Biosensor Based on Electrochemical Analysis for Staphylococcus aureus Detection with Molecular Imprinted Polymer Technique
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
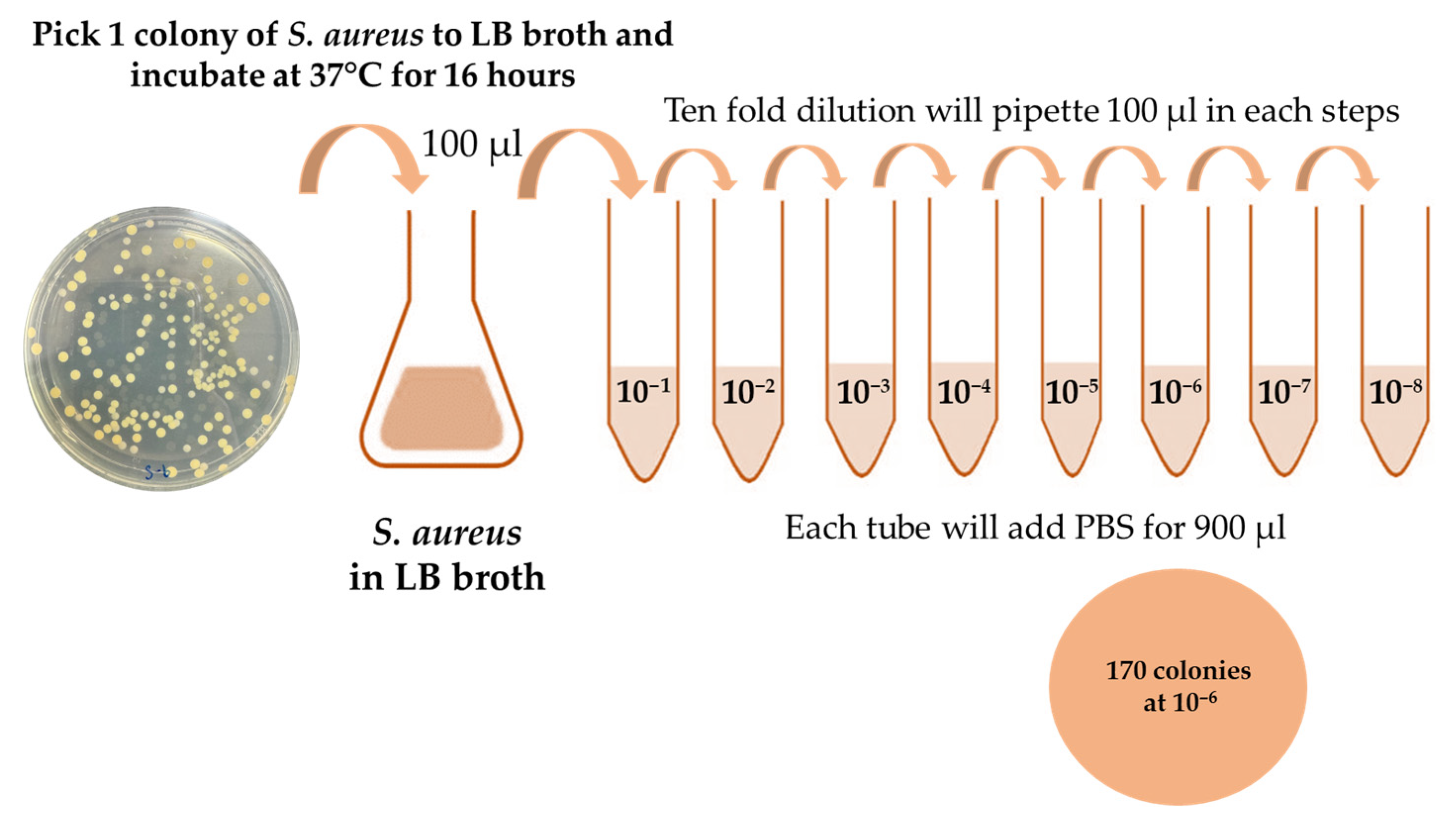
2.1. Staphylococcus aureus Preparation
2.2. Quantification of S. aureus Cells Applied to the Electrode Surface
2.3. Molecular Imprinted Polymer on Screen Printed Electrode
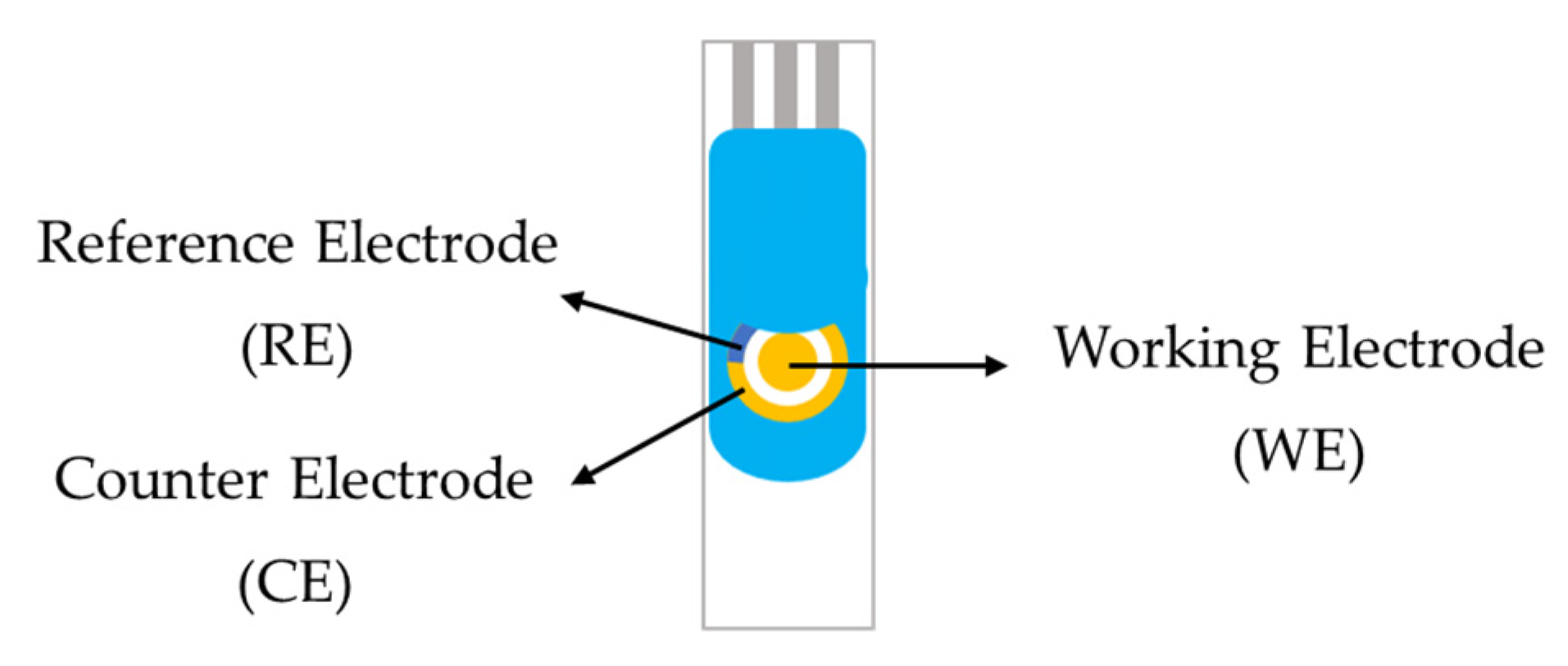
2.4. Electrochemical Sensors for Analysis
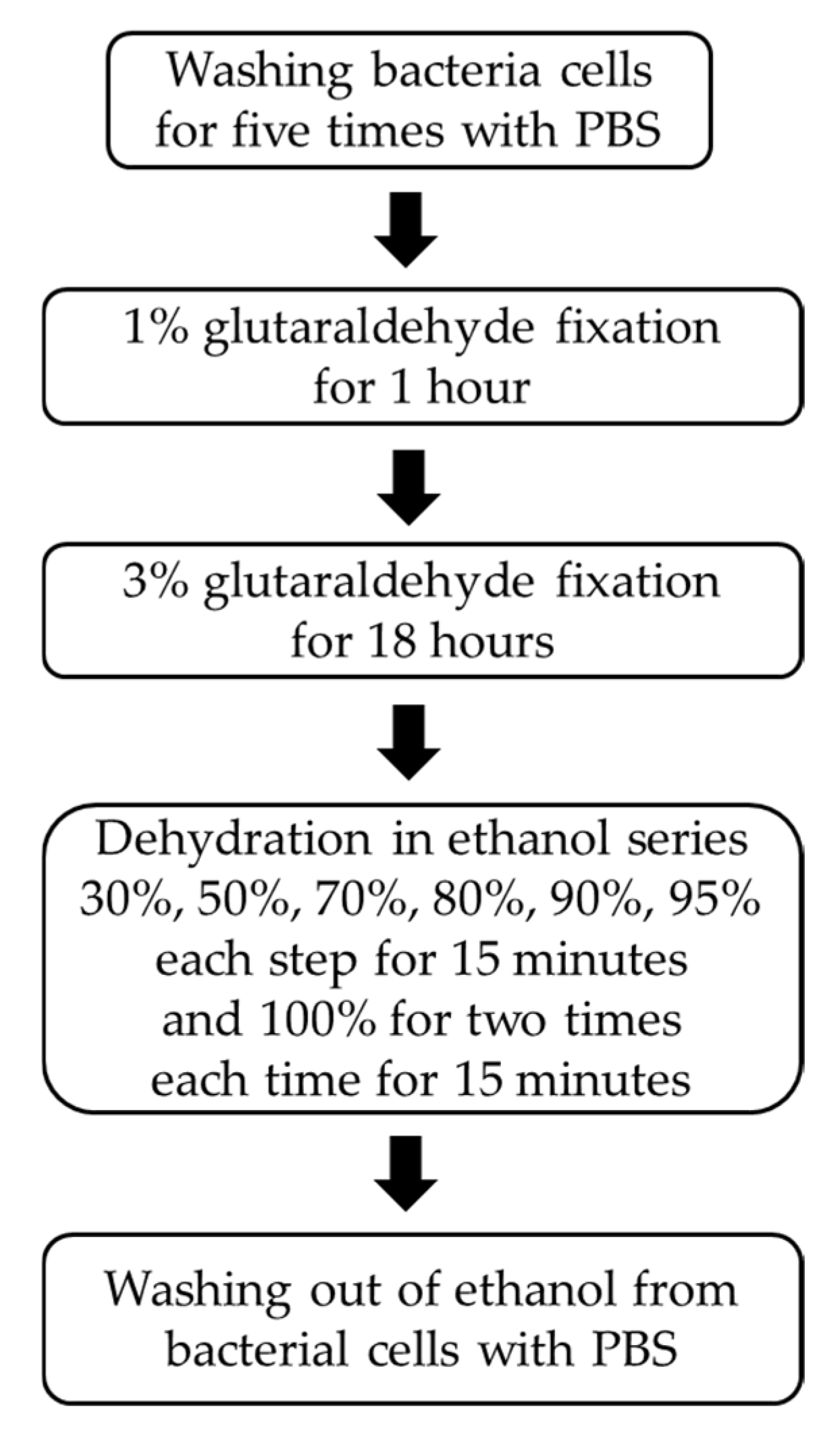
2.5. Metallurgical Optical Microscopy
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, Q.; Shi, M.; Wu, M.; Zhao, N.; Shi, P.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, A.; Ye, C.; Lin, C.-T.; Fu, L. Optimizing Graphene Dopants for Direct Electrocatalytic Quantification of Small Molecules and Ions. Catalysts 2024, 14, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyyed Mousavi, M.N.; Mehramuz, B.; Sadeghi, J.; Alizadeh, N.; Oskouee, M.A.; Kafil, H.S. The pathogenesis of Staphylococcus aureus in autoimmune diseases. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 111, 503–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwiecinski, J.M.; Horswill, A.R. Staphylococcus aureus bloodstream infections: Pathogenesis and regulatory mechanisms. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2020, 53, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aniba, R.; Dihmane, A.; Raqraq, H.; Ressmi, A.; Nayme, K.; Timinouni, M.; Barguigua, A. Exploring staphylococcus in urinary tract infections: A systematic review and meta-analysis on the epidemiology, antibiotic resistance and biofilm formation. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2024, 110, 116470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, T.; Mohammad, M.; Pullerits, R.; Ali, A. Bacteria and Host Interplay in Staphylococcus aureus Septic Arthritis and Sepsis. Pathogens 2021, 10, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touaitia, R.; Mairi, A.; Ibrahim, N.A.; Basher, N.S.; Idres, T.; Touati, A. Staphylococcus aureus: A Review of the Pathogenesis and Virulence Mechanisms. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berni, F.; Enotarpi, J.; Voskuilen, T.; Li, S.; van der Marel, G.A.; Codée, J.D.C. Synthetic carbohydrate-based cell wall components from Staphylococcus aureus. Drug Discov. Today Technol. 2020, 38, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasquel-Oliveira, F.S.; Ribeiro, J.M.; Martelossi-Cebinelli, G.; Costa, F.B.; Nakazato, G.; Casagrande, R.; Verri, W.A. Staphylococcus aureus in Inflammation and Pain: Update on Pathologic Mechanisms. Pathogens 2025, 14, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Léguillier, V.; Pinamonti, D.; Chang, C.-M.; Gunjan; Mukherjee, R.; Himanshu; Cossetini, A.; Manzano, M.; Anba-Mondoloni, J.; Malet-Villemagne, J.; et al. A review and meta-analysis of Staphylococcus aureus prevalence in foods. Microbe 2024, 4, 100131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mairi, A.; Ibrahim, N.A.; Idres, T.; Touati, A. A Comprehensive Review of Detection Methods for Staphylococcus aureus and Its Enterotoxins in Food: From Traditional to Emerging Technologies. Toxins 2025, 17, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, K.L.; Fey, P.D.; Rupp, M.E. Coagulase-Negative Staphylococcal Infections. Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2009, 23, 73–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palomares, C.; Torres, M.J.; Torres, A.; Aznar, J.; Palomares, J.C. Rapid detection and identification of Staphylococcus aureus from blood culture specimens using real-time fluorescence PCR. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2003, 45, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aborode, A.T.; Adesola, R.O.; Scott, G.Y.; Arthur-Hayford, E.; Otorkpa, O.J.; Kwaku, S.D.; Elebesunu, E.E.; Nibokun, E.O.; Aruorivwooghene, I.J.; Bakre, A.A.; et al. Bringing lab to the field: Exploring innovations in point-of-care diagnostics for the rapid detection and management of tropical diseases in resource-limited settings. Adv. Biomark. Sci. Technol. 2025, 7, 28–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Dong, Z.; Mi, J.; Zhao, H.; Wang, J.; Zeng, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, L. Evaluation and verification of the characteristic peptides for detection of Staphylococcus aureus in food by targeted LC-MS/MS. Talanta 2021, 235, 122794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Guo, W.; Lv, C.; Liu, X.; Yang, M.; Guo, M.; Fu, Q. Electrochemical biosensors represent promising detection tools in medical field. Adv. Sens. Energy Mater. 2023, 2, 100081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, D.; Paul, S.; Acharjee, T.; Ramachairy, S.S. Biosensors and their widespread impact on human health. Sens. Int. 2024, 5, 100257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naresh, V.; Lee, N. A Review on Biosensors and Recent Development of Nanostructured Materials-Enabled Biosensors. Sensors 2021, 21, 1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Chen, Y.; Liu, X.; Jiang, H.; Wang, X. Engineered Intelligent Electrochemical Biosensors for Portable Point-of-Care Diagnostics. Chemosensors 2025, 13, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Gupta, R.; Bansal, D.; Bhateria, R.; Sharma, M. A Review on Recent Trends and Future Developments in Electrochemical Sensing. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 7336–7356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saasa, V.; Chibagidi, R.; Ipileng, K.; Feleni, U. Advances in cancer detection: A review on electrochemical biosensor technologies. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2025, 49, 100826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawal, A.T. Recent developments in electrochemical sensors based on graphene for bioanalytical applications. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2023, 41, 100571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geleta, G.S. Recent advances in electrochemical sensors based on molecularly imprinted polymers and nanomaterials for detection of ascorbic acid, dopamine, and uric acid: A review. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2024, 43, 100610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banakar, M.; Hamidi, M.; Khurshid, Z.; Zafar, M.S.; Sapkota, J.; Azizian, R.; Rokaya, D. Electrochemical Biosensors for Pathogen Detection: An Updated Review. Biosensors 2022, 12, 927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curulli, A. Electrochemical Biosensors in Food Safety: Challenges and Perspectives. Molecules 2021, 26, 2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadhem, A.J.; Gentile, G.J.; Fidalgo de Cortalezzi, M.M. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers (MIPs) in Sensors for Environmental and Biomedical Applications: A Review. Molecules 2021, 26, 6233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sajini, T.; Mathew, B. A brief overview of molecularly imprinted polymers: Highlighting computational design, nano and photo-responsive imprinting. Talanta Open 2021, 4, 100072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Feng, L.; Deng, X.; Li, Y.; Mei, H.; Guo, H.; Zhu, J.; Hu, C. Application of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers in the Analysis of Explosives. Polymers 2025, 17, 1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalogiouri, N.P.; Kabir, A.; Furton, K.G.; Samanidou, V.F. A tutorial on the synthesis and applications of molecularly imprinted polymers in analytical chemistry. J. Chromatogr. Open 2025, 8, 100244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarvutiene, J.; Prentice, U.; Ramanavicius, S.; Ramanavicius, A. Molecular imprinting technology for biomedical applications. Biotechnol. Adv. 2024, 71, 108318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohde, M. The Gram-Positive Bacterial Cell Wall. Microbiol. Spectr. 2019, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.Y.; Nebl, T.; Glattauer, V.; Ramshaw, J.A.M. Incorporation of hydroxyproline in bacterial collagen from Streptococcus pyogenes. Acta Biomater. 2018, 80, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellitero, M.A.; Curtis, S.D.; Arroyo-Currás, N. Interrogation of Electrochemical Aptamer-Based Sensors via Peak-to-Peak Separation in Cyclic Voltammetry Improves the Temporal Stability and Batch-to-Batch Variability in Biological Fluids. ACS Sens. 2021, 6, 1199–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayappa, M.K.; Viswanathan, P.A.; Rattu, G.; Krishna, P.M. Nanomaterials Enabled and Bio/Chemical Analytical Sensors for Acrylamide Detection in Thermally Processed Foods: Advances and Outlook. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 4578–4603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satchanska, G.; Davidova, S.; Petrov, P.D. Natural and Synthetic Polymers for Biomedical and Environmental Applications. Polymers 2024, 16, 1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radka, C.D.; Batte, J.L.; Frank, M.W.; Young, B.M.; Rock, C.O. Structure and mechanism of Staphylococcus aureus oleate hydratase (OhyA). J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 296, 100252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinchliffe, J.D.; Parassini Madappura, A.; Syed Mohamed, S.M.; Roy, I. Biomedical Applications of Bacteria-Derived Polymers. Polymers 2021, 13, 1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahnaz, T.; Hayder, G.; Shah, M.A.; Ramli, M.Z.; Ismail, N.; Hua, C.K.; Zahari, N.M.; Mardi, N.H.; Selamat, F.E.; Kabilmiharbi, N.; et al. Graphene-based nanoarchitecture as a potent cushioning/filler in polymer composites and their applications. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 28, 2671–2698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aznar, P.R.; Junior, H.L. Advances and Applications of Graphene-Enhanced Textiles: A 10-Year Review of Functionalization Strategies and Smart Fabric Technologies. Textiles 2025, 5, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, H.X.; Zhou, H.; Chang, J.; Zhu, J.; Wei, T.X. Molecularly imprinted polymers for highly sensitive detection of morphine using surface plasmon resonance spectroscopy. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2011, 22, 477–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basak, S.; Venkatram, R.; Singhal, R.S. Recent advances in the application of molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs) in food analysis. Food Control 2022, 139, 109074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnwal, A.; Kumar Sachan, R.S.; Devgon, I.; Devgon, J.; Pant, G.; Panchpuri, M.; Ahmad, A.; Alshammari, M.B.; Hossain, K.; Kumar, G. Gold Nanoparticles in Nanobiotechnology: From Synthesis to Biosensing Applications. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 29966–29982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curulli, A. Functional Nanomaterials Enhancing Electrochemical Biosensors as Smart Tools for Detecting Infectious Viral Diseases. Molecules 2023, 28, 3777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, M.; Kashif, M.; Muhammad, S.; Azizi, S.; Sun, H. Various Methods of Synthesis and Applications of Gold-Based Nanomaterials: A Detailed Review. Cryst. Growth Des. 2025, 25, 2227–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tancharoen, C.; Sukjee, W.; Jaimipuk, T.; Auewarakul, P.; Thitithanyanont, A.; Sangma, C. An Electrochemical Biosensor Based on Surface Imprinting for Zika Virus Detection in Serum. ACS Sens. 2018, 4, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pintavirooj, C.; Vongmanee, N.; Sukjee, W.; Sangma, C.; Visitsattapongse, S. Biosensors for Klebsiella pneumoniae with Molecularly Imprinted Polymer (MIP) Technique. Sensors 2022, 22, 4638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nampeng, J.; Vongmanee, N.; Pintavirooj, C.; Chiu, W.-T.; Visitsattapongse, S. Electrochemical Biosensors by Means of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers (MIPs) Cortisol Recognition. Polymers 2025, 17, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Lee, K.C.; Noh, S.M. UV–thermally dual-curable 1K clearcoat via urethane and radical reactions. Prog. Org. Coat. 2023, 182, 107704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maghsoomi, S.; Walochnik, J.; Brandl, M.; Pham, M.-L. A Novel Methylene Blue Indicator-Based Aptasensor for Rapid Detection of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 11682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangwar, R.; Ray, D.; Rao, K.T.; Khatun, S.; Subrahmanyam, C.; Rengan, A.K.; Vanjari, S.R.K. Plasma Functionalized Carbon Interfaces for Biosensor Application: Toward the Real-Time Detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 21025–21034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamzami, M.; Ahmad, A.; Alamoudi, S.; Choudhry, H.; Hosawi, S.; Rabbani, G.; Shalaan, E.-S.; Arkook, B. A highly sensitive and specific Gold Electrode-Based electrochemical immunosensor for rapid On-Site detection of Salmonella enterica. Microchem. J. 2024, 199, 110190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.; So, H.; Kim, J.; Auh, J.-H.; Wall, M.M.; Li, Y.; Ho, K.; Jun, S. Selective Detection of Escherichia coli K12 and Staphylococcus aureus in Mixed Bacterial Communities Using a Single-Walled Carbon Nanotube (SWCNT)-Functionalized Electrochemical Immunosensor with Dielectrophoretic Concentration. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, X.; Ma, Y.; Li, H.; Sun, S.; Shi, L.; Yan, J.; Luan, D.; Zhao, Y.; Bian, X. A Dual-Recognition Electrochemical Sensor Using Bacteria-Imprinted Polymer and Concanavalin A for Sensitive and Selective Detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7. Foods 2025, 14, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Condition | Ratio (n:n) | Ratio (mmol:mmol) | HYP (mg) | MAM (mg) | AAM (mg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1:2 | 0.1:0.2 | 13.1 | 17.0 | - |
| 2 | 2:1 | 0.2:0.1 | 26.2 | 8.5 | - |
| 3 | 1:2 | 0.1:0.2 | 13.1 | - | 14.2 |
| 4 | 2:1 | 0.2:0.1 | 26.2 | - | 7.1 |
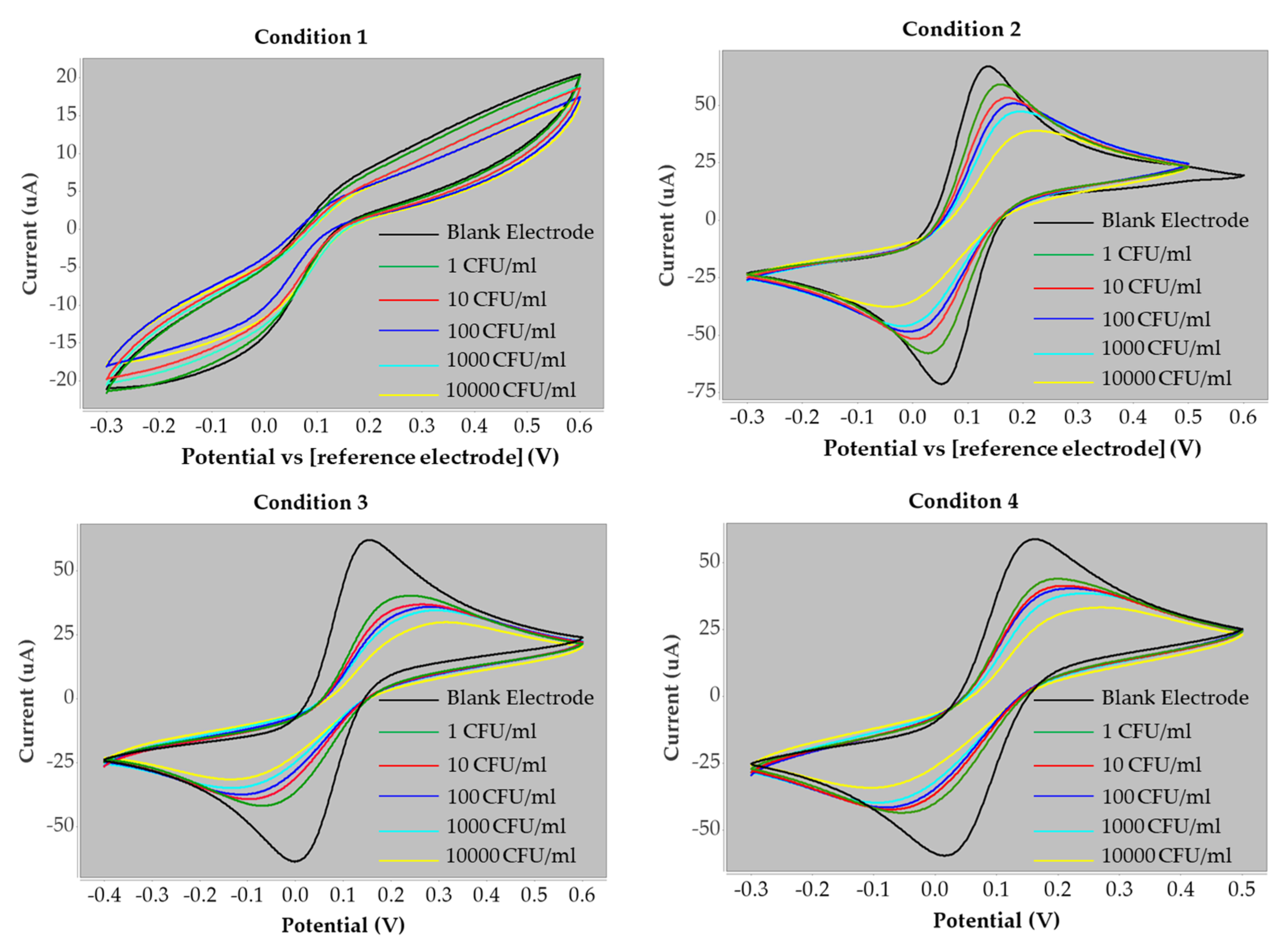
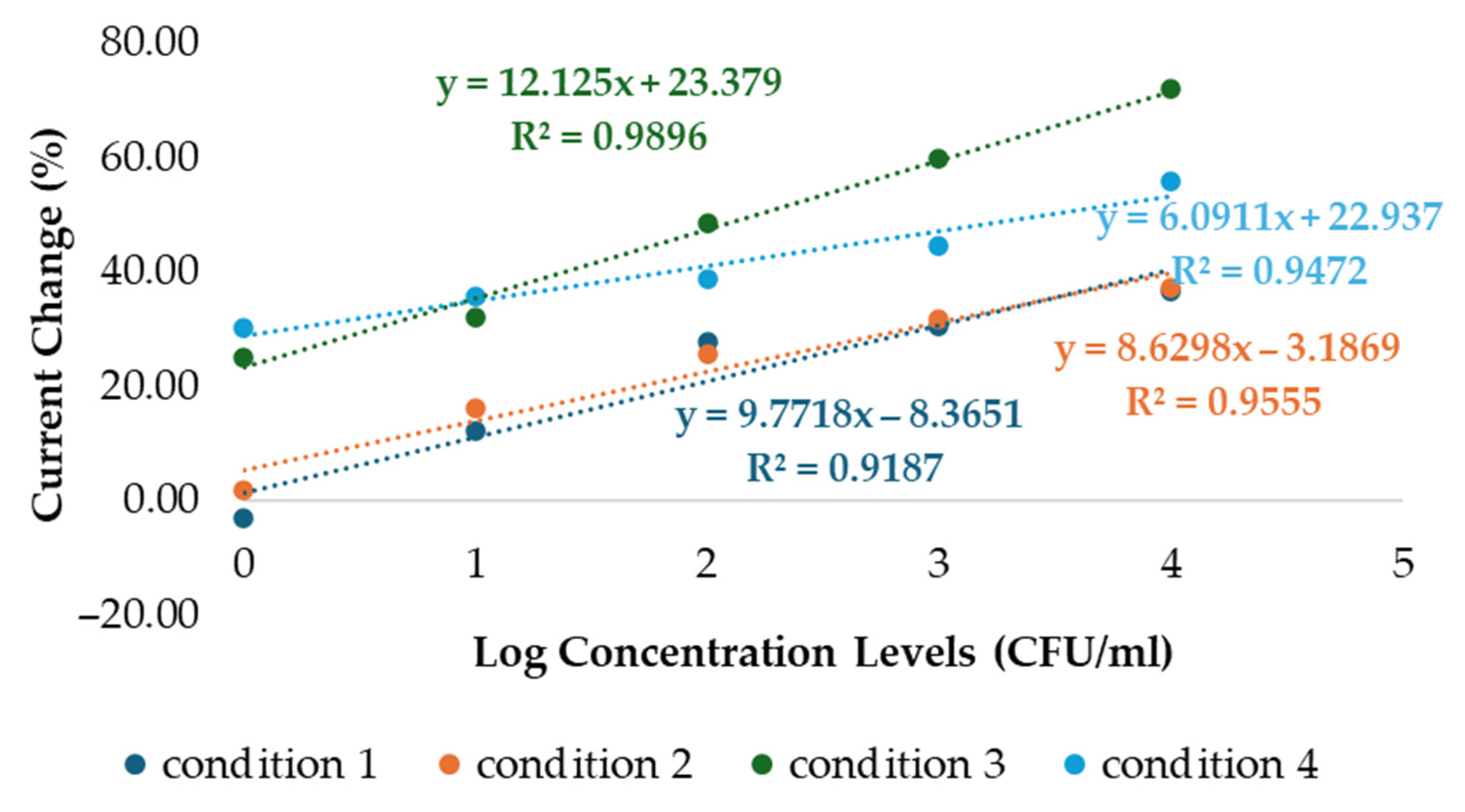
| Condition 1 | Current (µA) | ∆I (µA) | Current change (%) |
| Blank | 4.82 | ||
| 1 CFU/mL | 4.96 | −0.14 | −2.97 |
| 10 CFU/mL | 4.23 | 0.59 | 12.30 |
| 100 CFU/mL | 3.47 | 1.35 | 27.97 |
| 1000 CFU/mL | 3.34 | 1.49 | 30.81 |
| 10,000 CFU/mL | 3.05 | 1.77 | 36.64 |
| Condition 2 | Current (µA) | ∆I (µA) | Current change (%) |
| Blank | 71.85 | ||
| 1 CFU/mL | 70.43 | 1.42 | 1.97 |
| 10 CFU/mL | 60.09 | 11.76 | 16.37 |
| 100 CFU/mL | 53.22 | 18.63 | 25.93 |
| 1000 CFU/mL | 48.96 | 22.90 | 31.87 |
| 10,000 CFU/mL | 45.00 | 26.85 | 37.37 |
| Condition 3 | Current (µA) | ∆I (µA) | Current change (%) |
| Blank | 82.38 | ||
| 1 CFU/mL | 61.54 | 20.84 | 25.30 |
| 10 CFU/mL | 55.83 | 26.55 | 32.23 |
| 100 CFU/mL | 42.31 | 40.07 | 48.64 |
| 1000 CFU/mL | 33.06 | 49.32 | 59.87 |
| 10,000 CFU/mL | 22.98 | 59.40 | 72.10 |
| Condition 4 | Current (µA) | ∆I (µA) | Current change (%) |
| Blank | 57.95 | ||
| 1 CFU/mL | 40.43 | 17.52 | 30.23 |
| 10 CFU/mL | 37.19 | 20.76 | 35.82 |
| 100 CFU/mL | 35.36 | 22.59 | 38.99 |
| 1000 CFU/mL | 31.97 | 25.98 | 44.84 |
| 10,000 CFU/mL | 25.40 | 32.55 | 56.18 |
| C. albicans | Current (µA) | ∆I (µA) | Current change (%) |
| Blank | 2.11 | ||
| 1 CFU/mL | 1.89 | 0.22 | 10.33 |
| 10 CFU/mL | 1.70 | 0.41 | 19.43 |
| 100 CFU/mL | 1.47 | 0.64 | 30.28 |
| 1000 CFU/mL | 1.45 | 0.66 | 31.33 |
| 10,000 CFU/mL | 1.25 | 0.86 | 40.76 |
| E. coli | Current (µA) | ∆I (µA) | Current change (%) |
| Blank | 2.63 | ||
| 1 CFU/mL | 2.58 | 0.05 | 1.86 |
| 10 CFU/mL | 2.47 | 0.16 | 6.16 |
| 100 CFU/mL | 2.45 | 0.18 | 6.84 |
| 1000 CFU/mL | 2.10 | 0.53 | 20.30 |
| 10,000 CFU/mL | 1.84 | 0.79 | 29.92 |
| P. aeruginosa | Current (µA) | ∆I (µA) | Current change (%) |
| Blank | 2.59 | ||
| 1 CFU/mL | 2.35 | 0.24 | 9.31 |
| 10 CFU/mL | 1.84 | 0.75 | 28.96 |
| 100 CFU/mL | 1.77 | 0.82 | 31.81 |
| 1000 CFU/mL | 1.59 | 1.00 | 38.57 |
| 10,000 CFU/mL | 1.56 | 1.03 | 39.77 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vongmanee, N.; Nampeng, J.; Pintavirooj, C.; Visitsattapongse, S. Biosensor Based on Electrochemical Analysis for Staphylococcus aureus Detection with Molecular Imprinted Polymer Technique. Polymers 2025, 17, 2826. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17212826
Vongmanee N, Nampeng J, Pintavirooj C, Visitsattapongse S. Biosensor Based on Electrochemical Analysis for Staphylococcus aureus Detection with Molecular Imprinted Polymer Technique. Polymers. 2025; 17(21):2826. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17212826
Chicago/Turabian StyleVongmanee, Naphatsawan, Jindapa Nampeng, Chuchart Pintavirooj, and Sarinporn Visitsattapongse. 2025. "Biosensor Based on Electrochemical Analysis for Staphylococcus aureus Detection with Molecular Imprinted Polymer Technique" Polymers 17, no. 21: 2826. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17212826
APA StyleVongmanee, N., Nampeng, J., Pintavirooj, C., & Visitsattapongse, S. (2025). Biosensor Based on Electrochemical Analysis for Staphylococcus aureus Detection with Molecular Imprinted Polymer Technique. Polymers, 17(21), 2826. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17212826








