Effect of the Interior Fill Percentage on the Deterioration of the Mechanical Properties of FFF-3D-Printed PLA Structures
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
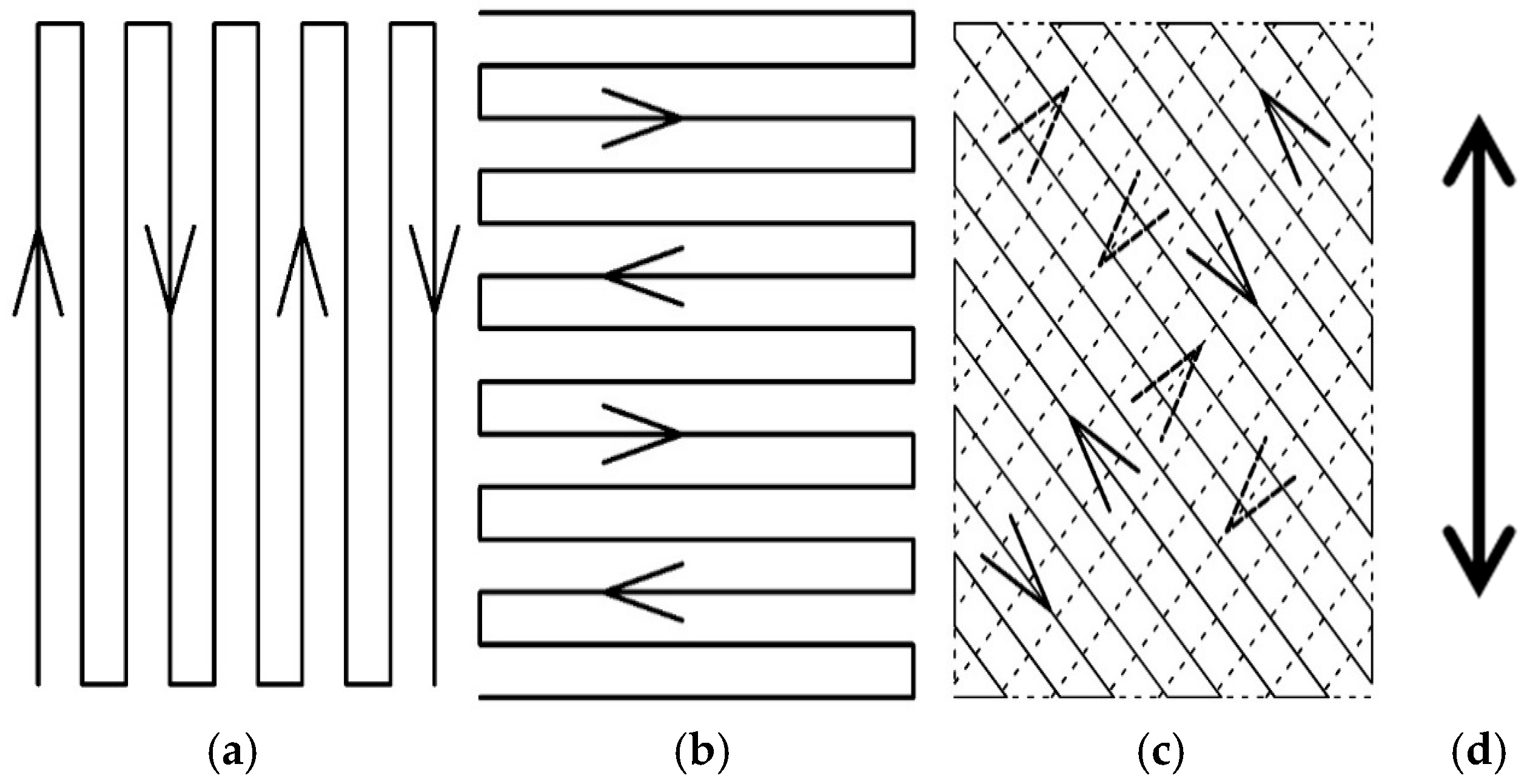
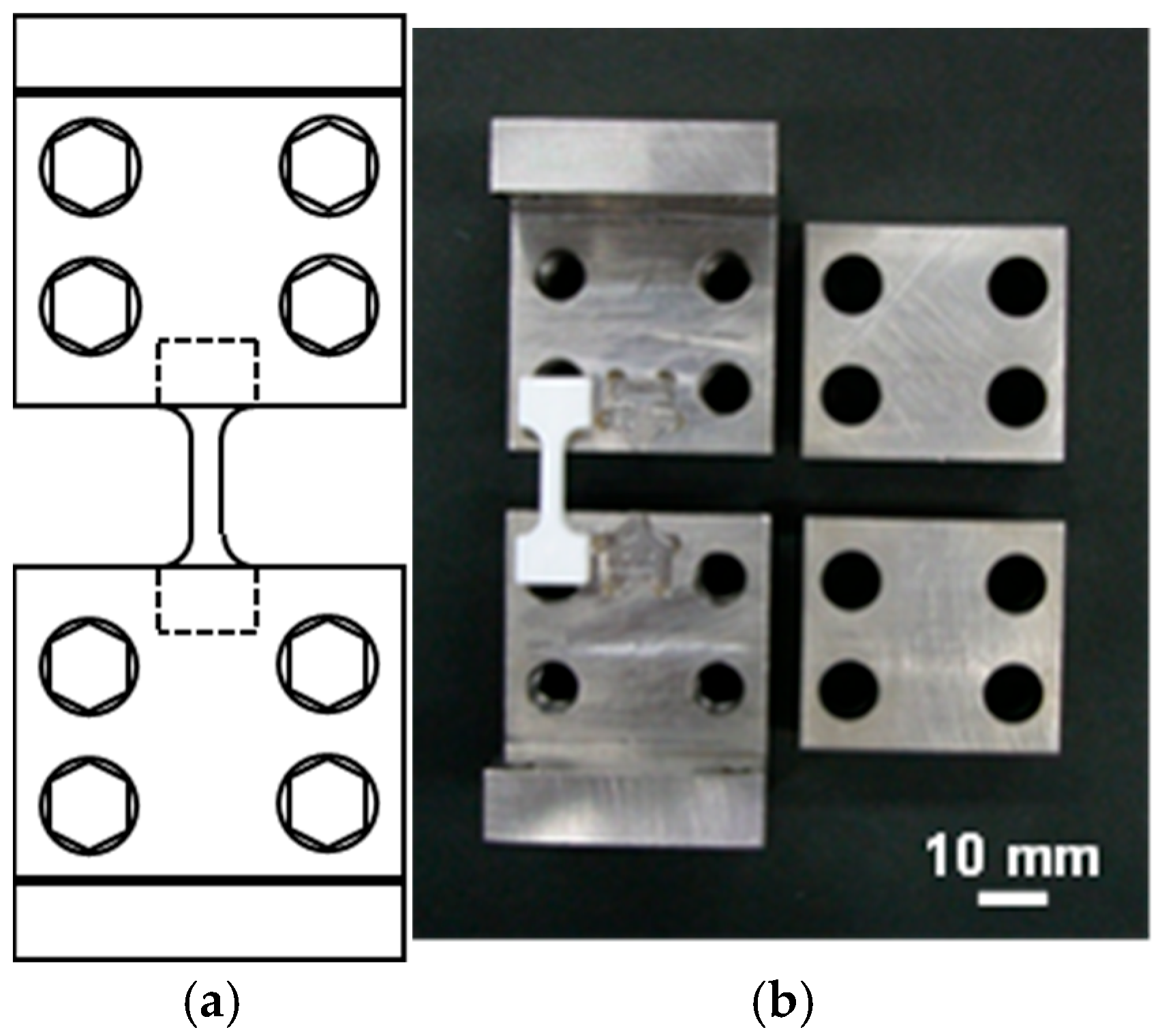
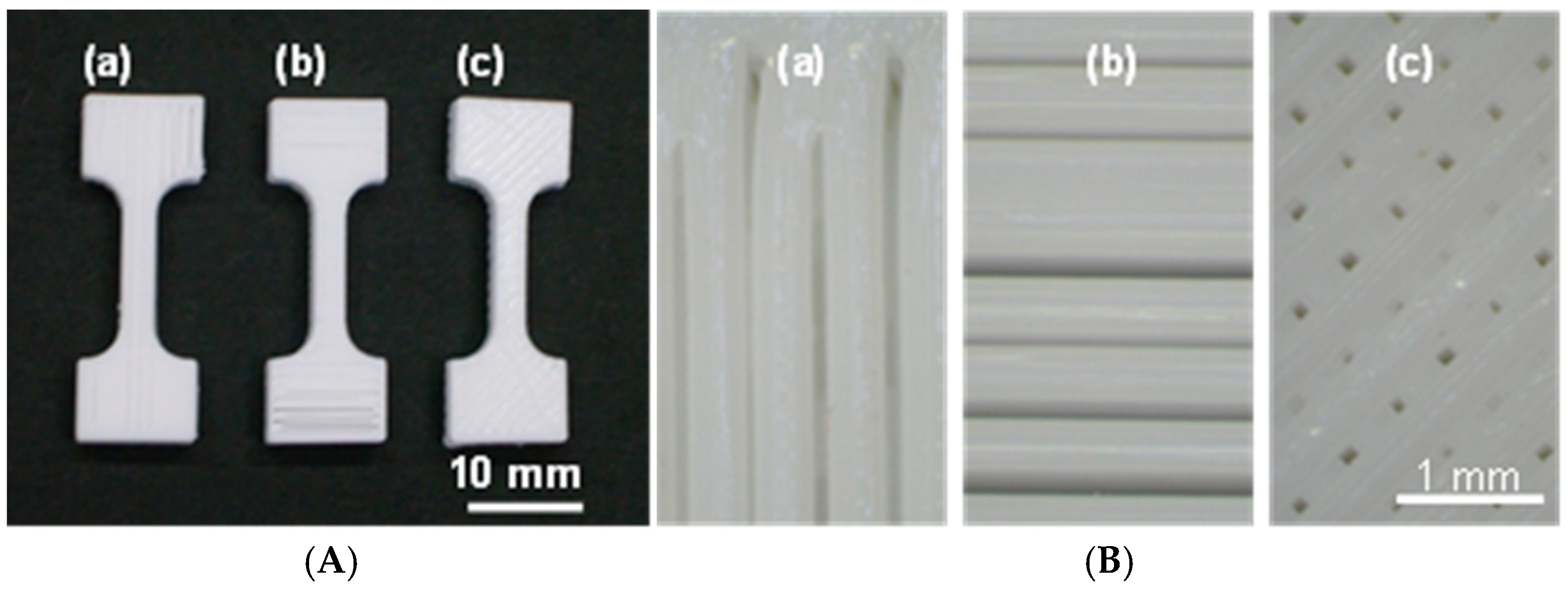
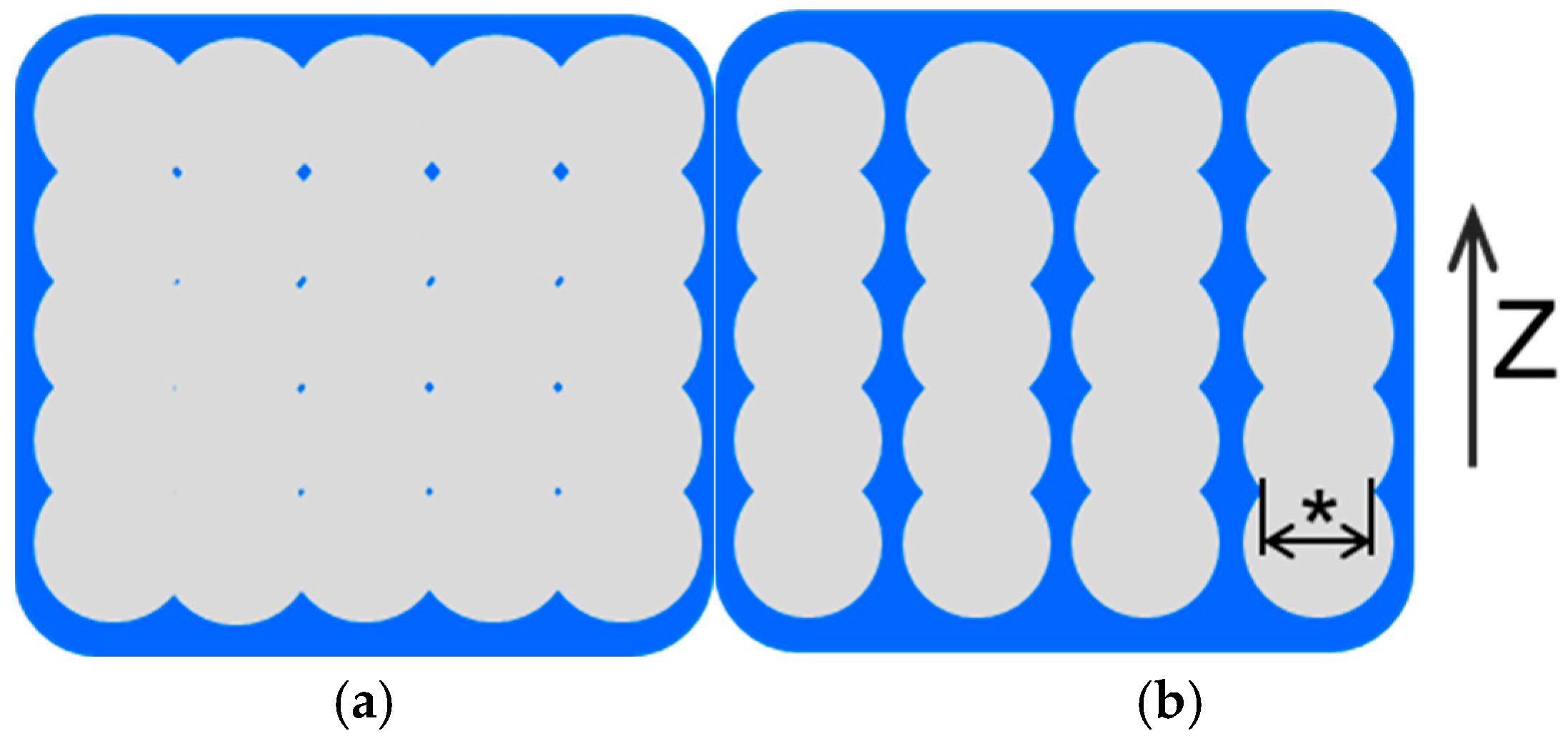
2.1. Preparation of the Test Pieces
2.2. Measurement of the Moisture Content
2.3. Evaluation of Mechanical Properties
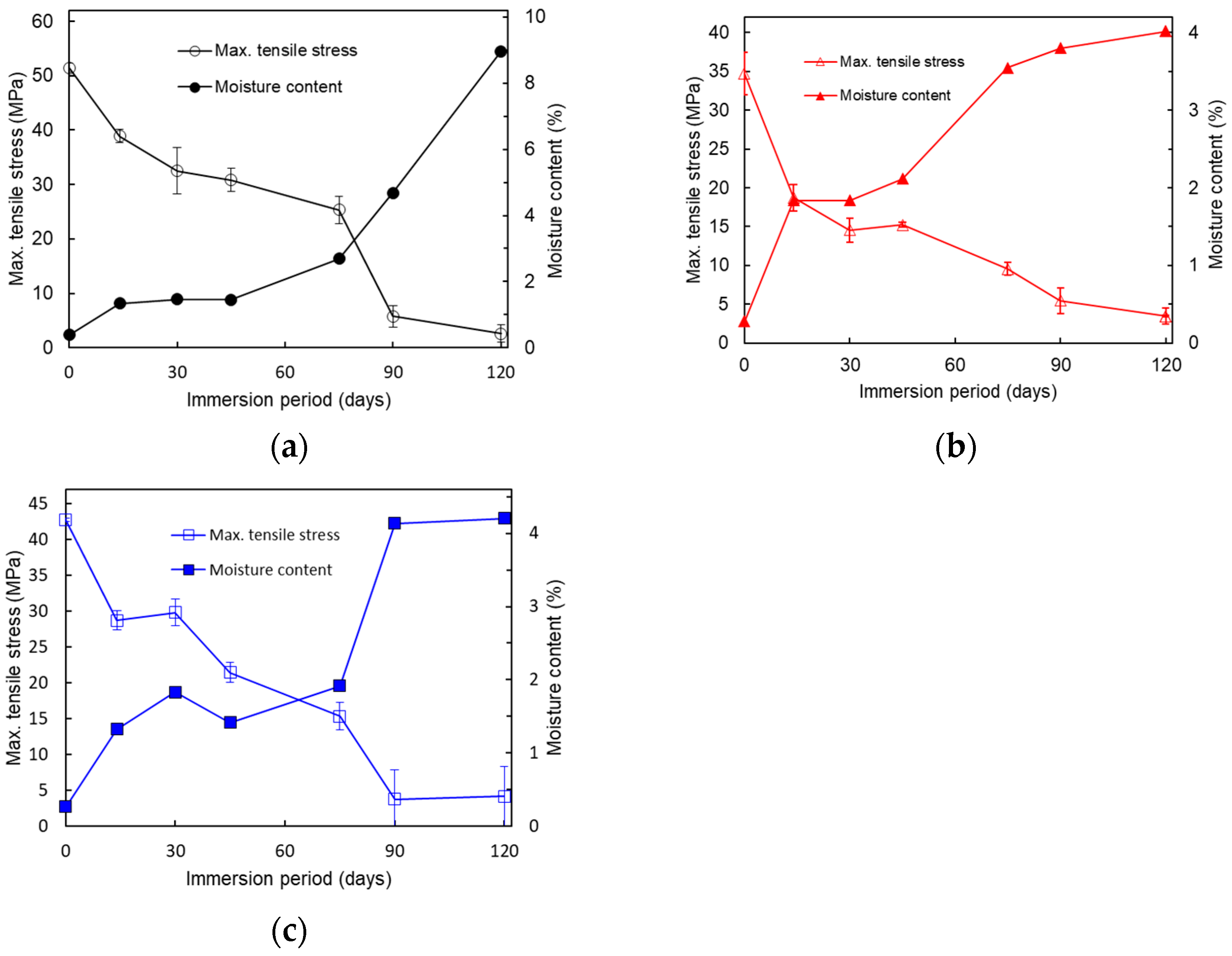
3. Results
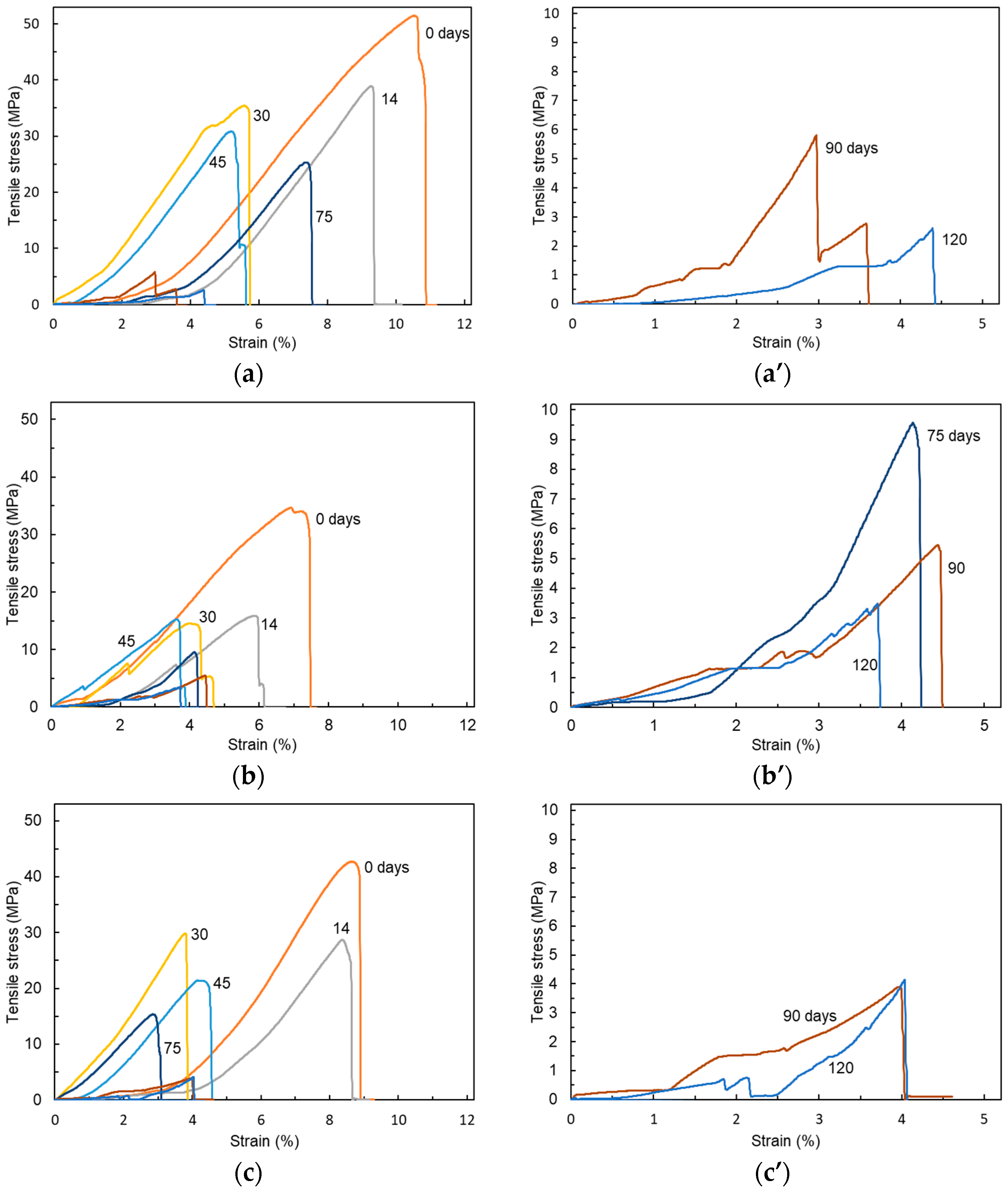
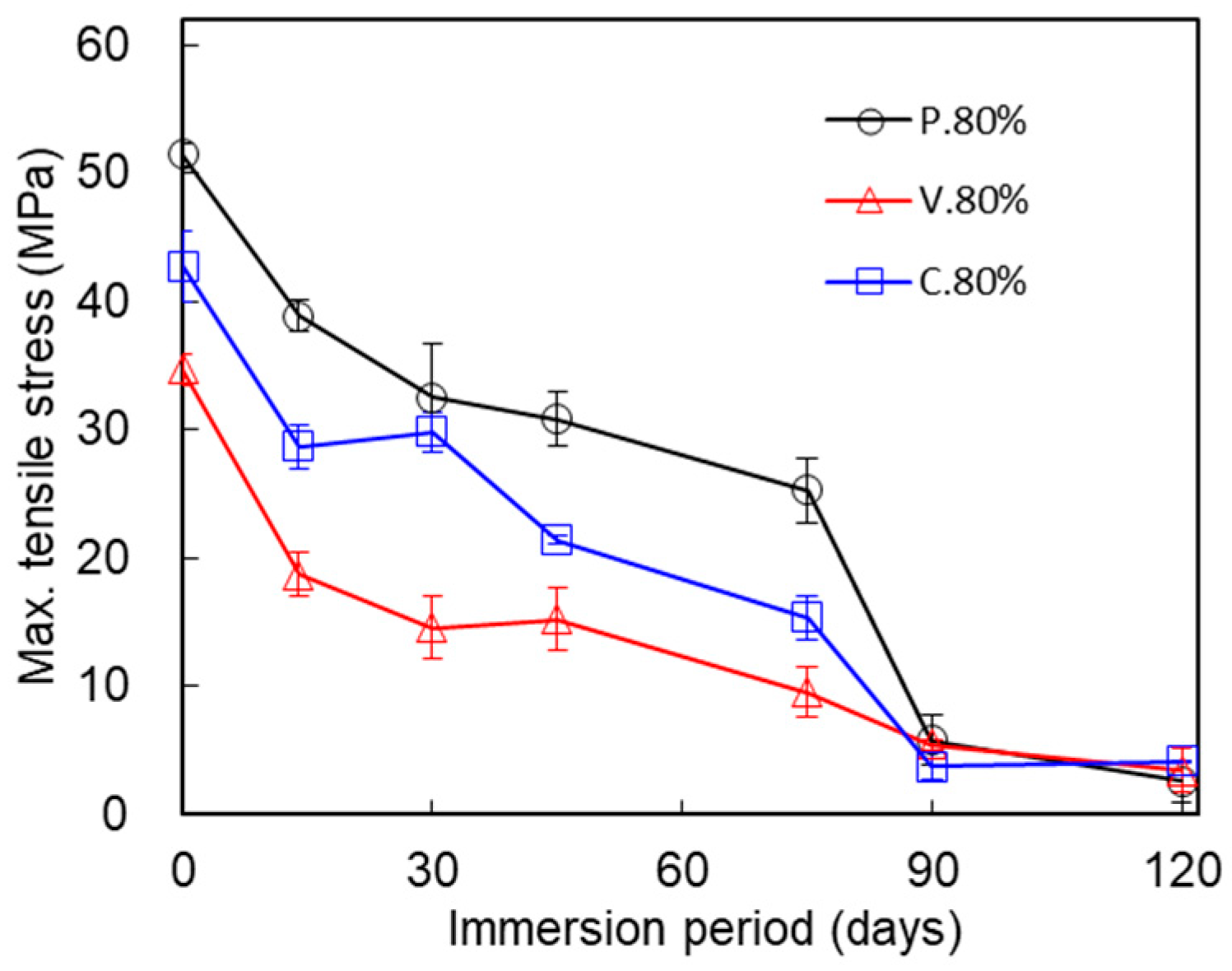
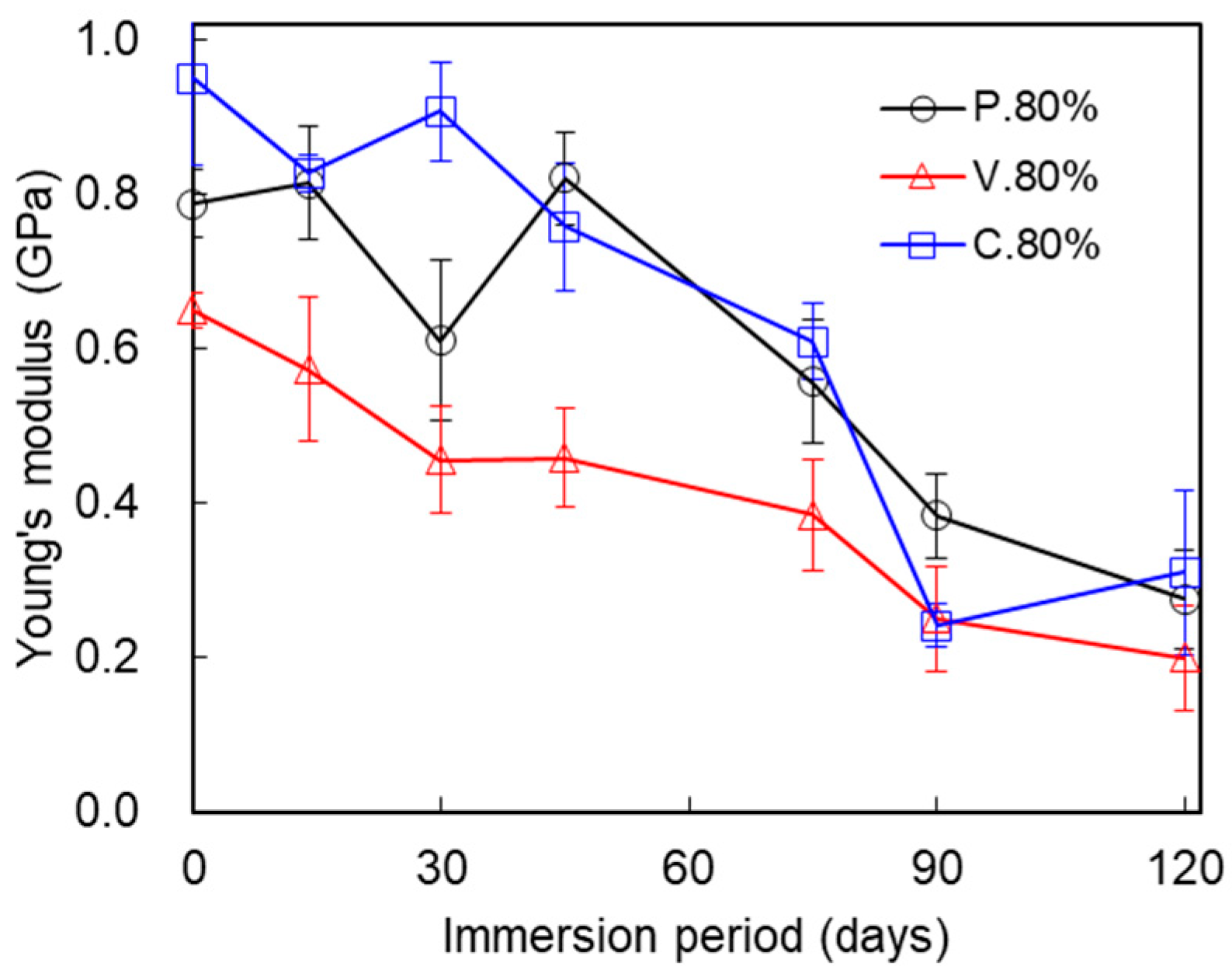
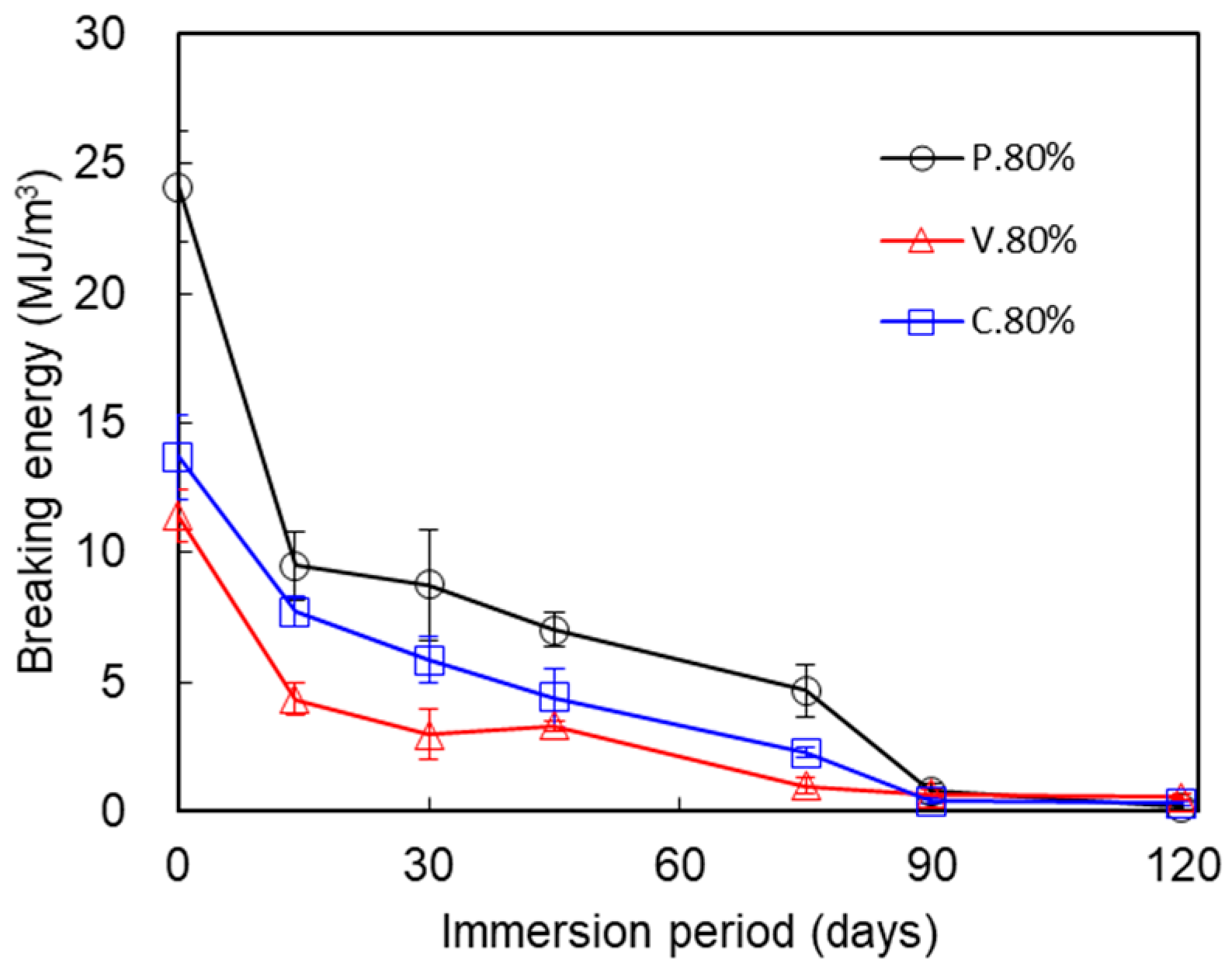
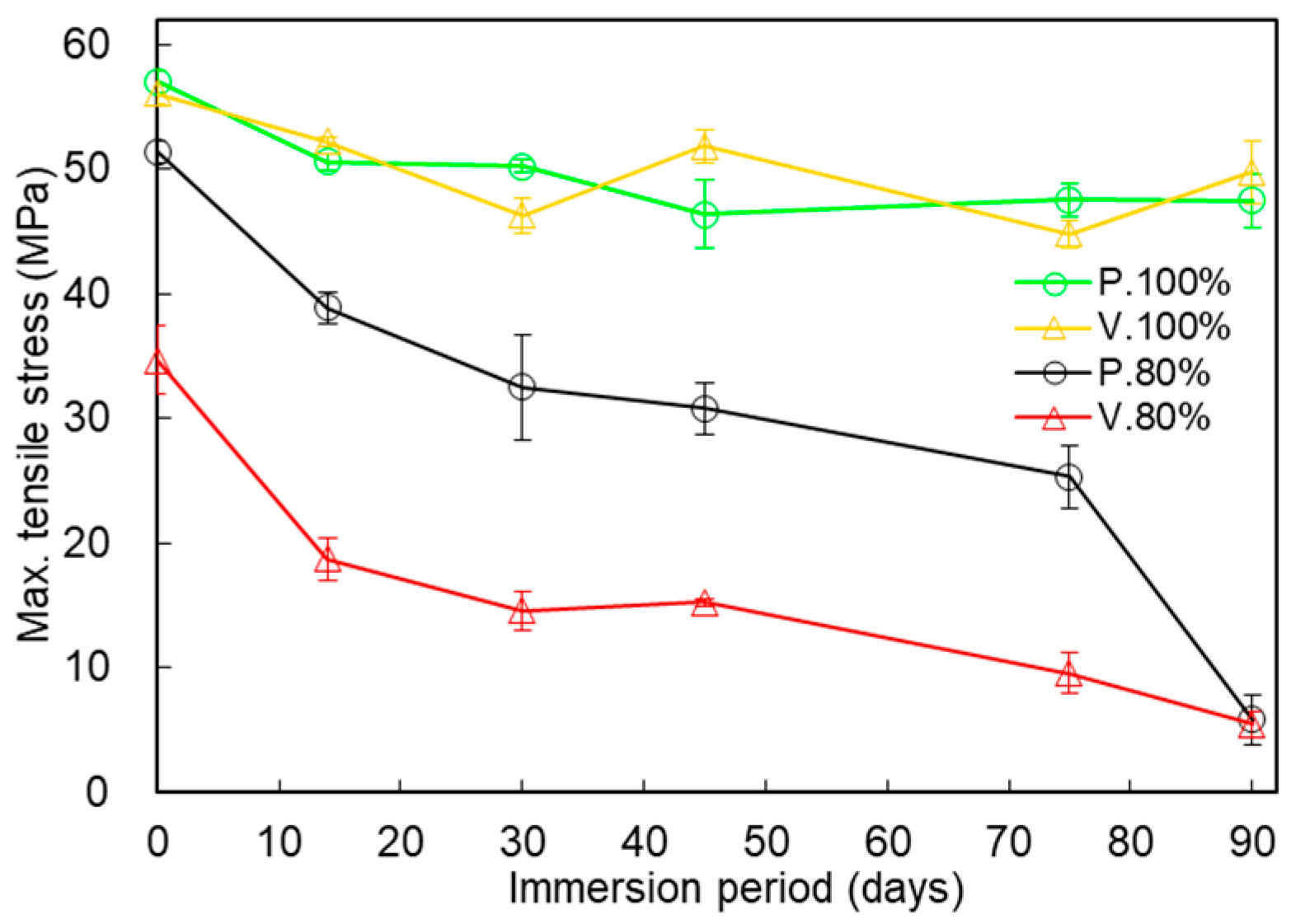
3.1. Mechanical Properties
3.2. Moisture Content
3.3. Relationships Between the Moisture Content and Mechanical Properties
4. Discussion
4.1. Deterioration of the Mechanical Properties of Structures with Internal Gaps
4.2. Moisture Behavior in a PLA Structure Formed by 3D Printing
4.3. Relationships Between the Moisture Content and Rate of Mechanical Property Deterioration
4.4. Two-Stage Deterioration and Mitigation Strategies
4.5. Test Methods
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lunt, J. Large-Scale Production, Properties and Commercial Applications of Polylactic Acid Polymers. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 1998, 59, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grillo, A.; Rusconi, Y.; D’Alterio, M.C.; De Rosa, C.; Talarico, G.; Poater, A. Ring Opening Polymerization of Six- and Eight-Membered Racemic Cyclic Esters for Biodegradable Materials. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singhvi, M.S.; Zinjarde, S.S.; Gokhale, D.V. Polylactic acid: Synthesis and biomedical applications. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 127, 1612–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeStefano, V.; Khan, S.; Tabada, A. Applications of PLA in modern medicine. Eng. Regen. 2020, 1, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, P.; Jia, J.; Liu, M.; Peng, S.; Zhao, Z.; Shuai, C. Degradation mechanisms and acceleration strategies of poly (lactic acid) scaffold for bone regeneration. Mater. Des. 2021, 210, 110066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Yin, G.; Sun, S.; Xu, P. Medical applications and prospects of polylactic acid materials. iScience 2024, 27, 111512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, V.C.; Gomes, D.d.S.; de Medeiros, E.L.G.; Santos, A.M.d.C.; de Lima, I.L.; Rosa, T.P.; Rocha, F.S.; de Souza Castro Filice, L.; Neves, G.d.A.; Menezes, R.R. Highly Porous 3D Nanofibrous Scaffold of Polylactic Acid/Polyethylene Glycol/Calcium Phosphate for Bone Regeneration by a Two-Step Solution Blow Spinning (SBS) Facile Route. Polymers 2024, 16, 3041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Młotek, M.; Gadomska-Gajadhur, A.; Sobczak, A.; Kruk, A.; Perron, M.; Krawczyk, K. Modification of PLA Scaffold Surface for Medical Applications. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaszczyńska, A.; Moczulska-Heljak, M.; Gradys, A.; Sajkiewicz, P. Advances in 3D Printing for Tissue Engineering. Materials 2021, 14, 3149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahatuzzaman, M.; Mahmud, M.; Rahman, S.; Hoque, M.E. Design, fabrication, and characterization of 3D-printed ABS and PLA scaffolds potentially for tissue engineering. Results Eng. 2024, 21, 101685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarea, R.N.; Doustkhahb, E.; Assadi, M.H.N. Three-dimensional bone printing using hydroxyapatite-PLA composite. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 42, 1531–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanajili, S.; Karami-Pour, A.; Oryan, A.; Talaei-Khozani, T. Preparation and characterization of PLA/PCL/HA composite scaffolds using indirect 3D printing for bone tissue engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 104, 109960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismail, R.; Fitriyana, D.F.; Bayuseno, A.P.; Munanda, R.; Muhamadin, R.C.; Nugraha, F.W.; Rusiyanto; Setiyawan, A.; Bahatmaka, A.; Firmansyah, H.N.; et al. Design, Manufacturing and Characterization of Biodegradable Bone Screw from PLA Prepared by Fused Deposition Modelling (FDM) 3D Printing Technique. J. Adv. Res. Fluid Mech. Therm. Sci. 2023, 103, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raziyan, M.S.; Palevicius, A.; Perkowski, D.; Urbaite, S.; Janusas, G. Development and Evaluation of 3D-Printed PLA/PHA/PHB/HA Composite Scaffolds for Enhanced Tissue-Engineering Applications. J. Compos. Sci. 2024, 8, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamanca, E.; Choy, C.S.; Aung, L.M.; Tsao, T.-C.; Wang, P.-H.; Lin, W.-A.; Wu, Y.-F.; Chang, W.-J. 3D-Printed PLA Scaffold with Fibronectin Enhances In Vitro Osteogenesis. Polymers 2023, 15, 2619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasparotto, M.; Bellet, P.; Scapin, G.; Busetto, R.; Rampazzo, C.; Vitiello, L.; Shah, D.I.; Filippini, F. 3D Printed Graphene-PLA Scaffolds Promote Cell Alignment and Differentiation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donate, R.; Paz, R.; Quintana, Á.; Bordón, P.; Monzón, M. Calcium Carbonate Coating of 3D-Printed PLA Scaffolds Intended for Biomedical Applications. Polymers 2023, 15, 2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Åkerlund, E.; Diez-Escudero, A.; Grzeszczak, A.; Persson, C. The Effect of PCL Addition on 3D-Printable PLA/HA Composite Filaments for the Treatment of Bone Defects. Polymers 2022, 14, 3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balletti, C.; Ballarin, M.; Guerra, F. 3D printing: State of the art and future perspectives. J. Cult. Herit. 2017, 26, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Davila, S.; González-Rodríguez, L.; Lama, R.; López-Álvarez, M.; Oliveira, A.L.; Serra, J.; Novoa, B.; Figueras, A.; González, P. 3D-Printed PLA Medical Devices: Physicochemical Changes and Biological Response after Sterilisation Treatments. Polymers 2022, 14, 4117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grizzi, I.; Garreau, H.; Li, S.; Vert, M. Hydrolytic degradation of devices based on poly(dl-lactic acid) size-dependence. Biomaterials 1995, 16, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaid, R.; Yildirim, E.; Pasquinelli, M.A.; King, M.W. Hydrolytic Degradation of Polylactic Acid Fibers as a Function of pH and Exposure Time. Molecules 2021, 26, 7554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogdanova, A.; Pavlova, E.; Polyanskaya, A.; Volkova, M.; Biryukova, E.; Filkov, G.; Trofimenko, A.; Durymanov, M.; Klinov, D.; Bagrov, D. Acceleration of Electrospun PLA Degradation by Addition of Gelatin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Li, Y.; Song, W.; Yee, K.; Lee, K.-Y.; Tagarielli, V.L. Measurements of the mechanical response of unidirectional 3D-printed PLA. Mater. Des. 2017, 123, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tymrak, B.M.; Kreiger, M.; Pearce, J.M. Mechanical Properties of Components Fabricated with Open-Source 3-D Printers Under Realistic Environmental Conditions. Mater. Des. 2014, 58, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrus, S.; Soporan, R.A.; Kazamer, N.; Pascal, D.T.; Muntean, R.; Dume, A.I.; Mărginean, G.M.; Serban, V.A. Characterization and mechanical properties of fused deposited PLA material. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 45, 4356–4363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrysafi, I.; Ainali, N.M.; Bikiaris, D.N. Thermal Degradation Mechanism and Decomposition Kinetic Studies of Poly(Lactic Acid) and Its Copolymers with Poly(Hexylene Succinate). Polymers 2021, 13, 1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chacón, J.M.; Caminero, M.A.; García-Plaza, E.; Núñez, P.J. Additive manufacturing of PLA structures using fused deposition modelling: Effect of process parameters on mechanical properties and their optimal selection. Mater. Des. 2017, 124, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedayati, R.; Alavi, M.; Sadighi, M. Effect of Degradation of Polylactic Acid (PLA) on Dynamic Mechanical Response of 3D Printed Lattice Structures. Materials 2024, 17, 3674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koçar, O.; Anaç, N.; Baysal, E.; Parmaksız, F.; Akgül, İ. Investigation of Mechanical Properties and Color Changes of 3D-Printed Parts with Different Infill Ratios and Colors After Aging. Materials 2024, 17, 5908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travieso-Rodriguez, J.A.; Jerez-Mesa, R.; Llumà, J.; Traver-Ramos, O.; Gomez-Gras, G.; Rovira, J.J.R. Mechanical Properties of 3D-Printing Polylactic Acid Parts subjected to Bending Stress and Fatigue Testing. Materials 2019, 12, 3859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solomon, I.J.; Sevvel, P.; Gunasekaran, J. A review on the various processing parameters in FDM. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 37, 509–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öteyaka, M.Ö.; Aybar, K.; Öteyaka, H.C. Effect of Infill Ratio on the Tensile and Flexural Properties of Unreinforced and Carbon Fiber-Reinforced Polylactic Acid Manufactured by Fused Deposition Modeling. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2021, 30, 5203–5215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaldo, E.; Ricci, M.; Marfia, S. Mechanical properties of 3D printed polylactic acid elements: Experimental and numerical insights. Mech. Mater. 2023, 177, 104551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunasekaran, K.N.; Aravinth, V.; Kumaran, C.B.M.; Madhankumar, K.; Kumar, S.P. Investigation of mechanical properties of PLA printed materials under varying infill density. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 45, 1849–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, L.; Mulholland, T.; Osswald, T.A. Characterization of mechanical properties and fracture mode of PLA and copper/PLA composite part manufactured by fused deposition modeling. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, M.; Yonezawa, A.; Takeda, K.; Yamada, A. Evaluation of the Deterioration of the Mechanical Properties of Poly(lactic acid) Structures Fabricated by a Fused Filament Fabrication 3D Printer. Inventions 2019, 4, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonezawa, A.; Yamada, A. Deterioration of the Mechanical Properties of FFF 3D-Printed PLA Structures. Inventions 2021, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farah, S.; Anderson, D.G.; Langer, R. Physical and mechanical properties of PLA, and their functions in widespread applications—A comprehensive review. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 107, 367–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, F.; Nicoulin, V.; Peloso, C.; Curia, S.; Richard, J.; Lopez-Noriega, A. In Vitro and In Vivo Hydrolytic Degradation Behaviors of a Drug-Delivery System Based on the Blend of PEG and PLA Copolymers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 55495–55509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Burkersroda, F.; Schedl, L.; Göpferich, A. Why degradable polymers undergo surface erosion or bulk erosion. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 4221–4231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banjo, A.D.; Agrawal, V.; Auad, M.L.; Celestine, A.-D.N. Moisture-induced changes in the mechanical behavior of 3D printed polymers. Compos. Part C Open Access 2022, 7, 100243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deroiné, M.; Duigou, A.L.; Corre, Y.-M.; Gac, P.-Y.L.; Davies, P.; César, G.; Bruzaud, S. Accelerated ageing of polylactide in aqueous environments: Comparative study between distilled water and seawater. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2014, 108, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver-Ortega, H.; Tarrés, Q.; Mutjé, P.; Delgado-Aguilar, M.; Méndez, J.A.; Espinach, F.X. Impact Strength and Water Uptake Behavior of Bleached Kraft Softwood-Reinforced PLA Composites as Alternative to PP-Based Materials. Polymers 2020, 12, 2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moliner, C.; Finocchio, E.; Arato, E.; Ramis, G.; Lagazzo, A. Influence of the Degradation Medium on Water Uptake, Morphology, and Chemical Structure of Poly(Lactic Acid)-Sisal Bio-Composites. Materials 2020, 13, 3974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimczuk, B.; Rudnicka, A.; Owczarek, O.; Puszkarz, A.K.; Szparaga, G.; Puchalski, M. Investigation of the Hydrolytic Degradation Kinetics of 3D-Printed PLA Structures under a Thermally Accelerated Regime. Materials 2024, 17, 1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsusue, Y.; Yamamuro, T.; Oka, M.; Shikinami, Y.; Hyon, S.-H.; Ikada, Y. In vitro and in vivo studies on bioabsorbable ultra-high-strength poly(L-lactide) rods. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1992, 26, 1553–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makino, K.; Arakawa, M.; Kondo, T. Preparation and in Vitro Degradation Properties of Polylactide Microcapsules. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1985, 33, 1195–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Therin, M.; Christel, P.; Li, S.; Garreau, H.; Vert, M. In vivo degradation of massive poly(α-hydroxy acids): Validation of In vitro findings. Biomaterials 1992, 13, 594–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; McCarthy, S. Further investigations on the hydrolytic degradation of poly (DL-lactide). Biomaterials 1999, 20, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrzejewska, A. One Year Evaluation of Material Properties Changes of Polylactide Parts in Various Hydrolytic Degradation Conditions. Polymers 2019, 11, 1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wittbrodt, B.; Pearce, J.M. The effects of PLA color on material properties of 3-D printed components. Addit. Manuf. 2015, 8, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.M.; Garreau, H.; Vert, M. Structure-property relationships in the case of the degradation of massive aliphatic poly-(α-hydroxy acids) in aqueous media, Part 1: Poly(dl-lactic acid). J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 1990, 1, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, M.A.; Orteu, J.-J.; Schreier, H. Image Correlation for Shape, Motion and Deformation Measurements. Basic Concepts, Theory and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Sutton, M.A.; Wolters, W.J.; Peters, W.H.; Ranson, W.F.; McNeill, S.R. Determination of displacements using an improved digital correlation method. Image Vis. Comput. 1983, 1, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yamada, A.; Tatebe, K. Effect of the Interior Fill Percentage on the Deterioration of the Mechanical Properties of FFF-3D-Printed PLA Structures. Polymers 2025, 17, 828. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17060828
Yamada A, Tatebe K. Effect of the Interior Fill Percentage on the Deterioration of the Mechanical Properties of FFF-3D-Printed PLA Structures. Polymers. 2025; 17(6):828. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17060828
Chicago/Turabian StyleYamada, Akira, and Kanta Tatebe. 2025. "Effect of the Interior Fill Percentage on the Deterioration of the Mechanical Properties of FFF-3D-Printed PLA Structures" Polymers 17, no. 6: 828. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17060828
APA StyleYamada, A., & Tatebe, K. (2025). Effect of the Interior Fill Percentage on the Deterioration of the Mechanical Properties of FFF-3D-Printed PLA Structures. Polymers, 17(6), 828. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17060828




