Phosphate Low-Melting Glasses as Synergist in Flame-Retardant Cable Sheath Composition: Performance and Mode of Action
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. Characterization Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Flame Retardant Properties of LMG in PE-EVA/ATH
3.1.1. Cone Calorimeter Tests
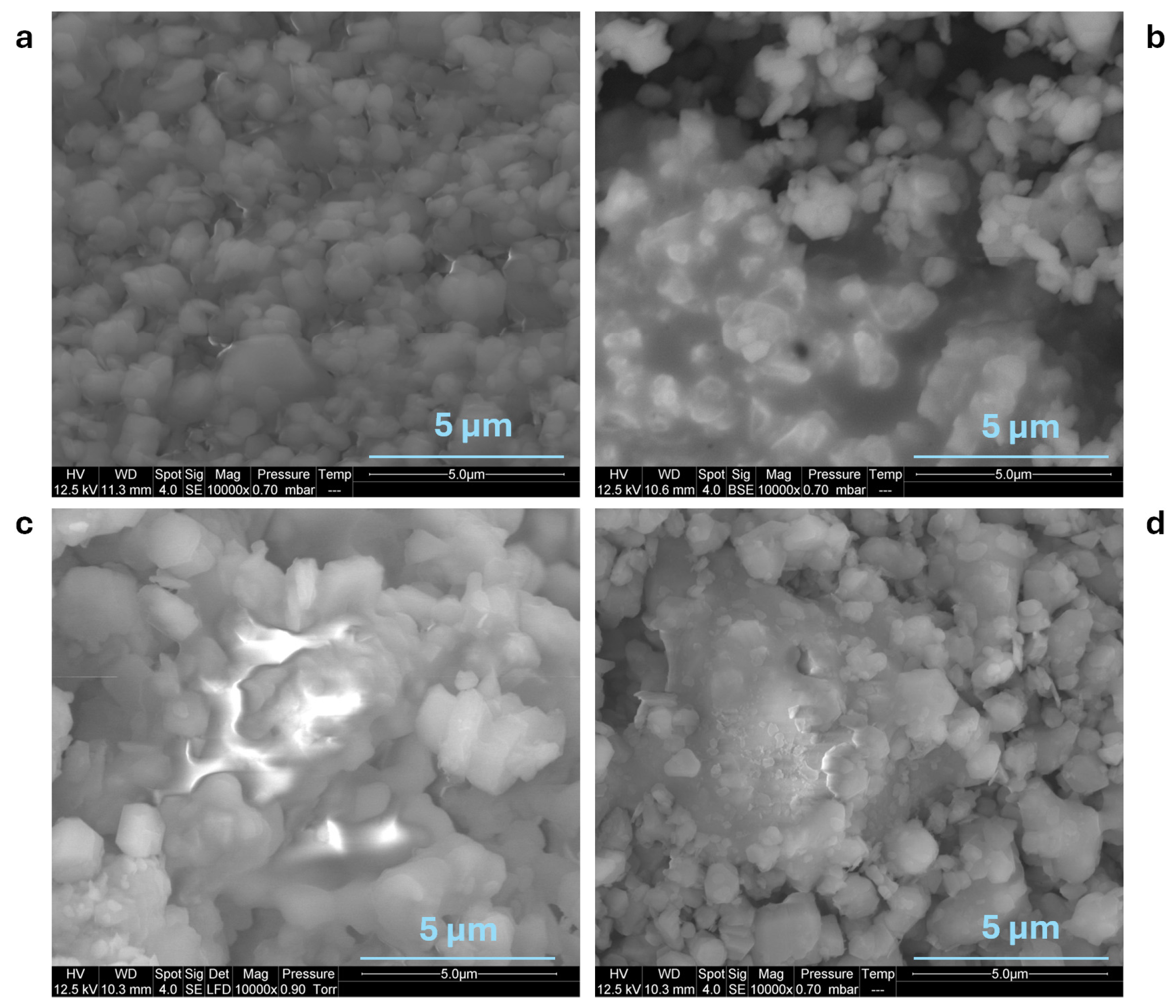
3.1.2. Characterization of the Residues
3.2. Study of the Flame-Retardant Mechanisms
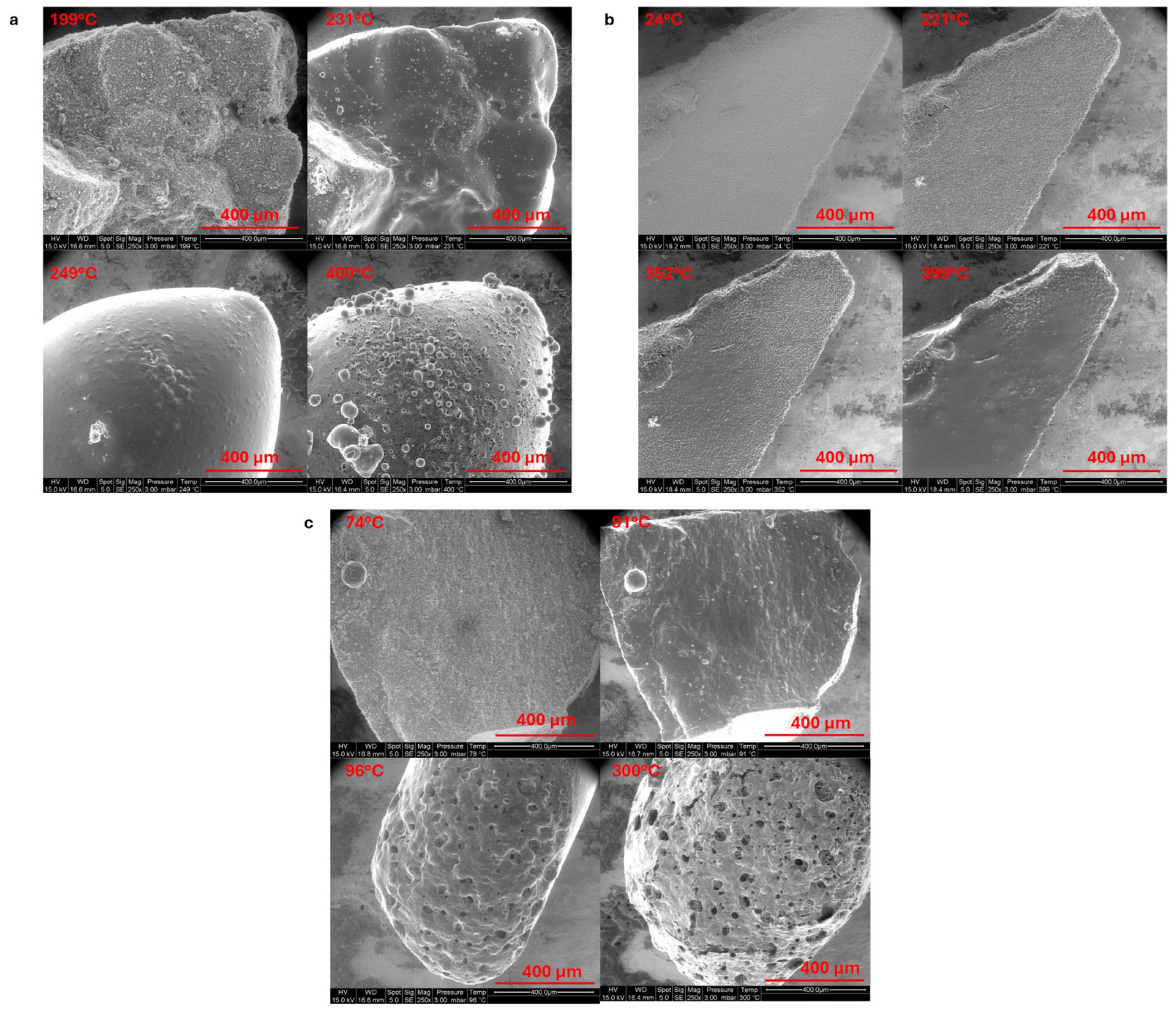
3.2.1. Thermal Behavior of LMG Powders
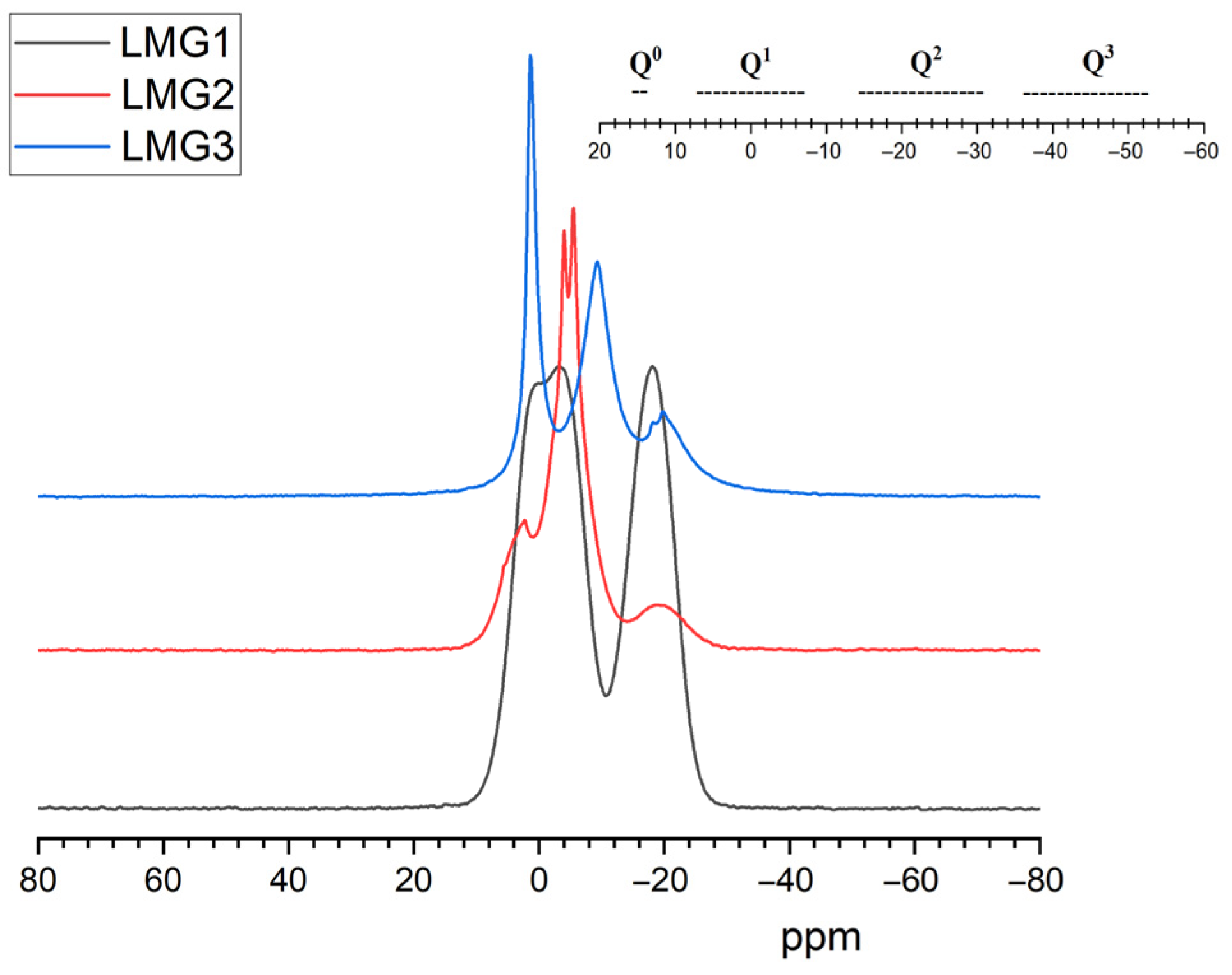
3.2.2. Structural Characterization of LMG Powders
NMR Spectroscopy
FTIR Spectroscopy
X-Ray Diffraction
3.3. Study of LMG-ATH Interactions
3.3.1. SEM Observations
3.3.2. Thermogravimetric Analysis
3.3.3. X-Ray Diffraction Analyses
3.3.4. 31P NMR Spectroscopy
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aigrain, P.R. Advances in Materials Science. In Globalization of Technology; Muroyama, J.H., Guyford Stever, H., Eds.; National Academy Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1988; pp. 41–44. [Google Scholar]
- Zilberman, J.; Hull, T.R.; Price, D.; Milnes, G.J.; Keen, F. Flame Retardancy of Some Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate Copolymer-Based Formulations. Fire Mater. 2000, 24, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagreve, C.; Ferry, L.; Lopez-Cuesta, J.-M. Flame Retardant Polymer Materials Design for Wire and Cable Applications. In Flame Retardant Polymeric Materials, 1st ed.; Hu, Y., Wang, X., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019; pp. 285–310. [Google Scholar]
- Hewitt, F.; Hull, T.R. Mineral Filler Fire Retardants. In Fillers for Polymer Applications. Polymers and Polymeric Composites: A Reference Series; Rothon, R., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 329–354. [Google Scholar]
- Hull, T.R.; Witkowski, A.; Hollingbery, L. Fire Retardant Action of Mineral Fillers. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2011, 96, 1462–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delfosse, L.; Baillet, C.; Brault, A.; Brault, D. Combustion of Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate Copolymer Filled with Aluminium and Magnesium Hydroxides. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 1989, 23, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duquesne, S.; Fontaine, G.; Cérin-Delaval, O.; Gardelle, B.; Tricot, G.; Bourbigot, S. Study of the Thermal Degradation of an Aluminium Phosphinate–Aluminium Trihydrate Combination. Thermochim. Acta 2013, 551, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyer, G. Flame Retardant Properties of EVA-Nanocomposites and Improvements by Combination of Nanofillers with Aluminium Trihydrate. Fire Mater. 2001, 25, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanetti, M.; Kashiwagi, T.; Falqui, L.; Camino, G. Cone Calorimeter Combustion and Gasification Studies of Polymer Layered Silicate Nanocomposites. Chem. Mater. 2002, 14, 881–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewin, M.; Pearce, E.M.; Levon, K.; Mey-Marom, A.; Zammarano, M.; Wilkie, C.A.; Jang, B.N. Nanocomposites at Elevated Temperatures: Migration and Structural Changes. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2006, 17, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilman, J.W.; Harris, R.H.; Shields, J.R.; Kashiwagi, T.; Morgan, A.B. A Study of the Flammability Reduction Mechanism of Polystyrene-Layered Silicate Nanocomposite: Layered Silicate Reinforced Carbonaceous Char. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2006, 17, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, A.B.; Harris, R.H.; Kashiwagi, T.; Chyall, L.J.; Gilman, J.W. Flammability of Polystyrene Layered Silicate (Clay) Nanocomposites: Carbonaceous Char Formation. Fire Mater. 2002, 26, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferry, L.; Gaudon, P.; Leroy, E.; Lopez-Cuesta, J.-M. Intumescence in Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate Copolymer Filled with Magnesium Hydroxide and Organoclays. In Fire Retardancy of Polymers; Le Bras, M., Wilkie, C.A., Bourbigot, S., Eds.; Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 2005; pp. 302–312. [Google Scholar]
- Clerc, L.; Ferry, L.; Leroy, E.; Lopez-Cuesta, J.-M. Influence of Talc Physical Properties on the Fire Retarding Behaviour of (Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate Copolymer/Magnesium Hydroxide/Talc) Composites. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2005, 88, 504–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hage, R.; Viretto, A.; Sonnier, R.; Ferry, L.; Lopez-Cuesta, J.M. Flame Retardancy of Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) Using New Aluminum-Based Fillers. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2014, 108, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonnier, R.; Viretto, A.; Dumazert, L.; Longerey, M.; Buonomo, S.; Gallard, B.; Longuet, C.; Cavodeau, F.; Lamy, R.; Freitag, A. Fire Retardant Benefits of Combining Aluminum Hydroxide and Silica in Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate Copolymer (EVA). Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2016, 128, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavodeau, F.; Otazaghine, B.; Sonnier, R.; Lopez-Cuesta, J.M.; Delaite, C. Fire Retardancy of Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate Composites-Evaluation of Synergistic Effects between ATH and Diatomite Fillers. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2016, 129, 246–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavodeau, F.; Sonnier, R.; Otazaghine, B.; Lopez-Cuesta, J.M.; Delaite, C. Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate Copolymer/Aluminium Trihydroxide Composites: A New Method to Predict the Barrier Effect during Cone Calorimeter Tests. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2015, 120, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroenke, W.J. Low-Melting Sulphate Glasses and Glass-Ceramics, and Their Utility as Fire and Smoke Retarder Additives for Poly(Vinyl Chloride). J. Mater. Sci. 1986, 21, 1123–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, R.E.; Licursi, E. Inorganic Glass Forming Systems as Intumescent Flame Retardants for Organic Polymers. J. Fire Sci. 1985, 3, 415–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, R.E. Low melting Phosphate-Sulfate Glasses as Intumescent Flame and/or Smoke Retardants for Polymers United States Patent. U.S. Patent 4,544,695, 1 October 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Myers, R.E.; Dickens, E.D.; Licursi, E.; Evans, R.E. Ammonium Pentaborate: An Intumescent Flame Retardant for Thermoplastic Polyurethanes. J. Fire Sci. 1985, 3, 432–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weil, E.D.; Patel, N.G.; Leeuwendal, R.M. Flame Retardant Polyamides. U.S. Patent 5,071,894, 10 December 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Bourbigot, S.; Le Bras, M.; Leeuwendal, R.; Shen, K.K.; Schubert, D. Recent Advances in the Use of Zinc Borates in Flame Retardancy of EVA. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 1999, 64, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpentier, F.; Bourbigot, S.; Le Bras, M.; Delobel, R.; Foulon, M. Charring of Fire Retarded Ethylene Vinyl Acetate Copolymer—Magnesium Hydroxide/Zinc Borate Formulations. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2000, 69, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durin-France, A.; Ferry, L.; Lopez Cuesta, J.-M.; Crespy, A. Magnesium Hydroxide/Zinc Borate/Talc Compositions as Flame-Retardants in EVA Copolymer. Polym. Int. 2000, 49, 1101–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crompton, G. Fire Barrier Materials. World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) WO2000068337A1, 16 November 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, G.M.; Schartel, B.; Kleemeier, M.; Hartwig, A. Flammability of Layered Silicate Epoxy Nanocomposites Combined with Low-Melting Inorganic Ceepree Glass. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2012, 52, 507–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Kleemeier, M.; Wu, G.M.; Schartel, B.; Liu, W.Q.; Hartwig, A. The Absence of Size-Dependency in Flame Retarded Composites Containing Low-Melting Organic-Inorganic Glass and Clay: Comparison between Micro- and Nanocomposites. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2011, 96, 1616–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Kleemeier, M.; Wu, G.M.; Schartel, B.; Liu, W.Q.; Hartwig, A. Phosphorus and Silicon Containing Low-Melting Organic-Inorganic Glasses Improve Flame Retardancy of Epoxy/Clay Composites. Macromo.l Mater. Eng. 2011, 296, 952–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Kleemeier, M.; Wu, G.M.; Schartel, B.; Liu, W.Q.; Hartwig, A. A Low Melting Organic-Inorganic Glass and Its Effect on Flame Retardancy of Clay/Epoxy Composites. Polymer 2011, 52, 2120–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Sanz, J.; Pecharromán, C.; Sobrados, I.; Lopez-Esteban, S.; Torrecillas, R.; Wang, D.-Y.; Moya, J.S.; Cabal, B. Synthesis, Characterization and Applications of Low Temperature Melting Glasses Belonging to P2O5-CaO-Na2O System. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 12234–12242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Pan, Y.-T.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L.; Moya, J.S.; Cabal, B.; Wang, D.-Y. Low-Melting Phosphate Glasses as Flame-Retardant Synergists to Epoxy: Barrier Effects vs Flame Retardancy. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2021, 185, 109495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brocheton, Y.A.H.; Jean, P. Low Melting Glass Powder Used as Additive for Flame Retardant Composition. World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) WO2024081120A1, 18 April 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Aitken, B.G.; George, H.B.; Dickinson, J.E., Jr. Cuprous Metaphosphate Glasses. U.S. Patent 5,529,960, 25 June 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández Navarro, J.M.; Oteo Mazo, J.L. Estudio de Propiedades de Vidrios de Borofosfatos Alcalinos. Boletín Soc. Española Cerámica Vidr. 1971, 10, 37–70. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 5660-1; Reaction-to-fire tests—Heat release, smoke production and mass loss rate. International Standard Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015.
- Cavodeau, F.; Viretto, A.; Otazaghine, B.; Lopez-Cuesta, J.-M.; Delaite, C. Influence of Colemanite on the Fire Retardancy of Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate and Ethylene-Methyl Acrylate Copolymers. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2017, 144, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schartel, B.; Hull, T.R. Development of Fire-Retarded Materials-Interpretation of Cone Calorimeter Data. Fire Mater. Int. J. 2007, 31, 327–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vangrevelynghe, M.; Le Nouvel, L.; Pesenti, C.; Sonnier, R.; Ferry, L.; Gesta, E.; Lagrève, C. A Method to Quantitatively Assess the Modes-of-Action of Flame-Retardants. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2022, 195, 109767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laoutid, F.; Ferry, L.; Leroy, E.; Lopez Cuesta, J.M. Intumescent Mineral Fire Retardant Systems in Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate Copolymer: Effect of Silica Particles on Char Cohesion. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2006, 91, 2140–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffendahl, C.; Fontaine, G.; Duquesne, S.; Taschner, F.; Mezger, M.; Bourbigot, S. The Combination of Aluminum Trihydroxide (ATH) and Melamine Borate (MB) as Fire Retardant Additives for Elastomeric Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA). Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2015, 115, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cárdenas, M.A.; García-López, D.; Gobernado-Mitre, I.; Merino, J.C.; Pastor, J.M.; Martínez, J.d.D.; Barbeta, J.; Calveras, D. Mechanical and Fire Retardant Properties of EVA/Clay/ATH Nanocomposites - Effect of Particle Size and Surface Treatment of ATH Filler. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2008, 93, 2032–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, H.; Yu, Z.; Li, J.; Liu, M.; Liu, J.; Li, X.; Luo, J. Flame-Retardant and Mechanical Performances of Crosslinked EVA Blend/Aluminum Trihydrate/Expandable Graphite Composite: The Impact of Microencapsulation of Expandable Graphite and Its Action Mechanism. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2025, 241, 111556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witkowski, A.; Stec, A.A.; Hull, T.R. The Influence of Metal Hydroxide Fire Retardants and Nanoclay on the Thermal Decomposition of EVA. Polym Degrad Stab 2012, 97, 2231–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Li, J.; Ye, Q.; Shen, L.; Lin, H. Flame-Retardant Ethylene Vinyl Acetate Composite Materials by Combining Additions of Aluminum Hydroxide and Melamine Cyanurate: Preparation and Characteristic Evaluations. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 589, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Choi, J.Y.; Choi, S. Mechanism of Heat Transfer through Porous Media of Inorganic Intumescent Coating in Cone Calorimeter Testing. Polymers 2019, 11, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lemos, M.J.S. Applications in Hybrid Media. In Turbulence in Porous Media; Elsevier: Waltham, MA, USA, 2012; pp. 199–352. [Google Scholar]
- Toyoda, S.; Fujino, S.; Morinaga, K. Density, Viscosity and Surface Tension of 50RO–50P2O5 (R: Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, and Zn) Glass Melts. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2003, 321, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, F.; Rocherullé, J.; Ahmed, I.; Hu, L. Phosphate Glasses. In Springer Handbooks; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 553–594. [Google Scholar]
- Sharmin, N.; Rudd, C.D. Structure, Thermal Properties, Dissolution Behaviour and Biomedical Applications of Phosphate Glasses and Fibres: A Review. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 52, 8733–8760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Senovilla, L.; Muñoz, F. Behaviour of Viscosity in Metaphosphate Glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2014, 385, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrt, D.; Flügel, S. Electrical Conductivity and Viscosity of Phosphate Glasses and Melts. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2018, 498, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, A.J. Phosphate Glasses. In Encyclopedia of Glass Science, History and Culture; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2021; Volume 2, pp. 901–917. [Google Scholar]
- Tricot, G. Mixed Network Phosphate Glasses: Seeing Beyond the 1D 31P MAS-NMR Spectra With 2D X/31P NMR Correlation Maps. In Annual Reports on NMR Spectroscopy; Academic Press Inc.: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; Volume 96, pp. 35–75. ISBN 9780081028520. [Google Scholar]
- Tricot, G.; Revel, B.; Wegner, S. Thermal Stability of a Low Tg Phosphate Glass Investigated by DSC, XRD and Solid State NMR. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2011, 357, 2708–2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brow, R.K.; Click, C.A.; Alam, T.M. Modifier Coordination and Phosphate Glass Networks. J. Non-Cristal. Solids 2000, 274, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, F.; Sánchez-Muñoz, L. The Glass-Forming Ability Explained from Local Structural Differences by NMR between Glasses and Crystals in Alkali Metaphosphates. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2019, 503–504, 94–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moustafa, Y.M.; El-Egili, K. Infrared Spectra of Sodium Phosphate Glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1998, 240, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaser, S.; Guérineau, T.; Strutynski, C.; Zaki, R.; Dussauze, M.; Durand, E.; Messaddeq, S.H.; Danto, S.; Messaddeq, Y.; Cardinal, T. Novel Optical Amorphous Phosphate Materials with a Low Melting Temperature. Mater. Adv. 2022, 3, 4600–4607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivascu, C.; Timar-Gabor, A.; Cozar, O. FT-IR and Thermoluminescence Investigation of P2O5-BaO-K2O Glass System. In Proceedings of the AIP Conference Proceedings, Cluj Napoca, Romania, 25–27 September 2013; Volume 1565, pp. 108–111. [Google Scholar]
- Ivascu, C.; Timar Gabor, A.; Cozar, O.; Daraban, L.; Ardelean, I. FT-IR, Raman and Thermoluminescence Investigation of P2O5-BaO-Li2O Glass System. J. Mol. Struct. 2011, 993, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobaz, V.; Konefał, M.; Kotov, N.; Lukešová, M.; Hromádková, J.; Šlouf, M.; Pánek, J.; Hrubý, M.; Chmela, T.; Krupička, P. Low-Melting Phosphate Glass Coatings for Structural Parts Composed of Depleted Uranium. Coatings 2022, 12, 1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abid, M.; Belfaquir, M.; Hafid, M.; Taibi, M. Study of Zinc and Lead Addition Effect on Structure-Properties of Phosphate Glasses. Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 13, 458–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elfeky, E.M.; Elbashar, Y.H.; Barakat, M.H.; Shehata, M.R.; Hassan, S.S. Structural Investigation and Applications of Glassy Sodium Phosphate Including the Kinetics of Dissolution Rates and Spectral Analysis of the Prepared Samples with a Focus on Their Effects on Water Treatment. Opt. Quantum Electron. 2019, 51, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banach, M.; Kowalski, Z.; Wzorek, Z.; Gorazda, K. A Chemical Method of the Production of “Heavy” Sodium Tripolyphosphate with the High Content of Form i or Form II. Pol. J. Chem. Technol. 2009, 11, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freschi, C.D.; Gouveia, J.T.; Marcondes, L.; Ferrari, J.L.; Cassanjes, F.C.; Poirier, G. Crystallization of Anatase TiO2 in Niobium Potassium Phosphate Glasses. Mater. Res. 2017, 20, 502–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farag, M.A.; Ibrahim, A.; Hassaan, M.Y.; Ramadan, R.M. Enhancement of Structural and Optical Properties of Transparent Sodium Zinc Phosphate Glass–Ceramics Nano Composite. J. Aust. Ceram. Soc. 2022, 58, 653–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapshin, A.E.; Petrova, M.A. Mixed Alkali-Zinc Diphosphates: Synthesis, Structure, and Properties. Glass Phys. Chem. 2012, 38, 491–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrova, M.A.; Volkov, S.N.; Bubnova, R.S. New Solid Solutions of Mixed Alkali-Zinc Diphosphates LiNa1−x K x ZnP2O7. Glass Phys. Chem. 2014, 40, 447–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Otsubo, M.; Honda, C.; Ohno, A. Suppression Effect of ATH Filler on the Erosion of Filled Silicone Rubber Exposed to Dry Band Arc Discharge. Polym. Test. 2005, 24, 893–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, A.D.V.; Arruda, C.C.; Fernandes, L.; Antunes, M.L.P.; Kiyohara, P.K.; Salomão, R. Characterization of Aluminum Hydroxide (Al(OH)3) for Use as a Porogenic Agent in Castable Ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2015, 35, 803–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Sun, J.; Xu, X.; Lv, Z.; Song, J. Thermal Analysis of Phosphorus-Modified Boehmite Nanosheets and Isoelectric Points (IEP) of the Corresponding γ-Alumina. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2017, 130, 2249–2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-S.; Alrefaei, Y.; Dai, J.-G. Silico-Aluminophosphate and Alkali-Aluminosilicate Geopolymers: A Comparative Review. Front. Mater. 2019, 6, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.-L.; Deng, J.-R.; Chao, Z.-S. Catalysis over Zinc-Incorporated Berlinite (ZnAlPO4) of the Methoxycarbonylation of 1,6-Hexanediamine with Dimethyl Carbonate to Form Dimethylhexane-1,6-Dicarbamate. Chem. Cent. J. 2007, 1, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Kroon, A.P.; Schäfer, G.W.; Aldinger, F. Crystallography of Potassium Aluminate K2O·Al2O3. J. Alloys Compd. 2001, 314, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dick, S.; Goßner, U.; Weiss, A.; Robl, C.; Grossmann, G.; Ohms, G.; Müller, M. The Potassium Aluminum Phosphate KAl(HPO4)2·H2O: X-Ray Diffraction, Neutron-Scattering, and Solid-State NMR Characterization. J. Solid State Chem. 1997, 132, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.J.; Lee, J.W.; Lee, H.J.; Zhang, S.; Lee, J.S.; Cheong, M.; Kim, H.S. K3PO4-Catalyzed Carbonylation of Amines to Formamides. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2015, 506, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkpatrick, R.J.; Brow, R.K. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Investigation of the Structures of Phosphate and Phosphate-Containing Glasses: A Review. Solid State Nucl. Magn. Reson. 1995, 5, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brow, R.K.; Kirkpatrick, R.J.; Turner, G.L. Nature of Alumina in Phosphate Glass: II, Structure of Sodium Alurninophosphate Glass. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1993, 76, 919–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
















| Oxide | LMG1 (%mol) | LMG2 (%mol) | LMG3 (%mol) |
|---|---|---|---|
| P2O5 | 65 | 40 | 65 |
| Na2O | 35 | 12 | |
| K2O | 7.5 | 35 | |
| ZnO | 29.9 | ||
| Li2O | 10.6 |
| Formulation | TTI (s) | pHRR1 (kW/m2) | pHRR2 (kW/m2) | tpHRR2 (s) | MAHRE (kW/m2) | THR (kJ/g) | EHC (kJ/g) | MLexp (%) | MLcalc (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PE-EVA | 53 | 2891 | - | - | 673 | 43.4 | 43.4 | 0 | 0 |
| PE-EVA/ATH | 83 | 220 | 295 | 385 | 154 | 14.9 | 24.1 | 38.1 | 39.2 |
| PE-EVA/ATH/LMG1 | 75 | 219 | 170 | 440 | 128 | 15.6 | 27.3 | 42.2 | 42.7 * |
| PE-EVA/ATH/LMG2 | 60 | 232 | 215 | 370 | 149 | 14.9 | 26.1 | 42.9 | 42.7 * |
| PE-EVA/ATH/LMG3 | 66 | 142 | 100 | 620 | 90 | 15.9 | 27.4 | 42.4 | 42.7 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Amin Alsayed, D.; Sonnier, R.; Otazaghine, B.; Jean, P.; Brocheton, Y.; Ferry, L. Phosphate Low-Melting Glasses as Synergist in Flame-Retardant Cable Sheath Composition: Performance and Mode of Action. Polymers 2025, 17, 2679. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17192679
Amin Alsayed D, Sonnier R, Otazaghine B, Jean P, Brocheton Y, Ferry L. Phosphate Low-Melting Glasses as Synergist in Flame-Retardant Cable Sheath Composition: Performance and Mode of Action. Polymers. 2025; 17(19):2679. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17192679
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmin Alsayed, Diana, Rodolphe Sonnier, Belkacem Otazaghine, Patrick Jean, Yves Brocheton, and Laurent Ferry. 2025. "Phosphate Low-Melting Glasses as Synergist in Flame-Retardant Cable Sheath Composition: Performance and Mode of Action" Polymers 17, no. 19: 2679. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17192679
APA StyleAmin Alsayed, D., Sonnier, R., Otazaghine, B., Jean, P., Brocheton, Y., & Ferry, L. (2025). Phosphate Low-Melting Glasses as Synergist in Flame-Retardant Cable Sheath Composition: Performance and Mode of Action. Polymers, 17(19), 2679. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17192679









