Numerical Simulation of Rotational Speed Sinusoidal Pulsation for Enhancing Polymer Processing Based on Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods and Implementation
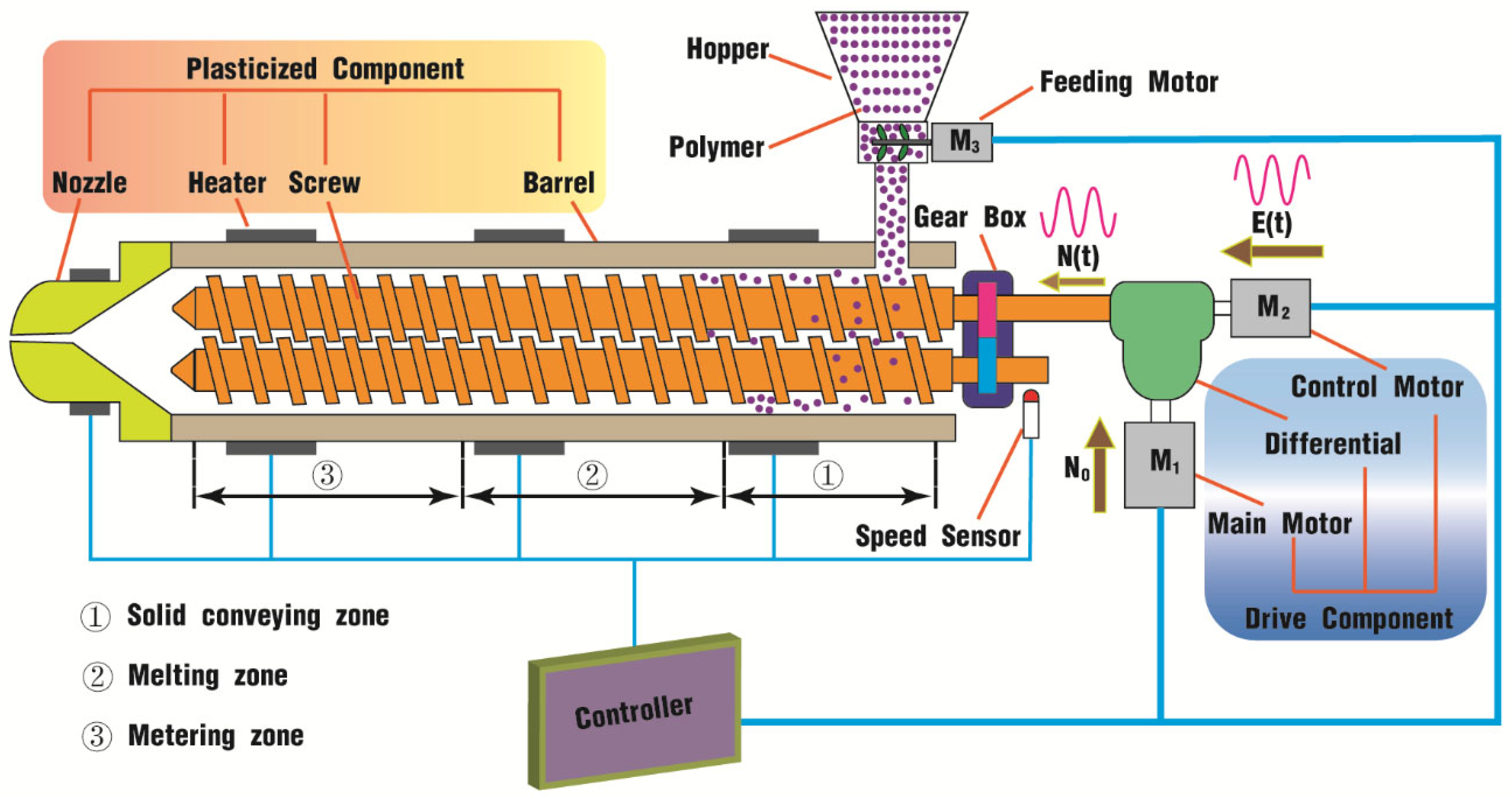
2.1. Differential Pulsating System
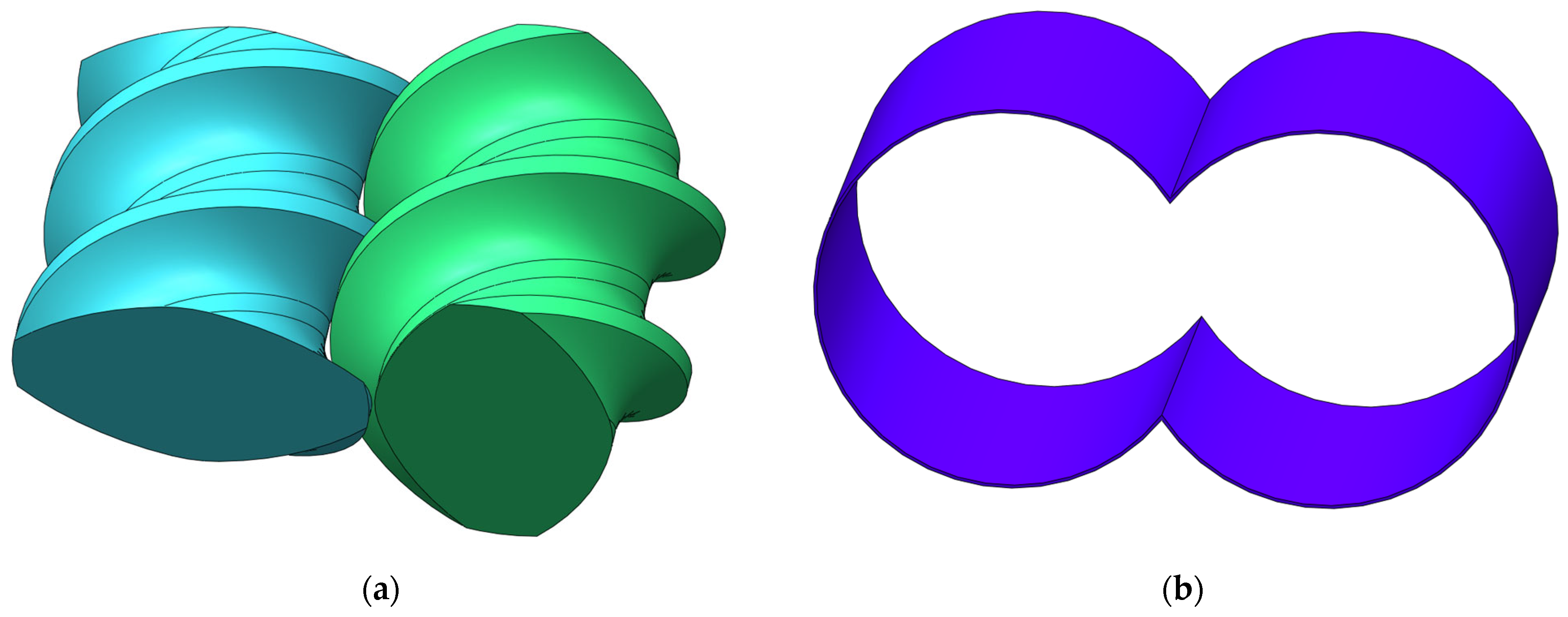
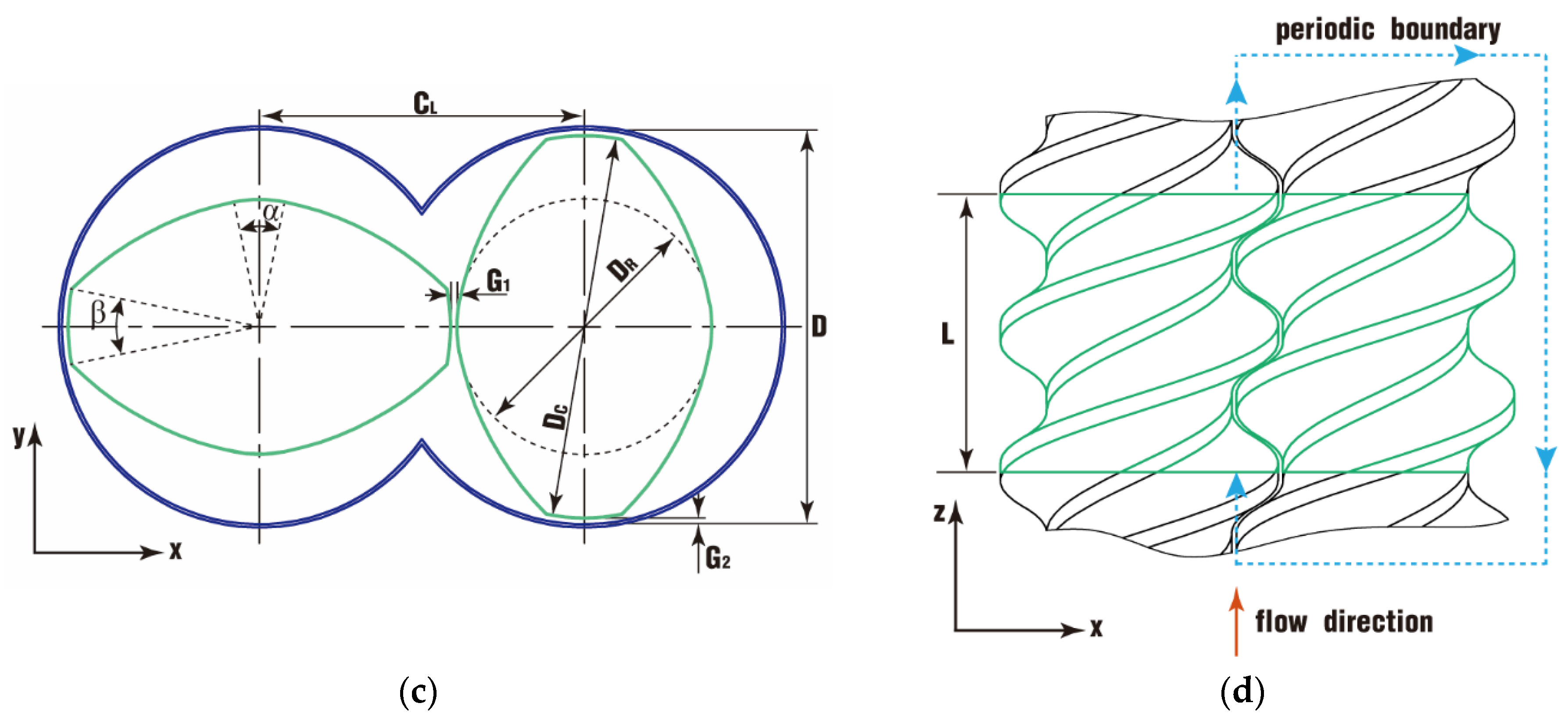
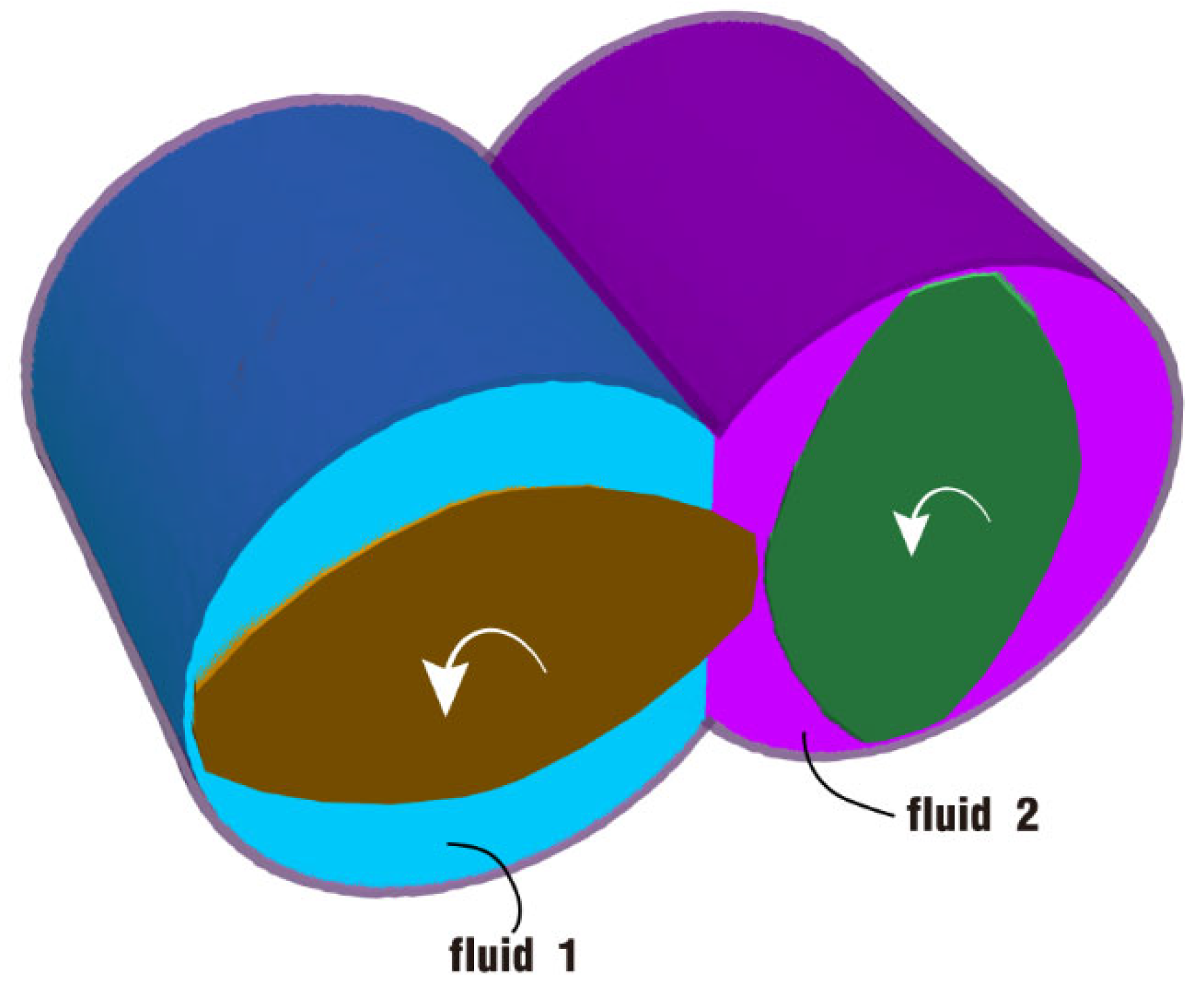
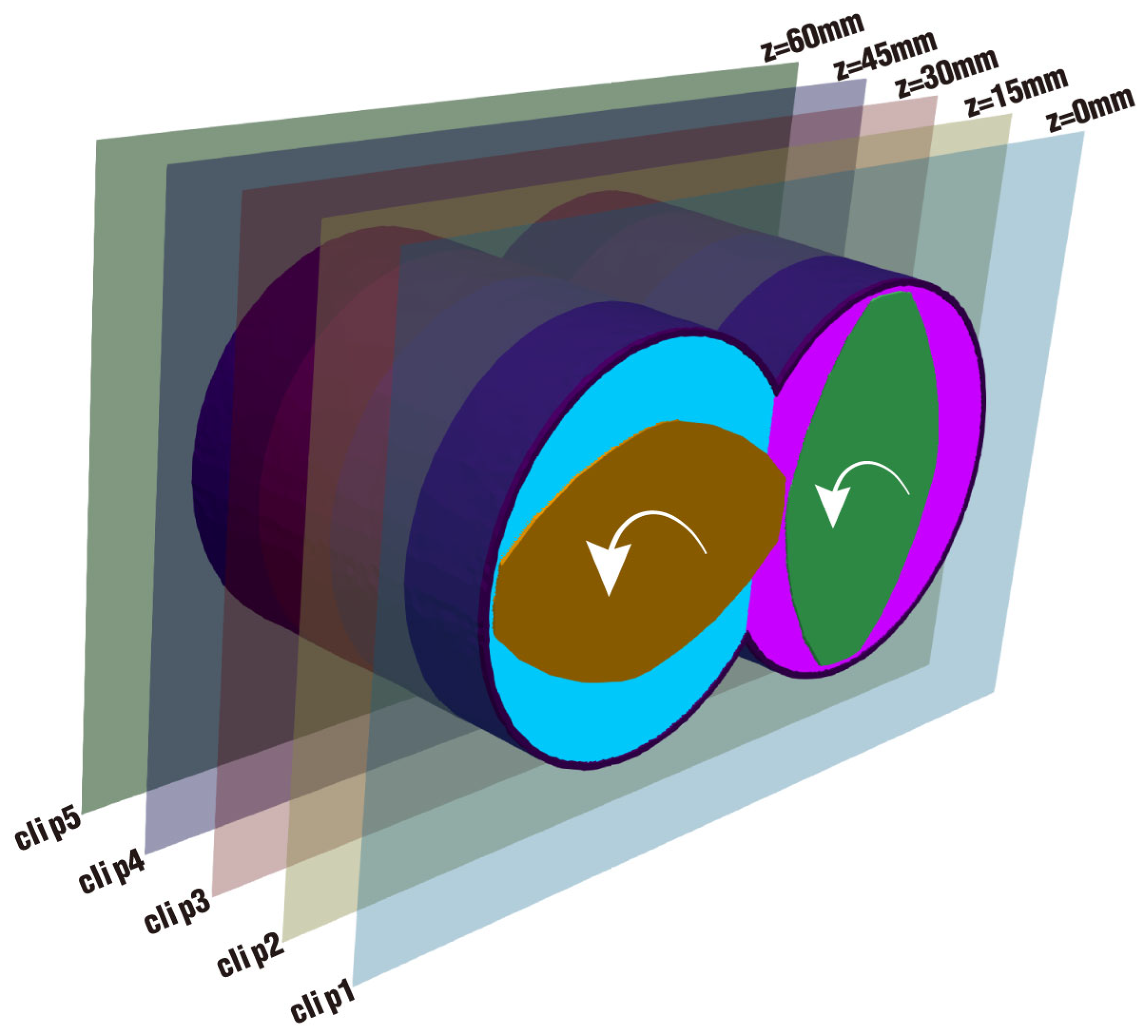
2.2. Geometric Model
2.3. Governing Equations and SPH Algorithm
2.4. Parameter Setting
2.5. Boundary Conditions
2.6. Computational Time
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Fully Filled State
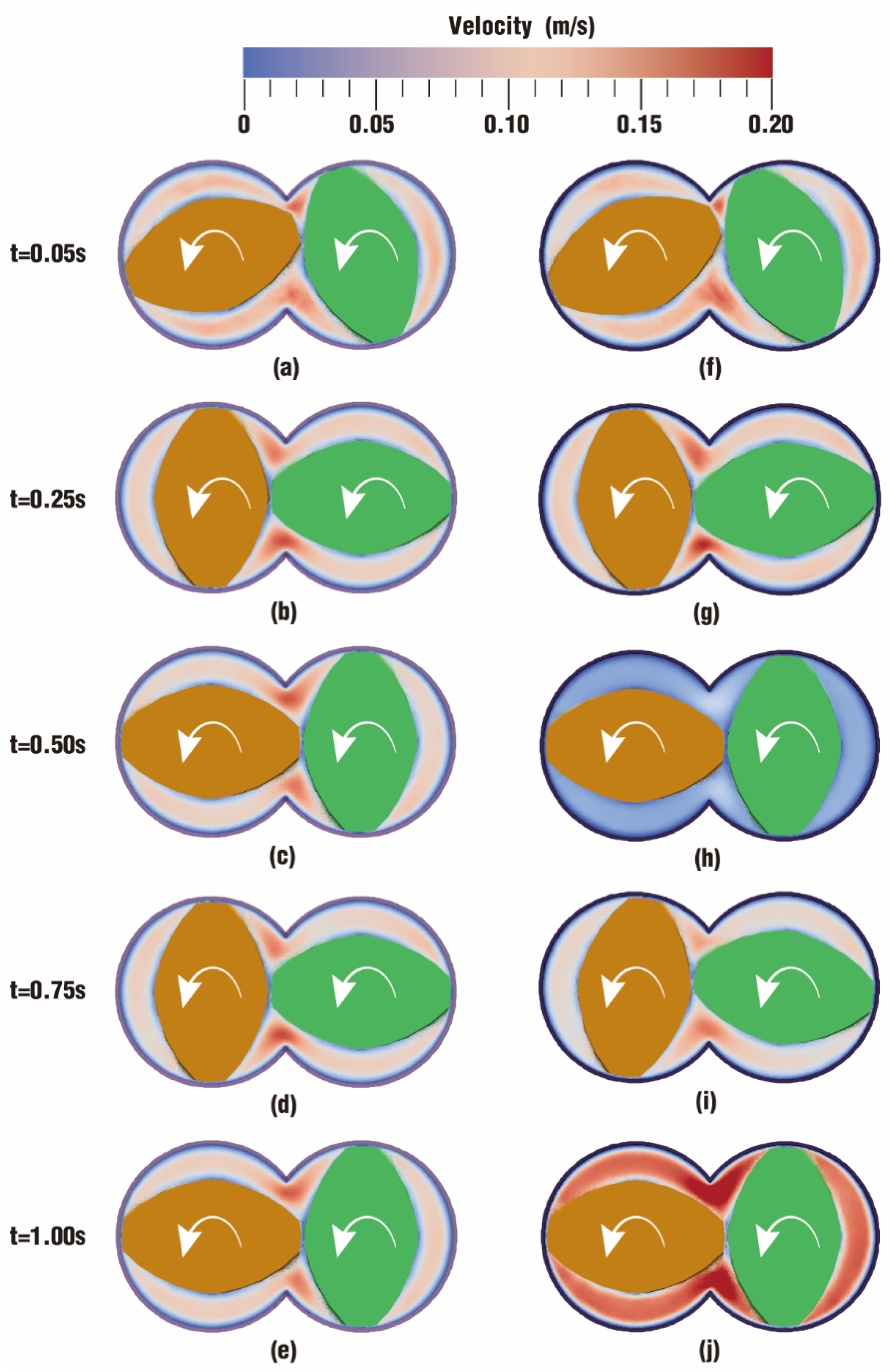
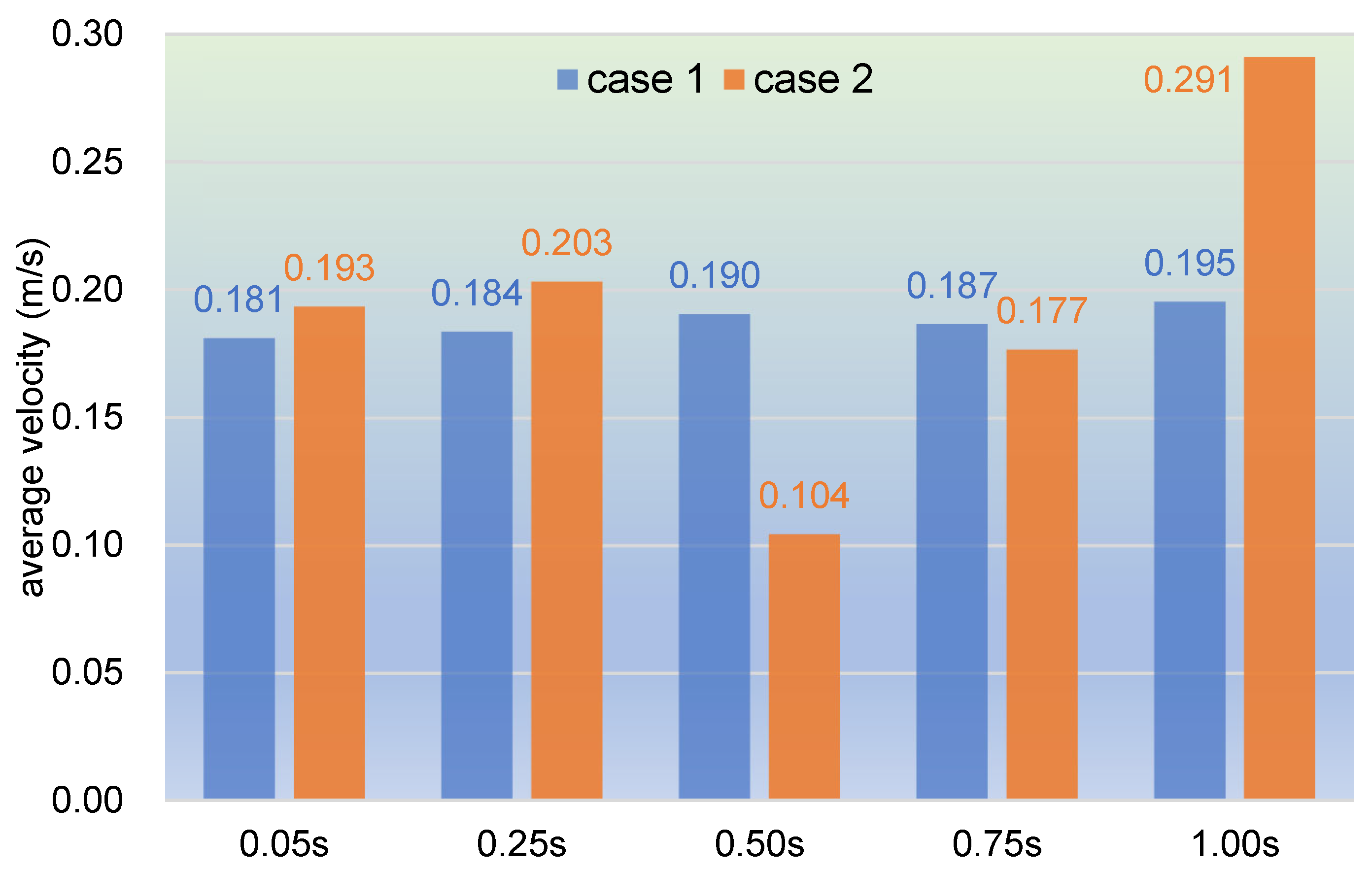
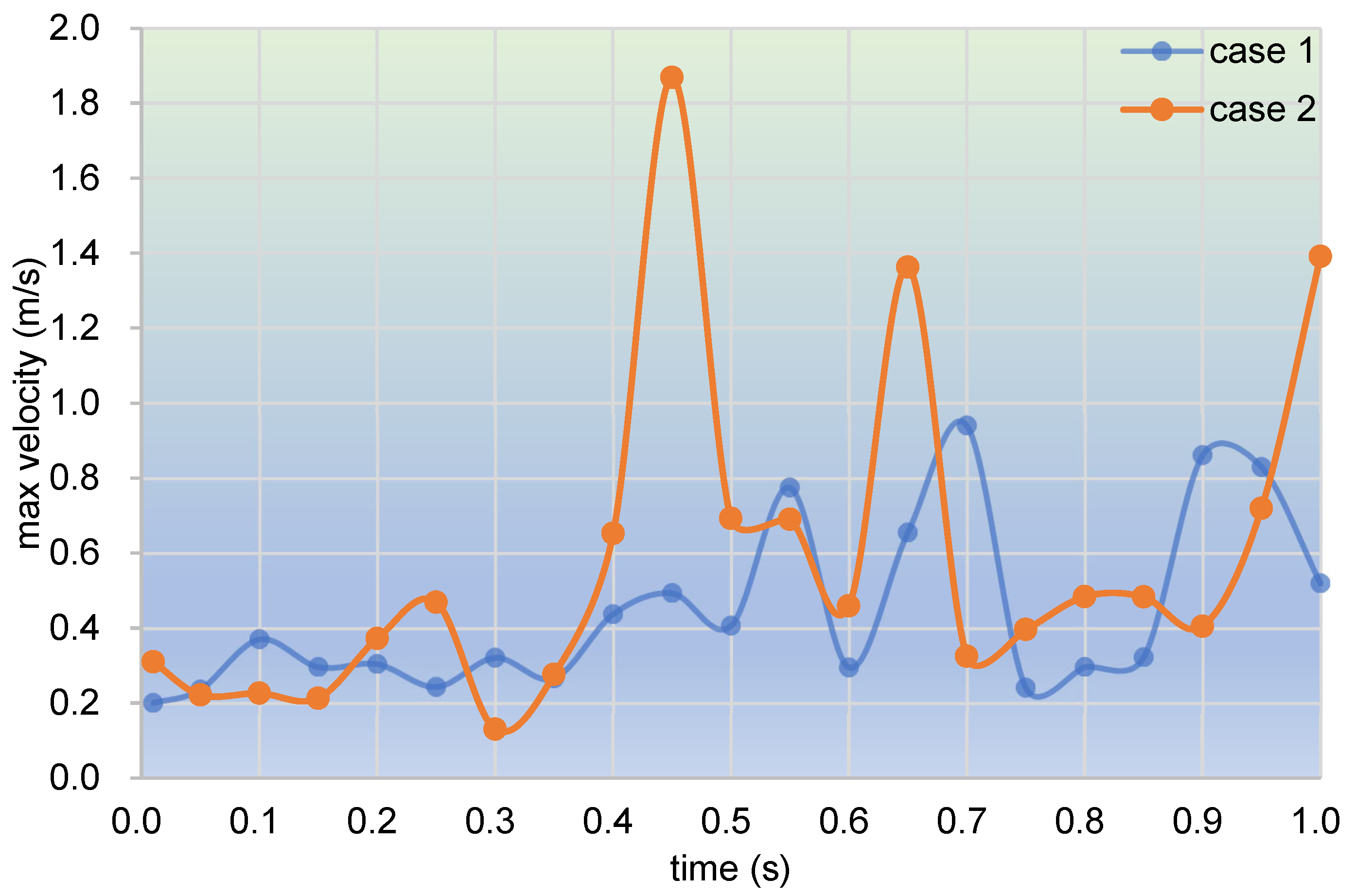
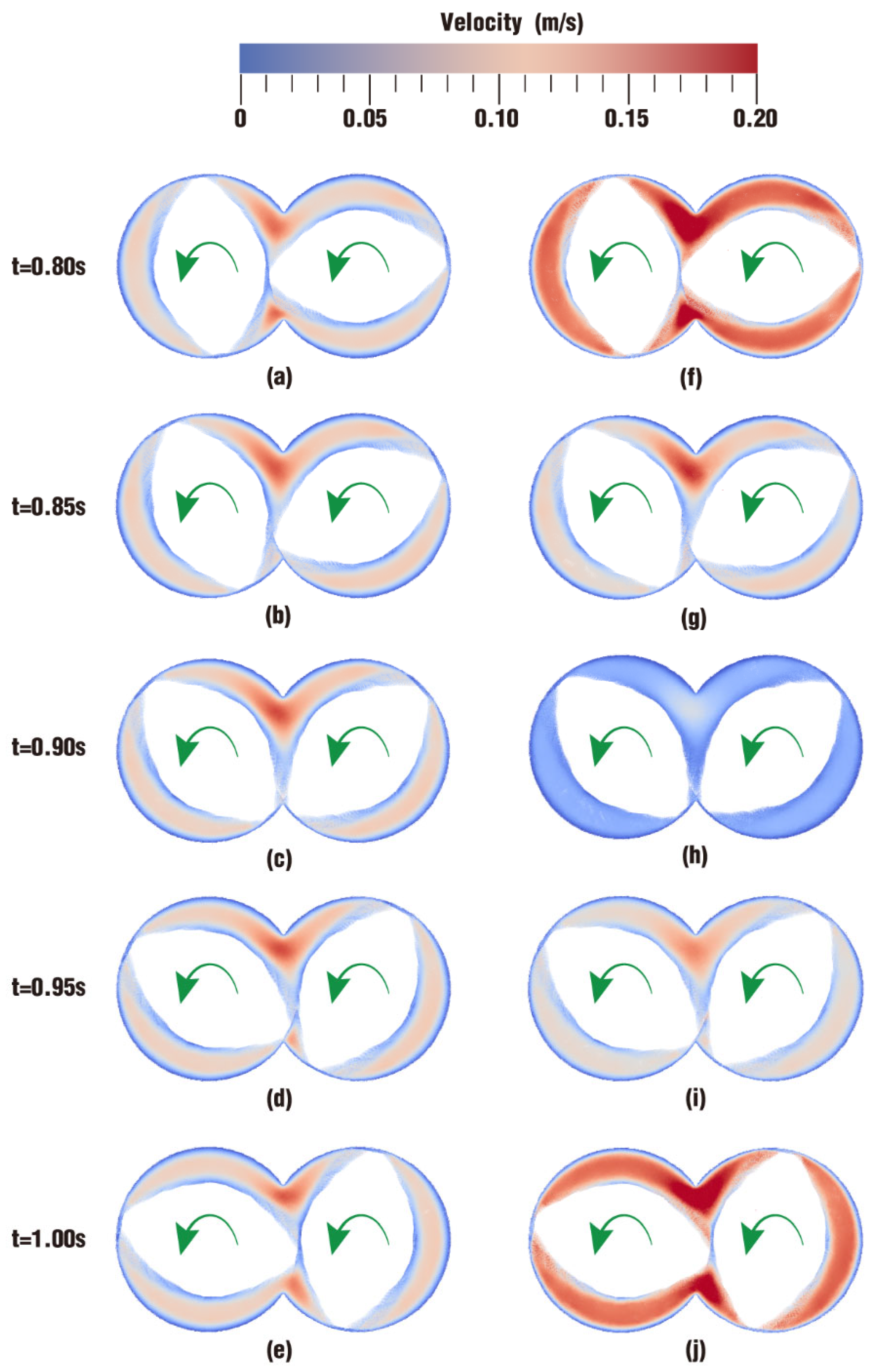
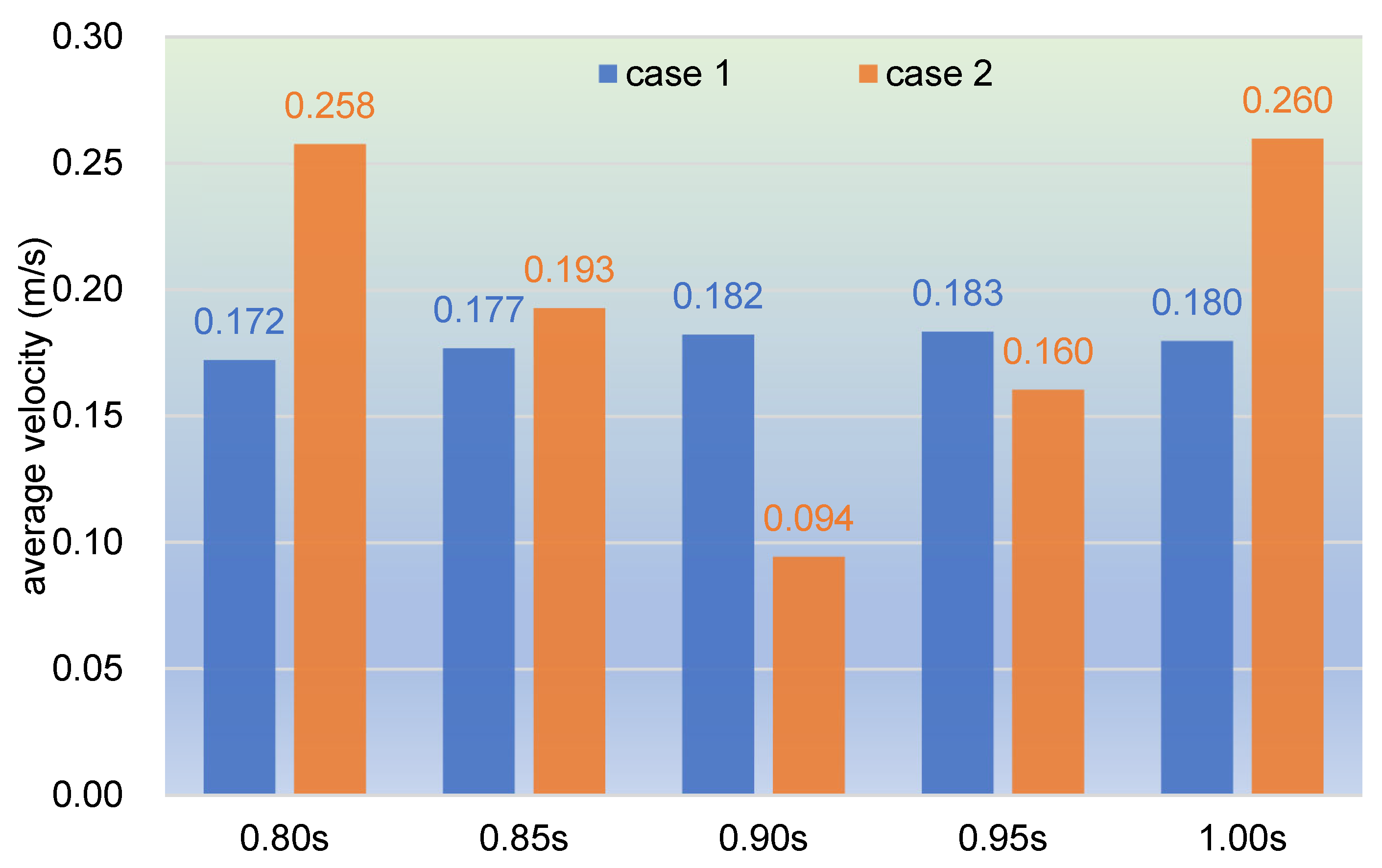
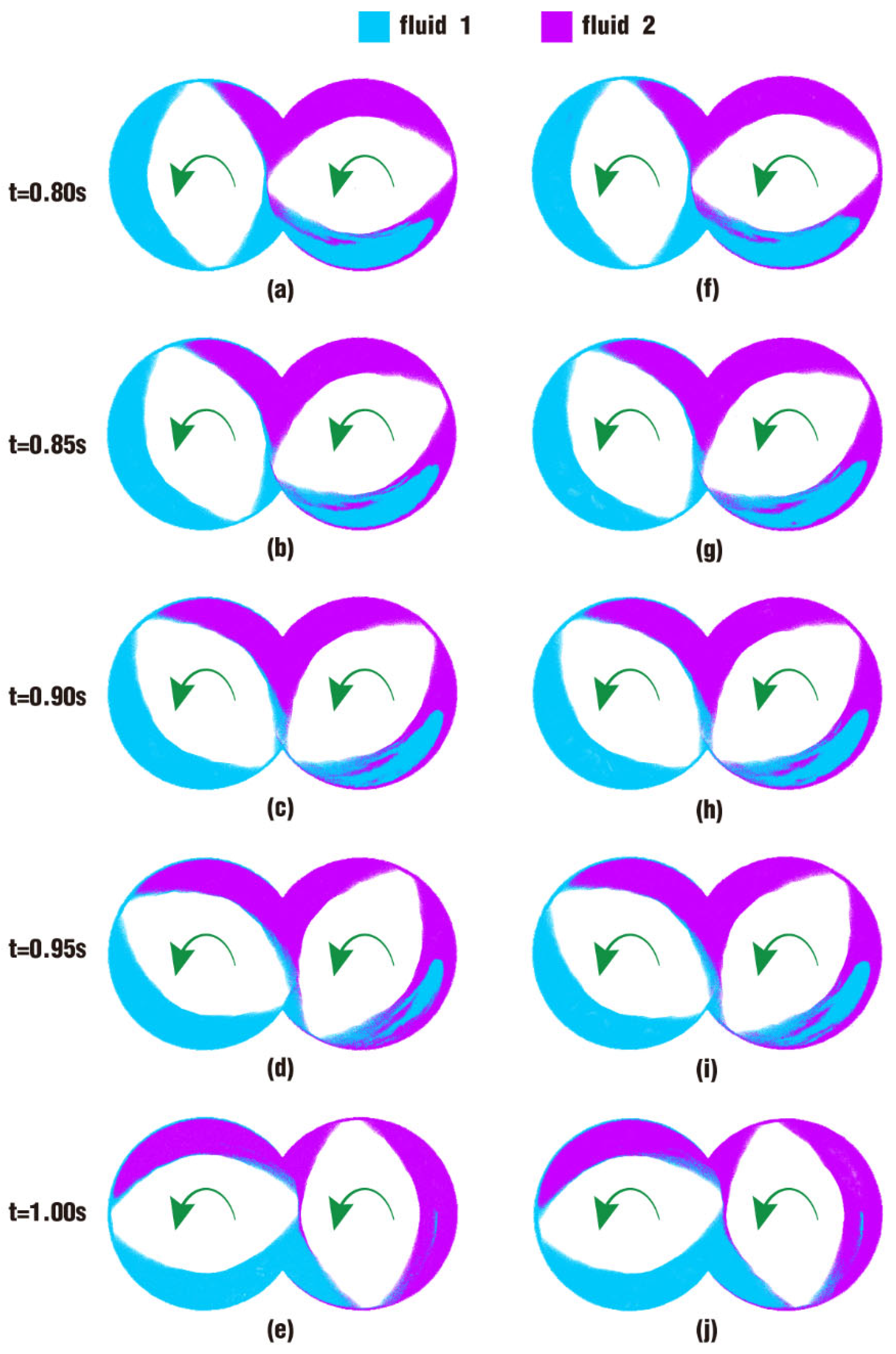
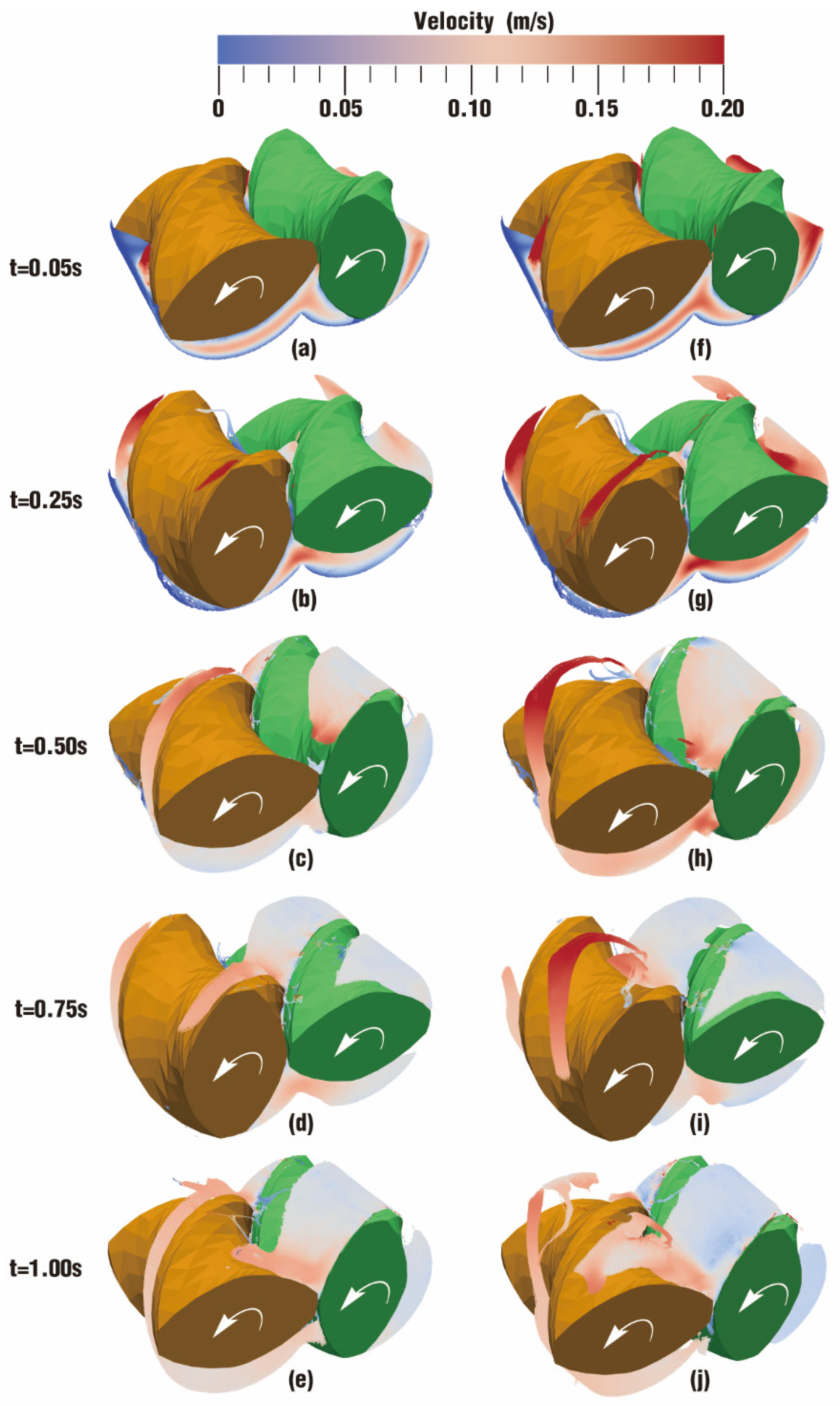
3.1.1. Velocity Distribution
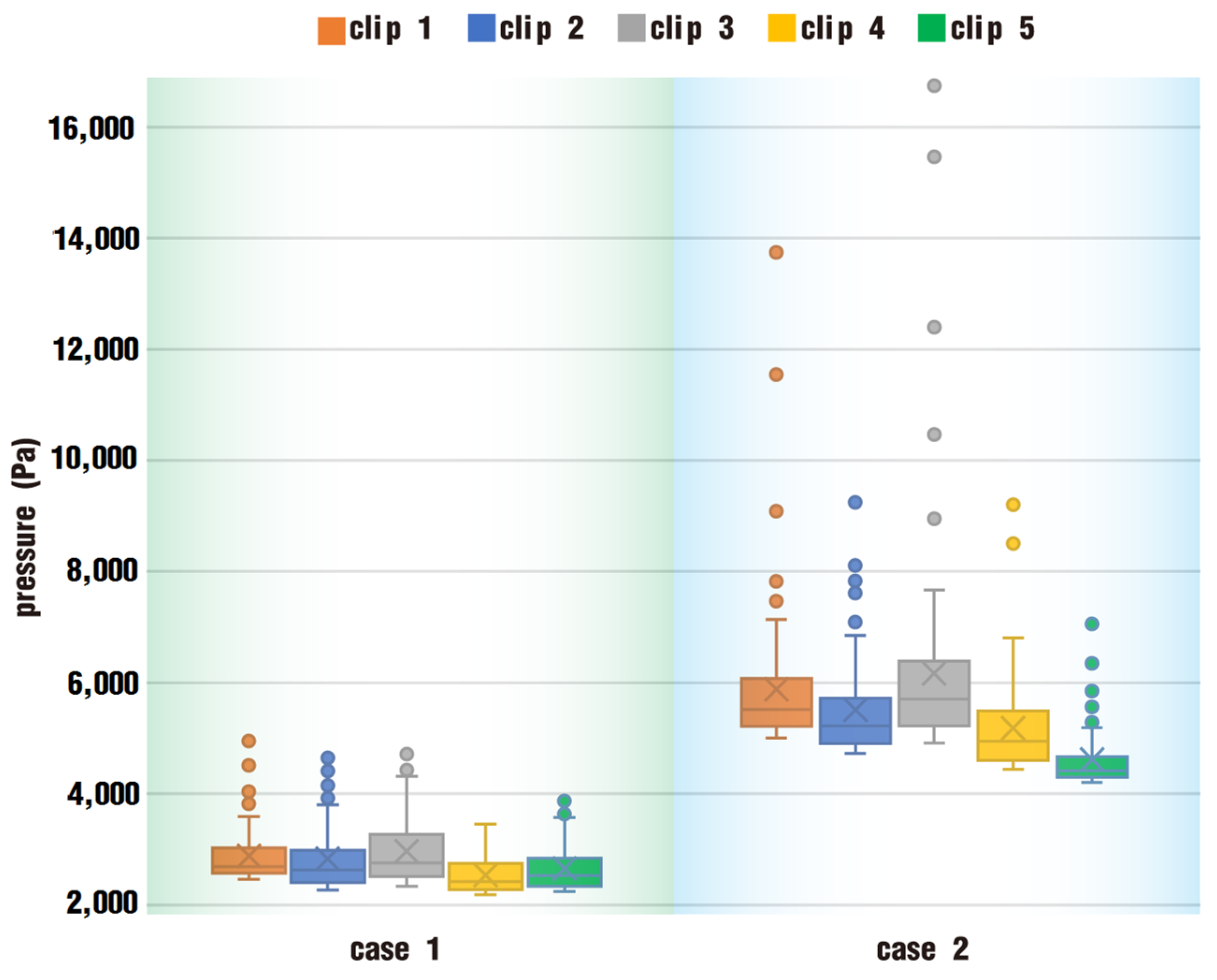
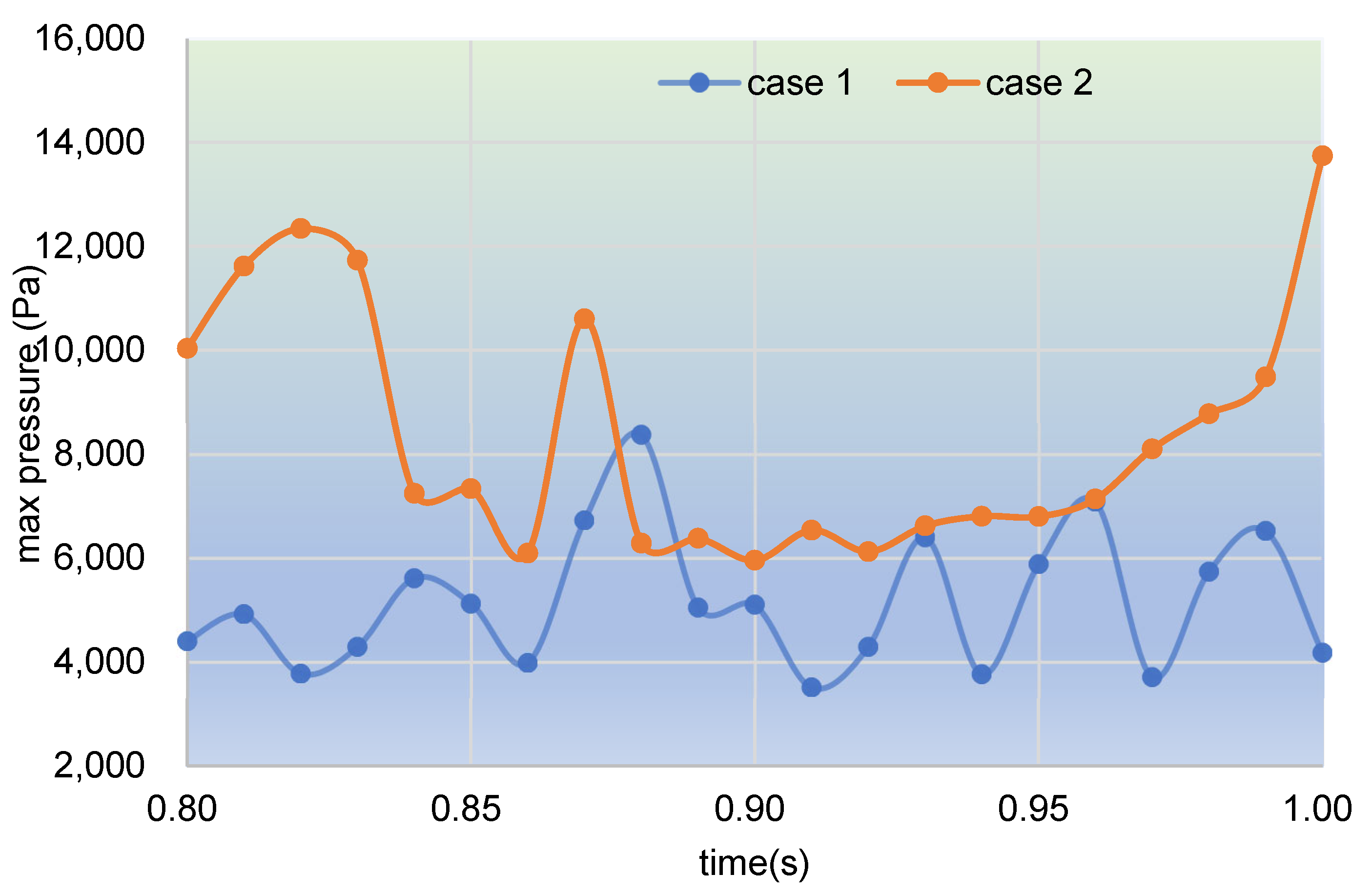
3.1.2. Particle Distribution and Pressure
3.2. Partially Filled State
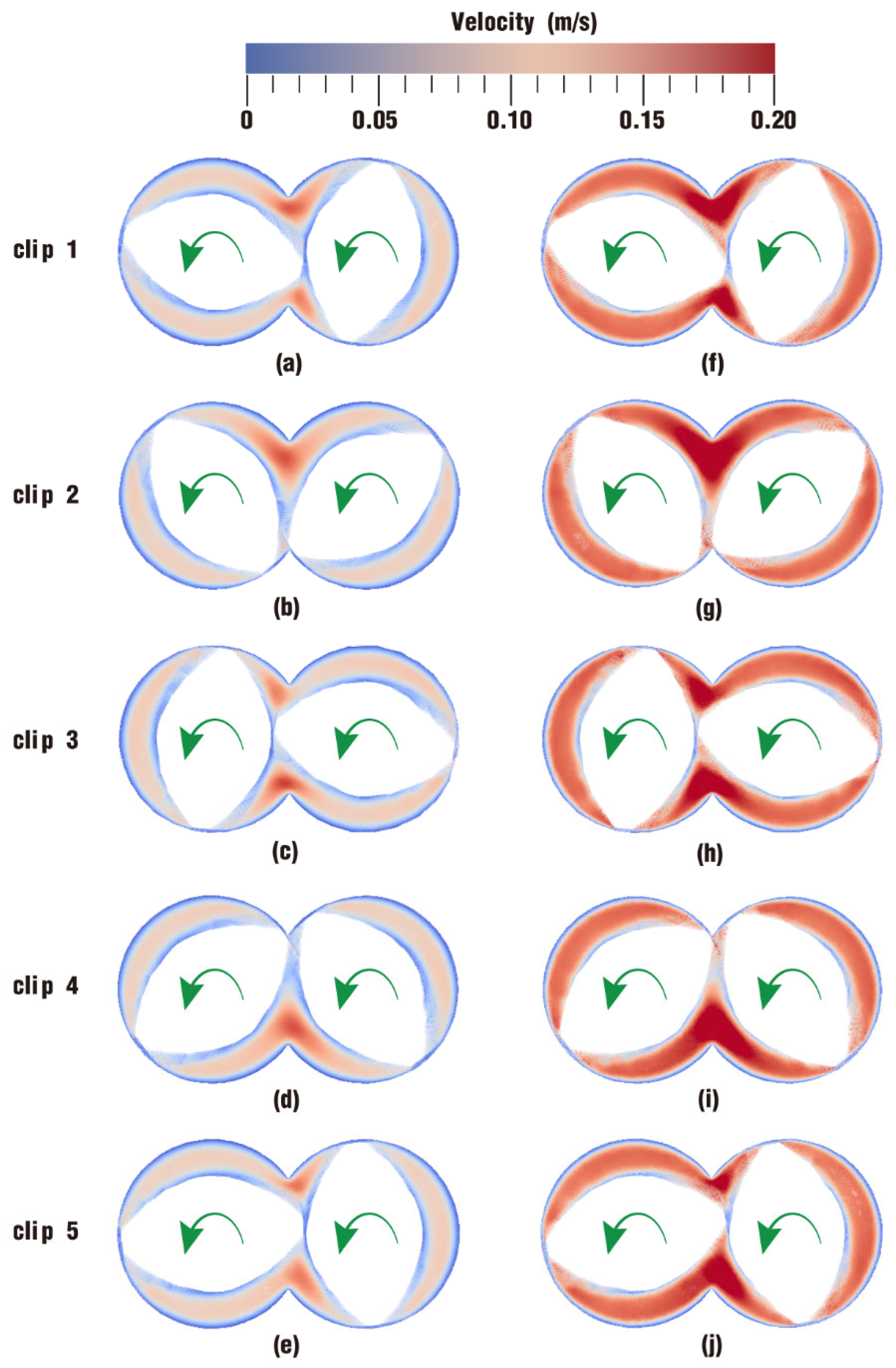
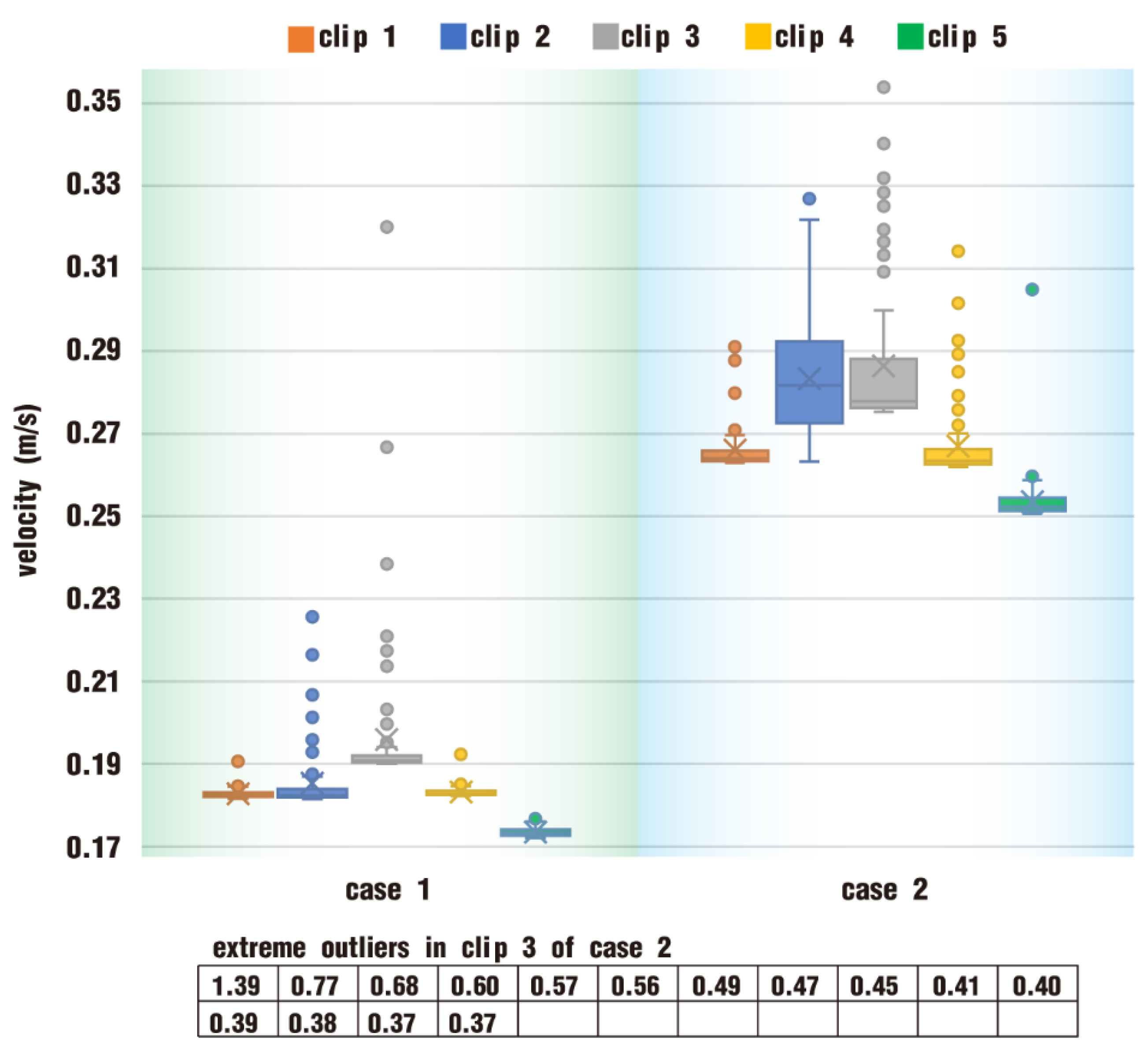
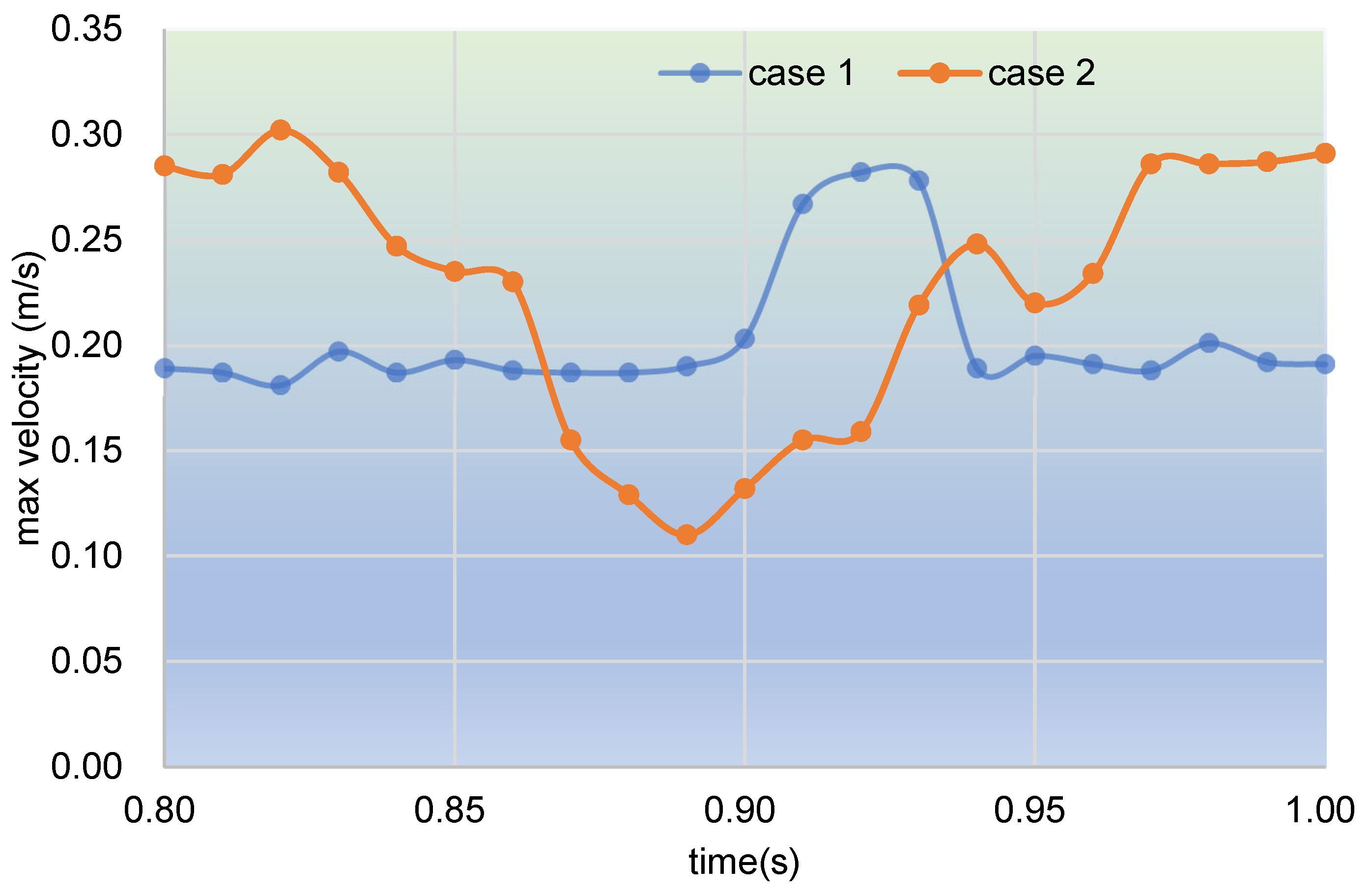
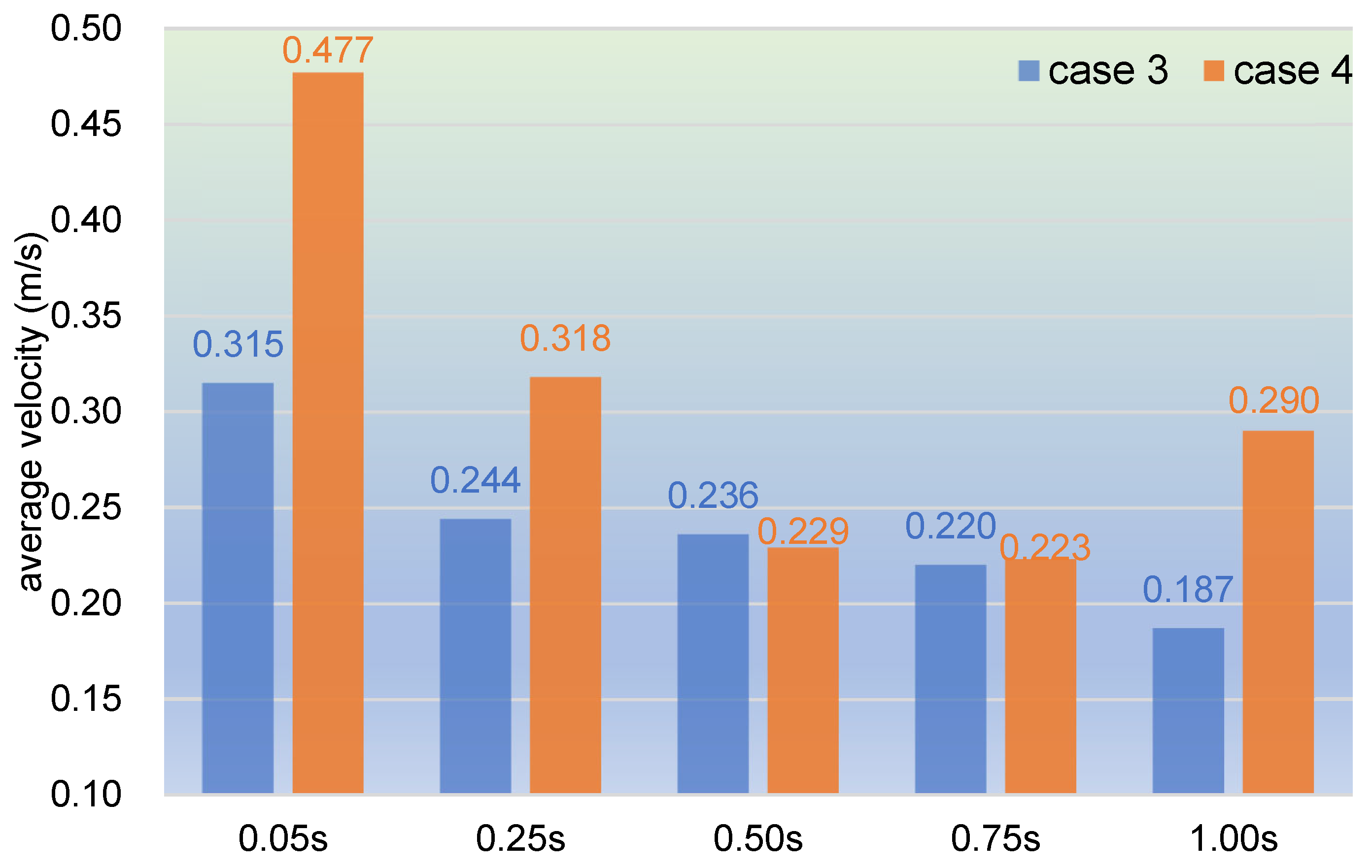
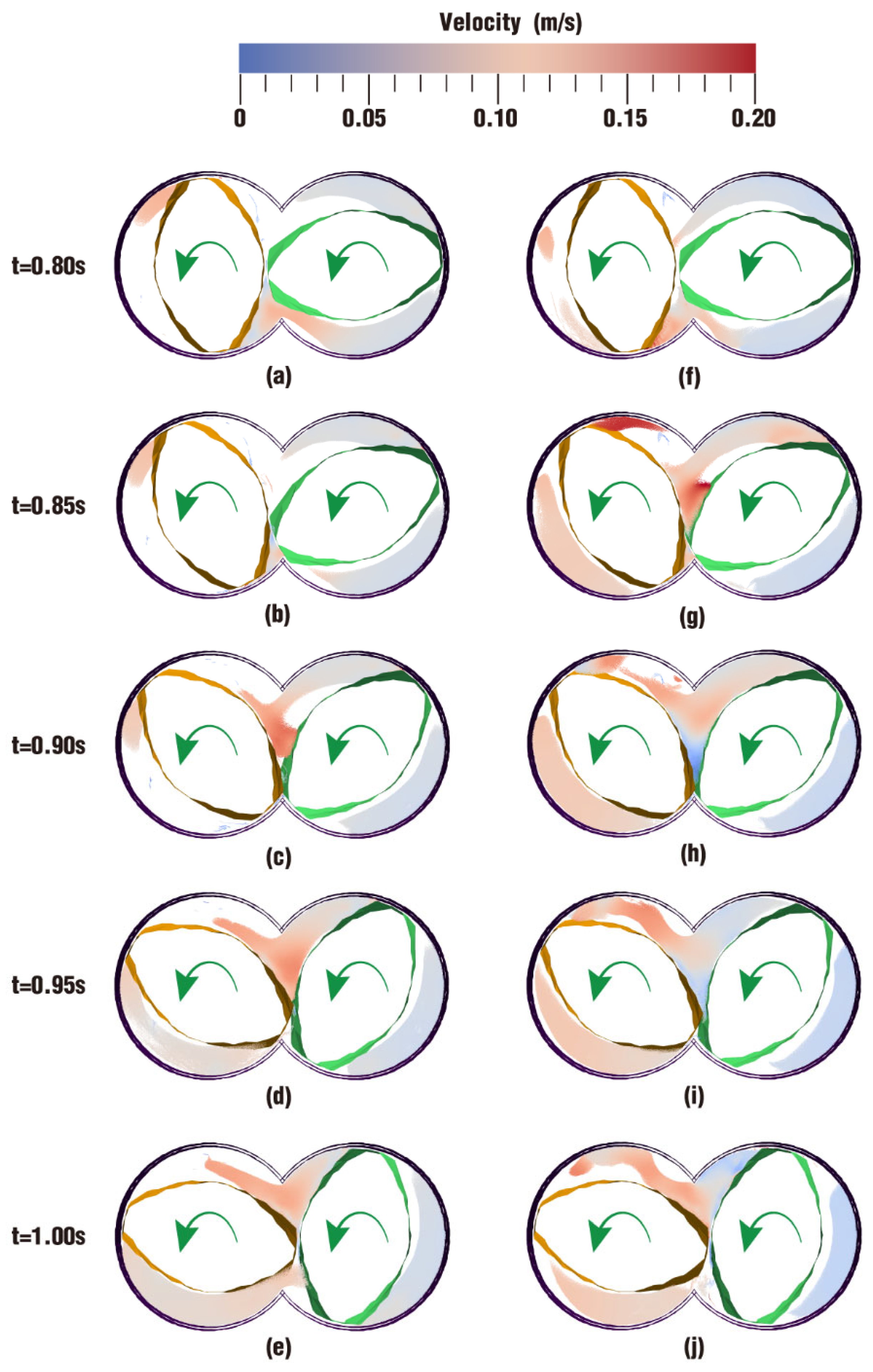
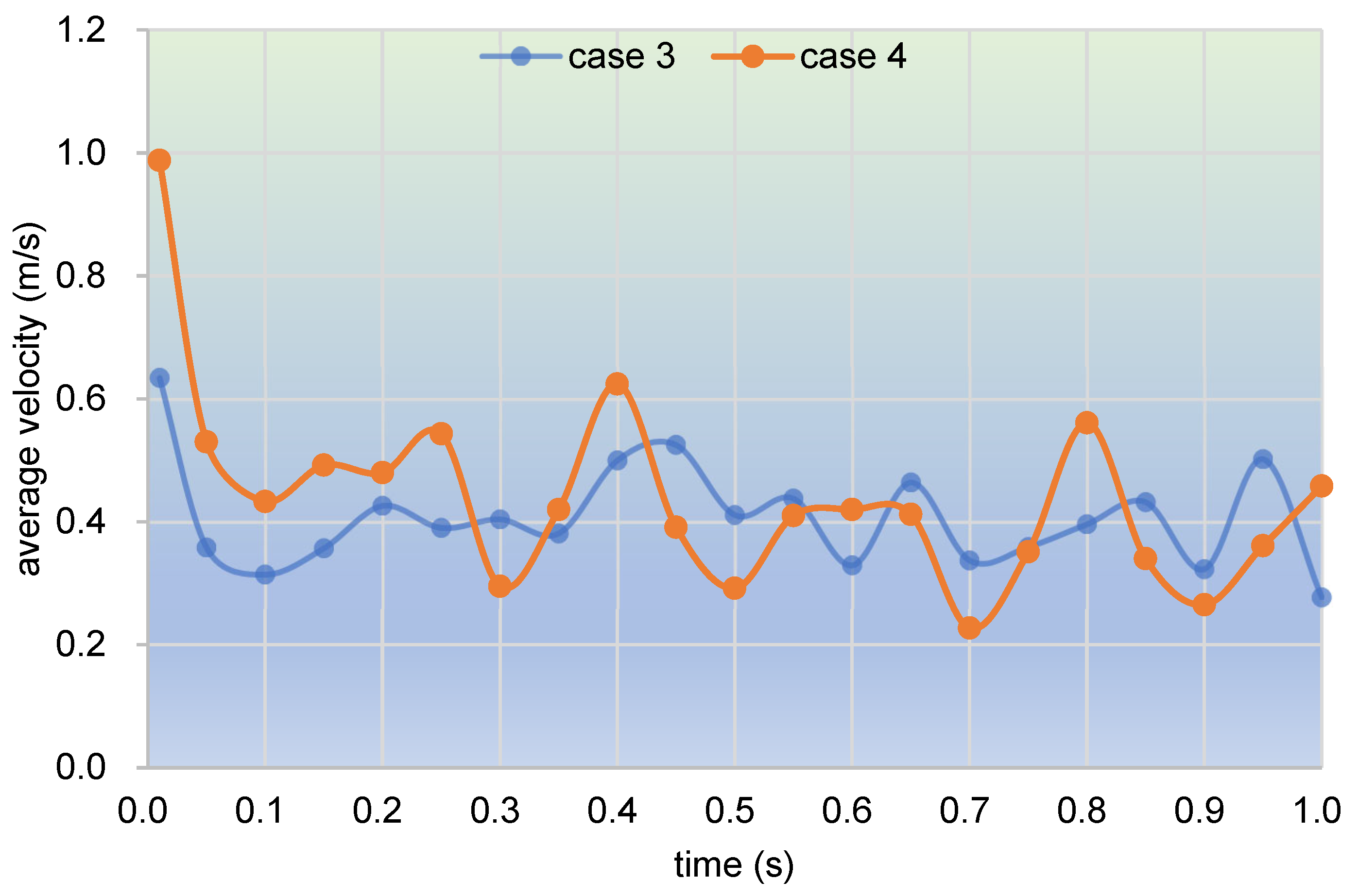
3.2.1. Velocity Distribution
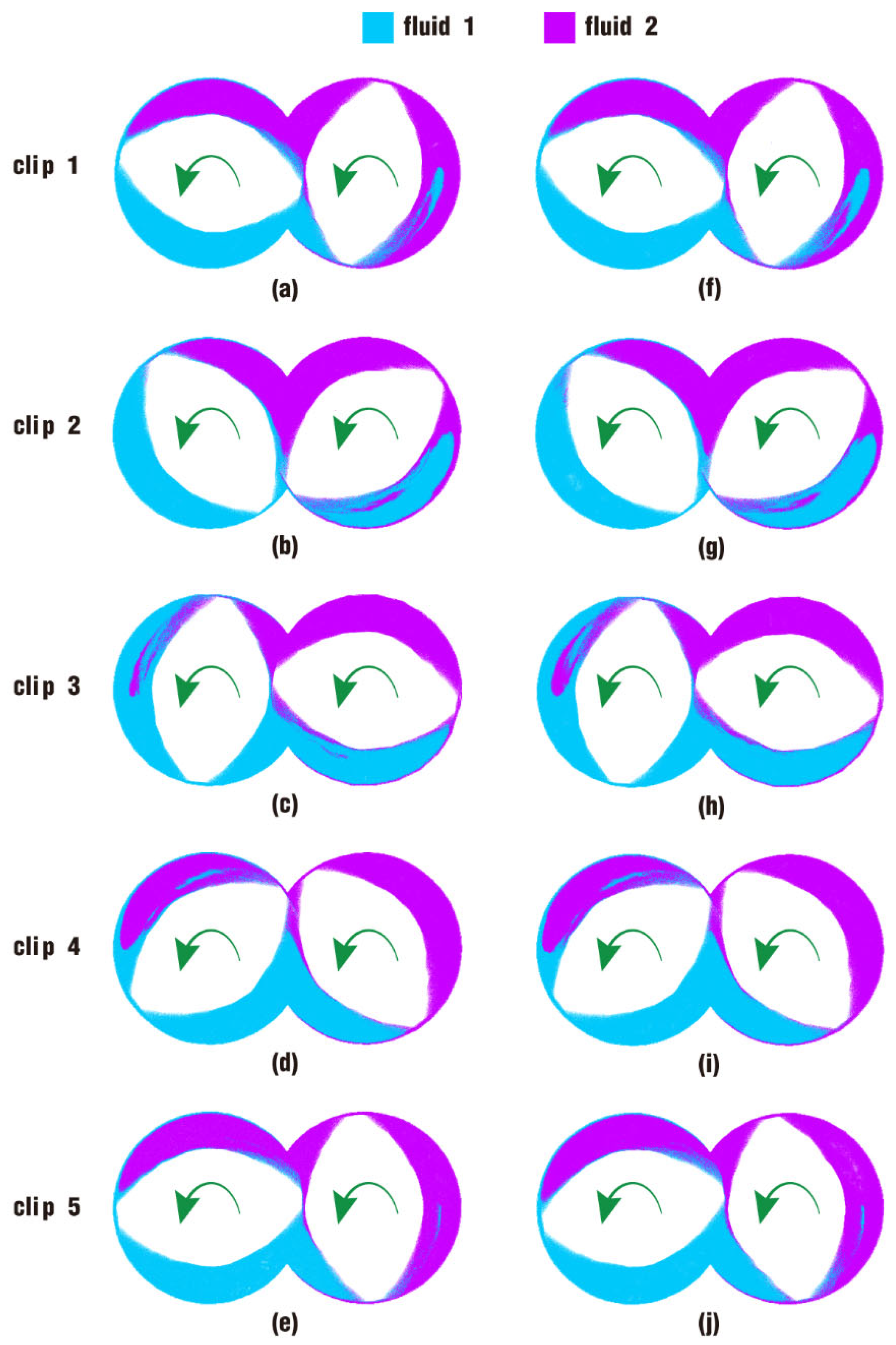
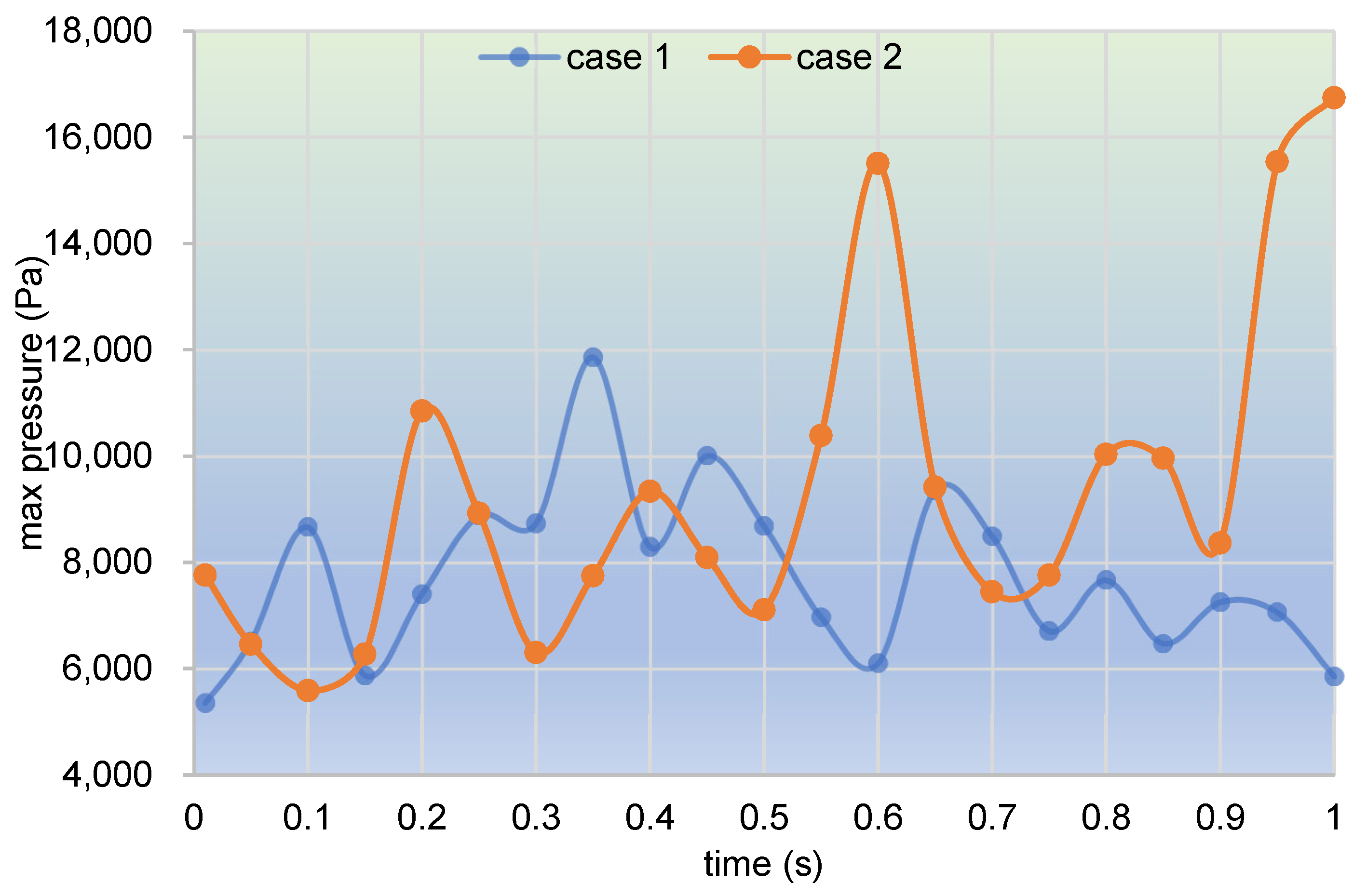
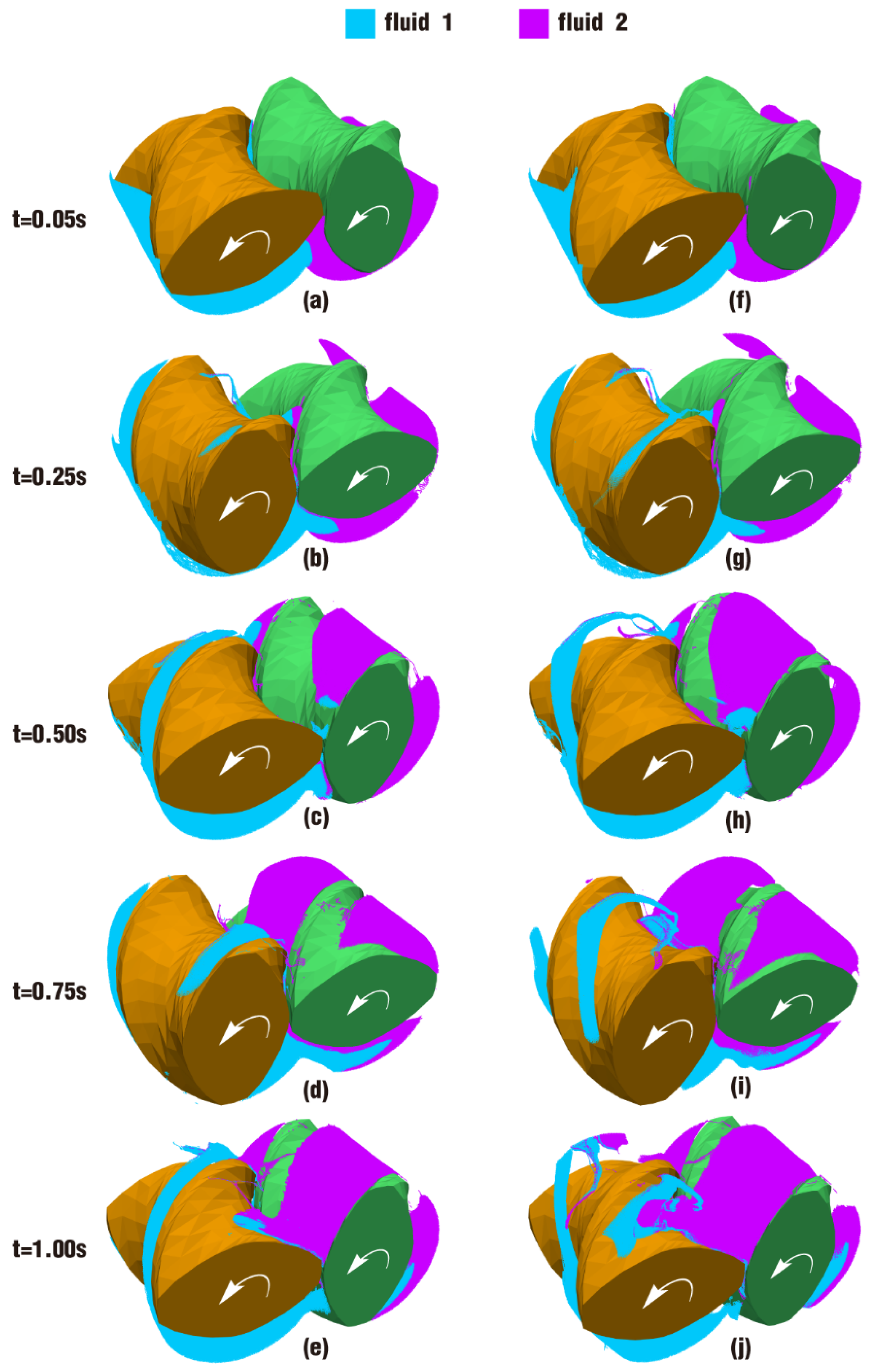
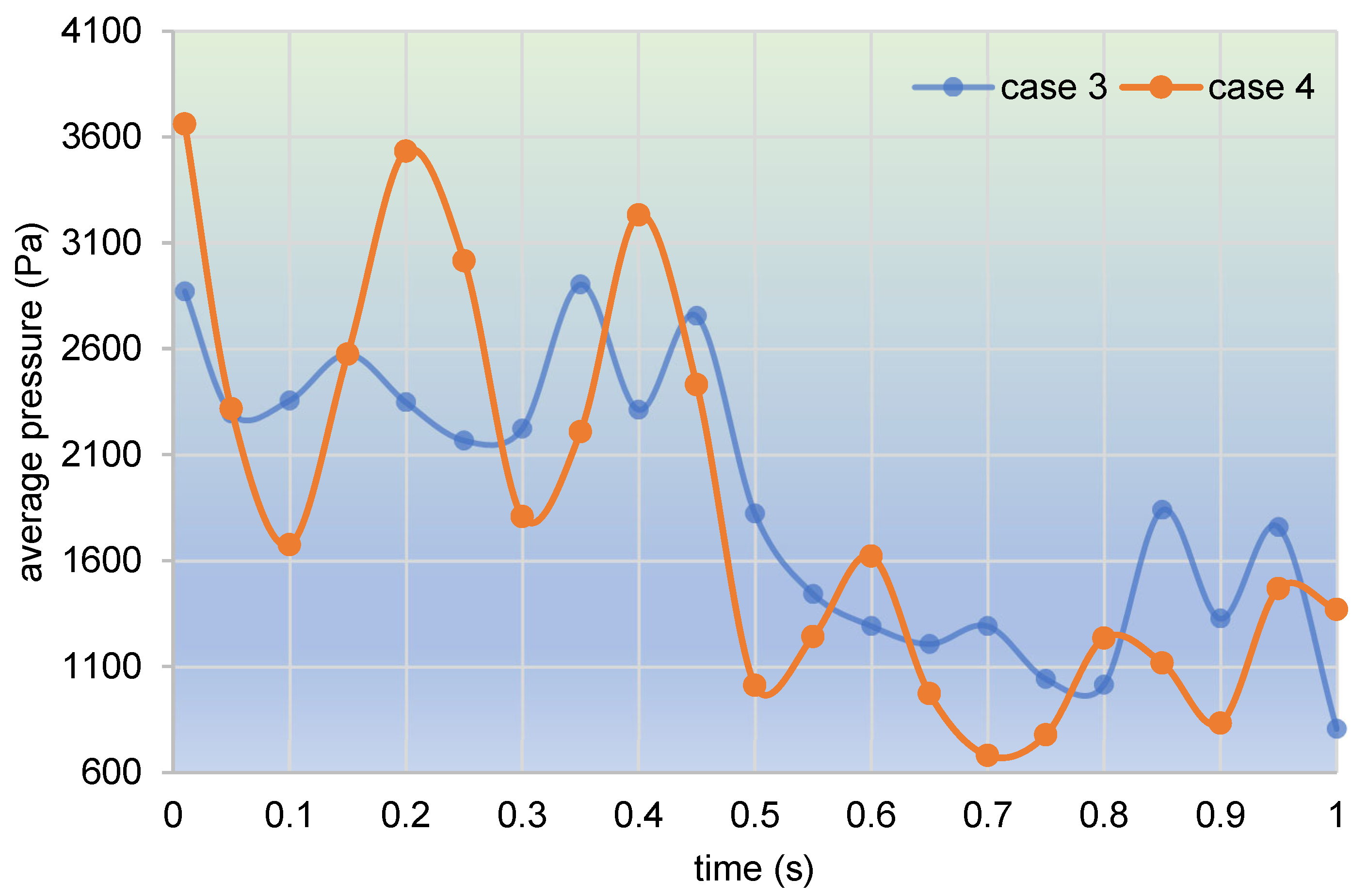
3.2.2. Particle Distribution and Pressure
4. Conclusions and Future Work
- (1)
- In the fully filled state, velocities in the intermeshing region are always larger than those in the non-meshing region as a result of the strong shear and tensile forces by the twin screws. The superimposed excitation can produce a changing velocity field, thus enhancing and weakening the flow field of polymers by turns. Meanwhile, the pulsation excitation can also form a much stronger pressure field, which is quite conducive to the flow of particles.
- (2)
- In the partially filled state, particles tend to bypass the gaps between the twin screws and the barrel resulting from the free surface flow produced by the partially filled channel. The free surface leads to a decreasing trend in both the velocity field and the pressure field, which makes it quite different from the fully filled state. Even though the superimposed excitation cannot change the decreasing trend as a whole, it can strengthen the velocity and pressure fields to some extent.
- (3)
- According to the statistical analysis results, the superimposed excitation loaded on twin screws can indeed change the physical fields, such as the velocity field and the pressure field, thus giving particles in the screw channel a more variable intensity of shearing and stretching action. Thus, there is a much better particle distribution for a case with superimposed excitation no matter whether it is in a fully filled state or in a partially filled state. Therefore, it can be predicted that the speed of sinusoidal pulsation would be beneficial for enhancing polymer processing.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Deduction of Equation (1)
References
- Du, Z.C.; Zhang, X.S.; Fu, Q.; Shen, K.Z.; Gao, X.Q. Effect of Ultrasonic Vibration on the Disentanglement of Polystyrene Melt. Polym. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 37, 96–101. [Google Scholar]
- Ibar, J.P. Control of Polymer Properties by Melt Vibration Technology: A Review. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1998, 38, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, F.Z.; Gao, X.Q.; Lei, J.; Deng, C.; Li, Z.M.; Shen, K.Z. Vibration assisted extrusion of polypropylene. Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 2015, 33, 688–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.M.; Chen, C.H.; Isayev, A.I. Flow of thermoplastics in an annular die under parallel oscillations. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1990, 30, 1574–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, D.J.; Yang, M.K.; Huang, Z.G.; Wen, J.S. Numerical Simulation of Mixing Characteristics in the Eccentric Rotor Extruder with Different Process Conditions and Structural Parameters. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2019, 2019, 8132308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.C.; Zeng, W.B.; He, G.J.; Yang, Z.T.; Qu, J.P. Influence of pressure oscillation on injection molding process. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2014, 27, 1417–1427. [Google Scholar]
- Du, J.S.; Cao, J.G.; Li, N.; Zhao, W.Q.; Shen, K.Z. The effect of the shish-kebab structure formation of middling-PE molded by dynamic packing injection. J. Funct. Mater. 2015, 46, 15133–15137. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, P.; Kundu, A.; Coulter, J. Vibration-assisted injection molding: An efficient process for enhanced crystallinity development and mechanical characteristics for poly lactic acid. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 121, 3111–3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, F.Z.; Wang, Z.W.; Hu, J.; Gao, X.Q.; Shen, K.Z.; Deng, C. Morphology control technologies of polymeric materials during processing. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2013, 299, 400–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eesa, M.; Barigou, M. CFD analysis of viscous non-Newtonian flow under the influence of a superimposed rotational Vibration. Comput. Fluids 2008, 37, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.B.; Ke, W.T.; Shen, K.Z. Tensile failure analysis on HDPE vibration injection moldings. Polym. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2015, 21, 245–248. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Liu, B.; Huang, C.H.; Sun, X. Study of rheological behavior of calcium carbonate-filled polypropylene in dynamic extrusion process. Polym. Compos. 2015, 36, 630–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridman, M.L.; Peshkovsky, S.L. Molding of polymers under conditions of vibration effects. Adv. Polym. Sci. 1993, 43–79. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, S.; Barigou, M. An improved vibration technique for enhancing temperature uniformity and heat transfer in viscous fluid flow. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2014, 123, 609–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, A.S.; Chuang, F.C.; Chen, C.K.; Lee, M.H.; Chen, S.W.; Su, T.L.; Yang, Y.C. A high performance micromixer using three-dimensional Tesla structures for bio-applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 263, 444–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.L.; Du, Y.X.; He, X.Y. Numerical simulation on the mixing behavior of double-wave screw under speed sinusoidal pulsating enhancement induced by differential drive. J. Polym. Eng. 2023, 43, 913–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.L.; Dong, T.W.; Liu, B.X. Effect of sinusoidal pulsating speed enhancement on the mixing performance of plastics machinery. Int. Polym. Proc. 2024, 39, 260–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sastrohartono, T.; Jaluria, Y.; Karwe, M.V. Numerical simulation of fluid flow and heat transfer in twin-screw extruders for non-newtonian materials. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1995, 35, 1213–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrera, M.A.; Vega, J.F.; Martínez-Salazar, J. Three-dimensional modelling of flow curves in co-rotating twin-screw extruder elements. J. Mater. Process Technol. 2008, 197, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.P.; Yu, H.W.; Turng, L.S. Distributive mixing in a corotating twin screw channel using Lagrangian particle calculations. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2018, 37, 2215–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalifeh, A.; Clermont, J.R. Numerical simulations of non-isothermal three-dimensional flows in an extruder by a finite-volume method. J. Non-Newton. Fluid. 2005, 126, 7–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, T.W.; Wu, J.C.; Ruan, Y.F.; Huang, J.W.; Jiang, S.Y. Simulation of multiphase flow and mixing in a conveying element of a co-rotating twin-screw extruder by using SPH. Int. J. Chem. Eng. 2023, 2023, 8383763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.X.; Lai, J.M.; Liu, H.S.; Huang, Z.C.; Liu, T.L.; Xia, Y.S.; Zhang, W. Finite element analysis of the effect for different thicknesses and stitching densities under the low-velocity impact of stitched composite laminates. Polymers 2023, 15, 4628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oldemeier, J.P.; Schöpper, V. Analysis of the dispersive and distributive mixing effect of screw elements on the co-rotating twin-screw extruder with particle tracking. Polymers 2024, 16, 2952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateev, V.; Ivanov, G.; Marinova, I. Modeling of fluid flow cooling of high-speed rotational electrical devices. In Proceedings of the XVI-th International Conference on Electrical Machines, Drives and Power Systems ELMA, Varna, Bulgaria, 6–8 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, J.X.; Liu, Y.M.; Huang, S.J.; Su, H.C.; Yao, L.G. 3-D magnetic field mathematical model considering the eccentricity and inclination of magnetic gears. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2024, 60, 3455796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.S.; Sakai, M. Numerical simulation of two-phase flows in complex geometries by using the volume-of-fluid/immersed-boundary method. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2016, 139, 221–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokriefke, G. CFD-Analysis of free surface flow inside a twin-screw extruder. In Proceedings of the International Congress on FEM Technology with ANSYS CFX & ICEM CFD Conference, Dresden, Germany, 10–12 November 2004; pp. 61–72. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Zong, Z.; Liu, M.B.; Zou, L.; Li, H.T.; Shu, C. An SPH model for multiphase flows with complex interfaces and large density differences. J. Comput. Phys. 2015, 283, 169–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, V.; Maia, J.M. Extension-dominated improved dispersive mixing in single-screw extrusion. Part 1: Computational and experimental validation. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2021, 138, 3–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gingold, R.A.; Monaghan, J.J. Smoothed particle hydrodynamics: Theory and application to non-spherical stars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1977, 181, 75–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Zhang, H.; Huang, C.; Liu, M.B. A stable SPH model with large CFL numbers for multi-phase flows with large density ratios. J. Comput. Phys. 2022, 453, 110944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, T.; He, Y.; Wu, J.-C.; Jiang, S.; Huang, X.; Yan, X. Numerical Simulation of Flow in Complex Geometries by Using Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 18236–18246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittek, P.; Pereira, G.G.; Emin, M.A.; Lemiale, V. Accuracy analysis of sph for flow in a model extruder with a kneading element. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2018, 187, 256–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, H.; Matic, J.; Khinast, J. Characteristic parameters and process maps for fully-filled twin-screw extruder elements. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2020, 230, 116202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eitzlmayr, A.; Khinast, J. Co-rotating twin-screw extruders: Detailed analysis of conveying elements based on smoothed particle hydrodynamics. part 1: Hydrodynamics. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2015, 134, 880–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, T.W.; Jiang, S.L.; Wu, J.C.; Liu, H.S.; He, Y.D. Simulation of flow and mixing for highly viscous fluid in a twin screw extruder with a conveying element using parallelized smoothed particle hydrodynamics. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2020, 212, 115311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.R.; Liu, M.B. Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics: A Meshfree Method; World Scientific Publishing Co.: Hackensack, HJ, USA, 2003; pp. 40–115. [Google Scholar]
- Molteni, D.; Colagrossi, A. A simple procedure to improve the pressure evaluation in hydrodynamic context using the SPH. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2009, 180, 861–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Yang, P.; Yu, G.M.; Yang, C.; Zhu, L.Y. 3D numerical modelling of tailings dam breach run out flow over complex terrain: A multidisciplinary procedure. Water 2020, 12, 2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, T.W.; Wu, J.C. Simulation of non-Newtonian flows in a partially filled twin-screw extruder by smoothed particle hydrodynamics. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2022, 63, 802–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leimkuhler, B.J.; Reich, S.; Skeel, R.D. Integration methods for molecular dynamic. In Mathematical Approaches to Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1996; pp. 161–189. [Google Scholar]
- Adami, S.; Hu, X.Y.; Adams, N.A. Transport-velocity formulation for smoothed particle hydrodynamics. J. Comput. Phys. 2013, 241, 29–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avalosse, T.; Crochet, M.J. Finite-Element Simulations of Mixing: 1. Two-Dimensional Flow in Periodic Geometry. Aiche J. 1997, 43, 577–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M.; Cleary, P.; Monaghan, J.J. Analysis of mixing in a Twin-Cam mixer. Aiche J. 2008, 54, 1987–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eitzlmayr, A.; Matić, J.; Khinast, J. Analysis of flow and mixing in screw elements of corotating twin-screw extruders via SPH. Aiche J. 2017, 63, 2451–2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez, J.M.; Fourtakas, G.; Altomare, C.; Canelas, R.B.; Tafuni, A.; García-Feal, O.; Martínez-Estévez, I.; Mokos, A.; Vacondio, R.; Crespo, A.J.C.; et al. DualSPHysics: From fluid dynamics to multiphysics problems. Comput. Part. Mech. 2022, 9, 867–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Item | Mark | Twin Screw | Barrel |
|---|---|---|---|
| Root diameter (mm) | DR | 40 | / |
| Crest diameter (mm) | DC | 60 | / |
| Root angle (degree) | α | 22.88 | / |
| Crest angle (degree) | β | 22.88 | / |
| Center line (mm) | CL | 51 | / |
| Lead/length (mm) | L | 60 | 60 |
| Gap between screws (mm) | G1 | 1 | / |
| Gap between screw and barrel (mm) | G2 | 1 | |
| Number of threads | NT | 2 | / |
| Inner diameter (mm) | D | / | 62 |
| Case No. | State | Excitation | Viscosity | dp | dt | ω | f | A | c | Number of Particles | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pa.s | mm | s | kg/m3 | °/s | Hz | ° | m/s | Total | Fluid | Boundary | |||
| 1 | fully filled | false | 1 | 0.25 | 3.75 × 10−6 | 1000 | 360 | 0 | 0 | 20 | 9,990,642 | 8,824,766 | 1,165,876 |
| 2 | true | 360 + 6sin(10πt) | 5 | 6 | |||||||||
| 3 | half filled | false | 360 | 0 | 0 | 5,563,596 | 4,397,720 | ||||||
| 4 | true | 360 + 6sin(10πt) | 5 | 6 | |||||||||
| Case No. | State | Max Velocity | Delta | Max Pressure | Delta |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| m/s | % | Pa | % | ||
| 1 | fully filled | 0.455 | 30.1% | 7842 | 19.8% |
| 2 | 0.592 | 9392 | |||
| 3 | half filled | 0.800 | −10.4% | 5452 | 23.5% |
| 4 | 0.717 | 6731 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, T.; Liu, H.; Dong, T.; Lai, J.; Yu, W.; Yu, Z.; Yu, H. Numerical Simulation of Rotational Speed Sinusoidal Pulsation for Enhancing Polymer Processing Based on Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics. Polymers 2025, 17, 415. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17030415
Liu T, Liu H, Dong T, Lai J, Yu W, Yu Z, Yu H. Numerical Simulation of Rotational Speed Sinusoidal Pulsation for Enhancing Polymer Processing Based on Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics. Polymers. 2025; 17(3):415. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17030415
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Tianlei, Hesheng Liu, Tianwen Dong, Jiamei Lai, Wei Yu, Zhong Yu, and Huiwen Yu. 2025. "Numerical Simulation of Rotational Speed Sinusoidal Pulsation for Enhancing Polymer Processing Based on Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics" Polymers 17, no. 3: 415. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17030415
APA StyleLiu, T., Liu, H., Dong, T., Lai, J., Yu, W., Yu, Z., & Yu, H. (2025). Numerical Simulation of Rotational Speed Sinusoidal Pulsation for Enhancing Polymer Processing Based on Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics. Polymers, 17(3), 415. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17030415






