Self-Adhesive and Reprocessable Ionogel Sensor from Controllable Ionized Corncob Cellulose
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
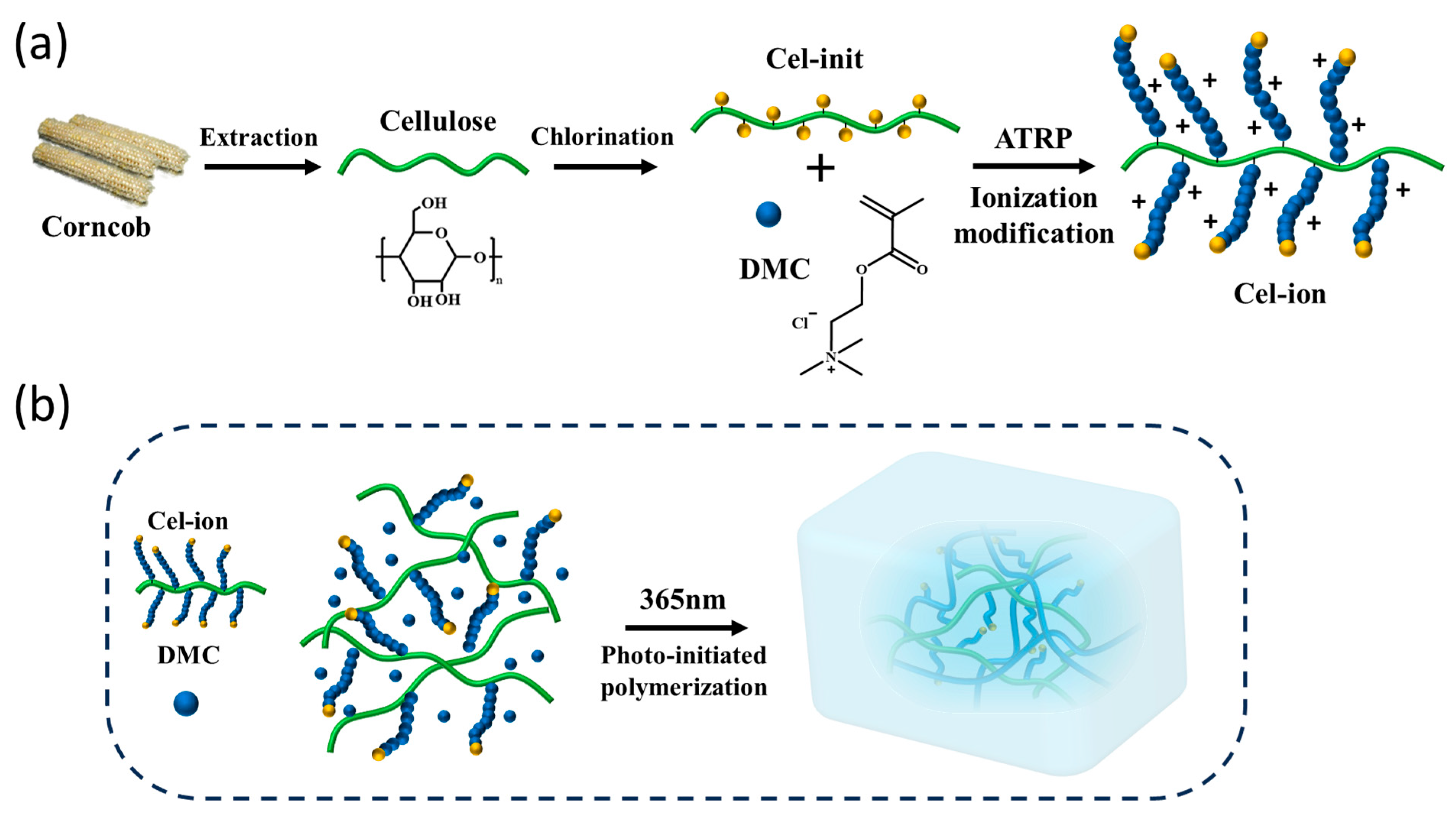
2.2. Extraction of Corncob Cellulose
2.3. Dissolution of Cellulose
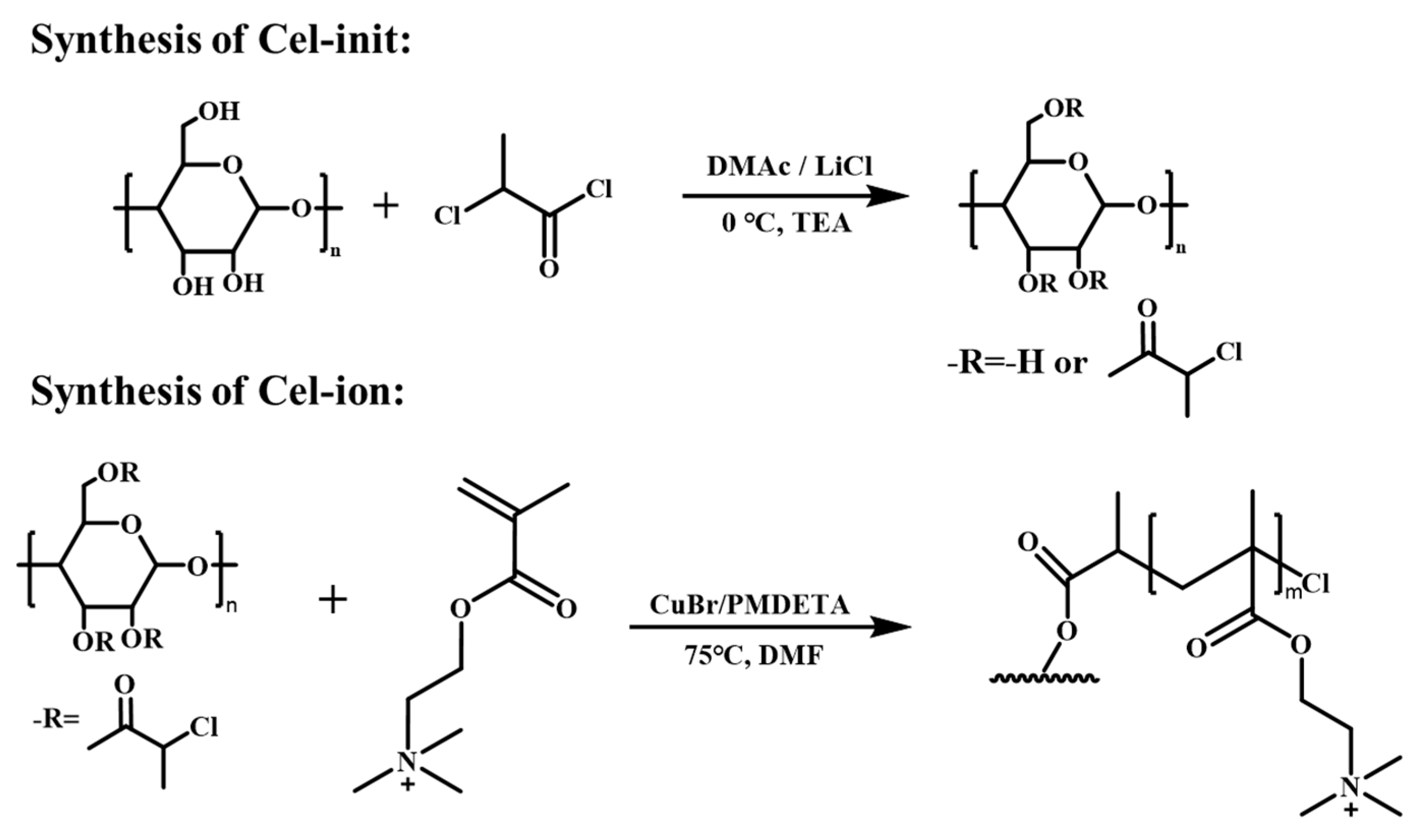
2.4. Synthesis of Cellulose Initiator (Cel-Init)
2.5. Synthesis of Ionized Cellulose (Cel-Ion)
2.6. Fabrication of Cellulose Cation/PDMC Ionogels
2.7. Characterization Methods
3. Results and Discussion
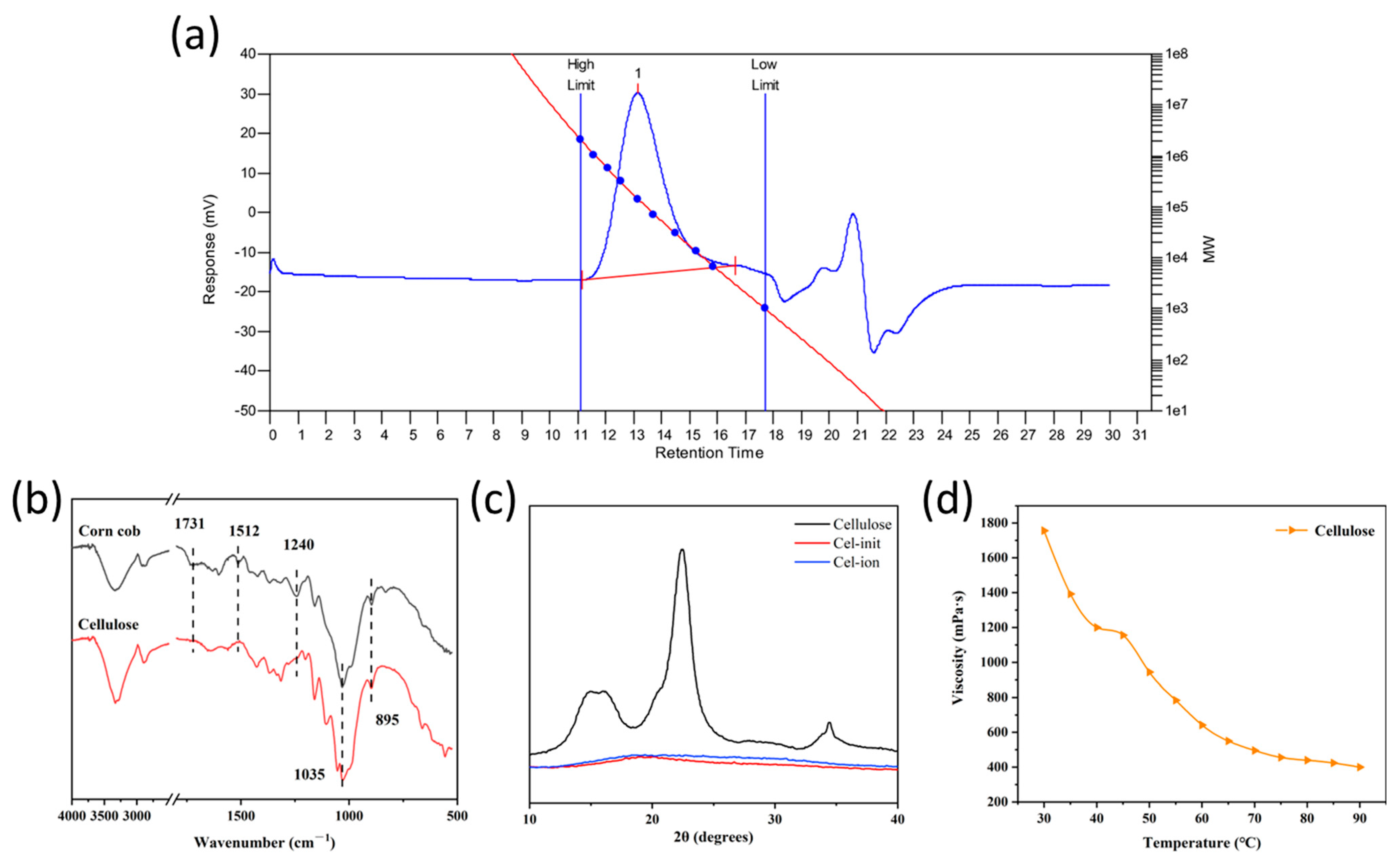
3.1. Structural Characterization of Corncob Cellulose and Its Derivatives
3.2. Thermal Property Characterization
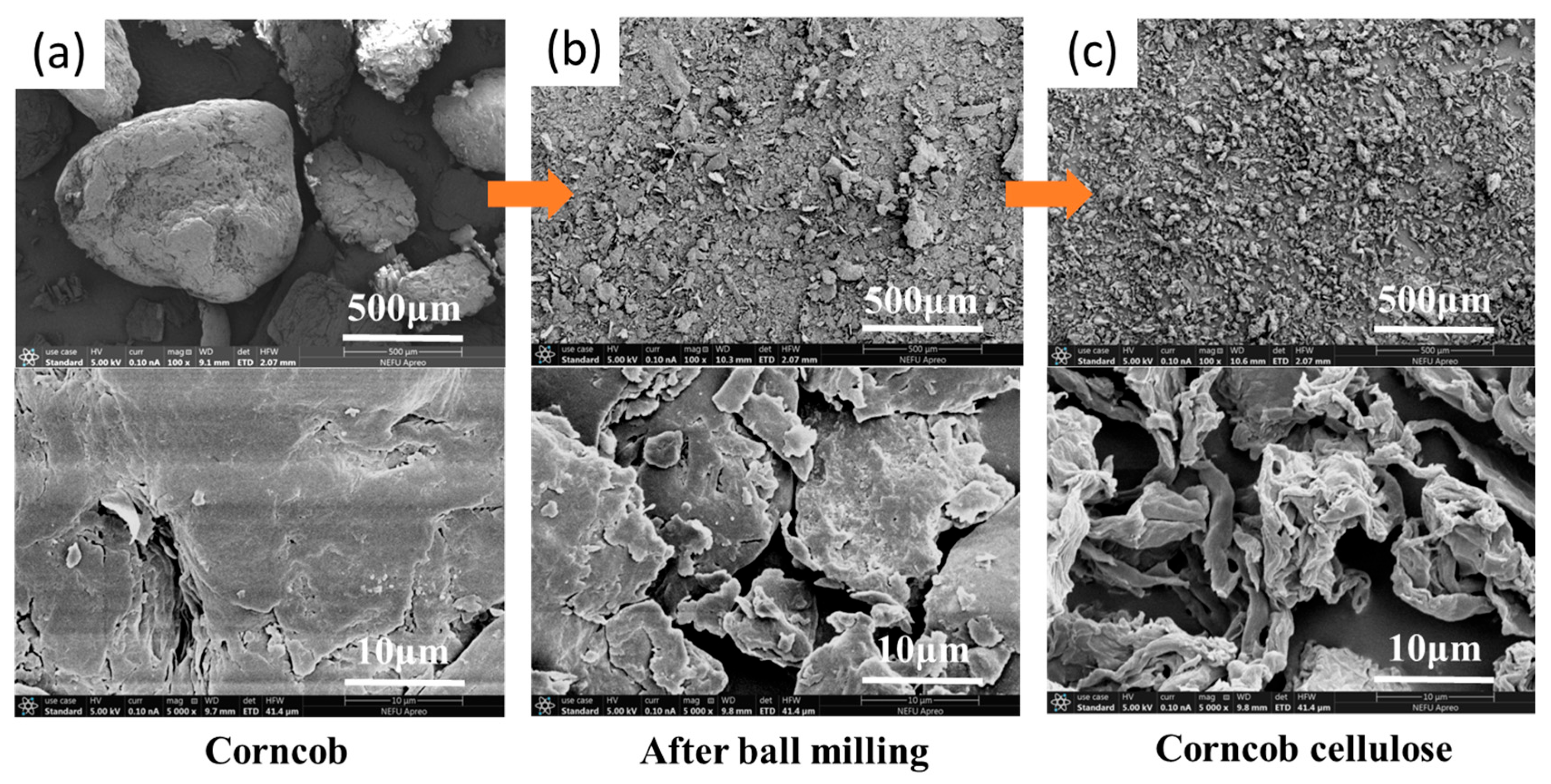
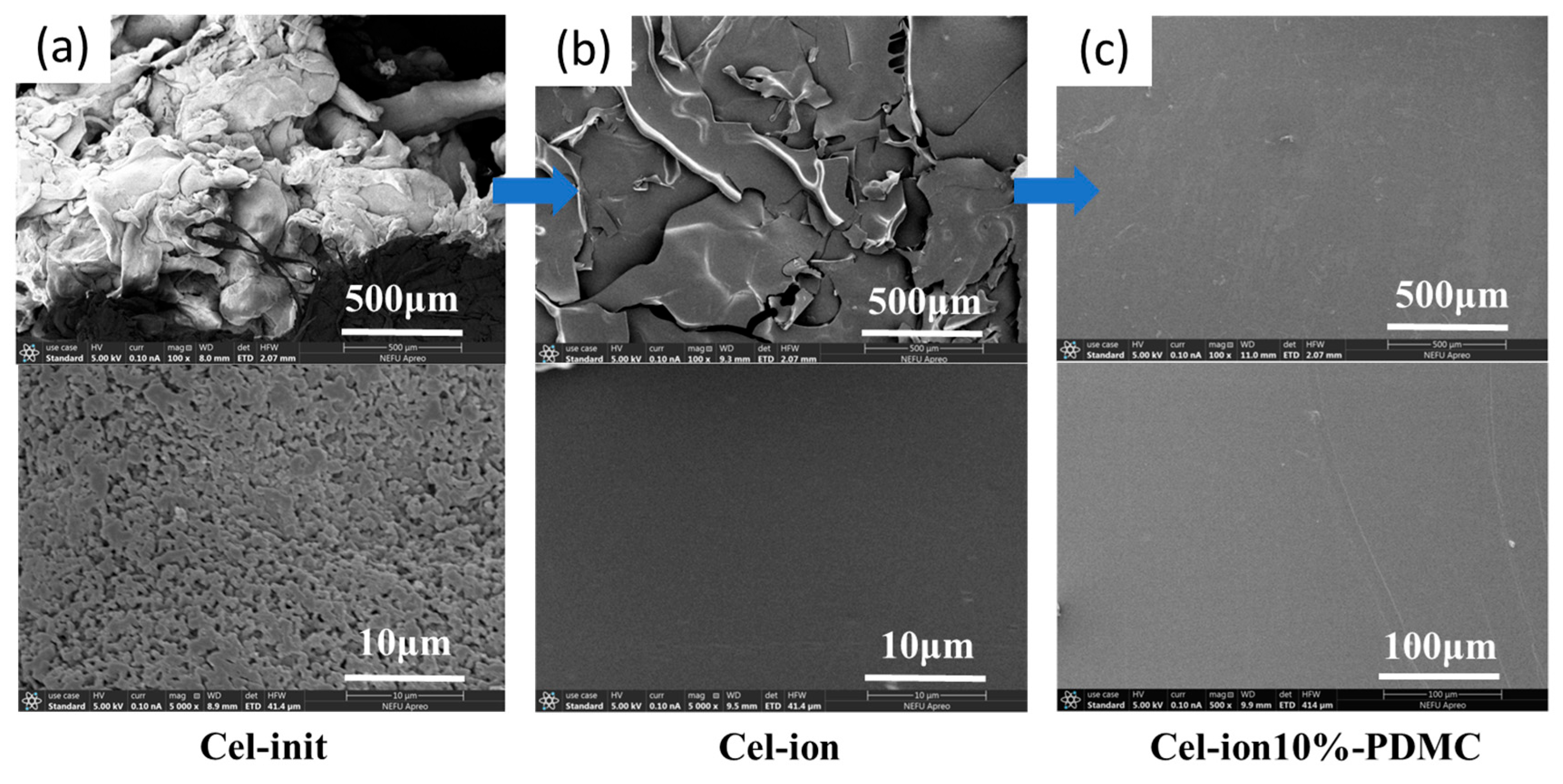
3.3. Surface Morphology Characterization
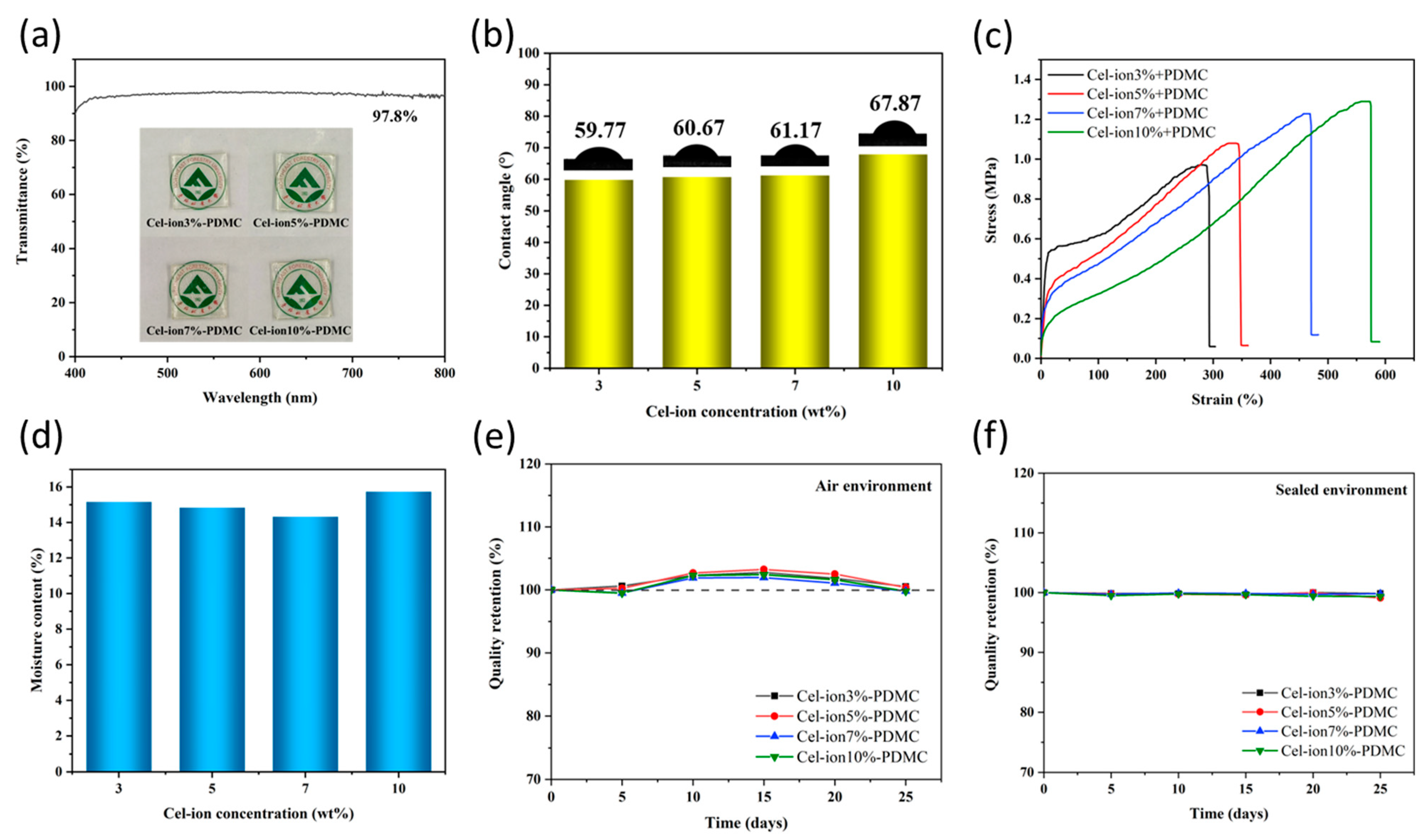
3.4. Transparency, Hydrophilicity, Mechanical Properties, Water Content, and Retention
3.5. Adhesive and Cohesive Performance
3.6. Recyclability and Self-Healing Properties
3.7. Sensing Performance Characterization
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Su, Z.; Cui, L.; Zhang, H.; Xiao, L.; Chi, B.; Xu, H.; Ning, L.; Jia, S.; Wang, X. Robust, waterproof, and degradable cellulose-based polyimine vitrimer for plastic replacement. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 471, 144501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Q.F.; Yang, H.B.; Han, Z.M.; Ling, Z.C.; Yang, K.P.; Yin, C.H.; Yu, S.H. Plant Cellulose Nanofiber-Derived Structural Material with High-Density Reversible Interaction Networks for Plastic Substitute. Nano Lett. 2021, 21, 8999–9004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, B.P.; Smith, C.; Caudill, E.R.; Lankone, R.S.; Carlin, K.; Benware, S.; Pedersen, J.A.; Fairbrother, D.H. Biodegradation of Functionalized Nanocellulose. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 10744–10757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Q.; Chen, C.; Yao, Y.; Li, J.; He, S.; Zhou, Y.; Li, T.; Pan, X.; Yao, Y.; Hu, L. A strong, biodegradable and recyclable lignocellulosic bioplastic. Nat. Sustain. 2021, 4, 627–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Xi, Y.; Weng, Y. Recent Advances in Cellulose-Based Hydrogels for Tissue Engineering Applications. Polymers 2022, 14, 3335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.; Liu, R.; Huang, Y. Cellulose derivatives and graft copolymers as blocks for functional materials. Polym. Int. 2013, 62, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.; Liu, R.; Huang, Y. Graft modification of cellulose: Methods, properties and applications. Polymer 2015, 70, A1–A16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, H.; Zhu, M.; Duan, B.; Zhang, L. Recent Progress in High-Strength and Robust Regenerated Cellulose Materials. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2000682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, T.; Farid, A.; Haq, F.; Kiran, M.; Ullah, A.; Zhang, K.; Li, C.; Ghazanfar, S.; Sun, H.; Ullah, R.; et al. A Review on the Modification of Cellulose and Its Applications. Polymers 2022, 14, 3206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, K.; Liu, Y.; Deng, L.; Chen, S.; Gu, S.; Wang, B. Covalently grafting polycation to bacterial cellulose for antibacterial and anti-cell adhesive wound dressings. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 269, 132157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Vargas, M.; Munguía-Quintero, M.F.; Alcaraz-Cienfuegos, J.; Rosas-Aburto, A.; Valdivia-López, M.; Hernández-Luna, M.G.; Vivaldo-Lima, E. Synthesis, characterization and evaluation of cellulose-graft-poly (4-vinylpirydine), using cellulose from a new pretreatment process, for heavy metal removal from wastewater. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 284, 137986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Han, L.; Li, J.; Fu, X.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Xu, X.; Pan, L.; Xu, M. Super-stretchable, elastic and recoverable ionic conductive hydrogel for wireless wearable, stretchable sensor. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 10291–10300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, H.; Han, W.; Lin, H.; Li, R.; Zhu, J.; Huang, W. 3D Printed Flexible Strain Sensors: From Printing to Devices and Signals. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2004782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Tian, Y.; Chen, L.; Du, Y.; Su, G.; Hu, Y. Multi-Physically Cross-Linked Hydrogels for Flexible Sensors with High Strength and Self-Healing Properties. Polymers 2023, 15, 3748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyun, J.E.; Lim, T.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, J.H. Wearable ion gel based pressure sensor with high sensitivity and ultra-wide sensing range for human motion detection. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 484, 149464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Gao, Z.; Wang, Y.; Guo, L.; Yin, C.; Zhang, X.; Hao, J.; Zhang, G.; Chen, L. Eco-Friendly, Self-Healing Hydrogels for Adhesive and Elastic Strain Sensors, Circuit Repairing, and Flexible Electronic Devices. Macromolecules 2019, 52, 2531–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tie, J.; Mao, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhong, Y.; Sui, X.; Xu, H. Polypyrrole nanorods coated on cellulose nanofibers by pickering emulsion as conductive medium for multimodal gel-based sensor. Cellulose 2022, 29, 6719–6732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Quan, J.; Wang, J.; Pan, H.; Chen, Y.; Xu, J.; Yang, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, T. Multi-response interval, highly sensitive cellulose ionic gel interlocking structure sensor for temperature and pressure measurement. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2025, 383, 116239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Zhang, W.; Wang, D.; Sun, P.; Tao, Y.; Xu, L.; Shi, L. A Packaged and Reusable Hydrogel Strain Sensor with Conformal Adhesion to Skin for Human Motions Monitoring. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 9, 2101786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Wang, L.; Ji, D.; Luo, M.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, G.; Chang, X.; Zhu, Y. Highly stretchable, conductive, and self-adhesive starch-based hydrogel for high-performance flexible electronic devices. Carbohydr. Polym. 2025, 352, 123220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.H.; Zhu, W.B.; Chen, J.Z.; Li, Y.Q.; Huang, P.; Liao, K.; Fu, S.Y. Flexible and electrically robust graphene-based nanocomposite paper with hierarchical microstructures for multifunctional wearable devices. Nano Mater. Sci. 2023, 5, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.B.; Luo, H.S.; Tang, Z.H.; Zhang, H.; Fan, T.; Wang, Y.Y.; Huang, P.; Li, Y.Q.; Fu, S.Y. Ti3C2Tx MXene/Bamboo Fiber/PDMS Pressure Sensor with Simultaneous Ultrawide Linear Sensing Range, Superb Environmental Stability, and Excellent Biocompatibility. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 3546–3556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mccormick, C.L.; Callais, P.A.; Hutchinson, B.H., Jr. Solution studies of cellulose in lithium chloride and N,N-dimethylacetamide. Macromolecules 1985, 18, 2394–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, R.; Xiang, J.; Kang, H.; Liu, Z.; Huang, Y. Dissolution Mechanism of Cellulose in N,N-Dimethylacetamide/Lithium Chloride: Revisiting through Molecular Interactions. J. Phys. Chem. B 2014, 118, 9507–9514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Samples | C (%) | H (%) | N (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cellulose | 42.22 | 5.994 | 0.00 |
| Cel-init | 41.75 | 4.365 | 0.00 |
| Cel-ion | 36.05 | 6.413 | 4.42 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jian, J.; Su, J.; Song, Y.; Wang, J.; Cong, J.; Wei, S.; Gao, Z.; Han, S. Self-Adhesive and Reprocessable Ionogel Sensor from Controllable Ionized Corncob Cellulose. Polymers 2025, 17, 921. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17070921
Jian J, Su J, Song Y, Wang J, Cong J, Wei S, Gao Z, Han S. Self-Adhesive and Reprocessable Ionogel Sensor from Controllable Ionized Corncob Cellulose. Polymers. 2025; 17(7):921. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17070921
Chicago/Turabian StyleJian, Jialin, Jiaqi Su, Yujian Song, Jingshun Wang, Jie Cong, Shuangying Wei, Zhenhua Gao, and Shuaiyuan Han. 2025. "Self-Adhesive and Reprocessable Ionogel Sensor from Controllable Ionized Corncob Cellulose" Polymers 17, no. 7: 921. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17070921
APA StyleJian, J., Su, J., Song, Y., Wang, J., Cong, J., Wei, S., Gao, Z., & Han, S. (2025). Self-Adhesive and Reprocessable Ionogel Sensor from Controllable Ionized Corncob Cellulose. Polymers, 17(7), 921. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17070921







