Adsorption of Organic Pollutants from Wastewater Using Chitosan-Based Adsorbents
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Mechanisms of Adsorption Processes
2.1. Freundlich and Langmuir Adsorption Isotherms
2.1.1. Langmuir Adsorption Isotherm
2.1.2. Freundlich Adsorption Isotherm Model
2.2. Kinetic Models
- qe (mg.g−1) = adsorption capacity at equilibrium.
- qt (mg.g−1) = adsorption capacity at time t.
- k1 (s−1) = rate constant for first-order adsorption.
- k2 (mol L−1 s−1) = rate constant for second-order adsorption.
- t (min) = time of adsorption.
- qt (mg.g−1) = adsorption capacity at time t.
- k (min−1) = Weber–Morris rate constant.
- t (min) = adsorption time.
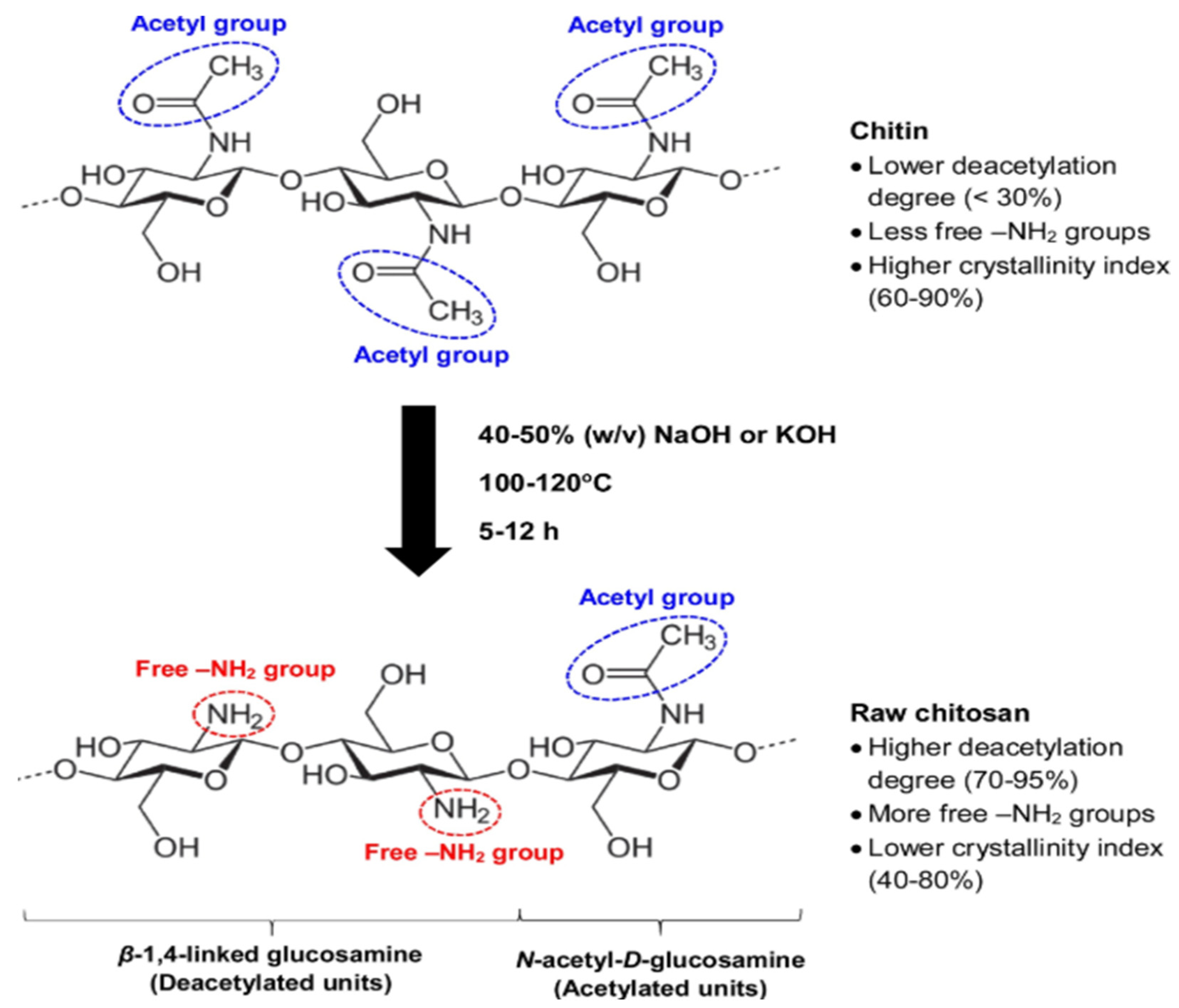
3. Structure and Characteristics of Chitosan and Its Derivatives
3.1. An Outline of the Chemical Structure of Chitosan
3.2. Sources and Formation of Chitosan
4. Physical and Chemical Properties of Chitosan and Its Derivatives
5. Modification of Chitosan
5.1. Cross-Linked Chitosan
5.2. Grafted Chitosan
5.3. Nanoparticles and Functionalized Form of Chitosan
6. Methods of Modifying Chitosan
6.1. Physical Modifications of Chitosan
6.2. Chemical Modifications of Chitosan
6.3. Impact of Modification on Adsorption Efficiency
7. Adsorption of Organic Pollutants by Chitosan-Based Materials
7.1. Adsorption of Antibiotics
7.2. Adsorption of Dyes
7.3. Adsorption of Pesticides
7.4. Adsorption of Microplastics
7.5. Adsorption of PAHs, Parabens, and PCBs
8. Environmental and Economic Viability of Chitosan
8.1. Environmental Viability of Chitosan
- 1.
- Source material utilization
- 2.
- Processing methods
- 3.
- Carbon footprint and energy use
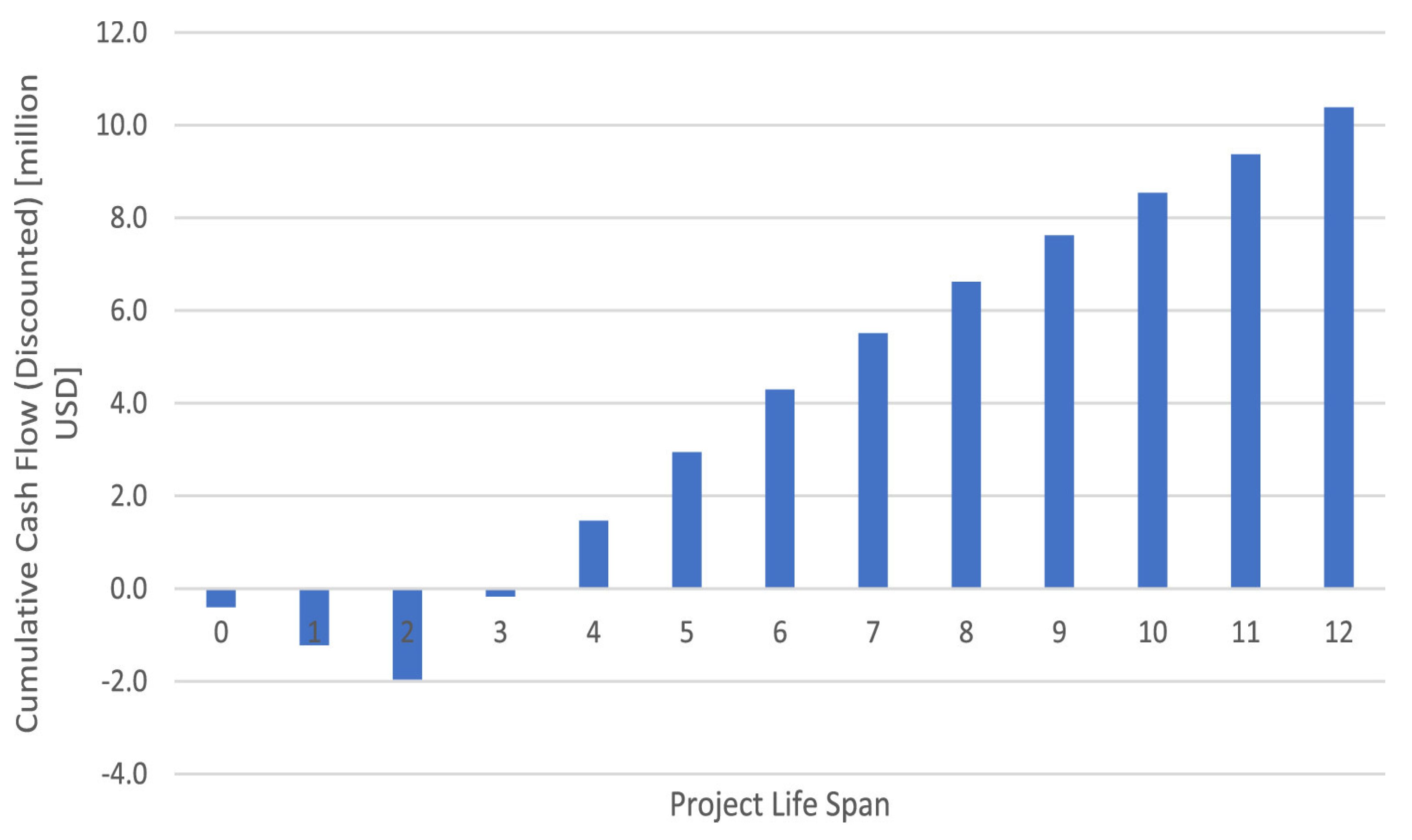
8.2. Economic Viability of Chitosan
9. Recovery and Reusability of Chitosan-Based Adsorbents
10. Conclusions and Future Research Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Atangana, E.; Chiweshe, T.T.; Roberts, H. Modification of novel chitosan-starch cross-linked derivatives polymers: Synthesis and characterization. J. Polym. Environ. 2019, 27, 979–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atangana, E.; Chiweshe, T.T. Metal adsorbance in abattoir wastewater using cross-linked chitosan derivatives. J. Polym. Environ. 2019, 27, 2624–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzhangi, T.R.; Atangana, E. Evaluation of the impact of coal mining on surface water in the Boesmanspruit, Mpumalanga, South Africa. Environ. Earth Sci. 2023, 83, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishnan, R.K.; Padil, V.V.T.; Wacławek, S.; Černík, M.; Varma, R.S. Eco-friendly and economic, adsorptive removal of cationic and anionic dyes by bio-based karaya gum—Chitosan sponge. Polymers 2021, 13, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Kou, H.; Zhou, Y.; Lan, X.; Yu, M.; Chen, H. Preparation of amphiphilic chitosan-loaded bentonite adsorbent and its performance in removing organic matter from coking wastewater. Polymers 2023, 15, 1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poshina, D.N.; Raik, S.V.; Poshin, A.N.; Skorik, Y.A. Accessibility of chitin and chitosan in enzymatic hydrolysis: A review. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2018, 156, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghani, M.H.; Ahmadi, S.; Ghosh, S.; Othmani, A.; Osagie, C.; Meskini, M.; AlKafaas, S.S.; Malloum, A.; Khanday, W.A.; Jacob, A.O.; et al. Recent advances on sustainable adsorbents for the remediation of noxious pollutants from water and wastewater: A critical review. Arab. J. Chem. 2023, 16, 105303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Falyouna, O.; Malloum, A.; Othmani, A.; Bornman, C.; Bedair, H.; Onyeaka, H.; Al-Sharify, Z.T.; Jacob, A.O.; Miri, T.; et al. A general review on the use of advance oxidation and adsorption processes for the removal of furfural from industrial effluents. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2022, 331, 111638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Malloum, A.; Bornman, C.; Othmani, A.; Osagie, C.; Esfahani, Z.K.; Khanday, W.A.; Ahmadi, S.; Dehghani, M.H. Novel green adsorbents for removal of aniline from industrial effluents: A review. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 345, 118167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Malloum, A.; Igwegbe, C.A.; Ighalo, J.O.; Ahmadi, S.; Dehghani, M.H.; Othmani, A.; Gökkuş, Ö.; Mubarak, N.M. New generation adsorbents for the removal of fluoride from water and wastewater: A review. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 346, 118257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magagula, M.; Atangana, E.; Oberholster, P. Assessment of the Impact of Coal Mining on Water Resources in Middelburg, Mpumalanga Province, South Africa: Using Different Water Quality Indices. Hydrology 2024, 11, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeedi, R.; Sadeghi, S.; Massoudinejad, M.; Oroskhan, M.; Mohagheghian, A.; Mohebbi, M.; Abtahi, M. Assessing drinking water quality based on water quality indices, human health risk, and burden of disease attributable to heavy metals in rural communities of Yazd County, Iran, 2015–2021. Heliyon 2024, 10, e33984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dehghani, R.; Kassiri, H. A Review on Epidemiology of Dengue Viral Infection as an Emerging Disease. Res. J. Pharm. Technol. 2021, 14, 2296–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vane, C.H.; Kim, A.W.; Beriro, D.J.; Cave, M.R.; Knights, K.; Moss-Hayes, V.; Nathanail, P.C. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH) and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCB) in urban soils of Greater London, UK. Appl. Geochem. 2014, 51, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nzengung, V.; Gugolz, S. Biochar-based constructed wetland for contaminants removal from manure wastewater. In Sustainable Biochar for Water and Wastewater Treatment; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 487–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, M.; Verma, N.; Dhanda, R.S. Impact of sexually transmitted infections on women health. Health 2013, 5, 1216–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Eldos, H.I.; Zouari, N.; Saeed, S.; Al-Ghouti, M.A. Recent advances in the treatment of PAHs in the environment: Application of nanomaterial-based technologies. Arab. J. Chem. 2022, 15, 103918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Li, N.; Lu, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhu, Y. Study on preparation and separation and adsorption performance of knitted tube composite β-cyclodextrin/chitosan porous membrane. Polymers 2019, 11, 1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, B.; Imran, M. Emerging Organic Contaminants, Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products (PPCPs): A Threat to Water Quality; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 105–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, T.B.; Case, P.; Chui, S.; Chung, D.; Haeffele, C.; Haston, K.; Lee, M.; Mai, V.P.; Marjuoa, Y.; Parker, J.; et al. Pesticide mixtures, endocrine disruption, and amphibian declines: Are we underestimating the impact? Environ. Health Perspect. 2006, 114 (Suppl. S1), 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouch, A.; Zaborska, A. Climate Change Influence on Migration of Contaminants in the Arctic Marine Environment. In Impact of Climate Changes on Marine Environments; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 75–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Yu, S.; Zeng, J.; Zheng, X.; Ren, Z.; Shu, Y.; Mai, B. Biomagnification of persistent organic pollutants (POPs) in detritivorous, phytophagous, and predatory invertebrates: How POPs enter terrestrial food web? Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 924, 171677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voulvoulis, N.; Arpon, K.D.; Giakoumis, T. The EU Water Framework Directive: From great expectations to problems with implementation. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 575, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I.; Basheer, A.A.; Mbianda, X.Y.; Burakov, A.; Galunin, E.; Burakova, I.; Mkrtchyan, E.; Tkachev, A.; Grachev, V. Graphene based adsorbents for remediation of noxious pollutants from wastewater. Environ. Int. 2019, 127, 160–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, A.L.; Chong, M.F.; Bhatia, S.; Ismail, S. Drinking water reclamation from palm oil mill effluent (POME) using membrane technology. Desalination 2006, 191, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benettayeb, A.; Seihoub, F.Z.; Pal, P.; Ghosh, S.; Usman, M.; Chia, C.H.; Usman, M.; Sillanpää, M. Chitosan Nanoparticles as Potential Nano-Sorbent for Removal of Toxic Environmental Pollutants. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benettayeb, A.; Ahamadi, S.; Ghosh, S.; Malbenia John, M.; Mitchel, C.R.; Haddou, B. Natural adsorbents for the removal of emerging pollutants and its adsorption mechanisms. In Sustainable Technologies for Remediation of Emerging Pollutants from Aqueous Environment; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024; pp. 63–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suyambulingam, I.; Gangadhar, L.; Sana, S.S.; Divakaran, D.; Siengchin, S.; Kurup, L.A.; Iyyadurai, J.; Albert Bernad Noble, K.E. Chitosan Biopolymer and Its Nanocomposites: Emerging Material as Adsorbent in Wastewater Treatment. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2023, 2023, 9387016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatnagar, A.; Sillanpää, M. Applications of chitin- and chitosan-derivatives for the detoxification of water and wastewater—A short review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 152, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood Aljamali, N.; Obaid Alfatlawi, I. Physical and Chemical Adsorption and its Applications. Int. J. Thermodyn. Chem. Kinet. 2021, 7, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajiboye, T.O.; Oyewo, O.A.; Onwudiwe, D.C. Adsorption and photocatalytic removal of Rhodamine B from wastewater using carbon-based materials. FlatChem 2021, 29, 100277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathi, B.S.; Kumar, P.S. Application of adsorption process for effective removal of emerging contaminants from water and wastewater. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 280, 116995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwiatkowski, M.; Broniek, E. An analysis of the porous structure of activated carbons obtained from hazelnut shells by various physical and chemical methods of activation. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2017, 529, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caroni, A.L.P.F.; De Lima, C.R.M.; Pereira, M.R.; Fonseca, J.L.C. The kinetics of adsorption of tetracycline on chitosan particles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 340, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swenson, H.; Stadie, N.P. Langmuir’s Theory of Adsorption: A Centennial Review. Langmuir 2019, 35, 5409–5426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karimi, S.; Tavakkoli Yaraki, M.; Karri, R.R. A comprehensive review of the adsorption mechanisms and factors influencing the adsorption process from the perspective of bioethanol dehydration. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 107, 535–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ghouti, M.A.; Da’ana, D.A. Guidelines for the use and interpretation of adsorption isotherm models: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 393, 122383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayawei, N.; Ebelegi, A.N.; Wankasi, D. Modelling and Interpretation of Adsorption Isotherms. J. Chem. 2017, 2017, 3039817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooney, D.O. On the basis for the Freundlich Adsorption Isotherm. Chem. Eng. Commun. 1990, 94, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Rothstein, D.; Madey, R.; Huang, J.-C. Pressure Swing Adsorption for a System with a Langmuir Isotherm. Sep. Sci. Technol. 1988, 23, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajiboye, T.O.; Oyewo, O.A.; Onwudiwe, D.C. Simultaneous removal of organics and heavy metals from industrial wastewater: A review. Chemosphere 2021, 262, 128379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adibzaleh, A.; Khodabakhshi, M.R.; Maleki, A. Preparation of novel and recyclable chitosan-alumina nanocomposite as superabsorbent to remove diazinon and tetracycline contaminants from aqueous solution. Heliyon 2024, 10, e23139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morais, W.; de Almeida, A.; Pereira, M.; Fonseca, J. Equilibrium and kinetic analysis of methyl orange sorption on chitosan spheres. Carbohydr. Res. 2008, 343, 2489–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khumalo, S.M.; Bakare, B.F.; Rathilal, S. Single and multicomponent adsorption of amoxicillin, ciprofloxacin, and sulfamethoxazole on chitosan-carbon nanotubes hydrogel beads from aqueous solutions: Kinetics, isotherms, and thermodynamic parameters. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2024, 13, 100404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Guo, X. Adsorption kinetic models: Physical meanings, applications, and solving methods. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 390, 122156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khumalo, S.M.; Bakare, B.F.; Tetteh, E.K.; Rathilal, S. Application of Response Surface Methodology on Brewery Wastewater Treatment Using Chitosan as a Coagulant. Water 2023, 15, 1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altrun, S.; Kadak, A.E.; Kucukgulmez, A.; Gulnaz, O.; Celik, M. Explanation of difenoconazole removal by chitosan with Langmuir adsorption isotherm and kinetic modeling. Toxicol. Res. 2022, 39, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adriano, W.S.; Veredas, V.; Santana, C.C.; Goncalves, L.R.B. Adsorption of amoxicillin on chitosan beads:Kinetics, equilibrium and validation of finite bath models. Biochem. Eng. J. 2005, 27, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadvarzi, S.B.; Amooey, A. Simultaneous adsorption of Amoxicillin and Cefixime by facile synthesized Chitosan@Polyacrylamide@ZIF-8; Isotherm and Kinetic study. Sci. Eur. 2023, 35, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, M.A.; Jasim, L.S. Characterization, isotherms kinetics and thermodynamics studies of amoxicillin in aqueous solution with a chitosan/poly acrylic amid-co-acrylic acid. In AIP Conference Proceedings; AIP Publishing: College Park, MD, USA, 2022; Volume 2398. [Google Scholar]
- Nezhadali, A.; Koushali, S.E.; Divsar, F. Synthesis of polypyrrole–chitosan magnetic nanocomposite for the removal of carbamazepine from wastewater: Adsorption isotherm and kinetic study. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, M.; Chauhan, D. Copper chitosan nanocomposite: Synthesis, characterization, and application in removal of organophosphorus pesticide from agricultural runoff. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2012, 19, 2055–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, A.; Kongot, M.; Saini, K.V.; Kumar, A. 2018. Removal of pentachlorophenol pesticide from aqueous solutions using modified chitosan. Arab. J. Chem. 2018, 13, 1821–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaudo, M. Chitin and chitosan: Properties and applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2006, 31, 603–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.-K.; Chun, S.-K.; Choi, W.-J.; Kim, J.-K.; Choi, S.-H.; Kim, A.; Oungbho, K.; Park, J.-S.; Ahn, W.S.; Kim, C.-K. The use of chitosan as a condensing agent to enhance emulsion-mediated gene transfer. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 2147–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Prakash, J.; Sinha, R. Chitosan: A versatile biopolymer. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 104, 1232–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crini, G.; Badot, P.-M. Application of chitosan, a natural aminopolysaccharide, for dye removal from aqueous solutions by adsorption processes using batch studies: A review of recent literature. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2008, 33, 399–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, R.R.L.; Moraes, J.S. Removal of organic pollutants from wastewater using chitosan: A literature review. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 16, 1741–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mali, S.; Sinha, R.; Prakash, J. Chitosan and its derivatives: A review on their applications. J. Adv. Res. 2015, 6, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangel-Mendez, J.; Monroy-Zepeda, R.; Leyva-Ramos, E.; Diaz-Flores, P.; Shirai, K. Chitosan selectivity for removing cadmium (II), copper (II), and lead (II) from aqueous phase: pH and organic matter effect. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 162, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.L.B.; Tai, M.-C.; Cheng, F.-H. Kinetics and Products of the Degradation of Chitosan by Hydrogen Peroxide. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 4845–4851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maia, M.T.; Sena, D.N.; Calais, G.B.; Luna, F.M.T.; Beppu, M.M.; Vieira, R.S. Effects of histidine modification of chitosan microparticles on metal ion adsorption. React. Funct. Polym. 2020, 154, 104694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, G.; Su, H.; Tan, T. Synthesis of core–shell bioaffinity chitosan–TiO2 composite and its environmental applications. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 283, 888–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabaharan, M.; Sivashankari, P.R. Prospects of Bioactive Chitosan-Based Scaffolds in Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine. In Chitin and Chitosan for Regenerative Medicine; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 41–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubentheren, V.; Ward, T.A.; Chee, C.Y.; Nair, P. Physical and chemical reinforcement of chitosan film using nanocrystalline cellulose and tannic acid. Cellulose 2015, 22, 2529–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Li, K.; Li, J.; Ying, D.; Wang, Y.; Jia, J. Comparative and competitive adsorption of Pb(II) and Cu(II) using tetraethylenepentamine modified chitosan/CoFe2O4 particles. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 326, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nthunya, L.N.; Masheane, M.L.; Malinga, S.P.; Nxumalo, E.N.; Mhlanga, S.D. Electrospun chitosan-based nanofibres for removal of phenols from drinking water. Water SA 2018, 44, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Jing, P.; Ruan, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, S.; Cai, Z.; Qian, B. Removal of off-flavours from radish (Raphanus sativus L.) anthocyanin-rich pigments using chitosan and its mechanism(s). Food Chem. 2014, 146, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annouar, A.; Moufti, A.; Mountadar, S.; Mountadar, M.; Soufiane, M. The influences of the presence of ions counter on the removal capacity of fluoride ions by chitosan. Orient. J. Chem. 2016, 32, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, M.; Cheng, Q.; Wang, C.; Li, H.; Han, X.; Fan, Z.; Su, G.; Pan, D.; Li, Z. Research progress of adsorption and removal of heavy metals by chitosan and its derivatives: A review. Chemosphere 2021, 279, 130927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwe, N.; Saha, S.; Ahsan, M. Chitosan-based drug delivery systems. Front. Biosci. 2008, 13, 1734–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norrio, C.M.; Kauffmann, J.B.; Alves, M.A. Chitin and chitosan: A review of their sources and production methods. Agronomy 2016, 6, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udoetok, I.A.; Karoyo, A.H.; Mohamed, M.H.; Wilson, L.D. Chitosan Biocomposites with Variable Cross-Linking and Copper-Doping for Enhanced Phosphate Removal. Molecules 2024, 29, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourya, V.K.; Inamdar, N.N. Chitosan-modifications and applications: Opportunities galore. Reactive and Functional. Polymers 2008, 68, 1013–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizardi-Mendoza, J.; Argüelles Monal, W.M.; Goycoolea Valencia, F.M. Chemical Characteristics and Functional Properties of Chitosan. In Chitosan in the Preservation of Agricultural Commodities; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 3–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasaai, M.R. A review of several reported procedures to determine the degree of N-acetylation for chitin and chitosan using infrared spectroscopy. Carbohydr. Polym. 2008, 71, 497–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolhe, P.; Kannan, R.M. Improvement in Ductility of Chitosan through Blending and Copolymerization with PEG: FTIR Investigation of Molecular Interactions. Biomacromolecules 2003, 4, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, C.N.; Teixeira, V.G.; Delpech, M.C.; Souza, J.V.S.; Costa, M.A.S. Viscometric study of chitosan solutions in acetic acid/sodium acetate and acetic acid/sodium chloride. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 133, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, I.A.; Ebeid, H.M.; Kishk, Y.F.; Abdel Fattah, A.F.A.K.; Mahmoud, K.F.; Ibrahim, A.I.; Ebeid, H.M.; Kishk, Y.F.M.; Abdel Fattah, A.A.; Mahmoud , K.F. Effect of grinding and particle size on some physical and rheological properties of chitosan. Arab Univ. J. Agric. Sci. 2019, 27, 1513–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Chen, D.; Chang, Z. Preparation and characterization of porous chitosan microspheres and adsorption performance for hexavalent chromium. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 135, 898–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Don, T.M.; King, C.F.; Chiu, W.Y. Synthesis and properties of chitosan-modified poly (vinyl acetate). J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2002, 86, 3057–3063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.C.; Tseng, R.L.; Juang, R.S. A review and experimental verification of using chitosan and its derivatives as adsorbents for selected heavy metals. J. Environ. Manag. 2010, 91, 798–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, K.Z.; Bikiaris, D.N. Recent modifications of chitosan for adsorption applications: A critical and systematic review. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 312–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elwakeel, K.Z.; Aly, M.H.; El-Howety, M.A.; El-Fadaly, E.; Al-Said, A. Synthesis of Chitosan@activated Carbon Beads with Abundant Amino Groups for Capture of Cu(II) and Cd(II) from Aqueous Solutions. J. Polym. Environ. 2018, 26, 3590–3602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guaresti, O.; García–Astrain, C.; Aguirresarobe, R.H.; Eceiza, A.; Gabilondo, N. Synthesis of stimuli–responsive chitosan–based hydrogels by Diels–Alder cross–linking click reaction as potential carriers for drug administration. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 183, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essel, T.Y.A.; Koomson, A.; Seniagya, M.O.; Cobbold, G.P.; Kwofie, S.K.; Asimeng, B.O.; Arthur, P.K.; Awandare, G.; Tiburu, E.K. Chitosan composites synthesized using acetic acid and tetraethylorthosilicate respond differently to methylene blue adsorption. Polymers 2018, 10, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Zhao, M.; Wang, Y. Immobilization of Laccase by Alginate–Chitosan Microcapsules and its Use in Dye Decolorization. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 23, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monier, M. Adsorption of Hg2+, Cu2+ and Zn2+ ions from aqueous solution using formaldehyde cross-linked modified chitosan–thioglyceraldehyde Schiff’s base. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2012, 50, 773–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kildeeva, N.R.; Perminov, P.A.; Vladimirov, L.V.; Novikov, V.V.; Mikhailov, S.N. About mechanism of chitosan cross-linking with glutaraldehyde. Russ. J. Bioorganic Chem. 2009, 35, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiou, M.-S.; Li, H.-Y. Equilibrium and kinetic modeling of adsorption of reactive dye on cross-linked chitosan beads. J. Hazard. Mater. 2002, 93, 233–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillet, G.; Boutevin, B.; Ameduri, B. Chemical reactions of polymer crosslinking and post-crosslinking at room and medium temperature. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2011, 36, 191–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzereme, A.; Christodoulou, E.; Kyzas, G.Z.; Kostoglou, M.; Bikiaris, D.N.; Lambropoulou, D.A. Chitosan grafted adsorbents for diclofenac pharmaceutical compound removal from single-component aqueous solutions and mixtures. Polymers 2019, 11, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, X.; Sun, C.; Li, K.; Guan, F.; Liu, X.; Duan, J.; Hou, B. Synthesis and characterization of chitosan–zinc composite electrodeposits with enhanced antibacterial properties. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 46081–46088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Pu, H.; Liu, S.; Kan, J.; Jin, C. Synthesis, characterization, bioactivity and potential application of phenolic acid grafted chitosan: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 174, 999–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radwan, R.R.; Abdel Ghaffar, A.M.; Ali, H.E. Gamma radiation preparation of chitosan nanoparticles for controlled delivery of memantine. J. Biomater. Appl. 2020, 34, 1150–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Xu, Z.; Jiang, X.; Hu, C.; Zou, X. Preparation and antibacterial activity of chitosan nanoparticles. Carbohydr. Res. 2004, 339, 2693–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Wang, A. Adsorption kinetics of Cu(II) ions using N,O-carboxymethyl-chitosan. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 131, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, A.M.; Eldin, T.A.S.; Hassan, M.A.; El-Anadouli, B.E. Efficient treatment of lead-containing wastewater by hydroxyapatite/chitosan nanostructures. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreica, B.-I.; Cheng, X.; Marin, L. Quaternary ammonium salts of chitosan. A critical overview on the synthesis and properties generated by quaternization. Eur. Polym. J. 2020, 139, 110016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.-T.; Zhang, J.-X.; Chen, Y.-W.; Cao, J.; Leng, M.-T.; Hu, S.-D.; Luo, X.-L. Preparation and characterization of chitosan composite membranes crosslinked by carboxyl-capped poly(ethylene glycol). Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 2014, 32, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, S.; Joshi, S.; Srivastava, R.K. A review on heavy metal biosorption utilizing modified chitosan. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, M.; Tripathi, S.; Shin, D.K. Biopolymeric Nanocomposites for Wastewater Remediation: An Overview on Recent Progress and Challenges. Polymers 2024, 16, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordin, A.; Ahmad, Z.; Husna, S.; Ilyas, R.; Azemi, A.; Ismail, N.; Nordin, M.; Ngadi, N.; Siti, N.; Nabgan, W.; et al. The State of the Art of Natural Polymer Functionalized Fe3O4 Magnetic Nanoparticle Composites for Drug Delivery Applications: A Review. Gels 2023, 9, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rukhsar, A.; Iqbal, Z.F.; Khan, M.S.; Zainab, S.A.; Nawaz, S.; Kim, T.H.; Mustafa, G.; Balčiūnaitė, A. Chitosan-Based Adsorbents and Catalysts for Removal of Toxic Pollutants from Water and Wastewater. Top. Catal. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Xue, C.; Mao, X. Chitosan: Structural modification, biological activity and application. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 4532–4546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, A.O.; Zaini, M.A.A.; Muhammad, I.M.; Abdulsalam, S.; El-Nafaty, U.A. Physicochemical modification of chitosan adsorbent: A perspective. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2023, 13, 5557–5575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Luo, C.; Lv, Z.; Lu, F.; Qiu, H. Preparation of magnetic modified chitosan and adsorption of Zn2+ from aqueous solutions. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2011, 88, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, C.-W.; Wu, M.-T.; Lee, J.C.-M.; Cheng, T.-Y. Isothermal adsorption properties for the adsorption and removal of reactive Blue 221 dye from aqueous solutions by cross-linked β-chitosan glycan as acid-resistant adsorbent. Polymers 2018, 10, 1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd El-Monaem, E.M.; Eltaweil, A.S.; Elshishini, H.M.; Hosny, M.; Abou Alsoaud, M.M.; Attia, N.F.; El-Subruiti, G.M.; Omer, A.M. Sustainable adsorptive removal of antibiotic residues by chitosan composites: An insight into current developments and future recommendations. Arab. J. Chem. 2022, 15, 103743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva Bruckmann, F.; Schnorr, C.E.; da Rosa Salles, T.; Nunes, F.B.; Baumann, L.; Müller, E.I.; Silva, L.F.O.; Dotto, G.L.; Rhoden, C.R.B. Highly efficient adsorption of tetracycline using chitosan-based magnetic adsorbent. Polymers 2022, 14, 4854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharrel, R.; Sangeeta, S.; Jisha, M.S.; Reshmy, R.; Arivalagan, P.; Aravind, M.; Parameswaran, B.; Mukesk, K.A.; Ashod, P.; Raveendran, S. Chitosan a versatile adsorbent in environmental remediation in the era of circular economy—A mini review. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2023, 32, 101004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasiri, A.; Rajabi, S.; Amiri, A.; Fattahizade, M.; Hasani, O.; Lalehzari, A.; Hashemi, M. Adsorption of tetracycline using CuCoFe2O4@ Chitosan as a new and green magnetic nanohybrid adsorbent from aqueous solutions: Isotherm, kinetic and thermodynamic study. Arab. J. Chem. 2022, 15, 104014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Lin, F.; Li, P.; Liu, J. Preparation of Chitosan-Modified Bentonite and Its Adsorption Performance on Tetracycline. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 19455–19463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaqubi, O.; Tai, M.H.; Mitra, D.; Gerente, C.; Neoh, K.G.; Wang, C.; Andres, Y. Adsorptive removal of tetracycline and amoxicillin from aqueous solution by leached carbon black waste and chitosan-carbon composite beads. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 104988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, J.Y.J.; Aqsha, A.; Ismadji, S.; Sunarso, J. Adsorption Kinetics of Amoxicillin, Ampicillin, and Doripenem on Organobentonite. AIP Conf. Proceeding 2024, 3073, 070013. [Google Scholar]
- Anchique, L.; Alcázar, J.J.; Ramos-Hernandez, A.; Méndez-López, M.; Mora, J.R.; Rangel, N.; Paz, J.L.; Márquez, E. Predicting the Adsorption of Amoxicillin and Ibuprofen on Chitosan and Graphene Oxide Materials: A Density Functional Theory Study. Polymers 2021, 13, 1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, B.; Kumar, R.; Kumar, R.; Chaudhuri, S.; Pramanik, P. Electrical behaviour of chitosan-silver nanocomposite in presence of water vapour. J. Water Environ. Nanotechnol. 2017, 2, 71–79. [Google Scholar]
- Dutta, J. A facile approach for the determination of degree of deacetylation of chitosan using acid-base titration. Heliyon 2022, 8, e09924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zhao, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, T. Review on preparation and adsorption properties of chitosan and chitosan composites. Polym. Bull. 2022, 79, 2633–2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Jin, J.; Liu, Z.; Liang, X.; Shang, C. Adsorption of acid dyes from aqueous solutions by the ethylenediamine-modified magnetic chitosan nanoparticles. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 185, 1045–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dandil, S.; Sahbaz, D.A.; Acikgoz, C. Adsorption of Cu (II) ions onto crosslinked chitosan/Waste Active Sludge Char (WASC) beads: Kinetic, equilibrium, and thermodynamic study. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 136, 668–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marotta, A.; Luzzi, E.; De Luna, M.S.; Aprea, P.; Ambrogi, V.; Filippone, G. Chitosan/zeolite composite aerogels for a fast and effective removal of both anionic and cationic dyes from water. Polymers 2021, 13, 1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehaghi, S.M.; Rahmanifar, B.; Moradi, A.M.; Azar, P.A. Removal of permethrin pesticide from water by chitosan–zinc oxide nanoparticles composite as an adsorbent. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2014, 18, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdeen, Z.; Mohammad, S.G. Study of the Adsorption Efficiency of an Eco-Friendly Carbohydrate Polymer for Contaminated Aqueous Solution by Organophosphorus Pesticide. Open J. Org. Polym. Mater. 2014, 4, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rissouli, L.; Benicha, M.; Chafik, T.; Chabbi, M. Decontamination of water polluted with pesticide using biopolymers: Adsorption of glyphosate by chitin and chitosan. J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 2017, 8, 4544–4549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, A.I.; Hosny, M.; Eltaweil, A.S.; Omar, S.; Elgarahy, A.M.; Farghali, M.; Yap, P.-S.; Wu, Y.-S.; Nagandran, S.; Batumalaie, K.; et al. Microplastic sources, formation, toxicity and remediation: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2023, 21, 2129–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wen, K.; Wang, X.; Huang, L.; Yang, Z.; Zheng, G.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, J. Enhanced flotation removal of polystyrene nanoplastics by chitosan modification: Performance and mechanism. Sci. Total. Environ. 2024, 946, 174254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risch, P.; Adlhart, C. A Chitosan Nanofiber Sponge for Oyster-Inspired Filtration of Microplastics. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2021, 3, 4685–4694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solano, M.A.; Galan, J.; Vallejo, W.; Arana, V.A.; Grande-Tovar, C.D. Chitosan Beads Incorporated with Graphene Oxide/Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles for Removing an Anionic Dye. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 9439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, M.; Rachna; Shanker, U. Metal oxide-chitosan based nanocomposites for efficient degradation of carcinogenic PAHs. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisticò, R.; Flavia Franzoso, F.; Cesano, F.; Scarano, D.; Magnacca, G.; Parolo, M.E.; Carlos, L. Chitosan-derived iron oxide systems for magnetically guided and efficient water purification processes from polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 793–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, M.; Lindeque, P.; Halsband, C.; Galloway, T.S. Microplastics as Contaminants in the Marine Environment: A Review. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 2588–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, S.L.; Thompson, R.C.; Galloway, T.S. The Physical Impacts of Microplastics on Marine Organisms: A Review. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 178, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi Kumar, M.N.V. A Review of Chitin and Chitosan Applications. React. Funct. Polym. 2000, 46, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Manhel, A.J.; Al-Hilphy AR, S.; Niamah, A.K. Extraction of chitosan, characterization and its use for water purification. J. Saudi Soc. Agric. Sci. 2018, 17, 186–190. [Google Scholar]
- Jayakumar, R.; Prabaharan, M.; Nair, S.V.; Tamura, H. Novel Chitin and Chitosan Nanofibers in Biomedical Applications. Biotechnol. Adv. 2010, 28, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabea, E.I.; Badawy, M.E.-T.; Stevens, C.V.; Smagghe, G.; Steurbaut, W. Chitosan as Antimicrobial Agent: Applications and Mode of Action. Biomacromolecules 2003, 4, 1457–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsabee, M.Z.; Abdou, E.S. Chitosan Based Edible Films and Coatings: A Review. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2013, l33, 1819–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, M.; Chen, X.G.; Xing, K.; Park, H.J. Antimicrobial Properties of Chitosan and Mode of Action: A State-of-the-Art Review. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2010, 144, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islem, Y.; Rinaudo, M. Chitin and chitosan preparation from marine sources. Structure, properties and applications. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 1133–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atangana, E. Development of Modified Biopolymer Adsorbents from Natural Polysaccharides For Renewal of Abattoir Wastewater. Ph.D. Thesis, Central University of Technology, Free State, Bloemfontein, South Africa, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Victor, O.; Kingsley Chukwuemeka, P.-I.; Eucharia Oluchi, N. Heavy Metals Contents and Health Risk Assessment of Classroom Corner Dusts in Selected Public Primary Schools in Rivers State, Nigeria. J. Environ. Pollut. Hum. Health 2018, 6, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piekarska, K.; Sikora, M.; Owczarek, M.; Jóźwik-Pruska, J.; Wiśniewska-Wrona, M. Chitin and chitosan as polymers of the future—Obtaining, modification, life cycle assessment and main directions of application. Polymers 2023, 15, 793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grifoll, V.; Bravo, P.; Pérez, M.N.; Pérez-Clavijo, M.; García-Castrillo, M.; Larrañaga, A.; Lizundia, E. Environmental Sustainability and Physicochemical Property Screening of Chitin and Chitin-Glucan from 22 Fungal Species. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 7869–7881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Tang, J.; Cropotova, J.; Sun, D.-W.; Tiwari, B.K. Green Technologies for Bio-refinery in Marine Crustacean Shell Valorisation from Chitin Perspective. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 150, 104580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iñiguez-Moreno, M.; Santiesteban-Romero, B.; Melchor-Martínez, E.M.; Parra-Saldívar, R.; González-González, R.B. Valorization of fishery industry waste: Chitosan extraction and its application in the industry. MethodsX 2024, 13, 102892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatami, N.; Guerrero, P.; Martín, P.; Quintela, E.; Ramos, V.; Saa, L.; Cortajarena, A.L.; De La Caba, K.; Camarero-Espinosa, S.; Abarrategi, A. Valorization of biological waste from insect-based food industry: Assessment of chitin and chitosan potential. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 324, 121529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Wang, X.; Sun, S.; Xie, L.; Dang, X. Extraction of chitin from flammulina velutipes waste: A low-concentration acid pretreatment and aspergillus Niger fermentation approach. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 273, 133224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoun, R.B.; Trabelsi, N.; Abdallah, M.; Mourtzinos, I.; Mhamdi, R. Towards a Greener Future: Exploring the Challenges of extraction of Chitin and Chitosan as Bioactive Polysaccharides. Mater. Today Commun. 2024, 39, 108761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.-Q.; Yu, T.-H.; Chen, S.-C.; Zhang, Z.-Q.; Guo, Z.-K.; Huang, G.-X.; Xiao, J.-H.; Huang, D.-W. Physical and chemical characterization of chitin and chitosan extracted under different treatments from black soldier fly. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 279, 135228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, C.; Antelo, L.T.; Franco-Uría, A.; Alonso, A.A.; Pérez-Martín, R. Chitin production from crustacean biomass: Sustainability assessment of chemical and enzymatic processes. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 4140–4151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iroegbu, A.O.C.; Ray, S.S. Chitin Nanomaterials as Multifunctional Systems in Advanced Applications–Progress and Challenges toward Sustainability. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2023, 308, 2300053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Ma, P.; Wei, C.-I.; Wang, Q. Chitin and chitosan: Pioneering sustainable substrates for next-generation soilless vertical farming. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 150, 104599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrezueta, S. Propuesta de Un Plan de Negocio Para Produciry Comercializar Quitina y Quitosano Como Materia PrimaBiodegradable. Bachelor Thesis, University of Guayaquil, Guayaquil, Ecuador, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Andrade, P. Estudio de Viabilidad de Ecportació n de DesechosProcesados de Camaron Generados Por Las Mayores ExportadorasEcuatorianas Hacia China. Engineer in Sciences. Business Thesis, Universidad de Especialidades Espiritu Santo, Guayaquil, Ecuador, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Chavez, D.; Lopez, M. Factibilidad Té cnica Para ElAprovechamiento Integral Del Camaró n de La Especia PenaeusVannamei. Bachelor Thesis, ESPOL, Hauts-de-France, France, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Bajaj, M.; Freiberg, A.; Winter, J.; Xu, Y.; Gallert, C. Pilot-ScaleChitin Extraction from Shrimp Shell Waste by Deproteination and Decalcification with Bacterial Enrichment Cultures. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 9835–9846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, J. Estudio de Viabilidad de Una Planta de Producció nde Quitosano. Master’s Thesis, E.T.S.I. Industriales (UPM), Madrid, Spain, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez-Ríos, D.; Barrera-Zapata, R.; Ríos-Estepa, R. Comparison of Process Technologies for Chitosan Production from ShrimpShell Waste: A Techno-Economic Approach Using Aspen Plus®. Food Bioprod. Process. 2017, 103, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turton, R. CapCost; Prentice Hall Publishing: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, Y.L.; Tan, J.H.; Lim, S.; Chong, W.C. A State-of-the-Art Review on Biowaste Derived Chitosan Biomaterials for Biosorption of Organic Dyes: Parameter Studies, Kinetics, Isotherms and Thermodynamics. Polymers 2021, 13, 3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskar, A.V.; Bolan, N.; Hoang, S.A.; Sooriyakumar, P.; Kumar, M.; Singh, L.; Jasemizad, T.; Padhye, L.P.; Singh, G.; Vinu, A.; et al. Recovery, regeneration and sustainable management of spent adsorbents from wastewater treatment streams: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 822, 153555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulrasool, M.M.; Ruaa, K.M.; Mays, A.D.; ALsailawi, H.A.; Mudhafae, M.; Bashi, A.M. Regeneration of chitosan-based adsorbents used in heavy metal adsorption. J. Life Sci. 2021, 15, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcalde-Garcia, F.; Prasher, S.; Kaliaguine, S.; Tavares, J.R.; Dumont, M. Desorption Strategies and Reusability of Biopolymeric Adsorbents and Semisynthetic Derivatives in Hydrogel and Hydrogel Composites Used in Adsorption Processes. ACS Eng. Au 2023, 3, 443–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Li, L.; Iqbal, J.; Yang, Z.; Du, Y. Preparation of magnetic chitosan corn straw biochar ant its application in adsorption of amaranth dye in aqueous solution. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 199, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gul, K.; Sohni, S.; Waqar, M.; Ahmad, F.; Norulaini, N.A.N.; Mohd Omar, A.K. Functionalization of magnetic chitosan with graphene oxide for removal of cationic and anionic dyes from aqueous solution. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 152, 520–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, K.T.; Wong, V.L.; Lim, S.S. Bio-sorptive Removal of Methyl Orange by Micro- Grooved Chitosan (GCS) Beads: Optimization of Process Variables Using Taguchi L9 Orthogonal Array. J. Polym. Environ. 2020, 29, 271–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakili, M.; Mojiri, A.; Zwain, H.M. Effect of beading parameters on cross-linked chitosan 618 adsorptive properties. React Funct. Polym. 2019, 144, 104354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirajudheen, P.; Karthikeyan, P.; Vigneshwaran, S.; Nikitha, M.; Hassan, C.A.; Meenakshi, S. Ce(III) networked chitosan/β-cyclodextrin beads for the selective removal of toxic dye molecules: Adsorption performance and mechanism. Carbohydr. Polym. Technol. Appl. 2020, 1, 100018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, S.; Schwarz, D.; Ohmann, W.; Neuber, S. Adsorption and desorption studies on reusing chitosan as an efficient adsorbent. In Proceedings of the 3rd World Congress on Civil, Structural, and Environmental Engineering (CSEE’18), Budapest, Hungary, 8–10 April 2018; pp. AWSPT 128-1–AWSPT 128-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, D.; Molla, T.H.; Bashar, A.; Islam, S.; Ahsan, S. Chitosan-based nano-sorbents:synthesis, surface modification, characterisation and application in Cd (II), Co (II), Cu (II) and Pb (II) ions removal from wastewater. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 6050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parlayici, S.; Aras, A. Synthesis of a novel green biopolymer-based composites beads for removal of methylene blue from aquatic medium: Isotherm, thermodynamic and kinetic investigation. Polym. Bull. 2024, 81, 6603–6640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilmioglu, N.; Yumat, E. Removal of Humic Acid from Water by Adsorption Using Chitosan and Metal Organic Framework ZIF 8 Loaded Chitosan Adsorbents. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2024, 235, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benettayeb, A.; Ghosh, S.; Usman, M.; Seihoub, F.Z.; Sohoo, I.; Chia, C.H.; Sillanpää, M. Some Well-Known Alginate and Chitosan Modifications Used in Adsorption: A Review. Water 2022, 14, 1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rout, D.R.; Jena, H.M. Synthesis of graphene oxide-modified porous chitosan cross-linked polyaniline composite for static and dynamic removal of Cr(VI). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 30, 22992–23011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.-R.; Sculley, J.; Zhou, H.-C. Metal–Organic Frameworks for Separations. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 869–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, T.; Chen, H.; Luo, Y.; Li, H.; Shao, X.; Zheng, Q.; Tu, D.; Yan, B.; Dai, J.; Bai, L.; et al. Preparation of β-cyclodextrin-reduced graphene oxide aerogel and its application for adsorption of herbicides. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 468, 143109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboughaly, M.; Babaei-Ghazvini, A.; Dhar, P.; Patel, R.; Acharya, B. Enhancing the Potential of Polymer Composites Using Biochar as a Filler: A Review. Polymers 2023, 15, 3981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, C.; Zhang, J.; Liu, J.; Liu, B.; Chen, G. Preparation and application of magnetic biochar in water treatment: A critical review. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 711, 134847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Cai, Y.; Yu, J.; Huang, J. Development and optimization of a polysilicon-aluminum alkali mineral-enhanced biochar composite for effective heavy metal removal in acidic environments. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 460, 142568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanush Raj, A.; Ahammed, M.M. Nano-zerovalent iron for water and wastewater treatment. In Nanomaterials in Environmental Analysis; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024; pp. 505–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashtbari, Y.; Sher, F.; Afshin, S.; Hamzezadeh, A.; Ahmadi, S.; Azhar, O.; Rastegar, A.; Ghosh, S.; Poureshgh, Y. Green synthesis of zero-valent iron nanoparticles and loading effect on activated carbon for furfural adsorption. Chemosphere 2022, 287, 132114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.N.; You, S.-J.; Hosseini-Bandegharaei, A.; Chao, H.-P. Mistakes and inconsistencies regarding adsorption of contaminants from aqueous solutions: A critical review. Water Res. 2017, 120, 88–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, T.-T.; Yap, P.-S.; Srinivasan, M.; Fane, A.G. TiO2/AC Composites for Synergistic Adsorption-Photocatalysis Processes: Present Challenges and Further Developments for Water Treatment and Reclamation. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 41, 1173–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes-Felipe, C.; Veloso-Fernández, A.; Vilas-Vilela, J.L.; Ruiz-Rubio, L. Hybrid Organic–Inorganic Membranes for Photocatalytic Water Remediation. Catalysts 2022, 12, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, K.; Sengupta, A. Recent advances in functionalized porous adsorbents for radioactive waste water decontamination: Current status, research gap and future outlook. Mater. Today Sustain. 2024, 25, 100703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
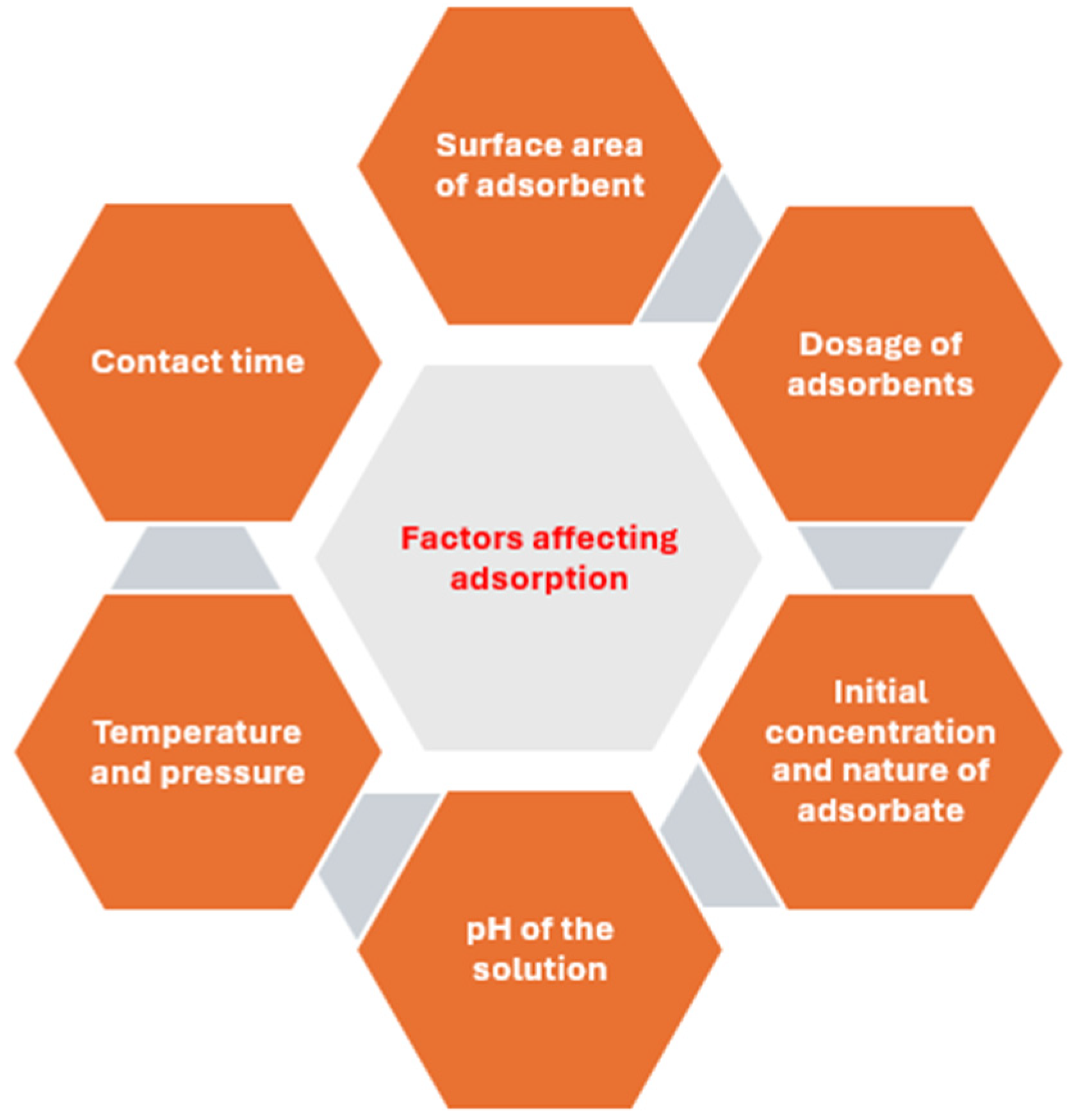



| Physisorption | Chemisorption |
|---|---|
| Van der Waals forces and electrostatic forces, which are weak forces, hold the adsorbent to the adsorbate. | Strong covalent bonds hold the adsorbent to the adsorbate. |
| Comparatively, physisorption is faster than chemisorption. | Comparatively, it is slower than physisorption. |
| Usually involve multilayers on the surface of the adsorbents. | Usually involve a monolayer on the surface of the adsorbents. |
| It is rapid at a low temperature and decreases with increasing temperature. | It increases to a point and then drops at a specific point. |
| Accompanied with a reduction in entropy and free energy than chemisorption. | There is a reduction in entropy and free energy, but unlike physisorption. |
| It is easy to reverse at the critical temperature of the adsorbates or at a temperature below their critical temperature. | It can only be reversed at a very high temperature. It cannot be reversed at a temperature below the critical temperature. |
| Physisorption does not require activation energy to occur. | It requires activation energy to occur. |
| The electronic structure of the adsorbate is unaffected. | There is alteration of the electronic structure of the adsorbate due to the formation of bonds. |
| Adsorbent | Adsorbate | Temperature | Adsorption Time | pH | Maximum Adsorption Capacity | Best Fitted Kinetic Model | R2 Value | Best Fitted Isotherm Model | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chitosan carbon nanotubes (CCNTs) | Amoxicillin and ciprofloxacin | - | - | - | 28.885 mg.g−1 for amoxicillin; 40.631 mg.g−1 for ciprofloxacin | PFO | ≥0.903 | Langmuir | [46] |
| Chitosan biopolymer | Difenoconazole pesticide | 40 OC | 60 min | 5.0 | 23.77 mg/g | PSO | 0.6965 | Langmuir | [47] |
| Chitosan beads | Amoxicillin | - | - | 6.5 | 8.71 ± 0.6 mg/g | Simplified kinetic model | - | Langmuir | [48] |
| Chitosan@Polyacrylamide coated by ZIF-8 | Amoxicillin and cefixime | 25 OC | 30 min | 4.0 | 910 mg/g for amoxicillin and 588 mg/g for cefixime | PFO PSO And intraparticle diffusion | 0.97 for amoxicillin; 0.99 for cefixime | Langmuir | [49] |
| Chitosan/poly (acrylic amide-co-acrylic acid) (CH/(AM-co-AA) | Amoxicillin | - | - | 1.2 | - | PSO | - | Freundlich | [50] |
| Polypyrrole-chitosan magnetic nanocomposites | Carbamazepine | - | - | - | 121.95 mg/g | PSO | 0.9901 | Langmuir | [51] |
| Copper chitosan nanocomposites | Melathion (pesticide) | 2.0 | 322.6 mg/g | PSO | Both Langmuir and Freundlich | [52,53] | |||
| 2-hydroxy-1-naphthaldehyde | Pentachlorophenol (pesticide) | 292–313 K | 4.7–8.0 | - | PSO | 1.0 | - | [53] |
| Antibiotic | Adsorption Rate (g mg−1 min−1) | Mass of Adsorbate/Mass of BC Adsorbent at Equilibrium |
|---|---|---|
| Amoxicillin | 6.056 × 10−3 | 53.569 mg g−1 |
| Ampicillin | 6.886 × 10−3 | 55.869 mg g−1 |
| Doripenem | 6.709 × 10−3 | 59.606 mg g−1 |
| Nanocomposites | PAHs | % Degradation |
|---|---|---|
| ZnFe2O4-CS | Anthracene Phenanthrene | 95 92 |
| CuO-Fe2O3-CS | Anthracene Phenanthrene | 93 90 |
| NiFe2O4-CS | Anthracene Phenanthrene | 90 88 |
| Co2O3-Fe3O4-CS | Anthracene Phenanthrene | 88 85 |
| FeCr2O4-CS | Anthracene Phenanthrene | 83 81 |
| Parameter | Chitin/Chitosan | Activated Carbon | Synthetic Resins |
|---|---|---|---|
| Raw material cost | Low (waste-derived) | Medium-high (energy-intensive) | High (petrochemical-based) |
| Adsorption efficiency | High | High | Medium-high |
| Environmental impact | Minimal (biodegradable) | Moderate (non-renewable) | High (persistent waste) |
| Processing complexity | Moderate | High | High |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Atangana, E.; Ajiboye, T.O.; Mafolasire, A.A.; Ghosh, S.; Hakeem, B. Adsorption of Organic Pollutants from Wastewater Using Chitosan-Based Adsorbents. Polymers 2025, 17, 502. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17040502
Atangana E, Ajiboye TO, Mafolasire AA, Ghosh S, Hakeem B. Adsorption of Organic Pollutants from Wastewater Using Chitosan-Based Adsorbents. Polymers. 2025; 17(4):502. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17040502
Chicago/Turabian StyleAtangana, Ernestine, Timothy Oladiran Ajiboye, Abolaji Abiodun Mafolasire, Soumya Ghosh, and Bello Hakeem. 2025. "Adsorption of Organic Pollutants from Wastewater Using Chitosan-Based Adsorbents" Polymers 17, no. 4: 502. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17040502
APA StyleAtangana, E., Ajiboye, T. O., Mafolasire, A. A., Ghosh, S., & Hakeem, B. (2025). Adsorption of Organic Pollutants from Wastewater Using Chitosan-Based Adsorbents. Polymers, 17(4), 502. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17040502








