Effect of Hydrocolloids on Penetration Tests, Sensory Evaluation, and Syneresis of Milk Pudding
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials
2.2. Milk Pudding Preparation
2.3. Analysis of Textural Characteristics
2.4. Measurement % Syneresis
2.5. Sensory Evaluation
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
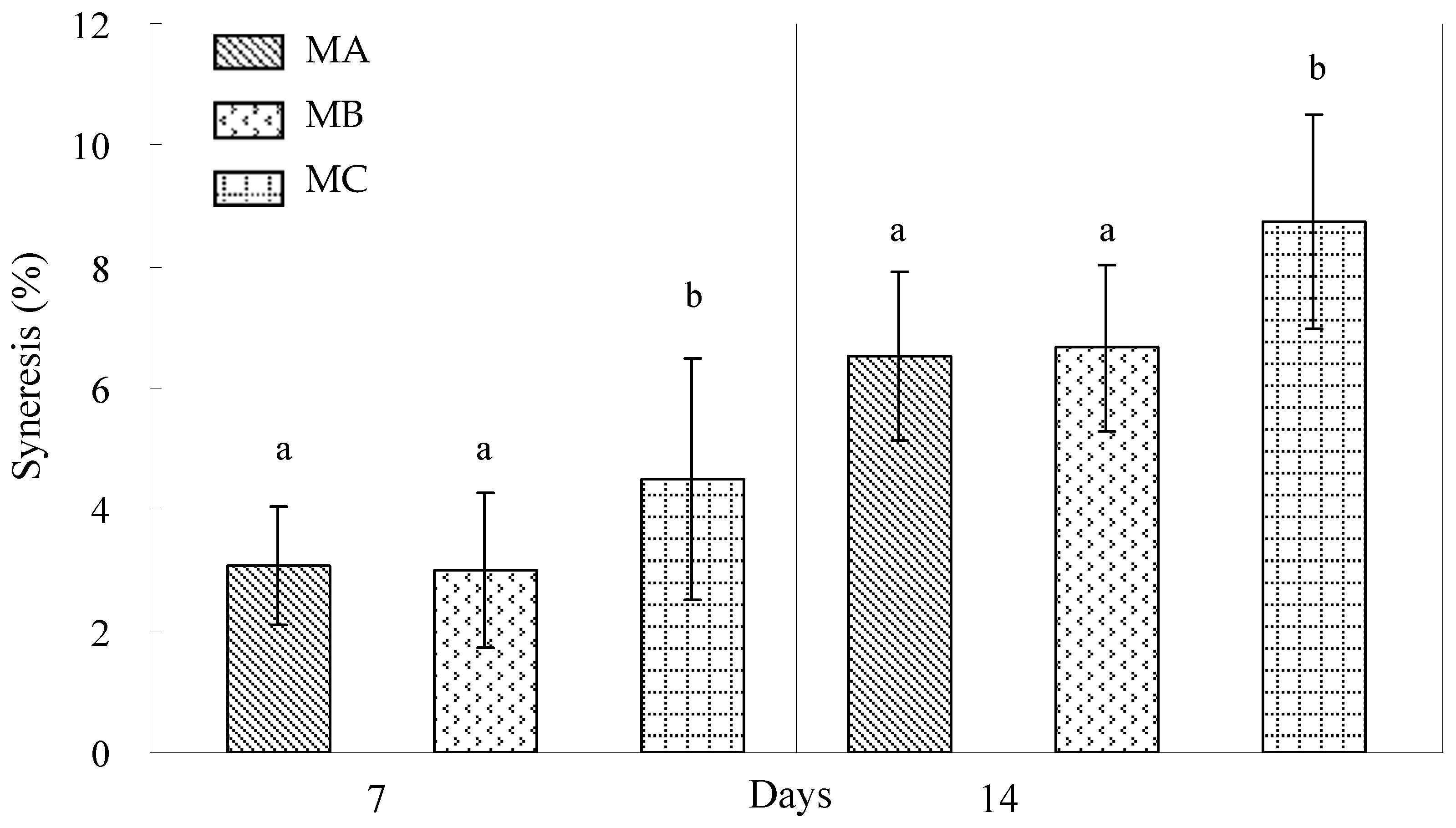
3.1. Analysis of Textural Characteristics and % Syneresis
| Type of Polysaccharide | Breaking Force (B.F.) | Breaking Point (B.P.) | Gel Strength (G.S.) | Rigidity (R.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (g) | (mm) | (g × mm) | (g/mm) | |
| κ-carrageenan | 22.7 ± 0.3 d | 5.41 ± 0.14 c | 123 ± 4 d | 4.20 ± 0.10 d |
| ι-carrageenan | 11.7 ± 0.3 a | 6.34 ± 0.13 e | 74 ± 3 a | 1.84 ± 0.02 a |
| Gellan gum | 18.8 ± 0.5 c | 5.23 ± 0.10 a | 98 ± 3 c | 3.59 ± 0.12 c |
| Gelatin | 14.6 ± 0.5 b | 6.25 ± 0.14 d | 91 ± 3 b | 2.34 ± 0.08 b |
| Agar | 26.6 ± 0.4 e | 5.37 ± 0.03 b | 143 ± 2 e | 4.95 ± 0.06 e |

3.2. Sensory Evaluation of Milk Pudding
4. Discussion
4.1. Analysis of Textural Characteristics and % Syneresis
4.2. Sensory Evaluation of Milk Pudding
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- de Wijk, R.A.; Van Gemert, L.J.; Terpstra, M.E.J.; Wilkinson, C.L. Texture of semi-solids; sensory and instrumental measurements on vanilla custard desserts. Food Qual. Prefer. 2003, 14, 305–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheidae, Z.; Sarmadi, B.; Hosseini, S.M.; Javanmardi, F.; Kianoush, K.D.; Mortazavian, A.M. Influence of κ-carrageenan, modified starch and inulin addition on rheological and sensory properties of non-fat and non-added sugar dairy dessert. Curr. Nutr. Food Sci. 2020, 16, 462–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imeson, A.P. Carrageenan. In Handbook of Hydrocolloids; Philips, G.O., Williams, P.A., Eds.; Wood-head Publishing Ltd.: Cambridge, UK, 2000; pp. 87–102. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, H.T.; Tsai, J.S.; Liao, H.H.; Sung, W.C. The effect of hydrocolloids on penetration tests and syneresis of binary gum gels and modified corn starch-gum gels. Gels 2023, 9, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langendorff, V.; Cuvelier, G.; Michon, C.; Launay, B.; Parker, A.; De Kruif, C.G. Effects of carrageenan type on the behaviour of carrageenan/milk mixtures. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 14, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbeken, D.; Bael, K.; Thas, O.; Dewettinck, K. Interactuions between κ-carrageenan, milk proteins and modified starch in sterilized dairy desserts. Int. Dairy J. 2006, 16, 482–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agoda-Tandjawa, G.; Le Garnec, C.; Boulenguer, P.; Gilles, M.; Langendorff, V. Rheological behavior of starch/carrageenan/milk proteins mixed systems: Role of each biopolymer type and chemical characteristics. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 73, 300–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depypere, F.; Verbeken, D.; Thas, O.; Dewettinck, K. Mixture design approach on the dynamic rheological and uniaxial compression behaviour of milk desserts. Food Hydrocoll. 2003, 17, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbeken, D.; Thas, O.; Dewettinck, K. Textural properties of gelled dairy desserts containing κ-carrageen and starch. Food Hydrocoll. 2004, 18, 817–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, K.; Kamilah, H.; Shang, P.L.; Sulaiman, S.; Ariffin, F.; Alias, A.K. A review: Interaction of starch/non-starch hydrocolloid blending and the recent food applications. Food Biosci. 2017, 19, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sodini, I.; Remeuf, F.; Haddad, S.; Corrieu, G. The relative effect of milk base, starter, and process on yogurt texture: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2004, 44, 113–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marta, H.; Cahyana, Y.; Djali, M. The effect of starch-hydrocolloid interaction on starch digestibility, pasting and physicochemical properties: A review. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 443, 012084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christianson, D.D. Hydrocolloid interactions with starches. In Food Carbohydrates; Lineback, R.D., Inglett, G.E., Eds.; AVI Publishing Co.: Westport, CT, USA, 1982; pp. 399–419. [Google Scholar]
- Lethuant, L.; Brossard, C.; Rousseau, F.; Bousseau, B.; Genot, C. Sweetness-texture interactions in model dairy desserts: Effect of sucrose concentration and the carrageenan type. Int. Dairy J. 2003, 13, 631–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, P.T.M.; Kravchuk, O.; Bhandari, B.; Prakash, S. Effect of different hydrocolloids on texture, rheology, tribology and sensory perception of texture and mouthfeel of low-fat pot-set yoghurt. Food Hydrycoll. 2017, 72, 90–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supavititpatana, P.; Wirjantoro, T.I.; Apichartsrangkoon, A.; Raviyan, P. Addition of gelatin enhanced gelation of corn-milk yogurt. Food Chem. 2008, 106, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duboc, P.; Mollet, B. Application of exopolysaccharides in the dairy industry. Int. Dairy J. 2001, 11, 759–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagal-Kestwal, D.R.; Pan, M.H.; Chiang, B.H. Properties and applications of gelatin, Pectin, and carrageenan gels. In Bio Monomers for Green Polymeric Composite Materials; Visakh, P.M., Bayraktar, O., Menon, G., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: West Sussex, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Therkelsen, G.H. Carrageenan. In Industrial Gums; Whister, R.L., BeMiller, J.N., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1993; pp. 145–180. [Google Scholar]
- Richardson, R.K.; Goycoolea, F.M. Rheological measurement of κ-carrageenan during gelation. Carbohydr. Polym. 1994, 24, 233–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.H.; Xu, S.Y.; Wang, Z. Gelation properties of flaxseed gum. J. Food Eng. 2006, 77, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, A.A.; Norziah, M.H.; Seow, C.C. Methods for the study of starch retrogradation. Food Chem. 2000, 7, 9–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Roos, Y.H.; Miao, S. Comparative studies of structural and thermal gelation behaviours of soy, lentil and whey protein: A pH-dependency evaluation. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 146 Pt A, 109240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charoenrein, S.; Tatirat, O.; Muadklay, J. Use of centrifugation-filtration fordetermination of syneresis in freeze-thaw starch gels. Carbohydr. Polym. 2008, 73, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moskowitz, H.R. Sensory intensity versus hedonic functions: Classical psychophysical approaches. J. Food Qual. 1982, 5, 109–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junaid, M.; Javed, I.; Abdullah, M.; Gulzar, M.; Younas, U.; Nasir, J.; Ahmad, N. Development and quality assessment of flavored probiotic acidophilus milk. J. Anim. Plant Sci. 2013, 23, 1342–1346. [Google Scholar]
- Morris, V.J. Starch gelation and retrogradation. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 1990, 1, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Ye, S.; Zuo, X.; Fang, S. Impact of guar gum and locust bean gum addition on the pasting, rheological properties, and freeze-thaw stability of rice starch gel. Foods 2022, 11, 2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arunyanart, T.; Charoenrein, S. Effect of sucrose on the freeze-thaw stability of rice starch gels: Correlation with microstructure and freezeable water. Carbohydr. Polym. 2008, 74, 514–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, L.A.; Rayas-Duarte, P. Freeze-thaw stability of amaranth starch and the effects of salt and sugars. Cereal Chem. 1998, 75, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Lim, S.T.; Chung, H.J. Physical modification of potato starch using mild heating and freezing with minor addition of gums. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 94, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, R.; Tang, J.; Swanson, B.G. Texture properties of high and low acyl mixed gellan gels. Carbohydr. Polym. 2000, 41, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.H.; Baek, M.H.; Cha, D.S.; Park, H.J.; Lim, S.T. Freeze-thaw stabilization of sweet potato starch gel by polysaccharide gums. Food Hydrocoll. 2002, 16, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogsa, I.; Cerar, J.; Jamnik, A.; Tomsic, M. Supramolecular structure of methyl cellulose and lambda- and kappa- carrageenan in water: SAXS study using the string-of-beads model. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 172, 184–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Vries, J.A. Interactions of starch and other hydrocolloids. Carbohydr. Neth. 2002, 8, 14–18. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, V.M.F.; Hung, A.L.; Lii, C.Y. Rheological properties and phase transition of red algal polysaccharide starch composites. Food Hydrocoll. 1999, 13, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Zhang, Y.; Hong, Y.; Gu, Z. Effects of hydrocolloids on corn starch retrogradation. Starch/Starke 2015, 67, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geonzon, L.C.; Kobayashi, M.; Tassieri, M.; Bacabac, R.G.; Adachi, Y.; Matsukawa, S. Microrheological properties and local structure of ι-carrageenan gels probed by using optical tweezers. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 137, 108325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prokopowich, D.J.; Biliaderis, C.G. A comparative study of the effect of sugars on the thermal and mechanical properties of concentrated waxy maize, wheat, potato and pea starch gels. Food Chem. 1995, 52, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhou, D.; Guo, Q.; Liu, C. Textural and structure properties of a κ-carrageenan-konjac gum mix gel: Effects of κ-carrageenan concentration, mixing ratio, sucrose and Ca2+ concentrations and its application in milk pudding. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 3021–3029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayarri, S.; Costell, E.; Duran, L. Influence of low sucrose concentrations on the compression resistance of gellan gum gels. Food Hydrocoll. 2002, 16, 593–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiszman, S.M.; Duran, L. Mechanical properties of kappa carrageen-locust bean gum mixed gels with added sucrose. Food Hydrocoll. 1989, 3, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishinari, K.; Fang, Y.; Rosenthal, A. Human oral processing and texture profile analysis parameters: Bridging the gap between the sensory evaluation and the instrumental measurements. J. Texture Stud. 2019, 50, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekpong, A.; Ngarmsak, T.; Winger, R.J. Comparing sensory methods for the optimization of mango gel snacks. Food Qual. Prefer. 2006, 17, 622–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Commercial Milk Pudding | Breaking Force (B.F.) | Breaking Point (B.P.) | Gel Strength (G.S.) | Rigidity (R.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (g) | (mm) | (g × mm) | (g/mm) | |
| MA | 15.0 ± 0.5 b | 8.75 ± 0.18 a | 131 ± 6 b | 1.72 ± 0.03 b |
| MB | 10.7 ± 0.4 a | 8.76 ± 0.25 a | 94 ± 5 a | 1.23 ± 0.04 a |
| MC | 17.4 ± 0.3 c | 9.82 ± 0.36 b | 171 ± 9 c | 1.77 ± 0.04 c |
| Type of Polysaccharide | Modified Corn Starch | Breaking Force (B.F.) | Breaking Point (B.P.) | Gel Strength (G.S.) | Rigidity (R.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (%) | (g) | (mm) | (g × mm) | (g/mm) | |
| κ-carrageenan | 1.0 | 22.7 ± 0.3 c | 5.41 ± 0.14 c | 123 ± 4 c | 4.20 ± 0.10 b |
| 3.0 | 21.4 ± 0.8 b | 5.12 ± 0.13 b | 109 ± 3 b | 4.18 ± 0.24 b | |
| 5.0 | 17.9 ± 0.6 a | 4.85 ± 0.04 a | 86 ± 2 a | 3.69 ± 0.12 a | |
| ι-carrageenan | 1.0 | 11.7 ± 0.3 c | 6.34 ± 0.13 a | 74 ± 3 c | 1.84 ± 0.02 c |
| 3.0 | 10.5 ± 0.4 b | 6.27 ± 0.22 a | 65 ± 3 b | 1.68 ± 0.10 b | |
| 5.0 | 8.38 ± 0.4 a | 7.27 ± 0.25 b | 60 ± 2 a | 1.16 ± 0.07 a | |
| Gellan gum | 1.0 | 18.8 ± 0.5 c | 5.23 ± 0.10 a | 98 ± 3 c | 3.59 ± 0.12 c |
| 3.0 | 16.1 ± 0.4 b | 5.48 ± 0.17 b | 88 ± 3 b | 2.94 ± 0.11 b | |
| 5.0 | 13.6 ± 0.6 a | 5.43 ± 0.07 b | 73 ± 3 a | 2.51 ± 0.09 a | |
| Gelatin | 1.0 | 14.6 ± 0.5 c | 6.25 ± 0.14 b | 91 ± 4 c | 2.34 ± 0.08 a |
| 3.0 | 13.5 ± 0.5 b | 5.37 ± 0.34 a | 72 ± 4 b | 2.53 ± 0.21 a | |
| 5.0 | 12.5 ± 0.4 a | 5.25 ± 0.19 a | 65 ± 2 a | 2.38 ± 0.13 a | |
| Agar | 1.0 | 26.6 ± 0.4 c | 5.37 ± 0.02 a | 143 ± 2 c | 4.95 ± 0.06 c |
| 3.0 | 24.6 ± 0.5 b | 5.49 ± 0.12 ab | 135 ± 5 b | 4.48 ± 0.08 b | |
| 5.0 | 20.4 ± 0.5 a | 5.55 ± 0.16 b | 113 ± 3 a | 3.68 ± 0.15 a |
| Type of Polysaccharide | Sucrose | Breaking Force (B.F.) | Breaking Point (B.P.) | Gel Strength (G.S.) | Rigidity (R.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (%) | (g) | (mm) | (g × mm) | (g/mm) | |
| κ-arrageenan | 2.5 | 20.4 ± 0.8 a | 5.03 ± 0.15 a | 103 ± 4 a | 4.05 ± 0.24 a |
| 5.0 | 21.4 ± 0.8 b | 5.12 ± 0.13 a | 109 ± 3 b | 4.18 ± 0.24 a | |
| 7.5 | 22.6 ± 0.4 c | 5.32 ± 0.15 b | 120 ± 5 c | 4.25 ± 0.08 a | |
| ι-carrageenan | 2.5 | 9.83 ± 0.7 a | 6.17 ± 0.16 a | 60.6 ± 4 a | 1.60 ± 0.14 a |
| 5.0 | 10.5 ± 0.4 a | 6.27 ± 0.22 a | 65.9 ± 3 b | 1.68 ± 0.10 a | |
| 7.5 | 11.1 ± 0.5 a | 6.30 ± 0.18 a | 70.2 ± 3 b | 1.77 ± 0.08 a | |
| Gellan gum | 2.5 | 15.5 ± 0.4 a | 5.38 ± 0.12 a | 83.4 ± 2 a | 2.88 ± 0.11 a |
| 5.0 | 16.1 ± 0.4 b | 5.48 ± 0.17 ab | 88.2 ± 3 b | 2.94 ± 0.11 a | |
| 7.5 | 16.8 ± 0.2 c | 5.62 ± 0.12 b | 94.4 ± 2 c | 2.29 ± 0.07 a | |
| Gelatin | 2.5 | 13.1 ± 0.8 a | 5.16 ± 0.13 a | 67.5 ± 3 a | 2.54 ± 0.14 a |
| 5.0 | 13.5 ± 0.5 ab | 5.37 ± 0.34 a | 72.6 ± 4 b | 2.53 ± 0.21 a | |
| 7.5 | 14.0 ± 0.6 b | 5.41 ± 0.16 a | 75.9 ± 4 b | 2.60 ± 0.12 a | |
| Agar | 2.5 | 22.8 ± 1.2 a | 5.27 ± 0.18 a | 120 ± 4 a | 4.34 ± 0.35 a |
| 5.0 | 24.6 ± 0.5 b | 5.49 ± 0.12 b | 135 ± 5 b | 4.48 ± 0.08 ab | |
| 7.5 | 27.3 ± 1.0 c | 5.75 ± 0.10 c | 157 ± 4 c | 4.76 ± 0.25 b |
| Milk Pudding | Color | Flavor | Sweetness | Springiness | Overall Acceptability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Commercial MA | 6.90 ± 0.99 a | 6.83 ± 1.15 a | 5.40 ± 1.07 a | 6.60 ± 1.19 a | 7.00 ± 1.01 a |
| Commercial MB | 5.77 ± 1.19 b | 5.97 ± 1.22 b | 5.17 ± 1.26 a | 5.53 ± 1.14 b | 5.73 ± 0.98 b |
| Commercial MC | 5.47 ± 1.31 b | 5.47 ± 1.41 b | 5.13 ± 1.22 a | 5.10 ± 1.06 b | 5.23 ± 1.19 b |
| κ-carrageenan | 5.10 ± 1.15 c | 5.67 ± 1.24 b | 5.25 ± 1.38 a | 4.20 ± 1.19 b | 4.53 ± 1.09 c |
| ι-carrageenan | 5.64 ± 0.89 b | 5.83 ± 1.14 b | 5.39 ± 1.11 a | 5.22 ± 1.05 b | 5.25 ± 1.14 b |
| Gellan gum | 5.75 ± 0.62 b | 5.51 ± 1.36 b | 5.41 ± 1.18 a | 5.55 ± 0.89 b | 5.72 ± 1.00 b |
| Gelatin | 5.27 ± 1.19 c | 5.47 ± 1.32 b | 5.16 ± 1.36 a | 5.31 ± 1.17 b | 5.13 ± 0.92 b |
| Agar | 5.12 ± 1.14 c | 5.58 ± 1.11 b | 4.87 ± 1.22 a | 4.07 ± 1.29 b | 4.22 ± 1.28 c |
| Type of Milk Pudding | Color | Flavor | Sweetness | Springiness | Overall Acceptability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Commercial milk pudding (MA) | 6.17 ± 1.18 b | 5.77 ± 1.25 b | 5.17 ± 1.49 ab | 6.07 ± 1.36 b | 7.03 ± 1.27 b |
| Milk pudding (B25) with 2.5% sucrose, 0.3% gellan, and 1% modified corn starch | 5.30 ± 1.64 a | 4.87 ± 1.59 a | 5.07 ± 1.44 ab | 5.17 ± 1.26 a | 5.07 ± 1.28 a |
| Milk pudding (B50) with 5.0% sucrose, 0.3% gellan, and 1% modified corn starch | 5.23 ± 1.65 a | 5.37 ± 1.56 ab | 5.70 ± 1.12 b | 5.73 ± 1.51 ab | 5.63 ± 1.22 a |
| Milk pudding (B75) with 7.5% sucrose, 0.3% gellan, and 1% modified corn starch | 5.47 ± 1.57 ab | 5.43 ± 1.43 ab | 4.80 ± 1.58 a | 5.40 ± 1.35 ab | 5.40 ± 1.45 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, H.-T.V.; Tsai, J.-S.; Liao, H.-H.; Sung, W.-C. Effect of Hydrocolloids on Penetration Tests, Sensory Evaluation, and Syneresis of Milk Pudding. Polymers 2025, 17, 300. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17030300
Lin H-TV, Tsai J-S, Liao H-H, Sung W-C. Effect of Hydrocolloids on Penetration Tests, Sensory Evaluation, and Syneresis of Milk Pudding. Polymers. 2025; 17(3):300. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17030300
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Hong-Ting Victor, Jenn-Shou Tsai, Hsiao-Hui Liao, and Wen-Chieh Sung. 2025. "Effect of Hydrocolloids on Penetration Tests, Sensory Evaluation, and Syneresis of Milk Pudding" Polymers 17, no. 3: 300. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17030300
APA StyleLin, H.-T. V., Tsai, J.-S., Liao, H.-H., & Sung, W.-C. (2025). Effect of Hydrocolloids on Penetration Tests, Sensory Evaluation, and Syneresis of Milk Pudding. Polymers, 17(3), 300. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17030300







