Ferulic Acid and Polyferulic Acid in Polymers: Synthesis, Properties, and Applications
Abstract
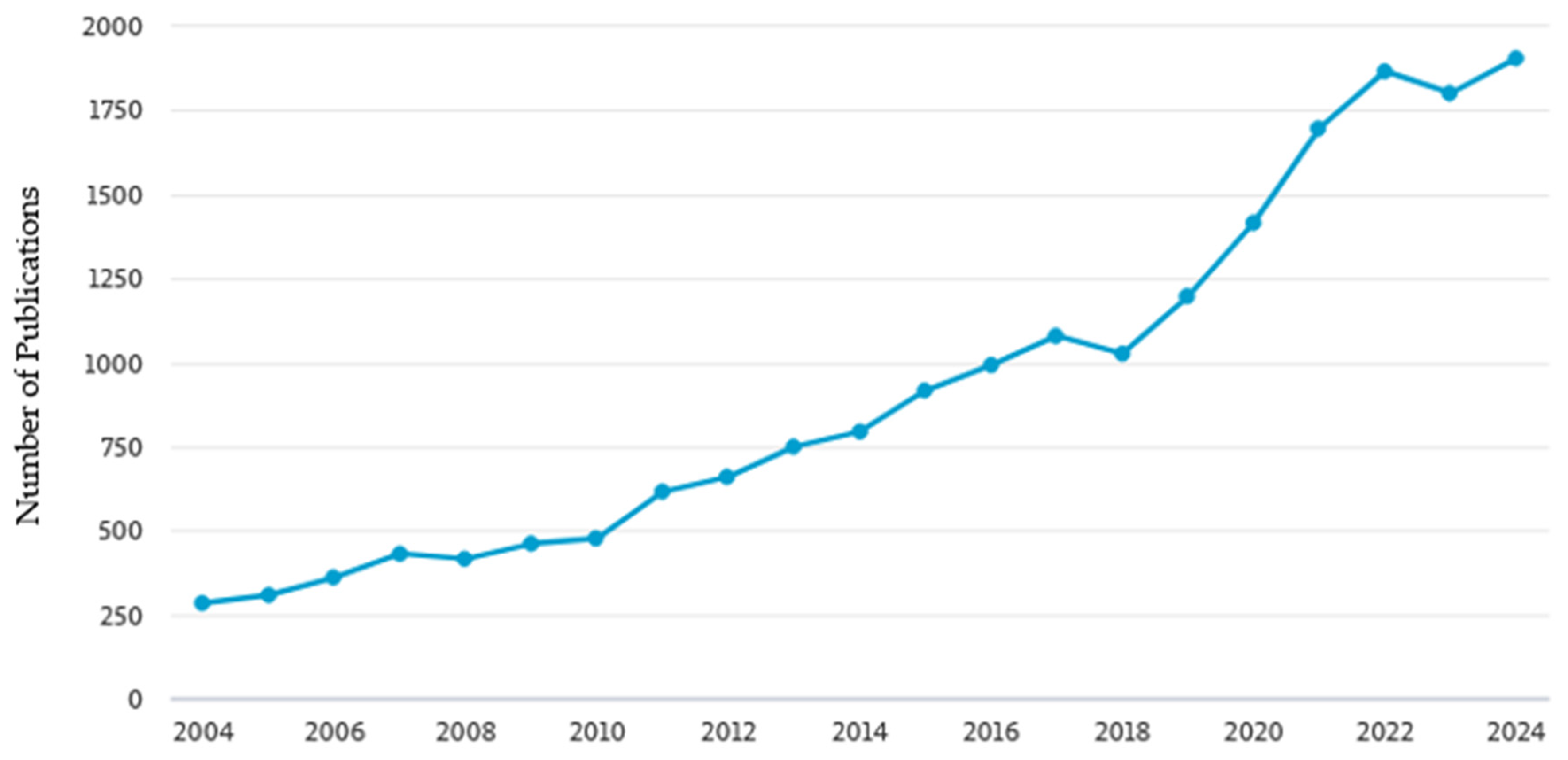
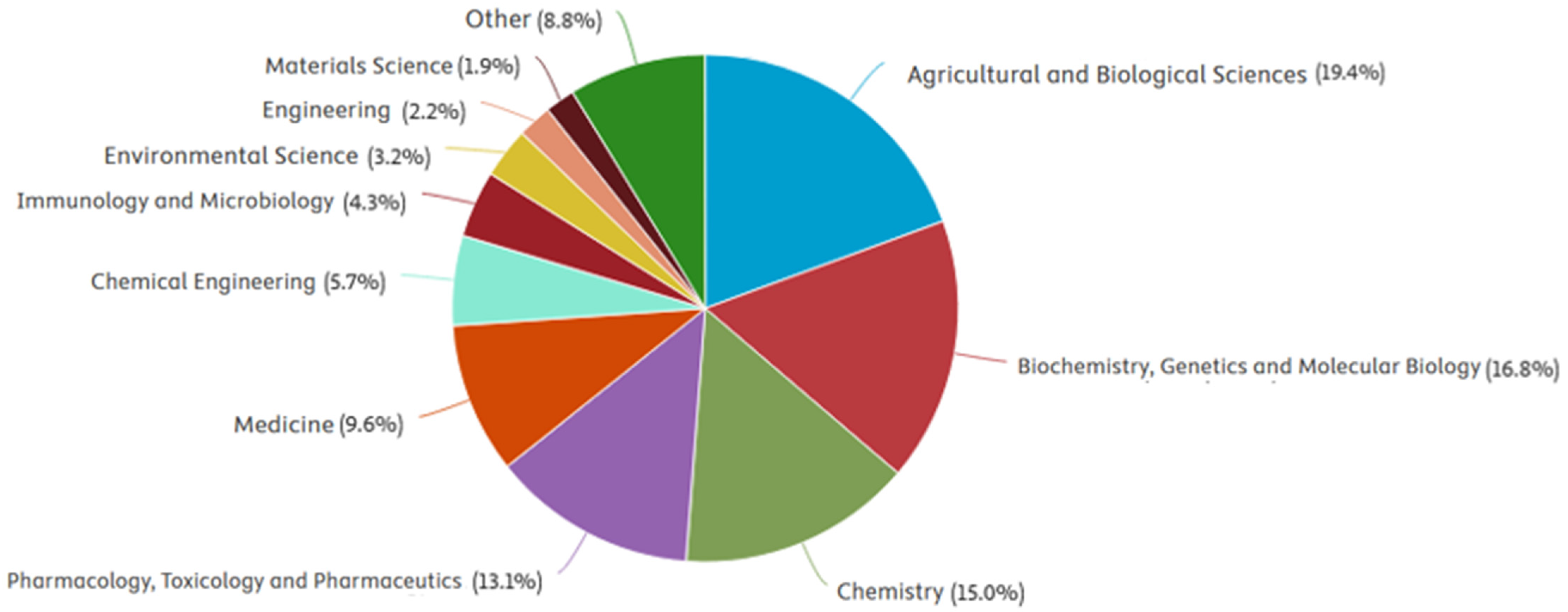
1. Introduction
2. Chemical Characteristics and Sources of Raw Materials
3. Methods of Synthesis and Modification
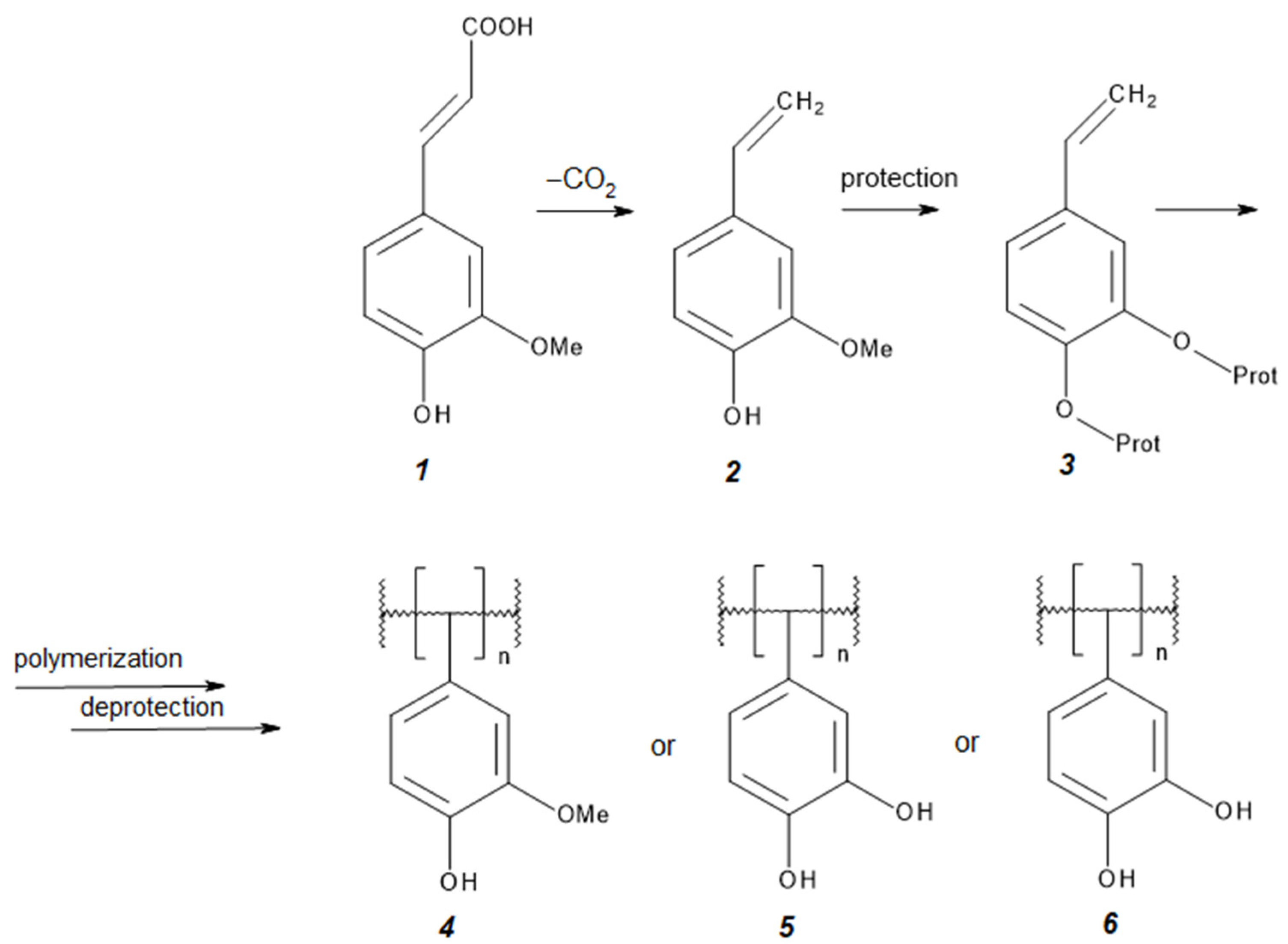
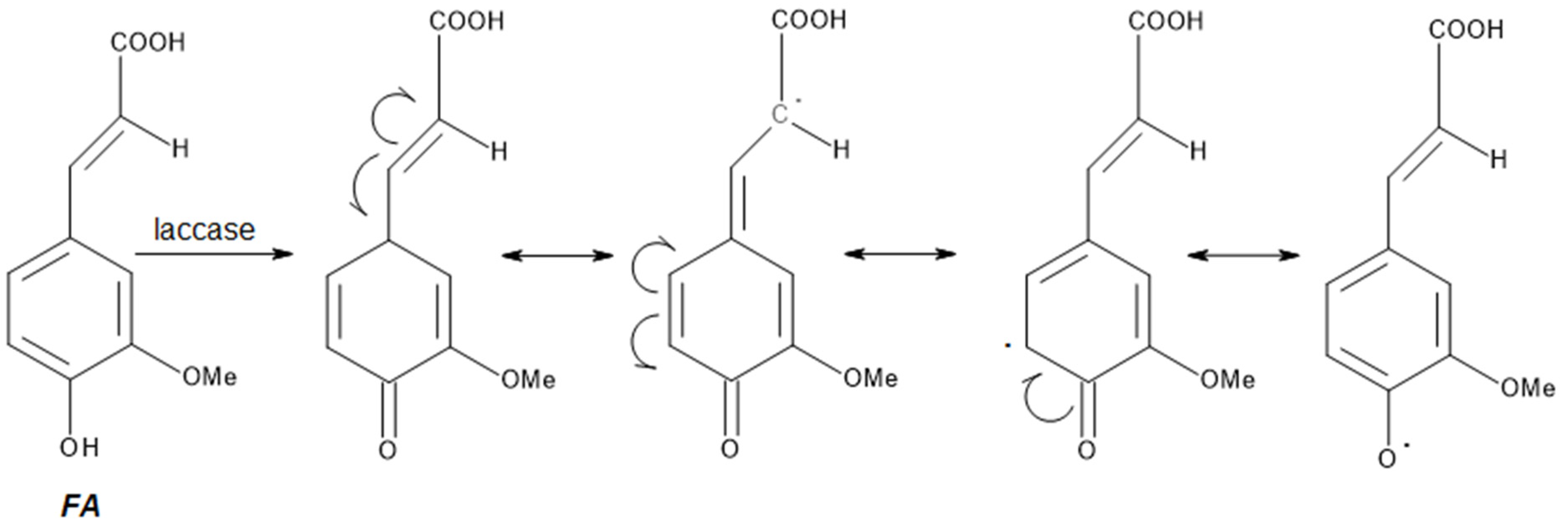
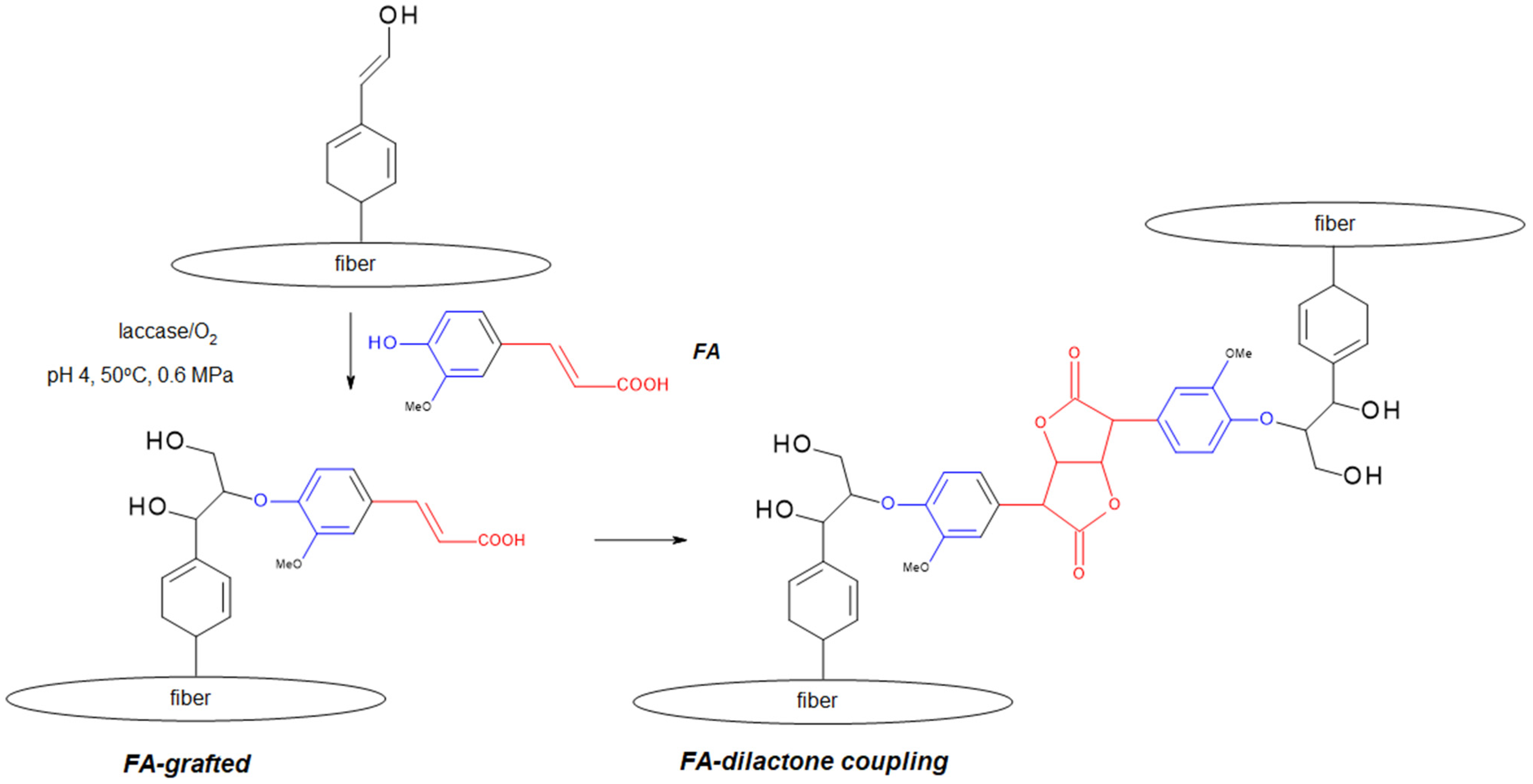
Synthesis of Polymers Based on Ferulic Acid and Derivatives
4. Functional Properties and Applications
4.1. Physicochemical Properties of Ferulic Acid: Stability, Release, Antioxidant Activity, Mechanical Properties
4.2. Applications of Ferulic Acid
4.2.1. Materials for Biomedical Applications (e.g., Drug Carriers, Skin Protection)
4.2.2. Food Packaging, Biodegradable Materials, UV-Protective Films
4.2.3. Adhesives
5. Challenges and Future Perspectives
5.1. Limitations of Current Ferulic Acid Solutions
5.2. Directions for Future Research and Potential New Applications of Ferulic Acid
5.3. Toxicity, Safety, and Regulatory Aspects
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BDF | Bis-O-dihydroferuloyl-1,4-butanediol |
| CFU | Colony forming units |
| CTS | Chitosan |
| DOI | Distinctness of Image |
| ECHA | European Chemical Agency |
| FA | Ferulic acid |
| GU | Gloss units |
| IUPAC | International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry |
| PHA | Polyhydroxyalkanoates |
| PHBV | Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) |
| phr | Parts per hundred resin |
| PLA | Polylactic acid |
| Tg | Glass transition temperature |
| TRL | Technology Readiness Level |
References
- Nurdiawati, A.; Urban, F. Towards Deep Decarbonisation of Energy-Intensive Industries: A Review of Current Status, Technologies and Policies. Energies 2021, 14, 2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swetha, T.; Bora, A.; Mohanrasu, K.; Balaji, P.; Raja, R.; Ponnuchamy, K.; Muthusamy, G.; Arun, A. A comprehensive review on polylactic acid (PLA)—Synthesis, processing and application in food packaging. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 234, 123715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, J.; González-Martínez, C.; Chiralt, A. Combination of Poly(lactic) Acid and Starch for Biodegradable Food Packaging. Materials 2017, 10, 952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazrin, A.; Sapuan, S.; Zuhri, M.; Ilyas, R.; Syafiq, R.; Sherwani, S. Nanocellulose Reinforced Thermoplastic Starch (TPS), Polylactic Acid (PLA), and Polybutylene Succinate (PBS) for Food Packaging Applications. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truax, T.R. Gluing Wood in Aircraft Manufacture; Technical Bulletin No. 151; United States Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1929. [Google Scholar]
- Galbis, J.A.; García-Martín, M.G. Monomers, Polymers and Composites from Renewable Resources; Belgacem, M.N., Gandini, A., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Anastas, P.T.; Warner, J.C. Green Chemistry: Theory and Practice; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima, H.; Dijkstra, P.; Loos, K. The Recent Developments in Biobased Polymers toward General and Engineering Applications: Polymers That Are Upgraded from Biodegradable Polymers, Analogous to Petroleum-Derived Polymers, and Newly Developed. Polymers 2017, 9, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamiński, M.Ł.; Toczyłowska-Mamińska, R. Bio-derived adhesives and matrix polymers for composites. In Handbook of Composites from Renewable Materials, Volume 1: Structure and Chemistry; Thakur, V.K., Thakur, M.K., Kessler, M.R., Eds.; Wiley-Scrivener: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 151–188. [Google Scholar]
- Wypij, M.; Trzcińska-Wencel, J.; Golińska, P.; Ávila-Quezada, G.; Ingle, A.; Rai, M. The strategic applications of natural polymer nanocomposites in food packaging and agriculture: Chances, challenges, and consumers’ perception. Front. Chem. 2023, 10, 1106230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isikgor, F.H.; Becer, C.R. Lignocellulosic Biomass: A Sustainable Platform for the Production of Bio-Based Chemicals and Polymers. Polym. Chem. 2015, 6, 4497–4559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwata, T. Biodegradable and Bio-Based Polymers: Future Prospects of Eco-Friendly Plastics. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 3210–3215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrison, T.; Murawski, A.; Quirino, R. Bio-Based Polymers with Potential for Biodegradability. Polymers 2016, 8, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hottle, T.A.; Bilec, M.M.; Landis, A.E. Sustainability Assessments of Bio-Based Polymers. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2013, 98, 1898–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siracusa, V.; Blanco, I. Bio-Polyethylene (Bio-PE), Bio-Polypropylene (Bio-PP) and Bio-Poly(ethylene terephthalate) (Bio-PET): Recent Developments in Bio-Based Polymers Analogous to Petroleum-Derived Ones for Packaging and Engineering Applications. Polymers 2020, 12, 1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luckachan, G.E.; Pillai, C.K.S. Biodegradable Polymers—A Review on Recent Trends and Emerging Perspectives. J. Polym. Environ. 2011, 19, 637–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthika, M.; Shaji, N.; Johnson, A.; Neelakandan, M.S.; Gopakumar, D.A.; Thomas, S. Biodegradation of Green Polymeric Composites Materials. In Bio Monomers for Green Polymeric Composite Materials; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 141–159. [Google Scholar]
- Engineer, C.; Parikh, J.; Raval, A. Review on Hydrolytic Degradation Behavior of Biodegradable Polymers from Controlled Drug Delivery Systems. Trends Biomater. Artif. Organs 2011, 25, 79–85. [Google Scholar]
- Samir, A.; Ashour, F.H.; Hakim, A.A.A.; Bassyouni, M. Recent Advances in Biodegradable Polymers for Sustainable Applications. Npj Mater. Degrad. 2022, 6, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vert, M.; Doi, Y.; Hellwich, K.-H.; Hess, M.; Hodge, P.; Kubisa, P.; Rinaudo, M.; Schué, F. Terminology for Biorelated Polymers and Applications (IUPAC Recommendations 2012). Pure Appl. Chem. 2012, 84, 377–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, T.M.; Unni, A.B.; Joshy, K.S.; Kar Mahapatra, D.; Haponiuk, J.; Thomas, S. Emerging Bio-Based Polymers from Lab to Market: Current Strategies, Market Dynamics and Research Trends. C J. Carbon Res. 2023, 9, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muringayil Joseph, T.; Mariya, H.J.; Haponiuk, J.T.; Thomas, S.; Esmaeili, A.; Sajadi, S.M. Electromagnetic Interference Shielding Effectiveness of Natural and Chlorobutyl Rubber Blend Nanocomposite. J. Compos. Sci. 2022, 6, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, S.; Kwok, K.C. Ferulic acid: Pharmaceutical functions, preparation and applications in foods. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2004, 84, 1261–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Moghadasian, M.H. Chemistry, natural sources, dietary intake and pharmacokinetic properties of ferulic acid: A review. Food Chem. 2008, 109, 691–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasantha, V.; Parthiban, A. Biorenewable functional oligomers and polymers—Direct copolymerization of ferulic acid to obtain polymeric UV absorbers and multifunctional materials. Polymer 2020, 188, 122122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannakopoulou, A.; Tsapara, G.; Troganis, A.N.; Koralli, P.; Chochos, C.L.; Polydera, A.C.; Katapodis, P.; Barkoula, N.-M.; Stamatis, H. Development of a Multi-Enzymatic Approach for the Modification of Biopolymers with Ferulic Acid. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Uhrich, K.; Ouimet, M.; Faig, J. Ferulic Acid-Based Polymers with Glycol Functionality as a Versatile Platform for Topical Applications. Biomacromolecules 2015, 16, 2911–2919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallos, A.; Torrieri, E.; Khan, M.; Fadlallah, S.; Flourat, A.; Allais, F. Effect of ferulic acid derivative concentration on the release kinetics, antioxidant capacity, and thermal behaviour of different polymeric films. Food Chem. 2023, 410, 135395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollet, E.; Avérous, L.; Bazin, A. Ferulic Acid as Building Block for the Lipase-Catalyzed Synthesis of Biobased Aromatic Polyesters. Polymers 2021, 13, 3693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, A.; Becker, S.; Hahn, C.; Frey, H. Anionic polymerization of ferulic acid-derived, substituted styrene monomers. Eur. Polym. J. 2024, 211, 113004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, K.; Takeshima, H.; Kamigaito, M. Bio-Based Functional Styrene Monomers Derived from Naturally Occurring Ferulic Acid for Poly(vinylcatechol) and Poly(vinylguaiacol) via Controlled Radical Polymerization. Macromolecules 2017, 50, 4206–4216. [Google Scholar]
- Llevot, A.; Grau, É.; Carlotti, S.; Grelier, S.; Cramail, H. From Lignin-derived Aromatic Compounds to Novel Biobased Polymers. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2016, 37, 9–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, P.; Chang, Y.; Yang, J. Preparation and characterization of ferulic acid-modified water soluble chitosan and poly (γ-glutamic acid) polyelectrolyte films through layer-by-layer assembly towards protein adsorption. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 171, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Kumar, N.; Vashisth, P.; Pruthi, V. Biomedical applications of ferulic acid encapsulated electrospun nanofibers. Biotechnol. Rep. 2015, 8, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowet, J.; Allais, F.; Dauchez, M.; Gallos, A.; Raghuwanshi, V.; Michely, L.; Garnier, G.; Langlois, V.; Mention, M. Blending Ferulic Acid Derivatives and Polylactic Acid into Biobased and Transparent Elastomeric Materials with Shape Memory Properties. Biomacromolecules 2021, 22, 1568–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Nandi, N.; Shukla, D.; Singh, C.; Narang, R.; Singh, A.; Kumar, B. Ferulic acid-loaded drug delivery systems for biomedical applications. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 75, 103621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruthi, V.; Kumar, N. Potential applications of ferulic acid from natural sources. Biotechnol. Rep. 2014, 4, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira Silva, E.; Batista, R. Ferulic Acid and Naturally Occurring Compounds Bearing a Feruloyl Moiety: A Review on Their Structures, Occurrence, and Potential Health Benefits. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2017, 16, 580–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, D.; Gong, C.; Zhang, J.; Cao, L.; Wang, C.; Fang, D.; Liu, X. Ferulic acid production from wheat bran by integration of enzymatic pretreatment and a cold-adapted carboxylesterase catalysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 385, 129435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Jabasingh, S.; Sibhatu, H.; Yimam, A. Ferulic acid production from brewery spent grains, an agro-industrial waste. LWT 2021, 135, 110009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Lee, J.; Kim, H.; Yoo, W.; Le, L.; Lee, C.; Lee, M.H.; Shin, S.; Hwang, J.; Jeon, S. Feruloyl Esterase (LaFae) from Lactobacillus acidophilus: Structural Insights and Functional Characterization for Application in Ferulic Acid Production. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, K.; Yang, K.; Ding, J.; Lim, S.; Kua, G. Expression of a Recombinant Cholesterol Esterase from Mustela putorius furo in Pichia pastoris and Its Applicability for γ-Oryzanol Hydrolysis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 21702–21710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Shang, H.; Meng, Y.; Zheng, R.; Hu, C.; Zhang, C.; Yang, Q.; Qiang, S. Engineering Caffeic Acid O—Methyltransferase for Efficient De Novo Ferulic Acid Synthesis. Eng. Life Sci. 2025, 25, 70018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Li, W.; Yuan, Q.; Li, X.; Shen, X.; Wu, J.; Sun, X. Targeting cofactors regeneration in methylation and hydroxylation for high level production of Ferulic acid. Metab. Eng. 2022, 73, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, H.; Shao, J.; Wang, Y. Ferulic acid production by metabolically engineered Escherichia coli. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2021, 8, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, F.; Zarepour, A.; Iftekhar, S.; Zarrabi, A.; Ashrafizadeh, M.; Agarwal, T.; Pizzetti, F.; Mohammadinejad, R.; Makvandi, P.; Padil, V.; et al. Functionalization of polymers and nanomaterials for water treatment, food packaging, textile and biomedical applications: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2020, 19, 583–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hu, Y.; Xu, F. Versatile Functionalization of Polysaccharides via Polymer Grafts: From Design to Biomedical Applications. Acc. Chem. Res. 2017, 50, 281–292. [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham, M.; Smeets, N.; Garcia-Valdez, O.; Cazotti, J.; Dubé, M.; Fritz, A. Graft modification of starch nanoparticles using nitroxide-mediated polymerization and the grafting to approach. Biomacromolecules 2020, 21, 4492–4501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carunchio, F.; Crescenzi, C.; Girelli, A.M.; Messina, A.; Tarola, A.M. Oxidation of ferulic acid by laccase: Identification of the products and inhibitory effects of some dipeptides. Talanta 2021, 55, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rencoret, J.; Aracri, E.; Gutiérrez, A.; del Río, J.C.; Torres, A.L.; Vidal, T.; Martínez, A.T. Structural insights on laccase biografting of ferulic acid onto lignocellulosic fibers. Biochem. Eng. J. 2014, 86, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashby, R.; Göktaş, M.; Aykaç, C.; Hazer, B. Synthesis of Poly(styrene)-g-Poly(oleic acid) Graft Copolymers via Reversible Addition/Fragmentation Transfer (RAFT) Polymerization Using a Poly Oleic Acid Macro-RAFT Agent. J. Polym. Environ. 2024, 32, 2629–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, W.; LaNasa, J.; Zofchak, E.; Hickey, R. Polymerization-Induced Nanostructural Transitions Driven by In Situ Polymer Grafting. ACS Macro Lett. 2018, 7, 822–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone-Howell, A.; Griffin, J.; Stebbins, N.; Ouimet, M.; Wu, W.; Uhrich, K.; Di, R. Biodegradable ferulic acid-containing poly(anhydride-ester): Degradation products with controlled release and sustained antioxidant activity. Biomacromolecules 2013, 14, 854–861. [Google Scholar]
- Villanueva, M.P.; Gioia, C.; Sisti, L.; Martí, L.; Llorens-Chiralt, R.; Verstichel, S.; Celli, A. Valorization of Ferulic Acid from Agro-Industrial by-Products for Application in Agriculture. Polymers 2022, 14, 2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancuso, A.; Paolino, D.; Cristiano, M.; Pandolfo, R.; Greco, M.; Fresta, M. Improvement of Ferulic Acid Antioxidant Activity by Multiple Emulsions: In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akashi, M.; Yoksan, R.; Woranuch, S. Ferulic acid-coupled chitosan: Thermal stability and utilization as an antioxidant for biodegradable active packaging film. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 115, 744–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xu, W.; Chen, Q.; Zheng, M.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, G. The Antioxidant Properties, Metabolism, Application and Mechanism of Ferulic Acid in Medicine, Food, Cosmetics, Livestock and Poultry. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kołodziejczak, A.; Zduńska, K.; Dana, A.; Rotsztejn, H. Antioxidant Properties of Ferulic Acid and Its Possible Application. Ski. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2018, 31, 322–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.; Jia, Y.; He, Y. The structure-antioxidant activity relationship of dehydrodiferulates. Food Chem. 2018, 269, 480–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Fang, K.; Li, J.; He, W.; Li, K. Preparation, characterization and physicochemical properties of cassava starch-ferulic acid complexes by mechanical activation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 160, 482–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.; Sohn, Y. Characterization of physicochemical properties of ferulic acid. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2003, 26, 1002–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Huang, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Zheng, Y.; You, X.; Guan, S. Poly(Ferulic Acid) with an Anticancer Effect as a Drug Nanocarrier for Enhanced Colon Cancer Therapy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1808646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonaccorso, A.; Musumeci, T.; Puglisi, G.; Anfuso, C.; Romeo, A.; Pignatello, R.; Corvo, S.; Lupo, G.; Carbone, C. Ferulic Acid-Loaded Polymeric Nanoparticles for Potential Ocular Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, U.; Rani, A.; Thakur, R. Brief review of trans-ferulic acid-loaded polymeric nanoformulations: Pharmacological applications and future perspectives. Polym. Bull. 2024, 81, 16329–16354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amić, A.; Dimitrić Marković, J.M.; Marković, Z.; Milenković, D.; Milanović, Ž.; Antonijević, M.; Mastil’ák Cagardová, D.; Rodríguez-Guerra Pedregal, J. Theoretical Study of Radical Inactivation, LOX Inhibition, and Iron Chelation: The Role of Ferulic Acid in Skin Protection against UVA Induced Oxidative Stress. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiralt, A.; Vargas, M.; Hernández-García, E. Active Starch-Polyester Bilayer Films with Surface-Incorporated Ferulic Acid. Membranes 2022, 12, 976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, S.; Duffy, B.; Sharma, S. Ferulic acid incorporated active films based on poly(lactide)/poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) blend for food packaging. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2020, 24, 100491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aly-Aldin, M.; Abdin, M.; Naeem, M. Enhancing the bioavailability and antioxidant activity of natamycin E235-ferulic acid loaded polyethylene glycol/carboxy methyl cellulose films as anti-microbial packaging for food application. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 266, 131249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyadarshi, R.; Tammina, S.; Bhattacharya, T.; Rhim, J.; Ezati, P.; Khan, A. Biopolymer-based UV protection functional films for food packaging. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 142, 108771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atarés, L.; Chiralt, A.; Ordoñez, R. Biodegradable active materials containing phenolic acids for food packaging applications. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2022, 21, 3910–3930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamilah, B.; Hean, G.; Lyn, H.; Adilah, Z.; Nabilah, B.; Hanani, Z. Enhancing the physicochemical and functional properties of gelatin/graphene oxide/cinnamon bark oil nanocomposite packaging films using ferulic acid. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2022, 34, 100960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczyk, A.; Kraśkiewicz, A.; Markowska-Szczupak, A.; Kowalczyk, K. Antimicrobial Coatings Based on a Photoreactive (Meth)acrylate Syrup and Ferulic Acid—The Effectiveness against Staphylococcus epidermidis. Polymers 2024, 16, 2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Jiang, F.; Shuai, L.; Zhao, C. Synthetic lignin derived from ferulic acid for UV-blocking sunscreen. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 283, 137694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 4624:2023; Paints and Varnishes—Pull-Off Test for Adhesion. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023.
- ISO 1522:2022; Paints and Varnishes—Pendulum Damping Test. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022.
- ISO 2813:2014; Paints and Varnishes—Determination of Gloss Value at 20°, 60° and 85°. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014.
- ASTM E2149-20; Standard Test Method for Determining the Antimicrobial Activity of Antimicrobial Agents under Dynamic Contact Conditions. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2020.
- ASTM D638-14; Standard Test Method for Tensile Properties of Plastics. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2014.
- Zhong, L.; Hao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wei, F.; Li, T.; Miao, M.; Zhang, D. Closed-Loop Recyclable Fully Bio-Based Epoxy Vitrimers from Ferulic Acid-Derived Hyperbranched Epoxy Resin. Macromolecules 2022, 55, 595–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D1002-05; Standard Test Method for Apparent Shear Strength of Single-Lap-Joint Adhesively Bonded Metal Specimens by Tension Loading (Metal-to-Metal). ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2021.
- Pezzana, L.; Malmström, E.; Johansson, M.; Casalegno, V.; Sangermano, M. Multiple approaches to exploit ferulic acid bio-based epoxy monomer for green thermoset. Ind. Crops Prod. 2024, 212, 118304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zang, Q.; Sun, S.; Li, J. Improving adhesion and antiaging properties of soybean oils-based pressure sensitive adhesives by phenolic acids grafting. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 189, 115760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 527-2:2012; Plastics—Determination of tensile properties—Part 2: Test conditions for moulding and extrusion plastics. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012.
- Pezzana, L.; Mousa, M.; Malmström, E.; Johansson, M.; Sangermano, M. Bio-based monomers for UV-curable coatings: Allylation of ferulic acid and investigation of photocured thiol-ene network. Prog. Org. Coat. 2021, 150, 105986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Ma, S.; Wang, B.; Chen, Q.; Huang, K.; Xu, X.; Li, Q.; Wang, S.; Lu, N.; Zhu, J. High-performance bio-based epoxies from ferulic acid and furfuryl alcohol: Synthesis and properties. Green Chem. 2021, 23, 1772–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldron, K.; Faulds, C.; Smith, A.; Robertson, J. Peroxidase-mediated oxidative cross-linking and its potential to modify mechanical properties in water-soluble polysaccharide extracts and cereal grain residues. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 1720–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, N.; Garrido, J.; Sirés, I.; Brillas, E.; Centellas, F.; Cabot, P.; Rodríguez, R. Degradation of trans-ferulic acid in acidic aqueous medium by anodic oxidation, electro-Fenton and photoelectro-Fenton. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 319, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margesin, R.; Volgger, G.; Wagner, A.O.; Zhang, D.; Poyntner, C. Biodegradation of lignin monomers and bioconversion of ferulic acid to vanillic acid by Paraburkholderia aromaticivorans AR20-38 isolated from Alpine forest soil. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 105, 2967–2977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.-G.; Dai, C.-C. Degradation of a model pollutant ferulic acid by the endophytic fungus Phomopsis liquidambari. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 179, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healy, J.B.; Young, L.Y.; Reinhard, M. Methanogenic decomposition of ferulic acid, a model lignin derivative. Sci. Total Environ. 1980, 39, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Fuente Arias, C.I.; González-Martínez, C.; Chiralt, A. Biodegradation behavior of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) containing phenolic compounds in seawater in laboratory testing conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 944, 173920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, P.D.; Yadav, G.D. Comparative studies of white-rot fungal strains (Trametes hirsuta MTCC-1171 and Phanerochaete chrysosporium NCIM-1106) for effective degradation and bioconversion of ferulic acid. ACS Omega. 2018, 3, 14858–14868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, L.; Zhang, H.; Yang, W.C.; Zhu, Y.H.; Yang, Z.H.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, Y.H. Biodegradation of ferulic acid by a newly isolated strain of Cupriavidus sp. B-8. J. Cent. South Univ. 2013, 20, 1964–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanshita; Monika; Chakraborty, S.; Odeku, O.A.; Singh, I. Ferulic acid’s therapeutic odyssey: Nano formulations, pre-clinical investigations, and patent perspective. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2024, 21, 479–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasr, M.; Hamzawy, M.; Rahsed, L.; El-Gogary, R. Ferulic acid nanocapsules as a promising treatment modality for colorectal cancer: Preparation and in vitro/in vivo appraisal. Life Sci. 2022, 298, 120500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, L.; Nowak, A.; Piotrowska, K.; Świątek, E.; Kucharski, Ł.; Kucharska, E.; Klimowicz, A.; Duchnik, W.; Januś, E.; Perużyńska, M.; et al. New Ferulic Acid and Amino Acid Derivatives with Increased Cosmeceutical and Pharmaceutical Potential. Pharmaceutics 2022, 15, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machaczka, M.; Stompor-Gorący, M. Recent Advances in Biological Activity, New Formulations and Prodrugs of Ferulic Acid. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandham, R.; Thapliyal, S.; Kumari, P.; Handu, S.; Bisht, M.; Srivastava, P.; Arya, P.; Singh, T. A Review on Potential Footprints of Ferulic Acid for Treatment of Neurological Disorders. Neurochem. Res. 2021, 46, 1043–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Liu, S.; Gu, T.; Soomro, L.; Li, Z.; Xin, F.; Wei, X.; Bao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wen, B.; et al. Directed evolution of feruloyl esterase from Lactobacillus acidophilus and its application for ferulic acid production. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 332, 124967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, M.; Sousa, A.; Filho, A.; Júnior, J.; De Souza, F.; De Fátima Formiga Melo Diniz, M.; Pessôa, H.; Sá, R. In silico and in vitro toxicity assessment of ferulic acid and nicotinamide: Analysis using admet tools and effects on bacteria, erythrocytes, and sun protection. Obs. Econ. Latinoam. 2024, 22, e8026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truzzi, F.; Valerii, M.; Tibaldi, C.; Zhang, Y.; Abduazizova, V.; Spisni, E.; Dinelli, G. Are Supplements Safe? Effects of Gallic and Ferulic Acids on In Vitro Cell Models. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Yu, W.; Duan, N.; Wang, Z.; Shen, Y.; Wu, S. Protective Effects of Ferulic Acid on Deoxynivalenol-Induced Toxicity in IPEC-J2 Cells. Toxins 2022, 14, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelainy, E.; Laila, I.; Ibrahim, S. The effect of ferulic acid against lead-induced oxidative stress and DNA damage in kidney and testes of rats. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 31675–31684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guvvala, P.; Ravindra, J.; Selvaraju, S.; Arangasamy, A.; Venkata, K. Ellagic and ferulic acids protect arsenic-induced male reproductive toxicity via regulating Nfe2l2, Ppargc1a and StAR expressions in testis. Toxicology 2019, 413, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh Tuli, H.; Kumar, A.; Ramniwas, S.; Coudhary, R.; Aggarwal, D.; Kumar, M.; Sharma, U.; Chaturvedi Parashar, N.; Haque, S.; Sak, K. Ferulic Acid: A Natural Phenol That Inhibits Neoplastic Events through Modulation of Oncogenic Signaling. Molecules 2022, 27, 7653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Chemicals Agency (ECHA). Registration Dossier: 4-Hydroxy-3-methoxycinnamic Acid. ECHA. Available online: https://echa.europa.eu/da/registration-dossier/-/registered-dossier/18980/7/2/1 (accessed on 8 October 2025).
| Derivative Type | Synthesis/Modification Method | Key Properties | Main Applications | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ferulate polyesters | Copolymerization of FA with diols | Biodegradable; UV-protective; hydrophilic; elongation at break 6–434% (PLA-based, Bis-O-dihydroferuloyl-1,4-butanediol (BDF)-modified) | Packaging, biomaterials, cosmetics | [25,28,35] |
| Ferulate polyanhydrides | Anhydride polymerization | Controlled release of active substances, biodegradability | Biomedical applications, cosmetics, drug delivery systems | [25,53] |
| Styrene polymers | Anionic/radical polymerization, protection of groups | Preservation of phenolic groups, tunable properties | Functional materials, elastomers | [30,31,34,51] |
| FA-based nanocomposites | Grafting, enzymatic modifications, incorporation | Improved mechanical properties (Tensile strength increased from 5.42 to 10.78 MPa), stability, bioactivity, antibacterial activity | Packaging, environmental engineering, biomaterials | [46,47,48,52,54] |
| FA-modified CTS polymers | Enzymatic modifications (e.g., laccase) | Enhanced antioxidant and antibacterial activity, biocompatibility, oxygen permeability resistance 0.1–20.6% | Biomaterials, coatings, protective films | [26,33,55] |
| Polyferulans (FA polymers) | Chemical, enzymatic, natural polymerization | Biodegradability, biological activity, potential for controlled release | Biomedical applications, packaging, drug delivery systems | [36,37,38] |
| Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|
| Opportunities | Threats |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Leszczyński, M.; Mamiński, M.Ł.; Parzuchowski, P.G. Ferulic Acid and Polyferulic Acid in Polymers: Synthesis, Properties, and Applications. Polymers 2025, 17, 2788. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17202788
Leszczyński M, Mamiński MŁ, Parzuchowski PG. Ferulic Acid and Polyferulic Acid in Polymers: Synthesis, Properties, and Applications. Polymers. 2025; 17(20):2788. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17202788
Chicago/Turabian StyleLeszczyński, Mateusz, Mariusz Ł. Mamiński, and Paweł G. Parzuchowski. 2025. "Ferulic Acid and Polyferulic Acid in Polymers: Synthesis, Properties, and Applications" Polymers 17, no. 20: 2788. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17202788
APA StyleLeszczyński, M., Mamiński, M. Ł., & Parzuchowski, P. G. (2025). Ferulic Acid and Polyferulic Acid in Polymers: Synthesis, Properties, and Applications. Polymers, 17(20), 2788. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17202788








