Regenerated Cellulose Films Coated with Waterborne Polyurethane with Enhanced Mechanical Properties
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of RC@PU Films
2.3. Characterization
2.4. Swelling and Water Evaporation Tests
2.5. Biodegradation Test
2.6. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Assay
3. Results and Discussion
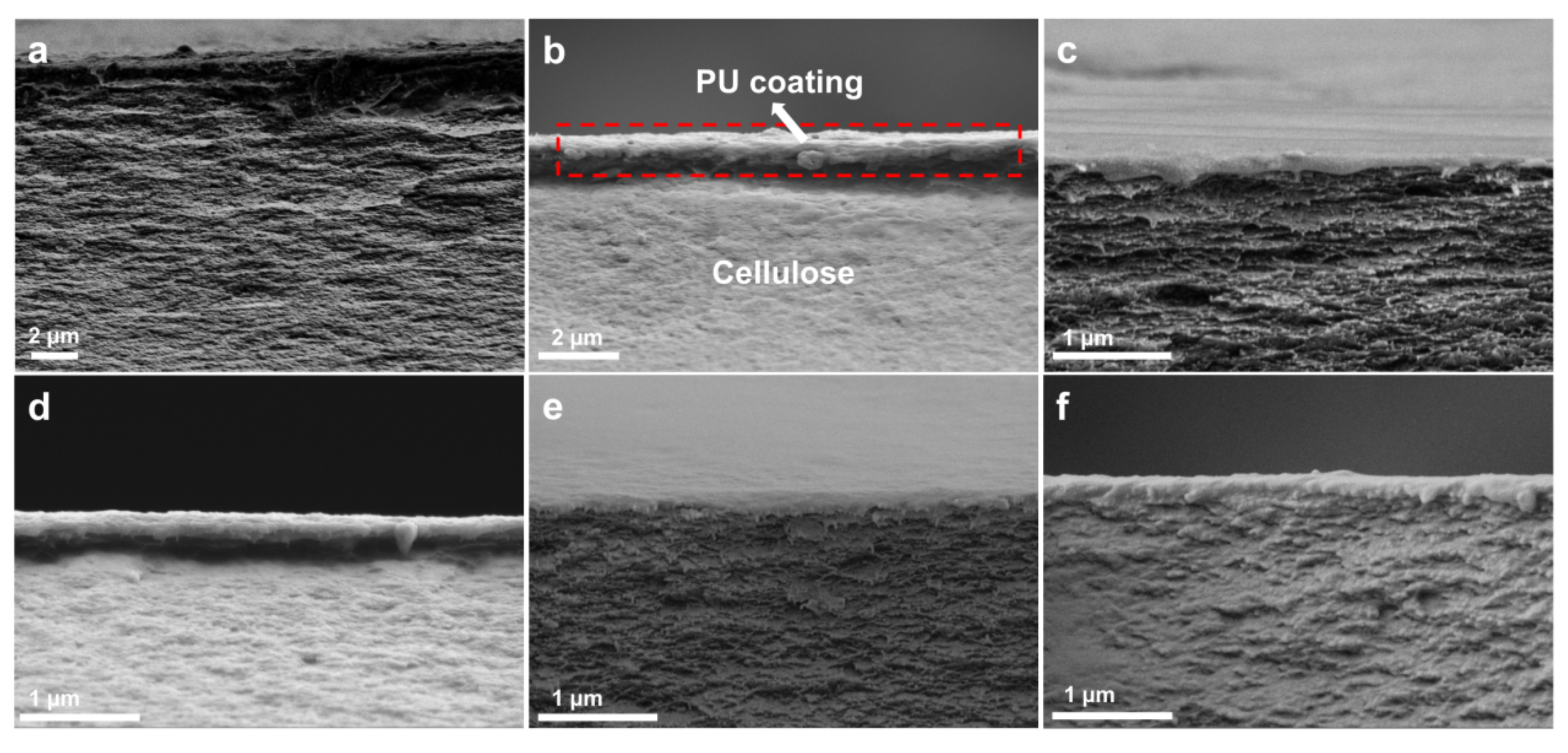
3.1. Structure and Morphology of RC@PU Films
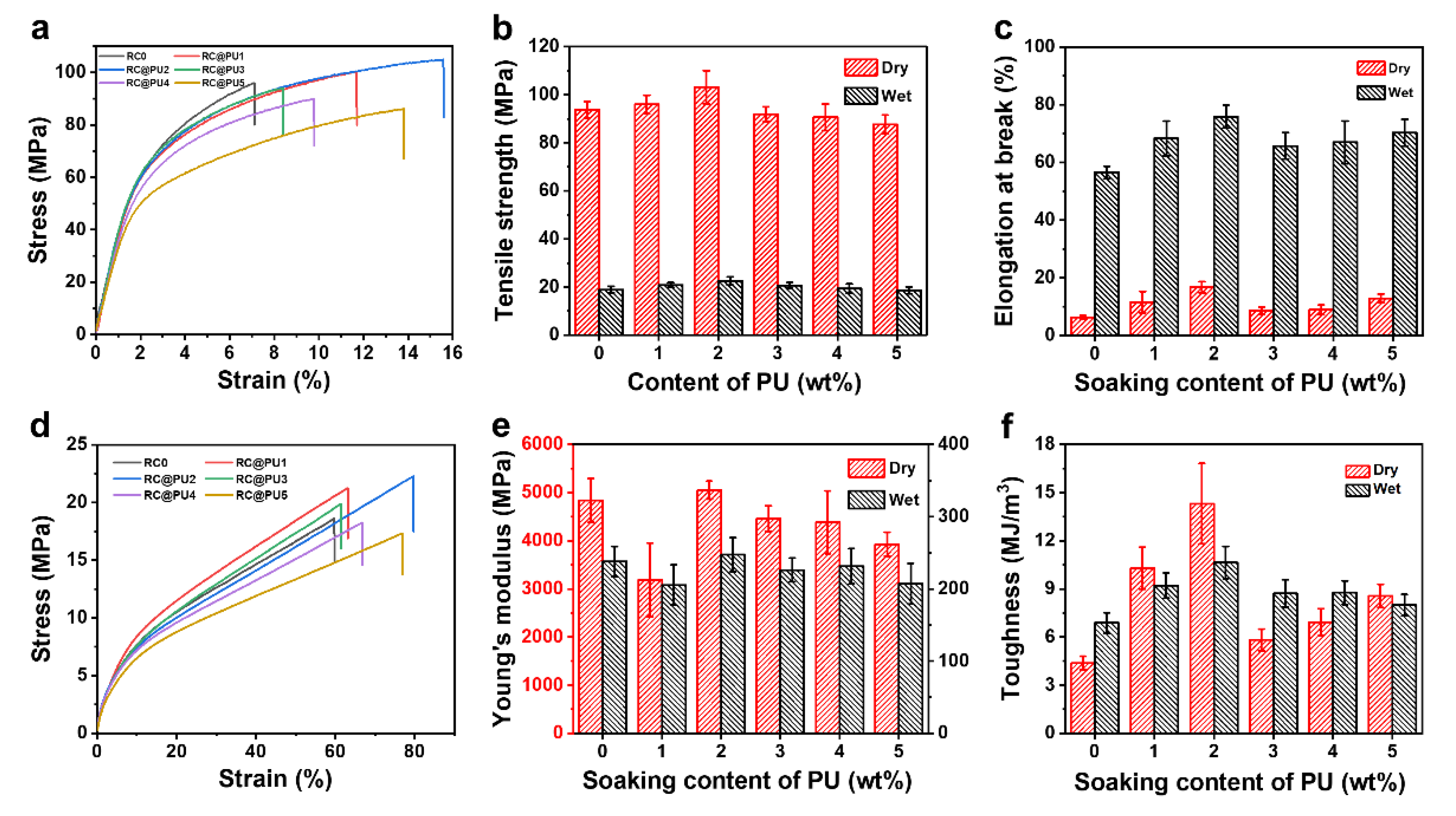
3.2. Physicochemical Properties of RC@PU Films
3.3. Biodegradability and Biocompatibility of RC@PU Films
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hou, D.-F.; Tan, H.; Li, M.-L.; Tang, Y.; Liu, Z.-Y.; Yang, W.; Yang, M.-B. Synthesis of thermoplastic cellulose grafted polyurethane from regenerated cellulose. Cellulose 2020, 27, 8667–8679. [Google Scholar]
- D’Acierno, F.; Hamad, W.Y.; Michal, C.A.; MacLachlan, M.J. Thermal degradation of cellulose filaments and nanocrystals. Biomacromolecules 2020, 21, 3374–3386. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sethi, J.; Farooq, M.; Österberg, M.; Illikainen, M.; Sirviö, J.A. Stereoselectively water resistant hybrid nanopapers prepared by cellulose nanofibers and water-based polyurethane. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 199, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yu, T.-Y.; Tseng, Y.-K.; Lin, T.-H.; Wang, T.-C.; Tseng, Y.-H.; Chang, Y.-H.; Wu, M.-C.; Su, W.-F. Effect of cellulose compositions and fabrication methods on mechanical properties of polyurethane-cellulose composites. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 291, 119549. [Google Scholar]
- Klemm, D.; Heublein, B.; Fink, H.P.; Bohn, A. Cellulose: Fascinating biopolymer and sustainable raw material. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 3358–3393. [Google Scholar]
- Rajala, S.; Siponkoski, T.; Sarlin, E.; Mettanen, M.; Vuoriluoto, M.; Pammo, A.; Juuti, J.; Rojas, O.J.; Franssila, S.; Tuukkanen, S. Cellulose nanofibril film as a piezoelectric sensor material. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 15607–15614. [Google Scholar]
- He, X.; Lu, W.; Sun, C.; Khalesi, H.; Mata, A.; Andaleeb, R.; Fang, Y. Cellulose and cellulose derivatives: Different colloidal states and food-related applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 255, 117334. [Google Scholar]
- Siró, I.; Plackett, D. Microfibrillated cellulose and new nanocomposite materials: A review. Cellulose 2010, 17, 459–494. [Google Scholar]
- Yekta, R.; Abedi-Firoozjah, R.; Azimi Salim, S.; Khezerlou, A.; Abdolmaleki, K. Application of cellulose and cellulose derivatives in smart/intelligent bio-based food packaging. Cellulose 2023, 30, 9925–9953. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, P.; Cai, J.; Zhang, L. High-Strength and Tough Crystalline Polysaccharide-Based Materials. Chin. J. Chem. 2020, 38, 761–771. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, Y.; Wu, S.; Zhu, T.; Gou, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Li, X.; Huang, J.; Lai, Y. Ecological packaging: Creating sustainable solutions with all-natural biodegradable cellulose materials. Giant 2024, 18, 100269. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, H.; Sun, T.; Wu, H.; Wang, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, J. Effect of draw-ratio on the structure and properties of wet-spun cyanoethyl cellulose fibers. Cellulose 2023, 30, 5489–5501. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Fu, Y.; Chen, L.; Wang, R.; Wang, X.; Miao, Y.; Ji, X.; Bian, H.; Dai, H. Diisocyanate modifiable commercial filter paper with tunable hydrophobicity, enhanced wet tensile strength and antibacterial activity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 248, 116791. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Li, T.; Chen, C.; Wang, C.; Liu, Y.; Kong, W.; Liu, D.; Jiang, B.; He, S.; Kuang, Y. A highly conductive cationic wood membrane. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1902772. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, X.; Tao, S.; Ren, X.; Hu, S. Modified cellulose films with controlled permeatability and biodegradability by crosslinking with toluene diisocyanate under homogeneous conditions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 88, 1272–1280. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Du, H.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, M.; Yu, G.; Liu, C.; Li, B.; Peng, H. Flexible cellulose nanopaper with high wet tensile strength, high toughness and tunable ultraviolet blocking ability fabricated from tobacco stalk via a sustainable method. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 13021–13030. [Google Scholar]
- Lakovaara, M.; Sirviö, J.A.; Wang, L.; Suopajärvi, T.; Pratiwi, F.; Zhang, H.; Peltonen, J.; Xu, C.; Liimatainen, H. Glass-like transparent and heat-sealable films of cellulose nanoworms via ethanol triggered swelling of esterified cellulose. J. Mater. Chem. A 2023, 11, 26000–26010. [Google Scholar]
- Pinto, E.R.; Barud, H.S.; Polito, W.L.; Ribeiro, S.J.; Messaddeq, Y. Preparation and characterization of the bacterial cellulose/polyurethane nanocomposites. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2013, 114, 549–555. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, K.; Liu, M.; Cheng, J.; Dong, S.; Wang, C.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, X.; Sun, H.; Chen, X.; Cui, G. Novel cellulose/polyurethane composite gel polymer electrolyte for high performance lithium batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 215, 261–266. [Google Scholar]
- Stanzione, M.; Oliviero, M.; Cocca, M.; Errico, M.; Gentile, G.; Avella, M.; Lavorgna, M.; Buonocore, G.; Verdolotti, L. Tuning of polyurethane foam mechanical and thermal properties using ball-milled cellulose. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 231, 115772. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Zhang, L. Solubility of cellulose in NaOH/urea aqueous solution. Polym. J. 2000, 32, 866–870. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, J.; Zhang, L. Rapid dissolution of cellulose in LiOH/urea and NaOH/urea aqueous solutions. Macromol. Biosci. 2005, 5, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- He, M.; Xu, M.; Zhang, L. Controllable stearic acid crystal induced high hydrophobicity on cellulose film surface. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 585–591. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Saraiva, S.; Rénio, F.; Pereira, P.; Santos, P.; Paula, C.T.; Ramalho, A.; Serra, A.C.; Fonseca, A.C. Tackling the Problem of Tendon Adhesions: Physical Barriers Prepared from α-Amino Acid-Based Poly (ester amide) s. Polymers 2025, 17, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.-S.; Chen, H.-H. Physical properties of bacterial cellulose composites for wound dressings. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 53, 75–83. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Hu, Y.; Lin, X.; Qian, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, J.; Lu, A. High-performance triboelectric nanogenerator based on chitin for mechanical-energy harvesting and self-powered sensing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 291, 119586. [Google Scholar]
- He, F.; Xie, C.; Xu, X. Hyaluronic acid-modified yeast β-glucan particles delivering doxorubicin for treatment of breast cancer. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 314, 120907. [Google Scholar]
- Isogai, A.; Usuda, M.; Kato, T.; Uryu, T.; Atalla, R.H. Solid-state CP/MAS carbon-13 NMR study of cellulose polymorphs. Macromolecules 1989, 22, 3168–3172. [Google Scholar]
- Langan, P.; Nishiyama, Y.; Chanzy, H. A revised structure and hydrogen-bonding system in cellulose II from a neutron fiber diffraction analysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999, 121, 9940–9946. [Google Scholar]
- Souza, A.L.d.; Oliveira, A.V.d.A.; Ribeiro, L.D.; Moraes, A.R.F.E.; Jesus, M.; Santos, J.; Oliveira, T.V.d.; Soares, N.d.F.F. Experimental and Theoretical Analysis of Dopamine Polymerization on the Surface of Cellulose Nanocrystals and Its Reinforcing Properties in Cellulose Acetate Films. Polymers 2025, 17, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, T.; Puglia, D.; Kenny, J.M.; Xu, P.; Zhang, R.; Ma, P. Multiple structure reconstruction by dual dynamic crosslinking strategy inducing self-reinforcing and toughening the polyurethane/nanocellulose elastomers. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2213294. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, L.; Hu, J.; Ying Rena, K.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, P. Quick water-responsive shape memory hybrids with cellulose nanofibers. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2017, 55, 767–775. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, L.; Xiao, H.; Wang, Q.; Sun, J. Thermal degradation characteristics of rigid polyurethane foam and the volatile products analysis with TG-FTIR-MS. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2013, 98, 2687–2696. [Google Scholar]
- Pauzi, N.N.P.N.; Majid, R.A.; Dzulkifli, M.H.; Yahya, M.Y. Development of rigid bio-based polyurethane foam reinforced with nanoclay. Compos. Part. B 2014, 67, 521–526. [Google Scholar]
- Repin, D.; Gablina, M.; Repina, N.; Cherednichenko, K.; Li, W.; Gushchina, Y.; Ivanov, E.; Melnikov, V.; Fakhrullin, R.; Vinokurov, V. Cellulose-Based Composite Materials for Fresh Water Extraction from Atmospheric Air. Polymers 2025, 17, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Chang, C.; Zhang, L. Surface engineering of cellulose film with myristic acid for high strength, self-cleaning and biodegradable packaging materials. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 269, 118315. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, D.; Wei, P.; Zhang, L.; Cai, J. New approach for the fabrication of carboxymethyl cellulose nanofibrils and the reinforcement effect in water-borne polyurethane. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 11850–11860. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, D.; Lei, X.; Li, T.; Cheng, Q.; Chang, C.; Hu, L.; Zhang, L. Ultrahigh tough, super clear, and highly anisotropic nanofiber-structured regenerated cellulose films. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 4843–4853. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P.; Guo, X.; Nan, F.; Duan, Y.; Zhang, J. Modifying mechanical, optical properties and thermal processability of iridescent cellulose nanocrystal films using ionic liquid. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 3085–3092. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.; Zhu, X.; Wang, L.; Wu, F.; Liu, S.; Chang, C.; Luo, X. A simple strategy to design 3-layered Au-TiO2 dual nanoparticles immobilized cellulose membranes with enhanced photocatalytic activity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 231, 115694. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.; Lin, X.; Chang, C.; Duan, B. Chitinous Bioplastic Enabled by Noncovalent Assembly. ACS Nano 2024, 18, 8906–8918. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Ying, D.; Chen, Y.; Xie, H.; Zhang, H.; Chang, C. Highly transparent, hydrophobic, and durable anisotropic cellulose films as electronic screen protectors. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 311, 120735. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Wei, P.; Huang, J.; Xu, D.; Zhong, Y.; Hu, L.; Zhang, L.; Cai, J. Mechanically strong shape-memory and solvent-resistant double-network polyurethane/nanoporous cellulose gel nanocomposites. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 15974–15982. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Gui, H.; Xu, Z.; Zhao, Y. Hydrophobic polyurethane polyHIPEs templated from mannitol within nonaqueous high internal phase emulsions for oil spill recovery. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2019, 57, 1315–1321. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, T.; Shen, H.; Zhao, X.; Wu, H.; Zhou, J. Blended cellulose/chitin membranes prepared by co-solvent method for pervaporation of water-butanol solutions. Cellulose 2024, 31, 5747–5761. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, L.; Xue, L.; Duraiarasan, S.; Haiying, C. Preparation of ε-polylysine/chitosan nanofibers for food packaging against Salmonella on chicken. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2018, 17, 134–141. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Z.; Li, B.; Chu, J.; Zhang, P. Silica in situ enhanced PVA/chitosan biodegradable films for food packages. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 184, 214–220. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, G.; Zhang, H.; Su, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, H.; Yu, L.; Chen, C.; Wang, X. A biodegradable, waterproof, and thermally processable cellulosic bioplastic enabled by dynamic covalent modification. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2301398. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, R.; Chen, G.; Tian, J.; He, M. Highly transparent, weakly hydrophilic and biodegradable cellulose film for flexible electroluminescent devices. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 227, 115366. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, Y.H.; Chang, T.-H.; Zhang, H.; Yao, C.; Zheng, Q.; Yang, V.W.; Mi, H.; Kim, M.; Cho, S.J.; Park, D.-W. High-performance green flexible electronics based on biodegradable cellulose nanofibril paper. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7170. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Shen, H.; Lan, J.; Wu, H.; Wang, L.; Zhou, J. Dual-network polyacrylamide/carboxymethyl chitosan-grafted-polyaniline conductive hydrogels for wearable strain sensors. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 295, 119848. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Willberg-Keyriläinen, P.; Vartiainen, J.; Pelto, J.; Ropponen, J. Hydrophobization and smoothing of cellulose nanofibril films by cellulose ester coatings. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 170, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chu, Y.; Popovich, C.; Wang, Y. Heat sealable regenerated cellulose films enabled by zein coating for sustainable food packaging. Compos. Part C 2023, 12, 100390. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.; Jiao, L.; Liu, W.; Dai, H. Manufacture of highly transparent and hazy cellulose nanofibril films via coating TEMPO-oxidized wood fibers. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Huang, C.; Ge, D.; Liao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, S.; Yu, H.-Y. Highly efficient dissolution and reinforcement mechanism of robust and transparent cellulose films for smart packaging. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 254, 128046. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Wang, T.; Dai, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, L. Surface engineering of regenerated cellulose nanocomposite films with high strength, ultraviolet resistance, and a hydrophobic surface. Polymers 2023, 15, 1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, M. Study on thermal and mechanical properties of cellulose/iron oxide bionanocomposites film. Compos. Commun. 2018, 10, 1–5. [Google Scholar]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiong, R.; Zhou, J. Regenerated Cellulose Films Coated with Waterborne Polyurethane with Enhanced Mechanical Properties. Polymers 2025, 17, 890. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17070890
Xiong R, Zhou J. Regenerated Cellulose Films Coated with Waterborne Polyurethane with Enhanced Mechanical Properties. Polymers. 2025; 17(7):890. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17070890
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiong, Renxiang, and Jinping Zhou. 2025. "Regenerated Cellulose Films Coated with Waterborne Polyurethane with Enhanced Mechanical Properties" Polymers 17, no. 7: 890. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17070890
APA StyleXiong, R., & Zhou, J. (2025). Regenerated Cellulose Films Coated with Waterborne Polyurethane with Enhanced Mechanical Properties. Polymers, 17(7), 890. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17070890







