Room Temperature Synthesis of a Novel Quinolinoxazine, Polymerization and Flammability Studies
Abstract
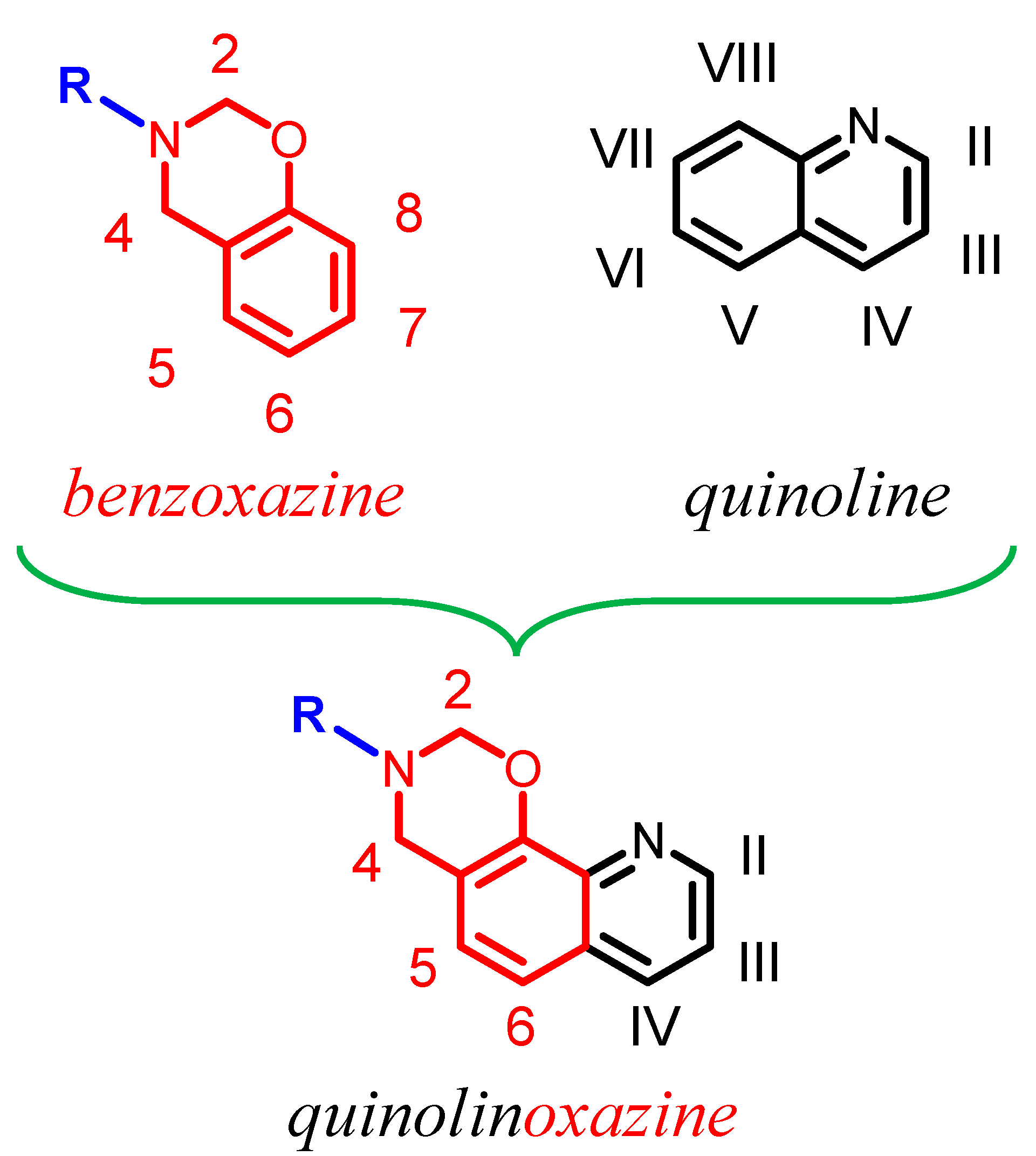
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of 3-(Furan-2-ylmethyl)-3,4-dihydro-2H-[1,3]oxazino[5,6-h]quinoline (Hereinafter Referred to as 8HQ-fa)
2.3. Characterization of 8HQ-fa
2.4. Preparation of Polybenzoxazine
2.5. Instrumentation
3. Results and Discussion
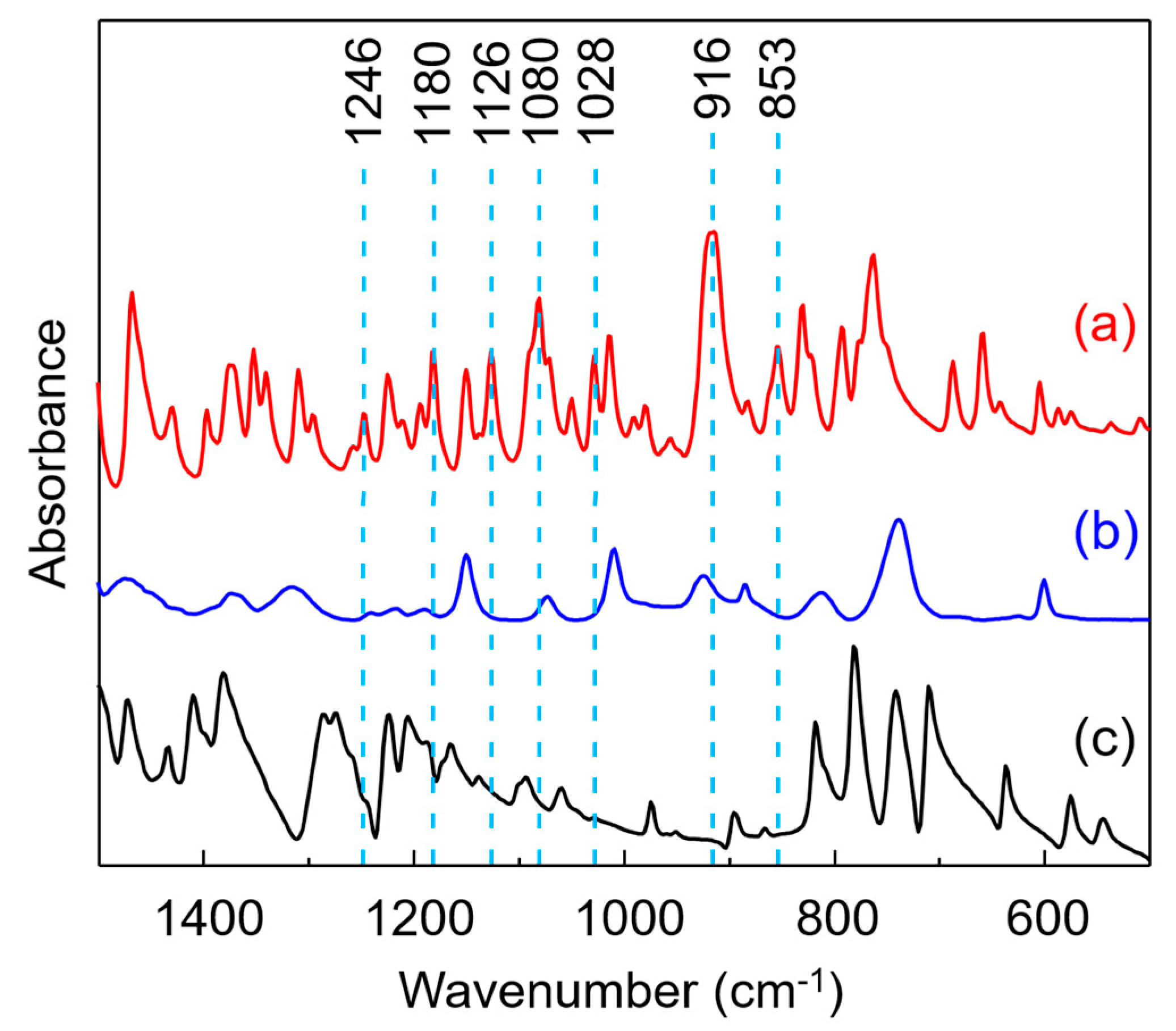
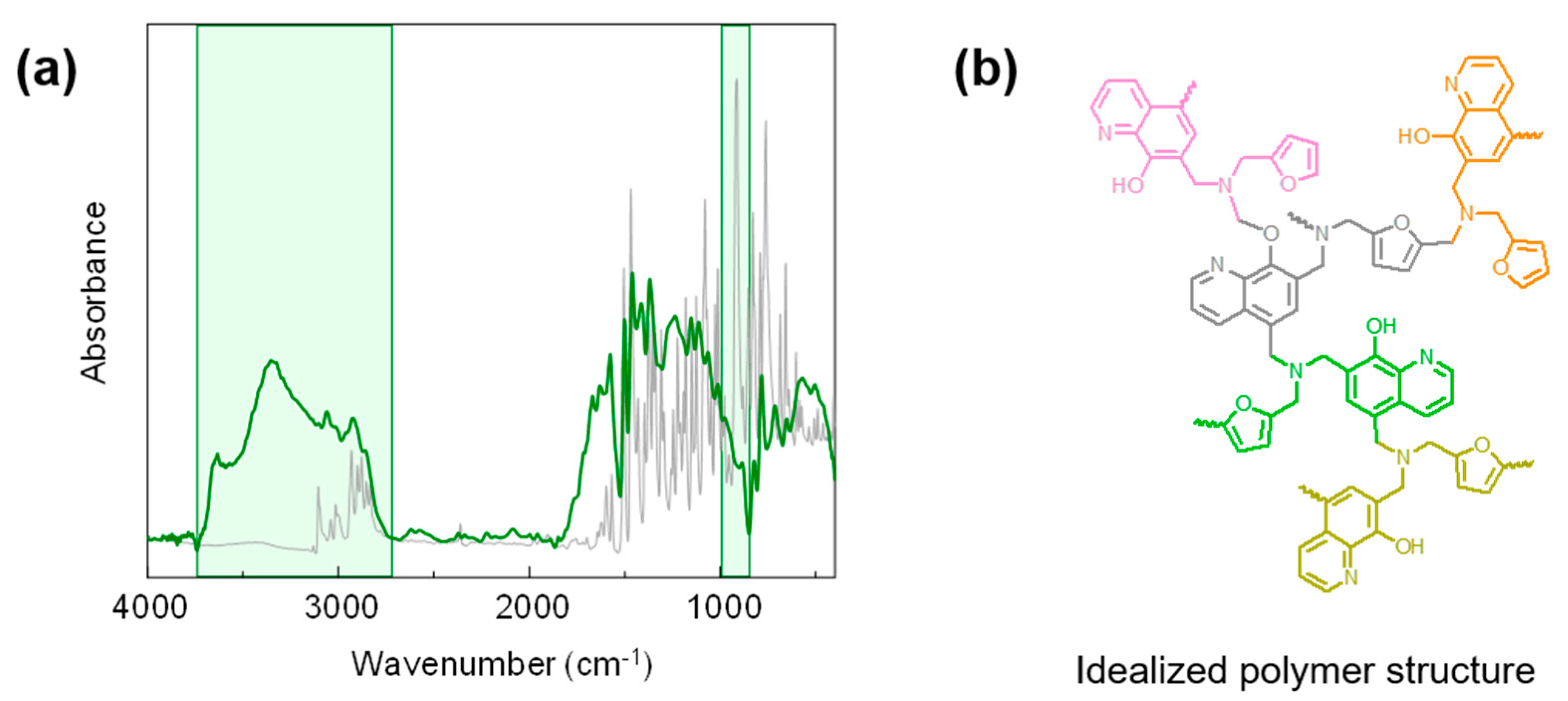
3.1. FT-IR Characterization of 8HQ-fa
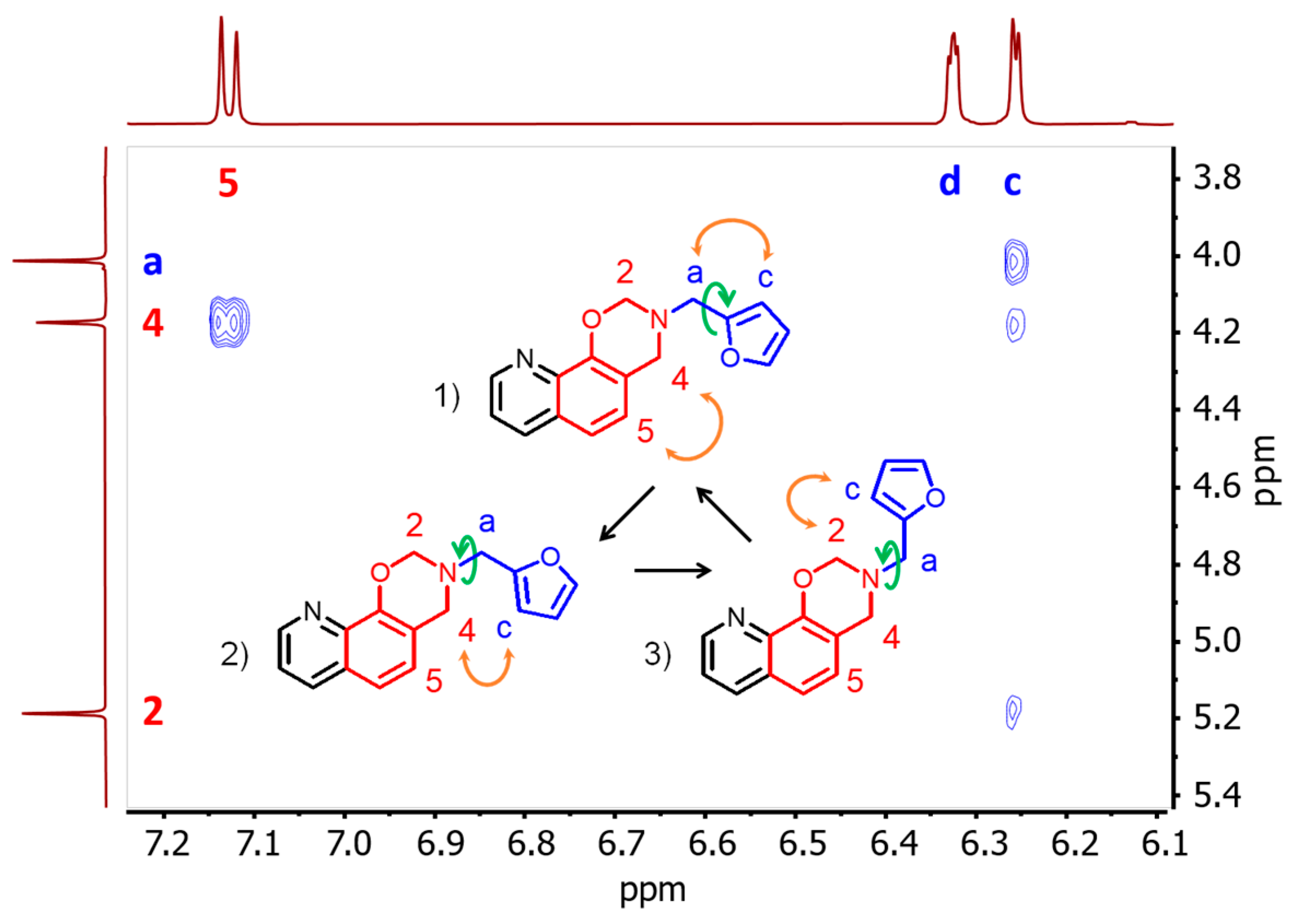
3.2. NMR Characterization of 8HQ-fa
3.3. Thermal Behavior of Quinolinoxazine Monomer 8HQ-fa
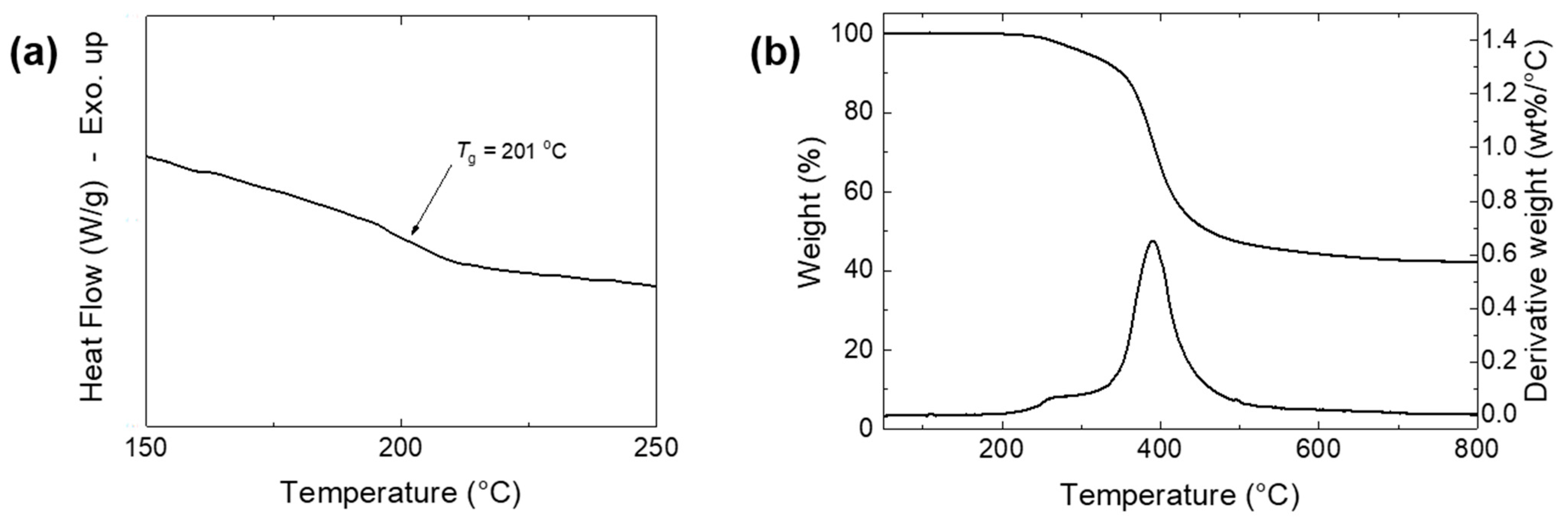
3.4. Thermal Behavior of Poly(8HQ-fa)
3.4.1. DSC and TGA Analyses
3.4.2. Flame Retardancy Based on Limiting Oxygen Index
- LOI values < 21 are flammable since they easily burn in air;
- LOI values between 21 and 28 slowly burn;
- LOI values > 28 are self-extinguishing since they cease burning once removed from the ignition source.
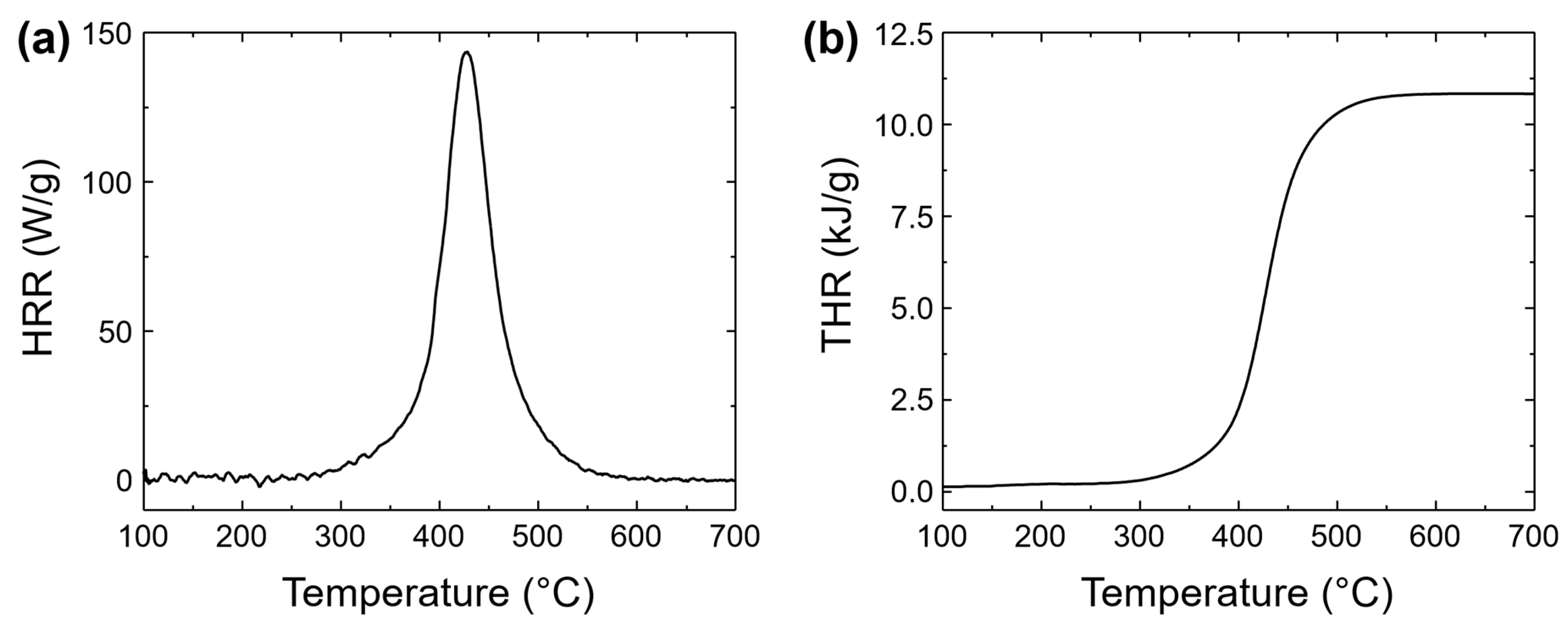
3.4.3. Microscale Combustion Calorimetry
- HRC values > 300 J/gK are flammable;
- HRC values < 300 J/gK are considered self-extinguishing;
- HRC values < 100 J/gK are considered nonignitable.
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Han, L.; Salum, M.L.; Zhang, K.; Froimowicz, P.; Ishida, H. Intrinsic self-initiating thermal ring-opening polymerization of 1,3-benzoxazines without the influence of impurities using very high purity crystals. J. Polym. Sci. Part A 2017, 55, 3434–3445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, H.; Froimowicz, P. Advanced and Emerging Polybenzoxazine Science and Technology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; 1097p. [Google Scholar]
- Appavoo, D.; Amarnath, N.; Lochab, B. Cardanol and eugenol sourced sustainable non-halogen flame retardants for enhanced stability of renewable polybenzoxazines. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirukumaran, P.; Sathiyamoorthi, R.; Shakila Parveen, A.; Sarojadevi, M. New benzoxazines from renewable resources for green composite applications. Polym. Compos. 2016, 37, 573–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaina, C.; Ursache, O.; Gaina, V.; Musteata, V.E. High performance thermosets based on multifunctional intermediates containing allyl, maleimide and benzoxazine groups. J. Polym. Res. 2013, 20, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froimowicz, P.; Arza, C.R.; Han, L.; Ishida, H. Smart, sustainable, and ecofriendly chemical design of fully bio-based thermally stable thermosets based on benzoxazine chemistry. ChemSusChem 2016, 9, 1921–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.Z.; Yan, Z.; Yang, Z.; Qian, B.; Liu, Z.; Lv, R.; Fei, Z.; Sha, X.L. Acetal-derived biomass benzoxazine resins: Excellent heat resistance, mechanical properties and flame retardant properties. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 513, 162617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulyuz, S.; Kiskan, B. Combination of polyethylenimine and vanillin-based benzoxazine as a straightforward self-healable system with excellent film-forming ability. Macromolecules 2024, 57, 2078–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, A.; Arumugam, H.; Luengrojanakul, P.; Boonnao, N.; Muthukaruppan, A.; Ahn, C.H.; Rimdusit, S. Development of new bio-based shape memory hybrid polybenzoxazines through green strategy. Eur. Polym. J. 2025, 231, 113926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Chen, B.; Zhang, K. Biobased bisbenzoxazine resins derived from natural renewable monophenols and diamine: Synthesis and property investigations. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 14783–14793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolter, N.; Carrillo Beber, V.; Haubold, T.; Sandinge, A.; Blomqvist, P.; Goethals, F.; Van Hove, M.; Jubete, E.; Mayer, B.; Koschek, K. Effects of flame-retardant additives on the manufacturing, mechanical, and fire properties of basalt fiber-reinforced polybenzoxazine. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2021, 61, 551–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haubold, T.S.; Wolter, N.; Sandinge, A.; Blomqvist, P.; Mayer, B.; Koschek, K. How phosphorous flame retardant additives affect benzoxazine-based monomer and polymer properties. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2023, 308, 2300132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.Q.; Wang, X.; Qin, H.R.; Lan, X.Y.; Ou, B.X.; Hu, Y.; Song, L. A bio-based polybenzoxazine derived from diphenolic acid with intrinsic flame retardancy, high glass transition temperature and dielectric properties. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2025, 46, 2400666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zúñiga, C.; Larrechi, M.S.; Lligadas, G.; Ronda, J.C.; Galià, M.; Cádiz, V. Polybenzoxazines from renewable diphenolic acid. J. Polym. Sci. Part A 2011, 49, 1219–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jehl, C.; Adjaoud, A.; Meyer, A.; Boulic, V.; Hesse, C.; Puchot, L.; Gonzalez-Gutierrez, J.; Shaplov, A.S.; Schmidt, D.F.; Verge, P. A recyclable, reshapable and UV-curable polybenzoxazine vitrimer enabling closed-loop 3D printing applications. J. Mater. Chem. A 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haubold, T.S.; Puchot, L.; Adjaoud, A.; Verge, P.; Koschek, K. Bio-based bisbenzoxazines with flame retardant linker. Polymers 2021, 13, 4330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chutayothin, P.; Ishida, H. 31P NMR spectroscopy in benzoxazine model compounds and benzoxazine chemistry—Main chain and end group studies. Eur. Polym. J. 2009, 45, 1493–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Z.; Li, Z.; Yue, Z. Thermally activated polymerization behavior of bisphenol-S/methylamine- based benzoxazine. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 124, 813–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaraj, K.; Spontón, M.E.; Arumugam, H.; Kannaiyan, S.K.; Ayyavu, C.; Casarino, A.F.; Estenoz, D.A.; Al-Lohedan, H.; Kumar, M.; Balu, R.; et al. Synthesis of new quinoline derivatives based on mono-functional polybenzoxazines for oil-water separation, anti-corrosion and antibacterial applications. Compos. Interfaces 2024, 31, 665–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adjaoud, A.; Puchot, L.; Federico, C.E.; Das, R.; Verge, P. Lignin-based benzoxazines: A tunable key-precursor for the design of hydrophobic coatings, fire resistant materials and catalyst-free vitrimers. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 453, 139895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Lu, X.; Xin, Z. Biobased polybenzoxazine vitrimer with imine bonds: Shape memory, reprocessing, and degradation. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 7739–7747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durukan, C.; Kiskan, B.; Yagci, Y. One-pot synthesis of amide-functional main-chain polybenzoxazine precursors. Polymers 2019, 11, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiou, K.; Froimowicz, P.; Landfester, K.; Taden, A.; Ishida, H. Triggered precision benzoxazine film formation by thermally induced destabilization of benzoxazine nanodroplets using a LCST-bearing surfactant. Macromolecules 2014, 47, 3297–3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, S.; Nayak, V.; Mahapatra, S.N.; Lochab, B. Benzoxazine-sulfur-chitosan based freestanding beads: Synthesis, characterization, stability, and removal of mercury and oil. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 320, 124063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhwaige, A.A.; Ishida, H.; Qutubuddin, S. Poly(benzoxazine-f-chitosan) films: The role of aldehyde neighboring groups on chemical interaction of benzoxazine precursors with chitosan. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 209, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Y.; Ishida, H. Natural-sourced benzoxazine resins, homopolymers, blends and composites: A review of their synthesis, manufacturing and applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2019, 99, 101168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lochab, B.; Monisha, M.; Amarnath, N.; Sharma, P.; Mukherjee, S.; Ishida, H. Review on the accelerated and low-temperature polymerization of benzoxazine resins: Addition polymerizable sustainable polymers. Polymers 2021, 13, 1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, W.J.; Griebel, J.J.; Kim, E.T.; Yoon, H.; Simmonds, A.G.; Ji, H.J.; Dirlam, P.T.; Glass, R.S.; Wie, J.J.; Nguyen, N.A.; et al. The use of elemental sulfur as an alternative feedstock for polymeric materials. Nat. Chem. 2013, 5, 518–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetoshkina, I.S.; Solodov, V.S.; Subbotin, S.P.; Vasileva, E.V.; Cherkasova, T.G.; Nevedrov, A.V. Valuable products from coal tar. Coke Chem. 2019, 62, 66–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Zhang, S.; Yao, Q.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, W.; Sun, M. A review of catalytic conversion of coal tar value-added chemicals at the molecular level based on first principles. Energy Convers. Manag. 2025, 326, 119466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, Q.; Di, J.; He, Y.; Ma, C. Improved synthesis of furfurylamine from a high titer of biomass-derived furfural by a thermostable triple mutant ω-transaminase in a three-component deep eutectic solvent ChCl/lactic acid/malonic acid system. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 7515–7525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, M.A.; Mohajeri, A.; Mirkouei, A. Comparison of pyrolysis and hydrolysis processes for furfural production from sugar beet pulp: A case study in southern Idaho, USA. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 311, 127695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Yao, J.; Kong, F.; Ren, J.; Wang, S. Efficient conversion of xylose and corncob to furfural using a novel carbon-based solid acid derived from black liquor lignin-tin complexes. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 114516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutlu, H.; Barner, L. Getting the terms right: Green, sustainable, or circular chemistry? Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2022, 223, 2200111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastas, P.T.; Warner, J.C. Green Chemistry: Theory and Practice; Oxford University Press: Oxfordshire, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Salum, M.L.; Iguchi, D.; Arza, C.R.; Han, L.; Ishida, H.; Froimowicz, P. Making benzoxazines greener: Design, synthesis, and polymerization of a biobased benzoxazine fulfilling two principles of green chemistry. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 13096–13106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arza, C.R.; Froimowicz, P.; Han, L.; Graf, R.; Ishida, H. Design, synthesis, characterization, and polymerization of fused-ring naphthoxazine resins. Macromolecules 2017, 50, 9249–9256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Hariharan, A.; Alagar, M.; Dinakaran, K. Low-k and UV shielding polybenzoxazine nanocomposites synthesised from quinoline amine and bio-silica. Compos. Interfaces 2021, 28, 905–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaraj, K.; Spontón, M.E.; Estenoz, D.A.; Forchetti Casarino, A.; Veerasamy, U.S.; Kumar, M.; Al-Mohaimeed, A.M.; Al-Onazi, W.A.; Kannaiyan, D. Development of quinoline-based heteroatom polybenzoxazines reinforced graphitic carbon nitride (GCN) carbonisation composites for emerging supercapacitor applications. Soft Matter 2024, 20, 1210–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.B.; Ishida, H. Synthesis and characterization of polyfunctional naphthoxazines and related polymers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1996, 61, 1595–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Yang, R.; Sheng, W.; Zhang, K. A new polycyclic naphthoxazine resin: Facile synthesis, characterization, polymerization, and thermal properties of its corresponding thermosets. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2024, 45, 2400399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kissinger, H.E. Reaction kinetics in differential thermal analysis. Anal. Chem. 1957, 29, 1702–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozawa, T. A new method of analyzing thermogravimetric data. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2006, 38, 1881–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozawa, T. Kinetics of non-isothermal crystallization. Polymer 1971, 12, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, H.; Agag, T. Handbook of Benzoxazine Resins; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.; Liu, Y.; Han, M.; Froimowicz, P. Smart and sustainable design of latent catalyst-containing benzoxazine-bio-resins and application studies. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 1209–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Froimowicz, P.; Arza, C.R.; Ohashi, S.; Xin, Z.; Ishida, H. Latent catalyst-containing naphthoxazine: Synthesis and effects on ring-opening polymerization. Macromolecules 2016, 49, 7129–7140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schinazi, G.; Price, E.J.; Schiraldi, D.A. Fire testing methods of bio-based flame-retardant polymeric materials. In Bio-based Flame-Retardant Technology for Polymeric Materials; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 61–95. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, M.I. A dynamical systems model of the limiting oxygen index test: II. Retardancy due to char formation and addition of inert fillers. Combust. Theor. Model. 2001, 5, 59–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
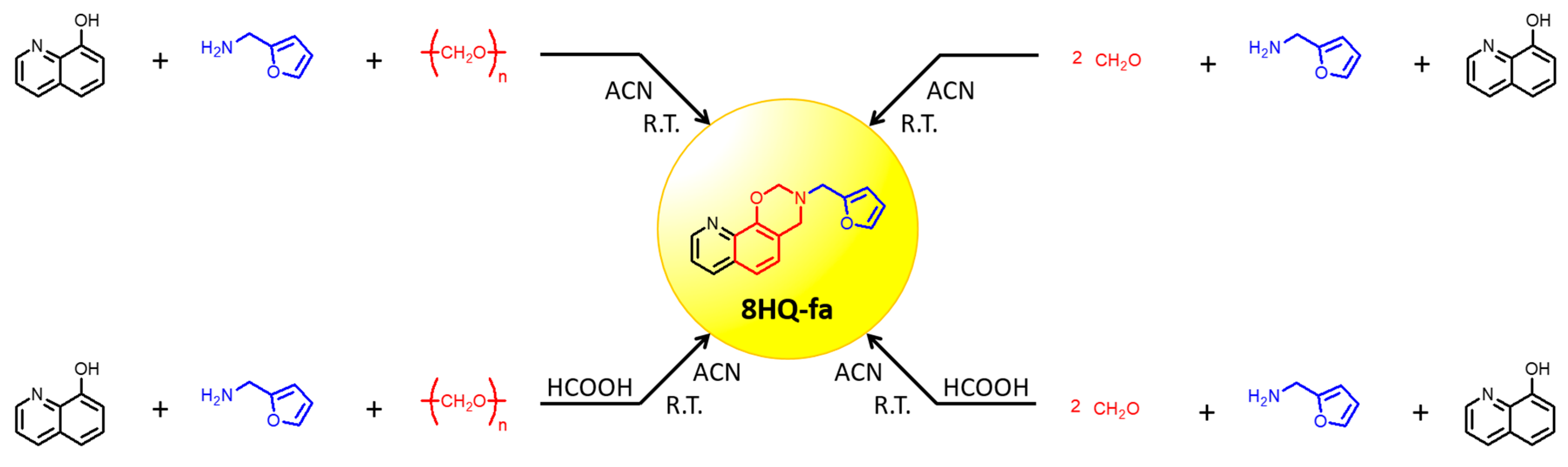



| Reaction | Quinoline | Amine | Formaldehyde Source | Acid | Reaction Yield (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 8HQ | fa | paraformaldehyde | - | 14 |
| 2 | 8HQ | fa | paraformaldehyde | HCOOH | 6 |
| 3 | 8HQ | fa | formalin | - | 80 |
| 4 | 8HQ | fa | formalin | HCOOH | 87 |
| Assigned FT-IR Signal Observed in Spectrum a (cm−1) | Assignment |
|---|---|
| 1246 | antisymmetric stretching of =C-O-C- |
| 1180 | antisymmetric stretching of C-N-C |
| 1126 | benzene ring mode, Wilson number 15 |
| 1080 | antisymmetric stretching of C-O-C and C-N-C |
| 1028 | symmetric stretching of =C-O-C- |
| 916 | oxazine ring mode |
| 853 | symmetric stretching of C-O-C |
| Thermoset | Tg (°C) a | Td5 (°C) b | Td10 (°C) c | Char Yield (%) d | LOI e | HRC (J g−1 K−1) f | THR (kJ g−1) g |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Poly(8HQ-fa) | 201 | 307 | 351 | 42 | 34.3 | 143 | 10.8 |
| Poly(BA-a) | 162 | 302 | 324 | 32 | 30.3 | 328 | 35.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Salum, M.L.; Iguchi, D.; Arza, C.R.; Pellegri, N.; Ishida, H.; Froimowicz, P. Room Temperature Synthesis of a Novel Quinolinoxazine, Polymerization and Flammability Studies. Polymers 2025, 17, 2546. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17182546
Salum ML, Iguchi D, Arza CR, Pellegri N, Ishida H, Froimowicz P. Room Temperature Synthesis of a Novel Quinolinoxazine, Polymerization and Flammability Studies. Polymers. 2025; 17(18):2546. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17182546
Chicago/Turabian StyleSalum, Maria Laura, Daniela Iguchi, Carlos Rodriguez Arza, Nora Pellegri, Hatsuo Ishida, and Pablo Froimowicz. 2025. "Room Temperature Synthesis of a Novel Quinolinoxazine, Polymerization and Flammability Studies" Polymers 17, no. 18: 2546. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17182546
APA StyleSalum, M. L., Iguchi, D., Arza, C. R., Pellegri, N., Ishida, H., & Froimowicz, P. (2025). Room Temperature Synthesis of a Novel Quinolinoxazine, Polymerization and Flammability Studies. Polymers, 17(18), 2546. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17182546








