High-Efficiency and Low-Resistance Melt-Blown/Electrospun PLA Composites for Air Filtration
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
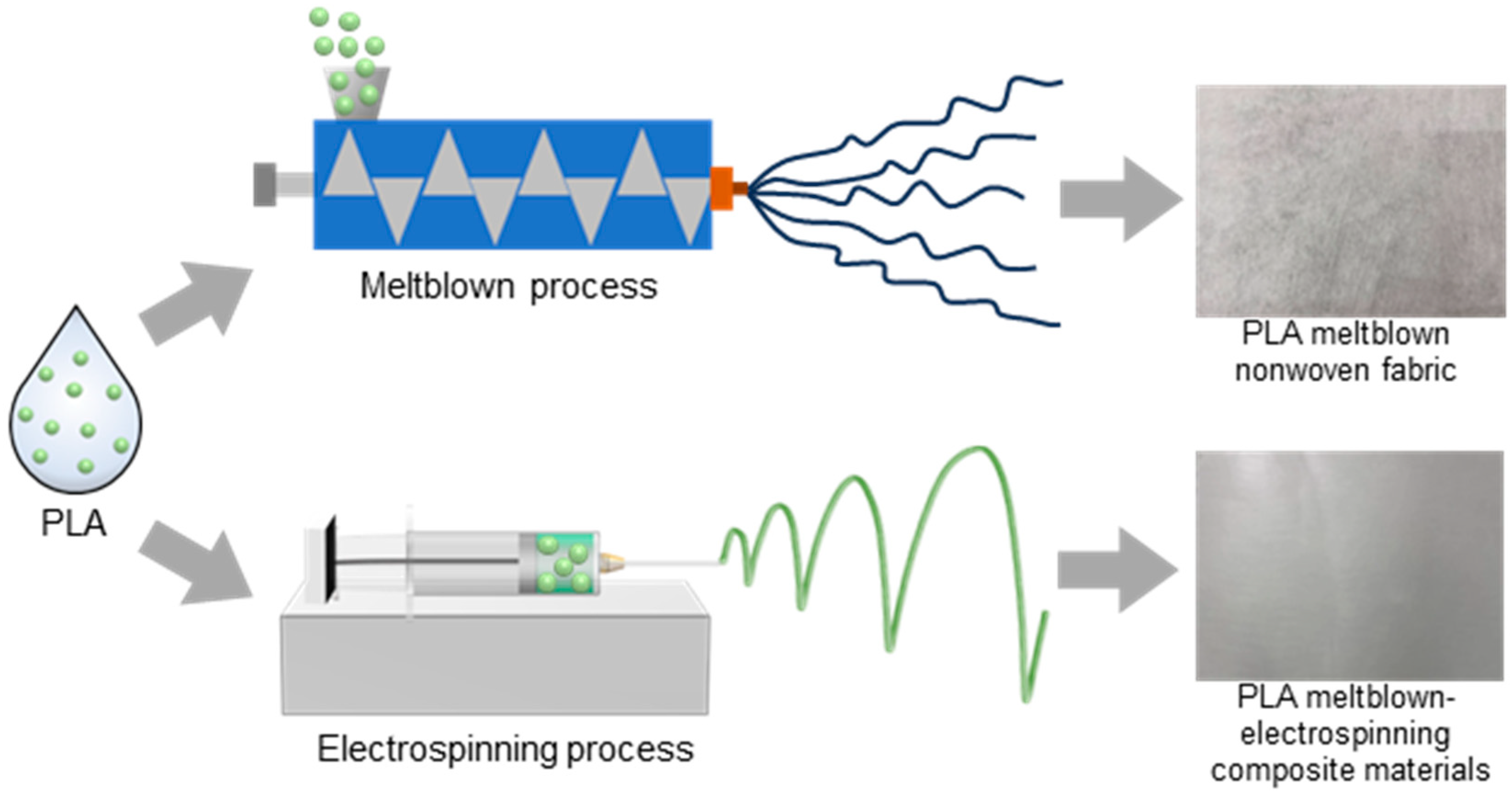
2.2. Preparation Procedure of the Polylactic Acid Melt-Blown Nonwoven Fabric
2.3. Preparation Procedure of the Polylactic Acid Melt-Blown/Electrospun Composites
2.4. Characterization of the Filtration Efficiency and Resistance of PLA Melt-Blown Nonwoven Fabric
2.5. Pore Size Characterization of the Polylactic Acid Melt-Blown Nonwoven Materials
2.6. Characterizations
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Morphology and Structure of the PLA Nonwoven Fabric
3.2. Morphology and Structure of the Polylactic Acid Melt-Blown/Electrospun Composites
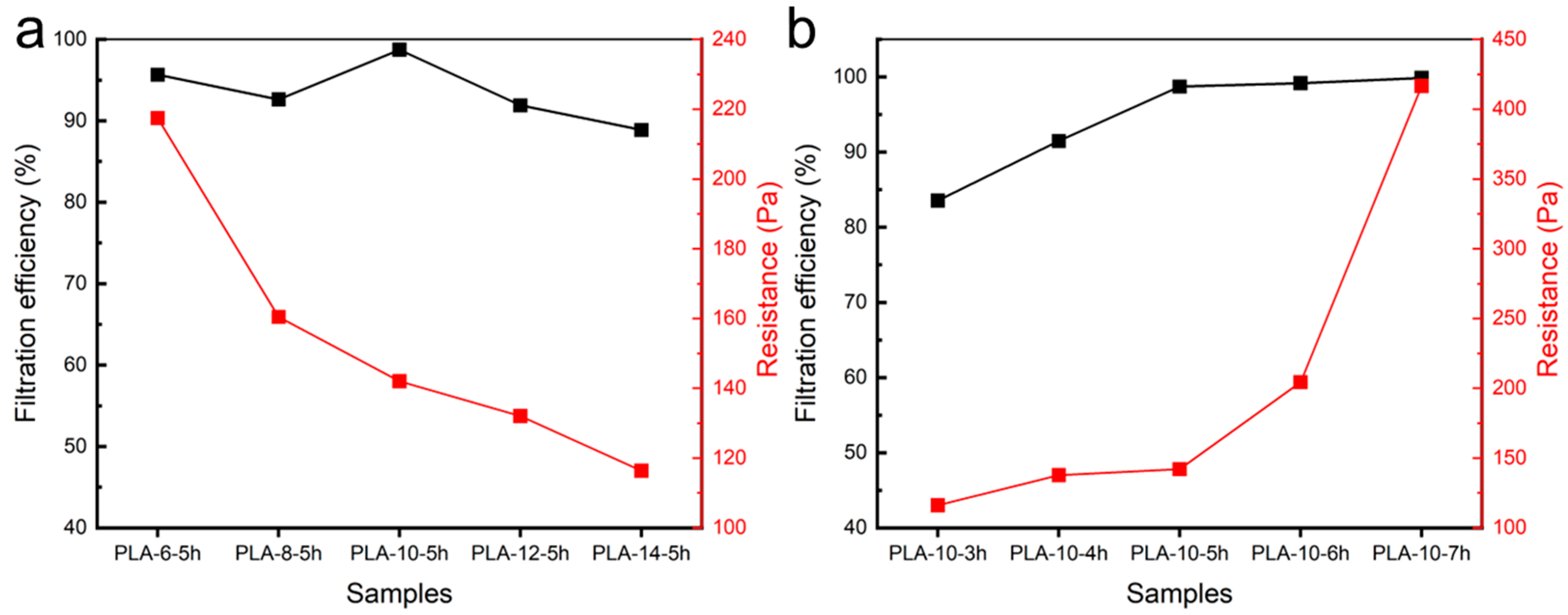
3.3. Filtration Efficiency of the Polylactic Acid Melt-Blown/Electrospun Composite Materials
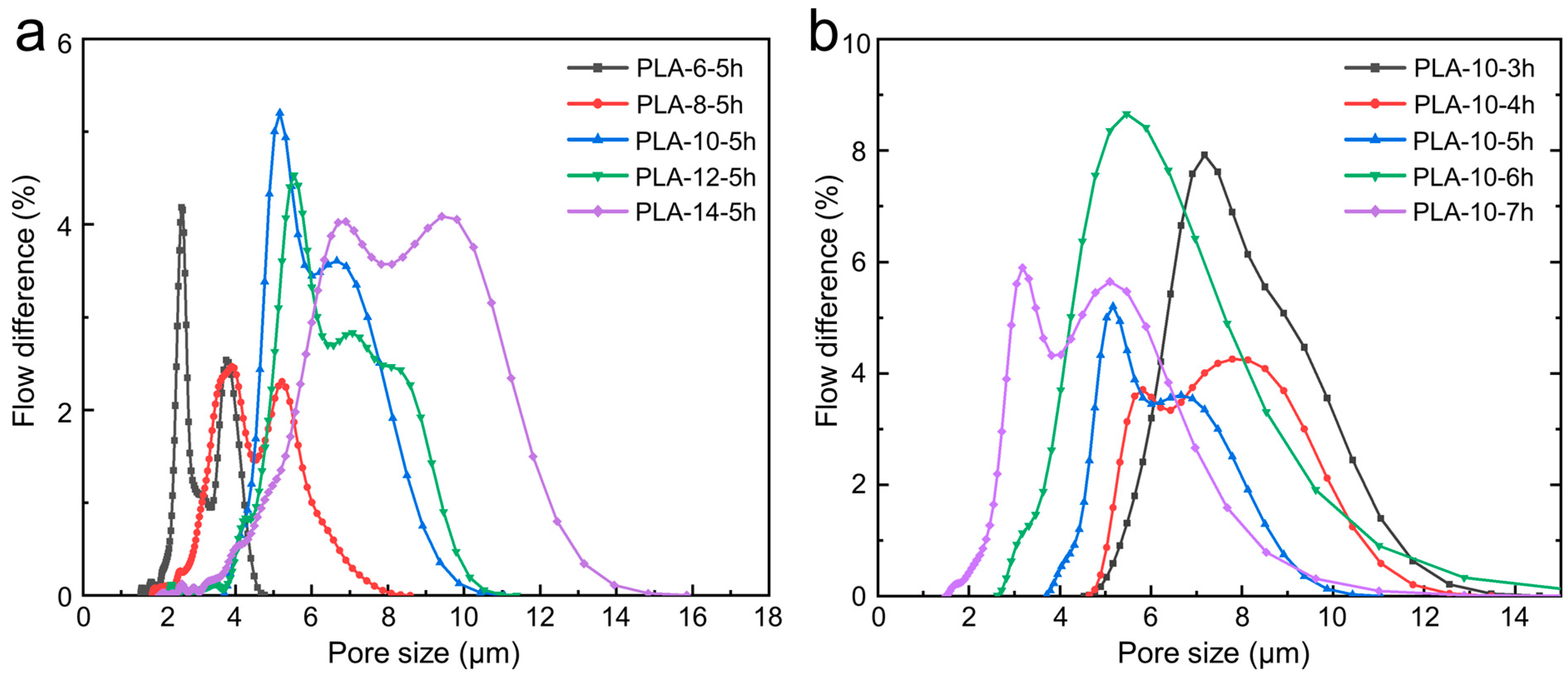
3.4. Pore Characteristic of the Polylactic Acid Melt-Blown/Electrospun Composites
3.5. Wettability of the Polylactic Acid Melt-Blown/Electrospun Composites
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, Z.; Hou, T.; Xu, J.; Wang, Y.; Ye, H.; Yang, B. Bio-based and bio-degradable nanofiber materials: A sustainable platform for energy, environmental, and biomedical applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 491, 152105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gough, C.R.; Callaway, K.; Spencer, E.; Leisy, K.; Jiang, G.; Yang, S.; Hu, X. Biopolymer-Based Filtration Materials. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 11804–11812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, D.; Zhu, M.; Jiang, Z.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Xiong, R.; Huang, C. Green Electrospun Nanofibers and Their Application in Air Filtration. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2018, 303, 1800336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.Z.; Hoque, M.E.; Alam, M.R.; Rouf, M.A.; Khan, S.I.; Xu, H.; Ramakrishna, S. Face Masks to Combat Coronavirus (COVID-19)—Processing, Roles, Requirements, Efficacy, Risk and Sustainability. Polymers 2022, 14, 1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borah, A.R.; Hazarika, P.; Duarah, R.; Goswami, R.; Hazarika, S. Biodegradable Electrospun Membranes for Sustainable Industrial Applications. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 11129–11147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.L.; Chung, J.W.Y.; Yan, V.C.M.; Wong, T.K.S. Polylactic Acid-Based Biomaterials in Wound Healing: A Systematic Review. Adv. Ski. Wound Care 2023, 36, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shekhar, N.; Mondal, A. Synthesis, properties, environmental degradation, processing, and applications of Polylactic Acid (PLA): An overview. Polym. Bull. 2024, 81, 11421–11457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divakara Shetty, S.; Shetty, N. Investigation of mechanical properties and applications of polylactic acids—A review. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 112002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kian, L.K.; Saba, N.; Jawaid, M.; Sultan, M.T.H. A review on processing techniques of bast fibers nanocellulose and its polylactic acid (PLA) nanocomposites. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 121, 1314–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolić, N.; Olmos, D.; González-Benito, J. Key Advances in Solution Blow Spinning of Polylactic-Acid-Based Materials: A Prospective Study on Uses and Future Applications. Polymers 2024, 16, 3044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaseem, M.; Ur Rehman, Z.; Hossain, S.; Singh, A.K.; Dikici, B. A Review on Synthesis, Properties, and Applications of Polylactic Acid/Silica Composites. Polymers 2021, 13, 3036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, T.; Lin, N. Melt Compounding of Poly(lactic acid)-Based Composites: Blending Strategies, Process Conditions, and Mechanical Properties. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2024, 45, 2400380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyas, R.A.; Sapuan, S.M.; Harussani, M.M.; Hakimi, M.Y.A.Y.; Haziq, M.Z.M.; Atikah, M.S.N.; Asyraf, M.R.M.; Ishak, M.R.; Razman, M.R.; Nurazzi, N.M.; et al. Polylactic Acid (PLA) Biocomposite: Processing, Additive Manufacturing and Advanced Applications. Polymers 2021, 13, 1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Huang, L.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Lu, X.; Wei, Z.; Mo, Q.; Zhang, S.; Sheng, Y.; Huang, C.; et al. Research progress in polylactic acid processing for 3D printing. J. Manuf. Process. 2024, 112, 161–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cojocaru, V.; Frunzaverde, D.; Miclosina, C.-O.; Marginean, G. The Influence of the Process Parameters on the Mechanical Properties of PLA Specimens Produced by Fused Filament Fabrication—A Review. Polymers 2022, 14, 886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.-H.; Hu, T.-G.; Wang, H.; Zong, M.-H.; Wu, H.; Wen, P. Electrospinning of PLA Nanofibers: Recent Advances and Its Potential Application for Food Packaging. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 8207–8221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajeshkumar, G.; Arvindh Seshadri, S.; Devnani, G.L.; Sanjay, M.R.; Siengchin, S.; Prakash Maran, J.; Al-Dhabi, N.A.; Karuppiah, P.; Mariadhas, V.A.; Sivarajasekar, N.; et al. Environment friendly, renewable and sustainable poly lactic acid (PLA) based natural fiber reinforced composites—A comprehensive review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 310, 127483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Padzil, F.N.B.M.; Lee, S.H.; Ainun, Z.M.A.A.; Abdullah, L.C. Potential for Natural Fiber Reinforcement in PLA Polymer Filaments for Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) Additive Manufacturing: A Review. Polymers 2021, 13, 1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmadifar, M.; Benfriha, K.; Shirinbayan, M.; Tcharkhtchi, A. Additive Manufacturing of Polymer-Based Composites Using Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF): A Review. Appl. Compos. Mater. 2021, 28, 1335–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardot, M.; Schulz, M.D. Biodegradable Poly(Lactic Acid) Nanocomposites for Fused Deposition Modeling 3D Printing. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milovanovic, S.; Pajnik, J.; Lukic, I. Tailoring of advanced Poly(lactic acid)-based materials: A review. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2021, 139, 51839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bax, B.; Müssig, J. Impact and tensile properties of PLA/Cordenka and PLA/flax composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2008, 68, 1601–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Liu, X.; Pu, X.; Shen, Z.; Xu, W.; Yang, J. Preparation Method and Application of Porous Poly(lactic acid) Membranes: A Review. Polymers 2024, 16, 1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, L.; Deng, J.; Ke, Q.; Li, X.; Ouyang, Y.; Huang, C.; Liu, X.; Qian, Y. Grooved Fibers: Preparation Principles Through Electrospinning and Potential Applications. Adv. Fiber Mater. 2021, 4, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, B.; Revagade, N.; Hilborn, J. Poly(lactic acid) fiber: An overview. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2007, 32, 455–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenken, B.; Barocio, E.; Favaloro, A.; Kunc, V.; Pipes, R.B. Fused filament fabrication of fiber-reinforced polymers: A review. Addit. Manuf. 2018, 21, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Pang, X.; Chen, X. Poly(Lactic Acid): Recent Stereochemical Advances and New Materials Engineering. Adv. Mater. 2024. early view. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dejene, B.K.; Gudayu, A.D. Eco-Friendly Packaging Innovations: Integrating Natural Fibers and ZnO Nanofillers in Polylactic Acid (PLA) Based Green Composites—A Review. Polym. Plast. Technol. Mater. 2024, 63, 1645–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Min, T.; Zhao, Y.; Cheng, C.; Yin, H.; Yue, J. The developments and trends of electrospinning active food packaging: A review and bibliometrics analysis. Food Control 2024, 160, 110291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, L.T.; Auras, R.; Rubino, M. Processing technologies for Poly(lactic acid). Prog. Polym. Sci. 2008, 33, 820–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Aguirre, E.; Iñiguez-Franco, F.; Samsudin, H.; Fang, X.; Auras, R. Poly(lactic acid)—Mass production, processing, industrial applications, and end of life. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 107, 333–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olonisakin, K.; Fan, M.; Zhang, X.X.; Ran, L.; Lin, W.; Zhang, W.; Yang, W.B. Key Improvements in Interfacial Adhesion and Dispersion of Fibers/Fillers in Polymer Matrix Composites; Focus on PLA Matrix Composites. Compos. Interfaces 2021, 29, 1071–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, W.; Zhong, Y.; Pan, X.; Ke, C.; Cui, P.; Lu, H.; Jiang, Z.; Yang, W. Poly(lactic acid) Electrospun Membranes for Sustainable Separation Processes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2024, 63, 16029–16050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lin, Y.; Liu, M.; Meng, L.; Li, C. A review of research and application of polylactic acid composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2022, 140, e53477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nirmal Kumar, K.; Dinesh Babu, P.; Surakasi, R.; Kumar, P.M.; Ashokkumar, P.; Khan, R.; Alfozan, A.; Gebreyohannes, D.T.; Puglia, D. Mechanical and Thermal Properties of Bamboo Fiber–Reinforced PLA Polymer Composites: A Critical Study. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2022, 2022, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, R.; Kyratzis, I.L.; Truong, Y.B.; Padhye, R.; Arnold, L. Structural and mechanical properties of polypropylene nanofibres fabricated by meltblowing. J. Text. Inst. 2014, 106, 629–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
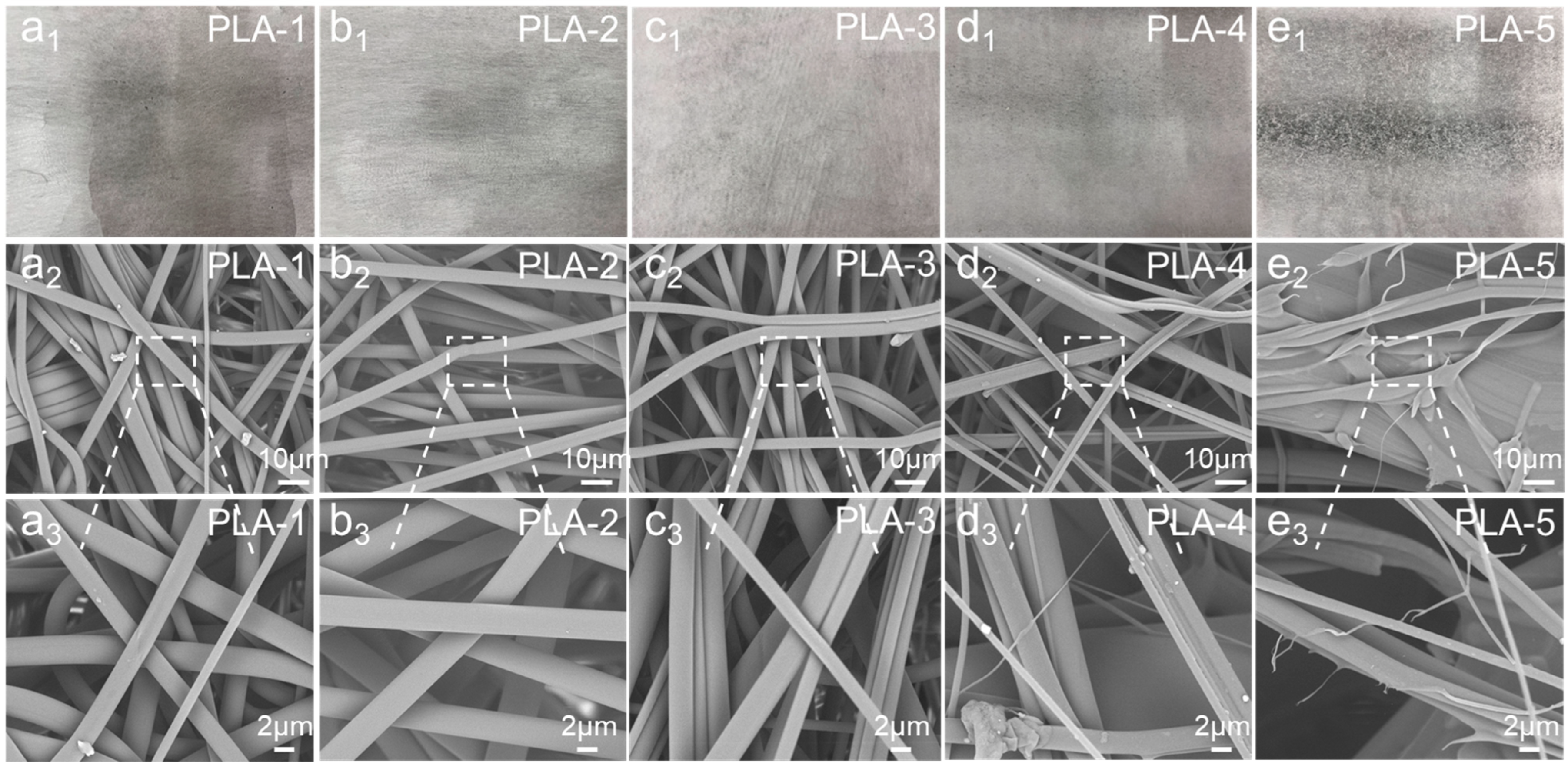

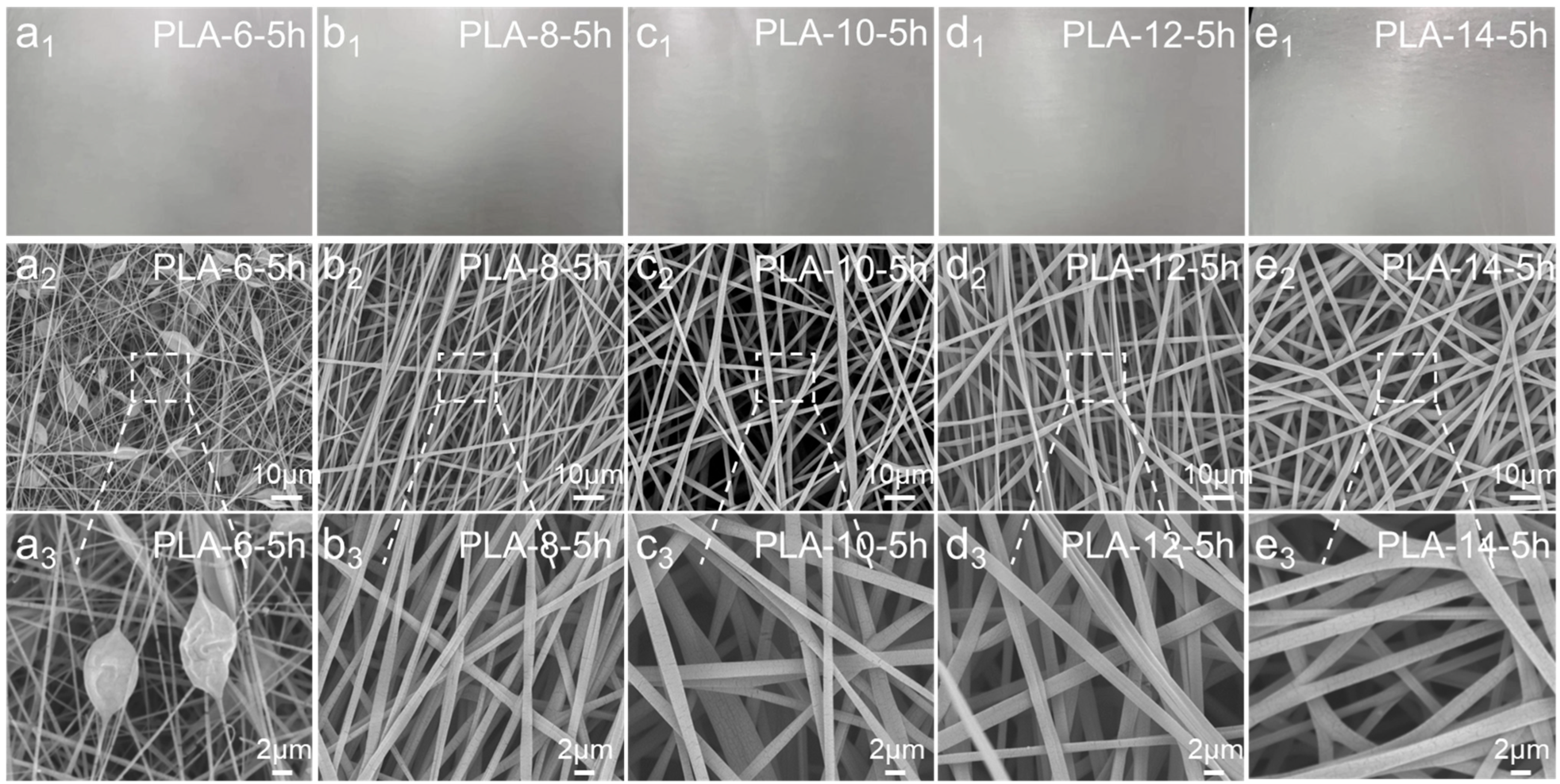
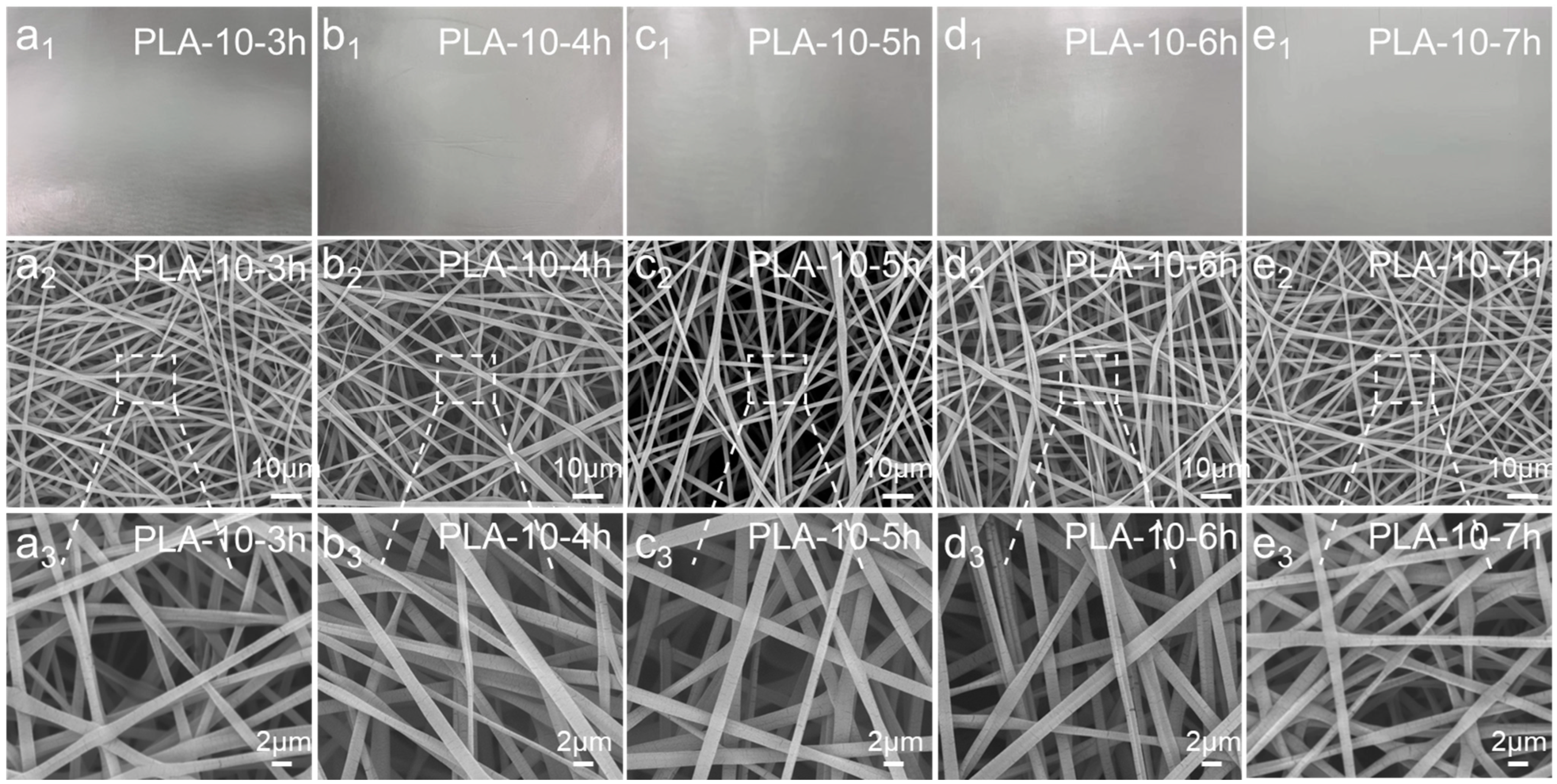

| Samples | Screw Temperature/°C | Melt Temperature/°C | Hot Air Temperature/°C | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zone 1 | Zone 2 | Zone 3 | Zone 4 | Zone 5 | |||
| PLA-1 | 160 | 180 | 180 | 180 | 180 | 180 | 230 |
| PLA-2 | 160 | 190 | 190 | 190 | 190 | 190 | 230 |
| PLA-3 | 160 | 200 | 200 | 200 | 200 | 200 | 230 |
| PLA-4 | 160 | 210 | 210 | 210 | 210 | 210 | 230 |
| PLA-5 | 160 | 220 | 220 | 220 | 220 | 220 | 230 |
| Samples | Solution Concentration | Spinning Time |
|---|---|---|
| PLA-6-5h | 6 wt.% | 5 h |
| PLA-8-5h | 8 wt.% | 5 h |
| PLA-10-5h | 10 wt.% | 5 h |
| PLA-12-5h | 12 wt.% | 5 h |
| PLA-14-5h | 14 wt.% | 5 h |
| Samples | Concentration of Solution | Spinning Time |
|---|---|---|
| PLA-10-3h | 10 wt.% | 3 h |
| PLA-10-4h | 10 wt.% | 4 h |
| PLA-10-5h | 10 wt.% | 5 h |
| PLA-10-6h | 10 wt.% | 6 h |
| PLA-10-7h | 10 wt.% | 7 h |
| Samples | Maximum Pore Size/μm | Minimum Pore Size/μm | Average Pore Size/μm |
|---|---|---|---|
| PLA-6-5h | 4.407 | 1.582 | 2.647 |
| PLA-8-5h | 7.652 | 1.924 | 3.912 |
| PLA-10-5h | 8.504 | 2.609 | 5.027 |
| PLA-12-5h | 9.792 | 2.652 | 5.776 |
| PLA-14-5h | 11.810 | 2.559 | 6.696 |
| Samples | Maximum Pore Size/μm | Minimum Pore Size/μm | Average Pore Size/μm |
|---|---|---|---|
| PLA-10-3h | 10.4268 | 2.436 | 6.910 |
| PLA-10-4h | 9.868 | 2.895 | 5.642 |
| PLA-10-5h | 8.504 | 2.609 | 5.027 |
| PLA-10-6h | 9.615 | 1.857 | 4.777 |
| PLA-10-7h | 7.672 | 1.247 | 3.468 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, Y.; Wu, M.; Ye, X.; Wei, S.; Huang, L.; Guo, H. High-Efficiency and Low-Resistance Melt-Blown/Electrospun PLA Composites for Air Filtration. Polymers 2025, 17, 424. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17030424
Guo Y, Wu M, Ye X, Wei S, Huang L, Guo H. High-Efficiency and Low-Resistance Melt-Blown/Electrospun PLA Composites for Air Filtration. Polymers. 2025; 17(3):424. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17030424
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Yongmei, Mingzhu Wu, Xiaojian Ye, Shengchao Wei, Luming Huang, and Hailing Guo. 2025. "High-Efficiency and Low-Resistance Melt-Blown/Electrospun PLA Composites for Air Filtration" Polymers 17, no. 3: 424. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17030424
APA StyleGuo, Y., Wu, M., Ye, X., Wei, S., Huang, L., & Guo, H. (2025). High-Efficiency and Low-Resistance Melt-Blown/Electrospun PLA Composites for Air Filtration. Polymers, 17(3), 424. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17030424






