Effect of UV Radiation Exposure and Simulated Particle Erosion Damage on the Mechanical Behavior of Carbon/Glass Hybrid Composites
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Experimental Methods
2.1. Material
2.2. Aging, Damage Introduction and Characterization Methods
2.3. Mechanical Tests
2.4. Non-Destructive Test
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Silica Particles
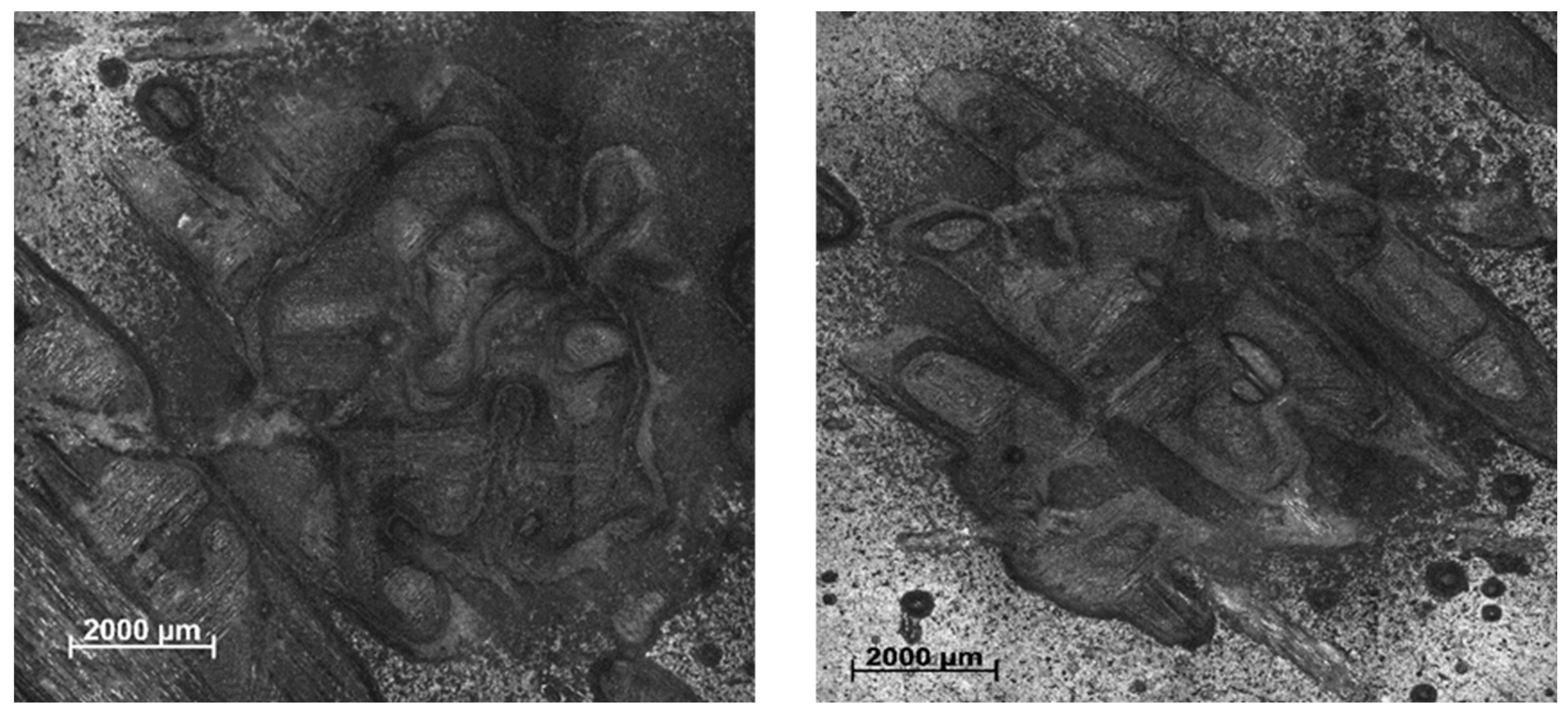
3.2. Microstructural Characterization of the Composite
3.3. Characterization of Surface Damage Caused by Sandblasting
3.4. Colorimetry
3.5. Infrared Analysis (FTIR)
3.6. Mechanical Behavior
3.6.1. ILSS
3.6.2. Bending: Impulse Excitation Test
3.6.3. Bending: Three-Point Bending
4. Conclusions
- During the analysis period used in this study (180 days), the damage caused by UV radiation in the epoxy matrix was restricted to the outer layers of the composite. Therefore, the interlaminar shear strength, therefore, was not affected by UV radiation since this parameter reflects the shear response of the internal layers of a composite.
- The flexural behavior showed that UV exposure caused a greater effect than sandblasting. Thus, samples that were first exposed to UV and then sandblasted showed the greatest drop in flexural strength. This behavior was attributed to the deterioration of the surface layer by the action of UV, which led to a greater ejection of material from the composite when sandblasted.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vieira, P.S.C.; da Silva, G.A.S.; Lopes, B.J.; d’Almeida, J.R.M.; da Silva, A.H.; Cardoso, D.C.T. Hygrothermal aging of steel/FRP pipe repair systems: A literature review. Int. J. Press. Vessel. Pip. 2023, 201, 104881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barile, C.; Casavola, C.; de Cillis, F. Mechanical comparison of new composite materials for aerospace applications. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 162, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ince, J.C.; Peerzada, M.; Mathews, L.D.; Pai, A.R.; Al, A.; Abbasi, S.; Yin, Y.; Hameed, N.; Duffy, A.R.; Lau, A.K.; et al. Overview of emerging hybrid and composite materials for space applications. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2023, 6, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordo, P.; Frederico, T.; Melicio, R.; Duzellier, S.; Amorim, A. System for space materials evaluation in LEO environment. Adv. Space Res. 2020, 66, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekar, R.I.; Rao, P.M.D.; Siddaramaiah; Padaki, V.C.; Kim, N.H.; Lee, J.H. Fibre-fibre hybrid composites for aerospace applications. Adv. Mater. Res. 2010, 123–125, 1231–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Ma, B.; Liu, F.; Huang, W.; Xu, B.; Qu, L.; Yang, Y. Progress in research on composite cryogenic propellant tank for large aerospace vehicles. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2021, 143, 106297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirshova, N.; Qian, H.; Shaffer, M.S.; Steinke, J.H.; Greenhalgh, E.S.; Curtis, P.T.; Kucernak, A.; Bismarck, A. Structural composite supercapacitors. Compos. Part A: Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2013, 46, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhang, D.; Gu, C.; Zhao, R.; Zuo, X.; Tong, L.; Shang, C.; Sun, H. Research and application of advanced resin matrix composites for aerospace shuttle vehicles abroad. Acta Mater. Compos. Sin. 2022, 39, 3029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.T.G.; Delkowki, M.; Anguita, J.V.; Cox, D.C.; Haas, C.; Silva, S.R.P. Complete Atomic Oxygen and UV Protection for Polymer and Composite Materials in a Low Earth Orbit. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 6670–6677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearsley, A.T.; Graham, G.A.; Yano, H.; Wright, I.P. Micrometeoroids&Orbital Debris Preserved on Multi-Layered Insulation Foils from the Japanese Space Flyer Unit Spacecraft. Lunar Planet. Sci. 2002, 33, 1122. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, D.Q.; Chi, R.G.; Liu, Y.Y.; Pang, B.J. Sensitivity analysis of spacecraft in micrometeoroids and orbital debris environment based on panel method. Def. Technol. 2023, 19, 126–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suliga, A.; Jakubczyk, E.M.; Hamerton, I.; Viquerat, A. Analysis of atomic oxygen and ultraviolet exposure effects on cycloaliphatic epoxy resins reinforced with octa-functional POSS. Acta Astronaut. 2018, 142, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrier, B.L.; Abbey, W.J.; Beegle, L.W.; Bhartia, R.; Liu, Y. Attenuation of Ultraviolet Radiation in Rocks and Minerals: Implications for Mars Science. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2019, 124, 2599–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royer, C.; Bernard, S.; Beyssac, O.; Balan, E.; Forni, O.; Gauthier, M.; Morand, M.; Garino, Y.; Rosier, P. Impact of UV radiation on the Raman and infrared spectral signatures of sulfates, phosphates and carbonates: Implications for Mars exploration. Icarus 2024, 410, 115894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemmon, M.T.; Smith, M.D.; Viudez-Moreiras, D.; de la Torre-Juarez, M.; Vicente-Retortillo, A.; Munguira, A.; Sanchez-Lavega, A.; Hueso, R.; Martinez, G.; Chide, B.; et al. Sand, and Winds Within an Active Martian Storm in Jezero Crater. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2022, 49, e2022GL100126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ainali, N.M.; Bikiaris, D.N.; Lambropoulou, D.A. Aging effects on low- and high-density polyethylene, polypropylene and polystyrene under UV irradiation: An insight into decomposition mechanism by Py-GC/MS for microplastic analysis. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2021, 158, 105207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokrieh, M.M.; Bayat, A. Effects of ultraviolet radiation on mechanical properties of glass/polyester composites. J. Compos. Mater. 2007, 41, 2443–2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayandi, K.; Rajini, N.; Ayrilmis, N.; Devi, M.P.I.; Siengchin, S.; Mohammad, F.; Al-Lohedan, H.A. An overview of endurance and ageing performance under various environmental conditions of hybrid polymer composites. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 15962–15988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roylance, M.; Roylance, D. Forms of polymer degradation. In Environmental Degradation of Advanced and Traditional Engineering Materials; Hihara, L.H., Adler, R.P.I., Latanision, R.M., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014; Chapter 13; pp. 337–348. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, B.G.; Singh, R.P.; Nakamura, T. Degradation of carbon fiber-reinforced epoxy composites by ultraviolet radiation and condensation. J. Compos. Mater. 2002, 36, 2713–2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, R.F.; d’Almeida, J.R.M.; Rabello, M.S. Elastic properties of degraded polypropylene. J. Mater. Sci. 2007, 42, 2167–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, R.F. Principles of Composite Materials Mechanics; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Lan, Z.; Deng, J.; Song, Y.; Xu, Z.; Nie, Y.; Chen, Y.; Ma, Y. Color Changes and Mechanical Properties of Glass Fiber Reinforced Polycarbonate Composites after Thermal Aging. Polymers 2022, 14, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Commission Internationale de l’Eclairage. CIE Technical Report: Colorimetry; CIE Pub No. 15.3.; CIE Central Bureau: Vienna, Austria, 2004; ISBN 3 901 906 33 9. [Google Scholar]
- Graham, G.A.; Kearsley, A.T.; Drolshagen, G.; Wright, I.P.; Grady, M.M.; Jones, C.G. Impact damage to space hardware: Identifying the culprits. Microsc. Anal. 2000, 27–28. [Google Scholar]
- Bijwe, J.; Indumathi, J.; Ghosh, A.K. On the abrasive wear behaviour of fabric-reinforced polyetherimide composites. Wear 2002, 253, 768–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hejjaji, A.; Zitoune, R.; Toubal, L.; Crouzeix, L.; Collombet, F. Influence of controlled depth abrasive water jet milling on the fatigue behavior of carbon/epoxy composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2019, 121, 397–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paciornik, S.; Maurício, M.H.P. Digital imaging. In ASM Handbook: Metallography and Microstructures; Voort, G.F.V., Ed.; ASM International: Materials Park, OH, USA, 2004; pp. 368–402. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 21920-2; Geometrical Product Specifications (GPS)—Surface Texture: Profile Part 2: Terms, Definitions and Surface Texture Parameters. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021.
- Whitehouse, D. Handbook of Surface and Nanometrology, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, A.A.C.; d’Almeida, J.R.M. Wear behavior of polyamide 11 reinforced with titanate nanotubes. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2023, 36, 510–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D790; Standard Test Methods for Flexural Properties of Unreinforced and Reinforced Plastics and Electrical Insulating Materials. American Society for Testing and Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2017.
- ASTM D2344; Standard Test Method for Short-Beam Strength of Polymer Matrix Composite Materials and Their Laminates. American Society for Testing and Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2022.
- ASTM E 1876; Standard Test Method for Dynamic Young’s Modulus, Shear Modulus, and Poisson’s Ratio by Impulse Excitation of Vibration. American Society for Testing and Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2022.
- de Silva, C.W. Vibration Damping, Control and Design; Taylor & Francis: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, H.J.; Hutton, R.E.; Clow, G.D.; Spitzer, C.R. Physical properties of the surface materials at the Viking landing sites on Mars. In USGS Numbered Series Professional Paper 1389; USGS: Reston, VA, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemmon, M.T.; Guzewich, S.D.; McConnochie, T.; de Vicente-Retortillo, A.; Martínez, G.; Smith, M.D.; Bell, J.F., III.; Wellington, D.; Jacob, S. Large dust aerosol sizes seen during the 2018 Martian global dust event by the curiosity rover. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 9448–9456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen-Chen, H.; Pérez-Hoyos, S.; Sánchez-Lavega, A.; Peralta, J. Characterization of deposited dust particles on Mars insight lander Instrument Context Camera (ICC) lens. Icarus 2023, 392, 115393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazumder, M.K.; Saini, D.; Bins, A.S.; Srirama, P.K.; Calle, C.; Buhie, C. Mars Dust: Characterization of Particle size and Electrostatic Charge Distributions; Report number: KSC-2004-032; Kennedy Space Center: Merritt Island, FL, USA.
- Mazumder, M.K.; Calle, C.I.; Srirama, P.K.; Wilson, J.D.; Zhang, J.; Buhler, C.H.; Ali, M. In-Situ and simultaneous measurements of size and charge distributions of dust on Mars: Instrumentation and analysis. In Proceedings of the Seventh International Conference on Mars, Pasadena, CA, USA, 9–13 July 2007. Paper 3391. [Google Scholar]
- Grossman, E.; Gouzman, I.; Verker, R. Debris/Micrometeoroid Impacts and Synergistic Effects on Spacecraft Materials. MRS Bull. 2010, 35, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeo, R.C.; Martina, R.N.; Bollweg, K. Discussions on radiation and space environment exposure of replicated optical mirrors produced from carbon composites. In Proceedings of the SPIE 9616, Nanophotonics and Macrophotonics for Space Environments IX, 961602, San Diego, CA, USA, 13–15 August 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, C.S.; Catugas, I.G.; Gillespie, J.W.; Haque, B.Z.G. Investigation of normal, lateral, and oblique impact of microscale projectiles into unidirectional glass/epoxy composites. Def. Technol. 2022, 18, 1960–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.N.; George, J.M.; Patlolla, V.R.; Asmatulu, R. Investigating the effects of UV light and moisture ingression on low-impact resistance of three different carbon fiber–reinforced composites. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2019, 2, 701–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schanda, J. Colorimetry: Understanding the CIE System; John Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Komorek, A.; Przybylek, P.; Brzozowski, D. The influence of UV radiation upon the properties of fibre reinforced polymers. Solid State Phenom. 2015, 223, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.; Hodgkin, J. Long-Term Aging in a Commercial Aerospace Composite Sample: Chemical and Physical Changes. J. O Fapplied Polym. Sci. 2010, 115, 2981–2985. [Google Scholar]
- Silverstein, R.M.; Webster, F.X.; Kiemle, D.J. Spectrometric Identification of Organic Compounds, 7th ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.; Yan, D.; Fu, J.; Chen, Y.; Ou, H. Ultraviolet-C and vacuum ultraviolet inducing surface degradation of microplastics. Water Res. 2020, 186, 116360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smoleń, J.; Olesik, P.; Nowacki, B.; Godzierz, M.; Kurtyka, K.; Chaber, P.; Czakiert, J.; Kozioł, M. The influence of UV radiation on the properties of GFRP laminates in underwater conditions. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 7446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniels, B.K.; Harakas, N.K.; Jackson, R.C. Short beam shear tests of graphite fiber composites. Fibre Sci. Technol. 1971, 3, 187–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, K.B.; Kim, C.G.; Hong, C.S.; Lee, H.H. Prediction of failure thermal cycles in graphite/epoxy composite materials under simulated low earth orbit environments. Compos. Part B 2000, 31, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liau, W.B.; Tseng, F.P. The effect of long-term ultraviolet light irradiation on polymer matrix composites. Polym. Compos. 1998, 19, 440–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Liu, X.; Feng, P. A comprehensive review on mechanical properties of pultruded FRP composites subjected to long-term environmental effects. Compos. Part B 2020, 191, 107958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, T.; Singh, R.P.; Vaddadi, P. Effects of Environmental Degradation on Flexural Failure Strength of Fiber Reinforced Composites. Exp. Mech. 2006, 46, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, S.S.; Helms, J.E.; Li, G.; Ibekwe, S.I. Influence of ultraviolet radiation on the Low velocity impact response of laminated composite. In Proceedings of the Engineering Technology Conference on Energy, Part B, Houston, TX, USA, 5–7 February 2001; pp. 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Ávila, D.; Orozco-Caballero, A.; Martínez, E.; Portolés, L.; Barea, R.; Carreño, F. High-accuracy compliance correction for nonlinear mechanical testing: Improving small punch test characterization. Nucl. Mater. Energy 2021, 26, 100914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, J.E.L., Jr.; Paciornik, S.; d’Almeida, J.R.M. Determination of the post-ballistic impact mechanical behavior of a ±45° glass–fabric composite. Polym. Test. 2004, 23, 599–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

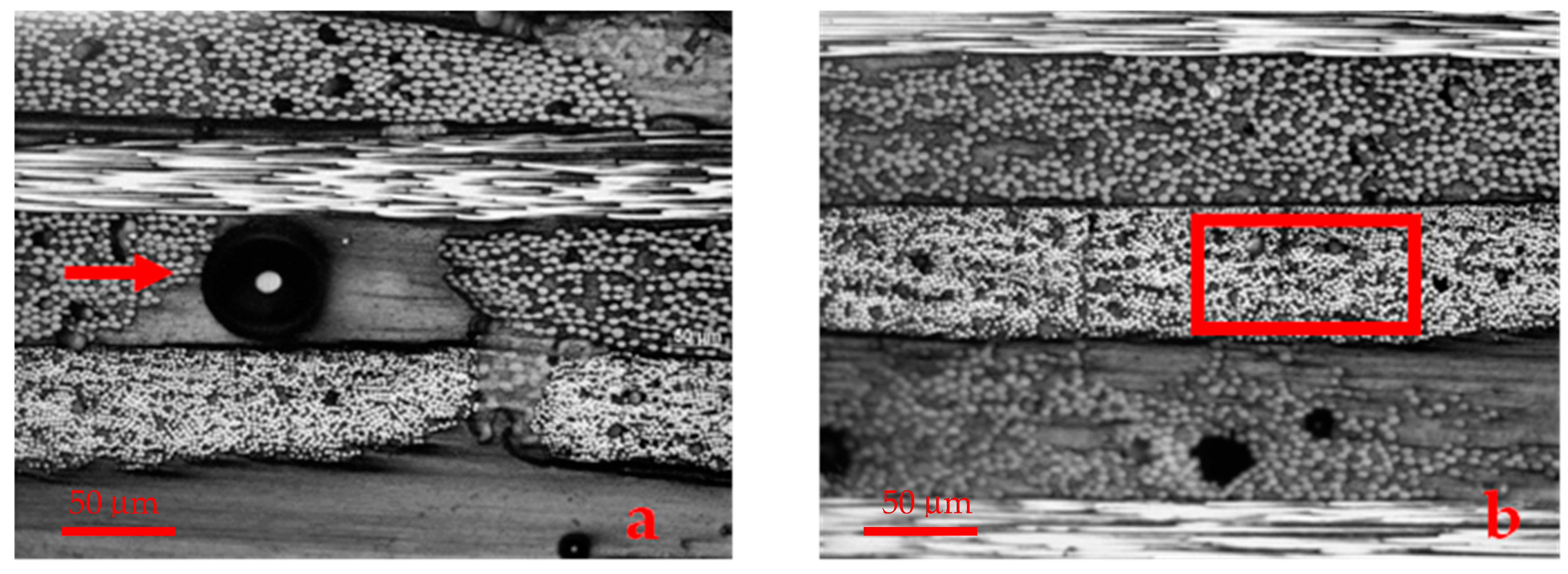

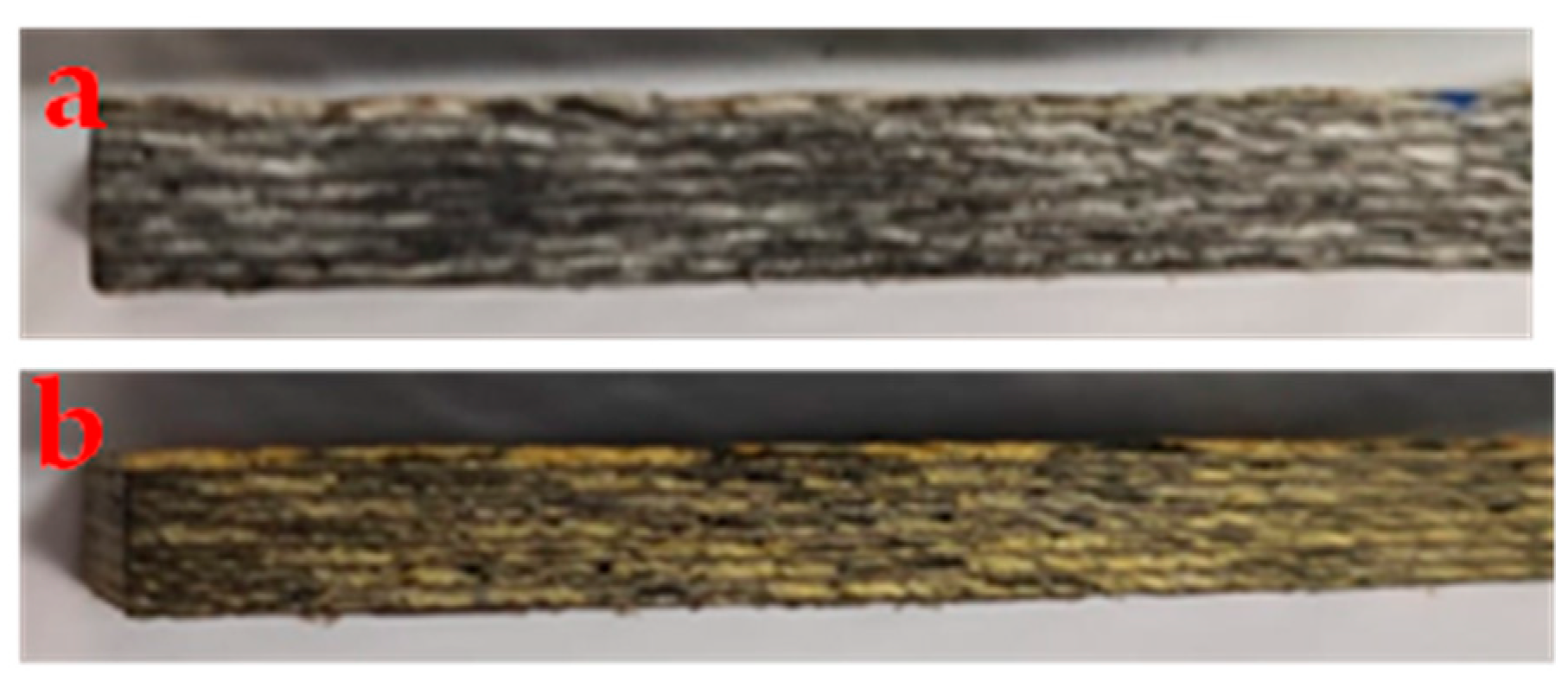
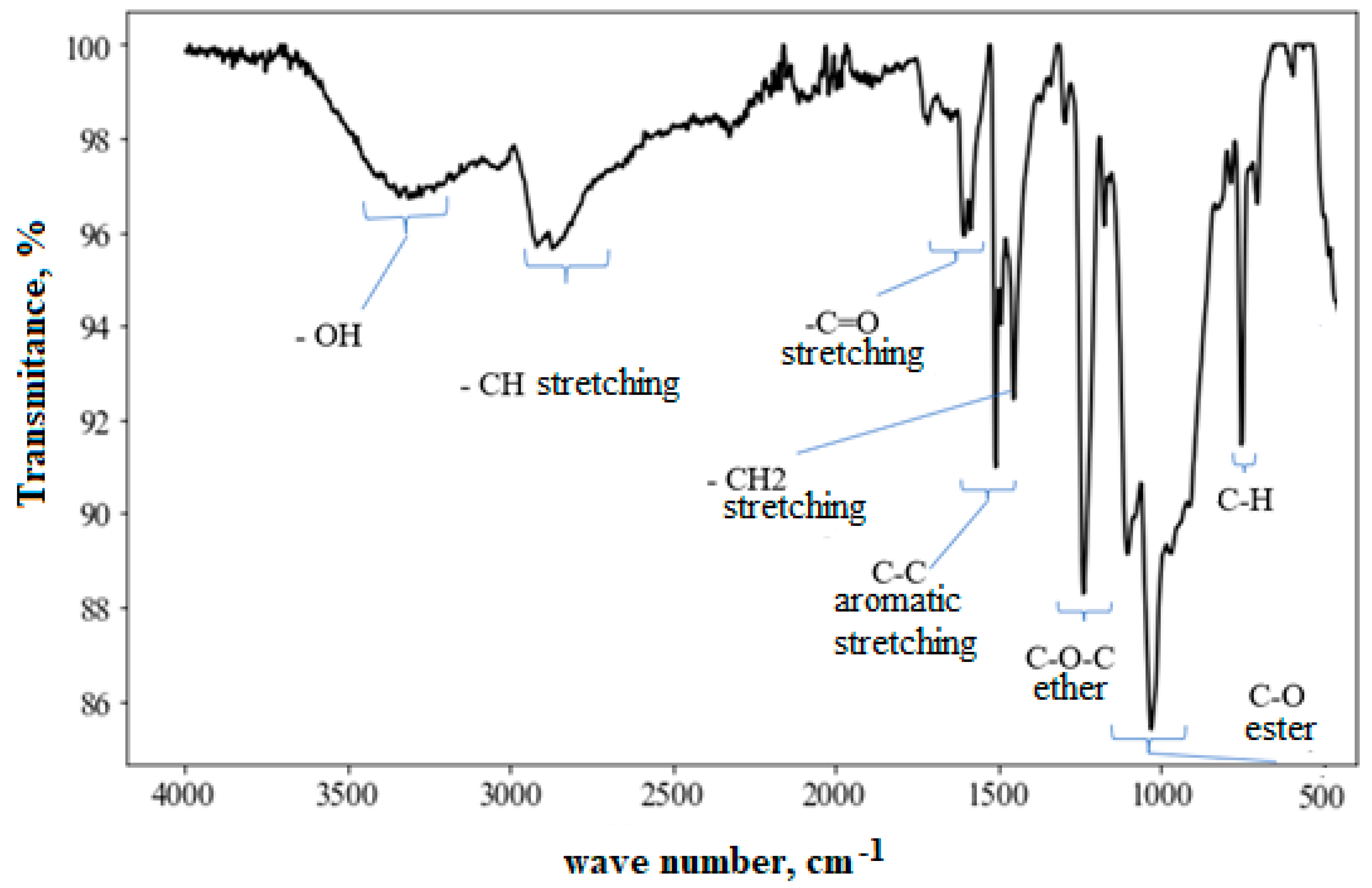


| Samples | Total Aging Time (Days) | Damage Introduction Procedure |
|---|---|---|
| #1 | 60 | UV aging for 60 days + sandblasting |
| #2 | 120 | UV aging for 60 days + sandblasting + aging for 60 days |
| #3 | UV aging for 120 days + sandblasting | |
| #4 | sandblasting + UV aging for 120 days | |
| #5 | 180 | UV aging for 60 days + sandblasting + aging for 120 days |
| Rv | Rp | Rt | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Average | 0.335 ± 0.130 | 1.387 ± 0.392 | 1.722 ± 0.477 |
| Surface | L* | a* | b* |
|---|---|---|---|
| As received | 18.876 ± 2.427 | −1.274 ± 0.410 | 4.227 ± 1.271 |
| UV 60 | 19.151 ± 2.795 | −1.500 ± 0.602 | 8.049 ± 1.161 |
| UV 120 | 20.017 ± 1.196 | −3.277 ± 0.842 | 10.515 ± 1.367 |
| UV 180 | 22.955 ± 1.415 | −3.215 ± 0.438 | 9.854 ± 1.718 |
| Lateral | L* | a* | b* |
| As received | 31.777 ± 8.737 | −0.802 ± 0.242 | 4.420 ± 0.567 |
| UV 60 | 36.064 ± 4.616 | −2.543 ± 0.525 | 12.877 ± 2.892 |
| UV 120 | 31.995 ± 3.369 | −2.312 ± 0.353 | 11.179 ± 1.631 |
| UV 180 | 37.446 ± 2.528 | −2.563 ± 0.247 | 12.422 ± 1.363 |
| Surface | ΔL* | Δa* | Δb* | ΔE* |
| UV 60 | 0.274 | −0.226 | 3.822 | 3.838 |
| UV 120 | 1.141 | −2.003 | 6.275 | 6.685 |
| UV 180 | 4.079 | −1.941 | 5.627 | 7.216 |
| Side | ΔL* | Δa* | Δb* | ΔE* |
| UV 60 | 4.287 | −1.743 | 8.457 | 9.641 |
| UV 120 | 0.218 | −1.509 | 6.759 | 6.929 |
| UV 180 | 5.668 | −1.761 | 8.003 | 9.964 |
| As-Manufactured | 60 Days | 120 Days | 180 Days | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| τ (MPa) | 34.3 ± 4.2 | 28.8 ± 6.1 | 35.3 ± 6.5 | 35.7 ± 6.1 |
| As-Manufactured | 60 Days | 120 Days | 180 Days | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| E (GPa) | 26.7 ± 0.4 | 23.5 ± 1.8 | 24.5 ± 1.7 | 24.5 ± 1.0 |
| CV (%) | 1.6 | 7.7 | 6.9 | 4.0 |
| Samples | E (GPa) | CV (%) | Median (GPa) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reference | 25.7 ± 0.8 | 2.9 | 25.7 |
| #1 | 22.6 ± 3.2 | 14.0 | 23.8 |
| #2 | 24.9 ± 0.1 | 2.0 | 24.7 |
| #3 | 24.3 ± 1.1 | 4.4 | 24.2 |
| #4 | 23.0 ± 2.1 | 9.3 | 23.6 |
| #5 | 23.4 ± 3.3 | 14.2 | 23.9 |
| As-Manufactured | 60 Days | 120 Days | 180 Days | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| E (GPa) | 19.9 ± 2.9 | 20.9 ± 2.1 | 20.5 ± 2.4 | 20.8 ± 1.9 |
| σr (MPa) | 392.5 ± 59.3 | 379.4 ± 36.3 | 411.0 ± 44.6 | 371.6 ± 61.1 |
| Samples | E (GPa) | CV (%) | σr (MPa) | CV (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reference | 20.7 ± 1.4 | 6.6 | 312.5 ± 42.2 | 13.5 |
| #1 | 21.4 ± 1.5 | 7.0 | 352.3 ± 65.5 | 18.6 |
| #2 | 20.2 ± 2.6 | 6.6 | 354.3 ± 44.2 | 12.5 |
| #3 | 21.9 ± 1.4 | 6.3 | 369.0 ± 15.7 | 4.2 |
| #4 | 22.0 ± 2.5 | 11.4 | 385.0 ± 45.7 | 11.9 |
| #5 | 20.3 ± 3.5 | 17.1 | 331.4 ± 38.9 | 11.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tostes, M.d.V.P.H.; d’Almeida, J.R.M. Effect of UV Radiation Exposure and Simulated Particle Erosion Damage on the Mechanical Behavior of Carbon/Glass Hybrid Composites. Polymers 2025, 17, 861. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17070861
Tostes MdVPH, d’Almeida JRM. Effect of UV Radiation Exposure and Simulated Particle Erosion Damage on the Mechanical Behavior of Carbon/Glass Hybrid Composites. Polymers. 2025; 17(7):861. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17070861
Chicago/Turabian StyleTostes, Marcello de Vasconcelos Porto Hermanny, and José Roberto Moraes d’Almeida. 2025. "Effect of UV Radiation Exposure and Simulated Particle Erosion Damage on the Mechanical Behavior of Carbon/Glass Hybrid Composites" Polymers 17, no. 7: 861. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17070861
APA StyleTostes, M. d. V. P. H., & d’Almeida, J. R. M. (2025). Effect of UV Radiation Exposure and Simulated Particle Erosion Damage on the Mechanical Behavior of Carbon/Glass Hybrid Composites. Polymers, 17(7), 861. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17070861






