A Rheological Study of the High-Temperature Properties of Fast-Melting SBS/Epoxy-Modified Asphalt Binders
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. Penetration and Softening Point Test
2.4. 60 °C Kinematic Viscosity Test
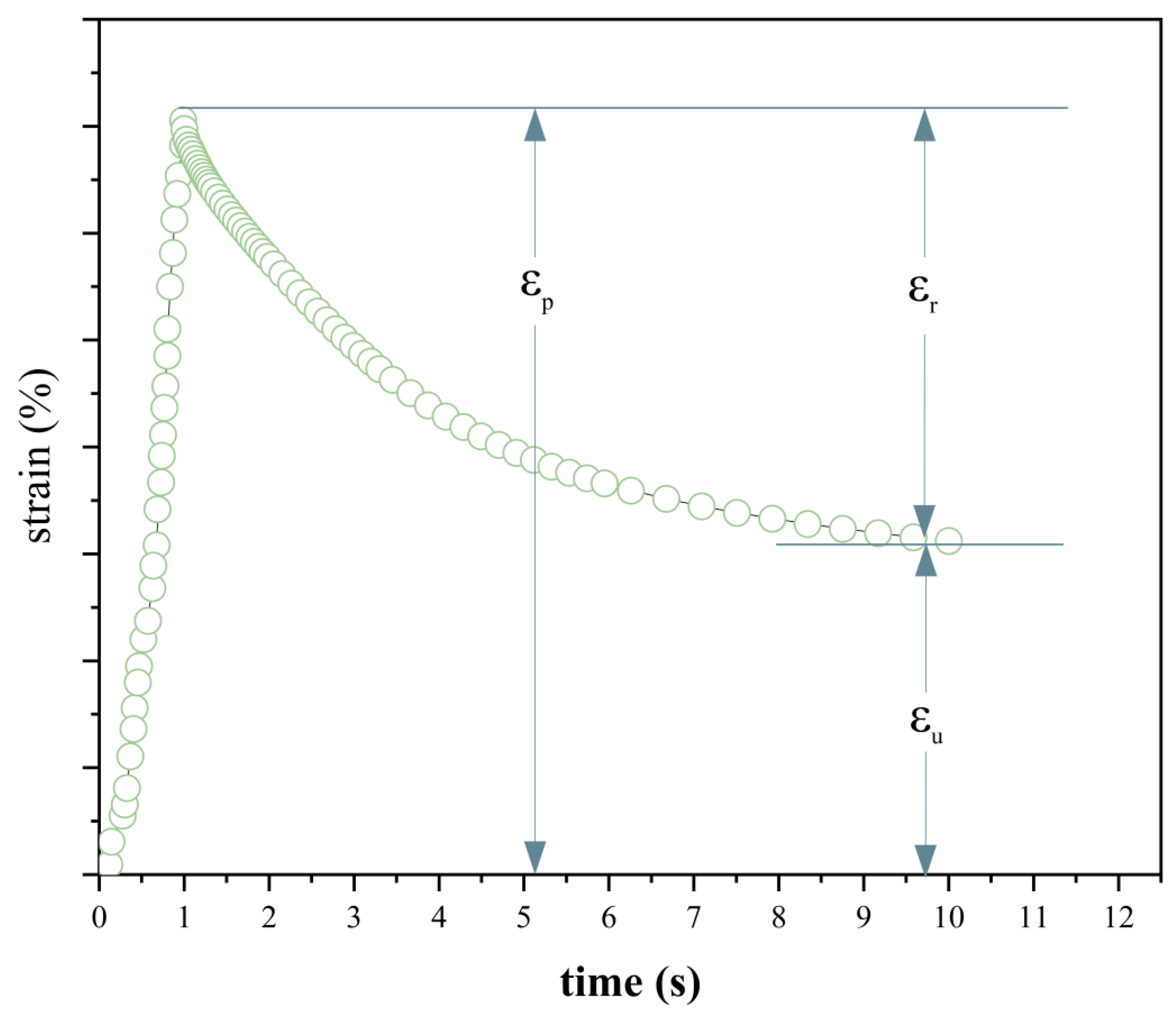
2.5. Multiple Stress Creep Recovery (MSCR) Tests
2.6. Zero-Shear Viscosity (ZSV) Test
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Test Results for Penetration and Softening Point
3.2. 60 ° C Kinematic Viscosity Outcomes
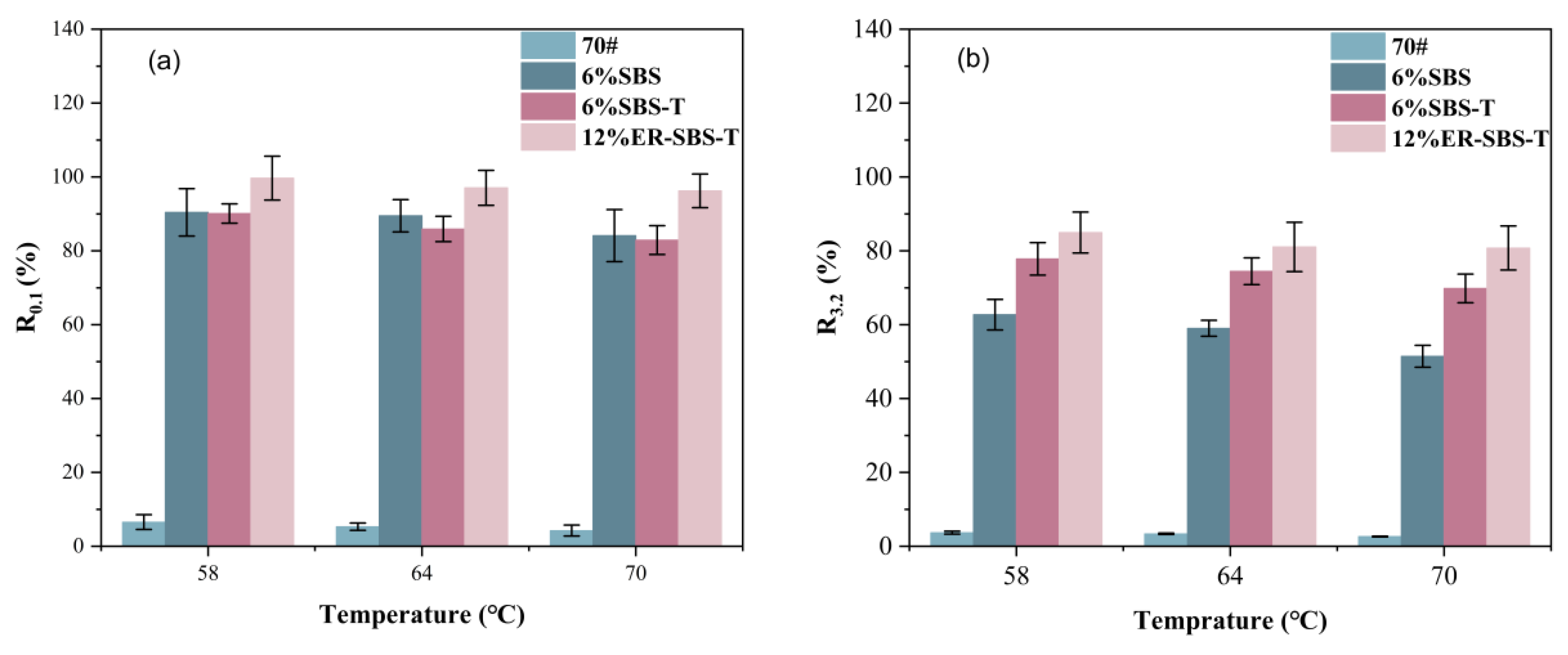
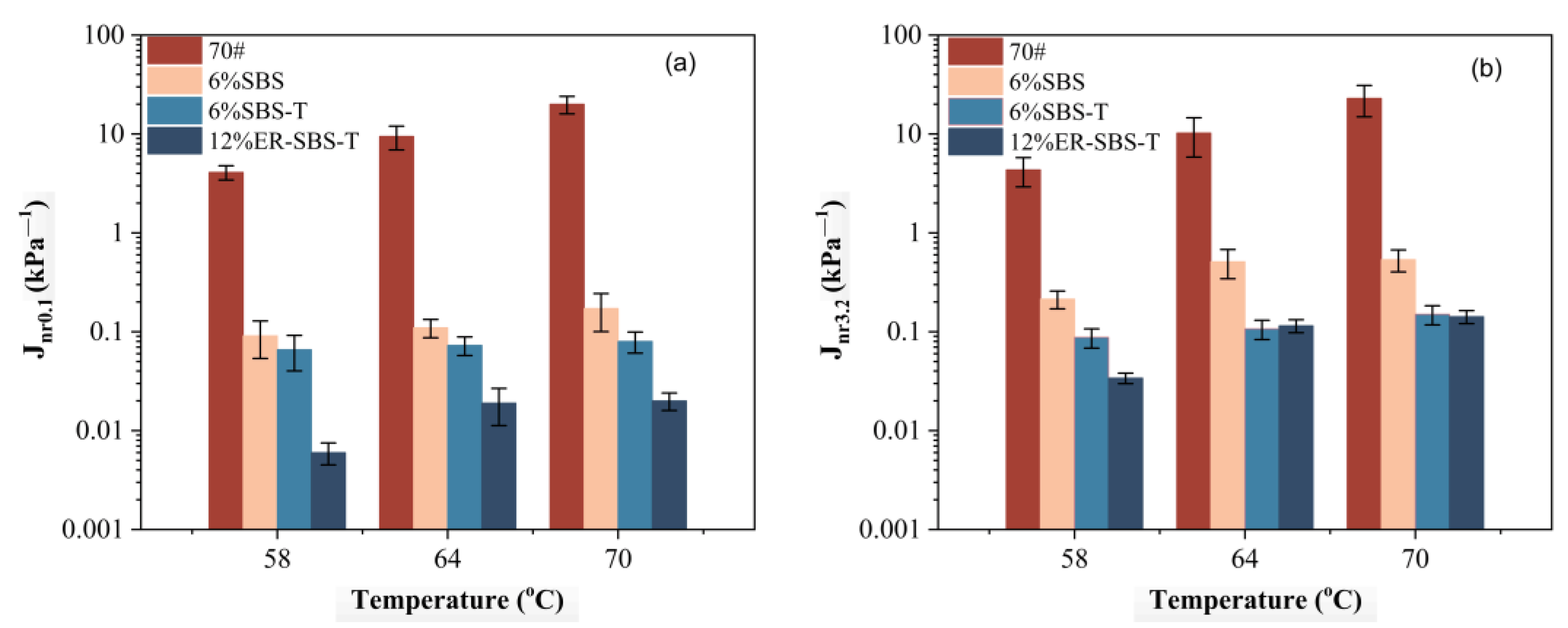
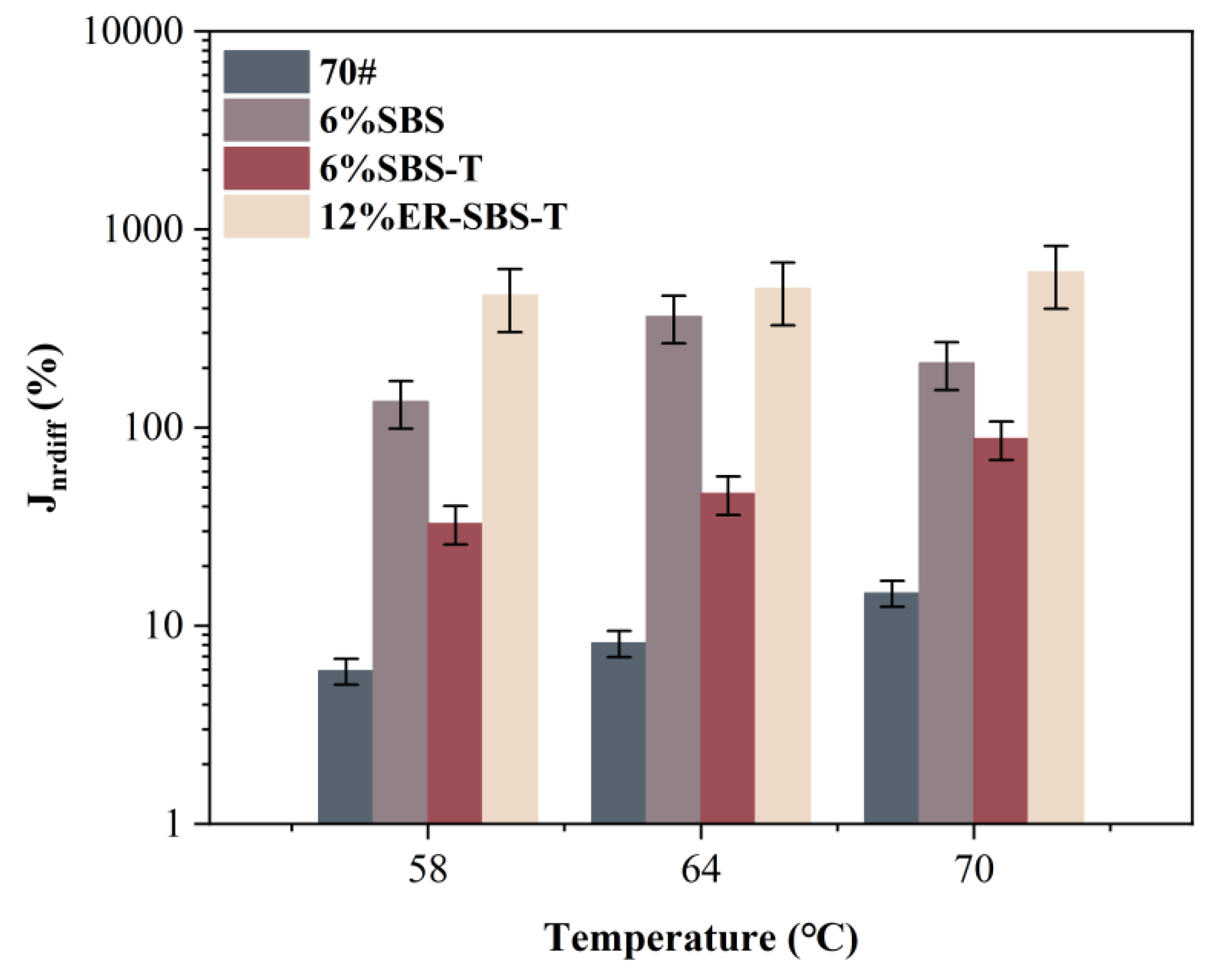
3.3. Temperature and Stress Level on MSCR-Related Parameters
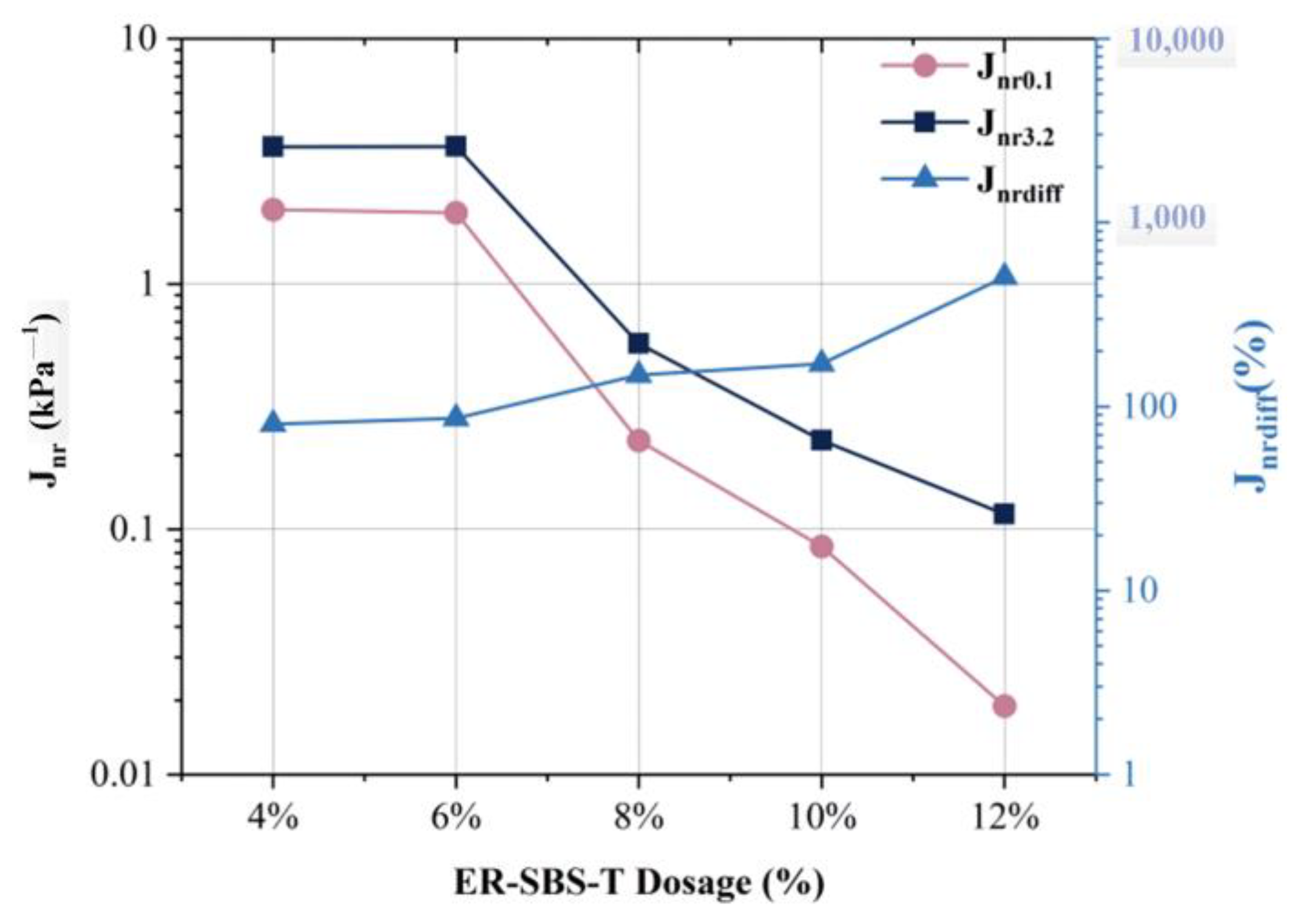
3.4. Influence of Modifier Dosage on MSCR-Related Parameters
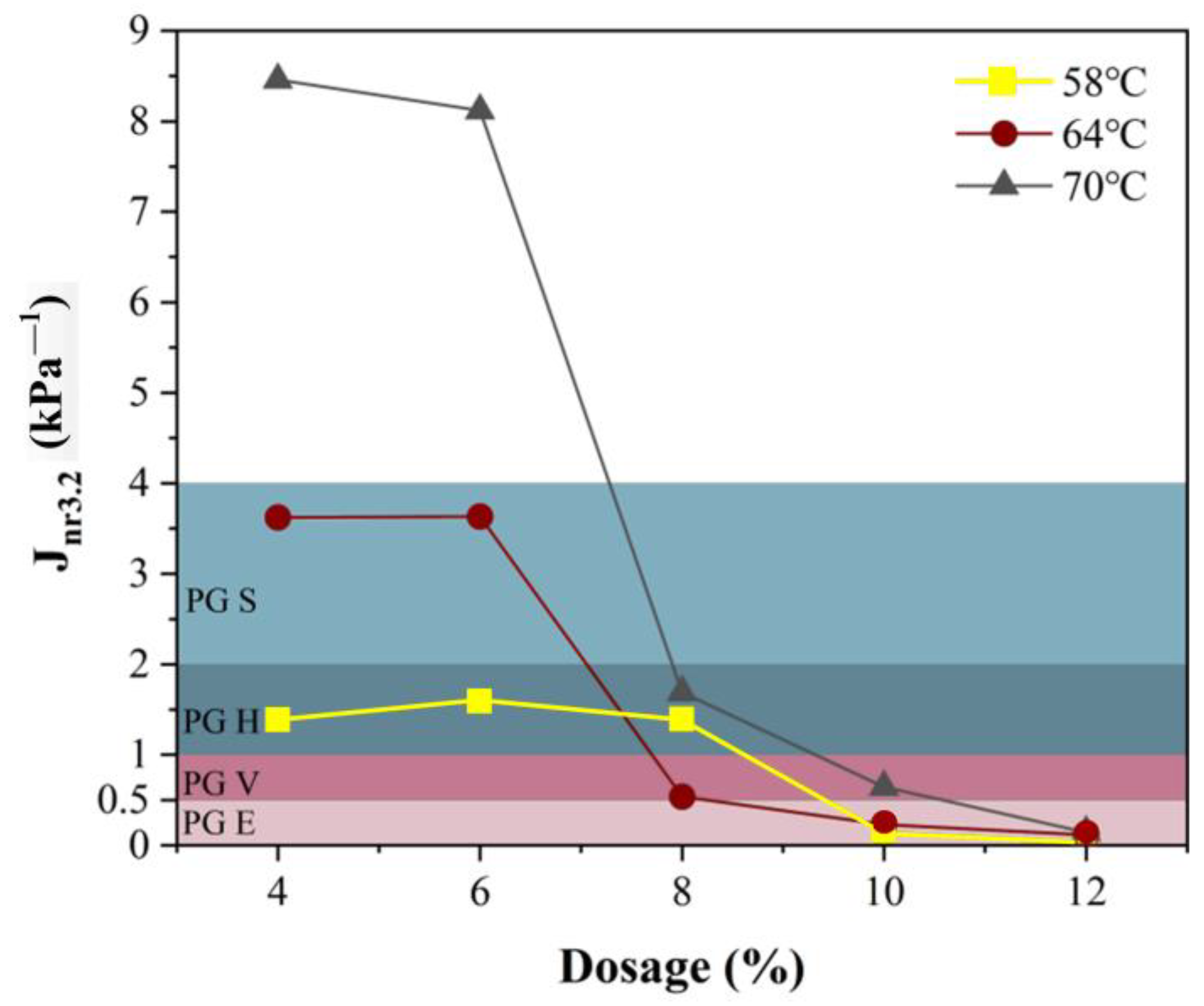
3.5. Pavement Performance Grading Based on the MSCR Test
3.6. Tests Results for ZSV Test
4. Conclusions
- Compared to the SBS-modified asphalt binder, the high-temperature performance of the SBS-T-modified asphalt binder is slightly better, and the high-temperature performance of the two modified asphalt binders stops improving after the content exceeds 6%, while the addition of the ER-SBS-T composite modifier can continue to enhance the high-temperature performance of the asphalt binder, and the high-temperature performance keeps improving after the content exceeds 6%. When the dosage is greater than 10%, the high-temperature performance jumps significantly, and it is better than the 6% SBS-modified asphalt binder, and the 6% SBS-T-modified asphalt binder. Therefore, in practice, a 6% dosage of the SBS- and SBS-T-modified asphalt binder can be chosen. For the ER-SBS-T composite-modified asphalt binder, a dosage of 10% or more can be chosen.
- The high-temperature performance of ER-SBS-T composite-modified asphalt at 58 °C, 64 °C, and 70 °C are all excellent. The temperature sensitivity of SBS-T-modified asphalt, SBS-modified asphalt, and ER-SBS-T composite-modified asphalt is low, and the high-temperature performance and stress sensitivity do not change significantly with the change in test temperature.
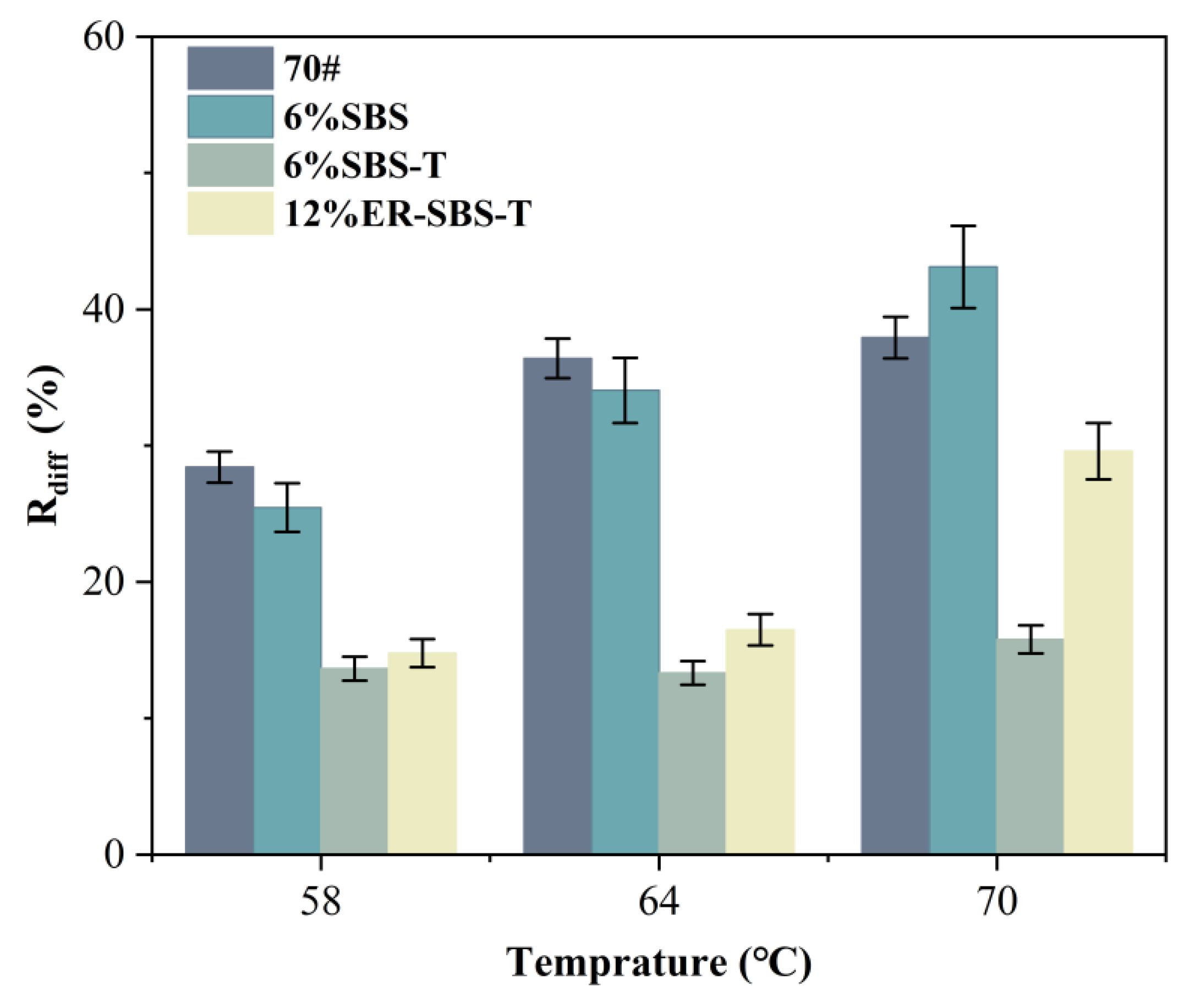
- The improvement in the high-temperature performance of asphalt binder at low and high stress levels is different with the addition of the ER-SBS-T composite modifier. This is due to the fact that this modifier improves the high-temperature performance of asphalt in the linear viscoelastic interval.
- For the penetration, is difficult to reflect the high-temperature performance of the SBS-T-modified asphalt. The average percentage recovery, average non-recoverable creep, and zero-shear viscosity fitted by the Cross model can reflect the high-temperature performance of the modified asphalt binder, and the 70 °C pavement performance grading can effectively distinguish the high-temperature performance of these three modified asphalt binders.
- Based on the PG system of MSCR, 70 °C can be used as the reference temperature for performance classification of the ER-SBS-T composite-modified asphalt binder when the content is less than 12%. The reference temperature for performance grading of the ER-SBS-T composite-modified asphalt binder at higher blends needs to be further investigated.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ameri, M.; Mirzaiyan, D.; Amini, A. Rutting resistance and fatigue behavior of gilsonite-modified asphalt binders. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2018, 30, 04018292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirim, Y. Polymer modified asphalt binders. Constr. Build. Mater. 2007, 21, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.; Amirkhanian, S.; Wang, H.; Hao, P. Rheological property investigations for polymer and polyphosphoric acid modified asphalt binders at high-temperatures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 64, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, M.; Xin, X.; Fan, W.; Luo, H.; Wang, X.; Xing, B. Investigation of the rheological properties and storage stability of CR/SBS modified asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 74, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Song, M.; Pu, L.; Liu, T. Rheological behaviors of epoxy asphalt binder in comparison of base asphalt binder and SBS modified asphalt binder. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 76, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Bors, J. Alternate uses of epoxy asphalt on bridge decks and roadways. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 78, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Zhang, L.; Muhammad, Y.; Cai, Z.; Guo, X.; Guo, Y.; Huang, K. Study on preparation and properties of new thermosetting epoxy asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 311, 125307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Zheng, C.; Yang, X.; Bao, C.; Liu, W.; Lin, Z. Development of technology to accelerate SBS modified asphalts swelling in dry modification mode. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 314, 125703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Zhu, Y.T. Experimental study of asphalt mixtures containing polyolefin/ethylene copolymer modifier by dry process. Adv. Energy Mater. 2013, 671, 1945–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Cao, D.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, X. Performance of a dry-method-epoxy modifier and a modified epoxy-asphalt mixture. Adv. Energy Mater. 2021, 266, 120229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polacco, G.; Kříž, P.; Filippi, S.; Stastna, J.; Biondi, D.; Zanzotto, L. Rheological properties of asphalt/SBS/clay blends. Eur. Polym. J. 2008, 44, 3512–3521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyin, S.O.; Yadykova, A.Y. Eco-friendly bitumen binders from heavy crude oil and a relaxation approach to predicting their resistance to rutting and cracking. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 434, 139942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahia, H.U.; Perdomo, D.; Turner, P. Applicability of Superpave binder testing protocols to modified binders. Transp. Res. Rec. 1997, 1586, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Kim, Y.R. Viscoelastic constitutive model for asphalt concrete under cyclic loading. J. Eng. Mech. 1998, 124, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, G. Grading highly modified binders by multiple stress creep recovery. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2017, 18, 1322–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zeiada, W.; Al-Khateeb, G.G.; Shanableh, A.; Samarai, M. Use of the multiple stress creep recovery (MSCR) test to characterize the rutting potential of asphalt binders: A literature review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 269, 121320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.A.; Le Hir, Y.M.; Planche, J.P.; Martin, D.; Shenoy, A. Zero shear viscosity of asphalt binders. Transp. Res. Rec. 2002, 1810, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morea, F.; Agnusdei, J.O.; Zerbino, R. The use of asphalt low shear viscosity to predict permanent deformation performance of asphalt concrete. Mater Struct. 2011, 44, 1241–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DuBois, E.; Mehta, Y.; Nolan, A. Correlation between multiple stress creep recovery (MSCR) results and polymer modification of binder. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 65, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoorob, S.E.; Castro-Gomes, J.P.; Oliveira, L.P.; O’connell, J. Investigating the multiple stress creep recovery asphalt binder characterisation test. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 30, 734–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Angelo, J.A. The relationship of the MSCR test to rutting. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2009, 10, 61–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasage, T.L.J.; Stastna, J.; Zanzotto, L. Rheological analysis of multi-stress creep recovery (MSCR) test. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2011, 12, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Ye, F. Experimental investigation on aging characteristics of asphalt based on rheological properties. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 231, 117158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; You, Z. high-temperature performance evaluation of bio-oil modified asphalt binders using the DSR and MSCR tests. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 76, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özdemir, D.K. High and low temperature rheological characteristics of linear alkyl benzene sulfonic acid modified asphalt binder. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 301, 124041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JTG E20-2011; Asphalt Kinematic Viscosity Test (Vacuum Decompression Capillary Method), Standard Test Methods of Bitumen and Bituminous Mixtures for Highway and Engineering. People’s Communications Press: Beijing, China, 2011.
- Yan, Y.; Cocconcelli, C.; Roque, R.; Nash, T.; Zou, J.; Hernando, D.; Lopp, G. Performance evaluation of alternative polymer-modified asphalt binders. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2015, 16 (Suppl. S1), 389–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marasteanu, M.O.; Clyne, T.; McGraw, J.; Li, X.; Velasquez, R. High-temperature rheological properties of asphalt binders. Transp. Res. Rec. 2005, 1901, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sybilski, D. Zero-shear viscosity of bituminous binder and its relation to bituminous mixture’s rutting resistance. Transp. Res. Rec. 1996, 1535, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeiada, W.; Liu, H.; Al-Khateeb, G.G.; Shanableh, A.; Samarai, M. Evaluation of test methods for measurement of zero shear viscosity (ZSV) of asphalt binders. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 325, 126794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, F.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, J.; Fan, W.; Yu, Y.; Wang, Z. Influence of SBS and asphalt on SBS dispersion and the performance of modified asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 62, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Xu, W.; Feng, H.; Cao, K. High and low temperature performance and fatigue properties of silica fume/SBS compound modified asphalt. Materials 2020, 13, 4446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Xia, Y.; Tsai, F.C.; Jiang, T.; Zhao, H.; Wen, J. Effects of compound curing agent on the thermo-mechanical properties and structure of epoxy asphalt. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2017, 18, 928–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Min, Z.; Wang, Q.; Huang, W.; Shi, Z. Influence of curing agent ratio, asphalt content and crosslinking degree on the compatibility and component distribution of epoxy asphalt in compound curing agent system. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2022, 24, 2136375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AASHTO M320 M; Standard Specification for Performance-Graded Asphalt Binder. American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials: Washington, DC, USA, 2017.








| Technical Parameter | Units | Values | Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Penetration (25 °C) | 0.1 mm | 72.4 | T0604-2011 |
| Ductility (15 °C, 5 cm/min) | cm | 114 | T0605-2011 |
| Softening point | °C | 47.7 | T0606-2011 |
| Modifiers | Parameters | Units | Values |
|---|---|---|---|
| SBS | S/B ratio | — | 28/72 |
| Tensile strength | MPa | 34.1 | |
| Elongation | % | 761 | |
| Oil content | % | 0.7 | |
| Melt flow rate | g/10 min | 0.82 | |
| SBS-T | Individual particle quality | g | 0.21 |
| Ash content | % | 0.48 | |
| Melting index | g/10 min | 2.39 | |
| ER-SBS-T | Individual particle quality | g | <0.001 |
| Ash content | % | 1.4 | |
| Melting index | g/10 min | 13.8 | |
| Density | g/cm3 | 0.975 |
| Parameters | Modifiers | Dosage | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4% | 6% | 8% | 10% | 12% | ||
| 60 °C kinematic viscosity (Pa∙s) | SBS | 3600 | 12,800 | 18,900 | — | — |
| SBS-T | 5900 | 16,700 | 22,000 | — | — | |
| ER-SBS-T | 2800 | 6000 | 19,000 | 58,000 | 148,900 | |
| Rate of change in the viscosity (%) | SBS | — | 258 | 47 | — | — |
| SBS-T | — | 183 | 34 | — | — | |
| ER-SBS-T | — | 114 | 223 | 203 | 156 | |
| Traffic Volume Classification | Test Temperature | Jnr3.2/kPa−1 | Jnr-diff/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 58 °C | 64 °C | 70 °C | |||
| Extremely heavy traffic (more than 30 million axles) | PG58E | PG64E | PG70E | ≤0.5 | ≤75 |
| Very heavy traffic (more than 30 million axles) | PG58V | PG64V | PG70V | ≤1.0 | ≤75 |
| heavy traffic (10 million to 30 million axles) | PG58H | PG64H | PG70H | ≤2.0 | ≤75 |
| Standard traffic (Less than 10 million axles) | PG58S | PG64S | PG70S | ≤4.0 | ≤75 |
| Bitumin | Jnr3.2/kPa−1 | Pavement Performance Grading | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 58 °C | 64 °C | 70 °C | 58 °C | 64 °C | 70 °C | |
| 70# | 4.34 | 10.22 | 22.94 | — | — | — |
| 6% SBS | 0.21 | 0.511 | 0.54 | PG58E | PG64V | PG70V |
| 6% SBS-T | 0.09 | 0.11 | 0.15 | PG58E | PG64E | PG70E |
| 4% ER-SBS-T | 1.39 | 3.62 | 8.46 | PG58H | PG64S | — |
| 6% ER-SBS-T | 1.60 | 3.63 | 8.11 | PG58H | PG64S | — |
| 8% ER-SBS-T | 1.4 | 0.57 | 1.69 | PG58H | PG64V | PG70H |
| 10% ER-SBS-T | 0.14 | 0.23 | 0.64 | PG58E | PG64E | PG70V |
| 12% ER-SBS-T | 0.03 | 0.12 | 0.14 | PG58E | PG64E | PG70E |
| Bitumin | Zero-Shear Viscosity (Pa·s) | Relative Coefficient R2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cross Model | Carreau Model | Model Difference (%) | Cross Model | Carreau Model | |
| 70# | 216.05 | 206.66 | 4.34 | 0.94 | 0.92 |
| 6% SBS | 2604.78 | 2651.30 | 1.04 | 0.98 | 0.99 |
| 6% SBS-T | 2894.25 | 2998.60 | 4.11 | 0.99 | 0.99 |
| 4% ER-SBS-T | 1038.58 | 1034.09 | 0.43 | 0.98 | 0.98 |
| 6% ER-SBS-T | 1641.04 | 618.16 | 62.33 | 0.99 | 0.99 |
| 8% ER-SBS-T | 3693.81 | 3628.68 | 1.76 | 0.96 | 0.97 |
| 10% ER-SBS-T | 4035.56 | 2452.29 | 39.23 | 0.99 | 0.99 |
| 12% ER-SBS-T | 7753.25 | 7766.17 | 0.09 | 0.96 | 0.99 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, L.; Zhang, X.; Sha, T.; Wang, D.; Niu, B.; Wang, R.; Hou, X. A Rheological Study of the High-Temperature Properties of Fast-Melting SBS/Epoxy-Modified Asphalt Binders. Polymers 2025, 17, 581. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17050581
Feng L, Zhang X, Sha T, Wang D, Niu B, Wang R, Hou X. A Rheological Study of the High-Temperature Properties of Fast-Melting SBS/Epoxy-Modified Asphalt Binders. Polymers. 2025; 17(5):581. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17050581
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Lei, Xinyong Zhang, Tianyu Sha, Decai Wang, Ben Niu, Riran Wang, and Xiyang Hou. 2025. "A Rheological Study of the High-Temperature Properties of Fast-Melting SBS/Epoxy-Modified Asphalt Binders" Polymers 17, no. 5: 581. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17050581
APA StyleFeng, L., Zhang, X., Sha, T., Wang, D., Niu, B., Wang, R., & Hou, X. (2025). A Rheological Study of the High-Temperature Properties of Fast-Melting SBS/Epoxy-Modified Asphalt Binders. Polymers, 17(5), 581. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17050581






