Modulating Cell–Scaffold Interaction via dECM-Decorated Melt Electrowriting PCL Scaffolds
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Decellularization of Porcine Skeletal Muscle Tissue
2.2. Characterization of dECM
2.3. Preparation of dECM/PCL Scaffold
2.4. Mechanical Testing
2.5. In Vitro Bioactivity of dECM Based Scaffolds
2.6. CCK8
2.7. Surface Morphology and Characterization with SEM, FTIR and Contact Angle
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
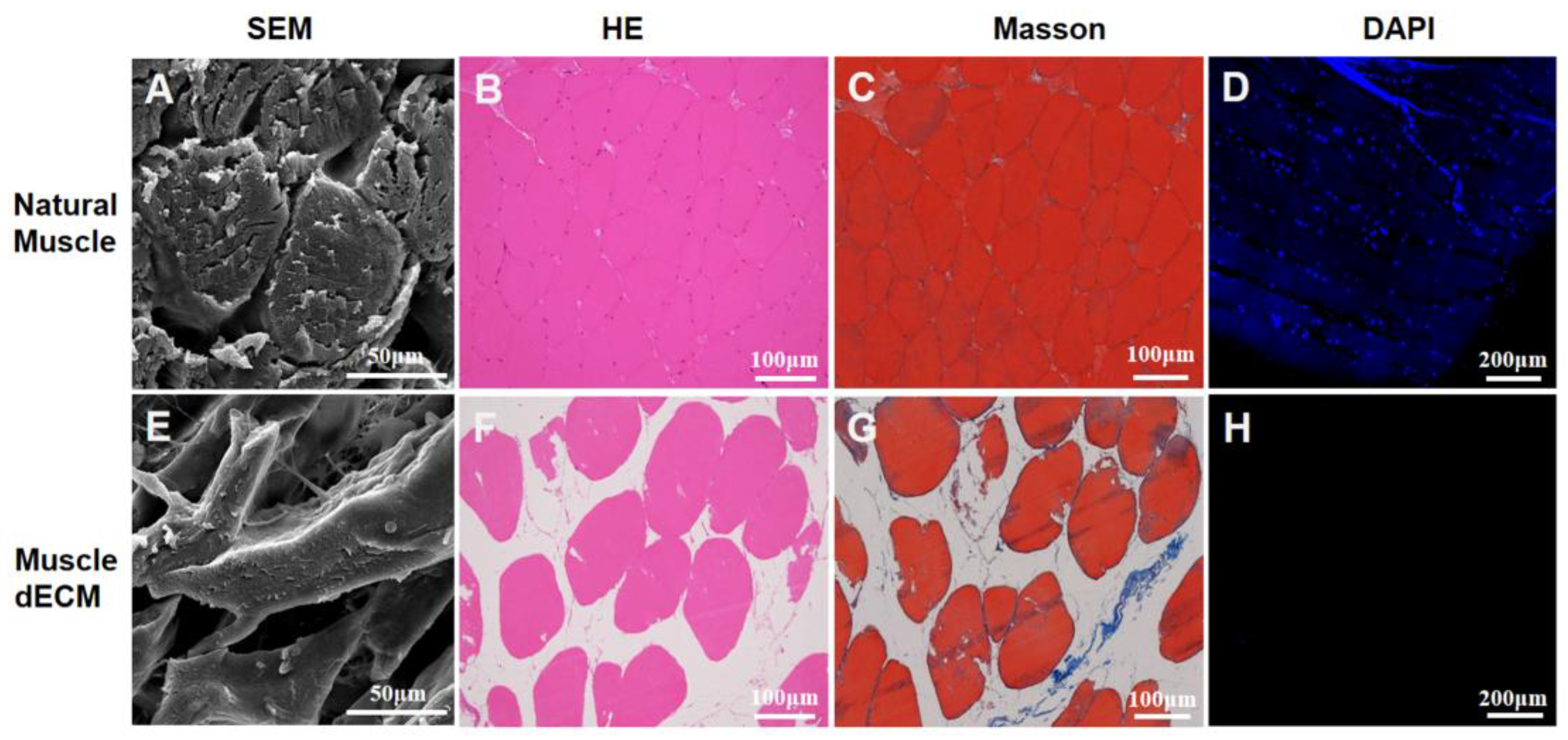
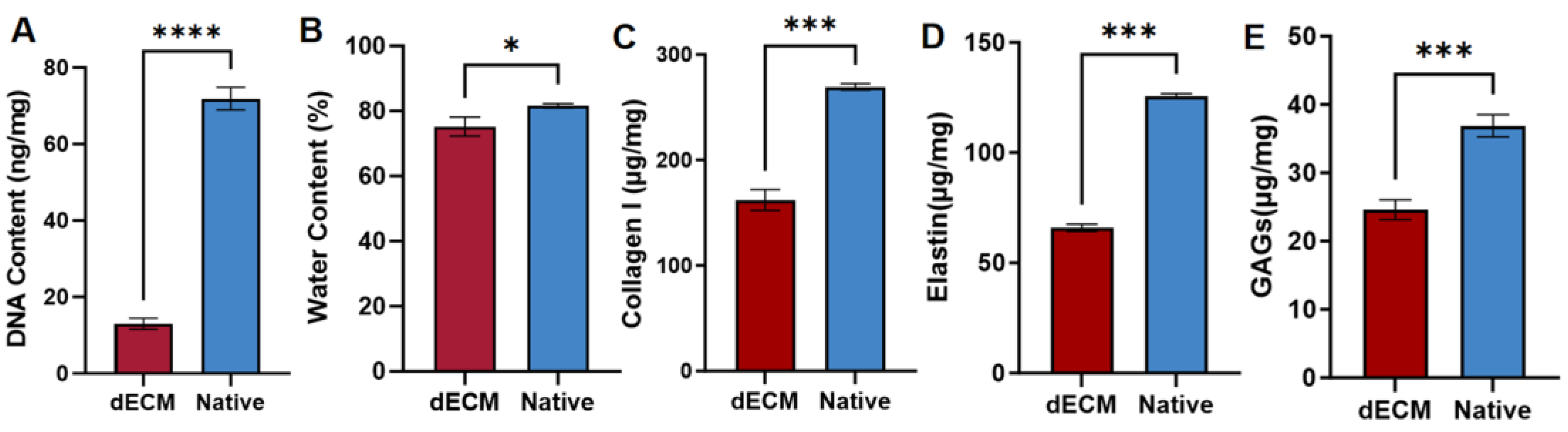
3.1. Decellularization of Skeletal Muscle Tissue
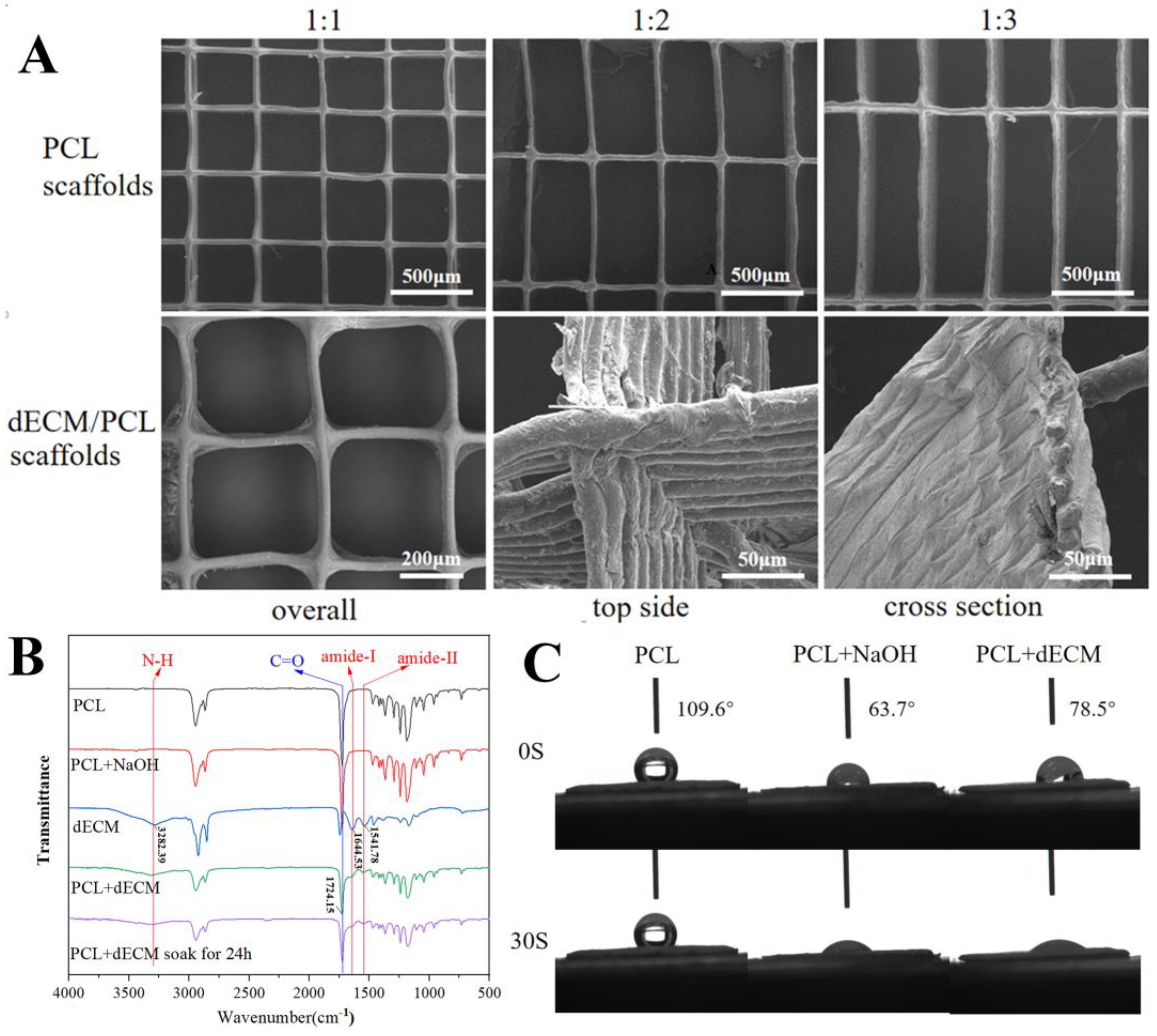
3.2. Surface Morphology and Characterization of dECM/PCL Scaffolds
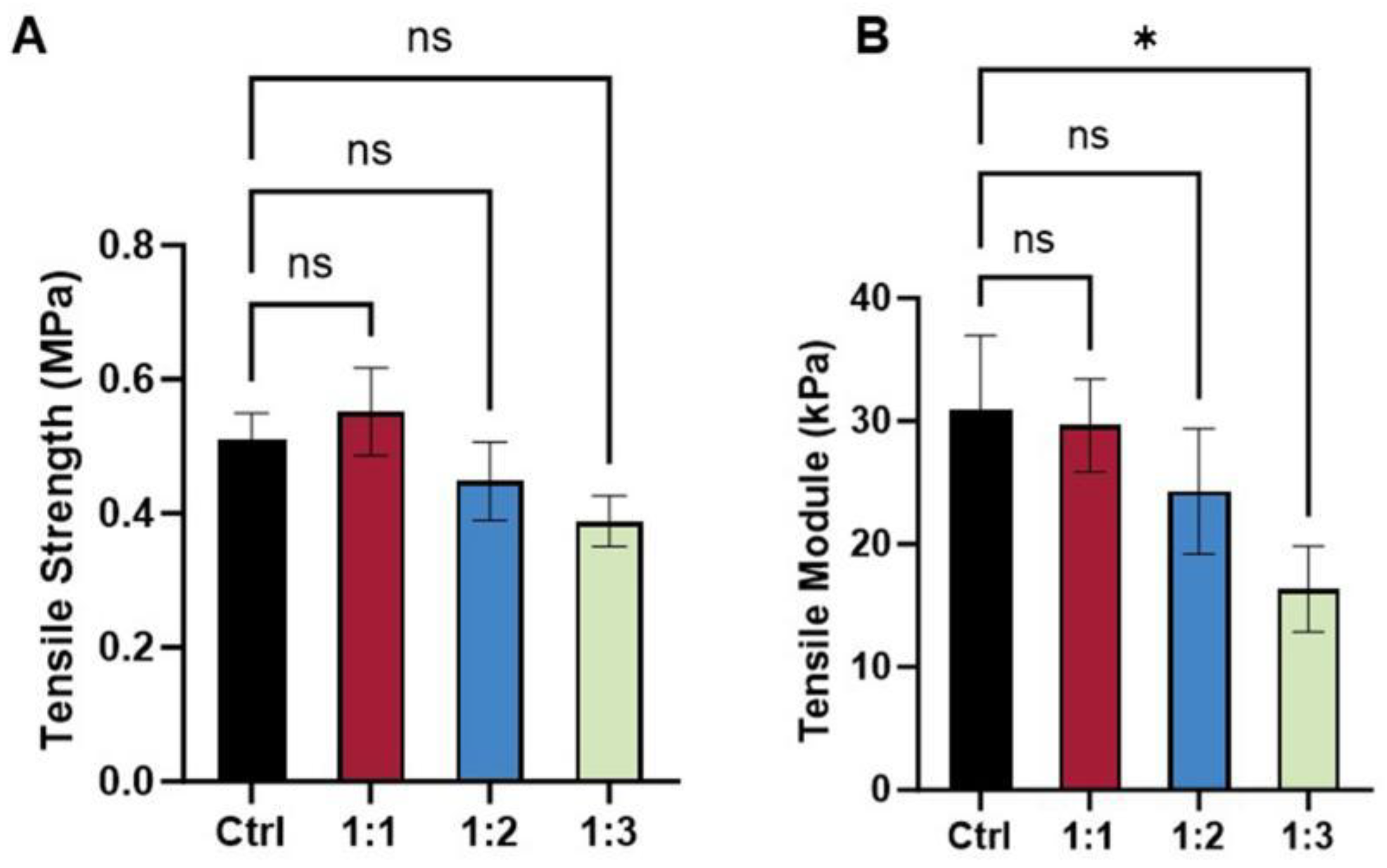
3.3. Mechanical Property of dECM/PCL Scaffolds
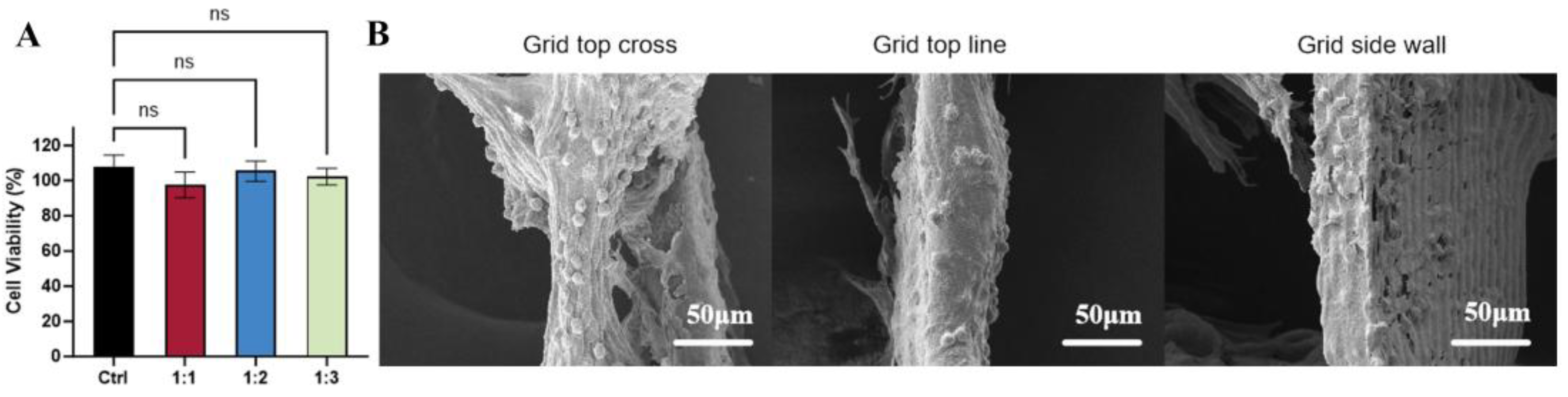
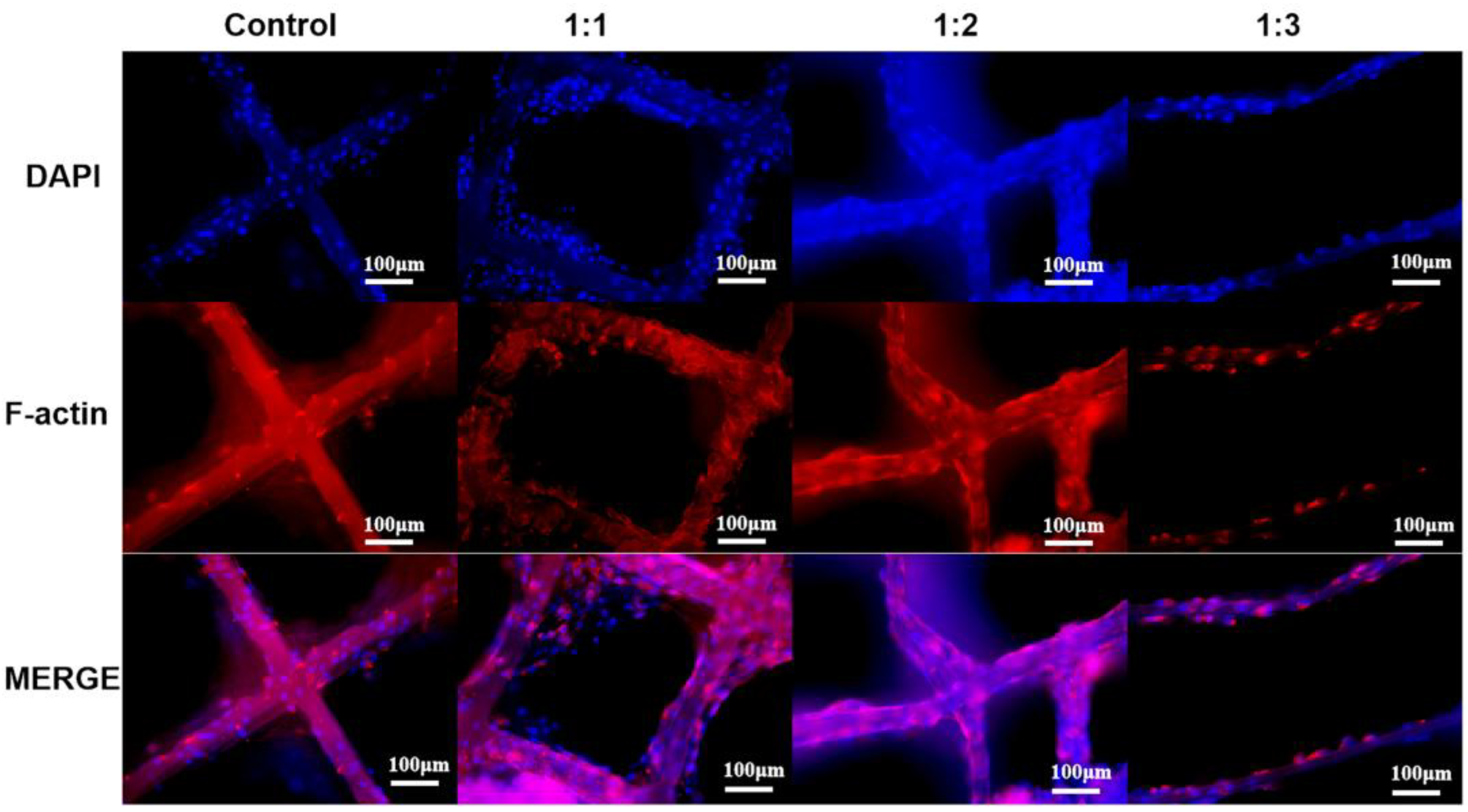
3.4. Cell Viability and Morphology on dECM/PCL Scaffolds
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pan, Y.; Zhu, H.; Hou, L. Epidemiological analysis and emergency nursing care of oral and craniomaxillofacial trauma: A narrative review. Ann. Palliat. Med. 2022, 11, 1518–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuya, M.; Shoji, T. In vitro construction of skeletal muscle tissues. Clin. Calcium 2017, 27, 383–389. [Google Scholar]
- Serbo, J.V.; Sharon, G. Vascular tissue engineering: Biodegradable scaffold platforms to promote angiogenesis. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2013, 4, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakhshandeh, B.; Zarrintaj, P.; Oftadeh, M.O.; Keramati, F.; Fouladiha, H.; Sohrabi-Jahromi, S.; Ziraksaz, Z. Tissue engineering; strategies, tissues, and biomaterials. Biotechnol. Genet. Eng. Rev. 2017, 33, 144–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, Y.M.; Shin, H.J.; Heo, Y.; Jun, I.; Chung, Y.-W.; Kim, K.; Lim, Y.M.; Jeon, H.; Shin, H. Engineering an aligned endothelial monolayer on a topologically modified nanofibrous platform with a micropatterned structure produced by femtosecond laser ablation. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 318–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jana, S.; Levengood, S.K.L.; Zhang, M. Anisotropic Materials for Skeletal-Muscle-Tissue Engineering. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 10588–10612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, C.S.; Behbehani, M.; Glen, A.; Basnett, P.; Gregory, D.A.; Lukasiewicz, B.B.; Nigmatullin, R.; Claeyssens, F.; Roy, I.; Haycock, J.W. Aligned polyhydroxyalkanoate blend electrospun fibers as intraluminal guidance scaffolds for peripheral nerve repair. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2023, 9, 1472–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loewner, S.; Heene, S.; Baroth, T.; Heymann, H.; Cholewa, F.; Blume, H.; Blume, C. Recent advances in melt electro writing for tissue engineering for 3D printing of microporous scaffolds for tissue engineering. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 896719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ladd, M.R.; Lee, S.J.; Stitzel, J.D.; Atala, A.; Yoo, J.J. Co-electrospun dual scaffolding system with potential for muscle–tendon junction tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2022, 32, 1549–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.J.; Hwang, K.S.; Kwon, H.J.; Lee, C.; Kim, C.H.; Kim, T.H.; Heo, S.W.; Kim, J.-H.; Lee, J.-Y. Rapid development of dual porous poly (lactic acid) foam using fused deposition modeling (FDM) 3D printing for medical scaffold application. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 110, 110693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Gao, Q.; Wang, P.; Shao, L.; Yuan, H.; Fu, J.; Chen, W.; He, Y. Structure-induced cell growth by 3D printing of heterogeneous scaffolds with ultrafine fibers. Mater. Des. 2019, 181, 108092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Jia, B.; Lian, M.; Sun, B.; Wu, Q.; Sun, B.; Qiao, Z.; Dai, K. High-precision, gelatin-based, hybrid, bilayer scaffolds using melt electro-writing to repair cartilage injury. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 6, 2173–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, M.; Dodi, G.; Gardikiotis, I.; Pasca, S.-A.; Mirdamadi, S.; Subra, G.; Echalier, C.; Puel, C.; Morent, R.; Ghobeira, R.; et al. 3D high-precision melt electro written polycaprolactone modified with yeast derived peptides for wound healing. Biomater. Adv. 2023, 149, 213361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cady, E.; Orkwis, J.A.; Weaver, R.; Conlin, L.; Madigan, N.N.; Harris, G.M. Micropatterning decellularized ECM as a bioactive surface to guide cell alignment, proliferation, and migration. Bioengineering 2020, 7, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Junka, R.; Zhou, X.; Wang, W.; Yu, X. Albumin-coated polycaprolactone (PCL)–decellularized extracellular matrix (dECM) scaffold for bone regeneration. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2022, 5, 5634–5644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.S.; Karan, A.; Tran, H.Q.; John, J.V.; Andrabi, S.M.; Shahriar, S.S.; Xie, J. Decellularized extracellular matrix-decorated 3D nanofiber scaffolds enhance cellular responses and tissue regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2024, 184, 81–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galarraga, J.H.; Locke, R.C.; Witherel, C.E.; Stoeckl, B.D.; Castilho, M.; Mauck, R.L.; Malda, J.; Levato, R.; Burdick, J.A. Fabrication of MSC-laden composites of hyaluronic acid hydrogels reinforced with MEW scaffolds for cartilage repair. Biofabrication 2021, 14, 014106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Hu, Z.Q.; Turner, N.J.; Teng, S.F.; Cheng, W.Y.; Zhou, H.Y.; Zhang, L.; Hu, H.W.; Wang, Q.; Badylak, S.F. Perfusion-decellularized skeletal muscle as a three-dimensional scaffold with a vascular network template. Biomaterials 2016, 89, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wunner, F.M.; Bas, O.; Saidy, N.T.; Dalton, P.D.; Pardo, E.M.D.; Hutmacher, D.W. Melt Electrospinning Writing of Three-dimensional Poly(ε-caprolactone) Scaffolds with Controllable Morphologies for Tissue Engineering Applications. J. Vis. Exp. 2017, 130, e56289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Hu, Y.; Shi, L.; Zhang, X.; Xiong, L.; Zhang, W.; Ullah, I. Electrospinning of Polycaprolactone/Pluronic F127 dissolved in glacial acetic acid: Fibrous scaffolds fabrication, characterization and in vitro evaluation. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2018, 29, 1155–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pati, F.; Jang, J.; Ha, D.-H.; Kim, S.W.; Rhie, J.-W.; Shim, J.-H.; Kim, D.-H.; Cho, D.-W. Printing three-dimensional tissue analogues with decellularized extracellular matrix bioink. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osahor, A.; Deekonda, K.; Lee, C.-W.; Sim, E.U.-H.; Radu, A.; Narayanan, K. Rapid preparation of adherent mammalian cells for basic scanning electron microscopy (SEM) analysis. Anal. Biochem. 2017, 534, 46–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Liu, S.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, B.; Su, Y.; Zheng, C.; Tian, R.; Wang, M.; Kuang, H.; Zhao, X.; et al. Mesenchymal stem cells and extracellular matrix scaffold promote muscle regeneration by synergistically regulating macrophage polarization toward the M2 phenotype. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2018, 9, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Ju, Y.M.; Kim, I.; Elsangeedy, E.; Lee, J.H.; Yoo, J.J.; Atala, A.; Lee, S.J. A novel decellularized skeletal muscle-derived ECM scaffolding system for in situ muscle regeneration. Methods 2020, 171, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crapo, P.M.; Gilbert, T.W.; Badylak, S.F. An overview of tissue and whole organ decellularization processes. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 3233–3243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewitt, E.; Mros, S.; Mcconnell, M.; Cabral, J.; Ali, A. Melt-electrowriting with novel milk protein/PCL biomaterials for skin regeneration. Biomed. Mater. 2019, 14, 055013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smoak, M.M.; Hogan, K.J.; Grande-Allen, K.J.; Mikos, A.G. Bioinspired electrospun dECM scaffolds guide cell growth and control the formation of myotubes. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabg4123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Discher, D.E.; Janmey, P.; Wang, Y.L. Tissue cells feel and respond to the stiffness of their substrate. Science 2005, 310, 1139–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elomaa, L.; Keshi, E.; Sauer, I.M.; Weinhart, M. Development of GelMA/PCL and dECM/PCL resins for 3D printing of acellular in vitro tissue scaffolds by stereolithography. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 112, 110958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.; Guo, W.; Chen, M.; Yuan, Z.; Wang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Xi, T.; Guo, Q. Fabrication and characterization of electrospun nanofibers composed of decellularized meniscus extracellular matrix and polycaprolactone for meniscus tissue engineering. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 2273–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, H.; Gong, B.; Yin, J.; Qian, J. 3D printing topographic cues for cell contact guidance: A review. Mater. Des. 2022, 218, 110663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, C.M.; Haugh, M.G.; O’brien, F.J. The effect of mean pore size on cell attachment, proliferation and migration in collagen–glycosaminoglycan scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shetty, S.S.; Shetty, S.; Venkatesh, S.B. Tissue engineering in oral and maxillofacial rehabilitation—current status and future prospects. Curr. Oral Health Rep. 2024, 11, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, N.; Abdal-Hay, A.; Hamlet, S.; Graham, E.; Ivanovski, S. Effects of gradient and offset architectures on the mechanical and biological properties of 3-D melt electrowritten (MEW) scaffolds. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 5, 3448–3461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, W.; Gao, X.; Zhang, P. Modulating Cell–Scaffold Interaction via dECM-Decorated Melt Electrowriting PCL Scaffolds. Polymers 2025, 17, 3133. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17233133
Li W, Gao X, Zhang P. Modulating Cell–Scaffold Interaction via dECM-Decorated Melt Electrowriting PCL Scaffolds. Polymers. 2025; 17(23):3133. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17233133
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Wenchao, Xiang Gao, and Peng Zhang. 2025. "Modulating Cell–Scaffold Interaction via dECM-Decorated Melt Electrowriting PCL Scaffolds" Polymers 17, no. 23: 3133. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17233133
APA StyleLi, W., Gao, X., & Zhang, P. (2025). Modulating Cell–Scaffold Interaction via dECM-Decorated Melt Electrowriting PCL Scaffolds. Polymers, 17(23), 3133. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17233133





