Engineering Thermo-Responsive Hydrogels with Tailored Mechanics for Biomedical Integration
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Morphological and Mechanical Characterization
2.3. Fabrication of Negative Molds
2.4. Preparation of P(NIPAAm-co-AAm)/PNIPAAm Hydrogels
2.5. Temperature-Dependent Dimensional Analysis of Hydrogels
2.6. Skin Penetration Test of P(NIPAAm-AAm)/P(NIPAAm) Microneedles
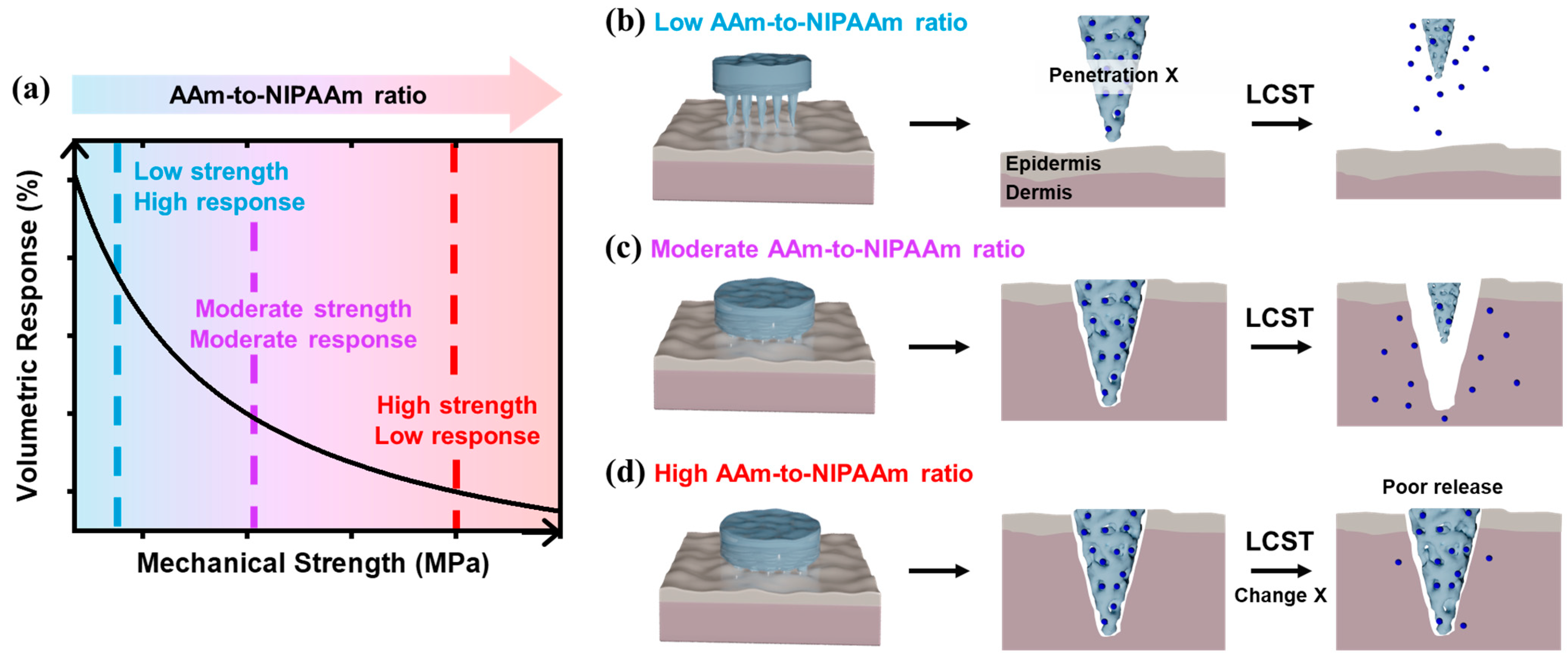
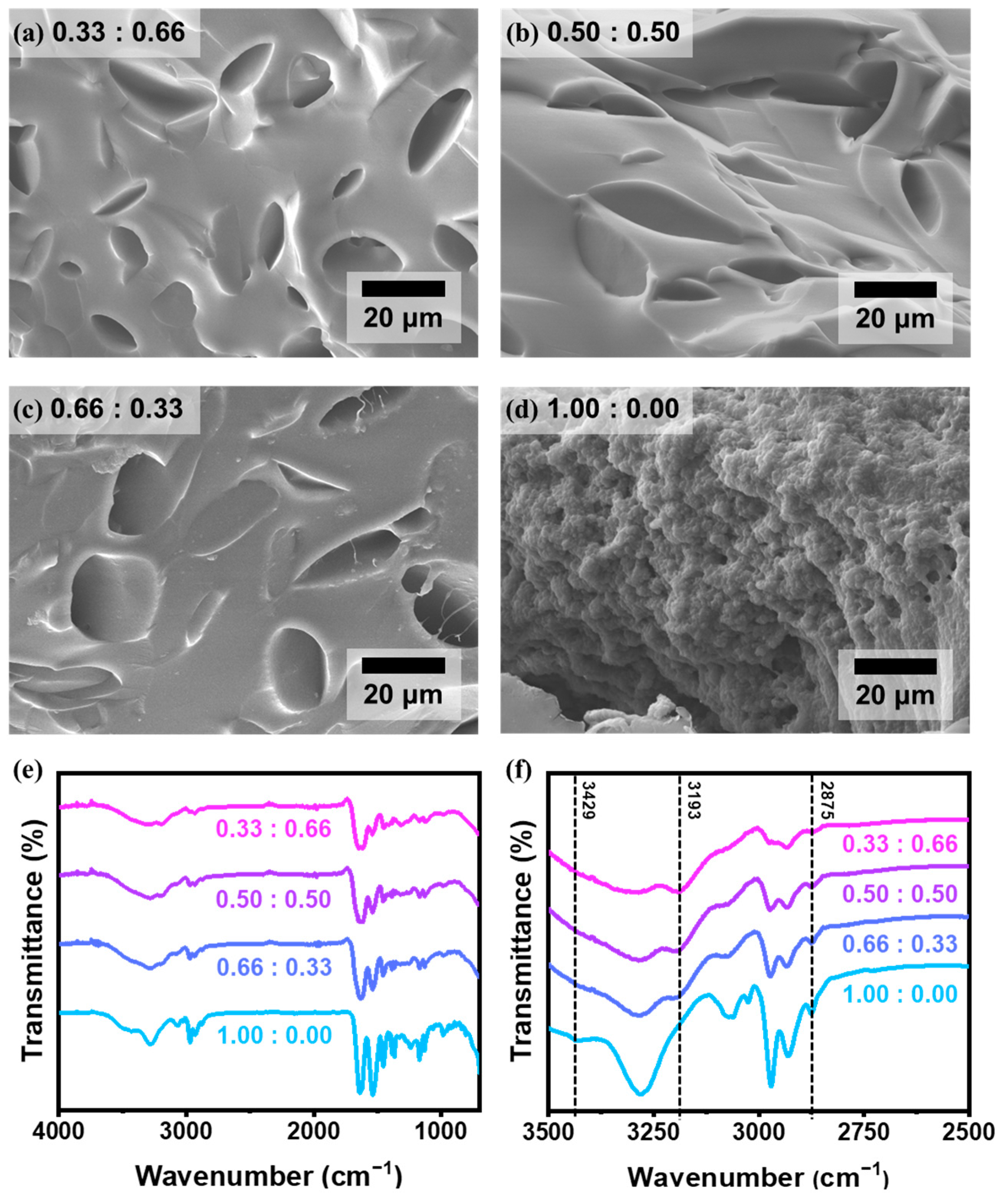
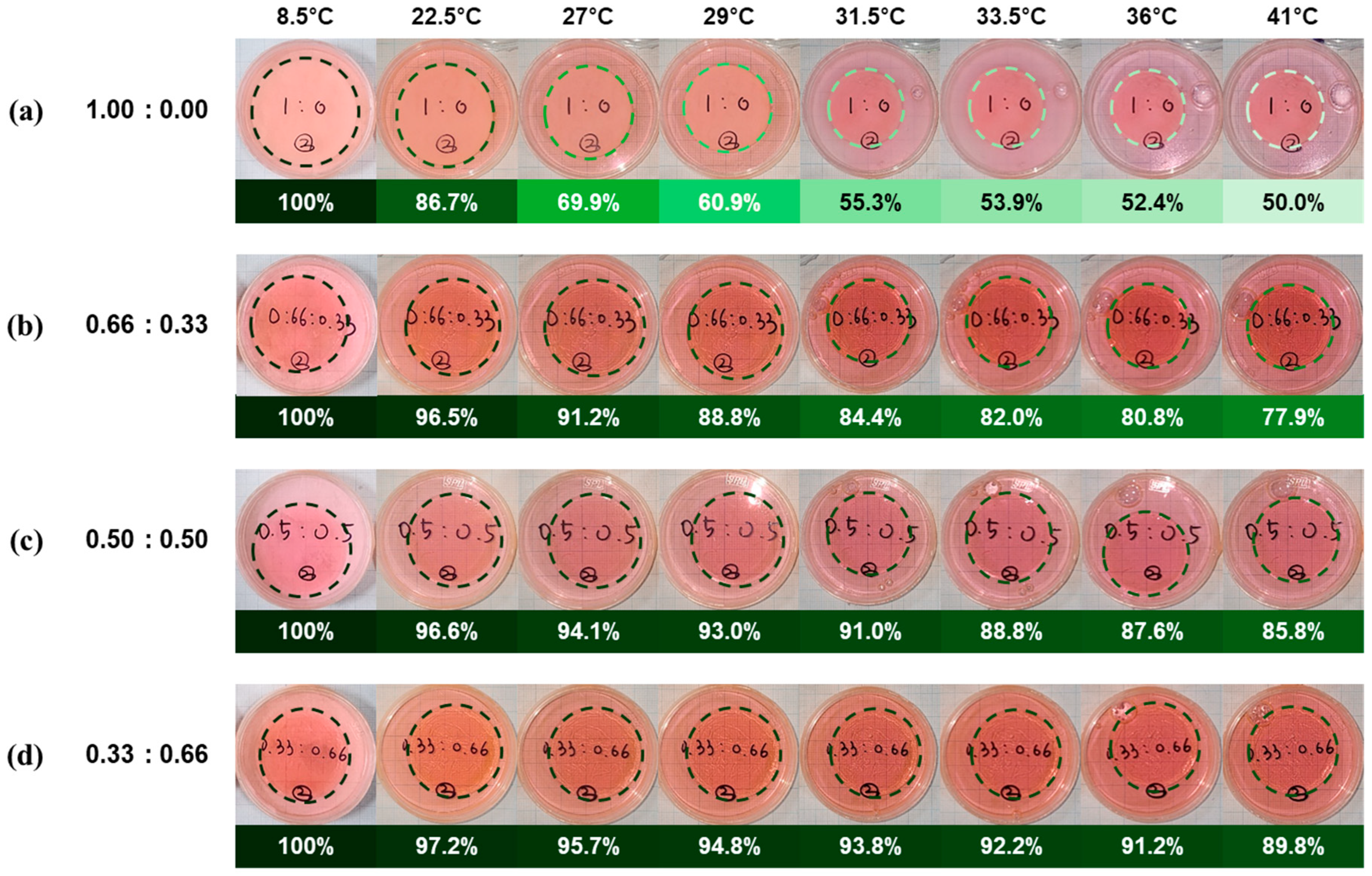
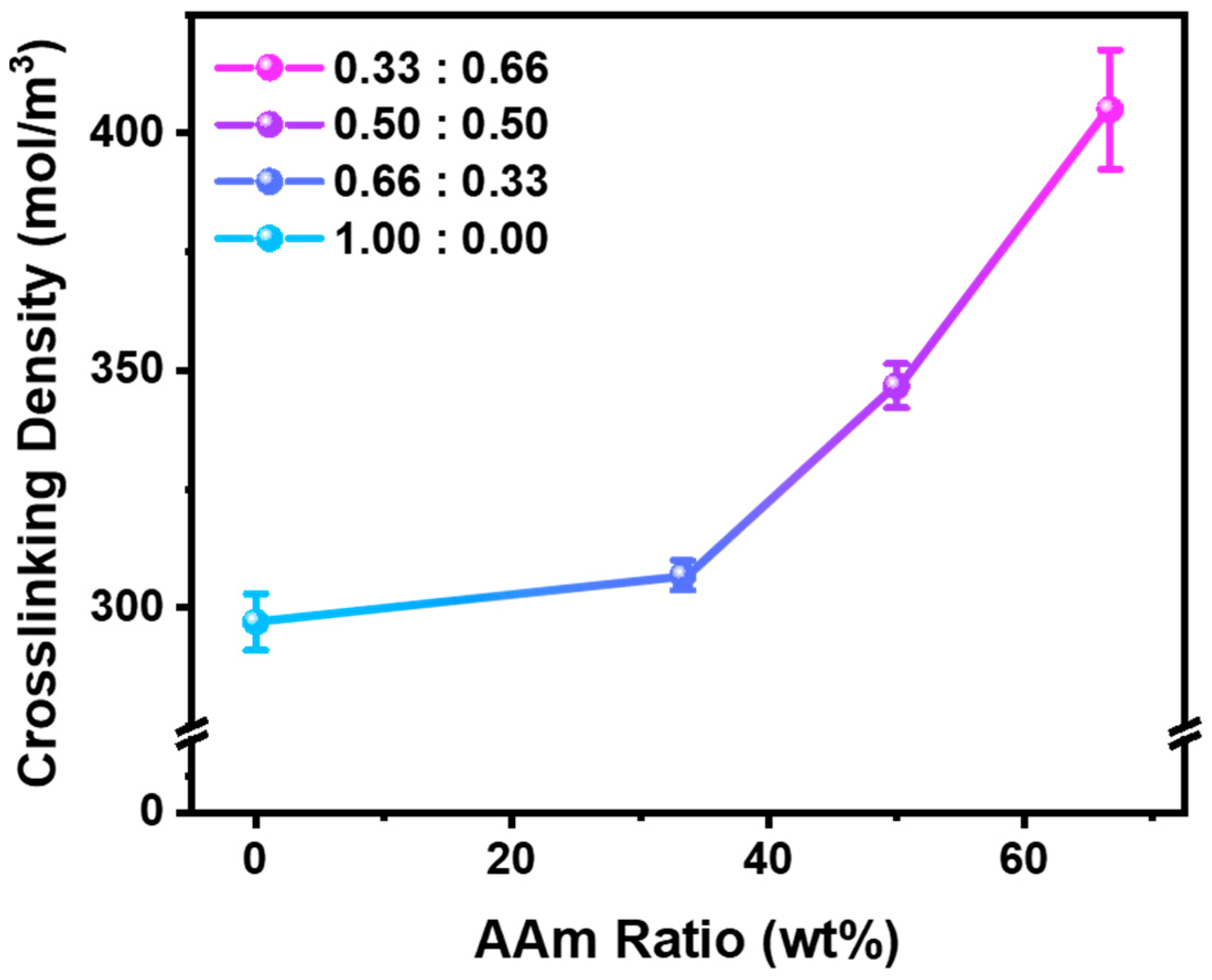
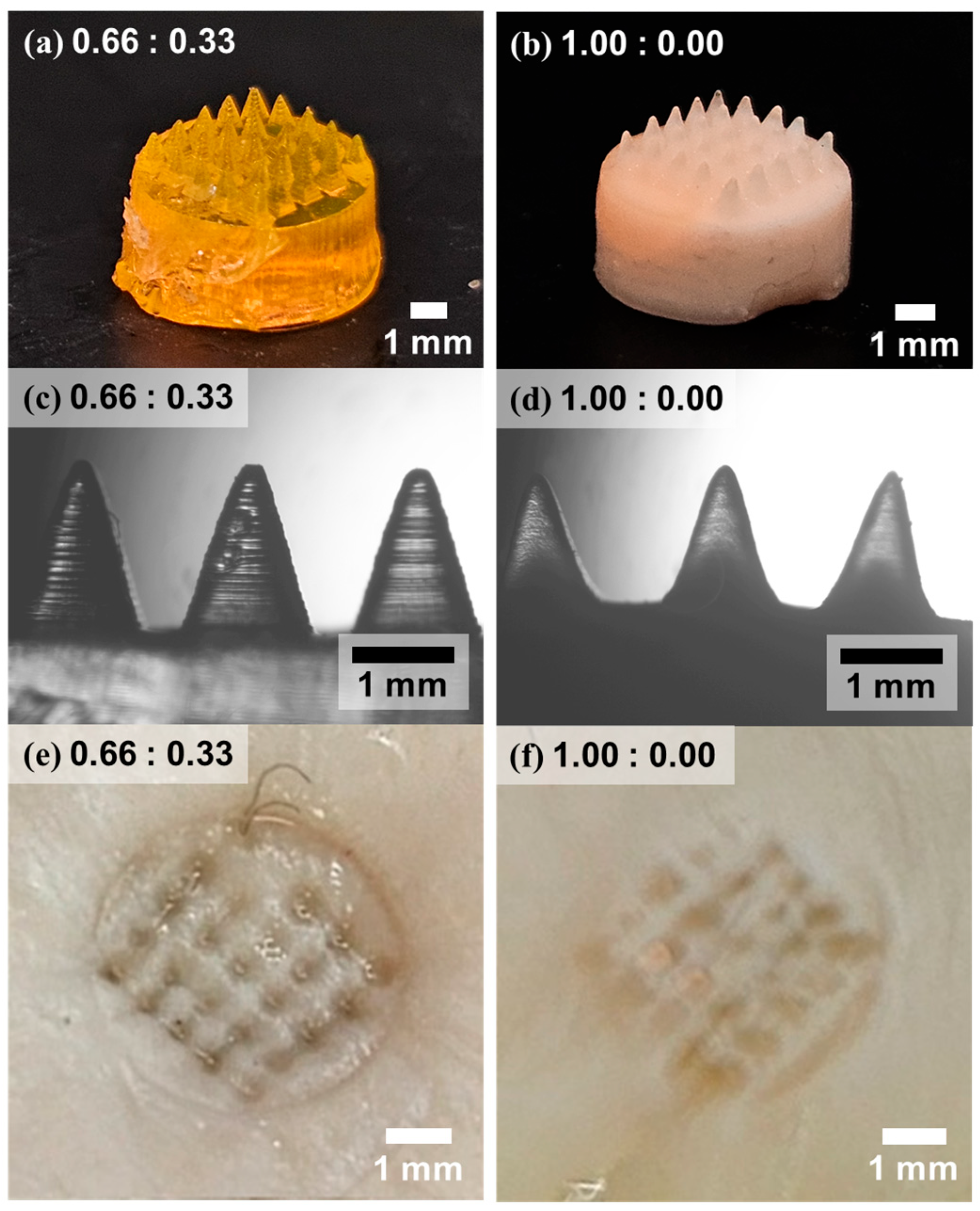
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jeon, S.J.; Hauser, A.W.; Hayward, R.C. Shape-Morphing Materials from Stimuli-Responsive Hydrogel Hybrids. Acc. Chem. Res. 2017, 50, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juodkazis, S.; Mukai, N.; Wakaki, R.; Yamaguchi, A.; Matsuo, S.; Misawa, H. Reversible phase transitions in polymer gels induced by radiation forces. Nature 2000, 408, 178–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, C.H.; Kim, T.; Lee, G.H.; Ku, K.H.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, B.J. Fluorescent Polymer-MoS-Embedded Microgels for Photothermal Heating and Colorimetric Monitoring. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 35415–35423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.H.; Yun, H.; Yang, H.; Lee, J.; Kim, B.J. Fluorescent Block Copolymer-MoS2 Nanocomposites for Real-Time Photothermal Heating and Imaging. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1604403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreiss, C.A. Hydrogel design strategies for drug delivery. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 48, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peñas-Núñez, S.J.; Rai, R.; Criado-Gonzalez, M. Key Trends and Insights in Smart Polymeric Skin Wearable Patches. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2025, 2500823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.H.; Yang, H.; Lee, J.; Cho, H.H.; Kim, D.; Lee, D.C.; Kim, B.J. Multicolor Emitting Block Copolymer-Integrated Graphene Quantum Dots for Colorimetric, Simultaneous Sensing of Temperature, pH, and Metal Ions. Chem. Mater. 2015, 27, 5288–5294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Yang, H.; Park, C.H.; Cho, H.H.; Yun, H.; Kim, B.J. Colorimetric Thermometer from Graphene Oxide Platform Integrated with Red, Green, and Blue Emitting, Responsive Block Copolymers. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 3446–3453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, M.A.; Ul Hassan, S.; Mahmood, A.; Al-Masry, W.; Lee, J.; Lee, H.J.; Akhter, T.; Park, C.H. Dual responsive phase behavior of nonionic cellulose-based polymer brushes by visible-light-driven organocatalyzed atom transfer radical polymerization. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 305, 140856. [Google Scholar]
- Iqbal, M.A.; Akhter, T.; Faheem, M.; Mahmood, A.; Al-Masry, W.; Nadeem, S.; Ul Hassan, S.; Park, C.H. Metal-free, visible light-mediated atom transfer radical polymerization of hydroxypropyl cellulose-graft-poly(methyl methacrylate)s: Effect of polymer side chains on thermo-responsive behavior of hydroxypropyl cellulose. Cellulose 2023, 30, 7519–7533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.H.; Kim, T.; Seo, M.; Kim, S.Y. Synthesis and Thermo-Responsive Behavior of Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)-b-Poly(N-vinylisobutyramide) Diblock Copolymer. Polymers 2024, 16, 830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayana, S.; Gowda, B.H.J.; Hani, U.; Ahmed, M.G.; Asiri, Z.A.; Paul, K. Smart Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)-Based Hydrogels: A Tour D’horizon of Biomedical Applications. Gels 2025, 11, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirupathi, K.; Phan, T.T.; Santhamoorthy, M.; Ramkumar, V.; Kim, S.-C. pH and Thermoresponsive PNIPAm-co-Polyacrylamide Hydrogel for Dual Stimuli-Responsive Controlled Drug Delivery. Polymers 2023, 15, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, J.G.; White, L.R.; Estrela, P.; Leese, H.S. Hydrogel-Forming Microneedles: Current Advancements and Future Trends. Macromol. Biosci. 2021, 21, e2000307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, D.; Chien, J.C.; Axpe, E.; Blankemeier, L.; Baker, S.W.; Swaminathan, S.; Piunova, V.A.; Zubarev, D.Y.; Maikawa, C.L.; Grosskopf, A.K.; et al. Combinatorial Polyacrylamide Hydrogels for Preventing Biofouling on Implantable Biosensors. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, e2109764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Chen, X.; Yuk, H.; Lin, S.; Liu, X.; Parada, G. Soft Materials by Design: Unconventional Polymer Networks Give Extreme Properties. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 4309–4372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makvandi, P.; Kirkby, M.; Hutton, A.R.J.; Shabani, M.; Yiu, C.K.Y.; Baghbantaraghdari, Z.; Jamaledin, R.; Carlotti, M.; Mazzolai, B.; Mattoli, V.; et al. Engineering Microneedle Patches for Improved Penetration: Analysis, Skin Models and Factors Affecting Needle Insertion. Nano-Micro Lett. 2021, 13, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matzelle, T.R.; Geuskens, G.; Kruse, N. Elastic properties of poly(isopropylacrylamide) and poly(acrylamide) hydrogels studied by scanning force microscopy. Macromolecules 2003, 36, 2926–2931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.Q.; Yang, T.; Ju, S.; Zhang, H.F.; Choi, T.Y.; Neogi, A. Thermally Tunable Dynamic and Static Elastic Properties of Hydrogel Due to Volumetric Phase Transition. Polymers 2020, 12, 1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.I.; Akhter, T.; Siddiqi, H.M.; Lee, Y.J.; Park, H.; ul Hassan, M.; Park, C.H. Oligoimide-Mediated Graphene Oxide-Epoxy Nanocomposites with Enhanced Thermal Conductivity and Mechanical Properties. Micromachines 2022, 13, 1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, G.; Kim, T.; Park, S.D.; Yoo, M.J.; Park, C.H.; Yang, H. N, S-Codoped Carbon Dots-Based Reusable Solvatochromic Organogel Sensors for Detecting Organic Solvents. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2024, 45, 2300542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baselga, J.; Hernández-Fuentes, I.; Masegosa, R.M.; Llorente, M.A. Effect of Crosslinker on Swelling and Thermodynamic Properties of Polyacrylamide Gels. Polym. J. 1989, 21, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamoto, C.; Kitada, T.; Kato, E. Pressure dependence on the Flory-Huggins interaction parameter of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) gels. Polym. Gels Netw. 1996, 4, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, K.I.; Chung, H.U.; Xu, S.; Lee, C.H.; Luan, H.W.; Jeong, J.; Cheng, H.Y.; Kim, G.T.; Han, S.Y.; Lee, J.W.; et al. Soft network composite materials with deterministic and bio-inspired designs. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rattan, S.; Li, L.Q.; Lau, H.K.; Crosby, A.J.; Kiick, K.L. Micromechanical characterization of soft, biopolymeric hydrogels: Stiffness, resilience, and failure. Soft Matter 2018, 14, 3478–3489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ausri, I.R.; Sadeghzadeh, S.; Biswas, S.; Zheng, H.J.; Ghavaminejad, P.; Huynh, M.D.T.; Keyvani, F.; Shirzadi, E.; Rahman, F.A.; Quadrilatero, J.; et al. Multifunctional Dopamine-Based Hydrogel Microneedle Electrode for Continuous Ketone Sensing. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, e2402009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keyvani, F.; Zheng, H.J.; Kaysir, M.R.; Mantaila, D.F.; Nejad, P.G.; Rahman, F.A.; Quadrilatero, J.; Ban, D.Y.; Poudineh, M. A Hydrogel Microneedle Assay Combined with Nucleic Acid Probes for On-Site Detection of Small Molecules and Proteins. Angew Chem. Int. Edit. 2023, 62, e202301624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larrañeta, E.; Moore, J.; Vicente-Pérez, E.M.; González-Vázquez, P.; Lutton, R.; Woolfson, A.D.; Donnelly, R.F. A proposed model membrane and test method for microneedle insertion studies. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 472, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, M.F.; Leung, B.C.; Premakumar, Y.; Szarko, M.; Butler, P.E. Comparison of the mechanical properties of different skin sites for auricular and nasal reconstruction. J. Otolaryngol.-Head Neck Surg. 2017, 46, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yazdi, S.J.M.; Cho, K.S.; Kang, N. Characterization of the viscoelastic model of in vivo human posterior thigh skin using ramp-relaxation indentation test. Korea-Aust. Rheol. J. 2018, 30, 293–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahlsten, A.; Stracuzzi, A.; Lüchtefeld, I.; Restivo, G.; Lindenblatt, N.; Giampietro, C.; Ehret, A.E.; Mazza, E. Multiscale mechanical analysis of the elastic modulus of skin. Acta Biomater. 2023, 170, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, X.; Li, J.; Hong, Y.; Ruan, H.; Long, M.; Feng, N.; Zhang, Y. Advances and Prospects for Hydrogel-Forming Microneedles in Transdermal Drug Delivery. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poudineh, M. Microneedle Assays for Continuous Health Monitoring: Challenges and Solutions. ACS Sens. 2024, 9, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusaia, V.S.; Kozhunova, E.Y.; Stepanova, D.A.; Pigareva, V.A.; Sybachin, A.V.; Zezin, S.B.; Bolshakova, A.V.; Shchelkunov, N.M.; Vavaev, E.S.; Lyubin, E.V.; et al. Synthesis of Magneto-Controllable Polymer Nanocarrier Based on Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-acrylic Acid) for Doxorubicin Immobilization. Polymers 2022, 14, 5440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aroche, A.F.; Nissan, H.E.; Daniele, M.A. Hydrogel-Forming Microneedles and Applications in Interstitial Fluid Diagnostic Devices. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2025, 14, e2401782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.H.; Thompson, I.A.P.; Newman, S.S.; Hein, L.A.; Lian, X.Z.; Fu, K.X.; Pan, J.; Eisenstein, M.; Soh, H.T. Real-Time Spatiotemporal Measurement of Extracellular Signaling Molecules Using an Aptamer Switch-Conjugated Hydrogel Matrix. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, e2306704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.K.; Kim, T.; Jang, Y.A.; Jeong, Y.; Lee, S.W.; Park, C.H. Near-Infrared Emissive CuInS/ZnS Quantum Dot-Embedded Polymer Scaffolds for Photon Upconversion Imaging. Adv. Mater. 2025, 37, 2502333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Liu, H.; Li, H. DLP 3D printing of high-resolution, temperature-responsive hydrogel microneedles with rapid customization capability. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2024, 2808, 012041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Fang, H.; Wei, X.; He, S.; Shao, W. Temperature and Near Infrared Light-Responsive Asymmetric Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)-based Hydrogel Tunable Actuators. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2024, 7, 27080–27089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omidian, H.; Dey Chowdhury, S. Multifunctional Hydrogel Microneedles (HMNs) in Drug Delivery and Diagnostics. Gels 2025, 11, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulimane Shivaswamy, R.; Binulal, P.; Benoy, A.; Lakshmiramanan, K.; Bhaskar, N.; Pandya, H.J. Microneedles as a Promising Technology for Disease Monitoring and Drug Delivery: A Review. ACS Mater. Au 2025, 5, 115–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Materials | Sample Notation | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.00:0.00 | 0.66:0.33 | 0.50:0.50 | 0.33:0.66 | |
| NIPAAm (mg) | 870 | 580 | 435 | 290 |
| AAm (mg) | 0 | 290 | 435 | 580 |
| MBAM (mg) | 60 | |||
| APS (100mg/mL) (μL) | 100 | |||
| TEMED (μL) | 7.5 | |||
| Rhodamine 6G (mg) | 0.5 | |||
| DI Water (μL) | 2700 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, S.; Pyo, M.; Lee, S.; Jeong, Y.; Nam, Y.; Park, S.; Jang, Y.-A.; Kim, K.; Park, C.H. Engineering Thermo-Responsive Hydrogels with Tailored Mechanics for Biomedical Integration. Polymers 2025, 17, 2424. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17172424
Choi S, Pyo M, Lee S, Jeong Y, Nam Y, Park S, Jang Y-A, Kim K, Park CH. Engineering Thermo-Responsive Hydrogels with Tailored Mechanics for Biomedical Integration. Polymers. 2025; 17(17):2424. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17172424
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Sungmo, Minkyeong Pyo, Sangmin Lee, Yunseo Jeong, Yuri Nam, Seonghyeon Park, Yoon-A Jang, Kisung Kim, and Chan Ho Park. 2025. "Engineering Thermo-Responsive Hydrogels with Tailored Mechanics for Biomedical Integration" Polymers 17, no. 17: 2424. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17172424
APA StyleChoi, S., Pyo, M., Lee, S., Jeong, Y., Nam, Y., Park, S., Jang, Y.-A., Kim, K., & Park, C. H. (2025). Engineering Thermo-Responsive Hydrogels with Tailored Mechanics for Biomedical Integration. Polymers, 17(17), 2424. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17172424







