Green Synthesis of Zwitterionic–Cyclodextrin Hybrid Polymer for Efficient Extraction of Polypeptides: Combination of Instrumental Analysis and DFT Calculation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Regents and Materials
2.2. Instrumentation
2.3. Preparation of the Poly(GMA-HP-γ-CD-co-MPC) Column
2.4. IT-SPME Procedure
2.5. HPLC-UV Condition
2.6. DFT Calculation
2.7. Sample Pretreatment
3. Results
3.1. Synthesis of GMA-HP-γ-CD-co-MPC Polymers
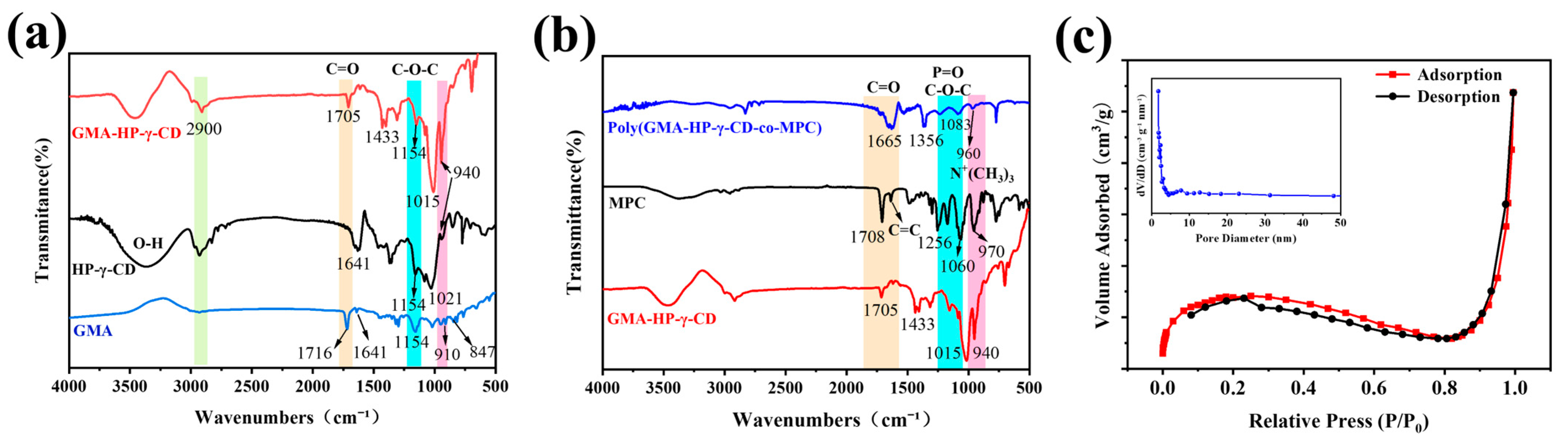
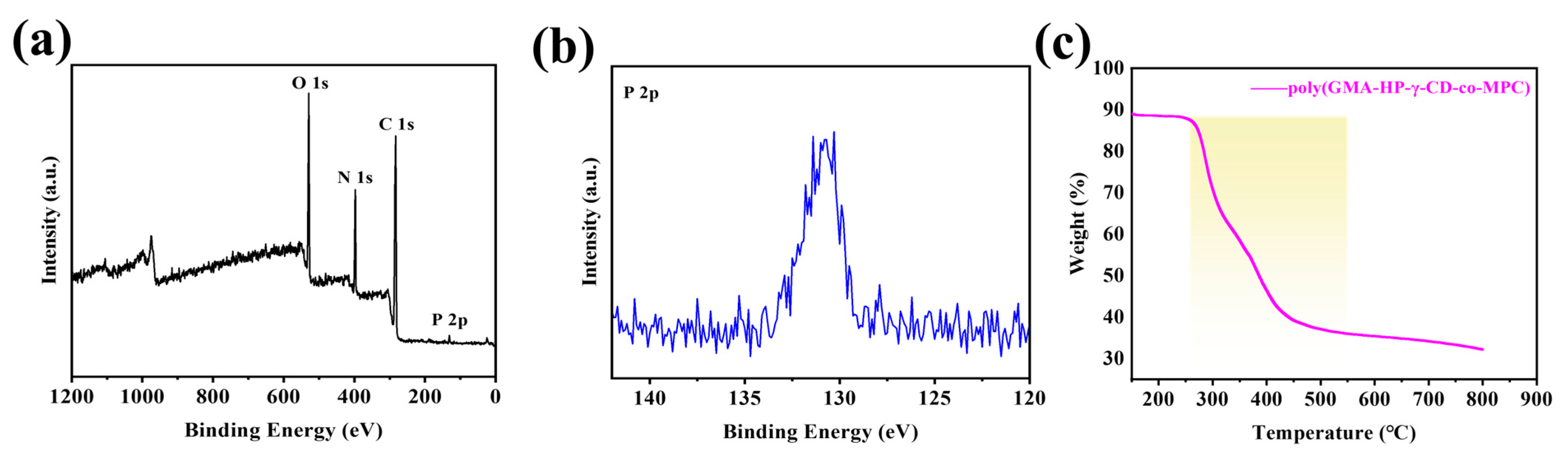
3.2. Characterization of GMA-HP-γ-CD-co-MPC Hybrid Monoliths
3.3. Optimization the IT-SPME Conditions
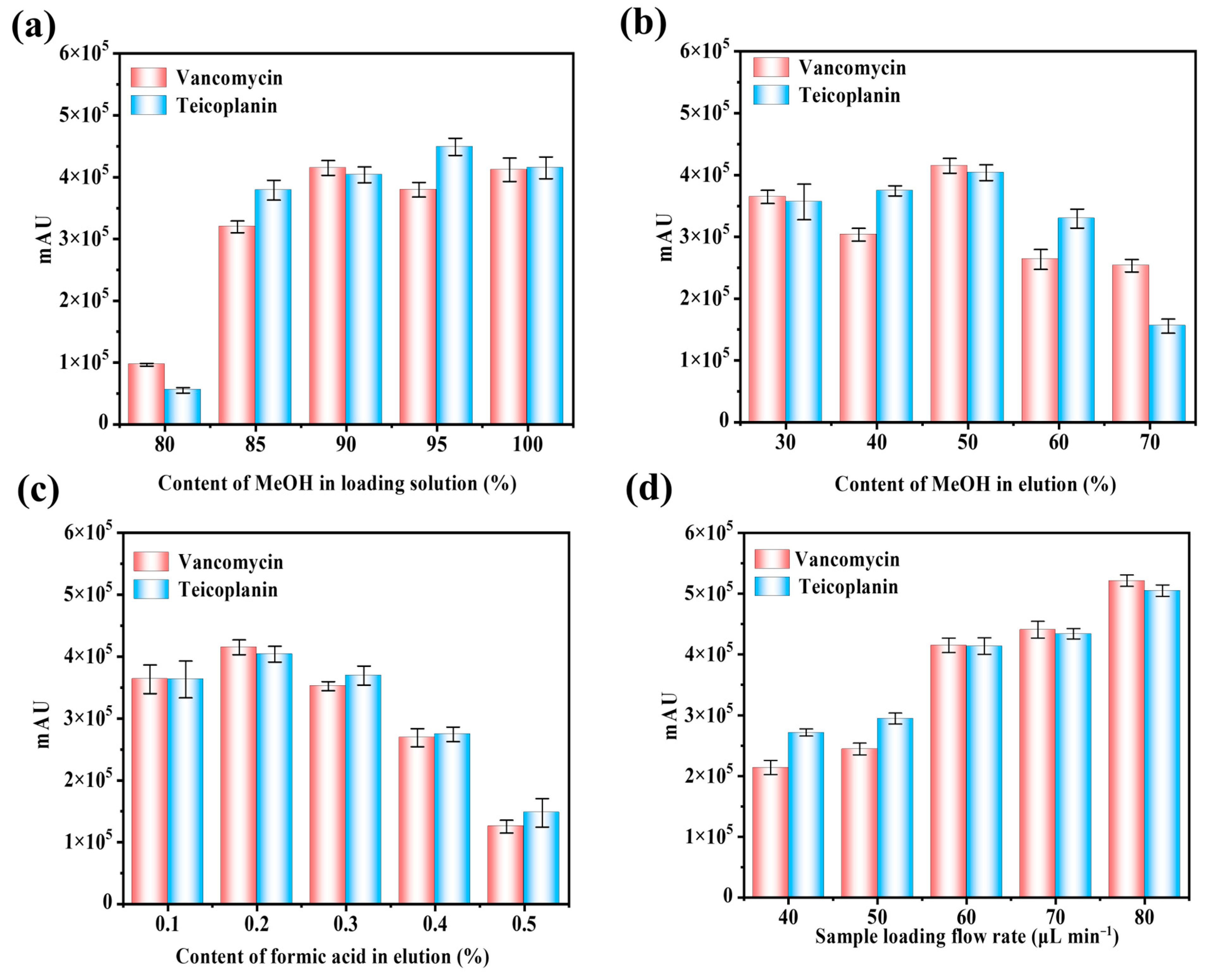
3.3.1. Influence of Sample Loading Solution
3.3.2. Influence of Composition and pH on Elution
3.3.3. Influence of Sample Loading Flow Rate
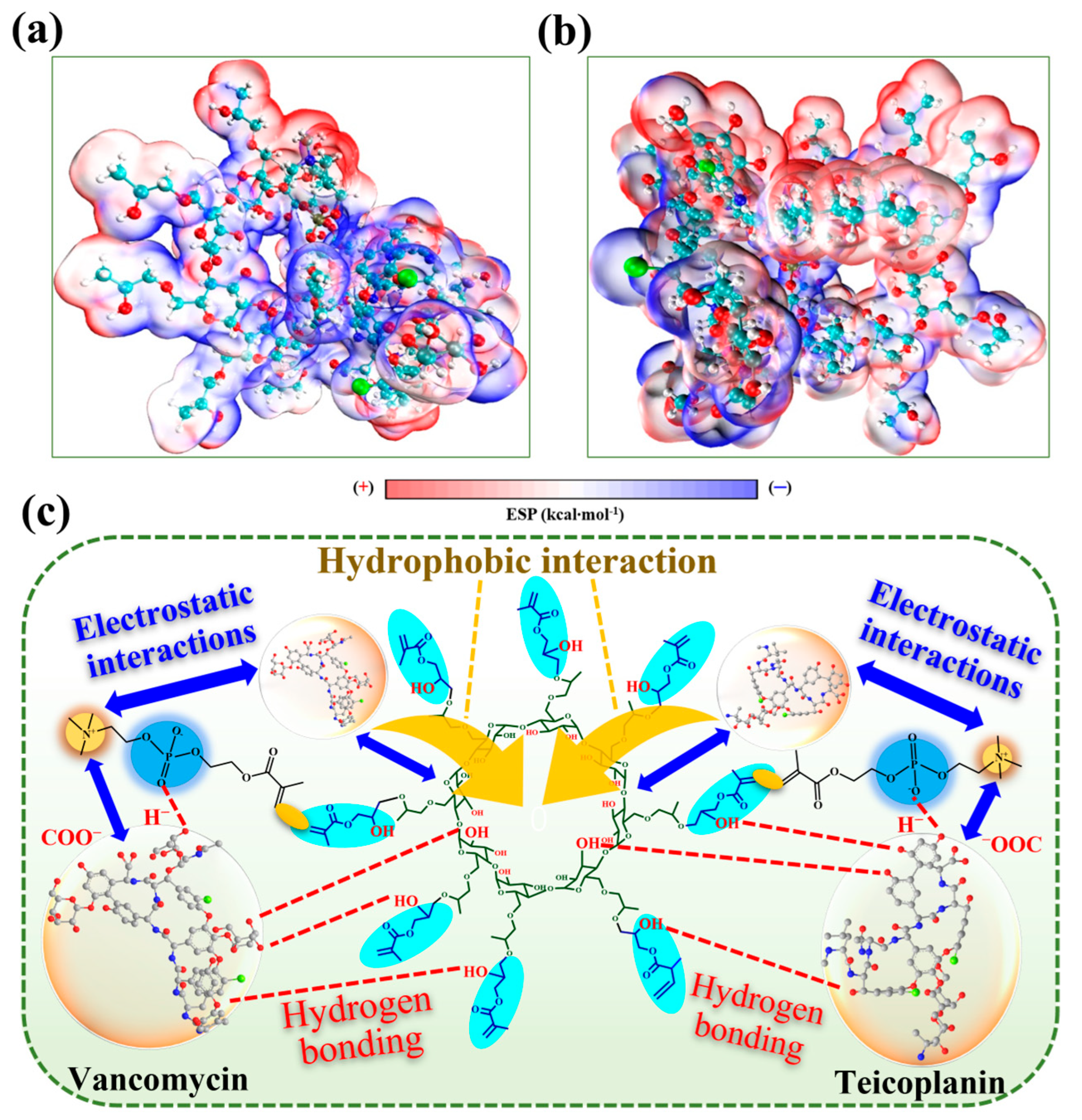
3.4. Potential Adsorption Mechanism by DFT Calculation
3.5. IT-SPME-HPLC-UV Method Detection
3.5.1. Method Validation
3.5.2. Real Sample Analysis
3.6. Comparison with Other Reported Methods
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Song, X.; Wang, J.; Wu, Y.; Huang, X. Strategy for the co-extraction and simultaneous quantification of organic pollutants and heavy metals by the on-line hyphenation of magnetic field-assisted in-tube solid phase microextraction and chromatographic technique. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 487, 137200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Su, B.; Zhang, K.; Lin, Y.; Wang, B.; Sun, M. Sensitive detection of phthalates in Chinese Baijiu by online in-tube SPME-HPLC-DAD based on carbonized COF-coated carbon fibers. Food Chem. 2025, 489, 144986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhendal, A.; Rashad, M.; Husain, A. Siloxane-Free Silicon-Based Copolymer for In-Tube Solid-Phase Microextraction. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2025, 7, 3968–3980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gałuszka, A.; Migaszewski, A.; Namieśnik, J. The 12 principles of green analytical chemistry and the SIGNIFICANCE mnemonic of green analytical practices. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2013, 50, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, W.A.; Fallah, A.H.; Moltajihagh, S.; Hamdi, F.; Alipour, F.; Mollahosseini, A.; Boczkaj, G. Automation and high throughput sample analysis with various platforms in microextraction techniques: A need for ecofriendly, green, and cost-effective sample preparation approaches—A review. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2025, 189, 118247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carasek, E.; Santos, A.V.; Turazzi, F.C.; Morés, L.; Effting, L.; Barra, G.M.O. Recent Trends in the Development of Green Analytical Sample Preparation Methods Using Advanced Materials. J. Sep. Sci. 2025, 48, e7017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torabi, E.; Abdar, A.; Lotfian, N.; Bazargan, M.; Simms, C.; Moussawi, M.A.; Amiri, A.; Mirzaei, M.; Parac-Vogt, T.N. Advanced Materials in Sorbent-Based Analytical Sample Preparation. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2024, 506, 215680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas Medina, D.A.; Cardoso, A.T.; Maciel, E.V.S.; Lanças, F.M. Current Materials for Miniaturized Sample Preparation: Recent Advances and Future Trends. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 165, 117120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, H.; Li, G.; Zhang, Z. Advanced Materials on Sample Preparation for Safety Analysis of Aquatic Products. J. Sep. Sci. 2021, 44, 1174–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghadasi, M.; Abbasi, M.; Mousavi, M.; Apoorvari, M.A.; Khoshghamat, A.; Hosseini, A.; Jalaeian, S.; Sheida, M.; Mobaraki, M.; Torabi, E.; et al. Porous Materials in Analytical Sample Preparation: Current Status and Future Perspectives. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2025, 186, 118193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felli, N.; Filardi, D.; Sergi, R.; Migneco, L.M.; De Cesaris, M.G.; Antonelli, L.; Francolini, I.; Gentili, A. Exploring the extraction capabilities of natural cyclodextrin-nanosponges: The improvement moving from α- to γ-cyclodextrin-based polymers. Adv. Sample Prep. 2025, 14, 100169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przybyla, M.A.; Yilmaz, G.; Becer, C.R. Natural cyclodextrins and their derivatives for polymer synthesis. Polym. Chem. 2020, 11, 7582–7602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cid-Samamed, A.; Rakmai, J.; Mejuto, J.C.; Simal-Gandara, J.; Astray, G. Cyclodextrins inclusion complex: Preparation methods, analytical techniques and food industry applications. Food Chem. 2022, 384, 132467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Shi, Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, Z.; Cao, N.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, K. Recent progress on the porous cyclodextrin polymers in water treatment. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2025, 541, 216826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Jiang, L.; Jia, Q. Advances in cyclodextrin polymers adsorbents for separation and enrichment: Classification, mechanism and applications. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2022, 33, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciel, E.V.S.; Pereira dos Santos, N.G.; Medina, D.A.V.; Lanças, F.M. Cyclodextrins-based sorbents for sustainable sample preparation focusing on food analysis. Green Anal. Chem. 2023, 7, 100077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lu, P.; Cheng, J.; Zhu, X.; Guo, W.; Liu, L.; Wang, Q.; He, C.; Liu, S. Novel microporous β-cyclodextrin polymer as sorbent for solid-phase extraction of bisphenols in water samples and orange juice. Talanta 2018, 187, 207–215. [Google Scholar]
- Alsbaiee, A.; Smith, B.J.; Xiao, L.; Ling, Y.; Helbling, D.E.; Dichtel, W.R. Rapid removal of organic micropollutants from water by a porous β-cyclodextrin polymer. Nature 2016, 529, 190–194. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.; Huang, Q.; Ji, H.; Tang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chai, K. Efficient adsorption of bisphenol A from water by a hierarchically porous hyper-crosslinked polymer containing β-cyclodextrin polyurethane. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 319, 124076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Zhou, G.; Chu, L.; Liu, Y.; Liu, C.; Luo, S.; Wei, Y. Efficient removal of heavy metal ions with an EDTA functionalized chitosan/polyacrylamide double network hydrogel. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 843–851. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Lin, Z.-W.; Klemes, M.J.; Ateia, M.; Trang, B.; Wang, J.; Ching, C.; Helbling, D.E.; Dichtel, W.R. A tunable porous β-cyclodextrin polymer platform to understand and improve anionic PFAS removal. ACS Cent. Sci. 2022, 8, 663–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.L.; Xu, M.Y.; Xie, Z.W.; Hai, W.; Xie, X.L.; He, F.A. Selective adsorption of anionic dyes from aqueous solution by a novel β-cyclodextrin-based polymer. J. Mol. Struct. 2020, 1203, 127373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.; Lv, N.; Yang, S.; Yuan, Q.; Wu, Y.; Guo, K.; Hu, C.; Dai, Y. Polyethyleneimine-functionalized β-cyclodextrin porous polymers for enhanced elimination of U (VI) from wastewater. New J. Chem. 2023, 47, 20456–20465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Xu, G.; Tu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Hu, X.; Yang, P.; Wu, D.; Liang, Y.; Wei, D.; Li, A. Multifunctional porous β-cyclodextrin polymer for water purification. Water Res. 2022, 222, 118917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, H.L.; Deng, X.; Wang, J.; Fan, L.; Yang, Y.C.; Zhang, Z.Q. Ethanolamine-and amine-functionalized porous cyclodextrin polymers for efficient removal of anionic dyes from water. Eur. Polym. J. 2020, 133, 109762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, A.; Ching, C.; Easler, M.; Helbling, D.E.; Dichtel, W.R. Cyclodextrin polymers with nitrogen-containing tripodal crosslinkers for efficient PFAS adsorption. ACS Mater. Lett. 2020, 2, 1240–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Fang, J. Promoting the Molecular Enrichment Effects in Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Detection via Cross-Linked β-Cyclodextrin Adsorption Layer Integrated Plasmonic Nanostructures. Chem. Mater. 2024, 36, 8391–8399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malatji, N.; Mpupa, A.; Mizaikoff, B.; Nomngongo, P.N. Magnetic beta cyclodextrin molecularly imprinted polymer for selective extraction of perfluorooctanoic acid from water. iScience 2025, 28, 113205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Wang, X.; Gong, C.; Zhao, T.; Guo, T.; Wang, C.; Du, J.; Zhang, A.; Feng, Z. Highly flexible β-cyclodextrin polymer surface-functionalized polyurethane membrane captures organic pollutant phenolphthalein from aqueous media. React. Funct. Polym. 2025, 211, 106194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Benedicto, D.F.C.; Ferreira, G.M.D.; Thomasi, S.S. β-cyclodextrin-functionalized coffee husk biochar for surfactant adsorption. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2024, 701, 134921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foroutan, R.; Tutunchi, A.; Foroughi, M.; Ramavandi, B. Efficient fluoride removal from water and industrial wastewater using magnetic chitosan/β-cyclodextrin aerogel enhanced with biochar and MOF composites. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 363, 132128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masotti, E.; Poma, N.; Guazzelli, E.; Fiaschi, I.; Glisenti, A.; Vivaldi, F.; Bonini, A.; Di Francesco, F.; Tavanti, A.; Galli, G.; et al. Fluorinated vs. Zwitterionic-Polymer Grafted Surfaces for Adhesion Prevention of the Fungal Pathogen Candida albicans. Polymers 2020, 12, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiao, Y.-H.; Sengupta, A.; Ang, M.B.M.Y.; Chen, S.-T.; Haan, T.Y.; Almodovar, J.; Hung, W.-S.; Wickramasinghe, S.R. Application of Zwitterions in Forward Osmosis: A Short Review. Polymers 2021, 13, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Wang, J.; Mao, X.; Xie, L.; Liu, Q.; Zeng, H. Molecular interaction mechanism for humic acids fouling resistance on charged, zwitterion-like and zwitterionic surfaces. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2024, 666, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wen, C.; Yang, J.; Zhou, X.; Zhu, Y.; Zheng, J.; Cheng, G.; Bai, J.; Xu, T.; Ji, J.; et al. Zwitterionic Biomaterials. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 17073–17154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.; Jiang, Y.; Li, Y.; Duan, Y.; Guo, T.; Zhang, T.; Zhao, Z.; Dai, H.; Ji, X. Zwitterionic-based hybrid monoliths for capillary microextraction of polypeptides in dairy products. Food Chem. 2025, 476, 143461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Srivastava, A.; Mandal, M. Unravelling the Potential of Zwitterionic Polymers in Molecular Imprinting. Langmuir 2025, 41, 5687–5704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Zhao, X.; Jing, W.; Zhang, X.; Wang, K.; Yan, L. New zwitterionic HP-β-CD-PEI-MPC polymer used as a transdermal penetration enhancer. React. Funct. Polym. 2020, 154, 104677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.Y.; Lei, X.Y.; Deng, L.J.; Li, M.S.; Yao, S.C.; Wu, X.P. Ultrafast preparation of a polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane-based ionic liquid hybrid monolith via photoinitiated polymerization, and its application to capillary electrochromatography of aromatic compounds. Microchim. Acta 2018, 185, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kühne, T.D.; Iannuzzi, M.; Ben, M.D.; Rybkin, V.V.; Seewald, P.; Stein, F.; Laino, T.; Khaliullin, R.A.; Schütt, O.; Schiffmann, F.; et al. CP2K: An electronic structure and molecular dynamics software package-Quickstep: Efficient and accurate electronic structure calculations. J. Chem. Phys. 2020, 152, 194103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdew, J.P.; Burke, K.; Ernzerhof, M. Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 77, 3865–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimme, S.; Antony, J.; Ehrlich, S.; Krieg, H. A consistent and accurate ab initio parametrization of density functional dispersion correction (DFT-D) for the 94 elements H-Pu. J. Chem. Phys. 2010, 132, 154104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayatloo, M.R.; Salehpour, N.; Alavi, A.; Nojavan, S. Introduction of maltodextrin nanosponges as green extraction phases: Magnetic solid phase extraction of fluoroquinolones. Carbohyd. Polym. 2022, 297, 119992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.; Chen, L.; Shen, R.; Li, P.; Shi, N. Quantification of ultratrace levels of fluoroquinolones in wastewater by molecularly imprinted solid phase extraction and liquid chromatography triple quadrupole mass. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 19, 100919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefatle, M.C.; Matong, J.M.; Mpupa, A.; Munonde, T.S.; Waleng, N.J.; Madikizela, L.M.; Pakade, V.E.; Nomngongo, P.N. Preparation, characterization, and application of chitosan–kaolin-based nanocomposite in magnetic solid-phase extraction of tetracycline in aqueous samples. Chem. Pap. 2023, 77, 1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Jiang, L.; Liu, C.; Ruan, G.; Du, F. Polyvinylpyrrolidone/single-walled carbon nanotubes incorporated polyhipe monoliths followed by HPLC for determination of tetracycline antibiotics in water samples. J. Water Chem. Technol. 2021, 43, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


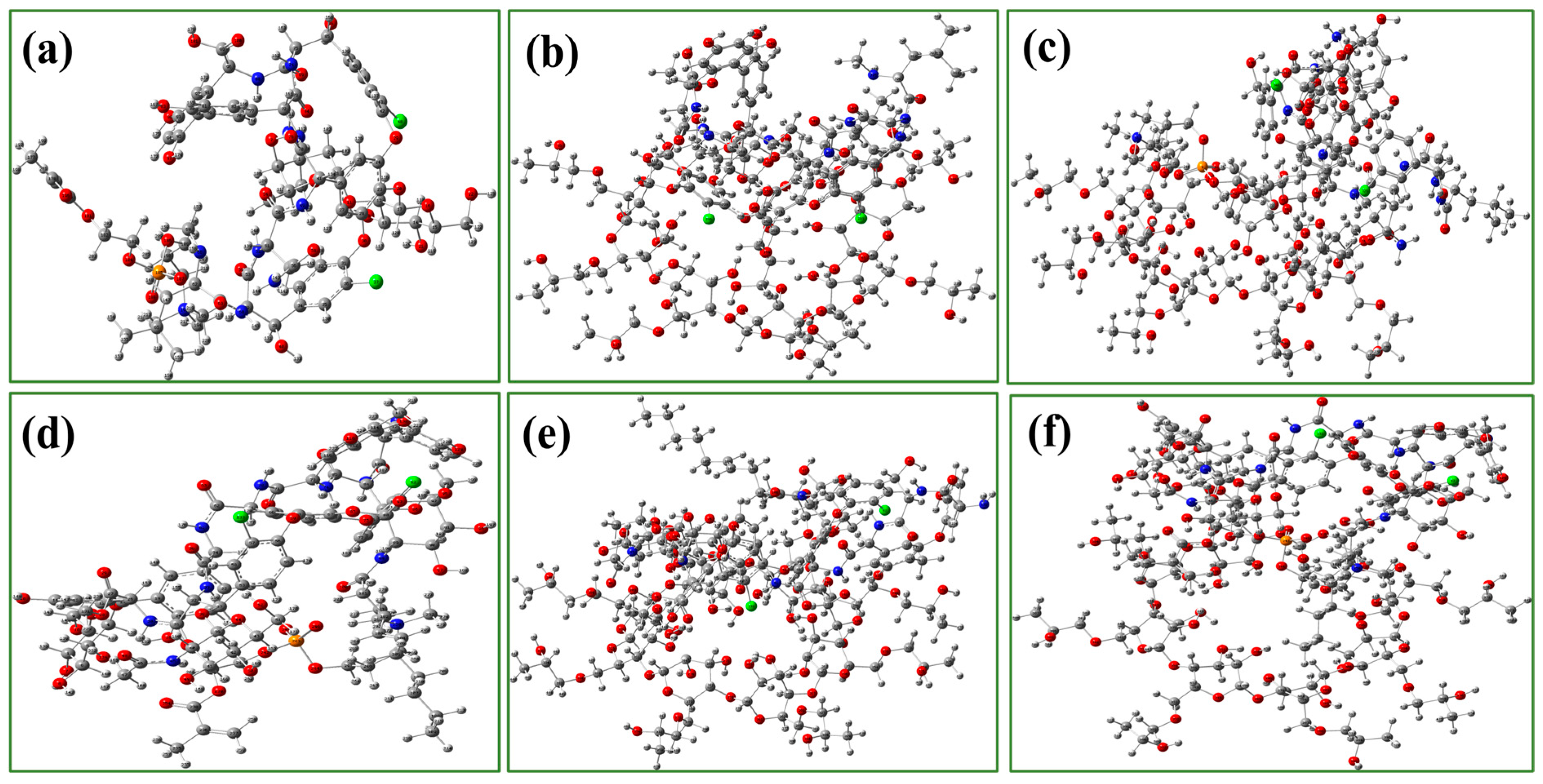

| Cluster | Hydrogen Bond Position * | Bond Length (Å) | Adsorption Energy ΔEads (kJ/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|
| MPC·vancomycin | P185-O187····H133 | 7.06 | −67.54 |
| P185-O187····H121 | 9.13 | ||
| P185-O187····H175 | 7.56 | ||
| P185-O187····H124 | 11.86 | ||
| MPC·teicoplanin | P243-O245····H232 | 8.38 | −80.08 |
| P243-O245····H152 | 6.04 | ||
| P243-O245····H142 | 9.73 | ||
| P243-O245····H141 | 10.66 | ||
| HP-γ-CD·vancomycin | O83-H189····O306 | 2.74 | −72.36 |
| O270-H373····O11 | 2.89 | ||
| O8-H136····Cl296 | 2.91 | ||
| O84-H190····O324 | 3.89 | ||
| HP-γ-CD·teicoplanin | O95-H196····O304 | 1.95 | −83.94 |
| O242-H31···O59 | 1.62 | ||
| O242-H361····Cl133 | 3.12 | ||
| O317-H423····O48 | 3.63 | ||
| HP-γ-CD-MPC·vancomycin | P9-O12····H197 | 3.90 | −151.48 |
| P9-O12····H198 | 2.32 | ||
| O95-H206····O20 | 3.61 | ||
| O116-H224····O20 | 3.86 | ||
| HP-γ-CD-MPC·teicoplanin | P243-O245····H431 | 3.23 | −158.24 |
| P243-O245····H151 | 2.62 | ||
| O10-H145····O380 | 3.01 | ||
| O25-H152····O254 | 3.77 |
| Analytes | Regression Equation | Linear Range (μg L−1) | LOD (μg L−1) | LOQ (μg L−1) | RSD% (n = 3) Run-To-Run |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Teicoplanin | Y = 318.14X − 15,005.7 | 60–500 | 15.0 | 50.0 | 5.9 |
| Vancomycin | Y = 275.91X − 17,043.06 | 80–800 | 20.0 | 66.0 | 8.2 |
| Polypeptides | Added (μg L−1) | Recovery (%) | RSD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vancomycin | 0 | ND | - |
| 70 | 87.5 | 4.8 | |
| 150 | 91.5 | 5.1 | |
| 300 | 95.4 | 6.7 | |
| Teicoplanin | 0 | ND | - |
| 70 | 88.2 | 5.0 | |
| 150 | 93.8 | 6.7 | |
| 300 | 93.2 | 9.2 |
| Analytical Methods | Sorbent | Antibiotics | Material Preparation Time | LOD (μg/L) | Linearity (μg/L) | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MSPE a-HPLC-UV | Maltodextrin nanosponges | Fluoroquinolones | 4–6 h | 0.09–0.30 | 0.5–1000 | [43] |
| MISPE b-LC-MS/MS | Molecularly imprinted polymer | Fluoroquinolones | >24 h | 0.002–0.007 | 0.01–50 | [44] |
| MSPE-HPLC-UV | Chitosan-kaolin nanocomposite | Tetracycline | >24 h | 0.09 | 0.3–100 | [45] |
| SPE-HPLC-DAD c | PVP/SWCNT-polyHIPE d | Tetracycline | >12 h | 0.07–0.30 | 0.5–100 | [46] |
| SPME-HPLC-UV | GMA-HP-γ-CD-co-MPC polymer | Polypeptides | 38 min | 15.0–20.0 | 60–800 | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lei, X.; Wang, X.; Cao, Y.; Ren, B.; Peng, Y.; Zhao, H. Green Synthesis of Zwitterionic–Cyclodextrin Hybrid Polymer for Efficient Extraction of Polypeptides: Combination of Instrumental Analysis and DFT Calculation. Polymers 2025, 17, 2524. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17182524
Lei X, Wang X, Cao Y, Ren B, Peng Y, Zhao H. Green Synthesis of Zwitterionic–Cyclodextrin Hybrid Polymer for Efficient Extraction of Polypeptides: Combination of Instrumental Analysis and DFT Calculation. Polymers. 2025; 17(18):2524. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17182524
Chicago/Turabian StyleLei, Xiaoyun, Xin Wang, Yuzhe Cao, Bingxing Ren, Yanyan Peng, and Hanghang Zhao. 2025. "Green Synthesis of Zwitterionic–Cyclodextrin Hybrid Polymer for Efficient Extraction of Polypeptides: Combination of Instrumental Analysis and DFT Calculation" Polymers 17, no. 18: 2524. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17182524
APA StyleLei, X., Wang, X., Cao, Y., Ren, B., Peng, Y., & Zhao, H. (2025). Green Synthesis of Zwitterionic–Cyclodextrin Hybrid Polymer for Efficient Extraction of Polypeptides: Combination of Instrumental Analysis and DFT Calculation. Polymers, 17(18), 2524. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17182524






