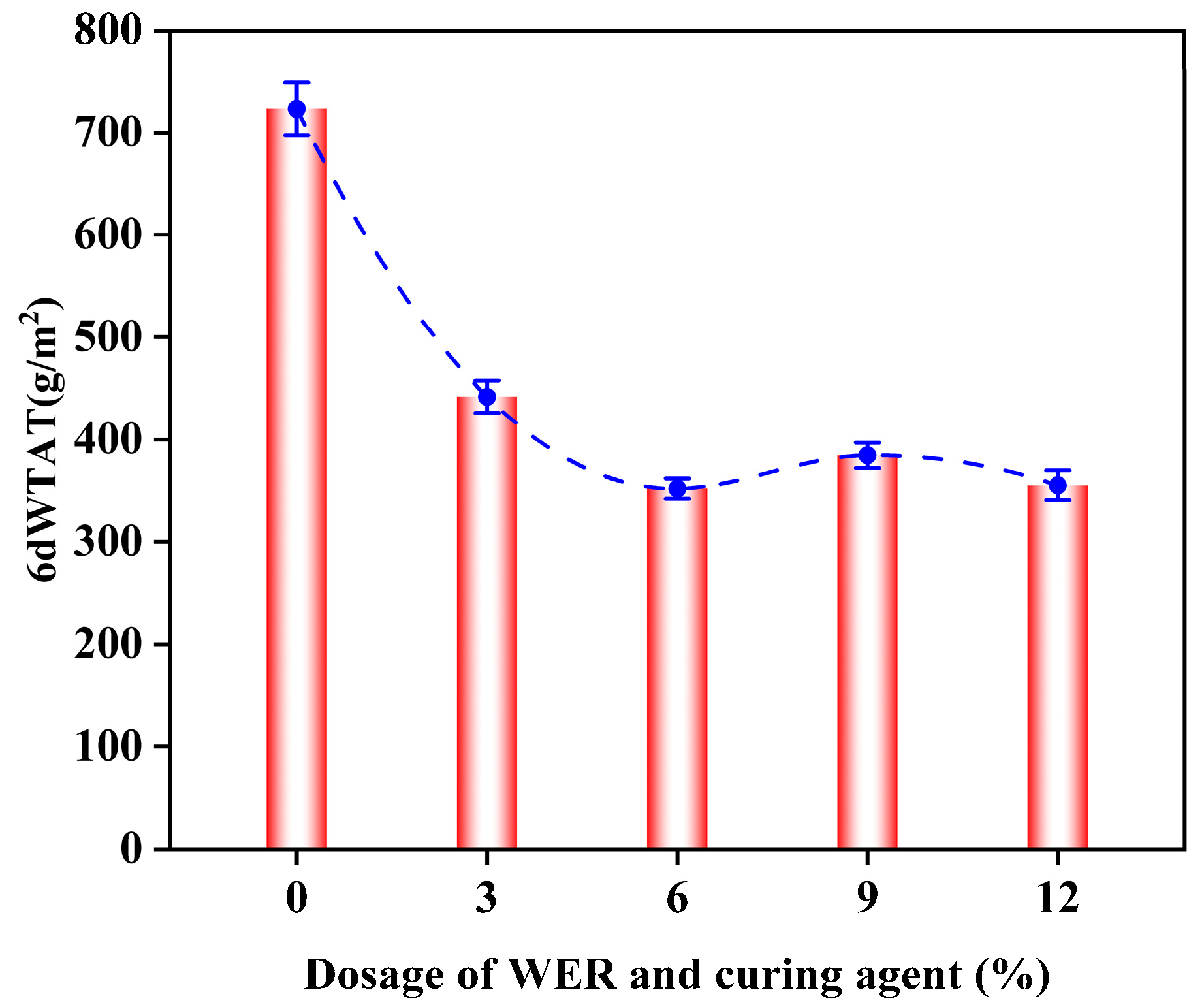
3.7.2. Dry–Wet Test Results
3.7.3. Salt Spray Test Results
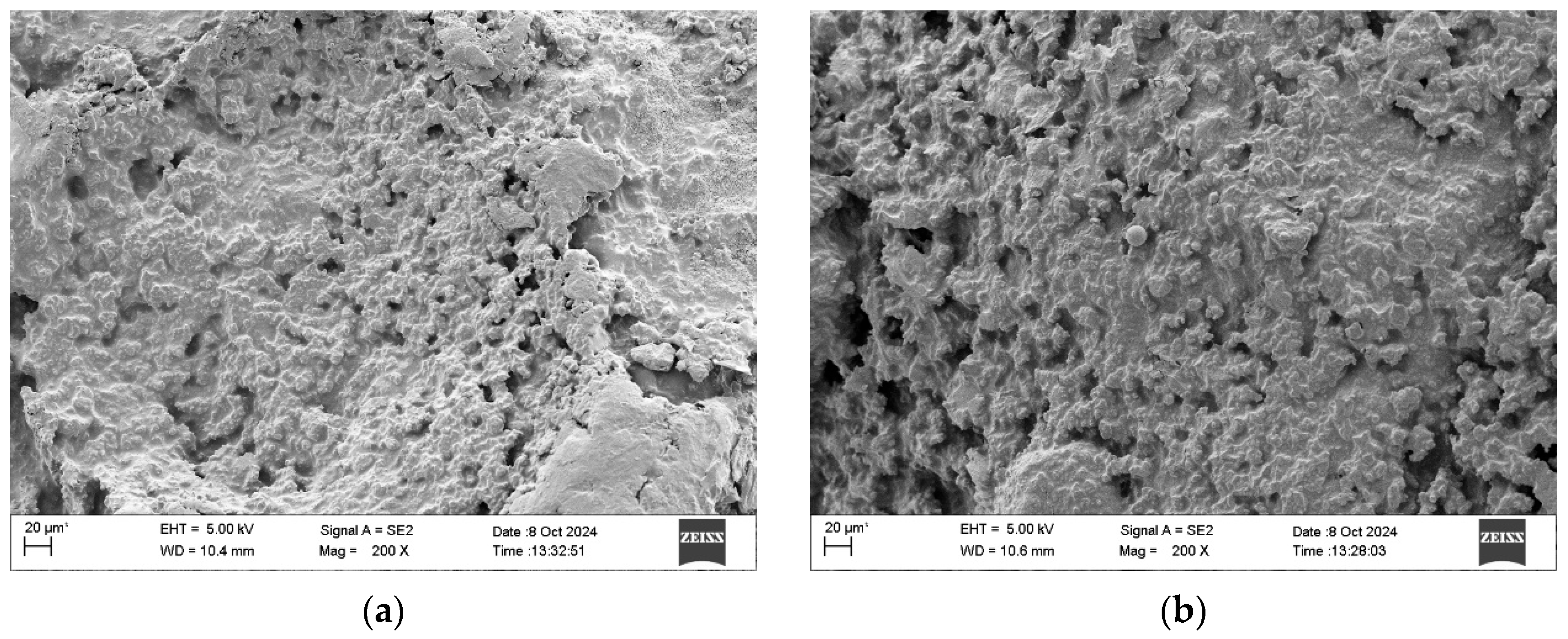
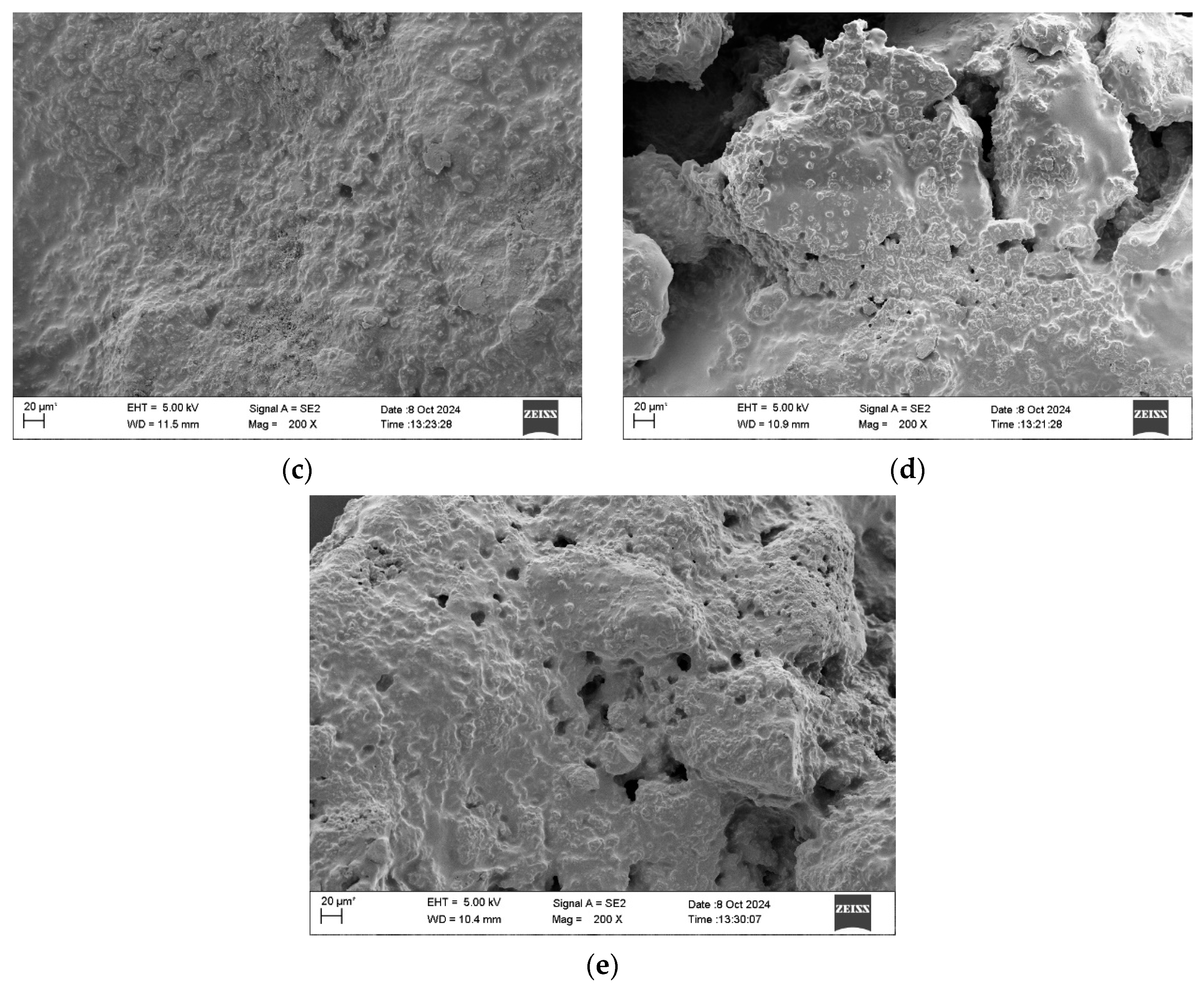
3.8. Microscopic Morphology
4. Conclusions
- The 1 h WTAT of WER-SBR mixtures decreases as the binder-to-aggregate ratio increases while LWT rises. The comprehensive binder-to-aggregate ratio range for WER-SBR mixtures is determined to be 6.5–8%. Based on the sample morphology, the binder-to-aggregate ratio selected in this study was 7%.
- Increasing WER content improves wear resistance, water stability, and rutting resistance. Improvements become less significant when WER content exceeds 6%. In terms of skid resistance and cracking resistance, WER-SBR mixtures with 3% and 6% WER exhibit slower BPN decay rates, and the low-temperature bending stress remains at a higher level.
- After freeze–thaw, wet–dry, and salt fog tests, the WTAT of WER-SBR mixtures increases. After the addition of WER, the WTAT of the mixtures starts to decrease. When the WER content reaches 6%, the difference in WTAT before and after the tests is minimized.
- SEM tests show that at 0% and 3% WER, the surfaces have loose aggregates. At 6% WER, a complete asphalt film forms on the surface. At 9% and 12% WER, the specimens exhibit cracking and void formation.
- The addition of 6% WER to SBR mixtures improves resistance to wheel wear, moisture penetration, rutting, and damage from extreme conditions like freeze–thaw, wet–dry cycles, and salt fog. The mixture demonstrates optimal road performance and durability. Therefore, the recommended WER content is 6%.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Rose, M.; Iuele, T.; Perri, G.; Vaiana, R. On the Mix Design Advances in Microsurfacing: A Systematic Surface Performance-Oriented Literature Review. Int. J. Pavement Res. Technol. 2023, 16, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byzyka, J.; Davie, H.; Al-Kheetan, M.J.; Rahman, M. A Study on Cold Laid Microsurfacing Containing Water-Based Epoxy-Modified Bitumen Emulsion. Int. J. Pavement Res. Technol. 2024, 17, 1047–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhargava, N.; Siddagangaiah, A.K.; Ryntathiang, T.L. Sustainable Development with Microsurfacing: A Review. J. Test. Eval. 2021, 49, 1284–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Liu, W.; Wu, S.; Gou, X. Study on the Mechanical Performance Damage in Laboratory-Simulated Periodic Salt Environment for Asphalt Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 411, 134306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwiatkowski, K.P.; Stipanovic Oslakovic, I.; Ter Maat, H.; Chinowsky, P. Modeling Cost Impacts and Adaptation of Freeze–Thaw Climate Change on a Porous Asphalt Road Network. J. Infrastruct. Syst. 2020, 26, 04020022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maia, R.S.; Lu, Y.; Hajj, R. Porous Asphalt Mixture Performance in Cold Regions: Case Study of Chicago. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2024, 20, e03250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Dong, W.; Fu, Z.; Wang, R.; Huang, Y.; Liu, J. Life cycle assessment of greenhouse gas emissions from asphalt pavement maintenance: A case study in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 288, 125595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Sha, A.; Wang, Z.; Jiao, W.; Li, X.; Xie, Y. The Stability of Emulsified Asphalt and Interfacial Behavior of Emulsified Asphalt-Aggregate Based on Molecular Dynamics Simulation: A Review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 467, 140239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Wu, H.; Chen, X.; Yuan, H. Fabrication of High-Performance Asphalt Mixture Using Waterborne Epoxy-Acrylate Resin Modified Emulsified Asphalt (WEREA). Polymers 2024, 16, 2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Ling, X.; Fan, Z.; Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, H. Viscoelasticity of PPA/SBS/SBR Composite Modified Asphalt and Asphalt Mixtures Under Pressure Aging Conditions. Polymers 2025, 17, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Hu, L.; Dong, S.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, S. Assessment of testing methods for higher temperature performance of emulsified asphalt. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 375, 134101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, K.; Wu, Y.; Cao, X.; Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Lin, W. Dual dynamic bonds approach for polyurethane recycling and self-healing of emulsified asphalt. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 885, 163915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Qian, C.; Shi, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, W. The influencing factors of evaporation residue of emulsified modified asphalt to optimize the environmental adaptability. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 356, 129169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Luo, J.; Lang, H.; Chen, Z. Study on the Micro-Surfacing Properties of SBR Modified Asphalt Emulsion with Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement. Materials 2025, 18, 802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, F.; Lv, S.; Gao, J.; Wang, L.; Zhou, H.; Xie, T. Performance and mechanism of asphalt modified by buton-rock asphalt and different types of styrene-butadiene-rubber. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Cui, B.; Tian, J.; Xu, T.; Zhou, X. Evaluating the effects of styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) and polyphosphoric acid (PPA) on asphalt adhesion performance. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 321, 126028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.G.; Tian, X.G.; Hu, H.L.; Li, G.Y.; Guo, C.H. Effect of SBR latex content on the performance of modified emulsified asphalt. J. Build. Mater. 2021, 24, 895–900. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Liang, F.; Li, Z.; Zhao, Q. Investigation on the Rheological Properties and Microscopic Characteristics of Graphene and SBR Composite Modified Asphalt. Coatings 2023, 13, 1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Chen, X.; Zhao, S.; Ouyang, J.; Zhang, Q. Rheological Properties and Performance Evaluation of Different Types of Composite-Modified Asphalt in Cold Regions. Coatings 2024, 14, 1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Jia, J.; Chen, Q. Road Performance Comprehensive Evaluation of Polymer Modified Emulsified Asphalt Fiber Microsurfacing. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2022, 2022, 5196074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Han, S.; Kong, H.; Zhang, L.; Xie, H. Optimization and performance evaluation of waterborne epoxy resin modified emulsified asphalt micro-surfacing based on tunnel driving environment. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 315, 125604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Zhang, X.; Sha, T.; Li, Z.; Li, X. A Rheological Study of the High-Temperature Properties of Fast-Melting SBS/Epoxy-Modified Asphalt Binders. Polymers 2025, 17, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.; Wang, C.; Fu, H.; Zhang, X.; Liu, D. Waterborne epoxy resin–polyurethane–emulsified asphalt: Preparation and properties. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2019, 31, 04019265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Fang, Y.; He, M.; Shi, T. Performance characterization of waterborne epoxy resin and styrene–butadiene rubber latex composite modified asphalt emulsion (WESAE). Coatings 2020, 10, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Leng, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, T.; Xu, M. Microstructure characterisation and constitutive modelling of waterborne epoxy resin modified bitumen emulsion. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2022, 23, 5077–5086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Yu, Z.; Peng, B.; Li, K.; Xia, S.; Zheng, H. Superhydrophobic waterborne epoxy composite coating with good mechanical properties, icing resistance, self-cleaning properties, and corrosion resistance. Langmuir 2024, 40, 15661–15676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Chen, Y.Y.; Leng, Z.; Zhu, H.; Chen, Z. Application of Waterborne Epoxy Resin Modified Bitumen Emulsion as a Tack Coat Material. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2024, 36, 04024163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Wang, C.; Niu, L.; Yang, Y.; Li, Z. Composition optimisation and performance evaluation of waterborne epoxy resin emulsified asphalt tack coat binder for pavement. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2022, 23, 4034–4048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Chen, D.; Wu, H.; Wu, Z.; Wada, S.A.; Yuan, H. Preparation and performance characterization of waterborne epoxy resin modified asphalt emulsion for tack coat. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 475, 143715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wu, Z.; Song, W.; Chen, D.; Yang, M.; Yuan, H. Investigation on One-Component Waterborne Epoxy Emulsified Asphalt (OWEEA) Used as Bonding Material. Buildings 2024, 14, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, O.; Li, Y.; Xu, R.; Liu, Y.; Dong, Y. Performance evaluation of waterborne epoxy resin modified emulsified asphalt mixtures for asphalt pavement pothole repair. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 325, 126709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Yang, L.; Zhou, Q.; Chen, Q.; Tang, S.; He, L. Research on pavement performance of waterborne epoxy resin-modified emulsified asphalt binders and pothole repair materials. Mater. Technol. 2025, 59, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Han, S.; Wang, Z.; Li, X.; Sun, H.; Zhang, Q. Performance evaluation of new waterborne epoxy resin modified emulsified asphalt micro-surfacing. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 214, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Zheng, M.; Fan, X.; Zhang, X.; Tan, Y. Performance evaluation of waterborne epoxy resin-SBR compound modified emulsified asphalt micro-surfacing. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 295, 123588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Yao, T.; Han, X.; Zhang, L.; Guo, L. Performance evaluation of waterborne epoxy resin modified hydrophobic emulsified asphalt micro-surfacing mixture. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 249, 118835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Su, S.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, Z. Microscale mechanism and key factors of waterborne epoxy resin emulsified asphalt enhancing interlayer bonding performance and shear resistance of bridge deck pavement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 419, 135570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Huang, W.; Lu, G.; Luo, S.; Li, Y. Investigation of the performance and micro-evolution mechanism of low-content thermosetting epoxy asphalt binder towards sustainable highway and bridge decks paving. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 384, 135588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Lu, T.; Fang, G.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, Y. Study on modification mechanism and properties of SBR/WER composite modified emulsified asphalt waterproof binder. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 465, 140246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Tan, L.; Xu, T.; Wang, S.; Wu, Z. Preparation, properties and compound modification mechanism of waterborne epoxy resin/styrene butadiene rubber latex modified emulsified asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 318, 126178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JTG5142-01-2021; Specifications for Preventive Maintenance of Asphalt Pavement. National Standards of the Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2021.
- JTG F40-2004; Specifications for Asphalt Pavement Construction. National Standards of the Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2004.
- GB 175-2023; General Portland Cement. National Standards of the Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2023.
- Moura, C.F.N.; Oliveira, J.R.M.; Silva, H.M.R.D.; Palha, C.A.O.F.; Sangiorgi, C. Development and Application of a Microsurfacing Mix Design Method to Assess the Influence of the Emulsion Type. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 7925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhu, R.; Li, W.; He, Q.; Yang, F.; Zhang, M.; Xue, Y.; Liu, Z. Preparation and properties of optimized waterborne epoxy resin mixed with SBR modified emulsified asphalt. Matéria 2025, 30, e20240734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Zheng, M.; Fan, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; Yang, L.; Wang, F. Properties and mechanism of waterborne epoxy resin-SBR composite modified emulsified asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 274, 122059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Hou, Y.; Yang, F. Study of the properties of Waterborne Epoxy Resin Emulsified asphalt and its modification mechanism. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2023, 35, 04023145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Zhao, J.; Leng, Z.; Xue, X.; Ma, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, C.; Yang, S. Laboratory evaluation of waterborne epoxy bitumen emulsion for pavement preventative maintenance application. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 197, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JTG E20-2011; Highway Asphalt Pavement Preventive Maintenance Technical Specifications. National Standards of the Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2011.
- Huang, S.; Jin, F.; Chen, D.; Xiao, Q.; Ding, Q. Study on Modification Mechanism and Performance of Waterborne Epoxy Resin Micro-Surfacing. Coatings 2023, 13, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Xu, H.; Xu, T.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wu, J.; Liu, L.; Yao, L. Mechanical properties and enhancement mechanisms of cold recycled mixture using waterborne epoxy resin/styrene butadiene rubber latex modified emulsified asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 352, 129021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Han, S.; Pan, J.; Ren, W.; Zhang, L. Study on cohesion performance of waterborne epoxy resin emulsified asphalt as interlayer materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 177, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Zheng, M.; Gao, Y.; Ding, X.; Zhang, W.; Chen, W. Study of long-term skid and wear resistance of waterborne epoxy resin-SBR compound modified emulsified asphalt microsurfacing. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2024, 141, e54937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Xu, T.; Zhang, C.; Liu, W.; Wu, T. Fatigue fracture and self-healing behaviors of cold recycled emulsified asphalt mixture containing microcapsules based on semicircular bending test. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 410, 137171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Zheng, M.; Liu, X.; Ding, X.; Wang, F.; Wang, Q. Performance evaluation of waterborne epoxy resin-SBR composite modified emulsified asphalt fog seal. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 301, 124106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Wang, C.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Feng, L.; Tan, S. Fog seal with polymer composite modified emulsified asphalt: Road performance and environmental adaptability. Wear 2025, 562, 205672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Luo, S.; Wang, Y.; Dong, Q.; Zhang, Z. Pre-treatment of steel slag and its applicability in asphalt mixtures for sustainable pavements. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 476, 146802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]














| Technical Parameters | Units | Values | Standard |
|---|---|---|---|
| Penetration (25 °C) | 0.1 mm | 90.5 | 45–150 |
| Evaporation Residue Content | % | 57.5 | ≥55 |
| Ductility (15 °C) | cm | 116 | ≥40 |
| Standard Viscosity | S | 15.6 | 10–60 |
| Solubility | % | 97.7 | ≥97.5 |
| 5-Day Storage Stability | % | 0.8 | ≤5 |
| Sieve Residue | % | 0.02 | ≤0.1 |
| Modifier | Parameters | Units | Values |
|---|---|---|---|
| WER | Appearance | - | Milky white |
| epoxy equivalent | G/EQ | 400–800 | |
| rotational viscosity | Pa·s | <1000 | |
| solid content | % | 47–53 | |
| pH value | - | 4.3 | |
| specific gravity | - | 1.01–1.08 | |
| Curing agent | Appearance | - | Pale yellow |
| rotational viscosity | Pa·s | >2000 | |
| solid content | % | 42–46 | |
| pH value | - | 10.2 | |
| specific gravity | - | 1.00–1.08 |
| Modifier | Parameters | Units | Values | Standard |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coarse aggregate | Crushing value | % | 10.8 | ≤26 |
| Los Angeles abrasion loss | % | 9.2 | ≤25 | |
| Polish value | BPN | 50 | ≥42 | |
| Toughness | % | 10.8 | ≤12 | |
| Flakiness content | % | 12.1 | ≤15 | |
| Fine aggregate | Toughness | % | 10.8 | ≤12 |
| Modifier | Parameters | Units | Values | Standard |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Limestone powder | Moisture content | % | 0.3 | ≤1 |
| Apparent relative density | - | 2.95 | ≥2.50 | |
| Hydrophilicity index | - | 0.4 | <1 | |
| Plasticity index | % | 3 | <4 | |
| Cement | Specific surface area | m2/kg | 341 | ≥300 |
| Density | kg/m3 | 3065 | - | |
| Initial setting time | min | 176 | ≥45 | |
| Final setting time | min | 284 | ≤600 | |
| 3-Day compressive strength | MPa | 28.5 | ≥17 | |
| 3-Day flexural strength | MPa | 4.8 | ≥3.5 |
| Experimental Group | Aggregate (g) | Mineral Filler (g) | Cement (g) | Water (g) | Modified Asphalt | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BC-1 Emulsified Asphalt (g) | WER System (g) | SBR Latex (g) | |||||
| 0%WER + 3%SBR | 100 | 4 | 2 | 7 | 6.79 | 0 | 0.21 |
| 3%WER + 3%SBR | 100 | 4 | 2 | 7 | 6.58 | 0.21 | 0.21 |
| 6%WER + 3%SBR | 100 | 4 | 2 | 7 | 6.37 | 0.42 | 0.21 |
| 9%WER + 3%SBR | 100 | 4 | 2 | 7 | 6.16 | 0.63 | 0.21 |
| 12%WER + 3%SBR | 100 | 4 | 2 | 7 | 5.95 | 0.84 | 0.21 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, L.; Li, W.; Zhang, C.; Yu, X.; Liu, A.; Huang, J. The Study on the Effect of Waterborne Epoxy Resin Content on the Performance of Styrene–Butadiene Rubber Modified Micro-Surface Mixture. Polymers 2025, 17, 1175. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17091175
Zhao L, Li W, Zhang C, Yu X, Liu A, Huang J. The Study on the Effect of Waterborne Epoxy Resin Content on the Performance of Styrene–Butadiene Rubber Modified Micro-Surface Mixture. Polymers. 2025; 17(9):1175. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17091175
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Lihua, Wenhe Li, Chunyu Zhang, Xinping Yu, Anhao Liu, and Jianzhe Huang. 2025. "The Study on the Effect of Waterborne Epoxy Resin Content on the Performance of Styrene–Butadiene Rubber Modified Micro-Surface Mixture" Polymers 17, no. 9: 1175. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17091175
APA StyleZhao, L., Li, W., Zhang, C., Yu, X., Liu, A., & Huang, J. (2025). The Study on the Effect of Waterborne Epoxy Resin Content on the Performance of Styrene–Butadiene Rubber Modified Micro-Surface Mixture. Polymers, 17(9), 1175. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17091175






