Polymers for Osmotic Self-Inflating Expanders in Oral Surgical Procedures: A Comprehensive Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Protocol and Registration
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
2.3. Search
2.4. Screening of Evidence Sources
2.5. Data Charting Process
2.6. Data Items
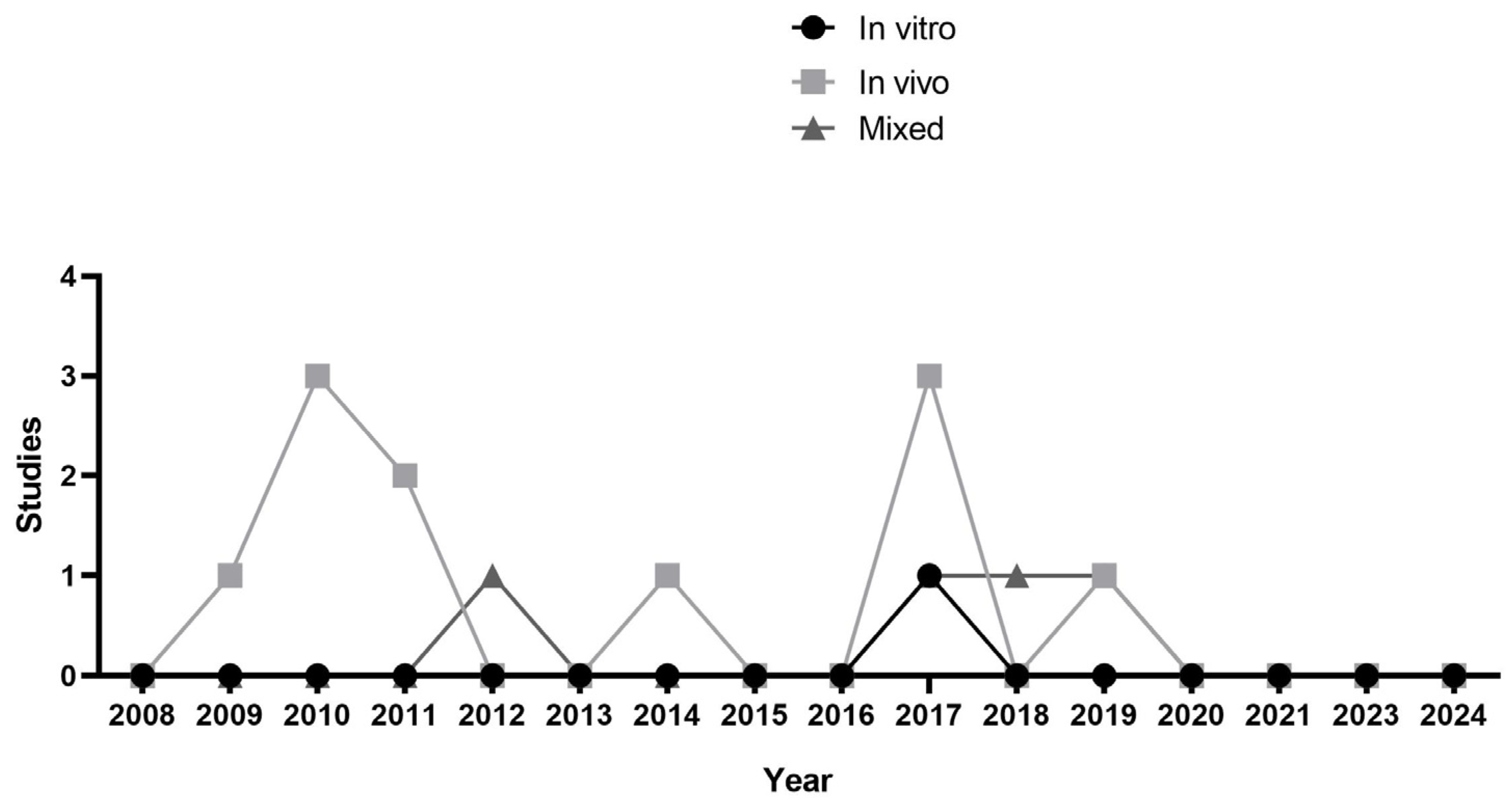
3. Results
3.1. Selection of Evidence Sources
3.2. Characteristics of Evidence Sources
3.2.1. Material Type
3.2.2. Selected Animal Models and Measurement Methods
3.2.3. Evaluation Period for the Expanders
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Araújo, M.G.; Lindhe, J. Dimensional ridge alterations following tooth extraction. An experimental study in the dog. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2005, 32, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cucchi, A.; Vignudelli, E.; Napolitano, A.; Marchetti, C.; Corinaldesi, G. Evaluation of complication rates and vertical bone gain after guided bone regeneration with non-resorbable membranes versus titanium meshes and resorbable membranes. A randomized clinical trial. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2017, 19, 821–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plonka, A.B.; Urban, I.A.; Wang, H.L. Decision Tree for Vertical Ridge Augmentation. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2018, 38, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matichescu, A.; Ardelean, L.C.; Rusu, L.-C.; Craciun, D.; Bratu, E.A.; Babucea, M.; Leretter, M. Advanced Biomaterials and Techniques for Oral Tissue Engineering and Regeneration-A Review. Materials 2020, 13, 5303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inchingolo, F.; Hazballa, D.; Inchingolo, A.D.; Malcangi, G.; Marinelli, G.; Mancini, A.; Maggiore, M.E.; Bordea, I.R.; Scarano, A.; Farronato, M.; et al. Innovative Concepts and Recent Breakthrough for Engineered Graft and Constructs for Bone Regeneration: A Literature Systematic Review. Materials 2022, 15, 1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chackartchi, T.; Romanos, G.E.; Sculean, A. Soft tissue-related complications and management around dental implants. Periodontol. 2000 2019, 81, 124–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz-Sánchez, I.; Sanz-Martín, I.; Ortiz-Vigón, A.; Molina, A.; Sanz, M. Complications in bone-grafting procedures: Classification and management. Periodontol. 2000 2022, 88, 86–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morad, G.; Khojasteh, A. Cortical tenting technique versus onlay layered technique for vertical augmentation of atrophic posterior mandibles: A split-mouth pilot study. Implant Dent. 2013, 22, 566–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windisch, P.; Orban, K.; Salvi, G.E.; Sculean, A.; Molnar, B. Vertical-guided bone regeneration with a titanium-reinforced d-PTFE membrane utilizing a novel split-thickness flap design: A prospective case series. Clin. Oral Investig. 2021, 25, 2969–2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Stavola, L.; Tunkel, J.; Fincato, A.; Fistarol, F. The Vestibular Shifted Flap Design for Vertical Bone Augmentation in the Maxilla: Case Report and Technical Notes. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2021, 41, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, J.; Farré-Guasch, E.; Sándor, G.K.; Gibbs, S.; Jager, D.J.; Forouzanfar, T. Soft Tissue Augmentation Techniques and Materials Used in the Oral Cavity: An Overview. Implant Dent. 2016, 25, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selvaprithiviraj, V.; Vaquette, C.; Ivanovski, S. Hydrogel based soft tissue expanders for orodental reconstruction. Acta Biomater. 2023, 172, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von See, C.; Rücker, M.; Bormann, K.H.; Gellrich, N.C. Using a novel self-inflating hydrogel expander for intraoral gingival tissue expansion prior to bone augmentation. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2010, 48, e5–e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertens, C.; Thiele, O.; Engel, M.; Seeberger, R.; Hoffmann, J.; Freier, K. The use of self-inflating soft tissue expanders prior to bone augmentation of atrophied alveolar ridges. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2015, 17, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hrib, J.; Sirc, J.; Lesny, P.; Hobzova, R.; Duskova-Smrckova, M.; Michalek, J.; Smucler, R. Hydrogel tissue expanders for stomatology. Part I. Methacrylate-based polymers. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2017, 28, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garner, J.; Davidson, D.D.; Barwinska, D.; Eckert, G.J.; Tholpady, S.S.; Park, K.; Barco, C.T. Reshapable hydrogel tissue expander for ridge augmentation: Results of a series of successive insertions at the same intraoral site. J. Periodontol. 2019, 90, 718–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.M.; Ben Amara, H.; Kim, M.K.; Song, J.D.; Koo, K.-T. Oral tissue response to soft tissue expanders prior to bone augmentation. J. Periodontal Implant Sci. 2018, 48, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barwinska, D.; Garner, J.; Davidson, D.D.; Cook, T.G.; Eckert, G.J.; Tholpady, S.S.; March, K.L.; Park, K.; Barco, C.T. Mucosal Perfusion Preservation by a Novel Shapeable Tissue Expander for Oral Reconstruction. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2017, 5, e1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tricco, A.C.; Lillie, E.; Zarin, W.; O’Brien, K.K.; Colquhoun, H.; Levac, D.; Moher, D.; Peters, M.D.; Horsley, T.; Weeks, L.; et al. PRISMA Extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR): Checklist and Explanation. Ann. Intern. Med. 2018, 169, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrahamsson, P.; Isaksson, S.; Gordh, M.; Andersson, G. Periosteal expansion of rabbit mandible with an osmotic self-inflatable expander. Scand. J. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Hand Surg. 2009, 43, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrahamsson, P.; Isaksson, S.; Gordh, M.; Andersson, G. Onlay bone grafting of the mandible after periosteal expansion with an osmotic tissue expander: An experimental study in rabbits. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2010, 21, 1404–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von See, C.; Gellrich, N.; Jachmann, U.; Laschke, M.W.; Bormann, K.; Rücker, M. Bone augmentation after soft-tissue expansion using hydrogel expanders: Effects on microcirculation and osseointegration. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2010, 21, 842–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uijlenbroek, H.J.; Liu, Y.; Wismeijer, D. Gaining Soft Tissue with a Hydrogel Soft Tissue Expander: A Case Report. Eur. J. Dent. 2023, 17, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrahamsson, P.; Isaksson, S.; Andersson, G. Guided bone generation in a rabbit mandible model after periosteal expansion with an osmotic tissue expander. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2011, 22, 1282–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swan, M.C.; Bucknall, D.G.; Czernuszka, J.T.; Pigott, D.W.; Goodacre, T.E.E. Development of a novel anisotropic self-inflating tissue expander: In vivo submucoperiosteal performance in the porcine hard palate. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2012, 129, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaner, D.; Zhao, H.; Terheyden, H.; Friedmann, A. Improvement of microcirculation and wound healing in vertical ridge augmentation after pre-treatment with self-inflating soft tissue expanders—A randomized study in dogs. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2015, 26, 720–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaner, D.; Zhao, H.; Arnold, W.; Terheyden, H.; Friedmann, A. Pre-augmentation soft tissue expansion improves scaffold-based vertical bone regeneration—A randomized study in dogs. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2017, 28, 640–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamadi, M.; Shokrollahi, P.; Houshmand, B.; Joupari, M.D.; Mashhadiabbas, F.; Khademhosseini, A.; Annabi, N. Poly (Ethylene Glycol)-Based Hydrogels as Self-Inflating Tissue Expanders with Tunable Mechanical and Swelling Properties. Macromol. Biosci. 2017, 17, 1600479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hrib, J.; Chylikova Krumbholcova, E.; Duskova-Smrckova, M.; Hobzova, R.; Sirc, J.; Hruby, M.; Michalek, J.; Hodan, J.; Lesny, P.; Smucler, R. Hydrogel Tissue Expanders for Stomatology. Part II. Poly(styrene-maleic anhydride) Hydrogels. Polymers 2019, 11, 1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salim, K.M.A.; Jalil, A.A.; Radzi, Z.; Ismail, S.M.; Czernuszka, J.T.; Rahman, M.T. Inflammatory Responses in Oro-Maxillofacial Region Expanded Using Anisotropic Hydrogel Tissue Expander. Materials 2020, 13, 4436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, S.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Lee, H.; Lim, H.K.; Kim, J.W.; Lee, U.L.; Lee, J.B.; Park, S.H.; Kim, S.J.; Song, J.D.; et al. Soft tissue expander for vertically atrophied alveolar ridges: Prospective, multicenter, randomized controlled trial. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2020, 31, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urban, I.; Montero, E.; Sanz-Sánchez, I.; Palombo, D.; Monje, A.; Tommasato, G.; Chiapasco, M. Minimal invasiveness in vertical ridge augmentation. Periodontol. 2000 2023, 91, 126–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiese, K.G. Osmotically induced tissue expansion with hydrogels: A new dimension in tissue expansion? A preliminary report. J. Craniomaxillofac. Surg. 1993, 21, 309–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- More, N.; Avhad, M.S.; Utekar, S.; More, A.P. Polylactic acid (PLA) membrane—Significance, synthesis, and applications: A review. Polym. Bull. 2022, 80, 1117–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, K.S.; Davis, K.M.; McKinley, T.O.; Anglen, J.O.; Chu, T.-M.G.; Boerckel, J.D.; Kacena, M.A. Evolution of Bone Grafting: Bone Grafts and Tissue Engineering Strategies for Vascularized Bone Regeneration. Clin. Rev. Bone Miner. Metab. 2015, 13, 232–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, R.; Vicent, M.J. Polymer therapeutics-prospects for 21st century: The end of the beginning. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethi, S.; Ray, B.C. Environmental effects on fibre reinforced polymeric composites: Evolving reasons and remarks on interfacial strength and stability. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 217, 43–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.Y.; Mustakim, K.R.; Eo, M.Y.; Kim, S.M. Gingivo-Periosteal Expansion of Edentulous Jaw Crest with An Osmotic Self-Inflatable Expander: A Preclinical in Vivo Study. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2024, 35, 1730–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Li, J.; Lei, X.; Cheng, P.; Song, Y.; Gao, Y.; Hu, J.; Wang, C.; Zhang, S.; Li, D.; et al. 3D-bioprinted functional and biomimetic hydrogel scaffolds incorporated with nanosilicates to promote bone healing in rat calvarial defect model. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2020, 112, 110905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Database | Keywords |
|---|---|
| PubMed/Medline | (((Tissue Expansion) OR (Expansion, Tissue) OR (Expansions, Tissue) OR (Tissue Expansions) OR (Controlled tissue expansion)) AND ((Tissue Expansion Devices) OR (Device, Tissue Expansion) OR (Devices, Tissue Expansion) OR (Tissue Expansion Device) OR (Tissue Expanders) OR (Expanders, Tissue) OR (polyhydroxyethylmethacrylate hydrogel) OR (Spheron 300) OR (Soflens) OR (2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate, N-vinyl pyrrolidone and 4-tertiary butyl-2-hydroxycyclohexyl methacrylate hydrogel) OR (polymacon) OR (Osmotic expanders) OR (Osmotic self-inflating expanders) OR (Self-Inflating Soft Tissue Expanders) OR (Osmotic expanders) OR (Self-filling osmotic tissue expanders))) AND ((Oral Surgical Procedures) OR (Surgical Procedures, Oral) OR (Procedures, Oral Surgical) OR (Surgical Procedure, Oral) OR (Oral Surgical Procedure) OR (Procedure, Oral Surgical) OR (Maxillofacial Procedures) OR (Maxillofacial Procedure) OR (Procedure, Maxillofacial) OR (Procedures, Maxillofacial) OR (Dentistry)) |
| Scopus | (ALL ((“Tissue Expansion”) OR (“Expansion, Tissue”) OR (“Expansions, Tissue”) OR (“Tissue Expansions”) OR (“Controlled tissue expansion”) )) AND (ALL ((“Tissue Expansion Devices”) OR (“Device, Tissue Expansion”) OR (“Devices, Tissue Expansion”) OR (“Tissue Expansion Device”) OR (“Tissue Expanders”) OR (“Expanders, Tissue”) OR (“polyhydroxyethylmethacrylate hydrogel”) OR (spheron 300) OR (soflens) OR (“2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate, N-vinyl pyrrolidone and 4-tertiary butyl-2-hydroxycyclohexyl methacrylate hydrogel”) OR (polymacon) OR (“Osmotic expanders”) OR (“Osmotic self-inflating expanders”) OR (“Self-Inflating Soft Tissue Expanders”) OR (“Osmotic expanders”) OR (“Self-filling osmotic tissue expanders”) )) AND (ALL ((“Oral Surgical Procedures”) OR (“Surgical Procedures, Oral”) OR (“Procedures, Oral Surgical”) OR (“Surgical Procedure, Oral”) OR (“Oral Surgical Procedure”) OR (“Procedure, Oral Surgical”) OR (“Maxillofacial Procedures”) OR (“Maxillofacial Procedure”) OR (“Procedure, Maxillofacial”) OR (“Procedures, Maxillofacial”) OR (dentistry) ) ) |
| Web of Science | (((Tissue Expansion) OR (Expansion, Tissue) OR (Expansions, Tissue) OR (Tissue Expansions) OR (Controlled tissue expansion)) AND ((Tissue Expansion Devices) OR (Device, Tissue Expansion) OR (Devices, Tissue Expansion) OR (Tissue Expansion Device) OR (Tissue Expanders) OR (Expanders, Tissue) OR (polyhydroxyethylmethacrylate hydrogel) OR (Spheron 300) OR (Soflens) OR (2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate, N-vinyl pyrrolidone and 4-tertiary butyl-2-hydroxycyclohexyl methacrylate hydrogel) OR (polymacon) OR (Osmotic expanders) OR (Osmotic self-inflating expanders) OR (Self-Inflating Soft Tissue Expanders) OR (Osmotic expanders) OR (Self-filling osmotic tissue expanders))) AND ((Oral Surgical Procedures) OR (Surgical Procedures, Oral) OR (Procedures, Oral Surgical) OR (Surgical Procedure, Oral) OR (Oral Surgical Procedure) OR (Procedure, Oral Surgical) OR (Maxillofacial Procedures) OR (Maxillofacial Procedure) OR (Procedure, Maxillofacial) OR (Procedures, Maxillofacial) OR (Dentistry)) |
| EMBASE | ((“Tissue Expansion”) OR (“Expansion, Tissue”) OR (“Expansions, Tissue”) OR (“Tissue Expansions”) OR (“Controlled tissue expansion”) )) AND (ALL ((“Tissue Expansion Devices”) OR (“Device, Tissue Expansion”) OR (“Devices, Tissue Expansion”) OR (“Tissue Expansion Device”) OR (“Tissue Expanders”) OR (“Expanders, Tissue”) OR (“polyhydroxyethylmethacrylate hydrogel”) OR (spheron 300) OR (soflens) OR (“2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate, N-vinyl pyrrolidone and 4-tertiary butyl-2-hydroxycyclohexyl methacrylate hydrogel”) OR (polymacon) OR (“Osmotic expanders”) OR (“Osmotic self-inflating expanders”) OR (“Self-Inflating Soft Tissue Expanders”) OR (“Osmotic expanders”) OR (“Self-filling osmotic tissue expanders”) )) AND (ALL ((“Oral Surgical Procedures”) OR (“Surgical Procedures, Oral”) OR (“Procedures, Oral Surgical”) OR (“Surgical Procedure, Oral”) OR (“Oral Surgical Procedure”) OR (“Procedure, Oral Surgical”) OR (“Maxillofacial Procedures”) OR (“Maxillofacial Procedure”) OR (“Procedure, Maxillofacial”) OR (“Procedures, Maxillofacial”) OR (dentistry) ) |
| Authors | Year | Journal | Country | Expansion Polymer | Study Type | Sample | n | Control | Inclusion Criteria | Experimental Animals | Expander Use Time | Increased Tissue Volume (mm or mm3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abrahamsson [20] | 2009 | Scandinavian Journal of Plastic and Reconstructive surgery and Hand Surgery | Sweden | Osmed | Animal study | Rabbits | 8 | NR | NR | Rabbits | 1 day | 5.5 mm (5.2–5.8 mm) |
| Von See [13] | 2010 | International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Implants | Germany | Osmed | Animal study | Lewis rats | 48 | Untreated group | NR | Rats | NR | NR |
| Abrahamsson [21] | 2010 | Clinical Oral Implants Research | Sweden | Osmed | Animal study | Rabbits | 13 | NR | Adult female Swedish lop rabbits | Rabbits | 90 days | 7.5 mm × 3 mm |
| Von See [22] | 2010 | Clinical Oral Implants Research | Germany | Osmed | Animal study | Lewis rats | 16 | NR | Isogenic male rats | Rats | 21 days | NR |
| Uijlenbroek [23] | 2011 | Clinical Oral Implants Research | Netherlands | Osmed | Animal study | Goats | 28 | Untreated group | NR | Goats | 40 days | NR |
| Abrahamsson [24] | 2011 | Clinical Oral Implants Research | Sweden | Osmed | Animal study | Rabbits | 11 | NR | Female Swedish lop rabbits | Rabbits | 98 days | 5.6 × 11 × 6 mm |
| Swan [25] Kaner [26] | 2012 | Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery | United Kingdom | Isotropic poly(methyl methacrylate-co-vinylpyrrolidone) hydrogels | Mixed study/Animal study | Pigs | 6 | Split-mouth design—untreated | Pigs | Pigs | 4 days | Hydrogel X2 540 mm3 Hydrogel X6 900 mm3 |
| Kaner [27] | 2015 | Clinical Oral Implants Research | Germany | Osmed | Animal study | Dogs | 10 | Granular biphasic calcium phosphate covered with polyethylene glycol membrane | Male beagle dogs | Dogs | 14 days | NR |
| Barwinska [18] Jamadi [28] | 2017 | Clinical Oral Implants Research | Germany | Osmed | Animal study | Dogs | 10 | Split-mouth design—untreated | Jaws of healthy beagle dogs | Dogs | 35 days | Experimental: 141 mm3 Control: 130 mm3 |
| Yoo [17] | 2017 | Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery–Global Open | United States | Restiex HTE | Animal study | Dogs | 9 | Nearby mucous gingiva not surgically treated | NR | Dogs | 42 days | 21.5 mm3 |
| Garner [16] | 2017 | Macromolecular Bioscience | United States | Poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) | Animal study | Wistar rats | 6 | NR | NR | Rats | 1461 days | NR |
| Hirb [29] | 2018 | Journal of Periodontal & Implant Science | Korea | Osstem | Mixed study/Animal study | Dogs | NR | NR | NR | Dogs | NR | NR |
| Ali Salim [30] Abrahamsson [20] | 2019 | Journal of Periodontology | United States | Cross-linked polymers of poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) and poly(lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA) connected by acrylate linkages | Animal study | Beagle dogs | 9 | NR | Beagle dogs | Dogs | 42 days | Experimental: 8.13 mm Control: 6.44 mm |
| Von See [13] | 2019 | Polymers | Czech Republic | Poly(styrene-alt-maleic anhydride) covalently cross-linked with p-divinylbenzene | Mixed study/Animal study | Rats | 9 | NR | NR | Rats | 29 days | 12.7 mm3 |
| Abrahamsson [21] | 2020 | Materials | Malaysia | Methyl methacrylate-N-vinylpyrrolidone copolymer (MMA-NVP) | Animal study | Dawley rats | 7 | Untreated group | Rats | Rats | 28 days | NR |
| Authors | Year | Journal | Country | Expansion Polymers | Study Type | Control | Expander Use Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Swan [25] | 2012 | Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery | United Kingdom | Poly(methyl methacrylate-co-vinylpyrrolidone) | Mixed/In vitro | Silicone and non-silicone cutlery | X2: 5 days X6: 22 days |
| Hrib [15] | 2017 | Journal of Materials ScienceMaterials in Medicine | Czech Republic | Poly(methyl methacrylate-co-vinylpyrrolidone) | In vitro | Polymer formulated with an anesthetic | 40 days |
| Jamadi [28] | 2017 | Macromolecular Bioscience | United States | Poly(ethylene glycol) diacrylate (PEGDA) | Mixed/In vitro | NR | 7 days |
| Yoo [17] | 2018 | Journal of Periodontal & Implant Science | Korea | Osstem | Mixed/In vitro | NR | NR |
| Hrib [29] | 2019 | Polymers | Czech Republic | Poly(styrene-alt-maleic anhydride) | Mixed/In vitro | NR | 30 days |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hernandez, A.E.; Bahr, N.L.; Blois, M.C.; Cuevas-Suarez, C.E.; Piva, E.; Santos, M.B.F.d.; Peña, C.L.D.; Lund, R.G. Polymers for Osmotic Self-Inflating Expanders in Oral Surgical Procedures: A Comprehensive Review. Polymers 2025, 17, 441. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17040441
Hernandez AE, Bahr NL, Blois MC, Cuevas-Suarez CE, Piva E, Santos MBFd, Peña CLD, Lund RG. Polymers for Osmotic Self-Inflating Expanders in Oral Surgical Procedures: A Comprehensive Review. Polymers. 2025; 17(4):441. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17040441
Chicago/Turabian StyleHernandez, Alejandro Elizalde, Natália Link Bahr, Matheus Coelho Blois, Carlos Enrique Cuevas-Suarez, Evandro Piva, Mateus Bertolini Fernandes dos Santos, Carla Lucia David Peña, and Rafael Guerra Lund. 2025. "Polymers for Osmotic Self-Inflating Expanders in Oral Surgical Procedures: A Comprehensive Review" Polymers 17, no. 4: 441. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17040441
APA StyleHernandez, A. E., Bahr, N. L., Blois, M. C., Cuevas-Suarez, C. E., Piva, E., Santos, M. B. F. d., Peña, C. L. D., & Lund, R. G. (2025). Polymers for Osmotic Self-Inflating Expanders in Oral Surgical Procedures: A Comprehensive Review. Polymers, 17(4), 441. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17040441









