Quantification of Hydrogen Peroxide in PVP and PVPVA Using 1H qNMR Spectroscopy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials
3. Methods
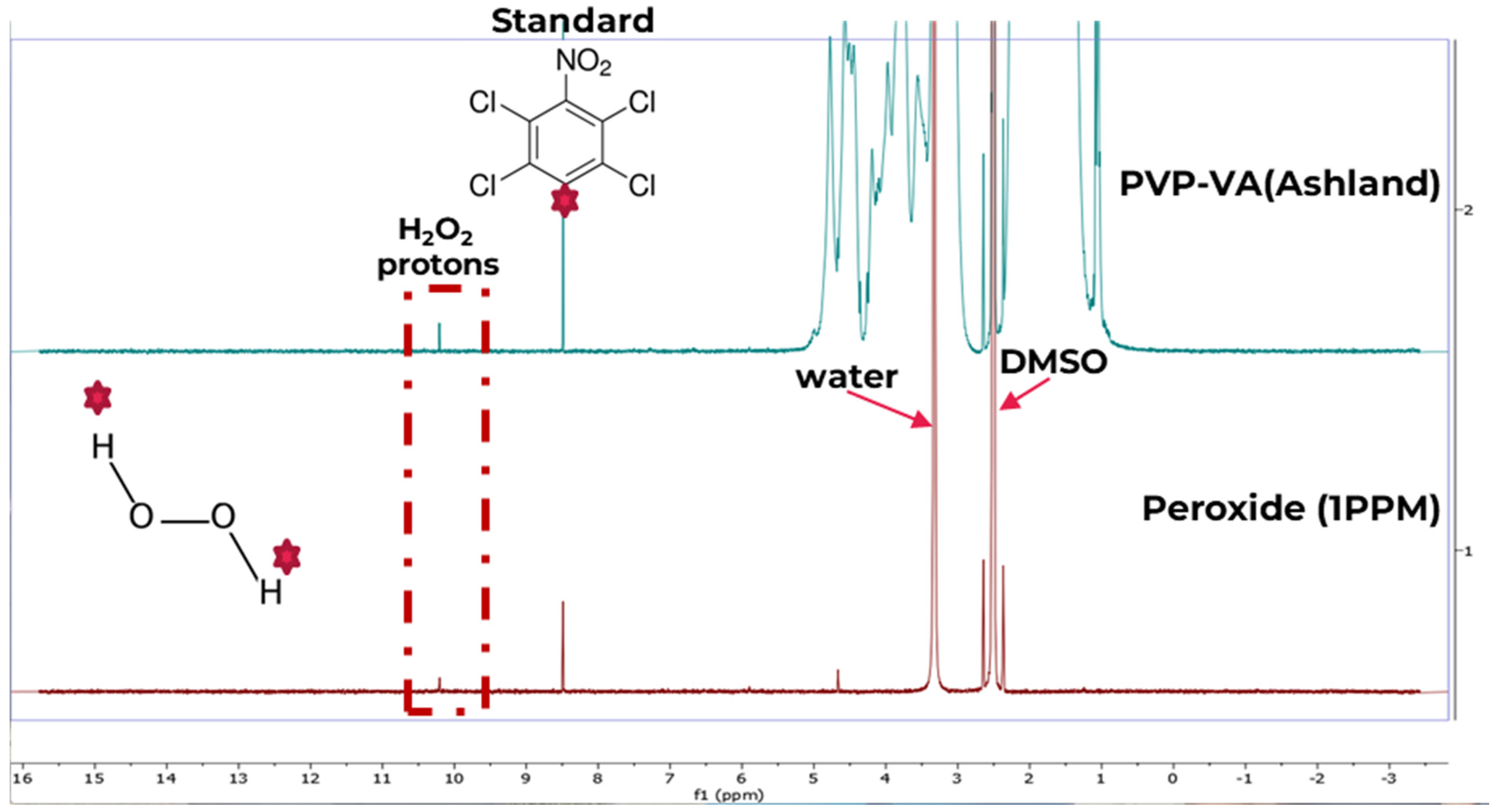
3.1. Peroxide Quantification Using 1H qNMR
3.1.1. Standards and Mixtures
3.1.2. Equipment
3.1.3. Method Development for Quantitative 1H-NMR (1H-qNMR)
3.2. Method Verification Using Commercial Samples
3.2.1. PVP and PVPVA Raw Material
Lot-to-Lot Variation
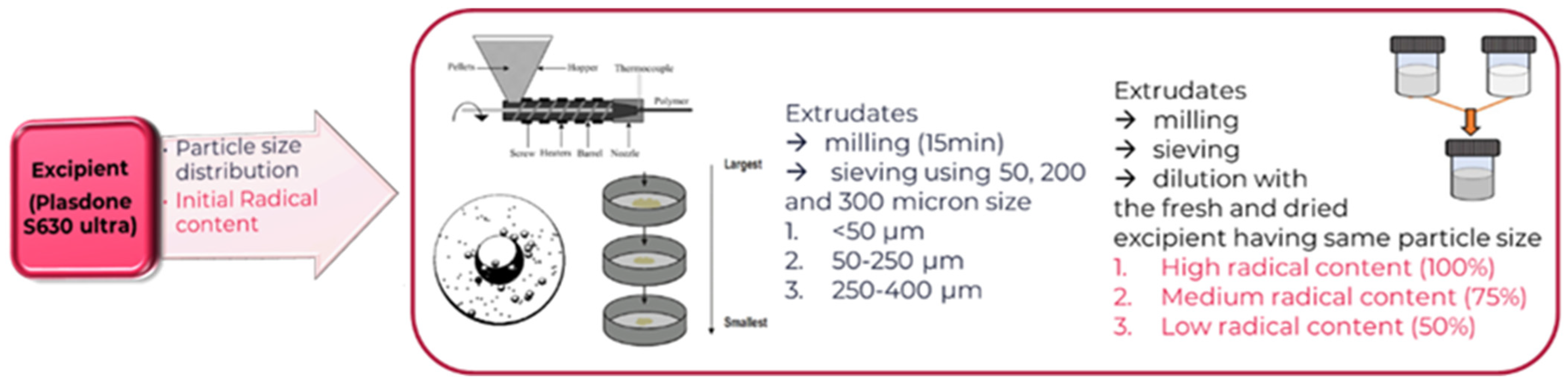
3.2.2. PVPVA Sample Treatment
Hot Melt Extrusion (HME)
Ball Mill to Generate Powder from Excipient Extrudate
Storage Stability
3.2.3. Design of Experiments (DoE): Impact of Process Conditions on the Hydrogen Peroxide Content in Micronized Extruded PVPVA-U-A-2
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Method Verification Using Commercial Samples
4.1.1. PVP and PVPVA Raw Material
Lot-to-Lot Variation
4.1.2. PVP-VA Sample Treatment
4.1.3. Design of Experiments (DoE): Impact of Process Conditions on the Hydrogen Peroxide Content in Micronized Extruded PVPVA-U-A-2
5. Industrial Applicability
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zarmpi, P.; Flanagan, T.; Meehan, E.; Mann, J.; Fotaki, N. Biopharmaceutical aspects and implications of excipient variability in drug product performance. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2017, 111, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pifferi, G.; Restani, P. The safety of pharmaceutical excipients. Il Farm. 2003, 58, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Levons, J.; Narang, A.S.; Raghavan, K.; Rao, V.M. Reactive Impurities in Excipients: Profiling, Identification and Mitigation of Drug–Excipient Incompatibility. AAPS PharmSciTech 2011, 12, 1248–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Pellett, J.D.; Narang, A.S.; Wang, Y.J.; Zhang, Y.T. Reactive impurities in large and small molecule pharmaceutical excipients—A review. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 101, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Levons, J.K.; Narang, A.S.; Raghavan, K.; Mantri, R.V. Reactive impurities in excipients. Excip. Appl. Formul. Des. Drug Deliv. 2015, 12, 37–65. [Google Scholar]
- Gabrič, A.; Hodnik, Ž.; Pajk, S. Oxidation of Drugs during Drug Product Development: Problems and Solutions. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, F.; Feng, X.; Yin, J.; Gao, H. Distinct H2O2-Scavenging System in Yersinia pseudotuberculosis: KatG and AhpC Act Together to Scavenge Endogenous Hydrogen Peroxide. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaboriau, F.; Vaultier, M.; Moulinoux, J.-P.; Delcros, J.-G. Antioxidative properties of natural polyamines and dimethylsilane analogues. Redox Rep. 2005, 10, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, C.D.; Soysa, P. Optimized enzymatic colorimetric assay for determination of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) scavenging activity of plant extracts. MethodsX 2015, 2, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, R.Q. Peroxidase-based colorimetric determination of L-ascorbic acid. Anal. Chem. 1987, 59, 1119–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keston, A.S.; Brandt, R. The fluorometric analysis of ultramicro quantities of hydrogen peroxide. Anal. Biochem. 1965, 11, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tantawi, O.; Baalbaki, A.; El Asmar, R.; Ghauch, A. A rapid and economical method for the quantification of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) using a modified HPLC apparatus. Sci. Total. Environ. 2018, 654, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krawczyk, T.; Baj, S. Review: Advances in the Determination of Peroxides by Optical and Spectroscopic Methods. Anal. Lett. 2014, 47, 2129–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.-S.; Hughes, E.W.; Giguère, P.A. The Crystal Structure of the Urea—Hydrogen Peroxide Addition Compound CO (NH2) 2· H2O2. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1941, 63, 1507–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monograph USP Povidone. Available online: https://online.uspnf.com/uspnf/document/1_GUID-CC6E908F-AE5A-43AD-BCC6-F4DDBC7A893F_6_en-US?source=SearchResults&highlight=povidone (accessed on 21 May 2024).
- Monograph USP Copovidone. Available online: https://online.uspnf.com/uspnf/document/1_GUID-D8A5F0D7-9622-47C3-B23A-4AA38DC95547_6_en-US?source=QuickSearch&highlight=copovidone (accessed on 21 May 2024).
- Sarabu, S.; Butreddy, A.; Bandari, S.; Batra, A.; Lawal, K.; Chen, N.N.; Kogan, M.; Bi, V.; Durig, T.; Repka, M.A. Preliminary investigation of peroxide levels of PlasdoneTM copovidones on the purity of atorvastatin calcium amorphous solid dispersions: Impact of plasticizers on hot melt extrusion processability. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 70, 103190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartauer, K.J.; Arbuthnot, G.N.; Baertschi, S.W.; Johnson, R.A.; Luke, W.D.; Pearson, N.G.; Rickard, E.C.; Tingle, C.A.; Tsang, P.K.S.; Wiens, R.E. Influence of Peroxide Impurities in Povidone and Crospovidone on the Stability of Raloxifene Hydrochloride in Tablets: Identification and Control of an Oxidative Degradation Product. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2000, 5, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heczko, D.; Hachuła, B.; Maksym, P.; Kamiński, K.; Zięba, A.; Orszulak, L.; Paluch, M.; Kamińska, E. The effect of various poly (N-vinylpyrrolidone)(PVP) polymers on the crystallization of flutamide. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperger, D.M.; Munson, E.J. Analysis of Structural Variability in Pharmaceutical Excipients Using Solid-State NMR Spectroscopy. Aaps Pharmscitech 2011, 12, 821–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lynch, C.C.; Khirich, G.; Lee, R.T. Quantification of Biopharmaceutically Relevant Nonionic Surfactant Excipients Using Benchtop qNMR. Anal. Chem. 2024, 96, 6746–6755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diehl, B.W.K.; Malz, F.; Holzgrabe, U. Quantitative NMR spectroscopy in the quality evaluation of active pharmaceutical ingredients and excipients. Spectrosc. Eur. 2007, 19, 15–19. [Google Scholar]
- Beyer, T.; Diehl, B.; Holzgrabe, U. Quantitative NMR spectroscopy of biologically active substances and excipients. Bioanal. Rev. 2010, 2, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraf, I.; Kushwah, V.; Contreras, L.; Carmody, A.; Liu, P.; Werner, B.; Zangger, K.; Paudel, A. Quantitative chemical profiling of cellulose acetate excipient via 13C NMR spectroscopy in controlled release formulations. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2022, 217, 114791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thulborn, K.R.; Ackerman, J.J.H. Absolute molar concentrations by NMR in inhomogeneous B1. A scheme for analysis of in vivo metabolites. J. Magn. Reson. 1983, 55, 357–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malet Martino, M.; Holzgrabe, U. NMR techniques in biomedical and pharmaceutical analysis. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2011, 55, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggio, R.M.; Calvo, N.L.; Vignaduzzo, S.E.; Kaufman, T.S. Pharmaceutical impurities and degradation products: Uses and applications of NMR techniques. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2014, 101, 102–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yau, W.; Goh, C.H.; Koh, H. Quality control and quality assurance of phytomedicines: Key considerations, methods, and analytical challenges. Phyther. Effic. safety, Regul. 2015, 18–48. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y. Quantitative NMR in Quality Control. In Quality Control of Chinese Medicines: Strategies and Methods; Springer Nature Singapore: Singapore, 2024; pp. 691–757. [Google Scholar]
- Elipe, M.V.S. NMR Detective Agency: Uncovering the Truth for Process Chemists. Org. Process. Res. Dev. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.B.; Taraban, M.B.; Wang, W.; Briggs, K.T. Improving Biopharmaceutical Safety through Verification-Based Quality Control. Trends Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 1140–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afonso Urich, J.A.; Marko, V.; Boehm, K.; Werner, B.; Zangger, K.; Saraf, I.; Paudel, A.; Kushwah, V. Accelerative Solid-State Oxidation Behaviour of Amorphous and Partially Crystalline Venetoclax. AAPS PharmSciTech 2024, 25, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, J.; Karn, A.; Brunsteiner, M.; Ray, A.; Davis, A.; Saraf, I.; Paudel, A. Screening autoxidation propensities of drugs in the solid-state using PVP and in the solution state using N-Methyl pyrrolidone. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraf, I.; Jakasanovski, O.; Stanić, T.; Kralj, E.; Petek, B.; Williams, J.D.; Dmytro, N.; Georg, G.; Bernd, W.; Klaus, Z. Investigation of the Influence of Copovidone Properties and Hot-Melt Extrusion Process on Level of Impurities, In Vitro Release, and Stability of an Amorphous Solid Dispersion Product. Mol. Pharm. 2024, 21, 5703–5715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awasthi, R.; Manchanda, S.; Das, P.; Velu, V.; Malipeddi, H.; Pabreja, K.; Pinto, T.D.J.A.; Gupta, G.; Dua, K. Poly (vinylpyrrolidone). In Engineering of Biomaterials for Drug Delivery Systems; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 255–272. [Google Scholar]
- Kurakula, M.; Rao, G.S.N.K. Pharmaceutical assessment of polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP): As excipient from conventional to controlled delivery systems with a spotlight on COVID-19 inhibition. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 60, 102046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narang, A.S.; Desai, D.; Badawy, S. Impact of excipient interactions on solid dosage form stability. Excip. Appl. Formul. Des. Drug Deliv. 2015, 29, 93–137. [Google Scholar]
- Alshahrouri, B.; Yang, F.; Schwing, Q.; Dürig, T.; Fassihi, R. Hot-melt extrusion based sustained release ibrutinib delivery system: An inhibitor of Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase (BTK). Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 607, 120981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshahrouri, B. Development of an Amorphous Based Sustained Release Tablet of Melt Extruded Ibrutinib a Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor; Temple University: Philadephia, PA, USA, 2021; ISBN 9798538103652. [Google Scholar]
- Iyer, J.; Barbosa, M.; Saraf, I.; Pinto, J.F.; Paudel, A. Mechanoactivation as a tool to assess the autoxidation propensity of amorphous drugs. Mol. Pharm. 2023, 20, 1112–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modhave, D.; Barrios, B.; Paudel, A. PVP-H2O2 Complex as a New Stressor for the Accelerated Oxidation Study of Pharmaceutical Solids. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachtermacher, M.G.; Rudin, A. Reactive processing of LLDPES in corotating intermeshing twin-screw extruder. II. Effect of peroxide treatment on processability. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1995, 58, 2433–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.J.; Ok, Y.S.; Kim, B.K. Crosslinking of polyethylene with peroxide and multifunctional monomers during extrusion. Eur. Polym. J. 1992, 28, 1487–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Tzoganakis, C.; Hamielec, A.E.; Vlachopoulos, J. Peroxide crosslinking of LLDPE during reactive extrusion. Adv. Polym. Technol. J. Polym. Process. Inst. 1989, 9, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubat, K.; Strojewski, D.; Majda, D.; Jakubiec, D.; Andrzejowska, A.; Bogdał, A.; Krupa, A.; Harańczyk, H. Molecular phenomena related to moisture uptake in amorphous solid dispersion loaded with bosentan monohydrate and copovidone. Powder Technol. 2023, 430, 119020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Lee, S.G. Preparation and swelling behavior of moisture-absorbing polyurethane films impregnated with superabsorbent sodium polyacrylate particles. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinoso, R.; Aboaba, S.A.; Olayanju, T.M.A. Effects of moisture content and heat treatment on peroxide value and oxidative stability of un-refined sesame oil. Afr. J. Food Agric. Nutr. Dev. 2010, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushwah, V.; Poms, J.; Vuylsteke, B.; Peter, A.; Paudel, A. Towards an Understanding of the Adsorption of Vaporized Hydrogen Peroxide (VHP) Residues on Glass Vials After a VHP Decontamination Process Using a Miniaturized Tool. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 109, 2454–2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, R.C.; Bochmann, E.S.; Kyeremateng, S.O.; Gryczke, A.; Wagner, K.G. Holistic QbD approach for hot-melt extrusion process design space evaluation: Linking materials science, experimentation and process modeling. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2019, 141, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widmann, C.; Ravasio, D.; Ladwig, T. Material selection as a control strategy to limit hydrogen peroxide residuals in drug products. TechnoPharm 2021, 11. Available online: https://www.ecv.de/beitrag/TechnoPharm/Material_selection_as_a_control_strategy_to_limit_hydrogen_peroxide_residuals_in_drug_products (accessed on 21 May 2024).
- Yue, H.; Bu, X.; Huang, M.-H.; Young, J.; Raglione, T. Quantitative determination of trace levels of hydrogen peroxide in crospovidone and a pharmaceutical product using high performance liquid chromatography with coulometric detection. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 375, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, K.; Zheng, T.; Hetrick, E.M. Comparative understanding of peroxide quantitation assays: A case study with peptide drug product degradation. Anal. Methods 2024, 16, 4755–4764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Polymer Grades | Lot 1 | Lot 2 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| PVP | K-30_Sigma | K30-S-1 | K30-S-2 |
| K-60_Sigma | K60-S-1 | K60-S-2 | |
| K-90_Sigma | K90-S-1 | K90-S-2 | |
| K-30_BASF | K30-B-1 | K30-B-2 | |
| K-90_BASF | K90-B-1 | K90-B-2 | |
| K-30_Ashland | K30-A-1 | K30-A-2 | |
| K-90_Ashland | K90-A-1 | K90-A-2 | |
| PVPVA | BASF | PVPVA-B-1 | PVPVA-B-2 |
| Ashland | PVPVA-A-1 | PVPVA-A-2 | |
| Ultra_Ashland | PVPVA-U-A-1 | PVPVA-U-A-2 |
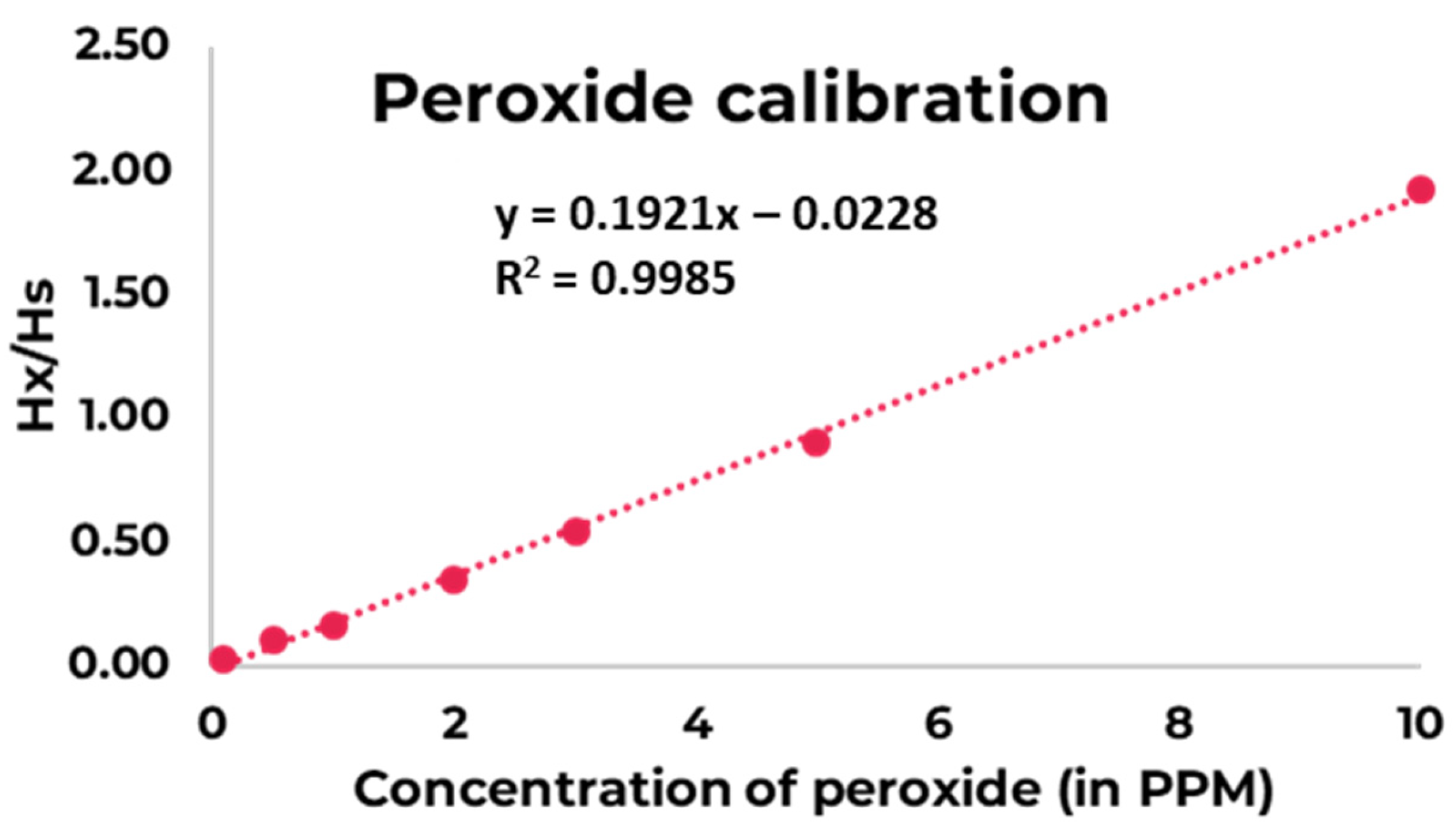
| Sample Nr. | Sample Name | Concentration of Peroxide in 1 mL DMSO (in PPM) | Hx | Hs | Hx/Hs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.00001% W/V (0.1 PPM) | 0.1 | 2073.4 | 85,642 | 0.02 |
| 2 | 0.00005% W/V (0.5 PPM) | 0.5 | 8469.7 | 85,165 | 0.10 |
| 3 | 0.0001% W/V (1 PPM) | 1 | 13,927 | 87,264 | 0.16 |
| 4 | 0.0002% W/V (2 PPM) | 2 | 29,272 | 85,345 | 0.34 |
| 5 | 0.0003% W/V (3 PPM) | 3 | 44,177 | 82,343 | 0.54 |
| 6 | 0.0005% W/V (5 PPM) | 5 | 75,527 | 83,576 | 0.90 |
| 7 | 0.001% W/V (10 PPM) | 10 | 167,247 | 86,954 | 1.92 |
| DOE Levels | Excipient (PVPVA-U-A-2) | Stability Conditions | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSD | Initial Radical Content | Temperature | Humidity | |
| −1 | <50 µm | Low | 25 °C | 0–20% |
| 0 | 50–250 µm | Medium | 40 °C | 45% |
| 1 | 250–400 µm | High | 70 °C | 75% |
| Control Samples | Excipient (PVPVA-U-A-2) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Sample Name | PSD of Excipient | Initial Radical Content in Excipient | |
| Day-0 | E1 | <50 µm | High |
| E2 | <50 µm | Medium | |
| E3 | <50 µm | Low | |
| E4 | 50–250 µm | High | |
| E5 | 50–250 µm | Medium | |
| E6 | 50–250 µm | Low | |
| E7 | 250–400 µm | High | |
| E8 | 250–400 µm | Medium | |
| E9 | 250–400 µm | Low | |
| Instability conditions at different points (3, 14, 28, d) | E3_(25C,20RH) | <50 µm | Low |
| E9_(70C,20RH) | 250–400 µm | Low | |
| E1_(70C,20RH) | <50 µm | High | |
| E1_(25C,75RH) | <50 µm | High | |
| E7_(25C,75RH) | 250–400 µm | High | |
| E3_(70C,75RH) | <50 µm | Low | |
| E5_(40C,45RH) | 50–250 µm | Medium | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saraf, I.; Kushwah, V.; Werner, B.; Zangger, K.; Paudel, A. Quantification of Hydrogen Peroxide in PVP and PVPVA Using 1H qNMR Spectroscopy. Polymers 2025, 17, 739. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17060739
Saraf I, Kushwah V, Werner B, Zangger K, Paudel A. Quantification of Hydrogen Peroxide in PVP and PVPVA Using 1H qNMR Spectroscopy. Polymers. 2025; 17(6):739. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17060739
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaraf, Isha, Varun Kushwah, Bernd Werner, Klaus Zangger, and Amrit Paudel. 2025. "Quantification of Hydrogen Peroxide in PVP and PVPVA Using 1H qNMR Spectroscopy" Polymers 17, no. 6: 739. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17060739
APA StyleSaraf, I., Kushwah, V., Werner, B., Zangger, K., & Paudel, A. (2025). Quantification of Hydrogen Peroxide in PVP and PVPVA Using 1H qNMR Spectroscopy. Polymers, 17(6), 739. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17060739







