Tensile Modeling PVC Gels for Electrohydraulic Actuators
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Elastic and Hyperelastic Constitutive Equations
2.1. Constitutive Equations
2.2. Determination of Hyperelastic Material Parameters
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. EPIC Actuator
3.2. Material Preparation of PVC Gel Samples
3.3. Tensile Testing
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Elastic Modeling
4.2. Hyperelastic Modeling
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PVC | Polyvinyl chloride |
| PX | Plasticizer to PVC weight ratio (X:1) |
| DBA | Dibutyl adipate plasticizer |
| THF | Tetrahydrofuran |
| DEA | Dielectric elastomer actuator |
| EPIC | Electrohydraulic actuator powered by induced interfacial charges |
| HASEL | Hydraulically amplified self-healing electrostatic |
| DE | Dielectric |
| KAIST | Korea Advanced Institute of Science & Technology |
| BOPP | Biaxially oriented polypropylene |
| LM | Levenberg–Marquardt |
| NRMSE | Normalized root-mean-square-error |
References
- Uddin, M.Z.; Yamaguchi, M.; Watanabe, M.; Shirai, H.; Hirai, T. Electrically induced creeping and bending deformation of plasticized poly(vinyl chloride). Chem. Lett. 2001, 30, 360–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.Z.; Watanabe, M.; Shirai, H.; Hirai, T. Effects of plasticizers on novel electromechanical actuations with different poly(vinyl chloride) gels. J. Polym. Sci. B Polym. Phys. 2003, 41, 2119–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.; Ueki, T.; Hirai, T. Electrical response and mechanical behavior of plasticized PVC actuators. Adv. Mater. Res. 2009, 79, 2063–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.; Hirai, T. Space charge distribution and mechanical properties in plasticized PVC actuators. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation, ICMA, Changchun, China, 9–12 August 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hashimoto, M. PVC gel based artificial muscles: Characterizations and actuation modular constructions. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2015, 233, 246–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hashimoto, M. PVC gel soft actuator-based wearable assist wear for hip joint support during walking. Smart Mater. Struct. 2017, 26, 125003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hashimoto, M. Design and prototyping of a novel lightweight walking assist wear using PVC gel soft actuators. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2016, 239, 26–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Maeda, Y.; Hashimoto, M. Lightweight, Soft Variable Stiffness Gel Spats for Walking Assistance. Int. J. Adv. Robot Syst. 2015, 12, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibagaki, M.; Matsuki, T.; Hashimoto, M.; Hirai, T. Application of a contraction type PVC gel actuator to brakes. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation, ICMA, Xi’an, China, 4–7 August 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, M.; Shibagaki, M.; Hirai, T. Development of a Negative Type Polymer Brake Using a Contraction Type PVC Gel Actuator. J. Robot. Soc. Jpn. 2011, 29, 667–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Sun, B.; Chen, T.; Hu, B.; Guo, M.; Li, Y. Design and prototyping of a novel gripper using PVC gel soft actuators. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2021, 60, 087001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, Z.; Olsen, Z.; Hwang, T.; Kim, K.J. A multi-degree of freedom bending actuator based on a novel cylindrical polyvinyl chloride gel. In Proceedings of the SPIE Smart Structures + Nondestructive Evaluation, Online, 22–27 March 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Hirai, T. Characteristics of the creep-induced bending deformation of a PVC gel actuator by an electric field. J. Mater. Sci. 2011, 46, 7681–7688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Ma, J.; Kim, M.; Nam, J.; Kyung, K.-U. High-Output Force Electrohydraulic Actuator Powered by Induced Interfacial Charges. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2021, 3, 2170045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkman, S.; Rothemund, P.; Acome, E.; Keplinger, C. Electromechanics of planar HASEL actuators. Extreme Mech. Lett. 2021, 48, 101408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Mitchell, S.K.; Rumley, E.H.; Rothemund, P.; Keplinger, C. High-Strain Peano-HASEL Actuators. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1908821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellaris, N.; Venkata, V.G.; Smith, G.M.; Mitchell, S.K.; Keplinger, C. Peano-HASEL actuators: Muscle-mimetic, electrohydraulic transducers that linearly contract on activation. Sci. Robot 2018, 3, eaar3276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acome, E.; Mitchell, S.K.; Morrissey, T.G.; Emmett, M.B.; Benjamin, C.; King, M.; Radakovitz, M.; Keplinger, C. Hydraulically amplified self-healing electrostatic actuators with muscle-like performance. Science 2018, 359, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Kim, S.; Cha, Y. Multimodal motion of soft origami tripod using electrohydraulic actuator. In Proceedings of the SPIE Smart Structures + Nondestructive Evaluation, Long Beach, CA, USA, 25–29 March 2024; p. 1294809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Washington, A.; Su, J.; Kim, K.J. Actuation Behavior of Hydraulically Amplified Self-Healing Electrostatic (HASEL) Actuator via Dimensional Analysis. Actuators 2023, 12, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faccinto, J.; Fisher, D.; Sennain, A.; Neubauer, J.; Kim, K.J. Electromechanical applications of PVC gels and EPIC actuators in varifocal lenses. In Proceedings of the SPIE Smart Structures + Nondestructive Evaluation, Long Beach, CA, USA, 12–17 March 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothemund, P.; Kellaris, N.; Keplinger, C. How inhomogeneous zipping increases the force output of Peano-HASEL actuators. Extreme Mech. Lett. 2019, 31, 100542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, A.T. Elastic properties of polvinyl chloride gels. J. Polym. Sci. 1954, 13, 207–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamano, M.; Ogawa, N.; Hashimoto, M.; Takasaki, M.; Hirai, T. A contraction type soft actuator using poly vinyl chloride gel. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics, ROBIO, Bangkok, Thailand, 22–25 February 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.; Hirai, T. Electric-field-induced local layer structure in plasticized PVC actuator. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 10756–10762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, Z.; Kim, K.J. On the mechanism of performance improvement of electroactive polyvinyl chloride (PVC) gel actuators via conductive fillers. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 10316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, T.; Frank, Z.; Neubauer, J.; Kim, K.J. High-performance polyvinyl chloride gel artificial muscle actuator with graphene oxide and plasticizer. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Tsuchiya, Y.; Suzuki, A.; Shirai, Y.; Hashimoto, M. Influence of the number of stacked layers on the performance of PVC gel actuators. In Proceedings of the IEEE/ASME International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics, AIM, Besacon, France, 8–11 July 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchiya, Y.; Hashimoto, M. Development of contraction type sheets using PVC gel. In Proceedings of the JSME Annual Conference on Robotics and Mechatronics (Robomec), Kobe, Japan, 21–24 September 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Guo, M.; Li, Y. Recent advances in plasticized PVC gels for soft actuators and devices: A review. J. Mater. Chem. C 2019, 7, 12991–13009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gent, A.N.; Shimizu, N. Elasticity, tear strength, and strength of adhesion of soft PVC gels. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1986, 32, 5385–5398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallego, F.; Muñoz, M.E.; Peña, J.J.; Santamaría, A. Dynamic viscoelastic measurements of pvc gels. Eur. Polym. J. 1988, 24, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, D.; Mijangos, C.; Muñoz, M.E.; Santamaría, A. Viscoelastic properties of thermoreversible gels from chemically modified PVCs. Macromolecules 1996, 29, 7108–7115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, G. Hyperelastic behavior of polymers. In Applied Mechanics of Polymers; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 117–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergström, J. Elasticity/Hyperelasticity. In Mechanics of Solid Polymers; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 209–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, S.K.; Keerthan, A. Power-Yeoh: A Yeoh-Type Hyperelastic Model with Invariant I2 for Rubber-like Materials. Eng. Proc. 2023, 59, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puglisi, G.; Saccomandi, G. The Gent model for rubber-like Materials: An appraisal for an ingenious and simple idea. Int. J. Non Linear. Mech. 2015, 68, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaliske, M.; Heinrich, G. An extended tube-model for rubber elasticity: Statistical-mechanical theory and finite element implementation. Rubber Chem. Technol. 1999, 72, 602–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D638-14; Standard Test Method for Tensile Properties of Plastics. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2014. [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Ueki, T.; Tsurumi, D.; Hirai, T. Influence of plasticizer content on the transition of electromechanical behavior of PVC gel actuator. Langmuir 2011, 27, 7902–7908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.C.; Geil, P.H. Morphology and Properties of PVC/Solvent Gels. J. Macromol. Sci. Part B 1983, 22, 463–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Weng, Z.; Huang, Z.; Pan, Z. The crystallinity of PVC and its effect on physical properties. Int. Polym. Process. 1996, 11, 369–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seki, M.; Yamamoto, S.; Aoki, Y.; Takagi, K.; Izumi, Y.; Nojima, S. Small-angle x-ray scattering study of thermoreversible poly(vinyl chloride) gels. J. Polym. Sci. B Polym. Phys. 2001, 39, 2340–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, J.W.; Shin, E.J.; Jeong, J.; Choi, D.S.; Lee, J.E.; Nam, B.U.; Lin, L.; Kim, S.Y. High-Performance PVC Gel for Adaptive Micro-Lenses with Variable Focal Length. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, E.J.; Park, W.H.; Kim, S.Y. Fabrication of a high-performance bending actuator made with a PVC Gel. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Hong, P.; Chen, J.H. Structure and properties of polyvinyl chloride physical gels. Polymer 1998, 39, 711–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Q.; Yi, X.; Yu, W.; Cheng, J.; Ou, S.; Xue, Q.; Jiang, H. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Plasticizing Effect of Mixed Dioctyl Phthalate and Isosorbide Diheptanoate on Polyvinyl Chloride Material. Polymers 2025, 17, 1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Oh, S.J.; Kim, D.; Kim, M.; Lee, C.; Joo, H.; Woo, I.; Bae, J.W.; Lee, J.H. Plasticized PVC-Gel Single Layer-Based Stretchable Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Harvesting Mechanical Energy and Tactile Sensing. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, e2201070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, Y.; Li, L.; Uchida, H.; Kakiuchi, M.; Watanabe, H. Rheological images of poly(vinyl chloride) gels. 5. Effect of molecular weight distribution. Macromolecules 1998, 31, 7472–7478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Aoki, Y. Rheological images of poly(vinyl chloride) gels. 3. Elasticity evolution and the scaling law beyond the sol-gel transition. Macromolecules 1998, 31, 740–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, Y.; Li, L.; Kakiuchi, M. Rheological images of poly(vinyl chloride) Gels. 6. Effect of temperature. Macromolecules 1998, 31, 8117–8123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakiuchi, M.; Aoki, Y.; Watanabe, H.; Osaki, K. Viscoelastic properties of poly(vinyl chloride) gels: Universality of gel elasticity. Macromolecules 2001, 34, 2987–2991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Aoki, Y. Rheological images of poly(vinyl chloride) gels. 1. The dependence of sol-gel transition on concentation. Macromolecules 1997, 30, 7835–7841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
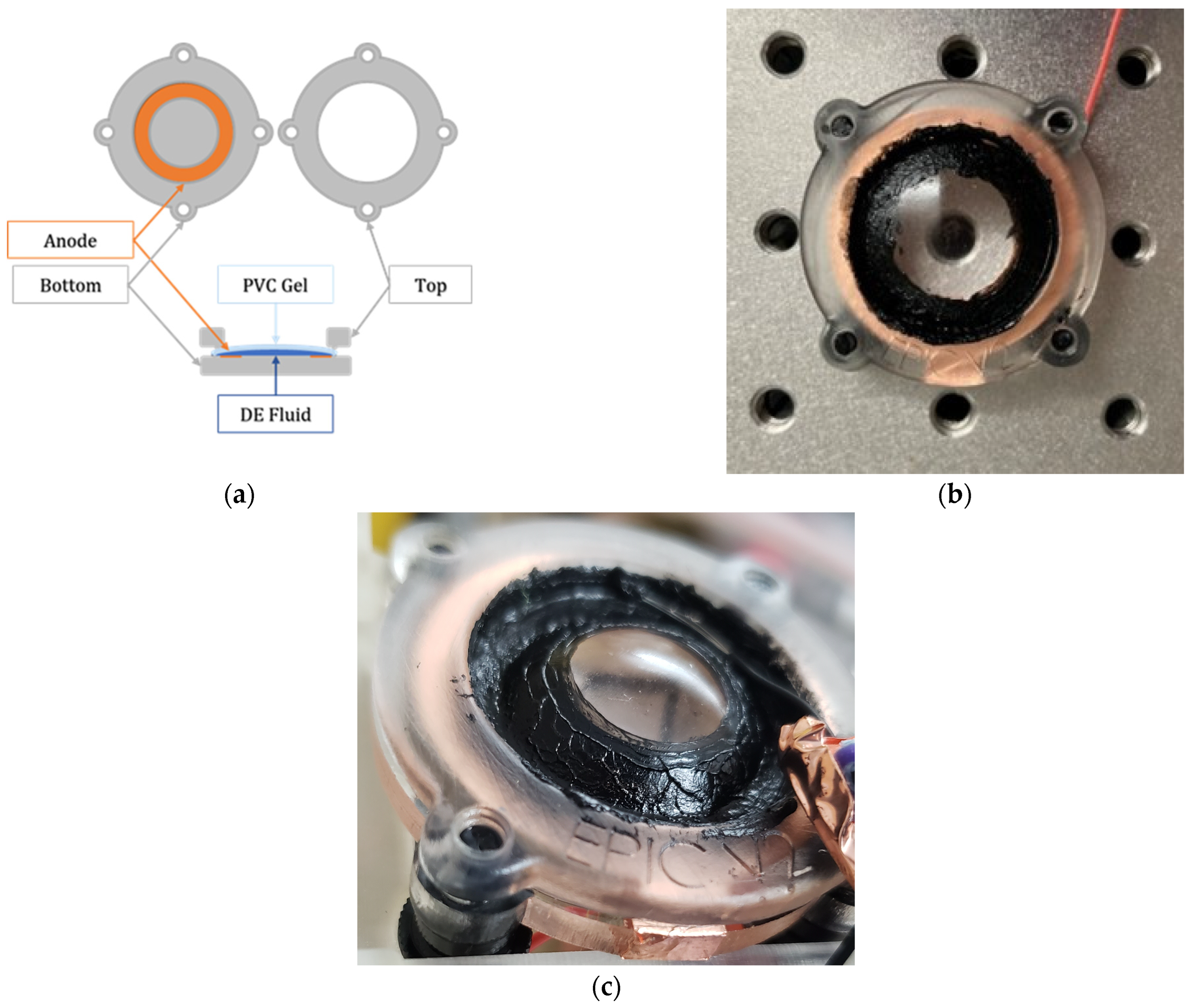
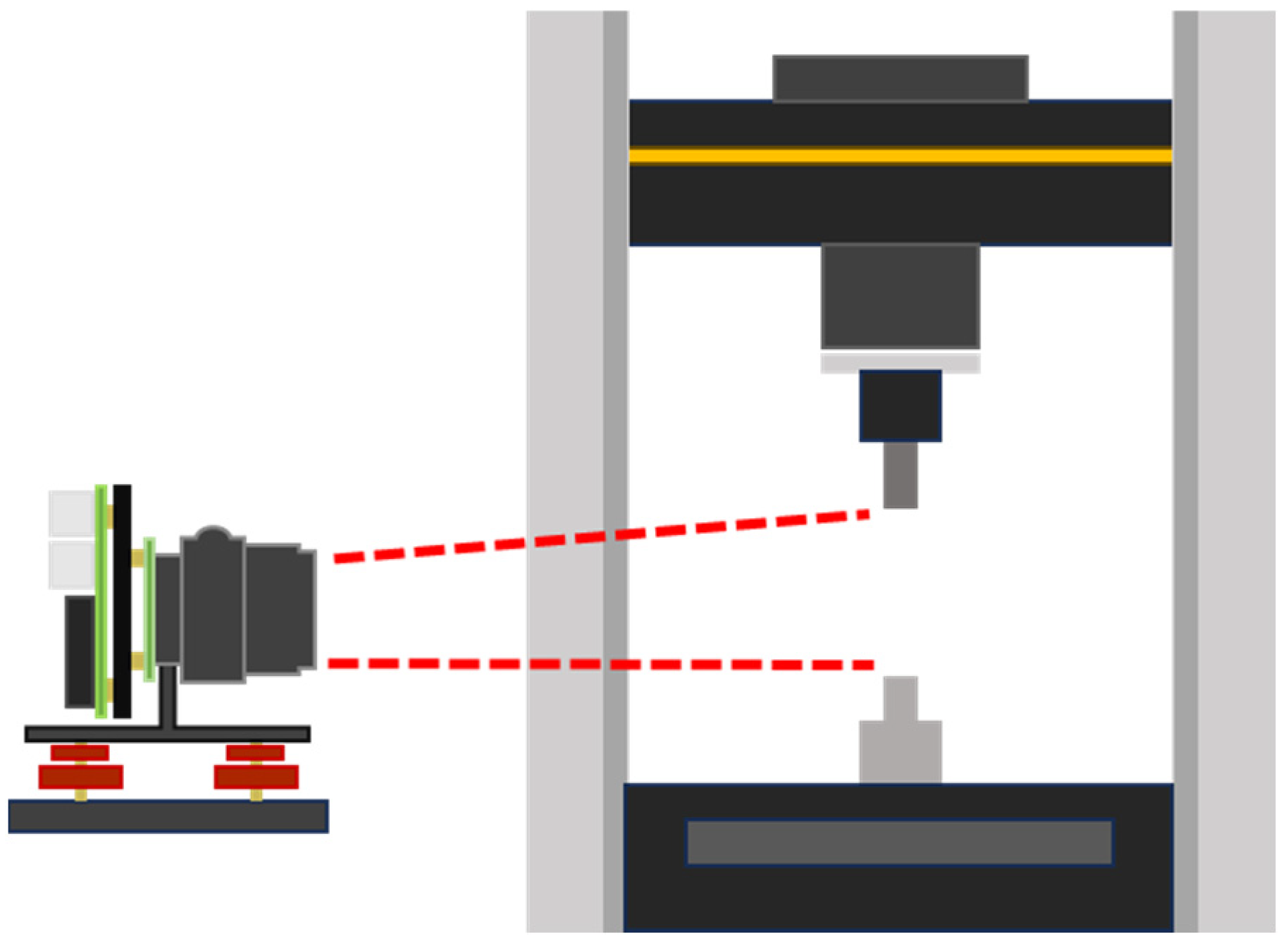


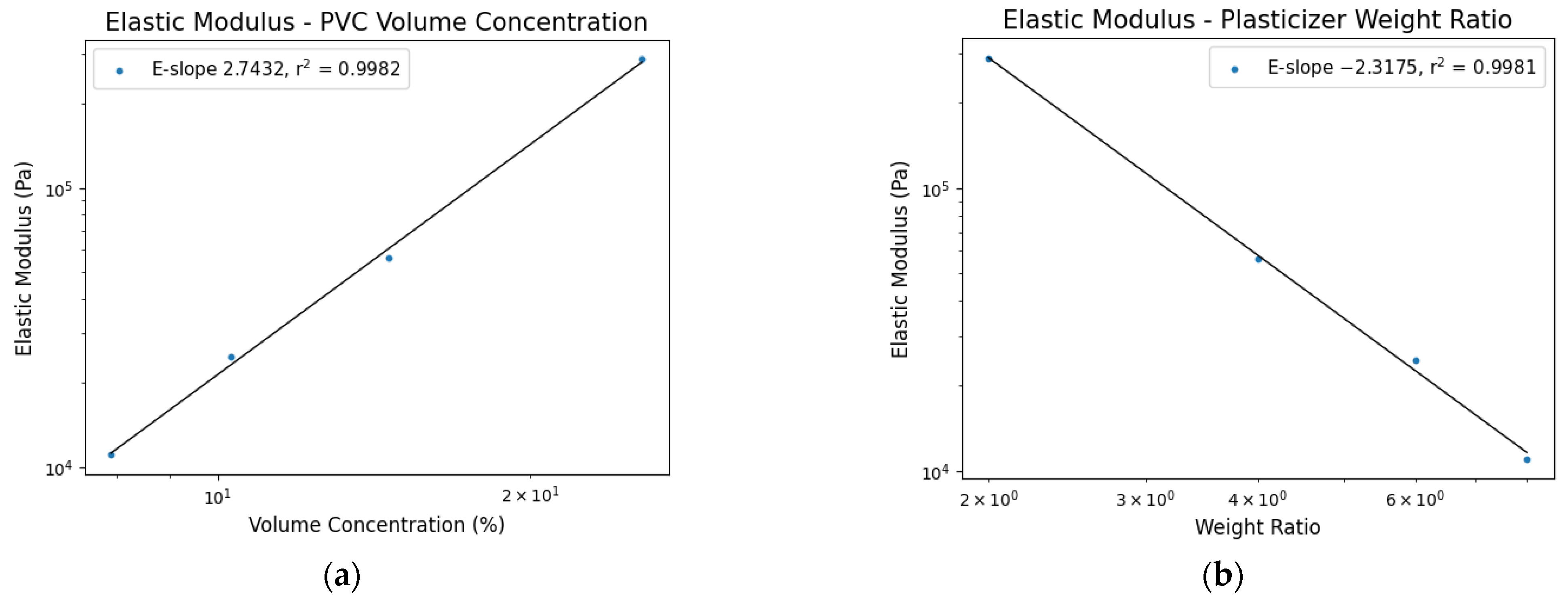
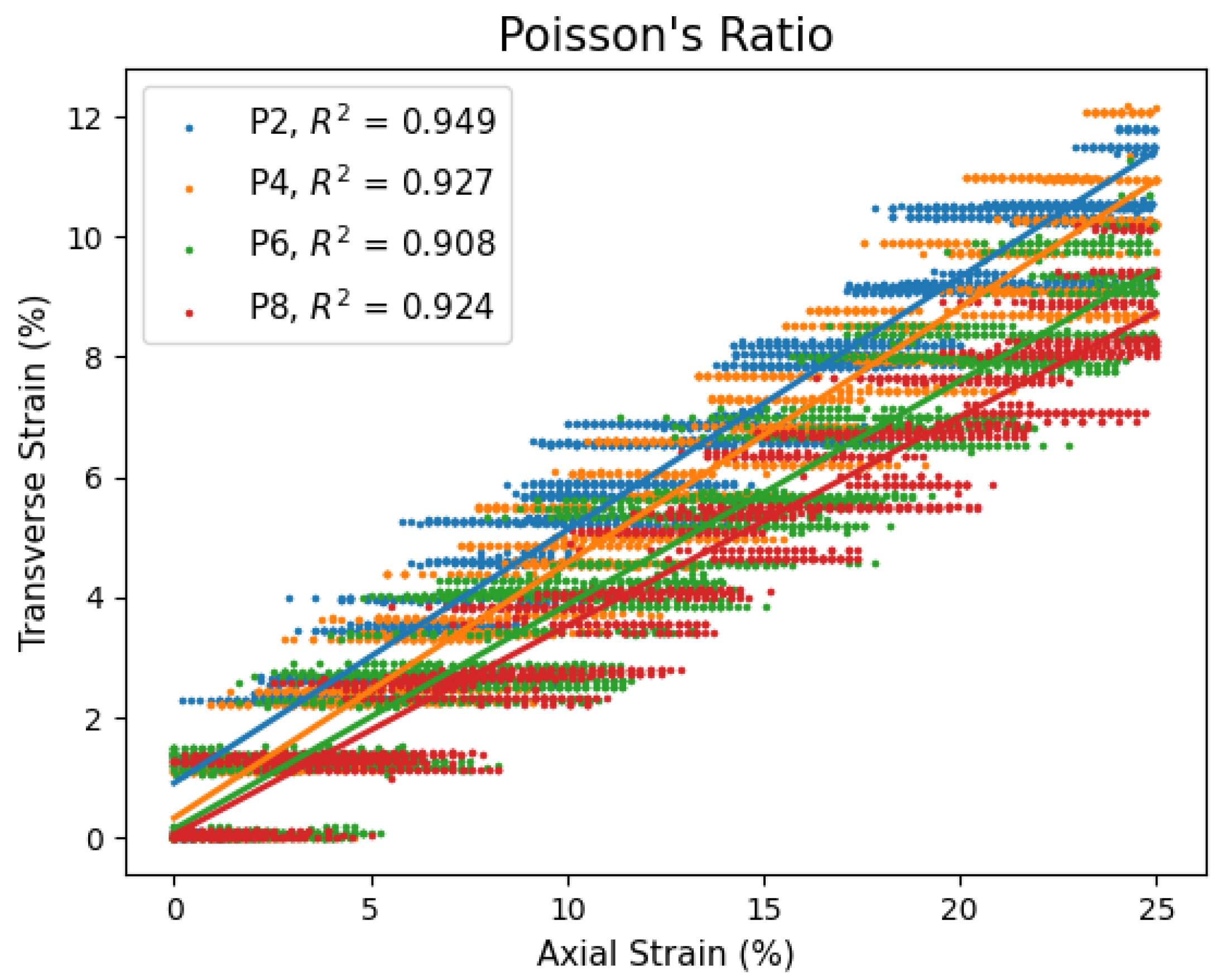

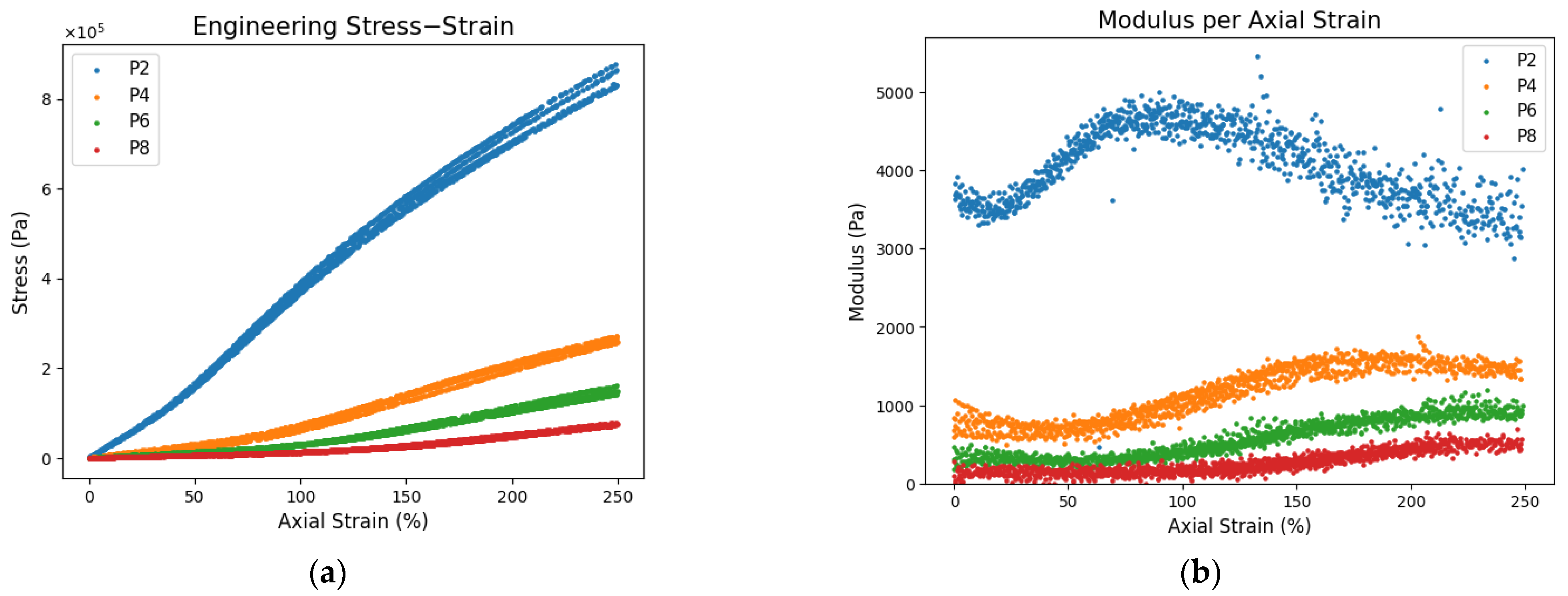

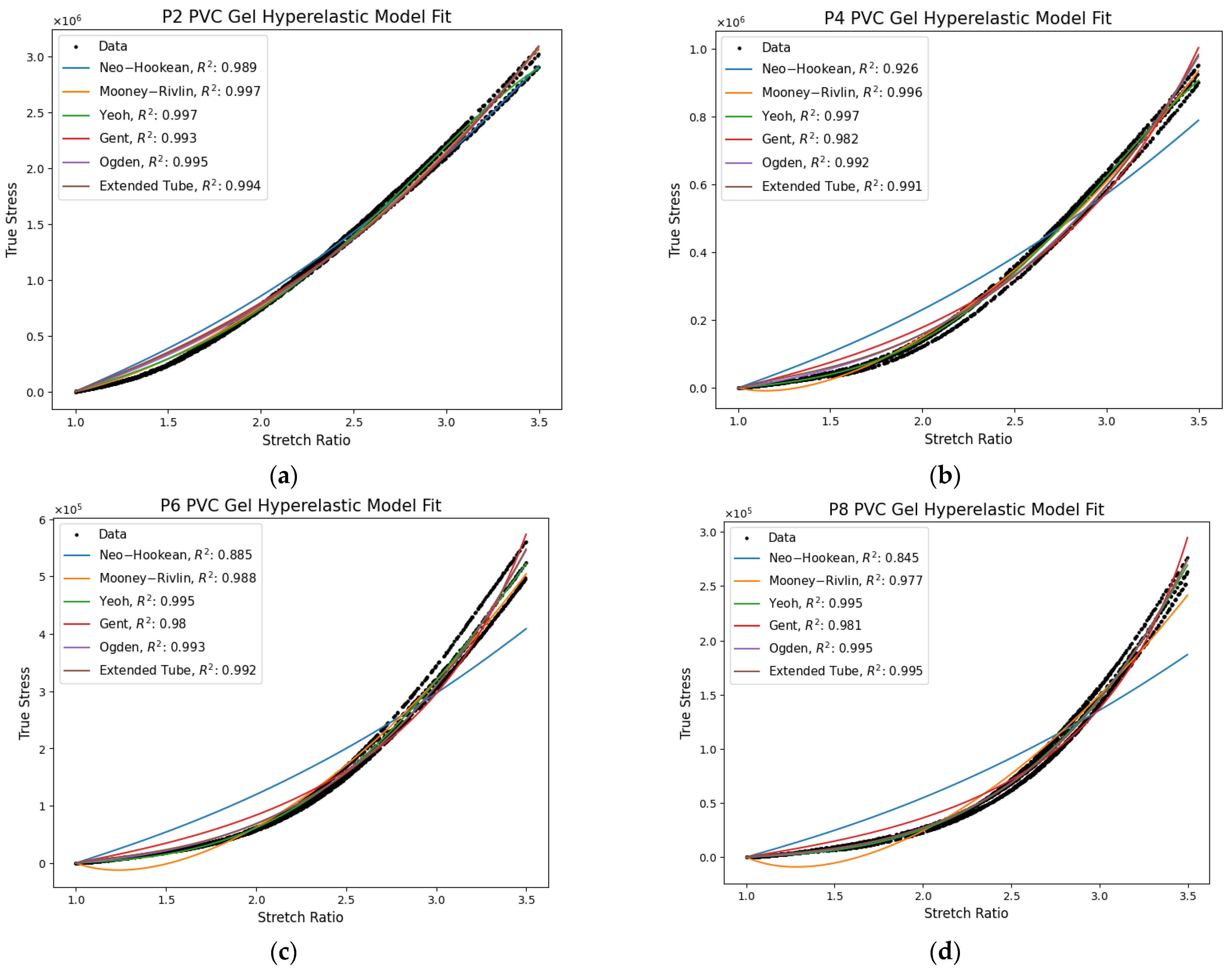
| Plasticizer Ratio | Elastic Modulus (Pa) |
|---|---|
| P2 | 288,751 |
| P4 | 56,058 |
| P6 | 24,707 |
| P8 | 11,047 |
| Plasticizer Ratio | Poisson’s Ratio |
|---|---|
| P2 | 0.42 |
| P4 | 0.43 |
| P6 | 0.37 |
| P8 | 0.35 |
| Plasticizer Ratio | Neo–Hookean | Mooney– Rivlin | Yeoh | Gent | Ogden | Extended Tube |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P2 | 8.4 | 4.53 | 4.15 | 6.63 | 5.73 | 6.32 |
| P4 | 24.71 | 6.01 | 4.9 | 12.24 | 7.97 | 8.58 |
| P6 | 31.48 | 10.13 | 6.85 | 13.18 | 8.03 | 8.21 |
| P8 | 37.58 | 14.35 | 6.63 | 13.3 | 6.88 | 6.9 |
| Plasticizer Ratio | Coefficient of Determination | |
|---|---|---|
| P2 | 0.9972 | [85,622, 5800, −272] |
| P4 | 0.9971 | [9061, 3175, −116] |
| P6 | 0.9946 | [3106, 1545, −40] |
| P8 | 0.9952 | [1365, 593, −5.99] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Faccinto, J.A.; Lee, J.; Kim, K.J. Tensile Modeling PVC Gels for Electrohydraulic Actuators. Polymers 2025, 17, 2641. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17192641
Faccinto JA, Lee J, Kim KJ. Tensile Modeling PVC Gels for Electrohydraulic Actuators. Polymers. 2025; 17(19):2641. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17192641
Chicago/Turabian StyleFaccinto, John Albert, Jongcheol Lee, and Kwang J. Kim. 2025. "Tensile Modeling PVC Gels for Electrohydraulic Actuators" Polymers 17, no. 19: 2641. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17192641
APA StyleFaccinto, J. A., Lee, J., & Kim, K. J. (2025). Tensile Modeling PVC Gels for Electrohydraulic Actuators. Polymers, 17(19), 2641. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17192641







