Recent Advances in Membrane-Based Air Filtration Technologies for Ambient Particulate Matter Separation
Abstract
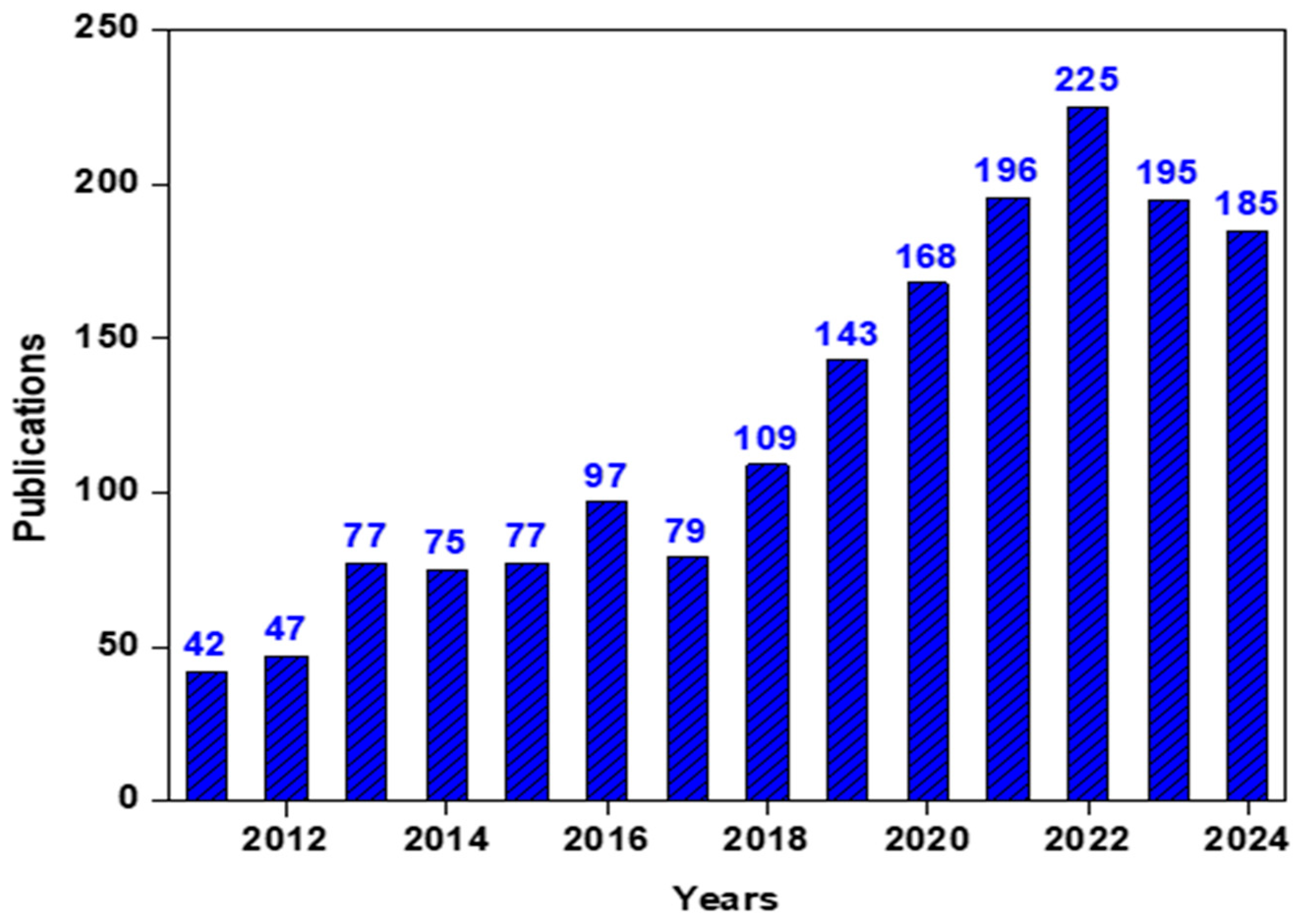
1. Introduction
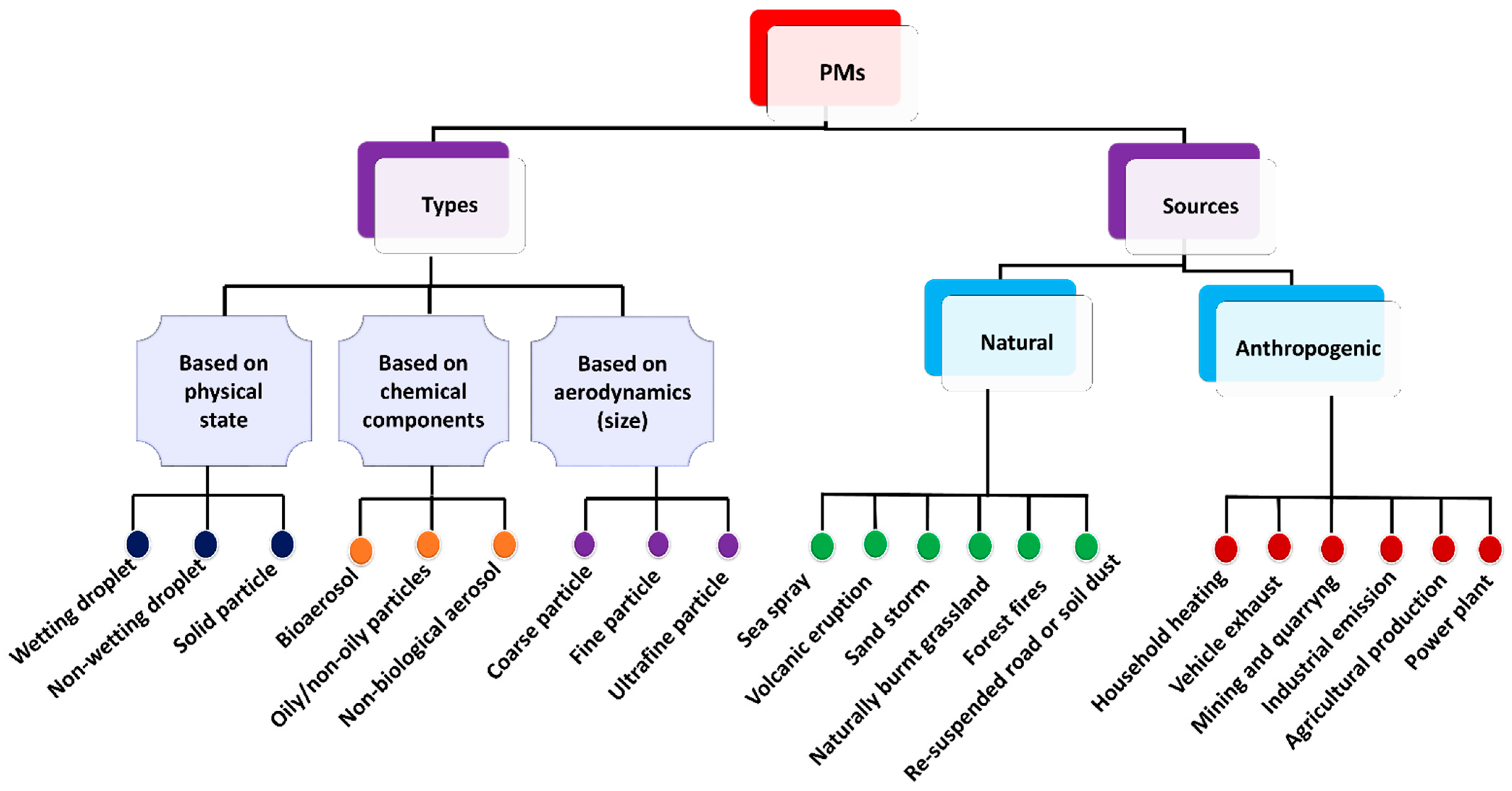
2. PM and Its Types
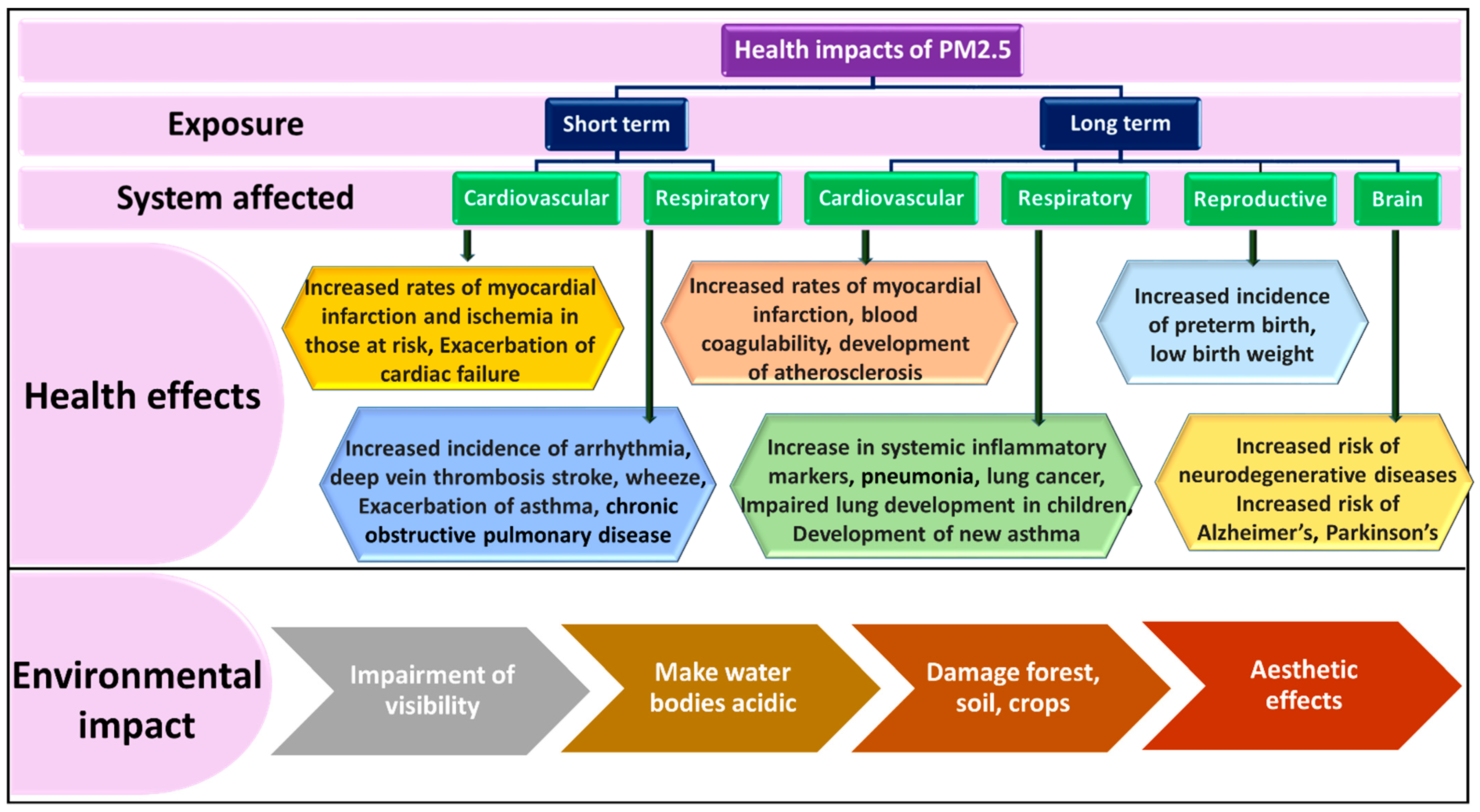
3. Influence of PM on Health and the Environment
4. Conventional Methods of PM Separation Versus Membrane
5. Strategic Approaches to Membrane Air Filter-Based PM Removal
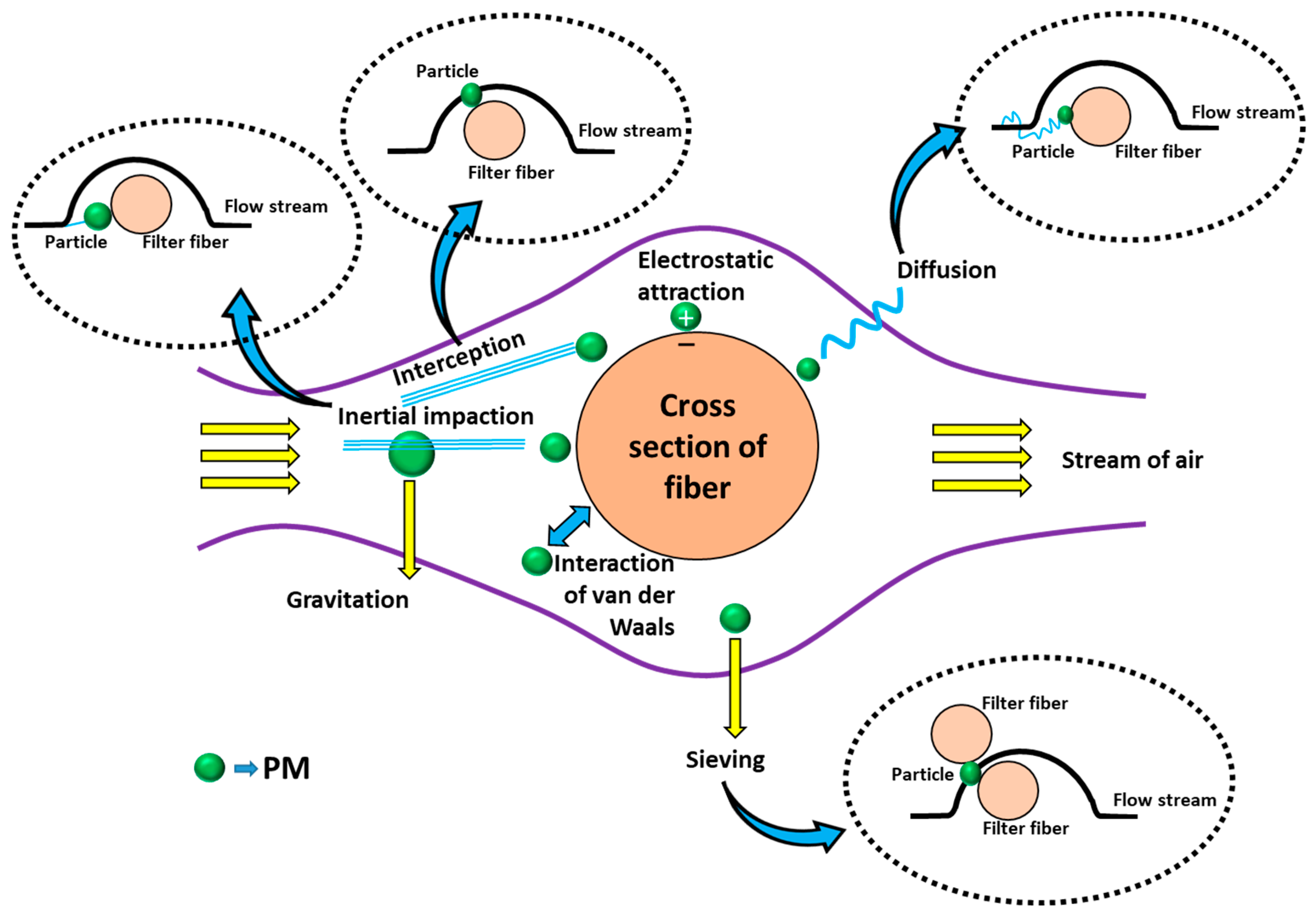
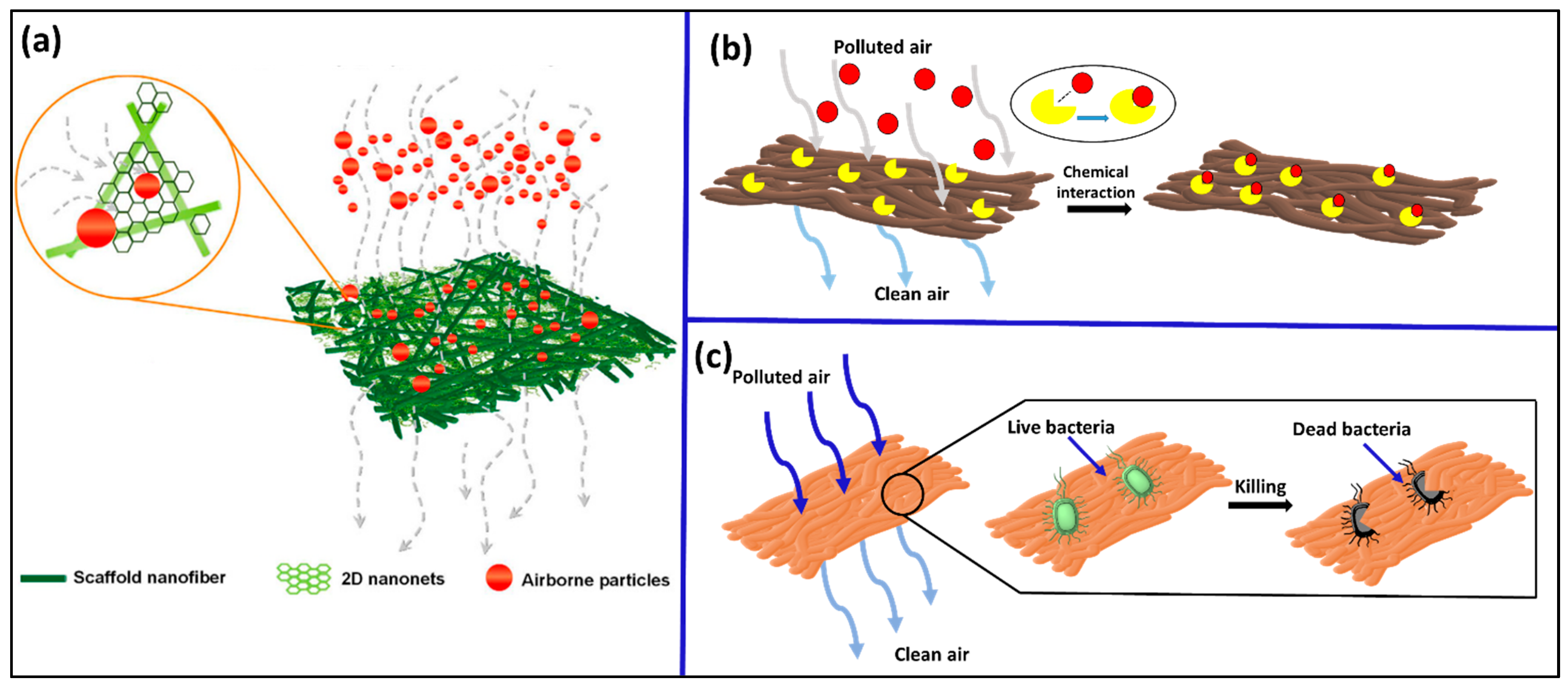
5.1. Physical Approach
5.1.1. Passive Trap
5.1.2. Proactive Capture
5.2. Chemical Approach
5.3. Biological Approach
6. Factors Considering the Performance of PM Filtration
6.1. Filtration Efficiency
6.2. Pressure Drop
6.3. Quality Factor
6.4. Optical Transparency
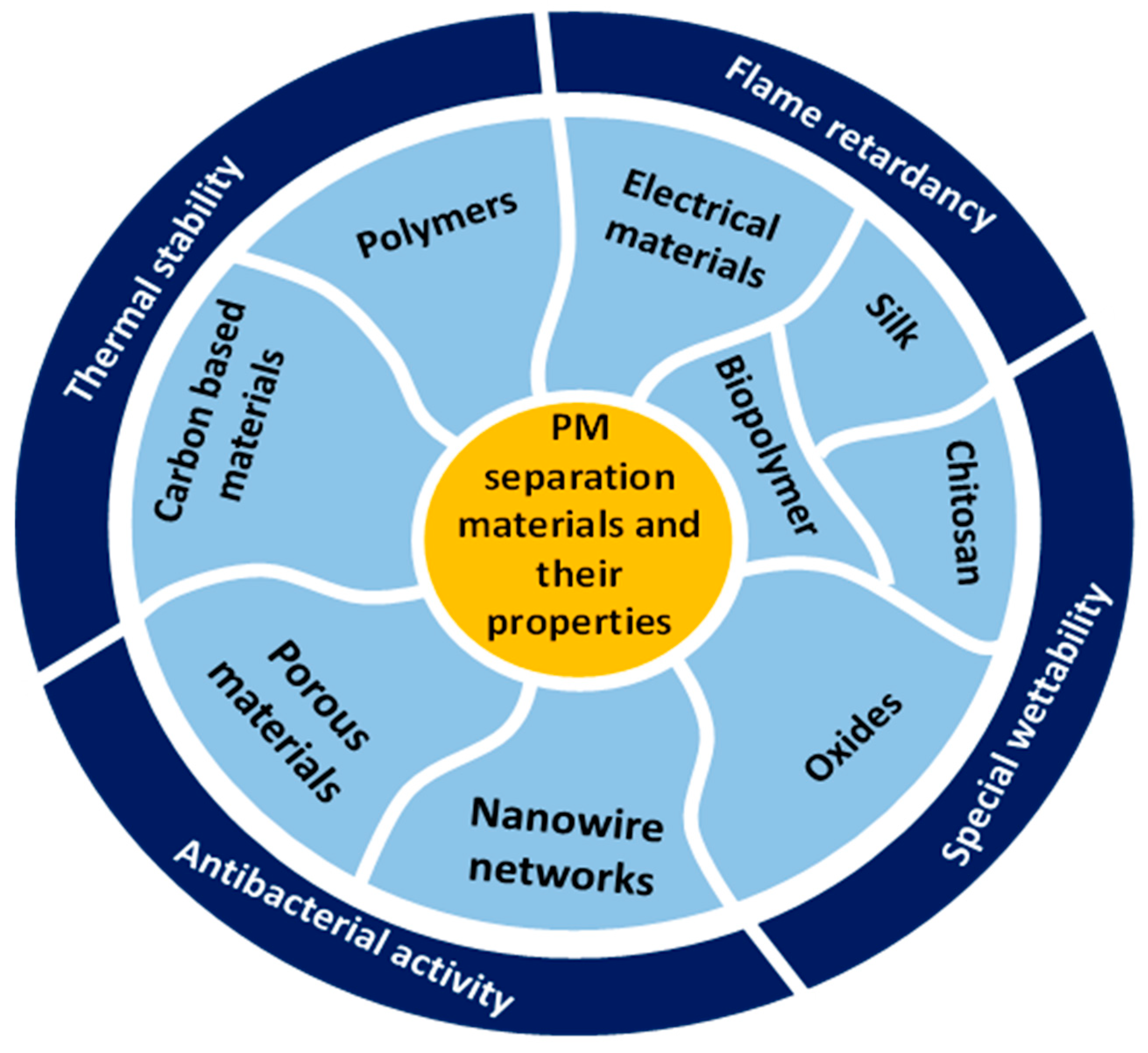
7. Material Scopes for PM Filtration
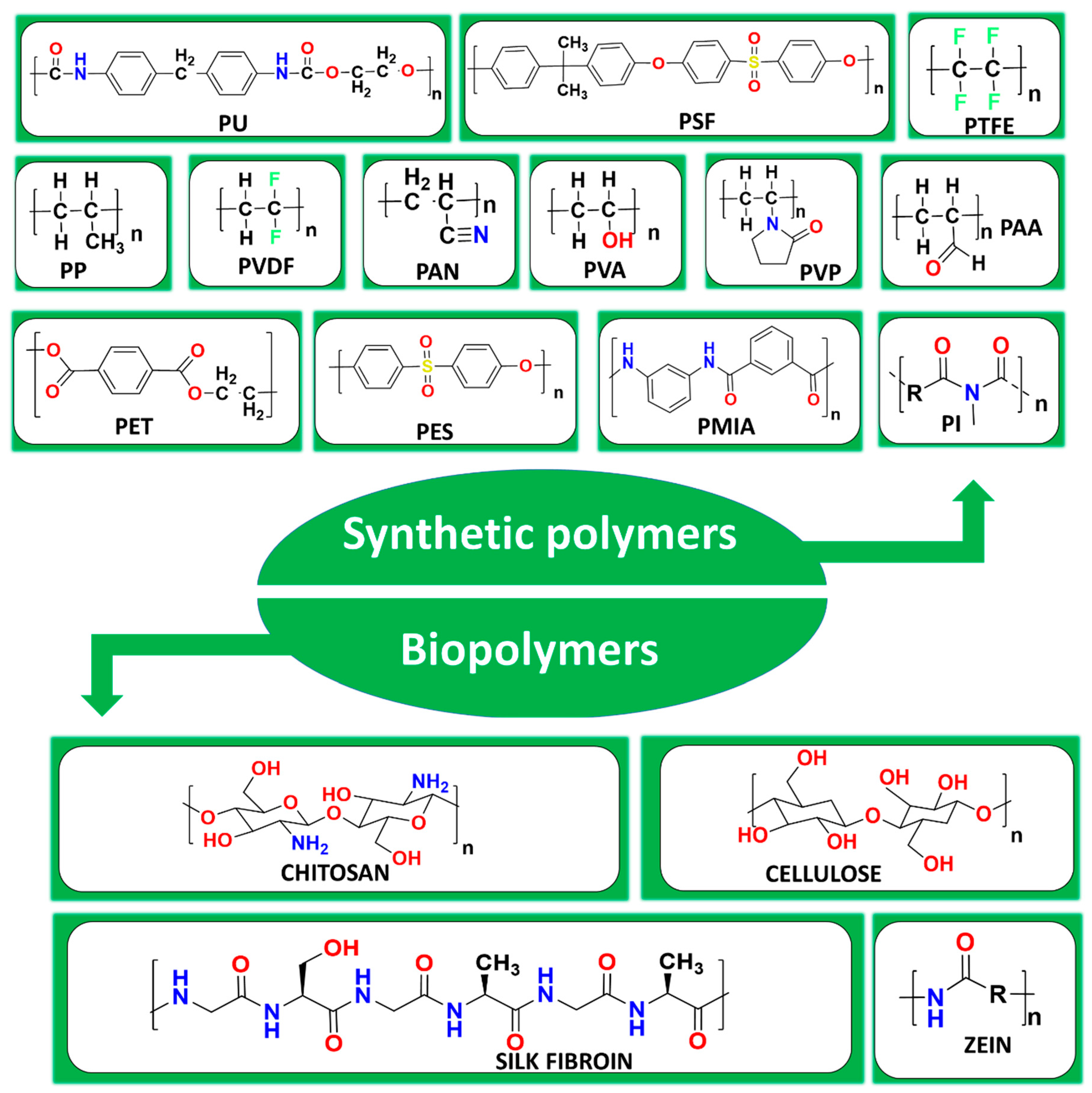
7.1. Polymers
7.2. Other Novel Materials
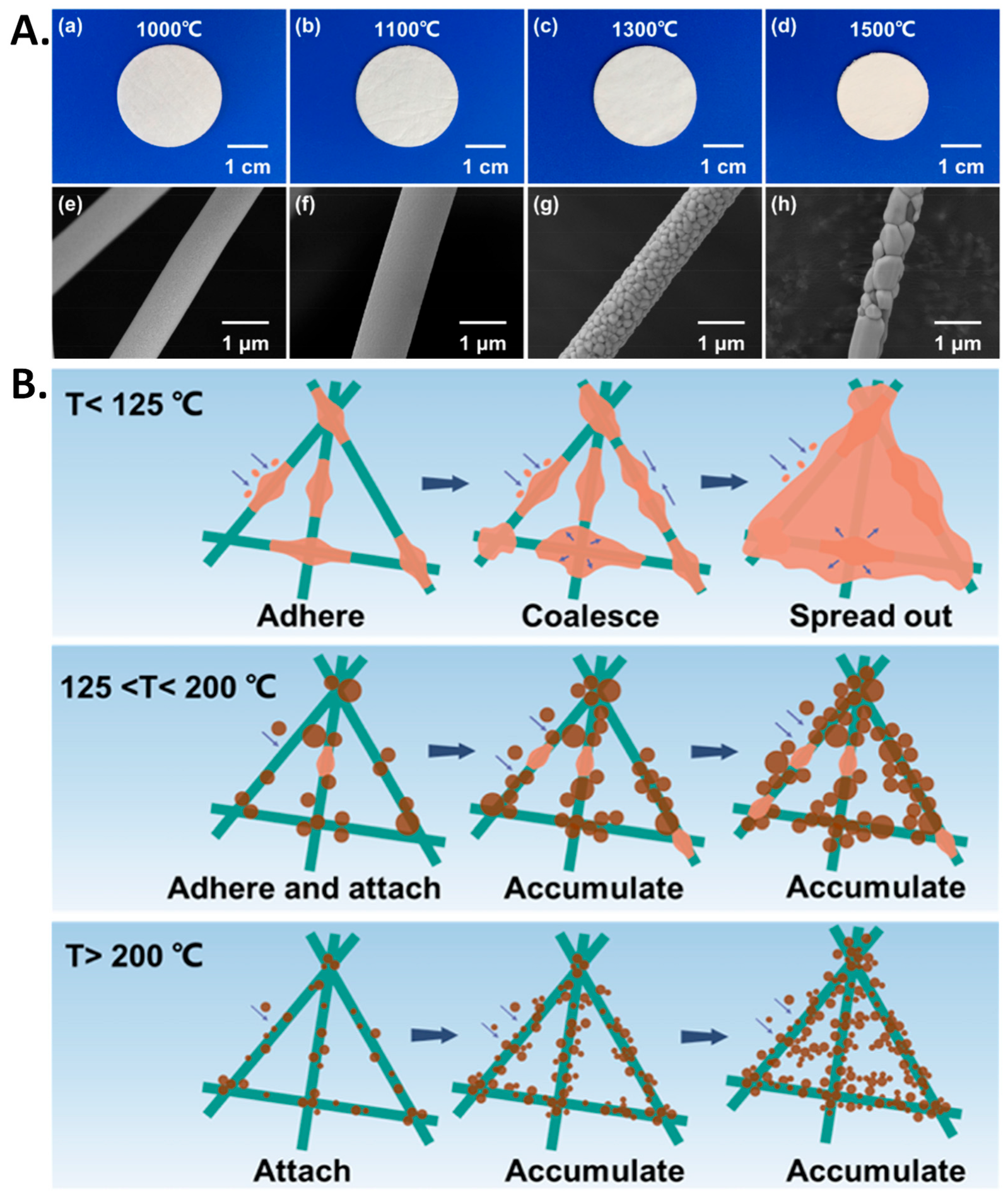
7.2.1. Porous Materials
7.2.2. Carbon-Based Materials
7.2.3. Electrical Filtration Materials
7.2.4. Nanowire Networks
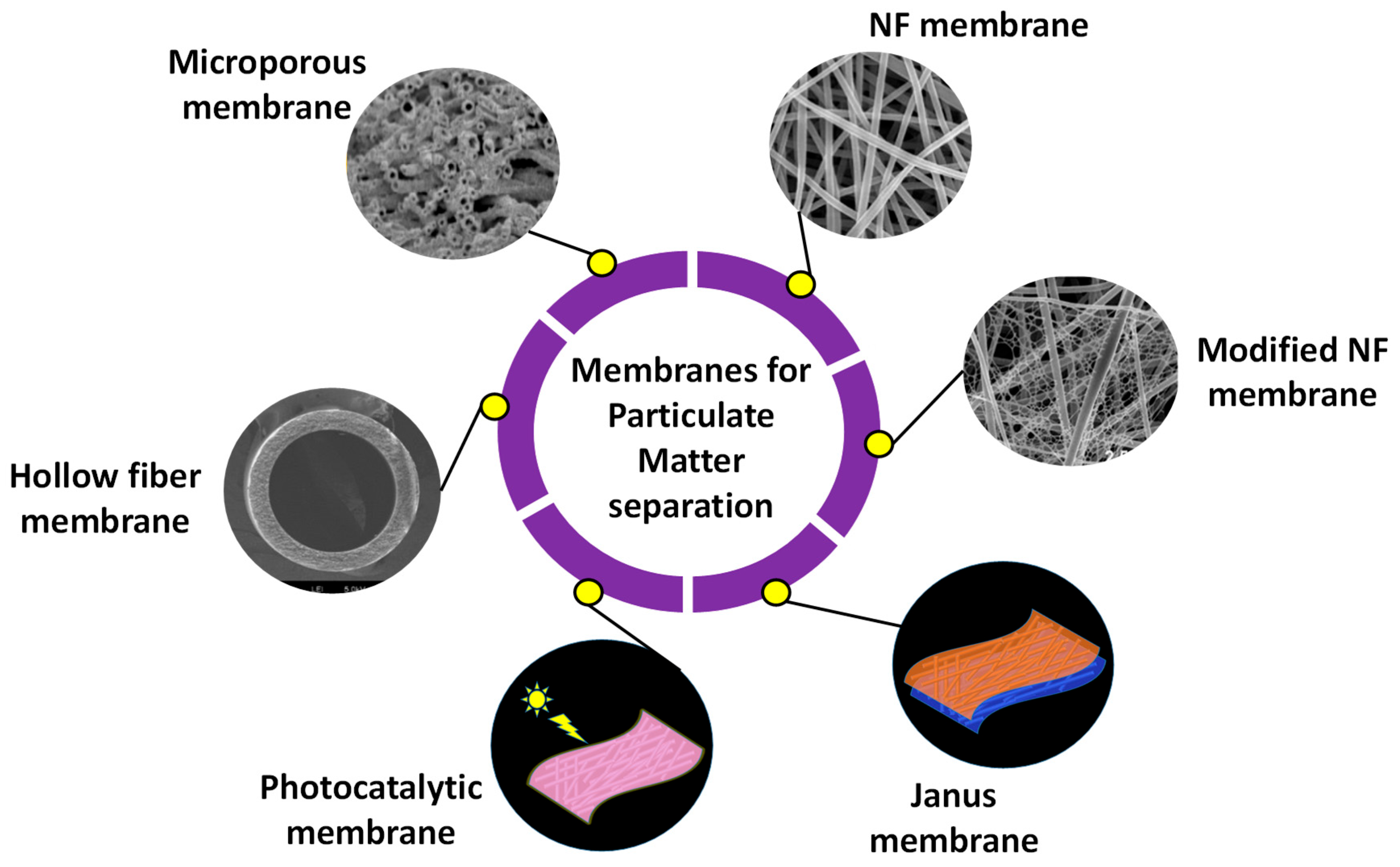
8. Membranes for PM Separation
8.1. NF Membranes
8.2. Surface-Modified NF Membranes
8.3. Microporous Membranes
8.4. Hollow Fiber Membranes (HFMs)
8.5. Janus Membranes
8.6. Photocatalytic Membranes
9. Critical Comparison of Cost, Durability and Scalability of Different Types of Membranes
10. Important Functionality of Membranes for Air Filtration
10.1. Antibacterial Activity
10.2. Wettability
10.3. Thermal Stability
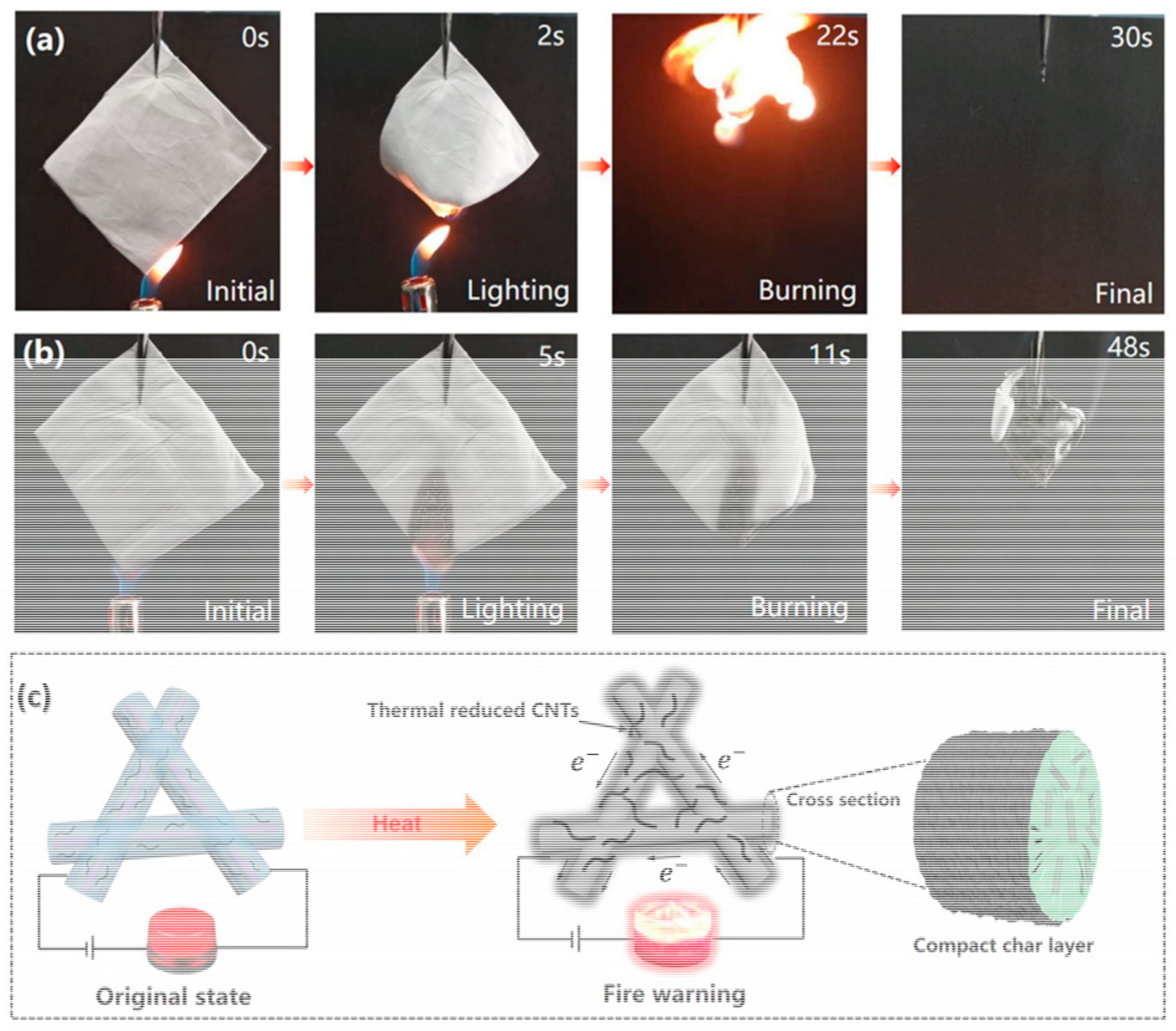
10.4. Flame Retardancy
10.5. Reusability
11. Commercial Air Filters for PM Separation: Availability and Challenges
12. Future Perspectives
13. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kampa, M.; Castanas, E. Human health effects of air pollution. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 151, 362–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jin, L.; Kan, H. Air pollution: A global problem needs local fixes. Nature 2019, 570, 437–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Li, B.; Yu, D.; Liu, J.; Ma, Z. Approaches to prevent the patients with chronic airway diseases from exacerbation in the haze weather. J. Thorac. Dis. 2016, 8, E1–E7. [Google Scholar]
- Quinn, P.K.; Bates, T.S. North American, Asian, and Indian haze: Similar regional impacts on climate? Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30, 1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britigan, N.; Alshawa, A.; Nizkorodov, S.A. Quantification of ozone levels in indoor environments generated by ionization and ozonolysis air purifiers. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2006, 56, 601–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhuyan, C.; Konwar, A.; Bora, P.; Rajguru, P.; Hazarika, S. Cellulose nanofiber-poly (ethylene terephthalate) nanocomposite membrane from waste materials for treatment of petroleum industry wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 442, 129955–129972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bora, P.; Bhuyan, C.; Borah, A.R.; Hazarika, S. Carbon nanomaterials for designing next-generation membranes and their emerging applications. Chem. Commun. 2023, 59, 11320–11336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, R.; Gogoi, M.; Borah, A.; Sarmah, H.; Borah, A.R.; Feng, X.; Hazarika, S. Quantum dot-β-Cyclodextrin nanofiller decorated thin film nanocomposite membrane for removal of cationic and anionic dyes from aqueous solution. Mater. Today Chem. 2024, 35, 101871–101882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nallathambi, G.; Robert, B.; Esmeralda, S.P.; Kumaravel, J.; Parthiban, V. Development of SPI/AC/PVA nano-composite for air-filtration and purification. Res. J. Text. Appar. 2020, 24, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reena, P.; Gobi, N.; Chitralekha, P.; Thenmuhil, D.; Kamaraj, V. Mesoporous titania-embedded polyacrylonitrile composite nanofibrous membrane for particulate matter filtration. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2021, 34, 1052–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Feng, S.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, F.; Xu, C.; Hu, M.; Zhong, Z.; Xing, W. Perfluorinated superhydrophobic and oleophobic SiO2@ PTFE nanofiber membrane with hierarchical nanostructures for oily fume purification. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 594, 117473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Ma, Q.; Zhang, J.B.; Liu, G.B. Electrospun SiO2 aerogel/polyacrylonitrile composited nanofibers with enhanced adsorption performance of volatile organic compounds. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 512, 145697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Huang, J.; Teng, L.; Li, S.; Li, X.; Cai, W.; Chen, Z.; Lai, Y. Advances in particulate matter filtration: Materials, performance, and application. Green Energy Environ. 2023, 8, 673–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Feng, Z.; Yu, D.G.; Wang, K. Electrospun nanofiber membranes for air filtration: A review. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Riccardis, M.F. Electrospun nanofibrous membranes for air filtration: A critical review. Compounds 2023, 3, 390–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valencia-Osorio, L.M.; Álvarez-Láinez, M.L. Global view and trends in electrospun nanofiber membranes for particulate matter filtration: A review. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2021, 306, 2100278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Cui, J.; Qu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xiong, R.; Ma, W.; Huang, C. Multistructured electrospun nanofibers for air filtration: A review. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 23293–23313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Lu, T.; Cui, J.; Samal, S.K.; Xiong, R.; Huang, C. Bio-based electrospun nanofiber as building blocks for a novel eco-friendly air filtration membrane: A review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 277, 119623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Ren, Q.; Qi, H.; Liu, S.; Liu, Y. Adverse effects of fine-particle exposure on joints and their surrounding cells and microenvironment. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 2729–2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Cao, C.; Huang, J.; Chen, Z.; Chen, G.; Lai, Y. Progress on particulate matter filtration technology: Basic concepts, advanced materials, and performances. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Sun, Y.; Yao, X.; Subramanian, K.; Ling, C.; Wang, H.; Chopra, S.S.; Xu, B.B.; Wang, J.X.; Chen, J.F.; et al. Masks for COVID-19. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2102189–2102219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Liu, B.; Yang, A.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhou, G.; Sun, J.; Hsu, P.C.; Zhao, W.; Lin, D.; et al. In situ investigation on the nanoscale capture and evolution of aerosols on nanofibers. Nano Lett. 2018, 18, 1130–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Sioutas, C.; Cho, A.; Schmitz, D.; Misra, C.; Sempf, J.; Wang, M.; Oberley, T.; Froines, J.; Nel, A. Ultrafine particulate pollutants induce oxidative stress and mitochondrial damage. Environ. Health Perspect. 2003, 111, 455–460. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.J.; Martin, R.V.; Henze, D.K.; Brauer, M.; Cohen, A.; Donkelaar, A.V. Response of global particulate-matter-related mortality to changes in local precursor emissions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 4335–4344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhou, S.; Fan, W. Effect of nano-Al2O3 on the toxicity and oxidative stress of copper towards Scenedesmus obliquus. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, A.; Agrawal, M. World air particulate matter: Sources, distribution, and health effects. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2017, 15, 283–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Hao, J. Air quality inside subway metro indoor environment worldwide: A review. Environ. Int. 2017, 107, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Kim, J.; Ko, S.H. Advances in air filtration technologies: Structure-based and interaction-based approaches. Mater. Today Adv. 2021, 9, 100134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archer, B.; Shaumbwa, V.R.; Liu, D.; Li, M.; Iimaa, T.; Surenjav, U. Nanofibrous mats for particulate matter filtration. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2021, 60, 7517–7534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, B.; Wang, S.; Yang, F.; Xing, J.; Morawska, L.; Ding, A.; Kulmala, M.; Kerminen, V.M.; Kujansuu, J.; et al. Particulate matter pollution over China and the effects of control policies. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 584, 426–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Tu, Y.; Yu, Z.; Lu, R. PM2.5 and cardiovascular diseases in the elderly: An overview. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 8187–8197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Zhu, X.; Yao, C.; Hou, L.; Zhang, J.; Cao, J.; Wang, A. Short-term exposure to particulate air pollution and risk of myocardial infarction: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2015, 22, 14651–14662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newby, D.E.; Mannucci, P.M.; Tell, G.S.; Baccarelli, A.A.; Brook, R.D.; Donaldson, K.; Forastiere, F.; Franchini, M.; Franco, O.H.; Graham, I.; et al. Expert position paper on air pollution and cardiovascular disease. Eur. Heart J. 2015, 36, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajbafzadeh, M.; Brauer, M.; Karlen, B.; Carlsten, C.; van Eeden, S.; Allen, R.W. The impacts of traffic-related and woodsmoke particulate matter on measures of cardiovascular health: A HEPA filter intervention study. Occup. Environ. Med. 2015, 72, 394–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.S.; Vos, T.; Flaxman, A.D.; Danaei, G.; Shibuya, K.; Adair-Rohani, H.; AlMazroa, M.A.; Amann, M.; Anderson, H.R.; Andrews, K.G.; et al. A comparative risk assessment of burden of disease and injury attributable to 67 risk factors and risk factor clusters in 21 regions, 1990–2010: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 2012, 380, 2224–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apte, J.S.; Marshall, J.D.; Cohen, A.J.; Brauer, M. Addressing global mortality from ambient PM2.5. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 8057–8066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maestas, M.M.; Brook, R.D.; Ziemba, R.A.; Li, F.; Crane, R.C.; Klaver, Z.M.; Bard, R.L.; Spino, C.A.; Adar, S.D.; Morishita, M. Reduction of personal PM2.5 exposure via indoor air filtration systems in Detroit: An intervention study. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2019, 29, 484–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Wang, H.; Zeng, X.; Yin, P.; Zhu, J.; Chen, W.; Li, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; et al. Mortality, morbidity, and risk factors in China and its provinces, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 2019, 394, 1145–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verdoni, L.; Mazza, A.; Gervasoni, A.; Martelli, L.; Ruggeri, M.; Ciuffreda, M.; Bonanomi, E.; D’Antiga, L. An outbreak of severe Kawasaki-like disease at the Italian epicentre of the SARS-CoV-2 epidemic: An observational cohort study. Lancet 2020, 395, 1771–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corman, V.M.; Landt, O.; Kaiser, M.; Molenkamp, R.; Meijer, A.; Chu, D.K.; Bleicker, T.; Brünink, S.; Schneider, J.; Schmidt, M.L.; et al. Detection of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) by real-time RT-PCR. Eurosurveillance 2020, 25, 2000045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Setti, L.; Passarini, F.; De Gennaro, G.; Barbieri, P.; Perrone, M.G.; Borelli, M.; Palmisani, J.; Di Gilio, A.; Torboli, V.; Fontana, F.; et al. SARS-CoV-2RNA found on particulate matter of Bergamo in Northern Italy: First evidence. Environ. Res. 2020, 188, 109754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Hsu, P.C.; Lee, H.W.; Ye, M.; Zheng, G.; Liu, N.; Li, W.; Cui, Y. Transparent air filter for high-efficiency PM2.5 capture. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grantz, D.A.; Garner, J.H.B.; Johnson, D.W. Ecological effects of particulate matter. Environ. Int. 2003, 29, 213–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thangavel, P.; Park, D.; Lee, Y.C. Recent insights into particulate matter (PM2.5)-mediated toxicity in humans: An overview. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 7511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayan, V.K.; Paramesh, H.; Salvi, S.S.; Dalal, A.A.K. Enhancing indoor air quality—The air filter advantage. Lung India 2015, 32, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.; Mishra, C.; Jain, S.; Solanki, N. A review of general and modern methods of air purification. J. Therm. Eng. 2019, 5, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambre, A. Effects of Carbon Filtration Type on Filter Efficiency and Efficacy: Granular Loose-Fill vs. Bonded Filters; Air Science Corporation: Fort Myers, FL, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Aarnink, A.J.; Hofschreuder, P.; Koerkamp, P.W.G. Evaluation of an impaction and a cyclone pre-separator for sampling high PM10 and PM2. 5 concentrations in livestock houses. J. Aerosol Sci. 2009, 40, 868–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, B.; Nallathambi, G. A concise review on electrospun nanofibres/nanonets for filtration of gaseous and solid constituents (PM2.5) from polluted air. Colloid Interface Sci. Commun. 2020, 37, 100275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, F. Air filtration in the free molecular flow regime: A review of high-efficiency particulate air filters based on carbon nanotubes. Small 2014, 10, 4543–4561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutten, I. Fabrics. In Handbook of Nonwoven Filter Media; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.Y. Filtration of aerosols by fibrous media. Chem. Rev. 1955, 55, 595–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, T.T.; Shin, M.K.; Jee, S.Y.; Long, D.X.; Hong, J.; Kim, M.G. Ferroelectric PVDF nanofiber membrane for high-efficiency PM0.3 air filtrations with low air flow resistance. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 640, 128418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Huang, J.; Mao, J.; Bao, Z.; Chen, Z.; Lai, Y. Charged graphene aerogel filter enabled superior particulate matter removal efficiency in harsh environment. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 395, 125086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Guo, F.; Mao, J.; Huang, J.; Chen, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Lai, Y. Freestanding MoS2@ carbonized cellulose aerogel derived from waste cotton for sustainable and highly efficient particulate matter capturing. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 254, 117571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Li, Y.; Si, Y.; Yin, X.; Yu, J.; Ding, B. Electrospun polyvinylidene fluoride/SiO2 nanofibrous membranes with enhanced electret property for efficient air filtration. Compos. Commun. 2019, 13, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, S.; Rajiv, S. Ethylenediamine functionalized metalloporphyrin loaded nanofibrous membrane: A new strategic approach to air filtration. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2020, 30, 2142–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakashima, H.; Ooshima, T. Analysis of inorganic antimicrobial agents in antimicrobial products: Evaluation of a screening method by X-ray fluorescence spectrometry and the measurement of metals by inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectroscopy. J. Health Sci. 2007, 53, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Camacho, A.P.; Cortez-Rocha, M.O.; Castillo-Ortega, M.M.; Burgos-Hernández, A.; Ezquerra-Brauer, J.M.; Plascencia-Jatomea, M. Antimicrobial activity of chitosan nanofibers obtained by electrospinning. Polym. Int. 2011, 60, 1663–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, H.; Yin, X.; Li, Z.; Yu, J.; Ding, B. Tailoring mechanically robust poly (m-phenylene isophthalamide) nanofiber/nets for ultrathin high-efficiency air filter. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, W.W.F.; Hung, C.H.; Yuen, P.T. Effect of face velocity, nanofiber packing density and thickness on filtration performance of filters with nanofibers coated on a substrate. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2010, 71, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, T.; Chen, C. Evolution of pressure drop across electrospun nanofiber filters clogged by solid particles and its influence on indoor particulate air pollution control. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 402, 123479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, N.; Lee, Y.S.; Kaang, B.K.; Jang, W.; Koo, H.Y.; Choi, W.S. A lottery draw machine-inspired movable air filter with high removal efficiency and low pressure drop at a high flow rate. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 6001–6011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Cheng, Z.; Kang, L.; Lin, M.; Han, L. Patterned nanofiber air filters with high optical transparency, robust mechanical strength, and effective PM2.5 capture capability. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 20155–20161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yuan, W.L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, G.H.; Chen, H.; Zhao, N.; He, L.; Tao, G.H. Self-assembled ionic nanofibers derived from amino acids for high-performance particulate matter removal. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 4619–4625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z.; Wu, J.; Wang, C.; Liu, J. Electrospun polyimide/metal–organic framework nanofibrous membrane with superior thermal stability for efficient PM2.5 capture. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 11904–11909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.X.; Kuang, S.Y.; Chen, Y.H.; Wang, Z.L.; Li, C.; Zhu, G. In situ active poling of nanofiber networks for gigantically enhanced particulate filtration. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 24332–24338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Raza, A.; Si, Y.; Yu, J.; Sun, G.; Ding, B. Tortuously structured polyvinyl chloride/polyurethane fibrous membranes for high-efficiency fine particulate filtration. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 398, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, Q.; Young, T.M.; Harper, D.P.; Wang, S. A novel method for fabricating an electrospun poly(vinyl alcohol)/cellulose nanocrystals composite nanofibrous filter with low air resistance for high-efficiency filtration of particulate matter. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 8706–8714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajak, A.; Hapidin, D.A.; Iskandar, F.; Munir, M.M.; Khairurrijal, K. Electrospun nanofiber from various sources of expanded polystyrene (EPS) waste and their characterization as potential air filter media. Waste Manag. 2020, 103, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Y.; Ding, S.; Wang, B.; Wang, J.; Sun, Q.; Jin, X.; Li, X. Controllable morphology of electrospun nanofiber membranes with tunable groove structure and the enhanced filtration performance for ultrafine particulates. Nanotechnology 2021, 32, 315708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, F.; Zhang, S.; Liu, H.; Fong, H.; Yin, X.; Yu, J.; Ding, B. Free-standing polyurethane nanofiber/nets air filters for effective PM capture. Small 2017, 13, 1702139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balgis, R.; Murata, H.; Goi, Y.; Ogi, T.; Okuyama, K.; Bao, L. Synthesis of dual-size cellulose–polyvinylpyrrolidone nanofiber composites via one-step electrospinning method for high-performance air filter. Langmuir 2017, 33, 6127–6134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Q.; Liang, W.; Fan, T.T.; Li, X.; Yan, S.Y.; Yu, M.; Ning, X.; Long, Y.Z. Polyvinylidene fluoride composite nanofibrous filter for high-efficiency PM2.5 capture. Compos. Commun. 2020, 22, 100533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Hanif, A.; Shang, J.; Deka, B.J.; Zhi, N.; An, A.K. PAA@ZIF-8 incorporated nanofibrous membrane for high-efficiency PM2.5 capture. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 405, 126584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhao, C.; Pan, Z. Porous bead-on-string poly(lactic acid) fibrous membranes for air filtration. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 441, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackiewicz-Zagórska, A.; Mika, K.; Penconek, A.; Moskal, A. Non-woven filters made of PLA via solution blowing process for effective aerosol nanoparticle filtration. Processes 2022, 10, 2598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Zheng, Z.; Wang, X.; Kaplan, D.L. Low-density silk nanofibrous aerogels: Fabrication and applications in air filtration and oil/water purification. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 1048–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.; Jeon, H.; Jang, M.; Kim, H.; Shin, G.; Koo, J.M.; Lee, M.; Sung, H.K.; Eom, Y.; Yang, H.S.; et al. Biodegradable, efficient, and breathable multi-use face mask filter. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2003155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Z.; Lin, J.; Li, X.; Bian, F.; Wang, J. Hierarchically structured nanocellulose-implanted air filters for high-efficiency particulate matter removal. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 12408–12416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Li, C.; Tian, H.; Yuan, L.; Xiang, A.; Li, J.; Wang, C.; Rajulu, A.V. Hydrophobic cross-linked zein-based nanofibers with efficient air filtration and improved moisture stability. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 396, 125373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Fu, X.; Zheng, M.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Xiang, A.; Zhong, W.H. Natural polypeptides treat pollution complex: Moisture-resistant multifunctional protein nanofabrics for sustainable air filtration. Nano Res. 2018, 11, 4265–4277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthil, R.; Sumathi, V.; Tamilselvi, A.; Kavukcu, S.B.; Aruni, A.W. Functionalized electrospun nanofibers for high efficiency removal of particulate matter. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 8411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Su, Y.; Yang, L.; Su, M.; Niu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Sun, H.; Zhu, Z.; Liang, W.; Li, A. Highly efficient removal of PM and VOCs from air by a self-supporting bifunctional conjugated microporous polymers membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 659, 120728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.T.; Ge, Y.Y.; He, Y.; Xu, M.X.; Cui, X.M. A porous gradient geopolymer-based tube membrane with high PM removal rate for air pollution. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 217, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Q.; Li, J.; Li, X.; Du, X.; Wu, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, X. Incorporating nano-ZnCo-ZIF particles in electrospinning polylactide membranes to improve their filtration and antibacterial performances. Polym. Bull. 2024, 81, 14067–14081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Niu, C.; Cao, X.; Zhu, Z.; Sun, H.; Liang, W.; Li, J.; Li, A. Efficient capture of airborne PM by membranes based on holey reduced graphene oxide nanosheets. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, W.T.; Jang, J.S.; Qiao, S.; Hwang, W.; Jha, G.; Penner, R.M.; Kim, I.D. Hierarchical metal–organic framework-assembled membrane filter for efficient removal of particulate matter. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 19957–19963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmakar, K.; Hossain, M.; Sarkar, P.; Rao, K.D.M. Silk nanofibrous network for biodegradable PM0.3 filters rejuvenated with in-situ Joule heating for self-sanitization. SSRN Preprint 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaang, B.K.; Lee, H.B.; Koo, H.Y.; Choi, W.S. Wastepaper-Based Cylindrical Hollow Air Filter Module for the Removal of Particulate Matter (PM10 and PM2.5) and HCHO. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 13984–13996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, H.; Yoo, D.K.; Jhung, S.H. Highly improved performance of cotton air filters in particulate matter removal by the incorporation of metal–organic frameworks with functional groups capable of large charge separation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 28885–28893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, J.; Park, H.; Ryu, T.; Park, J. Core–shell structured mixed cellulose ester–alumina composite membranes for air filters with improved environmental resistance. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 309, 123012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, D.; Yu, B.; Zhao, T.; Chen, M. Filtration performance of NH2-MIL-53/chitosan-modified paper-based functional materials against airborne particulate matter. ACS Omega 2025, 10, 57830–57838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Xie, D.; Song, L.; Yang, C.; Yuan, Z. Rapid and sustainable fabrication of antibacterial chitosan/PVA–SiO2 nanofiber air filters by needleless electrospinning. AIP Adv. 2025, 15, 105220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Li, N.; Pang, H. Metal–organic frameworks-derived metal phosphides for electrochemistry application. Green Energy Environ. 2022, 7, 636–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Zhang, M.; Nie, J.; Tan, J.; Yang, B.; Song, S. Design of double-component metal–organic framework air filters with PM2.5 capture, gas adsorption and antibacterial capacities. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 203, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
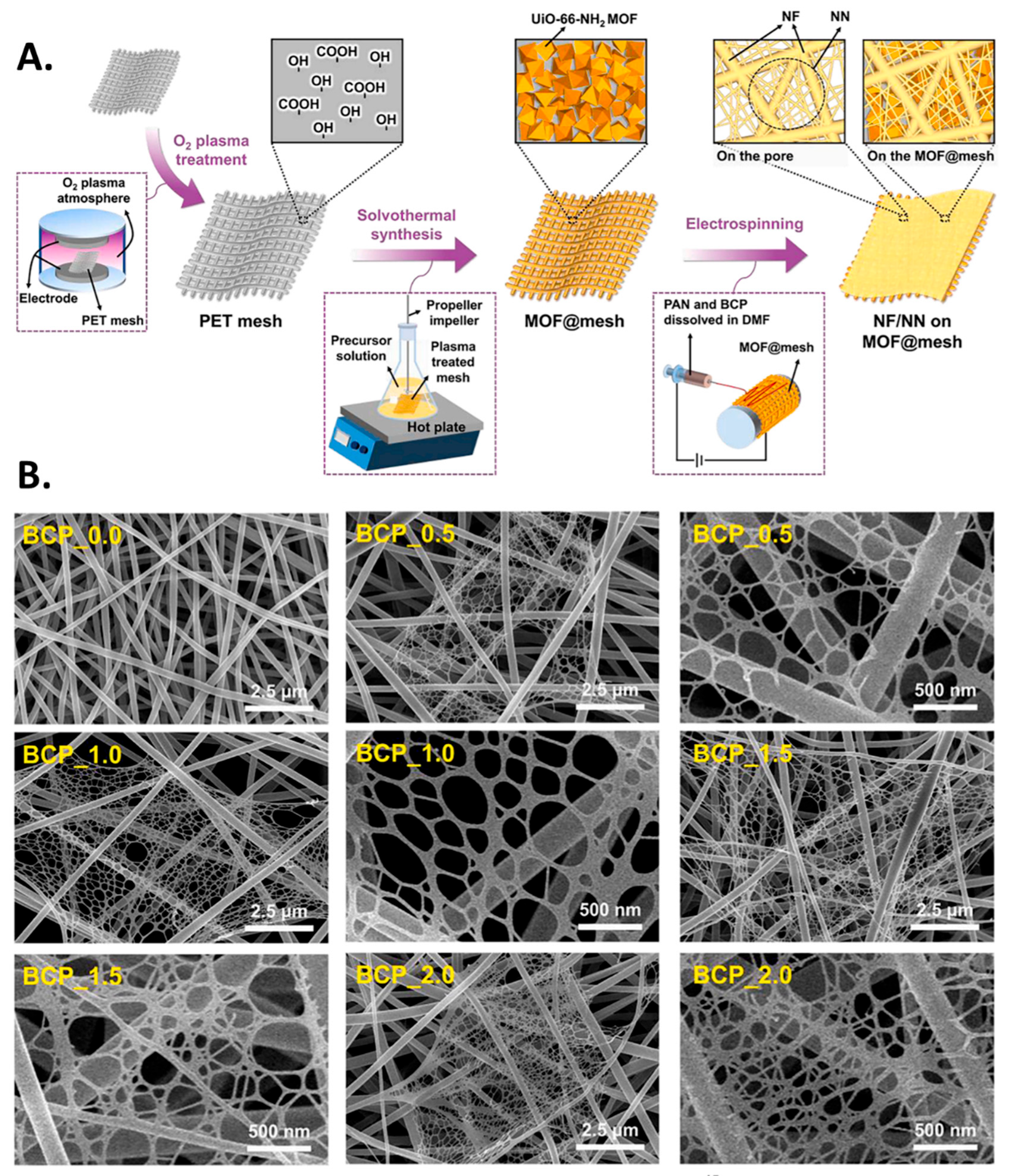
- Wang, H.; Xu, H.; Li, H.; Liu, X.; Du, Z.; Yu, W. Electrospun polyurethane/zeolitic imidazolate framework nanofibrous membrane with superior stability for filtering performance. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2020, 3, 710–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, H.C.; Yoo, D.K.; Jhung, S.H. Particulate matters removal by using cotton coated with isomeric metal–organic frameworks (MOFs): Effect of voidage of MOFs on removal. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2021, 95, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, D.K.; Woo, H.C.; Jhung, S.H. Removal of particulate matters by using zeolitic imidazolate framework-8s (ZIF-8s) coated onto cotton: Effect of the pore size of ZIF-8s on removal. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 35214–35222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.; Ge, M.; Chen, I.W.P.; Ng, Y.H.; Zhu, T.; Liu, H.; Huang, J.; Cai, W.; Lai, Y. In situ recycling of particulate matter for a high-performance supercapacitor and oxygen evolution reaction. Mater. Chem. Front. 2021, 5, 2742–2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Bai, J.; Innocent, M.T.; Wang, Q.; Xiang, H.; Tang, J.; Zhu, M. Lignin-based carbon fibers: Formation, modification and potential applications. Green Energy Environ. 2022, 7, 578–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, K.; Feng, S.; Zhang, F.; Zhong, Z.; Xing, W. Steric configuration-controllable carbon nanotubes-integrated SiC membrane for ultrafine particles filtration. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 19680–19688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Jiang, J.; Feng, S.; Low, Z.X.; Zhong, Z.; Xing, W. Graphene oxide functionalized polyvinylidene fluoride nanofibrous membranes for efficient particulate matter removal. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 635, 119463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, T.Y.; Wang, H.C.; Krichtafovitch, I.; Mamishev, A.V. Novel electrodes of an electrostatic precipitator for air filtration. J. Electrost. 2015, 73, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.; Cho, H.; Han, S.; Won, P.; Lee, H.; Hong, S.; Yeo, J.; Kwon, J.; Ko, S.H. High efficiency, transparent, reusable, and active PM2.5 filters by hierarchical Ag nanowire percolation network. Nano Lett. 2017, 17, 4339–4346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.R.; He, Z.; Wang, J.L.; Liu, J.W.; Yu, S.H. Mass production of nanowire–nylon flexible transparent smart windows for PM2.5 capture. iScience 2019, 12, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Y.; Han, C.B.; He, C.; Gu, G.Q.; Nie, J.H.; Shao, J.J.; Xiao, T.X.; Deng, C.R.; Wang, Z.L. Washable multilayer triboelectric air filter for efficient particulate matter PM2.5 removal. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1706680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Hong, S.; Ham, J.; Yeo, J.; Lee, J.; Kang, B.; Lee, P.; Kwon, J.; Lee, S.S.; Yang, M.Y.; et al. Fast plasmonic laser nanowelding for a Cu-nanowire percolation network for flexible transparent conductors and stretchable electronics. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 5808–5814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Z.C.; Yang, R.L.; Zhu, Y.J.; Chen, F.F.; Dong, L.Y. Flexible hydroxyapatite ultralong nanowire-based paper for highly efficient and multifunctional air filtration. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 17482–17491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souzandeh, H.; Wang, Y.; Netravali, A.N.; Zhong, W.H. Towards sustainable and multifunctional air-filters: A review on biopolymer-based filtration materials. Polym. Rev. 2019, 59, 651–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Liu, H.; Feng, M.; Ma, Q.; Wang, B. Metal-organic frameworks for air pollution purification and detection. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2304773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attia, Y.A.; Ezet, A.E.; Saeed, S.; Galmed, A.H. Nano carbon-modified air purification filters for removal and detection of particulate matters from ambient air. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhang, W.; Zeng, Z.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Y.; Shao, B.; Liang, Q.; Tang, W.; et al. Advances in the application, toxicity and degradation of carbon nanomaterials in environment: A review. Environ. Int. 2020, 134, 105298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Park, J.; Tsai, P.J.; Yoon, C. The effects of temperature and humidity on electrostatic changes in respirators and their filtration efficiency. Indoor Air 2024, 2024, 5503400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, S.; Rathmell, A.R.; Chen, Z.; Stewart, I.E.; Wiley, B.J. Metal nanowire networks: The next generation of transparent conductors. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 6670–6687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thavasi, V.; Singh, G.; Ramakrishna, S. Electrospun nanofibers in energy and environmental applications. Energy Environ. Sci. 2008, 1, 205–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Han, J.; Wang, F.; Shao, W.; Xiong, R.; Zhang, Q.; Pan, H.; Yang, Y.; Samal, S.K.; Zhang, F.; et al. Electrospun nanofibers membranes for effective air filtration. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2017, 302, 1600353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, T.; Kajiwara, K.; McIntyre, J.E. (Eds.) Advanced Fiber Spinning Technology; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Borah, A.R.; Hazarika, P.; Duarah, R.; Goswami, R.; Hazarika, S. Biodegradable electrospun membranes for sustainable industrial applications. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 11129–11147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uppal, R.; Bhat, G.; Eash, C.; Akato, K. Meltblown nanofiber media for enhanced quality factor. Fibers Polym. 2013, 14, 660–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huan, S.; Liu, G.; Han, G.; Cheng, W.; Fu, Z.; Wu, Q.; Wang, Q. Effect of experimental parameters on morphological, mechanical and hydrophobic properties of electrospun polystyrene fibers. Materials 2015, 8, 2718–2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Si, Y.; Wang, N.; Sun, G.; El-Newehy, M.; Al-Deyab, S.S.; Ding, B. Multilevel structured polyacrylonitrile/silica nanofibrous membranes for high-performance air filtration. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 126, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, K.; Kim, K.; Wang, X.; Fang, D.; Hsiao, B.S.; Chu, B. High flux ultrafiltration membranes based on electrospun nanofibrous PAN scaffolds and chitosan coating. Polymer 2006, 47, 2434–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Cai, M.; Yang, X.; Yang, Y. Electret nanofibrous membrane with enhanced filtration performance and wearing comfortability for face mask. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 530, 695–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Park, M.; Ding, B.; Kim, J.; El-Newehy, M.; Al-Deyab, S.S.; Kim, H.Y. Facile electrospun polyacrylonitrile/poly(acrylic acid) nanofibrous membranes for high efficiency particulate air filtration. Fibers Polym. 2015, 16, 629–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, B.; Nallathambi, G. Structural design and development of multilayered polymeric nanofibrous membrane for multifaceted air filtration/purification applications. Polym.-Plast. Technol. Mater. 2023, 62, 1435–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, H.J.; Pant, H.R.; Kang, Y.S.; Jeon, K.S.; Pant, B.; Kim, C.S.; Kim, H.Y. Synthesis and characterization of spider-web-like electrospun mats of meta-aramid. Polym. Int. 2012, 61, 1675–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Lee, C.; Kim, J. Fabrication of electrospun meta-aramid nanofibers in different solvent systems. Fibers Polym. 2010, 11, 1032–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthil, R.; Vedakumari, W.S.; Kavukcu, S.B. Wood-based cellulose nanofiber membrane: A novel approach to high-performance air filters. Cellulose 2024, 31, 3053–3063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.J.; Karim, Z.; Pongchaikul, P.; Posoknistakul, P.; Intra, P.; Laosiripojana, N.; Wu, K.C.W.; Sakdaronnarong, C. Nitrogen and sulfur doped carbon dots coupled cellulose nanofibers: A surface functionalized nanocellulose membrane for air filtration. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2024, 160, 105324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, W.; Niu, J.; Han, R.; Liu, S.; Wang, K.; Cao, Y.; Han, P.; Li, X.; Zhang, H.; Yu, H.; et al. Electrospun multiscale poly(lactic acid) nanofiber membranes with a synergistic antibacterial effect for air-filtration applications. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2023, 5, 9632–9641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
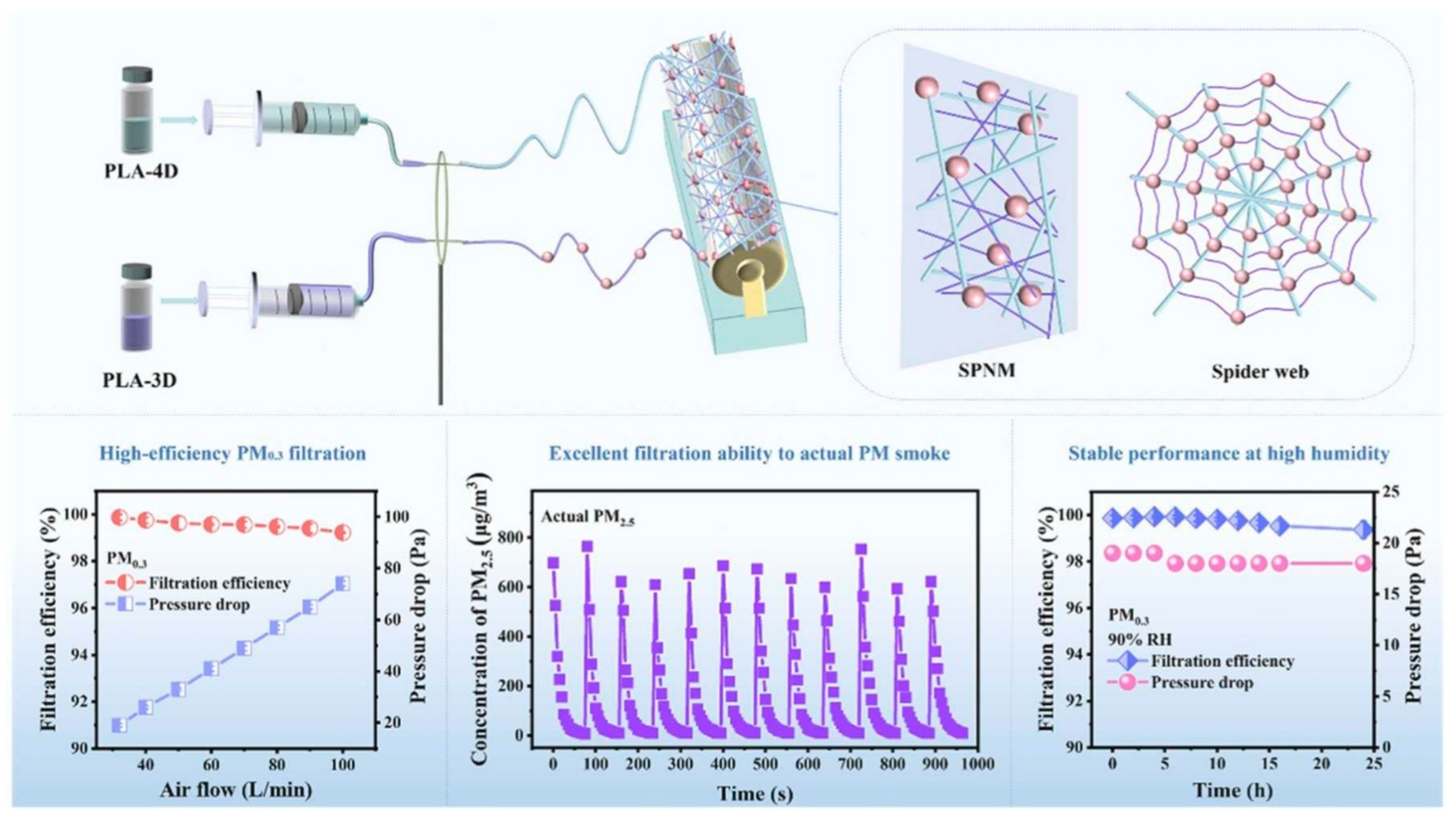
- Zhao, Y.; Ming, J.; Cai, S.; Wang, X.; Ning, X. One-step fabrication of polylactic acid (PLA) nanofibrous membranes with spider-web-like structure for high-efficiency PM0.3 capture. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 465, 133232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Xiao, D.; Fang, Y.; Ning, G.; Ye, J. Polarity-dominated chitosan biguanide hydrochloride-based nanofibrous membrane with antibacterial activity for long-lasting air filtration. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 254, 127729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, R.; Shao, Z.; Chen, R.; Wang, Q.; Gui, Z.; Qi, Y.; Song, W.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, G. Fully bio-based zein/chitosan hydrochloride/phloretin bimodal fibrous membrane for high-performance and antibacterial air filtration based on green electrospinning. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 341, 126893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Yang, Y.; Al-Deyab, S.S.; El-Newehy, M.; Yu, J.; Ding, B. Ultra-light 3D nanofibre-nets binary structured nylon 6–polyacrylonitrile membranes for efficient filtration of fine particulate matter. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 23946–23954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, H.; Zuo, F.; Yin, X.; Yu, J.; Ding, B. A controlled design of ripple-like polyamide-6 nanofiber/nets membrane for high-efficiency air filter. Small 2017, 13, 1603151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Zhang, S.; Wang, X.; Yu, J.; Ding, B. Efficient and reusable polyamide-56 nanofiber/nets membrane with bimodal structures for air filtration. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 457, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, H.; Yin, X.; Yu, J.; Ding, B. Anti-deformed polyacrylonitrile/polysulfone composite membrane with binary structures for effective air filtration. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 8086–8095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Gao, Y.; Nie, G.; Yan, X.; Wang, S.; Zhang, T.; Ramakrishna, S.; Long, Y.Z.; Han, W. Biodegradable poly(L-lactic acid) fibrous membrane with ribbon-structured fibers and ultrafine nanofibers enhances air filtration performance. Small 2024, 20, 2402317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xu, W.; Yan, X.; Chen, Y.; Guo, M.; Zhou, G.; Tong, S.; Ge, M.; Liu, Y.; Chen, C. MOF-based fibrous membranes adsorb PM efficiently and capture toxic gases selectively. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 17782–17790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.I.; Park, J.H.; Kim, S.D.; Lee, J.Y.; Yim, J.H.; Jeon, J.K.; Park, S.H.; Park, Y.K. Comparison of removal ability of indoor formaldehyde over different materials functionalized with various amine groups. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2011, 17, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.; Yusuf, M.; Son, Y.; Han, S.; Lee, H.; Mahadadalkar, M.A.; Park, S.; Youn, B.; Lee, J.M.; Park, K.H. An efficient atmospheric pollution control using hierarchical porous nanofibers containing zeolitic-imidazolate-frameworks and hydroxyapatite nanoparticles. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 111798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvam, A.K.; Baskar, D.; Nallathambi, G. Layer by layer nanocomposite filter for ABC filtration. Chem. Eng. Commun. 2021, 208, 863–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Oh, H.J.; Park, Y.K.; Kim, Y.; Lee, G.; Doh, S.J.; Lee, W.; Choi, S.J.; Yoon, K.R. Multi-scale nanofiber membrane functionalized with metal-organic frameworks for efficient filtration of both PM2.5 and CH3CHO with colorimetric NH3 detection. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 464, 142725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
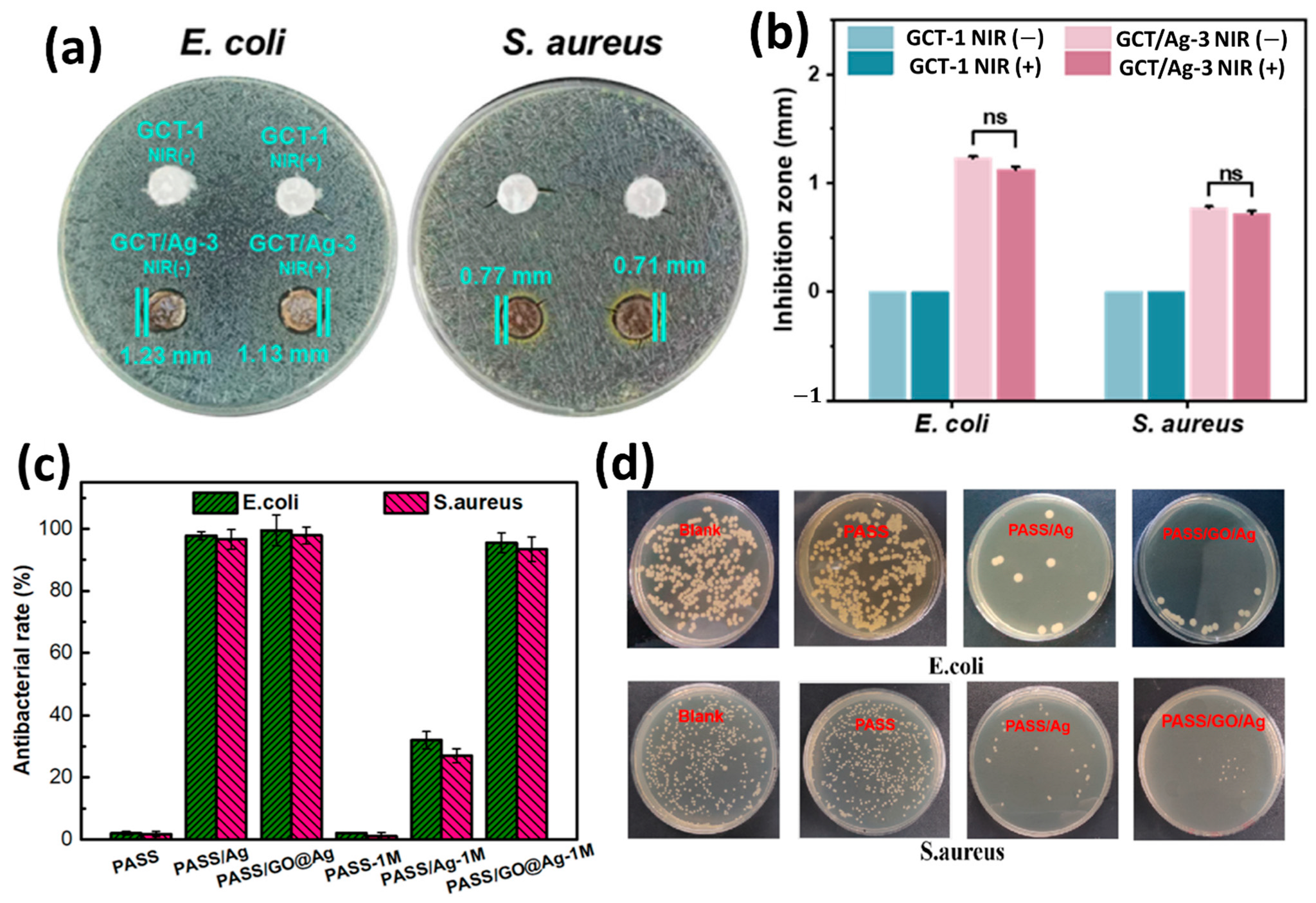
- Su, Q.; Huang, Y.; Wei, Z.; Zhu, C.; Zeng, W.; Wang, S.; Long, S.; Zhang, G.; Yang, J.; Wang, X. A novel multi-gradient PASS nanofibrous membrane with outstanding particulate matter removal efficiency and excellent antimicrobial property. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 307, 122652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Hu, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhang, W.; Chen, M. Electrospun poly(m-phenyleneisophthalamide)/TiO2 nanofiber membranes for particulate matter removal under high-temperature conditions. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2024, 6, 1633–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chueachot, R.; Promarak, V.; Saengsuwan, S. Enhancing antibacterial activity and air filtration performance in electrospun hybrid air filters of chitosan (CS)/AgNPs/PVA/cellulose acetate: Effect of CS/AgNPs ratio. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 338, 126515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.X.; Su, F.; Niu, H.; Wood, C.D.; Campbell, N.L.; Khimyak, Y.Z.; Cooper, A.I. Conjugated microporous poly(phenylene butadiynylene)s. Chem. Commun. 2008, 4, 486–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Tian, Z.; Sun, H.; Zhu, Z.; Liang, W.; Li, A. Self-cleaning and flexible filters based on aminopyridine conjugated microporous polymer nanotubes for bacteria sterilization and efficient PM2.5 capture. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 766, 142594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Lei, Y.; Fan, Y.; Zhou, P.; Liu, F.; Zhu, Z.; Sun, H.; Liang, W.; Li, A. Efficient capture of PM2.5 by intertwined tubular conjugated microporous polymer-based filters with high stability in a humid environment. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 7703–7711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.X.; Su, F.; Trewin, A.; Wood, C.D.; Campbell, N.L.; Niu, H.; Dickinson, C.; Ganin, A.Y.; Rosseinsky, M.J.; Khimyak, Y.Z.; et al. Conjugated microporous poly(aryleneethynylene) networks. Angew. Chem. 2007, 119, 8728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.J.; Kang, Z.; Zhu, W.Q.; Ding, Y.N.; Xu, H.Y.; Tan, D.Z.; Chen, Y.G. Conjugated microporous polymers as novel adsorbent materials for VOCs capture: A computational study. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2019, 170, 109207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, L.; Cao, X.; Chan, W.; Jing, Y.; Sun, H.; Zhu, Z.; Liang, W.; Li, J.; Li, A. Removal of PM and oil mist from automobile exhaust by a “hamburger”-structured conjugated microporous polymer membrane. Eur. Polym. J. 2023, 195, 112167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Lei, Y.; Ye, X.; Fan, Y.; Zhou, P.; Zhu, Z.; Sun, H.; Liang, W.; Li, A. Efficient capture of airborne PM by nanotubular conjugated microporous polymer-based filters under harsh conditions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 423, 127047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Niu, C.; Cao, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Sun, H.; Liang, W.; Li, J.; Li, A. Mechanically robust conjugated microporous polymer membranes prepared using polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) electrospun nanofibers as a template for efficient PM capture. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 637, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, B.; Wang, S.; Li, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, X.; Cui, M.; Yu, X.; Xu, Y.; Lei, Y.; Zhao, L. Simple synthesis of acyl coupling conjugated microporous polymer monolithic material for synergistic capture of PM and CO2 in flue gas and process simulation. Fuel 2024, 369, 131776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Tian, Z.; Sun, H.; Liu, F.; Zhu, Z.; Liang, W.; Li, A. Low-resistance thiophene-based conjugated microporous polymer nanotube filters for efficient particulate matter capture and oil/water separation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 5823–5833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, N.; Widjojo, N.; Sukitpaneenit, P.; Teoh, M.M.; Lipscomb, G.G.; Chung, T.S.; Lai, J.Y. Evolution of polymeric hollow fibers as sustainable technologies: Past, present, and future. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2012, 37, 1401–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Feng, X.; Lawless, D. Separation of gasoline vapor from nitrogen by hollow fiber composite membranes for VOC emission control. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 271, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogoi, M.; Goswami, R.; Borah, A.; Bhuyan, C.; Sarmah, H.; Hazarika, S. Functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotube thin-layered hollow fiber membrane for enantioselective permeation of racemic β-substituted-α-amino acids. J. Chem. Sci. 2022, 134, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Cai, T.; Chung, T.S. Anti-fouling behavior of hyperbranched polyglycerol-grafted poly(ether sulfone) hollow fiber membranes for osmotic power generation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 9898–9907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Feng, Y.; Wang, K.; Yong, W.F.; Yu, L.; Chung, T.S. Novel hollow fiber air filters for the removal of ultrafine particles in PM2.5 with repetitive usage capability. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 10041–10049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Jin, W.; Wang, F.; Li, C.; Wang, J.; Zhu, H.; Guo, Y. Preparation and properties of PTFE hollow fiber membranes for the removal of ultrafine particles in PM2.5 with repetitive usage capability. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 38245–38258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Chen, X.; Chen, M.; Luo, J.; Jin, W.; Zhu, H.; Guo, Y. Development of antibacterial PTFE hollow fiber membranes containing silver-carried zirconium phosphate as air filtration units for the removal of ultrafine particles. Fibers Polym. 2022, 23, 423–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulejko, P.; Dohnal, M.; Pospíšil, J.; Svěrák, T. Air filtration performance of symmetric polypropylene hollow-fiber membranes for nanoparticle removal. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 197, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y. Directional water transfer Janus nanofibrous porous membranes for particulate matter filtration and volatile organic compound adsorption. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 3109–3118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, W.; Fan, T.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Lu, C.; Ramakrishna, S.; Long, Y.Z. Robust functional Janus nanofibrous membranes for efficient harsh environmental air filtration and oil/water separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 663, 121018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Jiang, L.; Qu, X.; Sun, Y.; Zhu, J.; Li, X.; Ma, C.; Liu, R.; Ramakrishna, S. A porous Janus nanofiber membrane with unidirectional water vapor transport for efficient dust personal protection. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 353, 128531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, G.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Li, H.; Wang, L.; Li, Z.; Chen, J.; Wu, Y. Antibacterial biodegradable nanofibrous membranes by hybrid needleless electrospinning for high-efficiency particulate matter removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 461, 142137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, T.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Shang, Z.; Gong, J. Constructing Janus Microsphere Membranes for Particulate Matter Filtration, Directional Water Vapor Transfer, and High-Efficiency Broad-Spectrum Sterilization. Small 2022, 18, 2205010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Zhang, S.; Wan, D.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, Z.; Shao, G. Multilevel polarization-fields enhanced capture and photocatalytic conversion of particulate matter over flexible Schottky-junction nanofiber membranes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 395, 122639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, X.; Yang, Y.; Gou, Y.; Yang, Y.; Li, W.; Huang, J.; Cai, W.; Lai, Y. Electrospun heterojunction nanofibrous membranes for photoinduced enhancement of fine particulate matter capture in harsh environment. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 320, 124209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Si, Y.; Han, Y.; Wu, T.; Iqbal, M.I.; Fei, B.; Li, R.K.; Hu, J.; Qu, J. Recent progress in protective membranes fabricated via electrospinning: Advanced materials, biomimetic structures, and functional applications. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2107938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Li, T.; Ramakrishna, S.; Liu, Y. Progress of improving mechanical strength of electrospun nanofibrous membranes. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2020, 305, 2000230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiohara, A.; Prieto-Simon, B.; Voelcker, N.H. Porous polymeric membranes: Fabrication techniques and biomedical applications. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 2129–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, H.S.; Yong, W.F. Recent progress and prospects of polymeric hollow fiber membranes for gas application, water vapor separation and particulate matter removal. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 26454–26497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.C.; Xie, Y.; Hou, J.; Cheetham, A.K.; Chen, V.; Darling, S.B. Janus membranes: Creating asymmetry for energy efficiency. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1801495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Ji, D.; Zhou, G.; Liu, Z.; Xu, Q.; Ramakrishna, S. Electrospun nanofibers for personal protection in mines. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 404, 126558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yin, X.; Yu, J.; Ding, B. Electrospun nanofibers for high-performance air filtration. Compos. Commun. 2019, 15, 6–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Lai, W.; Shi, Y.; Tian, L.; Li, K.; Bian, L.; Xi, Z.; Lin, B. Ag-decorated electrospun polymer/GO fibrous membranes for simultaneous bacterial filtration and termination. J. Membr. Sci. 2024, 695, 122498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekin, D.; Birhan, D.; Kiziltas, H. Thermal, photocatalytic, and antibacterial properties of calcinated nano-TiO2/polymer composites. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 251, 123067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabila, M.I.; Kannabiran, K. Biosynthesis, characterization and antibacterial activity of copper oxide nanoparticles (CuO NPs) from actinomycetes. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2018, 15, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, G.; Huang, Z.; Wang, H.; Cui, C.; Zhang, Y. Polycaprolactone nanofiber membrane modified with halloysite and ZnO for anti-bacterial and air filtration. Appl. Clay Sci. 2022, 223, 106512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Yang, X.; Tang, B.; Yuan, L.; Wang, K.; Liu, X.; Zhu, X.; Li, J.; Ge, Z.; Chen, S. New insights into synergistic antimicrobial and antifouling cotton fabrics via dually finished with quaternary ammonium salt and zwitterionic sulfobetaine. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 336, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, C.; Wu, F.; Jiao, W.; Liu, X.; Yin, X.; Si, Y.; Yu, J.; Ding, B. Antibacterial and antiviral N-halamine nanofibrous membranes with nanonet structure for bioprotective applications. Compos. Commun. 2021, 24, 100668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saikaew, R.; Intasanta, V. Versatile nanofibrous filters against fine particulates and bioaerosols containing tuberculosis and virus: Multifunctions and scalable processing. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 275, 119171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Xiong, Y.; Xuan, S.; Kang, J.; Wang, D.; Wang, H.; Wang, L.; Wu, Z. Nanocellulose-reinforced air filter with gradient hierarchical structure for highly effective and reusable antibacterial air filtration. J. Membr. Sci. 2024, 693, 122340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Khan, M.S.A.; Borah, K.K.; Goswami, Y.; Hakeem, K.R.; Chakrabartty, I. The potential exposure and hazards of metal-based nanoparticles on plants and environment, with special emphasis on ZnO NPs, TiO2 NPs, and AgNPs: A review. Environ. Adv. 2021, 6, 100128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Yang, B.J.; Bae, G.N.; Jung, J.H. Herbal extract incorporated nanofiber fabricated by an electrospinning technique and its application to antimicrobial air filtration. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 25313–25320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, B.C.; Park, C.H.; Kim, C.S. Fabrication of antimicrobial nanofiber air filter using activated carbon and cinnamon essential oil. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2020, 20, 4376–4380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Dai, K.; Liu, C.; Hu, H.; Luo, F.; Qi, Q.; Wang, L.; Ye, F.; Jin, J.; Tang, J.; et al. Berberine-coated biomimetic composite microspheres for simultaneously hemostatic and antibacterial performance. Polymers 2021, 13, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, G.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Jiang, L.; Liu, R.; Wang, Y. Effect of different antibacterial agents doping in PET-based electrospun nanofibrous membranes on air filtration and antibacterial performance. Environ. Res. 2024, 243, 117877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Z.; Xie, J.; Jiang, J.; Shen, R.; Gui, Z.; Li, H.; Wang, X.; Li, W.; Guo, S.; Liu, Y.; et al. Research on topological effect of natural small molecule and high–performance antibacterial air filtration application by electrospinning. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 909, 168654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Ji, Z.; Qi, Q. Effect of surface wettability on filtration performance of gas–liquid coalescing filters. Powder Technol. 2019, 357, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Zong, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, M.; Zhang, R.; Li, S.; Wei, F. In situ fabrication of depth-type hierarchical CNT/quartz fiber filters for high-efficiency filtration of sub-micron aerosols and high water repellency. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 3367–3372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, P.; Zhao, X.; Li, Y.; Liao, Y.; Hua, T.; Yin, X.; Yu, J.; Ding, B. Moisture and oily molecules stable nanofibrous electret membranes for effectively capturing PM2.5. Compos. Commun. 2017, 6, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Li, Y.; Hua, T.; Jiang, P.; Yin, X.; Yu, J.; Ding, B. Cleanable air filter transferring moisture and effectively capturing PM2.5. Small 2017, 13, 1603306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Chen, F.; Wang, H.; Zhou, H.; Ji, Z.; Lin, T. Efficient removal of aerosol oil-mists using superoleophobic filters. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 871–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Liu, C.; Hsu, P.C.; Zhang, C.; Liu, N.; Zhang, J.; Lee, H.R.; Lu, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Chu, S.; et al. Nanofiber air filters with high-temperature stability for efficient PM2.5 removal from the pollution sources. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 3642–3649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Si, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yang, L.; Zhao, F.; Ding, B.; Yu, J. Silica nanofibrous membranes with robust flexibility and thermal stability for high-efficiency fine particulate filtration. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 12216–12223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, W.; Xia, Y.; Jiao, X.; Chen, D. Electrospun flexible self-standing γ-alumina fibrous membranes and their potential as high-efficiency fine particulate filtration media. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 15124–15131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Chen, J.; Feng, S.; Zhou, H.; Zhou, F.; Low, Z.X.; Zhong, Z.; Xing, W. Efficient removal of high-temperature particulate matters via a heat resistant and flame retardant thermally-oxidized PAN/PVP/SnO2 nanofiber membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 662, 120985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.; Liu, Y.; Li, L.; Song, J.; Wang, H.; Liu, Z.; Li, Z.; Li, B.; Fang, M.; Wu, H. A foldable all-ceramic air filter paper with high efficiency and high-temperature resistance. Nano Lett. 2020, 20, 4993–5000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, J.; Zeng, Y.; Low, Z.X.; Lin, Z.; Xu, X.; Feng, S.; Zhong, Z.; Xing, W. Zr-doped flexible TiO2 nanofibrous membranes for high-efficiency oily particulate matter removal from high-temperature flue gas. J. Membr. Sci. 2023, 679, 121700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Liu, C.; Hsu, P.C.; Xu, J.; Kong, B.; Wu, T.; Zhang, R.; Zhou, G.; Huang, W.; Sun, J.; et al. Core–shell nanofibrous materials with high particulate matter removal efficiencies and thermally triggered flame retardant properties. ACS Cent. Sci. 2018, 4, 894–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, T.; Teng, D.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Zeng, Y. Multi-functional air filters with excellent flame retardancy and fire-warning capability. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 617, 236–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, N.; Yan, L.; Ma, Y.; Sun, H.; Zhu, Z.; Liang, W.; Li, J.; Li, A. Electrospun modified SiO2 nanofiber membranes as superamphiphobic self-cleaning filters with high heat stability for efficient particle matter capture. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2022, 5, 9871–9881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Liu, J.; Chu, H.; Dong, B. Pretreatment and membrane hydrophilic modification to reduce membrane fouling. Membranes 2013, 3, 226–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petukhov, D.I.; Johnson, D.J. Membrane modification with carbon nanomaterials for fouling mitigation: A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2024, 327, 103140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuyan, C.; Bora, P.; Rajguru, P.; Hazarika, S. Thin film nanocomposite membrane ornamented with Z-scheme heterojunction carbon dot/NiFe–LDH for removal of organic contaminants from industrial wastewater. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 356, 129791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.researchandmarkets.com/report/hepa-filter (accessed on 25 November 2025).
- Available online: https://www.gminsights.com/industry-analysis/hvac-filters-market (accessed on 25 November 2025).
- Ribeiro, B.; Vázquez-López, A.; Vazquez-Pufleau, M.; Llamosí, M.; Sempere, J.; Yuste, J.; Domenech, M.; Wang, D.Y.; Vilatela, J.J.; Llorca, J.; et al. Control of microbial agents by functionalization of commercial air filters with metal oxide particles. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2024, 313, 128684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bächler, P.; Szabadi, J.; Meyer, J.; Dittler, A. Simultaneous measurement of spatially resolved particle emissions in a pilot plant scale baghouse filter applying distributed low-cost particulate matter sensors. J. Aerosol Sci. 2020, 150, 105644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Huo, Q.; Zhou, Y.Y.; Wang, H.H.; Li, G.P.; Wang, Y.W.; Wang, Y.Y. Textiles/metal–organic frameworks composites as flexible air filters for efficient particulate matter removal. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 17368–17374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Jang, J.; Kim, J.; Lim, S.H. A recyclable indoor air filter system based on a photocatalytic metal–organic framework for the removal of harmful volatile organic compounds. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 430, 132891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinke, F.; Meyer, J.; Dittler, A. Investigation of the potential of in-line particle concentration measurements in gas particle separation processes by using low-cost particulate matter sensors. J. Aerosol Sci. 2025, 183, 106476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, D.; Zhu, M.; Jiang, Z.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Xiong, R.; Huang, C. Green electrospun nanofibers and their application in air filtration. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2018, 303, 1800336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ángel-Gómez, S.; Berger, S.; Niessner, J.; Álvarez-Láinez, M.L. Air filtration performance of nanofiber membranes with different morphologies produced by green electrospinning. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2024, 141, e54870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Pollutant | Averaging Time | Air Quality Guideline Levels Set by WHO b | Air Quality Guideline Levels Set by NAAQS a | Air Quality Guideline Levels in UK |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM2.5 | Annual | 5 μg/m3 | 40 μg/m3 | - |
| 24 h | 15 μg/m3 | 60 μg/m3 | - | |
| PM10 | Annual | 15 μg/m3 | 60 μg/m3 | - |
| 24 h | 45 μg/m3 | 100 μg/m3 | 40 μg/m3 |
| Methods | Separation Principle | Cost | Pollutants | Merits | Demerits | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mechanical air filter | Size exclusion | High | PM2.5 PM0.3 | Good separation efficiency | Pore clogging | [46] |
| HEPA | Brownian motion | High | PM2.5 (≤) PM0.3 | High separation efficiency | Pore clogging, Low durability | |
| ESP | Electric voltage | High | PM (all) | Separates pollutants irrespective of size | Requires high voltage | |
| AC | Size exclusion | - | Gaseous pollutants | Offers separation of gas pollutant | Not applicable to pollutants like PM | |
| UV light purification | Oxidative degradation | - | Bacteria, pathogens | Simple operation | Not applicable to pollutants like PM | |
| NF filters | Size exclusion, adsorption | Low | PM2.5, PM10 | Tunable pore size, pore density, and significant aspect ratio, cost-effective, energy efficiency, high permeability | Poor thermal and mechanical properties, pore clogging | [15] |
| Membranes | Size exclusion | Low | PM2.5, PM10 | Poor mechanical and thermal properties, membrane fouling | ||
| Cyclone separator | Centrifugal force | Low to moderate | PM10 | Low maintenance, cost-effectiveness, durability, robustness, versatility | Low efficiency for fine particles, significant pressure drop, sensitivity to sticky/wet materials, etc. | [48] |
| Materials | Polymers | PM Size (μm) | EPM (%) | ∆P (Pa) | QF (Pa−1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synthetic polymers | PI | 2.5 | 99.97 | 73 | 0.1072 | [13] |
| PS | 2.5 | 99.99 | 145 | 0.15 | ||
| PU | 2.5 | 99.73 | 28 | 0.211 | ||
| PAN | 2.5 | 96.12 | 133 | 0.024 | ||
| PVA | 2.5 | 96.70 | 178 | 0.019 | ||
| PVP | 2.5 | 95 | 101 | 0.029 | ||
| PAA | 2.5 | 99.6 | 146.3 | 0.034 | ||
| PVDF | 2.5 | 98.16 | 30 | 0.12 | ||
| PVA/carbon nanoparticle/tea leaf extract | 10 | 99.29 | 110 | - | [83] | |
| Self-supporting CMP membrane (SS-CMPs-M) | 2.5 | 99.7 | 550 | 0.01337 | [84] | |
| 10 | 99.9 | 550 | 0.01383 | |||
| Porous gradient geopolymer-based tube membrane (PGTM) | 2.5 | 96.5–98.7 | 0.01 MPa | - | [85] | |
| 10 | 98.0–99.5 | |||||
| PLA/ZnCo-ZIF fibrous membranes | 2.5 | 90.88 | - | - | [86] | |
| 10 | 93 | |||||
| Holey-reduced graphene oxide membrane | 1.0 | 98.99 | - | - | [87] | |
| 2.5 | 99.91 | |||||
| 5 | 99.99 | |||||
| 10 | 99.99 | |||||
| Zn-based zeolite imidazole frameworks (2D-ZIF-Ls) | 2.5 | 92.5 | 10.5 | - | [88] | |
| 10 | 99.5 | |||||
| Biopolymers | Silk fibroin | 0.3 | 91.4 | 92 | - | [89] |
| 0.5 | 95.4 | |||||
| 1.0 | 98.3 | |||||
| Cellulose nanofibril | 0.3 | 94.6 | 174.2 | 0.0168 | [80] | |
| Zein | 0.3 | 97 | - | - | [81] | |
| Chitosan | 2.5 | 98.3 | 59 | - | [79] | |
| Cellulose | 10 | 99.08 | 31–34 | - | [90] | |
| Zr-MOF-NO2/cotton | 10 | 89.5 | 31 | 185.6 | [91] | |
| Ultrathin Al2O3 on microporous cellulose ester membranes | 1 | 76.4 | 135 | - | [92] | |
| 2.5 | 94 | |||||
| 10 | 95.1 | |||||
| PVA/Cellulose nanocrystal composite nanofibrous filter | 2.5 | 99.1 | 91 | 0.052 | [69] | |
| Chitosan/NH2-MIL-53 | 2.5 | 98.41 | 24.10 | 0.1718 | [93] | |
| 10 | 99.05 | |||||
| Chitosan/PVA–SiO2 nanofiber | 2.5 | 96.94 | 15.7 | 0.05941 | [94] | |
| 10 | 99.34 |
| Air Filter Materials | Advantages | Limitations | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Synthetic polymers |
|
| [110] |
| Biopolymers |
|
| [82] |
| Porous materials |
|
| [95,111] |
| Carbon-based materials |
|
| [112,113] |
| Electrical filter materials |
|
| [114] |
| Nanowire networks |
|
| [108,115] |
| Polymer | Fabrication Technique | a TS (MPa) | Basic Weight (g/m2) | Target Molecule | EPM (%) | ∆P (Pa) | QF (Pa−1) | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PMIA | ESN | 72.8 | 0.365 | 300–500 nm NaCl aerogel particles | 99.999 | 92 | 0.183 | [60] |
| PU | ESN | 13–15 | 0.36 | PM1–0.5 PM2.5–1 | >99.00 >99.73 | 28 | 0.12 | [117] |
| N6/PAN | ESN | - | 2.94 | 300 nm NaCl aerosol particle | 99.99 | 37–60 | 0.1163 | [135] |
| PA-6 | ESN | - | 0.9 | 300–500 nm NaCl aerogel particles | 99.996 | 95 | >0.11 | [136] |
| PA-56 | ESN | 11.02 | ~0.63 | 300–500 nm NaCl aerogel particles | 99.995 | 111 | 0.108 | [137] |
| PLA | ES | - | 5.21 | NaCl aerosol particles of 260 nm average diameter | 99.997 | 165.3 | 0.06 | [76] |
| PEO@PAN/PSU | ES | 8.2 | 3.5 | 300–500 nm NaCl aerogel particles | 99.992 | 95 | 0.1 | [138] |
| PLLA b | ES | - | - | PM2.5 PM0.3 | >99.9 >99.5 | ≈20 | - | [139] |
| PLA | ES | 14.19 | - | PM0.3 | 99.992 | 107 | - | [131] |
| Polymer | Additive | Fabrication Technique | a TS (MPa) | Target Molecule | EPM (%) | ∆P (Pa) | QF (Pa−1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVDF | b GPS@SiO2 NPs | ES | - | NaCl aerosols | 99.996 | 14–18.5 | 0.14 | [56] |
| PEI | MgTPP @EDA | ES | - | CO2 PM2.5 | 74 | 436 | - | [57] |
| PAN | MOF | ES | - | PM | 99.99 | 30.5 | - | [140] |
| PAN | c AgNPs d MA NPs | ES | - | PM2.5 | 99.1 | - | - | [143] |
| PAN | MOF@ e BCP | ESN | - | Sub-100 nm particles | 86.2% | 51.4 | 0.0387 | [144] |
| f CNF | Carbon nanoparticle | ES | 26.48 ± 0.4 | - | 99.99% | - | - | [129] |
| PVDF | GO | ES | 3.76 | PM2.5 | 99.31 | 28.17 | 0.049 | [103] |
| g PASS | GO@Ag | ES | 2.39 ± 0.07 | PM0.30–2.50 | 99.63 ± 0.34 | 79.17 ± 1.07 | ~0.065 | [145] |
| PMIA | TiO2 | ES | - | PM2.5 | 99.3 | 61 | - | [146] |
| PS | HAP/ZIF-8 | ES | - | PM2.5 PM10 | 96.68 96.98 | - | - | [142] |
| h CA, PVA, chitosan | Ag NPs | - | - | PM2.5 | 99.78 | 61.15 | 0.09 | [147] |
| Polymer | Modified with/Monomer | Target Molecule | EPM (%) | ∆P (Pa) | QF (Pa−1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CMPs | Aminopyridine | PM2.5 PM10 | ≥99.57 ± 0.19 ≥99.98 ± 0.01 | 30–270 | 0.42 | [149] |
| Tubular CMPs | Bromated monomers | PM2.5 PM10 | 99.97 >99 | 25 | - | [150] |
| CMPs | - | PM2.5 PM10 | 99.7 99.9 | 60–550 | - | [84] |
| CMPs | - | PM0.3 PM2.5–10 | >95 >99.5 | - | - | [153] |
| CMPs | PVP | PM0.3 PM0.5 PM2.5–10 | 95.18 98 >99 | 35–40 | - | [155] |
| CMPs | Acyl functional group | PM0.3 PM2.5–10 | >99.24 ± 0.13 99.99 | - | - | [156] |
| CMP nanotube | - | PM0.3 PM2.5–10 | 99.4 99.9 | 10 | - | [154] |
| CMP nanotube | Thiophene | PM0.3 PM2.5 | 99.798 ± 0.055 99.998 ± 0.002 | 5 | 2.03, 1.01 | [157] |
| Polymer | Modified with | Target Molecule | EPM (%) | ∆P (Pa) | QF (kPa−1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PES | - | Ultrafine particles in PM2.5 | 99.995 | - | - | [162] |
| PTFE | - | PM0.3 PM2.5 | 90 99.99 | <400 | - | [163] |
| PTFE | AgZrP | PM0.3 PM2.5 | 97.7324 99.9984 | - | - | [164] |
| PP | - | Particle size > 60 nm 35.9–40 nm | 99 82–86 | - | 2–28 | [165] |
| Polymer | Modified with | Contact Angle (Hydrophobic /Hydrophilic) | Target Molecule | EPM (%) | ∆P (Pa) | QF (Pa−1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
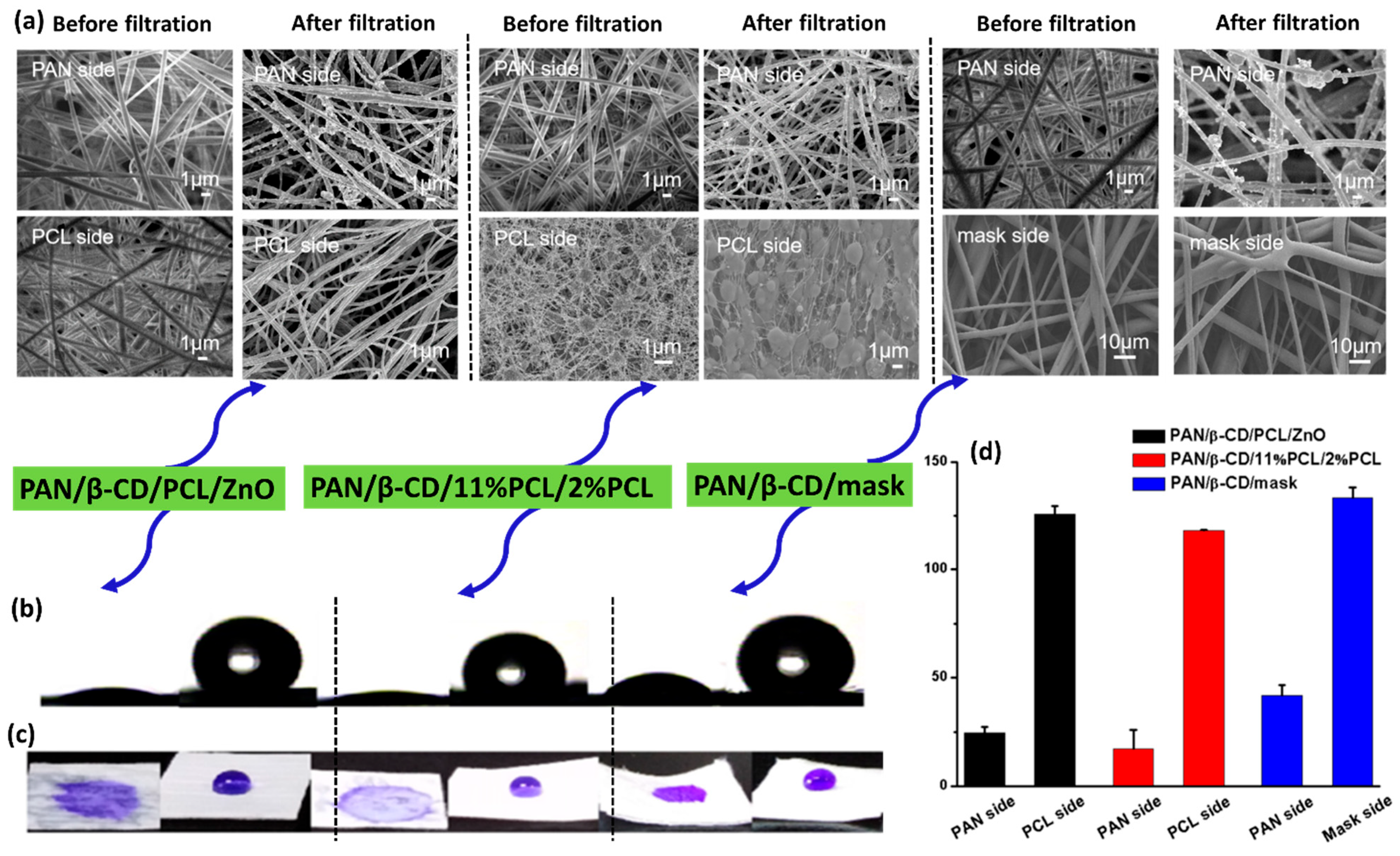
| PAN | β-CD/PCL/ZnO | 125.6°/24.6° | PM | 99.99 | 156.5 | 0.05885 | [166] |
| β-CD/11% PCL/2% PCL | 118.1°/17.4° | 99.98 | 165.1 | 0.05159 | |||
| β-CD/mask | 133.1°/41.7° | 91.56 | 15.2 | 0.1626 | |||
| PAN | TiO2/(PVDF-HFP)@SiO2 | 150 ± 2.5°/0° | PM0.3 | 99.7 | 27 | 0.2152 | [167] |
| PP and cotton fiber | 12-hydroxystearic acid and halicin | 157.1°/0° | PM2.5 PM10 | 93.54 98.35 | 57 | 0.072 | [170] |
| PAN/PVP | PCL | 145°/0° | Dust particles | 99.98 | 134.7 | 0.065 | [168] |
| CA | Quaternary chitosan | - | PM0.3 PM1.0 PM2.5 | 96.4 99.9 100 | 48 | - | [169] |
| Polymer | Modified with | Antibacterial Activity | Target Molecule | EPM (%) | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pathogen | Antibacterial Efficiency | |||||
| PCL | a HNTs-ZnO/PCL | S. aureus | 97.9% | PM2.5 | 92.10 | [183] |
| E. coli | 95.9% | |||||
| b HEI-PVP | Sophora flavescens | S. epidermidis | ∼99.98% | PM0.5–20 | 99.99 | [189] |
| PU | AC/c CO | S. aureus | 11.1 (d ZI) | 300–500 nm NaCl | 68.23 | [190] |
| E. coli | 12.7 (d ZI) | |||||
| PP and cotton fiber | 12-hydroxystearic acid and halicin | E. coli | 99.9999 | PM2.5 PM10 | 93.54 98.35 | [170] |
| CA | Quaternary chitosan | E. coli | 98.27 ± 0.45% | PM0.3 PM1.0 PM2.5 | 96.4 99.9 100 | [169] |
| S. aureus | 98.65 ± 0.26% | |||||
| PET/PVA | TiO2 and Ag | E. coli | 98.7% | NaCl | 99.87 | [192] |
| S. aureus | 95.9% | e DEHS | 99.89 | |||
| Chitosan/PVA/CA | Ag NPs | E. coli | 100–141% | PM2.5 | 99.78 | [147] |
| S. aureus | ||||||
| Ethyl cellulose | Tea polyphenol | E. coli | 99.99% | 0.3 μm NaCl particles | 99.991 | [193] |
| S. aureus | ||||||
| PSF | Ag NPs and GO nanosheet | S. aureus | >99.99% | S. aureus | >99.9 | [180] |
| E. coli | ||||||
| K. pneumoniae | ||||||
| C. albicans, | ||||||
| B. subtilis | ||||||
| PAN | Chitosan biguanide hydrochloride | E. coli | >99.99% | PM | 98 | [133] |
| S. aureus | ||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bora, P.; Bhuyan, C.; Lakshmi, D.S.; Hazarika, S.; Tanczyk, M.; Srimath, S.T.G. Recent Advances in Membrane-Based Air Filtration Technologies for Ambient Particulate Matter Separation. Polymers 2025, 17, 3265. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17243265
Bora P, Bhuyan C, Lakshmi DS, Hazarika S, Tanczyk M, Srimath STG. Recent Advances in Membrane-Based Air Filtration Technologies for Ambient Particulate Matter Separation. Polymers. 2025; 17(24):3265. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17243265
Chicago/Turabian StyleBora, Prarthana, Chinmoy Bhuyan, Duraikkanu Shanthana Lakshmi, Swapnali Hazarika, Marek Tanczyk, and Srinivas T. G. Srimath. 2025. "Recent Advances in Membrane-Based Air Filtration Technologies for Ambient Particulate Matter Separation" Polymers 17, no. 24: 3265. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17243265
APA StyleBora, P., Bhuyan, C., Lakshmi, D. S., Hazarika, S., Tanczyk, M., & Srimath, S. T. G. (2025). Recent Advances in Membrane-Based Air Filtration Technologies for Ambient Particulate Matter Separation. Polymers, 17(24), 3265. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17243265







