Valorising Insect Exoskeleton Biomass Filler in Bioplastic-Based Eco-Friendly Rigid Items for Agriculture Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Composite Materials
2.2. Composite Preparation on Laboratory Scale
2.3. Composite Characterisations
2.4. Scale-Up Production of Prototypes
- PBSA/PHBV 70/30 (M).
- PBSA/PHBV 70/30 + 15 wt.% of insect exoskeleton filler (M_15).
2.5. Compost Degradation Tests
3. Discussion
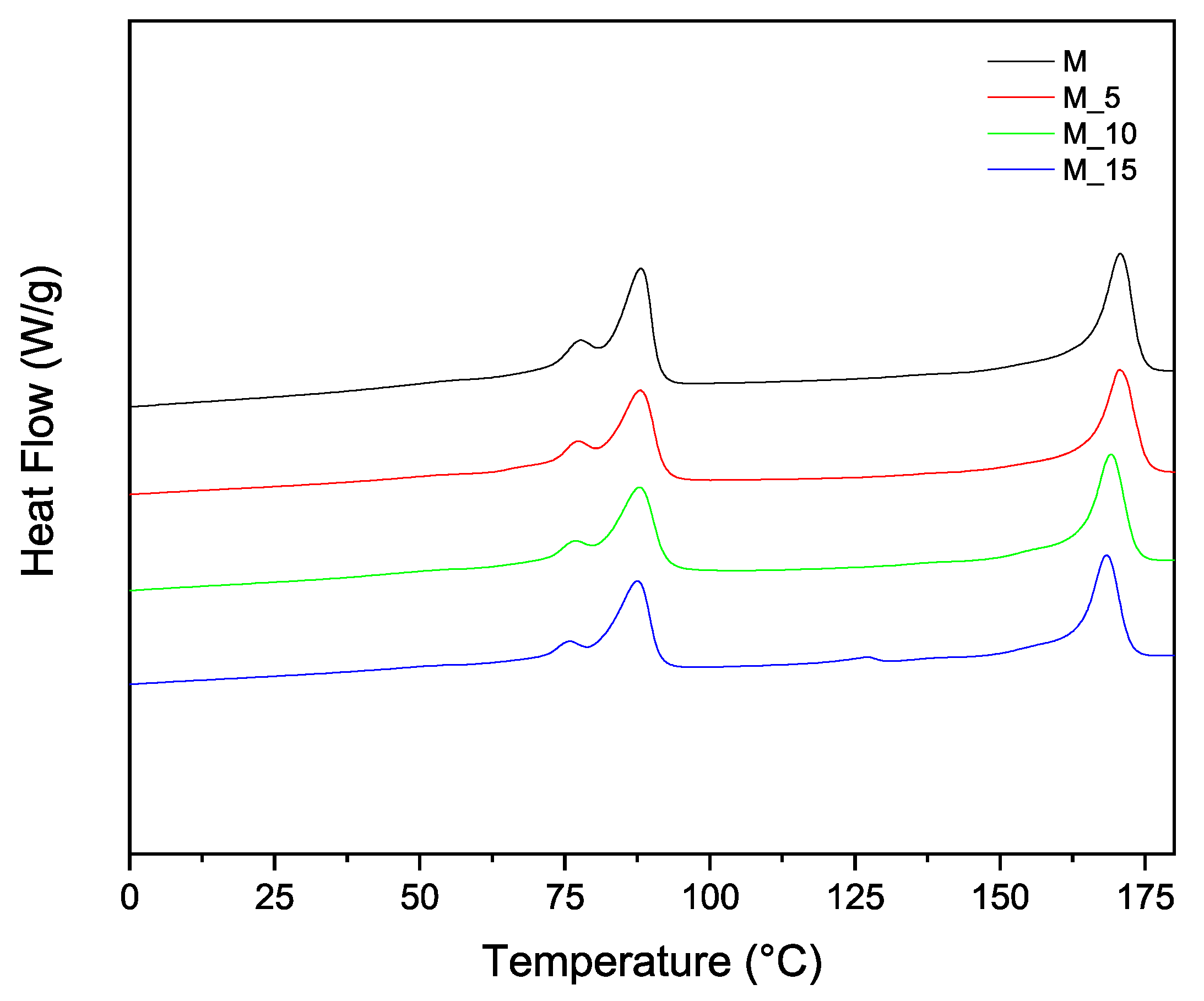
3.1. Thermal Analysis of Composites
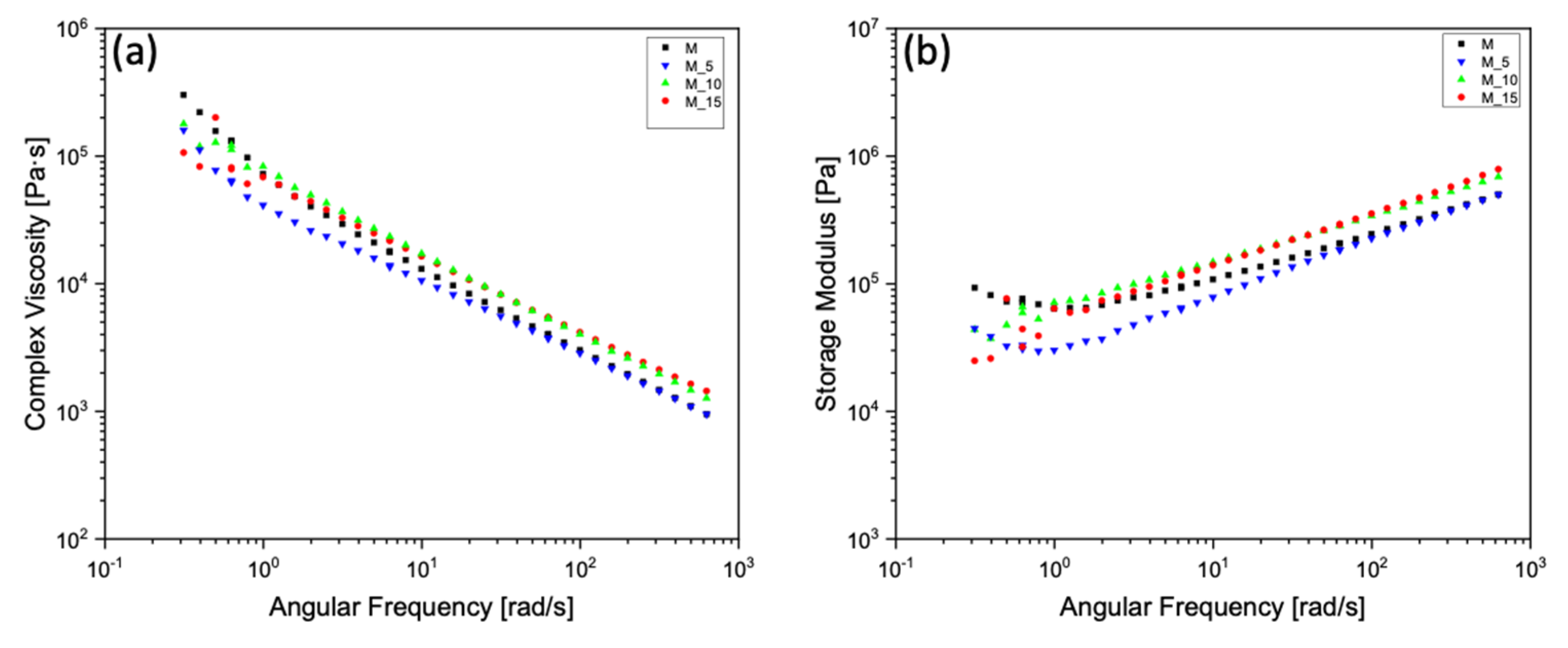
3.2. Mechanical and Rheological Analyses of Composites
3.3. Morphological Analysis of Composites
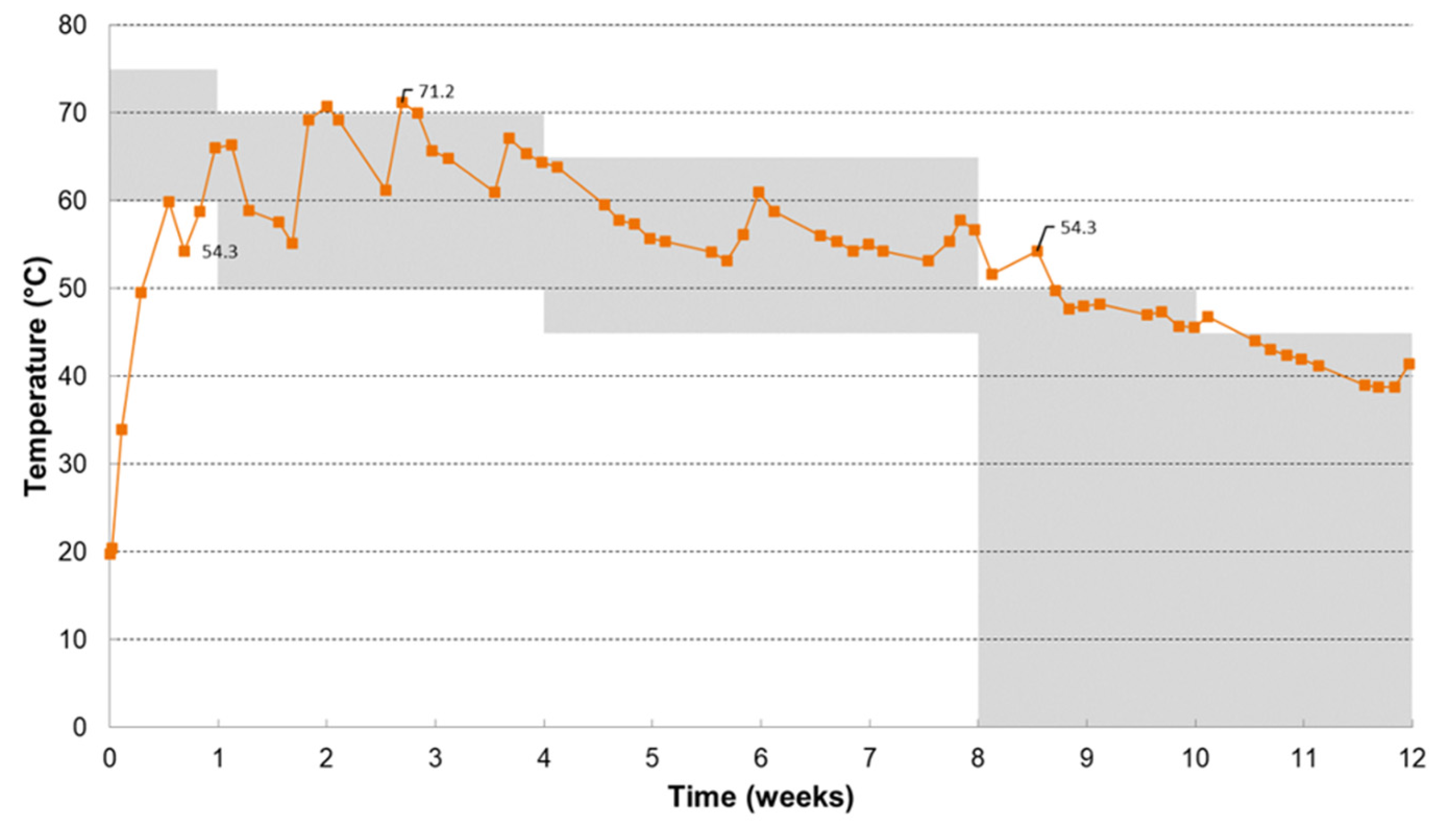
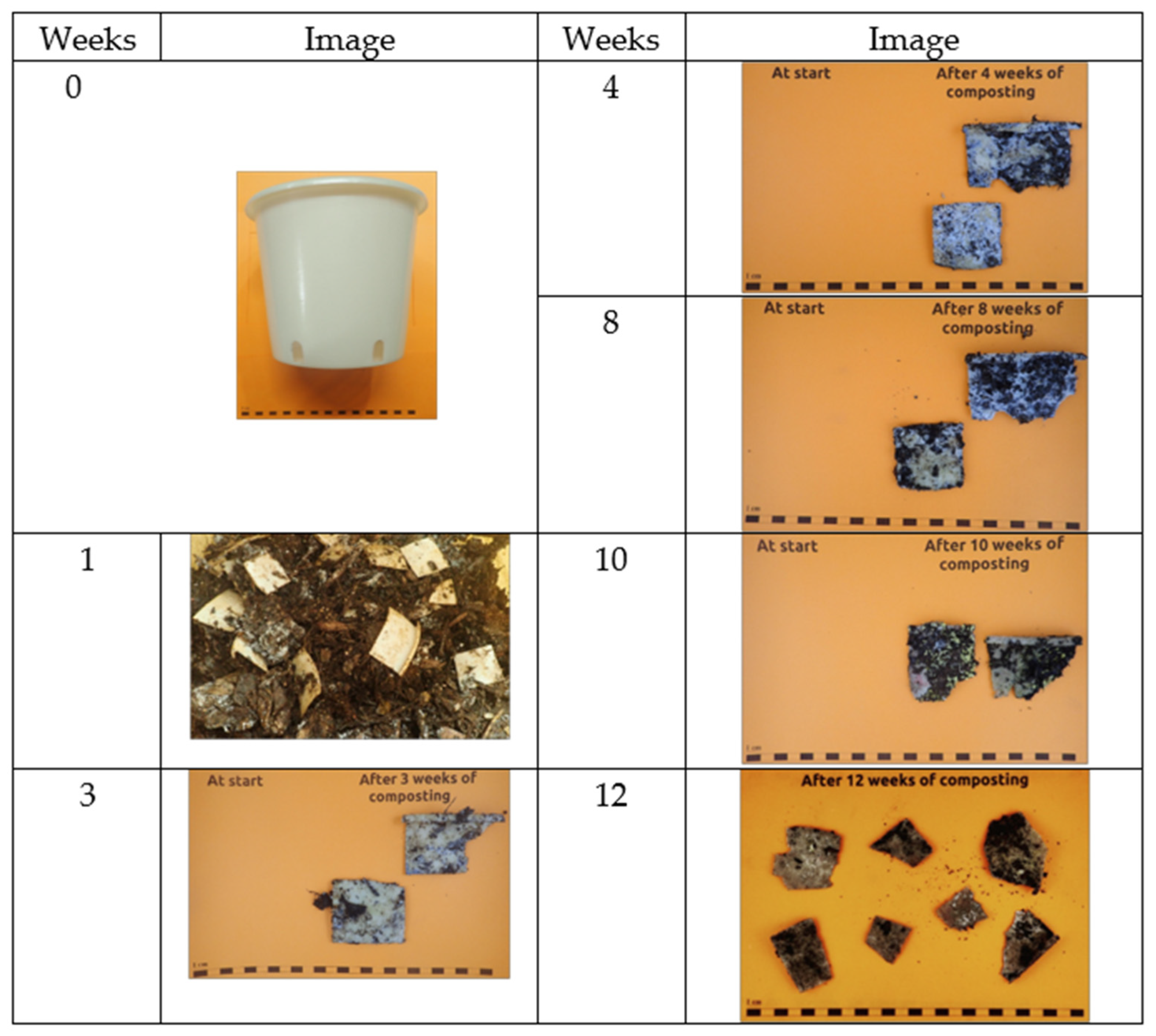
3.4. Disintegration in Compost
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- UN Environment Programme. Available online: https://www.unep.org/interactives/beat-plastic-pollution/ (accessed on 23 January 2024).
- Nath, D.; Misra, M.; Al-Daoud, F.; Mohanty, A.K. Studies on Poly(Butylene Succinate) and Poly(Butylene Succinate-Co-Adipate)-Based Biodegradable Plastics for Sustainable Flexible Packaging and Agricultural Applications: A Comprehensive Review. RSC Sustain. 2025, 3, 1267–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barletta, M.; Genovesi, A.; Desole, M.P.; Gisario, A. Melt Processing of Biodegradable Poly(Butylene Succinate) (PBS)—A Critical Review. Clean. Technol. Environ. Policy 2024, 27, 683–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliotta, L.; Seggiani, M.; Lazzeri, A.; Gigante, V.; Cinelli, P. A Brief Review of Poly (Butylene Succinate) (PBS) and Its Main Copolymers: Synthesis, Blends, Composites, Biodegradability, and Applications. Polymers 2022, 14, 844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimaki, T. Processability and Properties of Aliphatic Polyesters, “BIONOLLE”, Synthesized by Polycondensation Reaction. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 1998, 59, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratto, J.A.; Stenhouse, P.J.; Auerbach, M.; Mitchell, J.; Farrell, R. Processing, Performance and Biodegradability of a Thermoplastic Aliphatic Polyester/Starch System. Polymer 1999, 40, 6777–6788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappello, M.; Rossi, D.; Filippi, S.; Cinelli, P.; Seggiani, M. Wood Residue-Derived Biochar as a Low-Cost, Lubricating Filler in Poly(Butylene Succinate-Co-Adipate) Biocomposites. Materials 2023, 16, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasirajan, S.; Ngouajio, M. Polyethylene and Biodegradable Mulches for Agricultural Applications: A Review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2012, 32, 501–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padovani, G.; Carlozzi, P.; Seggiani, M.; Cinelli, P.; Vitolo, S.; Lazzeri, A. PHB-Rich Biomass and BioH2 Production by Means of Photosynthetic Microorganisms. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2016, 49, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bugnicourt, E.; Cinelli, P.; Lazzeri, A.; Alvarez, V. Polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA): Review of Synthesis, Characteristics, Processing and Potential Applications in Packaging. Express Polym. Lett. 2014, 8, 791–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudesh, K.; Abe, H.; Doi, Y. Synthesis, Structure and Properties of Polyhydroxyalkanoates: Biological Polyesters. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2000, 25, 1503–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laycock, B.; Halley, P.; Pratt, S.; Werker, A.; Lant, P. The Chemomechanical Properties of Microbial Polyhydroxyalkanoates. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2013, 38, 536–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keskin, G.; Klzll, G.; Bechelany, M.; Pochat-Bohatier, C.; Öner, M. Potential of Polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) Polymers Family as Substitutes of Petroleum Based Polymers for Packaging Applications and Solutions Brought by Their Composites to Form Barrier Materials. Pure Appl. Chem. 2017, 89, 1841–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seggiani, M.; Cinelli, P.; Balestri, E.; Mallegni, N.; Stefanelli, E.; Rossi, A.; Lardicci, C.; Lazzeri, A. Novel Sustainable Composites Based on Poly(Hydroxybutyrate-Co-Hydroxyvalerate) and Seagrass Beach-CAST Fibers: Performance and Degradability in Marine Environments. Materials 2018, 11, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deroiné, M.; Le Duigou, A.; Corre, Y.M.; Le Gac, P.Y.; Davies, P.; César, G.; Bruzaud, S. Seawater Accelerated Ageing of Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate-Co-3-Hydroxyvalerate). Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2014, 105, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN 13432:2000; Packaging—Requirements for Packaging Recoverable Through Composting and Biodegradation—Test Scheme and Evaluation Criteria for the Final Acceptance of Packaging. UNI: Rome, Italy, 2000.
- Salomez, M.; George, M.; Fabre, P.; Touchaleaume, F.; Cesar, G.; Lajarrige, A.; Gastaldi, E.; Mélanie, S.; Matthieu, G.; Pascale, F.; et al. A Comparative Study of Degradation Mechanisms of PBSA and PHBV under Laboratory Scale Composting Conditions. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2019, 167, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satyanarayana, K.G.; Arizaga, G.G.C.; Wypych, F. Biodegradable Composites Based on Lignocellulosic Fibers—An Overview. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2009, 34, 982–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, A.K.; Misra, M.; Hinrichsen, G. Biofibres, Biodegradable Polymers and Biocomposites: An Overview. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2000, 276–277, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faruk, O.; Bledzki, A.K.; Fink, H.P.; Sain, M. Biocomposites Reinforced with Natural Fibers: 2000-2010. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2012, 37, 1552–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, J.K.; Ahn, S.H.; Lee, C.S.; Mohanty, A.K.; Misra, M. Recent Advances in the Application of Natural Fiber Based Composites. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2010, 295, 975–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrew, J.J.; Dhakal, H.N. Sustainable Biobased Composites for Advanced Applications: Recent Trends and Future Opportunities—A Critical Review. Compos. Part C Open Access 2022, 7, 100220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.V.; Singh, A.; Sabyasachi Mohanty, S.; Kumar Srivastava, V.; Varjani, S. Organic Solid Waste: Biorefinery Approach as a Sustainable Strategy in Circular Bioeconomy. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 349, 126835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seggiani, M.; Cinelli, P.; Mallegni, N.; Balestri, E.; Puccini, M.; Vitolo, S.; Lardicci, C.; Lazzeri, A. New Bio-Composites Based on Polyhydroxyalkanoates and Posidonia Oceanica Fibres for Applications in a Marine Environment. Materials 2017, 10, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strangis, G.; Rossi, D.; Cinelli, P.; Seggiani, M. Seawater Biodegradable Poly(Butylene Succinate-Co-Adipate)—Wheat Bran Biocomposites. Materials 2023, 16, 2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smetana, S.; Bhatia, A.; Batta, U.; Mouhrim, N.; Tonda, A. Environmental Impact Potential of Insect Production Chains for Food and Feed in Europe. Anim. Front. 2023, 13, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraijo-Valenzuela, A.; Arias-Moscoso, J.L.; García-Pérez, O.D.; Rodriguez-Anaya, L.Z.; Gonzalez-Galaviz, J.R. The Biotechnological Potential of Crickets as a Sustainable Protein Source for Fishmeal Replacement in Aquafeed. BioTech 2024, 13, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brogan, E.N.; Park, Y.-L.; Matak, K.E.; Jaczynski, J. Characterization of Protein in Cricket (Acheta domesticus), Locust (Locusta migratoria), and Silk Worm Pupae (Bombyx mori) Insect Powders. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 152, 112314. [Google Scholar]
- Mitsubishi Chemical Group. Available online: https://www.m-chemical.co.jp/en/products/departments/mcc/sustainable/product/1201025_7964.html (accessed on 15 March 2025).
- ISO 1133-1:2011; Plastics—Determination of the Melt Mass-Flow Rate (MFR) and Melt Volume-Flow Rate (MVR) of Thermoplastics—Part 1: Standard Method. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011.
- Malz, F.; Arndt, J.H.; Balko, J.; Barton, B.; Büsse, T.; Imhof, D.; Pfaendner, R.; Rode, K.; Brüll, R. Analysis of the Molecular Heterogeneity of Poly(Lactic Acid)/Poly(Butylene Succinate-Co-Adipate) Blends by Hyphenating Size Exclusion Chromatography with Nuclear Magnetic Resonance and Infrared Spectroscopy. J. Chromatogr. A 2021, 1638, 461819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montanheiro, T.L.d.A.; de Menezes, B.R.C.; Montagna, L.S.; Beatrice, C.A.G.; Marini, J.; Lemes, A.P.; Thim, G.P. Non-Isothermal Crystallization Kinetics of Injection Grade PHBV and PHBV/Carbon Nanotubes Nanocomposites Using Isoconversional Method. J. Compos. Sci. 2020, 4, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Delliou, B.; Vitrac, O.; Castro, M.; Bruzaud, S.; Domenek, S. Characterization of a New Bio-Based and Biodegradable Blends of Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate-Co-3-Hydroxyvalerate) and Poly(Butylene-Co-Succinate-Co-Adipate). J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2022, 139, 52124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D638; Standard Test Method for Tensile Properties of Plastics. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2022.
- ISO 16929; Plastics—Determination of the Degree of Disintegration of Plastic Materials Under Defined Composting Conditions in a Pilot-Scale Test. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021.
- Rodriguez-Uribe, A.; Wang, T.; Pal, A.K.; Wu, F.; Mohanty, A.K.; Misra, M. Injection Moldable Hybrid Sustainable Composites of BioPBS and PHBV Reinforced with Talc and Starch as Potential Alternatives to Single-Use Plastic Packaging. Compos. Part C Open Access 2021, 6, 100201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masanabo, M.A.; Tribot, A.; Luoma, E.; Sharmin, N.; Sivertsvik, M.; Emmambux, M.N.; Keränen, J. Faba Bean Lignocellulosic Sidestream as a Filler for the Development of Biodegradable Packaging. Polym. Test. 2023, 123, 108047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, E.S.; Im, S.S. Melting Behavior of Poly(Butylene Succinate) during Heating Scan by DSC. J. Polym. Sci. B Polym. Phys. 1999, 37, 1357–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliotta, L.; Vannozzi, A.; Cinelli, P.; Coltelli, M.B.; Lazzeri, A. Essential Work of Fracture and Evaluation of the Interfacial Adhesion of Plasticized PLA/PBSA Blends with the Addition of Wheat Bran By-Product. Polymers 2022, 14, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gigante, V.; Cinelli, P.; Sandroni, M.; D’ambrosio, R.; Lazzeri, A.; Seggiani, M. On the Use of Paper Sludge as Filler in Biocomposites for Injection Moulding. Materials 2021, 14, 2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gigante, V.; Aliotta, L.; Canesi, I.; Sandroni, M.; Lazzeri, A.; Coltelli, M.B.; Cinelli, P. Improvement of Interfacial Adhesion and Thermomechanical Properties of PLA Based Composites with Wheat/Rice Bran. Polymers 2022, 14, 3389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afshar, S.V.; Boldrin, A.; Christensen, T.H.; Corami, F.; Daugaard, A.E.; Rosso, B.; Hartmann, N.B. Disintegration of Commercial Biodegradable Plastic Products under Simulated Industrial Composting Conditions. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 8569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liwarska-Bizukojc, E. Phytotoxicity Assessment of Biodegradable and Non-Biodegradable Plastics Using Seed Germination and Early Growth Tests. Chemosphere 2022, 289, 133132. [Google Scholar]
- Altieri, R.; Seggiani, M.; Esposito, A.; Cinelli, P.; Stanzione, V. Thermoplastic Blends Based on Poly(Butylene Succinate-Co-Adipate) and Different Collagen Hydrolysates from Tanning Industry—II: Aerobic Biodegradation in Composting Medium. J. Polym. Environ. 2021, 29, 3375–3388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.H.D.; Zhou, J. Ecotoxicity of Biodegradable Microplastics and Bio-Based Microplastics: A Review of in Vitro and in Vivo Studies. Environ. Manag. 2024, 75, 663–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Name | Insect Exoskeleton Content (wt-%) |
|---|---|
| M | 0 |
| M_5 | 5 |
| M_10 | 10 |
| M_15 | 15 |
| Characteristics | Biowaste |
|---|---|
| Total solids (TSs, %) | 26.9 |
| Moisture content (%) | 73.1 |
| Volatile solids (VSs, % of TSs) | 85.3 |
| Ash content (% of TSs) | 14.7 |
| pH | 5.6 |
| Electrical conductivity (EC, µS/cm) | 3990 |
| Volatile fatty acids (VFAs, g/L) | 2.6 |
| NOx--N (mg/L) | <10.0 |
| NH4+-N (mg/L) | 528 |
| Total N (g/kg TS) | 15.4 |
| C/N | 28 |
| Sample | Tm (°C) | Tc (°C) | Xc (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PBSA | PHBV | PBSA | PHBV | PBSA | PHBV | |
| M | 88.2 | 170.6 | 51.5 | 113.1 | 49.8 | 60 |
| M_5 | 88 | 170.5 | 49.5 | 113.8 | 44.8 | 63.6 |
| M_10 | 87.8 | 169.1 | 49.2 | 114.7 | 42.6 | 66.2 |
| M_15 | 87.5 | 168.3 | 48.3 | 114.5 | 41 | 67.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mallegni, N.; Gigante, V.; Verstichel, S.; Sandroni, M.; Malik, N.; Cappello, M.; Rossi, D.; Filippi, S.; Lazzeri, A.; Seggiani, M.; et al. Valorising Insect Exoskeleton Biomass Filler in Bioplastic-Based Eco-Friendly Rigid Items for Agriculture Applications. Polymers 2025, 17, 943. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17070943
Mallegni N, Gigante V, Verstichel S, Sandroni M, Malik N, Cappello M, Rossi D, Filippi S, Lazzeri A, Seggiani M, et al. Valorising Insect Exoskeleton Biomass Filler in Bioplastic-Based Eco-Friendly Rigid Items for Agriculture Applications. Polymers. 2025; 17(7):943. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17070943
Chicago/Turabian StyleMallegni, Norma, Vito Gigante, Steven Verstichel, Marco Sandroni, Neetu Malik, Miriam Cappello, Damiano Rossi, Sara Filippi, Andrea Lazzeri, Maurizia Seggiani, and et al. 2025. "Valorising Insect Exoskeleton Biomass Filler in Bioplastic-Based Eco-Friendly Rigid Items for Agriculture Applications" Polymers 17, no. 7: 943. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17070943
APA StyleMallegni, N., Gigante, V., Verstichel, S., Sandroni, M., Malik, N., Cappello, M., Rossi, D., Filippi, S., Lazzeri, A., Seggiani, M., & Cinelli, P. (2025). Valorising Insect Exoskeleton Biomass Filler in Bioplastic-Based Eco-Friendly Rigid Items for Agriculture Applications. Polymers, 17(7), 943. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17070943













