Microwave-Assisted In-Situ Synthesis of Polyethersulfone–ZnO Nanocomposite Membranes for Dye Removal: Enhanced Antifouling, Self-Cleaning, and Antibacterial Properties
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Microwave-Assisted Synthesis of Zinc-Oxide Nanoparticles
2.3. Membrane Preparation
2.4. Nanoparticle Characterization
2.5. Membrane Characterization
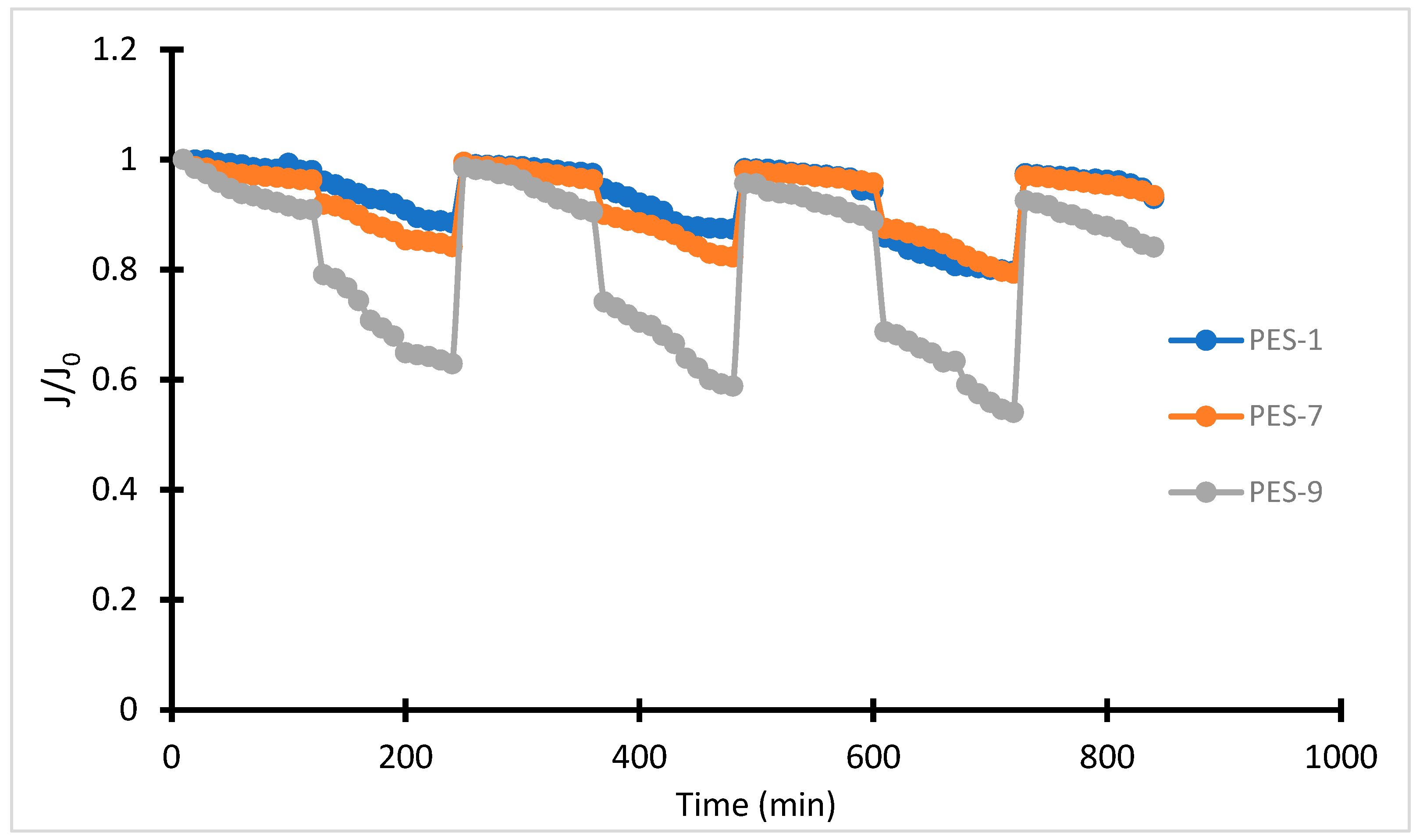
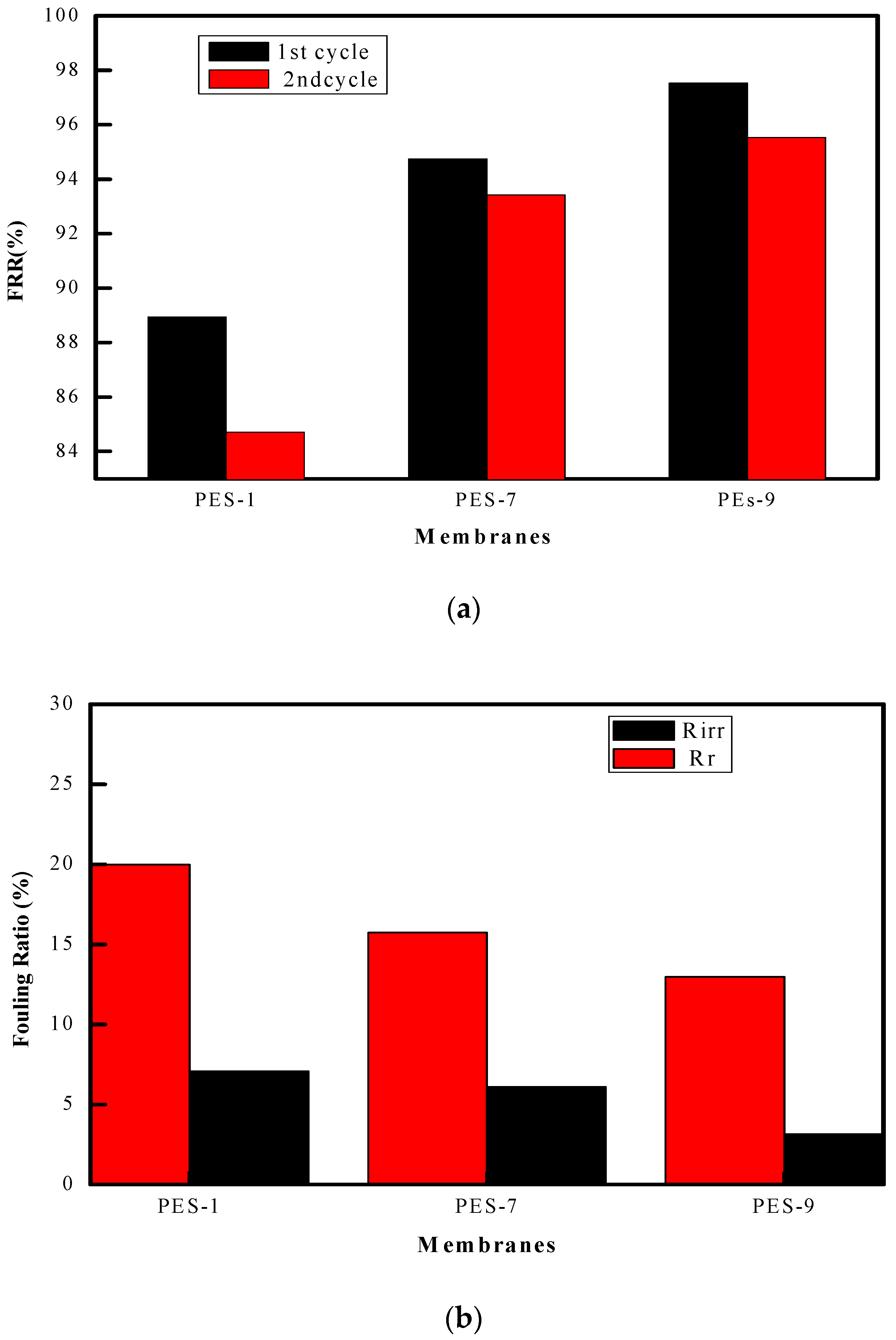
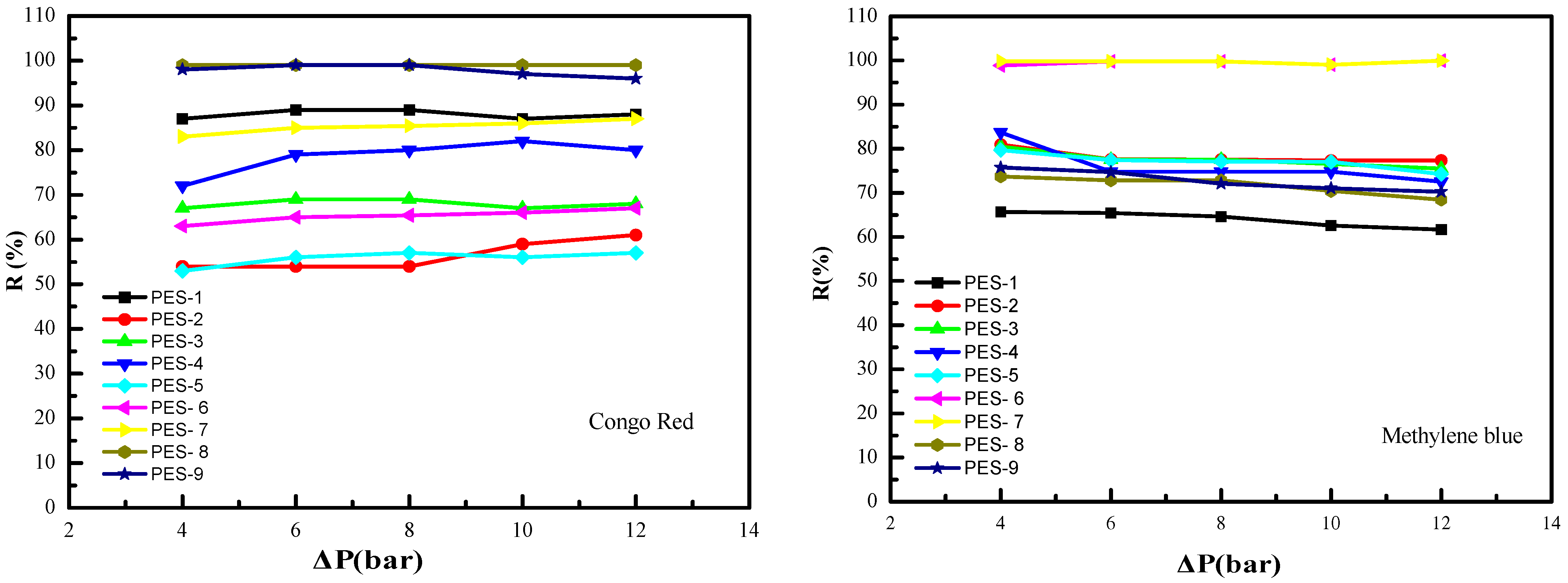
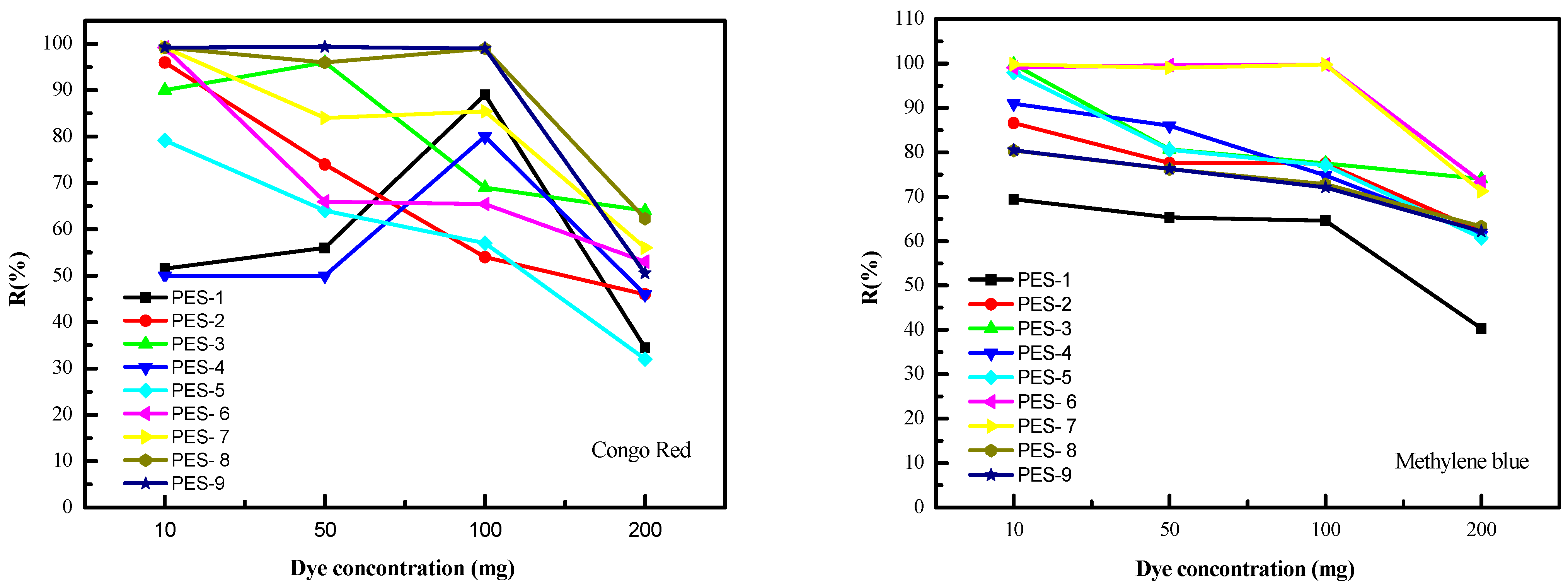
2.6. Antifouling Property
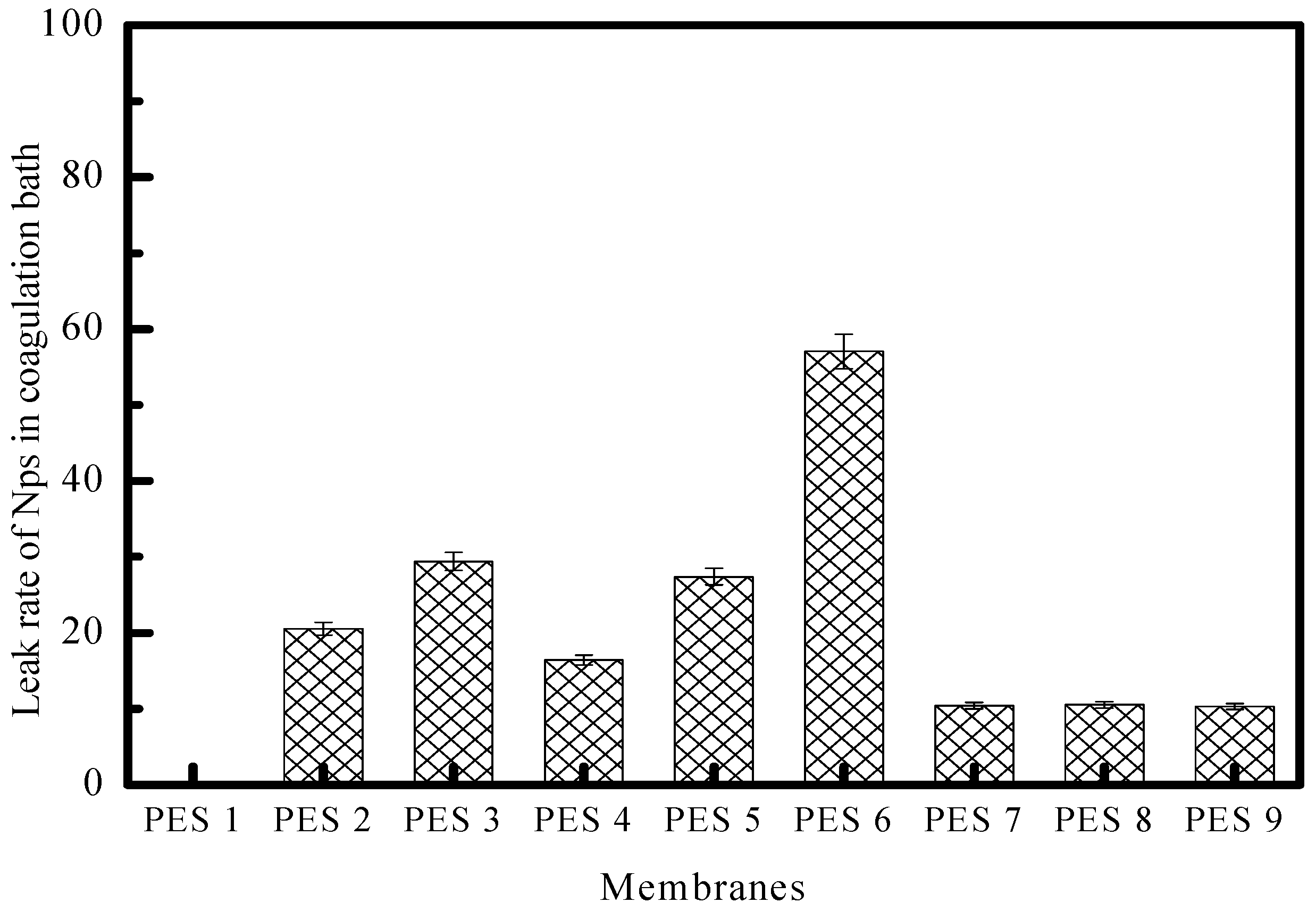
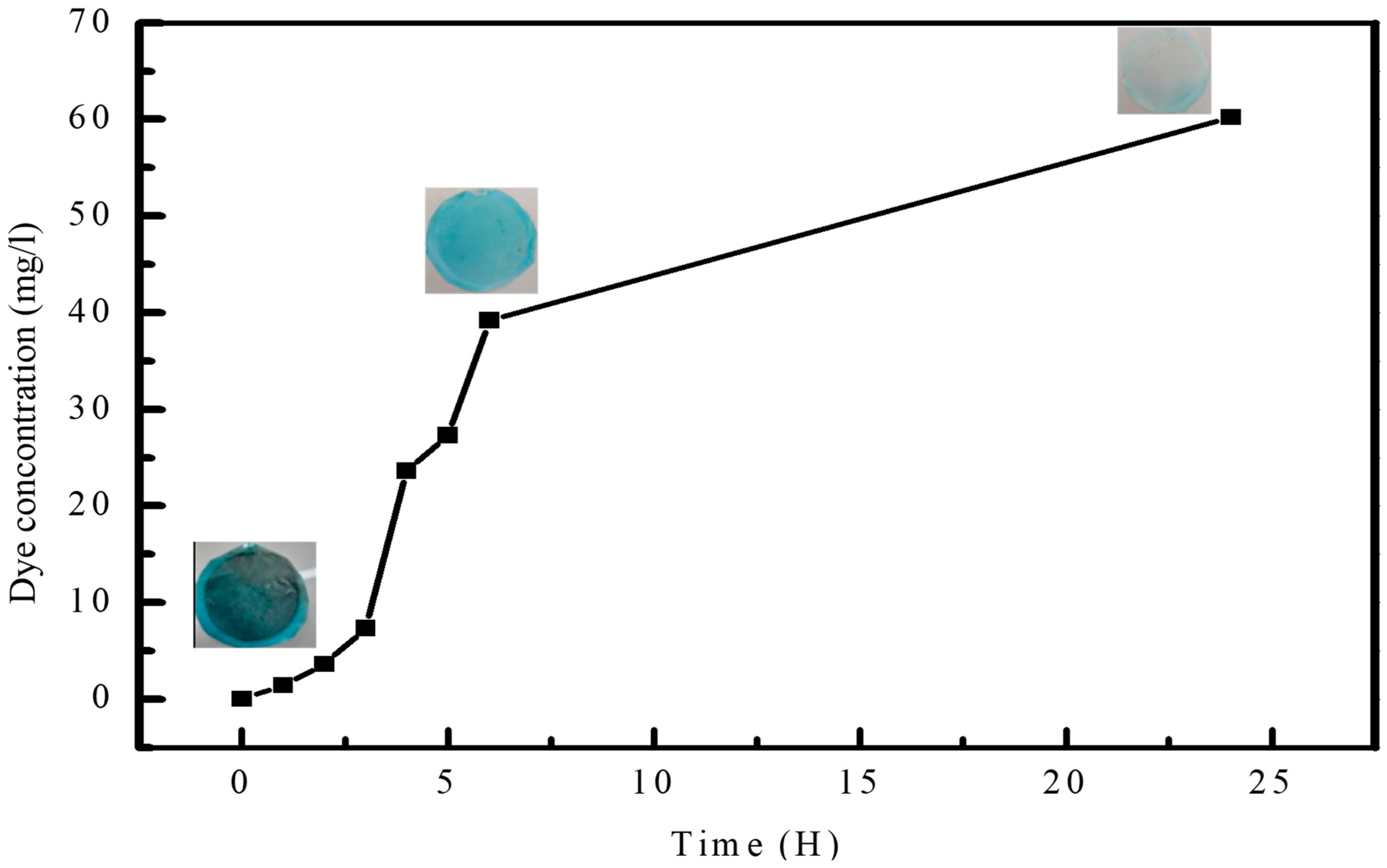
2.7. ZnO Nanoparticle Leakage During NIPS
2.8. Antibacterial Activity
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Nanoparticle Characterization
| The Authors | ƛmax (nm) | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| N. M. Shamhari et al. | 357 | [31] |
| M. Pudukudy et al. | 378 | [32] |
| P. Fageria et al. | 369 | [33] |
| S. Fakhari et al. (bulk) | 385 | [28] |
| S. Fakhari et al. (NPs) | 350 | [28] |
| A. Samy et al. | 376 | [34] |
| C. Taranath et al. | 374 | [35] |
| A. M. Ismail et al. | 370 | [36] |
| B. Bulcha et al. | 376 | [37] |
| In this work | 356 | - |
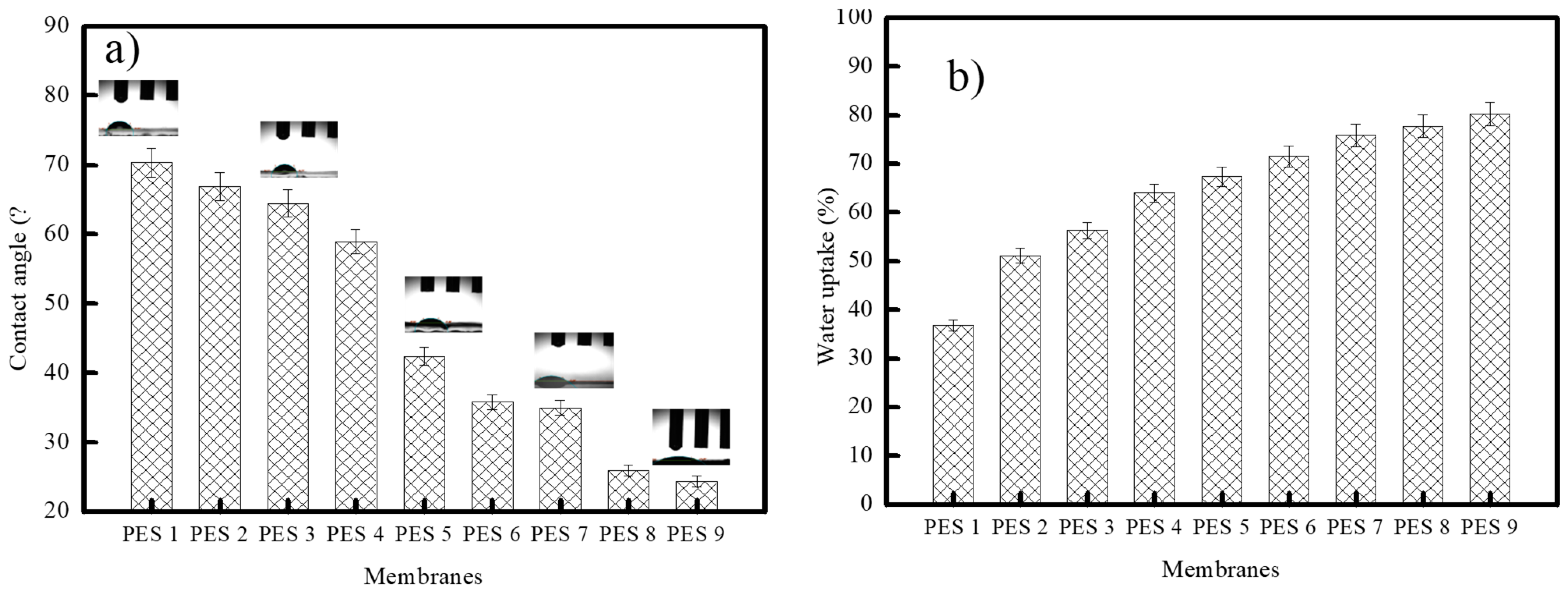
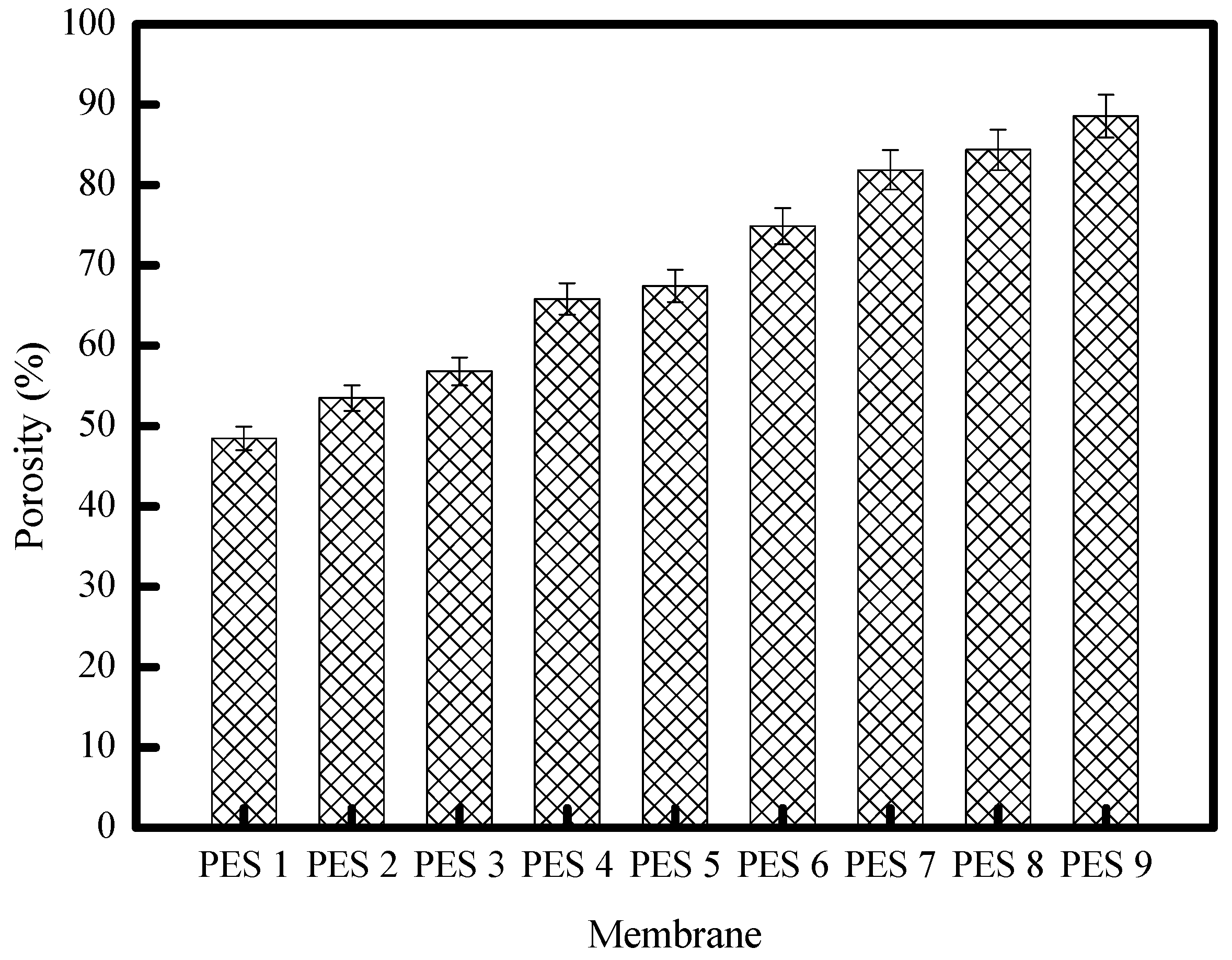
3.2. Membrane Characterization
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CA | cellulose acetate |
| PES | Polyethersulfone |
| PVDF | polyvinylidene fluoride |
| PVP | Polyvinylpyrrolidone |
| BSA | bovine serum albumin |
| MB | methylene blue |
| RG | Congo red |
| DMF | N,N, Dimethylformamide |
| MF | Microfiltration |
| UF | Ultrafiltration |
| NF | Nanofiltration |
| OR | reverse osmosis |
| SEM | Scanning Electron Microscopy |
| AFM | Atomic Force Microscopy |
| FTIR | Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy |
| ZnO | zinc oxide |
References
- Kusworo, T.D.; Nugraheni, R.E.; Aryanti, N. The Effect of Membrane Modification Using TiO2, ZnO, and GO Nanoparticles: Challenges and Future Direction in Wastewater Treatment. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2021; Volume 1053, p. 012135. [Google Scholar]
- Shirkoohi, M.G.; Tyagi, R.D.; Vanrolleghem, P.A.; Drogui, P. Artificial intelligence techniques in electrochemical processes for water and wastewater treatment: A review. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2022, 20, 1089–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.; Yu, D.; Wang, D.; Yang, T.; Li, Z.; Wu, M.; Petru, M.; Crittenden, J. Accelerating Fe(III)/Fe(II) cycle via Fe(II) substitution for enhancing Fenton-like performance of Fe-MOFs. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2021, 286, 119859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Wang, Y.; Wu, M.; Zhang, L.; Wang, L.; Ni, H. Surface functionalization of cellulose with hyperbranched polyamide for efficient adsorption of organic dyes and heavy metals. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 232, 774–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ounifi, I.; Guesmi, Y.; Ursino, C.; Castro-Muñoz, R.; Agougui, H.; Jabli, M.; Hafiane, A.; Figoli, A. Synthesis and Characterization of a Thin-Film Composite Nanofiltration Membrane Based on Polyamide-Cellulose Acetate: Application for Water Purification. J. Polym. Environ. 2022, 30, 707–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.A.; Rehan, Z.A.; Alharthi, S.S.; Alosaimi, E.H.; Gzara, L.; El-Shahawi, M.S.; Alamry, K.A.; Akhtar, K.; Bakhsh, E.M.; Asiri, A.M.; et al. Polyethersulphone coated Ag-SiO2 nanoparticles: A multifunctional and ultrafiltration membrane with improved performance. Desalination Water Treat. 2021, 239, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatanpour, V.; Pasaoglu, M.E.; Barzegar, H.; Teber, O.O.; Kaya, R.; Bastug, M.; Khataee, A.; Koyuncu, I. Cellulose acetate in fabrication of polymeric membranes: A review. Chemosphere 2022, 295, 133914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ounifi, I.; Saidi, N.; Kahloul, M.; Sealey, K.S.; Hafiane, A.; Ferjani, E. Synthesis and characterization of ultrafiltration membranes by phase inversion and by UroPathogenic Escherichia coli retention performance. Desali. Wat. Treat. 2019, 163, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Xiao, K.; Mo, Y.; Huang, X. A novel ZnO nanoparticle blended polyvinylidene fluoride membrane for anti-irreversible fouling. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 394, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arefi-Oskoui, S.; Khataee, A.; Behrouz, S.J.; Vatanpour, V.; Gharamaleki, S.H.; Orooji, Y.; Safarpour, M. Development of MoS2/O-MWCNTs/PES blended membrane for efficient removal of dyes, antibiotic, and protein. Separ. Purif. Technol. 2022, 280, 119822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ounifi, I.; Guesmi, Y.; Ursino, C.; Santoro, S.; Mahfoudhi, S.; Figoli, A.; Ferjani, E.; Hafiane, A. Antifouling membranes based on cellulose acetate (CA) blended with poly (acrylic acid) for heavy metal remediation. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gzara, L.; Rehan, Z.A.; Simone, S.; Galiano, F.; Hassankiadeh, N.T.; Al-Sharif, S.F.; Figoli, A.; Drioli, E. Tailoring PES membrane morphology and properties via selected preparation parameters. J. Polym. Eng. 2016, 37, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, L.; Sugumaran, J.; Shoparwe, N.F. Antifouling properties of PES membranes by blending with ZnO nanoparticles and NMP–acetone mixture as solvent. Membranes 2018, 8, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, K.; Hane, Y.; Watanabe, Y.; Amy, G.; Ohkuma, N. Irreversible membrane fouling during ultrafiltration of surface water. Water Res. 2004, 38, 3431–3441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otitoju, T.A.; Ahmad, A.L.; Ooi, B.S. Recent advances in hydrophilic modification and performance of polyethersulfone (PES) membrane via additive blending. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 22710–22728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, A.L.; Pang, W.Y.; Shafie, Z.M.H.M.; Zaulkiflee, N.D. PES/PVP/TiO2 mixed matrix hollow fiber membrane with antifouling properties for humic acid removal. J. Water Process Eng. 2019, 31, 100827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boughdiri, A.; Ounifi, I.; Chemingui, H.; Ursino, C.; Gordano, A.; Zouaghi, M.O.; Hafiane, A.; Figoli, A.; Ferjani, E. A preliminary study on cellulose acetate composite membranes: Effect of nanoparticles types in their preparation and application. Mater. Res. Express 2022, 9, 015003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallada, R.; Menéndez, M. (Eds.) Inorganic Membranes: Synthesis, Characterization and Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Huang, H.; Bernstein, R. Zwitterionic hydrogel modified reduced graphene oxide/ZnO nanocomposite blended membrane with high antifouling and antibiofouling performances. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 613, 426–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, R.Z.; Gzara, L.; Khan, S.B.; Alamry, K.A.; ElShahawi, M.S.; Albeirutty, M.H.; Figoli, A.; Drioli, E. Synthesis and characterization of silver Nanoparticles- filled polyethersulfone membranes for antibacterial and anti-biofouling application. Recent Pat. Nanotech. 2016, 10, 231–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gzara, L.; Ahmad, R.Z.; Khan, S.B.; Alamry, K.A.; ElShahawi, M.S.; Figoli, A.; Drioli, E. Preparation and characterization of PES-cobalt nanocomposite membranes with enhanced anti-fouling properties and performances. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2016, 66, 405–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Yan, W.T.; Shi, M.Q.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J.X.; Wang, S.C. Improving permeability and antifouling performance of polyethersulfone ultrafiltration membrane by incorporation of ZnO-DMF dispersion containing nano-ZnO and polyvinylpyrrolidone. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 478, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusworo, T.D.; Widayat, W.; Utomo, D.P.; Pratama, Y.H.S.; Arianti, R.A.V. Performance evaluation of modified nanohybrid membrane polyethersulfone-nanoZnO (PES-nanoZnO) using three combination effect of PVP, irradiation of ultraviolet and thermal for biodiesel purification. Renew. Energy 2020, 148, 935–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusworo, T.D.; Utomo, D.P. Performance evaluation of double stage process using nanohybrid PES/SiO2-PES membrane and PES/ZnO-PES membranes for oily wastewater treatment to clean water. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 6077–6086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, Y.J.; Choi, E.Y.; Kim, S.W.; Kim, C.K. Fabrication and characterization of a novel polyethersulfone/aminated polyethersulfone ultrafiltration membrane assembled with zinc oxide nanoparticles. Polymer 2016, 87, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Huang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Li, R.; Xu, Y.; Jakaj, G.; Lin, H. Polymeric membranes incorporated with ZnO nanoparticles for membrane fouling mitigation: A brief review. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figoli, A.; Ursino, C.; Santoro, S.; Ounifi, I.; Chekir, J.; Hafiane, A.; Ferjani, E. Cellulose acetate nanofiltration membranes for cadmium remediation. J. Membr. Sci. Res. 2020, 6, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhari, S.; Jamzad, M.; Fard, H.K. Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles: A comparison. Green Chem. Lett. Rev. 2019, 12, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayalakshmi, U.; Chellappa, M.; Anjaneyulu, U.; Manivasagam, G.; Sethu, S. Influence of Coating Parameter and Sintering Atmosphere on the Corrosion Resistance Behavior of Electrophoretically Deposited Composite Coatings. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2016, 31, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pudukudy, M.; Yaakob, Z. Facile synthesis of quasi-spherical ZnO nanoparticles with excellent photocatalytic activity. J. Clust. Sci. 2015, 26, 1187–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamhari, N.M.; Wee, B.S.; Chin, S.F.; Kok, K.Y. Synthesis and characterization of zinc oxide nanoparticles with small particle size distribution. Acta Chim. Slov. 2018, 65, 578–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pudukudy, M.; Yaakob, Z. Facile solid state synthesis of ZnO hexagonal nanogranules with excellent photocatalytic activity. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 292, 520–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fageria, P.; Gangopadhyay, S.; Pande, S. Synthesis of ZnO/Au and ZnO/Ag nanoparticles and their photocatalytic application using UV and visible light. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 24962–24972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samy; El-Sherbiny, A.E.; Menazea, A.A. Green synthesis of high impact zinc oxide nanoparticles. Egypt. J. Chem. 2019, 62, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, N.; Taranath, T.C. Limonia acidissima L. leaf mediated synthesis of zinc: A potent tool against Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Int. J. Microbiol. 2016, 5, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismail, M.; Menazea, A.A.; Kabary, H.A.; El-Sherbiny, A.E.; Samy, A. The influence of calcination temperature on structural and antimicrobial characteristics of zinc oxide nanoparticles synthesized by Sol–Gel method. J. Mol. Struct. 2019, 1196, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulcha, B.; Tesfaye, J.L.; Anatol, D.; Shanmugam, R.; Dwarampudi, L.P.; Nagaprasad, N.; Krishnaraj, R.; Nagaprasad, N.; Bhargavi, V.L.N.; Krishnaraj, R. Synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles by hydrothermal methods and spectroscopic investigation of ultraviolet radiation protective properties. J. Nanomat. 2021, 2021, 8617290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badavar, F.; Hajilary, N. Novel ultrafiltration membrane with MXene nanosheet/zinc oxide for water purification with high performance and enhanced antifouling properties. Energy Source Part A 2024, 46, 14404–14422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenzel, R.W. Resistance of Solid Surfaces to Wetting by Water. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1936, 28, 988–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Liu, Z.; Xiao, C. Excellent performance of novel superhydrophobic composite hollow membrane in the vacuum membrane distillation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 268, 118603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamzah, N.; Leo, C.P.; Ooi, B.S. Superhydrophobic PVDF/TiO2-SiO2 Membrane with Hierarchical Roughness in Membrane Distillation for Water Recovery from Phenolic Rich Solution Containing Surfactant. Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 2019, 37, 609–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusworo, T.D.; Aryanti, N.; Utomo, D.P.; Nurmala, E. Performance Evaluation of PES-ZnO Nanohybrid using a Combination of UV Irradiation and Cross-linking for Wastewater Treatment of the Rubber Industry to Clean Water. J. Membr. Sci. Res. 2021, 7, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, S.H.; Park, C.H. First-Principles Study of the Surface of Wurtzite ZnO and ZnS—Implications for Nanostructure Formation. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 2009, 54, 867–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dipheko, T.D.; Matabola, K.P.; Kotlhao, K.; Moutloali, R.M.; Klink, M. Fabrication and assessment of ZnO modified polyethersulfone membranes for fouling reduction of bovine serum albumin. Inter. J. Polymer Sci. 2017, 2017, 3587019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Bockstaller, M.R.; Matyjaszewski, K. Synthesis and applications of ZnO/polymer nanohybrids. ACS Mat. Lett. 2021, 3, 599–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, N.R.; Hammad, A.; Tahir, M.B.; Rafique, M.; Iqbal, T.; Nabi, G.; Hussain, M.K. Enhanced photocatalytic activity of Al and Fe co-doped ZnOnanorods for methylene blue degradation. Ceram. Inter. 2019, 45, 21430–21435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, Y.; Khoo, L.H.; Ng, L.Y.; Ong, C.B.; Mahmoudi, E.; Rohani, R.; Mohammad, A.W. Novel polyethersulfone-cellulose composite thin film using sustainable empty fruit bunches from Elaeis guineensis for methylene blue removal. Polym. Test. 2020, 86, 106494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houas; Lachheb, H.; Ksibi, M.; Elaloui, E.; Guillard, C.; Herrmann, J.M. Photocatalytic degradation pathway of methylene blue in water. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2001, 31, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasrollahi, N.; Vatanpour, V.; Aber, S.; Mahmoodi, N.M. Preparation and characterization of a novel polyethersulfone (PES) ultrafiltration membrane modified with a CuO/ZnO nanocomposite to improve permeability and antifouling properties. Sep. Purif. Tech. 2018, 192, 369–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, Y.J.; Choi, E.Y.; Choi, N.W.; Kim, C.K. Antibacterial and Hydrophilic Characteristics of Poly(ether sulfone) Composite Membranes Containing Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Grafted with Hydrophilic Polymers. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 7801–7809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padmavathy, N.; Vijayaraghavan, R. Enhanced bioactivity of ZnO nanoparticles—An antimicrobial study. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2008, 9, 035004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



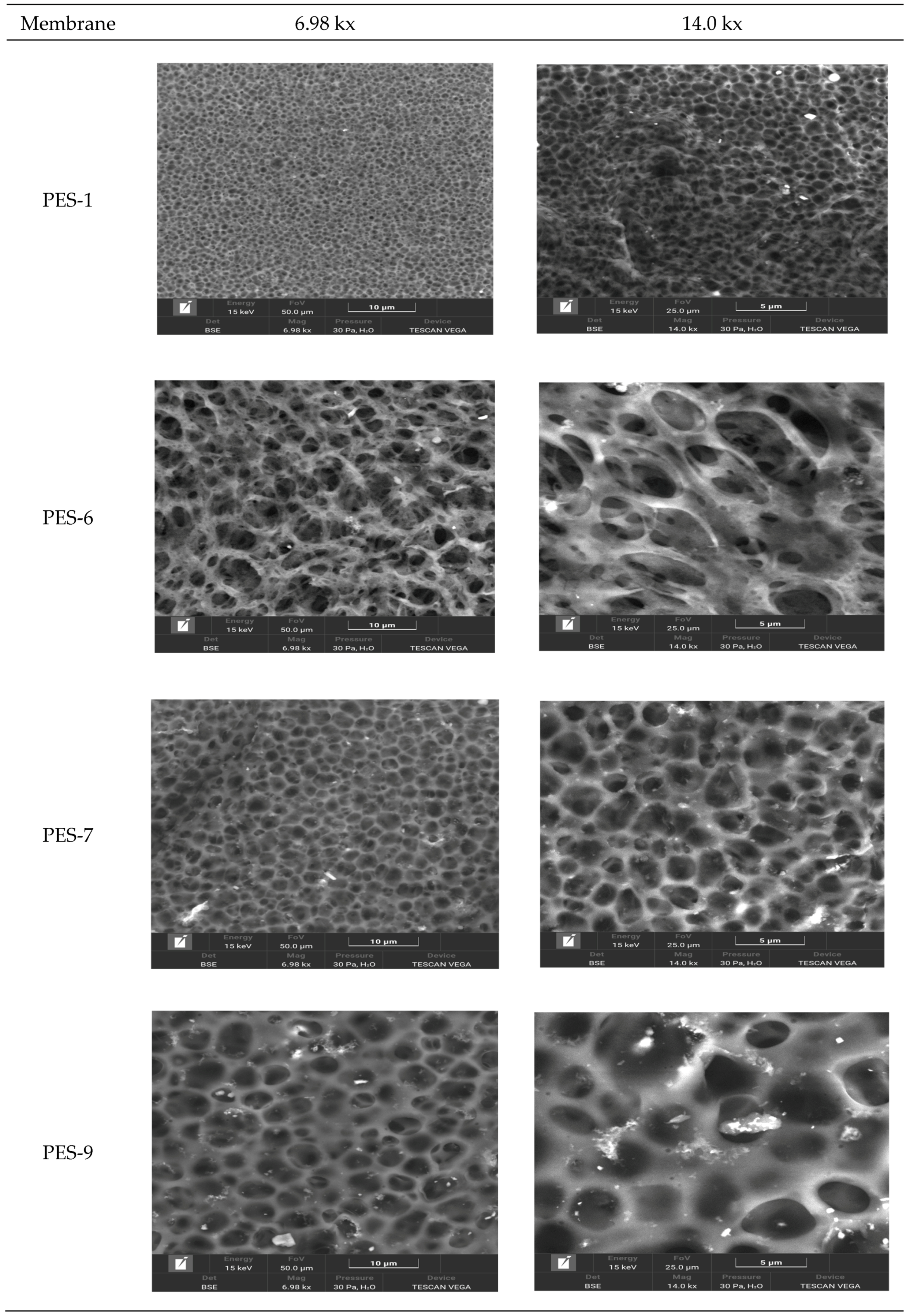
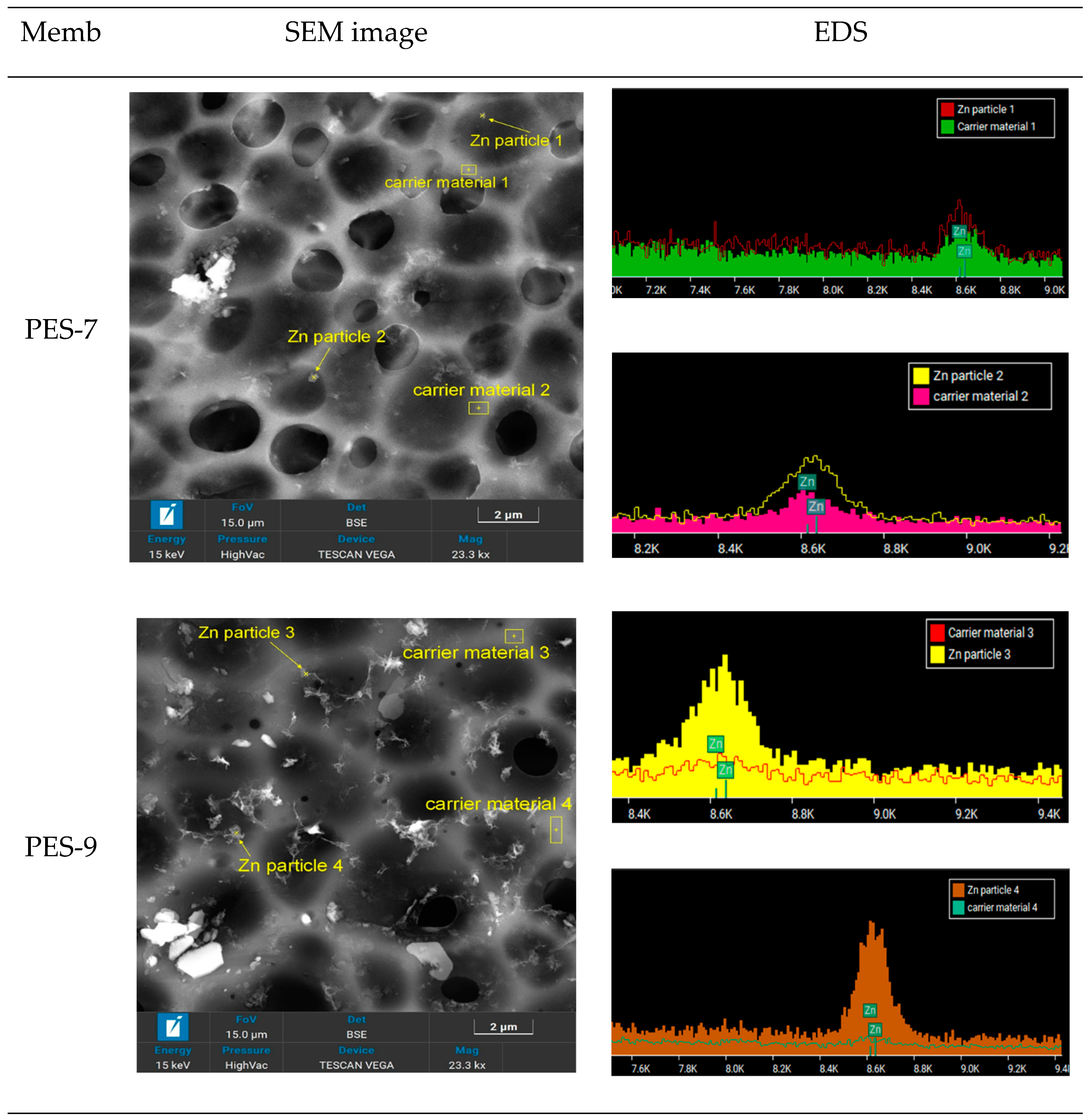
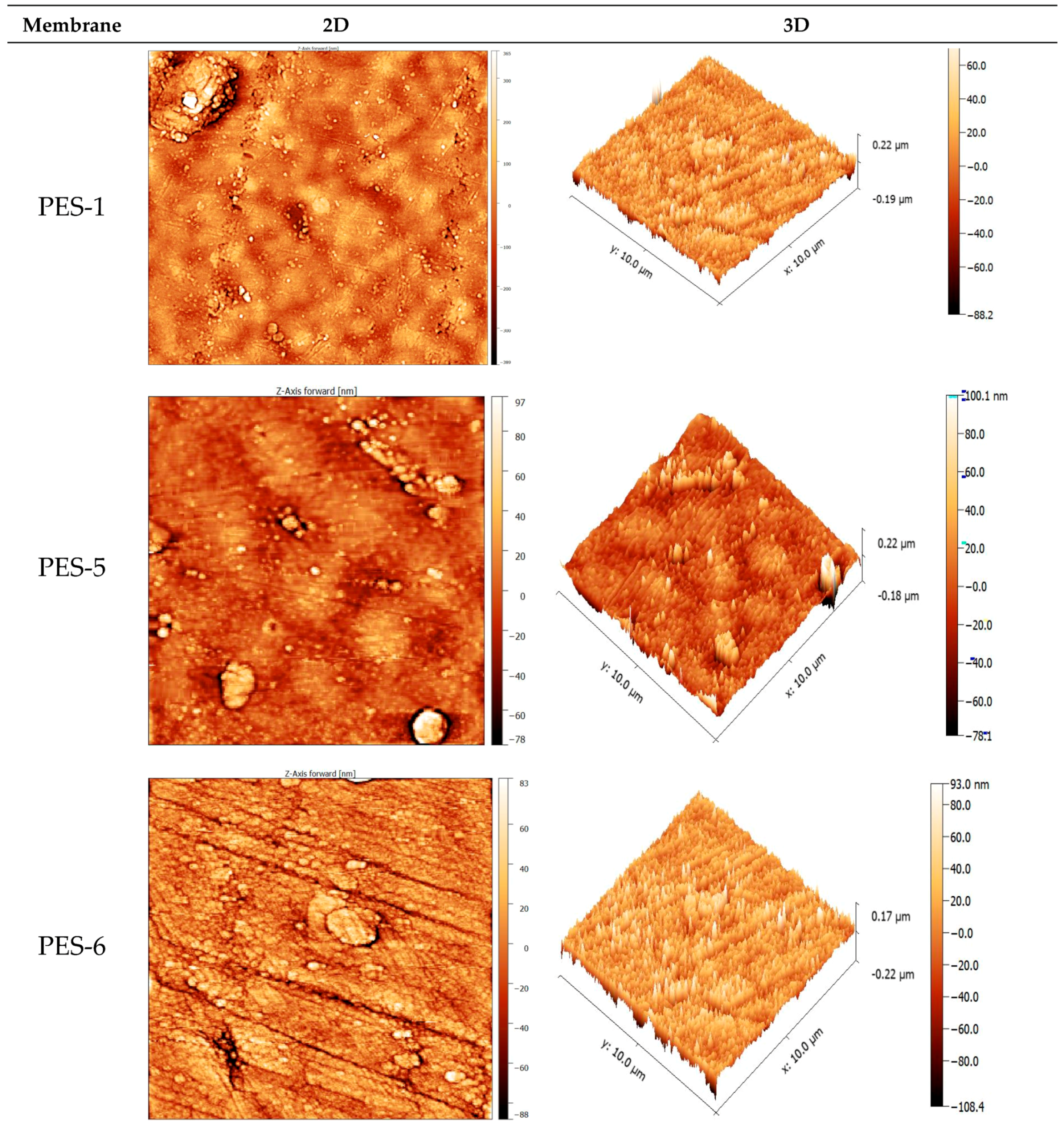

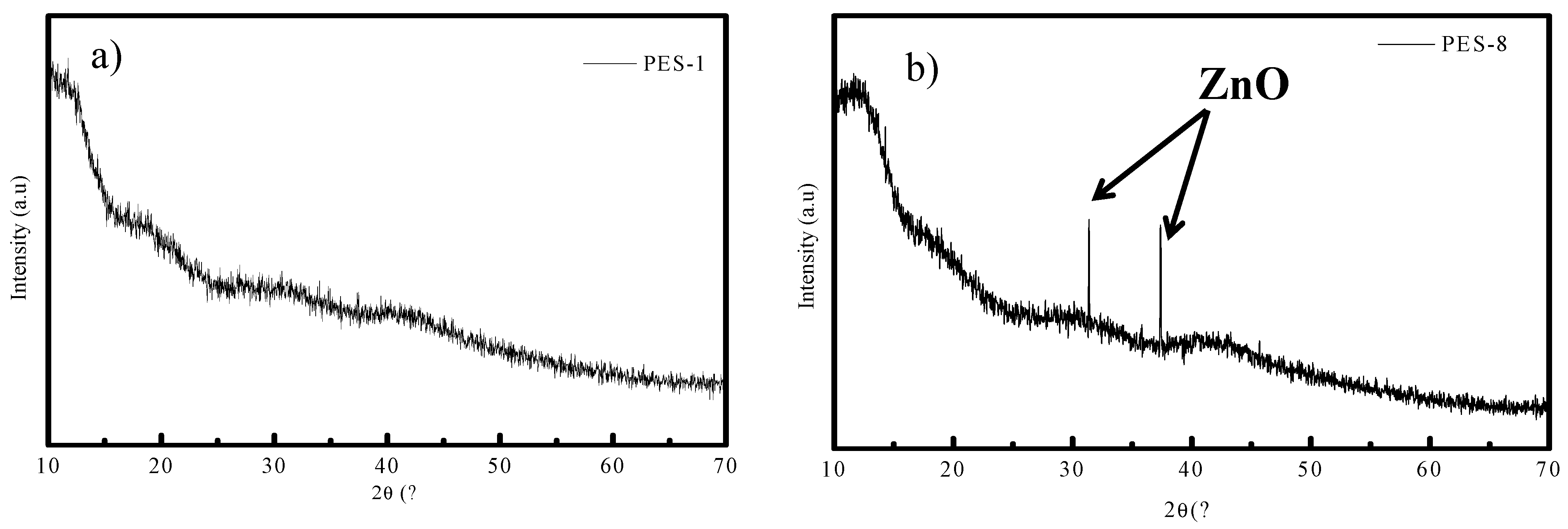

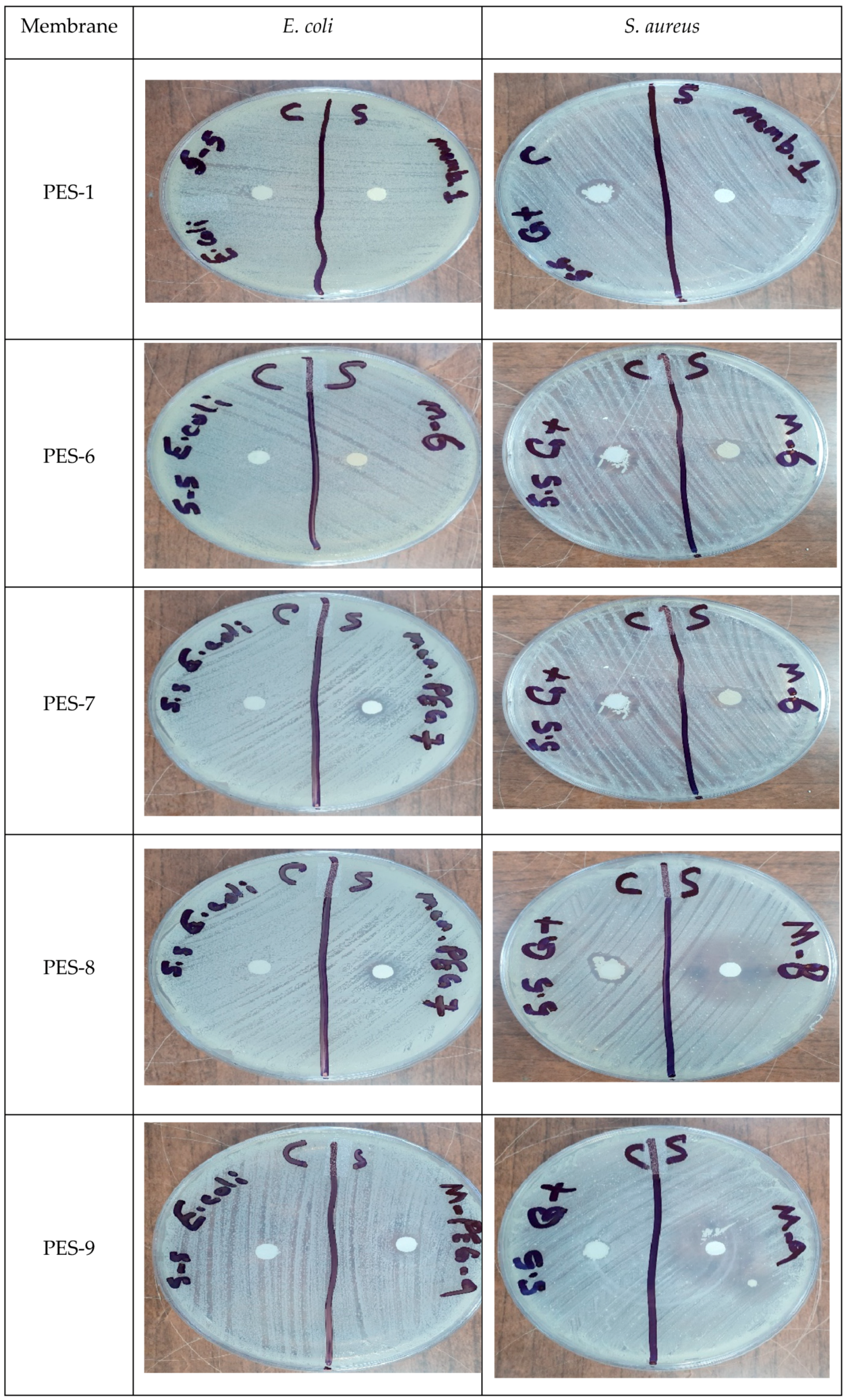
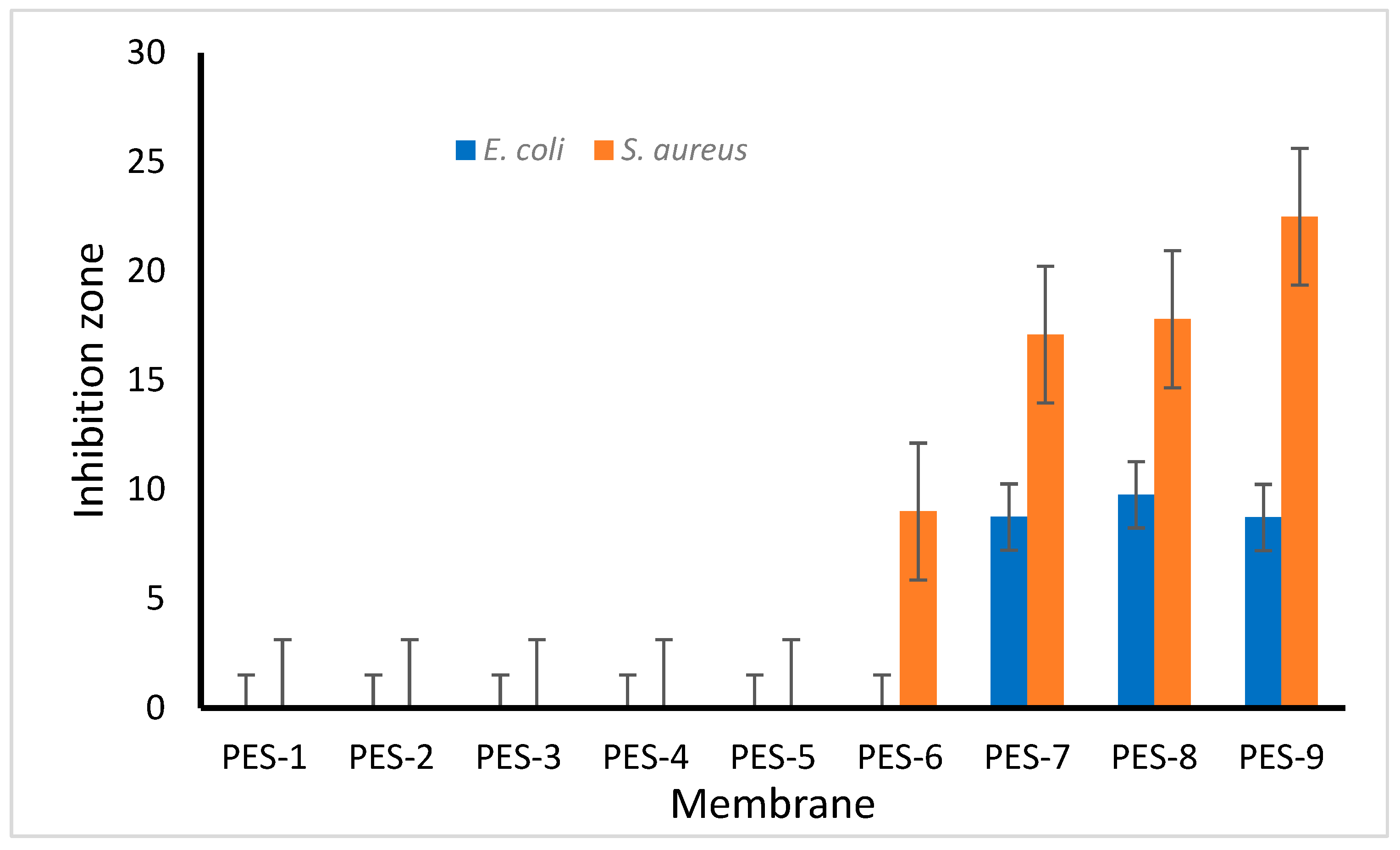
| ZnCl2 (wt%) | PVP (wt%) | Glucose (wt%) | NaOH (5M) (wt%) | PES (wt%) | DMF (wt%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NPs-1 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 70 |
| NPs-2 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 0 | 1 | 69 |
| NPs-3 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 0 | 2 | 68 |
| NPs-4 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 0 | 3 | 67 |
| NPs-5 | 10 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 80 |
| NPs-6 | 10 | 10 | 0 | 10 | 0 | 70 |
| NPs-7 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 0 | 60 |
| NPs-8 | 10 | 10 | 0 | 10 | 1 | 69 |
| NPs-9 | 10 | 10 | 0 | 10 | 2 | 68 |
| NPs-10 | 10 | 10 | 0 | 10 | 3 | 67 |
| PES (wt%) | ZnCl2 (wt%) | DMF (wt%) | Glucose (wt%) | PVP (wt%) | NaOH (5M) (wt%) | Microwave Treatment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PES-1 | 15 | 0 | 83 | 1 | 1 | 0 | With |
| PES-2 | 15 | 0.1 | 82.9 | 1 | 1 | 0 | With |
| PES-3 | 15 | 0.2 | 82.8 | 1 | 1 | 0 | With |
| PES-4 | 15 | 0.5 | 82.5 | 1 | 1 | 0 | With |
| PES-5 | 15 | 1 | 82 | 1 | 1 | 0 | Without |
| PES-6 | 15 | 1 | 82 | 1 | 1 | 0 | With |
| PES-7 | 15 | 1 | 82 | 0 | 1 | 1 | With |
| PES-8 | 15 | 2 | 81 | 0 | 1 | 1 | With |
| PES-9 | 15 | 5 | 78 | 0 | 1 | 1 | With |
| Membrane | PES-1 | PES-5 | PES-6 | PES-7 | PES-8 | PES-9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sa (nm) | 108.6 | 42.3 | 34.8 | 52.9 | 86.7 | 129.2 |
| Sq (nm) | 156.3 | 54.7 | 46.8 | 78.9 | 129.5 | 178.6 |
| Permeability (L.m−2.h−1.bar−1) | R2 | |
|---|---|---|
| PES-1 | 12.08 | 0.9957 |
| PES-2 | 21.84 | 0.9846 |
| PES-3 | 32.89 | 0.9926 |
| PES-4 | 37.90 | 0.9959 |
| PES-5 | 47.57 | 0.9914 |
| PES-6 | 63.18 | 0.9992 |
| PES-7 | 69.40 | 0.9877 |
| PES-8 | 70.28 | 0.9877 |
| PES-9 | 76.15 | 0.9933 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gzara, L.; Ounifi, I.; Organji, H.; Khlissa, F.; Moujdin, I.A.; Alsaiari, A.O.; Abdel Salam, M.; Hafiane, A. Microwave-Assisted In-Situ Synthesis of Polyethersulfone–ZnO Nanocomposite Membranes for Dye Removal: Enhanced Antifouling, Self-Cleaning, and Antibacterial Properties. Polymers 2025, 17, 398. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17030398
Gzara L, Ounifi I, Organji H, Khlissa F, Moujdin IA, Alsaiari AO, Abdel Salam M, Hafiane A. Microwave-Assisted In-Situ Synthesis of Polyethersulfone–ZnO Nanocomposite Membranes for Dye Removal: Enhanced Antifouling, Self-Cleaning, and Antibacterial Properties. Polymers. 2025; 17(3):398. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17030398
Chicago/Turabian StyleGzara, Lassaad, Ibtissem Ounifi, Hussam Organji, Faïçal Khlissa, Iqbal Ahmed Moujdin, Abdulmohsen Omar Alsaiari, Mohamed Abdel Salam, and Amor Hafiane. 2025. "Microwave-Assisted In-Situ Synthesis of Polyethersulfone–ZnO Nanocomposite Membranes for Dye Removal: Enhanced Antifouling, Self-Cleaning, and Antibacterial Properties" Polymers 17, no. 3: 398. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17030398
APA StyleGzara, L., Ounifi, I., Organji, H., Khlissa, F., Moujdin, I. A., Alsaiari, A. O., Abdel Salam, M., & Hafiane, A. (2025). Microwave-Assisted In-Situ Synthesis of Polyethersulfone–ZnO Nanocomposite Membranes for Dye Removal: Enhanced Antifouling, Self-Cleaning, and Antibacterial Properties. Polymers, 17(3), 398. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17030398









