Red Cabbage Anthocyanin-Loaded Bacterial Cellulose Hydrogel for Colorimetric Detection of Microbial Contamination and Skin Healing Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Microorganisms
2.2. Anthocyanin Extraction
2.2.1. Hydrogel Fabrication and Purification
2.2.2. Quantification of RCA Uptake and Release
2.3. Anthocyanins’ Hydrogel Characterization
2.3.1. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.3.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
Sample Color Determination with Smartphone-Based Sensor System
Sample Colorimetric Characterization
2.4. Biological Activities
2.4.1. In Vitro Cell Cultures
2.4.2. Cytotoxicity Assay (Lactate Dehydrogenase Release, LDH)
2.4.3. Human Cell Line Activation Test (h-CLAT)
2.4.4. Apoptosis Assay
2.4.5. Antimicrobial Activity
2.5. Statistics
3. Results
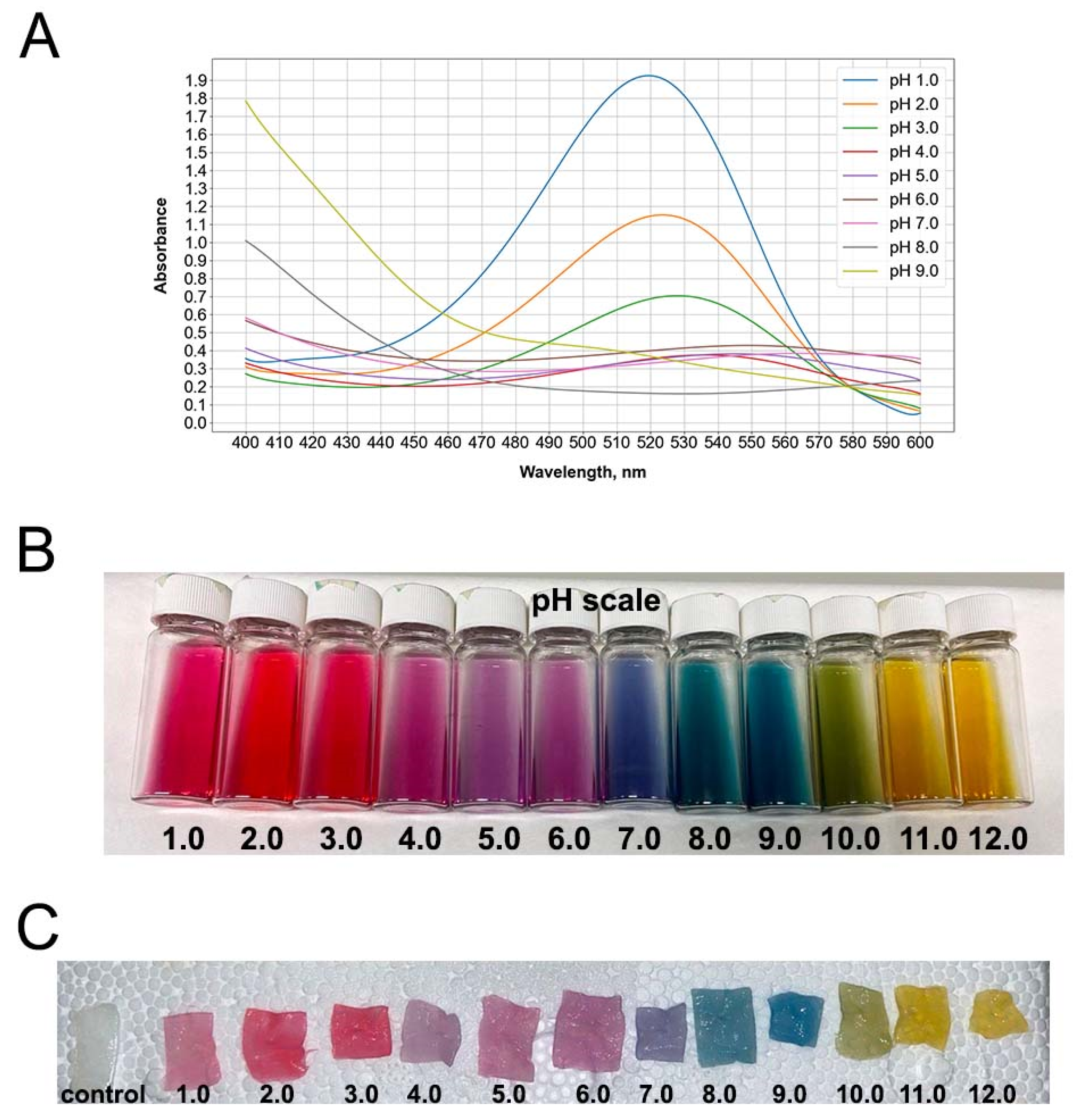
3.1. Red Cabbage Anthocyanin Extract and Impregnated Bacterial Cellulose Hydrogel Films Showed pH-Dependent Colors
3.2. A Color Level Visualization and Its Measurement
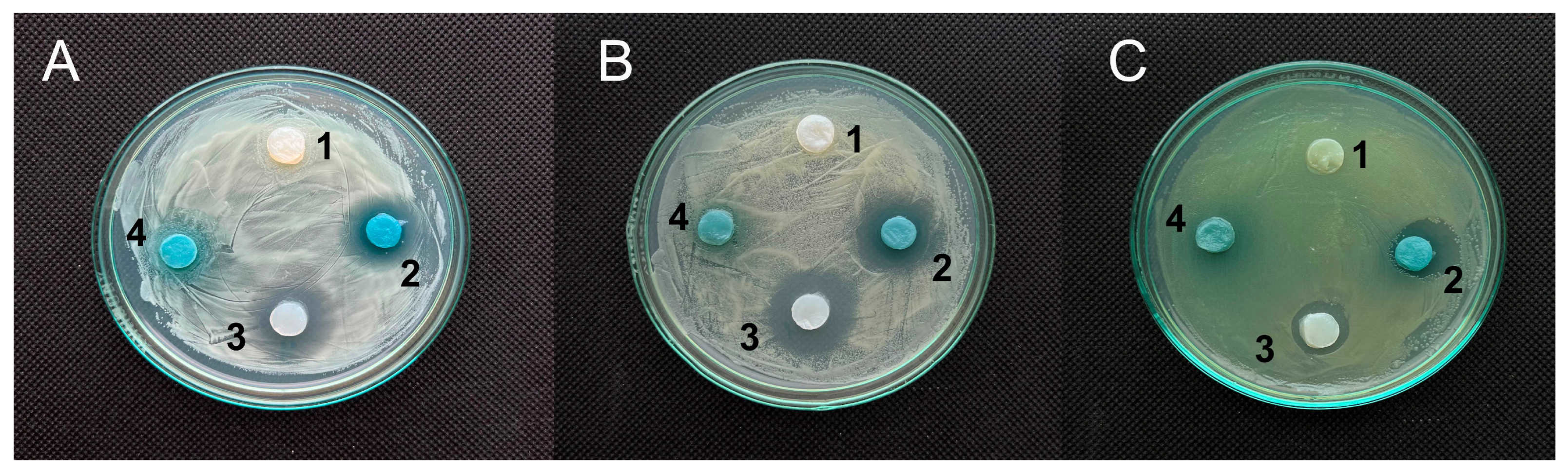
3.2.1. RCA-Impregnated BC Films for the Control of Bacterial Contamination
3.2.2. Colorimetry of BC/RCA Films
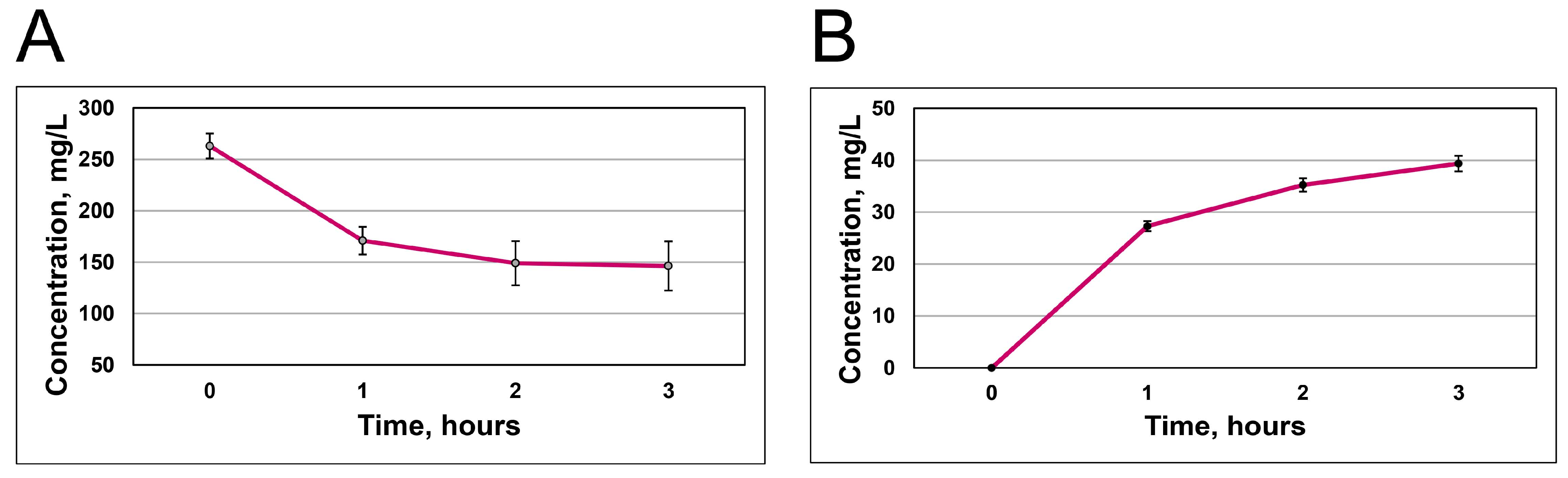
3.3. Quantification of RCA Uptake and Release
3.4. Biological Activities Characterization
3.4.1. Antimicrobial Activity
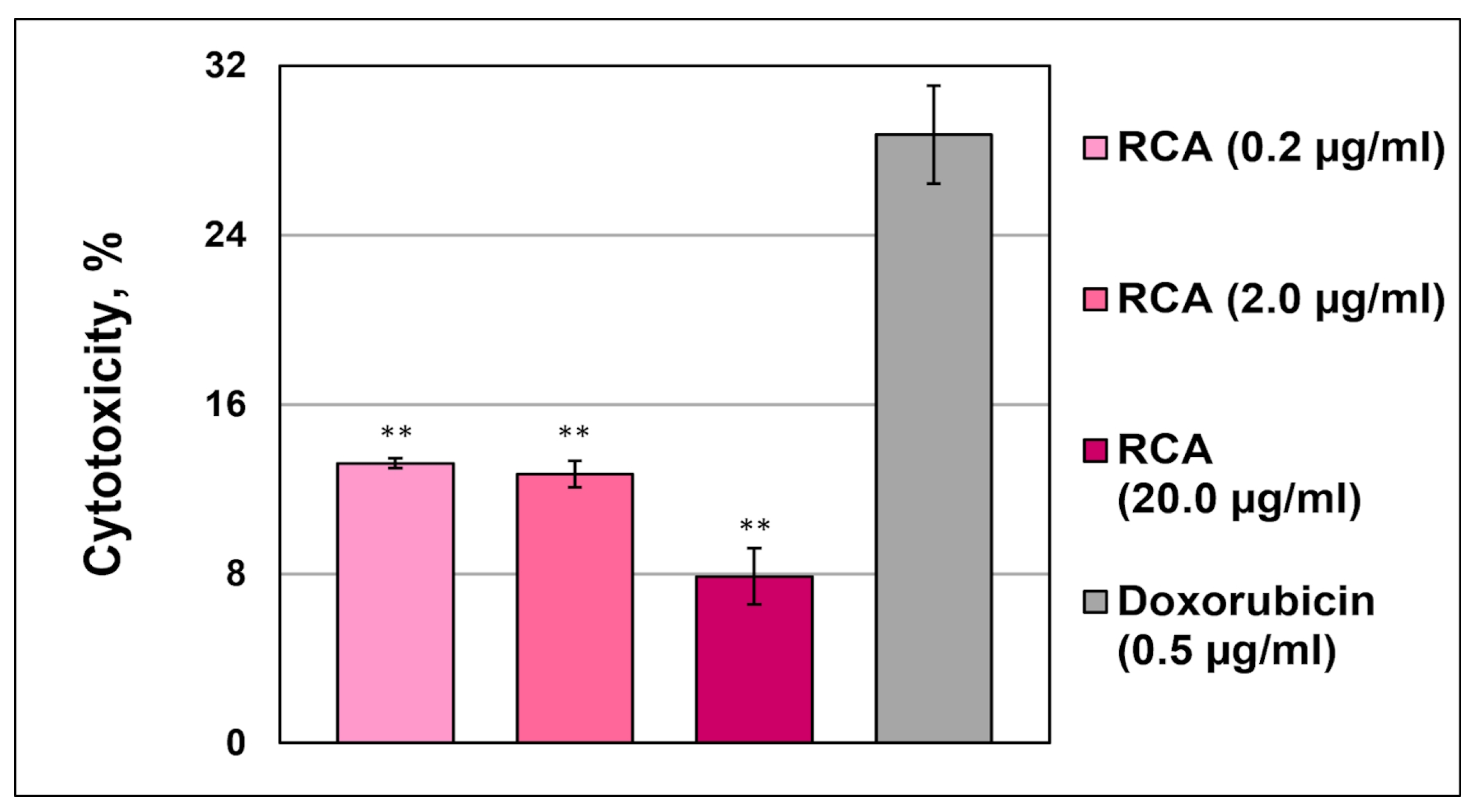
3.4.2. Cytotoxicity Assays
No Cytotoxicity via LHD Release in Leukemic Monocytes THP-1
3.4.3. h-CLAT
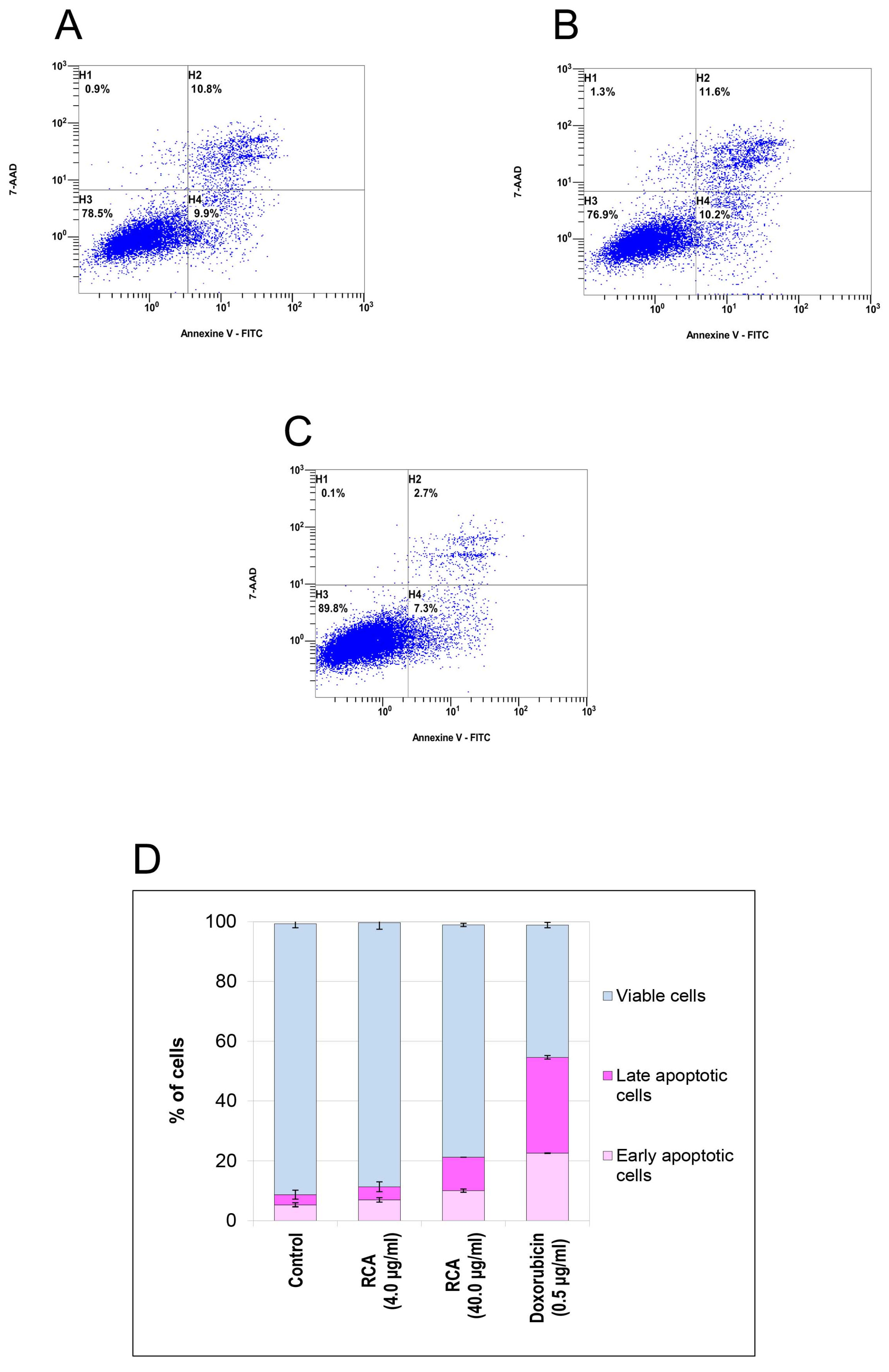
3.4.4. Apoptosis in Human MDA-MB-231 In Vitro Cells
3.5. Physicochemical Characterization
3.5.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy
3.5.2. FTIR Spectroscopy
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gethin, G. The Significance of Surface pH in Chronic Wounds. Wounds UK 2007, 3, 52–56. [Google Scholar]
- Youssef, K.; Ullah, A.; Rezai, P.; Hasan, A.; Amirfazli, A. Recent Advances in Biosensors for Real Time Monitoring of pH, Temperature, and Oxygen in Chronic Wounds. Mater. Today Bio 2023, 22, 100764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.; Kushare, A.; Gupta, M.N.; Ambre, P. Advanced Dressings for Chronic Wound Management. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2024, 7, 2660–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhong, B.; Lou, Z.; Han, W.; Wang, L. The Advancement of Intelligent Dressings for Monitoring Chronic Wound Infections. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 484, 149643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Xi, Y.; Weng, Y. Functional Electrospun Nanofibers: Fabrication, Properties, and Applications in Wound-Healing Process. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 3359–3378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zubova, G.; Melnyk, H.; Zaets, I.; Sergeyeva, T.; Havryliuk, O.; Rogalsky, S.; Khirunenko, L.; Zaika, L.; Ruban, T.; Antonenko, S.; et al. Halochromic Bacterial Cellulose/Anthocyanins Hybrid Polymer Film with Wound-Healing Potential. Polymers 2024, 16, 2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zmejkoski, D.Z.; Marković, Z.M.; Budimir, M.D.; Zdravković, N.M.; Trišić, D.D.; Bugárová, N.; Danko, M.; Kozyrovska, N.O.; Špitalský, Z.; Kleinová, A.; et al. Photoactive and Antioxidant Nanochitosan Dots/Biocellulose Hydrogels for Wound Healing Treatment. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 122, 111925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Gu, Z.; Zhou, L.; Hao, M.; An, H.; Song, K.; Wu, X.; Zhang, K.; Zhao, Z.; Dong, Y.; et al. Recent Progress in Intelligent Wearable Sensors for Health Monitoring and Wound Healing Based on Biofluids. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 765987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.; Ershad, F.; Zhao, M.; Isseroff, R.R.; Duan, B.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yu, C. Wearable Electronics for Skin Wound Monitoring and Healing. Soft Sci. 2022, 2, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Tan, P.; Rao, Y.; Bhattacharya, S.; Wang, Z.; Kim, S.; Gangopadhyay, S.; Shi, H.; Jankovic, M.; Huh, H.; et al. E-Tattoos: Toward Functional but Imperceptible Interfacing with Human Skin. Chem. Rev. 2024, 124, 3220–3283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjarnia, P.; Picchio, M.L.; Polegre Solis, A.N.; Schuhladen, K.; Fliss, P.M.; Politakos, N.; Metterhausen, L.; Calderón, M.; Osorio-Blanco, E.R. Bringing Innovative Wound Care Polymer Materials to the Market: Challenges, Developments, and New Trends. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2024, 207, 115217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Che, Y.; Zhou, R.; Wang, L.; Huang, J.; Kong, W.; Liu, C.; Guo, L.; Tang, Y.; Wang, X.; et al. Research Progress of Natural Polysaccharide-Based and Natural Protein-Based Hydrogels for Bacteria-Infected Wound Healing. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 496, 153803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satchanska, G.; Davidova, S.; Petrov, P.D. Natural and Synthetic Polymers for Biomedical and Environmental Applications. Polymers 2024, 16, 1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuperkar, K.; Atanase, L.; Bahadur, A.; Crivei, I.; Bahadur, P. Degradable Polymeric Bio(Nano)Materials and Their Biomedical Applications: A Comprehensive Overview and Recent Updates. Polymers 2024, 16, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Lin, X.; Cao, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Y. Developing Natural Polymers for Skin Wound Healing. Bioact. Mater. 2024, 33, 355–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Xu, G.; Huang, H.; Wang, K.; Wang, H.; Lang, M.; Gao, H.; Zhao, S. Sequential Release of Small Extracellular Vesicles from Bilayered Thiolated Alginate/Polyethylene Glycol Diacrylate Hydrogels for Scarless Wound Healing. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 6352–6368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Pan, C.; Xu, P.; Liu, K. Hydrogel-Mediated Extracellular Vesicles for Enhanced Wound Healing: The Latest Progress, and Their Prospects for 3D Bioprinting. J. Nanobiotechnol 2024, 22, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Zhu, Y.; Tian, Z.; Zhang, C.; Han, X.; Jiang, S.; Liu, K.; Duan, G. Preparation of Nanocellulose and Its Applications in Wound Dressing: A Review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 254, 127997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, S.; Xia, Z.; Pan, J.; Wang, N.; Gao, H.; Ren, J.; Xia, X. Bacterial Cellulose Applied in Wound Dressing Materials: Production and Functional Modification–A Review. Macromol. Biosci. 2024, 24, 2300333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jabbari, F.; Babaeipour, V. Bacterial Cellulose as a Potential Biopolymer for Wound Care. A Review. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2024, 73, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitale, S.; Colanero, S.; Placidi, M.; Di Emidio, G.; Tatone, C.; Amicarelli, F.; D’Alessandro, A.M. Phytochemistry and Biological Activity of Medicinal Plants in Wound Healing: An Overview of Current Research. Molecules 2022, 27, 3566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Roy Maulik, S. Recent Approaches and Advancements in Natural Dyes. In Natural Dyes and Sustainability; Muthu, S.S., Ed.; Sustainable Textiles: Production, Processing, Manufacturing & Chemistry; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 63–78. ISBN 978-3-031-47470-5. [Google Scholar]
- Li, N.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, J.; Li, S.; Liu, J.; Chen, H. Insight into the Progress on Natural Dyes: Sources, Structural Features, Health Effects, Challenges, and Potential. Molecules 2022, 27, 3291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wardani, N.I.; Alahmad, W.; Varanusupakul, P. A Review of Utilizing Anthocyanins as Natural Reagents for Eco-Friendly Solid-State Colorimetric Sensors: A Green Perspective. Green Anal. Chem. 2024, 9, 100117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosales-Murillo, S.S.; Sánchez-Bodón, J.; Hernández Olmos, S.L.; Ibarra-Vázquez, M.F.; Guerrero-Ramírez, L.G.; Pérez-Álvarez, L.; Vilas-Vilela, J.L. Anthocyanin-Loaded Polymers as Promising Nature-Based, Responsive, and Bioactive Materials. Polymers 2024, 16, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Jing, P. Red Cabbage Anthocyanins Attenuate Cognitive Impairment By Attenuating Neuroinflammation and Regulating Gut Microbiota in Aging Mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 15064–15072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tena, N.; Martín, J.; Asuero, A.G. State of the Art of Anthocyanins: Antioxidant Activity, Sources, Bioavailability, and Therapeutic Effect in Human Health. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Jia, Y.; Wu, Y.; Ren, F. Anthocyanin and Its Bioavailability, Health Benefits, and Applications: A Comprehensive Review. Food Rev. Int. 2024, 40, 3666–3689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catacutan, M.K.; Kim, T.-Y.; Lee, S. Selective Cytotoxicity of Anthocyanins on Breast Cancer Cells 2024. Available online: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/Delivery.cfm/62fa8122-ccbd-4352-a46b-0ed812649a38-MECA.pdf?abstractid=5125245&mirid=1 (accessed on 7 February 2025).
- Ghareaghajlou, N.; Hallaj-Nezhadi, S.; Ghasempour, Z. Red Cabbage Anthocyanins: Stability, Extraction, Biological Activities and Applications in Food Systems. Food Chem. 2021, 365, 130482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelkader, R.M.M.; Hamed, D.A.; Gomaa, O.M. Red Cabbage Extract Immobilized in Bacterial Cellulose Film as an Eco-Friendly Sensor to Monitor Microbial Contamination and Gamma Irradiation of Stored Cucumbers. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2024, 40, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, X.; Wang, Y.; Sun, F.; Shi, S.; Xia, X. A Review on Improving the Sensitivity and Color Stability of Naturally Sourced pH-sensitive Indicator Films. Comp. Rev. Food Sci. Food Safe 2024, 23, e13390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Ameijide, V.; Maggio, A.; Pozo, M.; Gómez, M.; Naranjo, P.; Roca-Jalil, M. Assessment of Sorption of Anthocyanins from Red Cabbage onto Bentonites from Patagonia (Argentina). Minerals 2024, 14, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Durst, R.W.; Wrolstad, R.E. Determination of Total Monomeric Anthocyanin Pigment Content of Fruit Juices, Beverages, Natural Colorants, and Wines by the pH Differential Method: Collaborative Study. J. AOAC Int. 2005, 88, 1269–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Cheng, C.; Wang, H.; Wang, D. Swollen Hydrogel Nanotechnology: Advanced Applications of the Rudimentary Swelling Properties of Hydrogels. ChemPhysMater 2024, 3, 357–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. Test No. 442E: In Vitro Skin Sensitisation: In Vitro Skin Sensitisation Assays Addressing the Key Event on Activation of Dendritic Cells on the Adverse Outcome Pathway for Skin Sensitisation; OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 4; OECD: Paris, France, 2024; ISBN 978-92-64-26435-9. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Kong, D.; Wu, H. Comprehensive Chemical Analysis of the Flower Buds of Five Lonicera Species by ATR-FTIR, HPLC-DAD, and Chemometric Methods. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2018, 28, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourjavaher, S.; Almasi, H.; Meshkini, S.; Pirsa, S.; Parandi, E. Development of a Colorimetric pH Indicator Based on Bacterial Cellulose Nanofibers and Red Cabbage (Brassica oleraceae) Extract. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 156, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.; Li, N.; Peng, H.; Yang, X.; Lin, D. The Development of Highly pH-Sensitive Bacterial Cellulose Nanofibers/Gelatin-Based Intelligent Films Loaded with Anthocyanin/Curcumin for the Fresh-Keeping and Freshness Detection of Fresh Pork. Foods 2023, 12, 3719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Shen, Q.; Song, T.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, A.; Yang, W. Facile Fabrication of Anthocyanin-Nanocellulose Hydrogel Indicator Label for Intelligent Evaluation of Minced Pork Freshness. Foods 2023, 12, 2602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, N.F.; Khattab, T.A.; Fouda, M.M.G.; Abu Zaid, A.S.; Aboshanab, K.M. Electrospun Cellulose Nanofibers Immobilized with Anthocyanin Extract for Colorimetric Determination of Bacteria. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 257, 128817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alisaac, A.; Alsahag, M.; Alshareef, M.; Snari, R.M.; Alhasani, M.; Abumelha, H.M.; El-Metwaly, N.M. Development of Smart Cotton Fabrics Immobilized with Anthocyanin and Potassium Alum for Colorimetric Detection of Bacteria. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2022, 145, 110023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Wu, J.; Xu, J.; Mosselhy, D.A.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, S. Bacterial Cellulose: Functional Modification and Wound Healing Applications. Adv. Wound Care 2021, 10, 623–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Zhu, T.; Cheng, Y.; Zhao, K.; Meng, Z.; Huang, J.; Cai, W.; Lai, Y. Recent Advances in Functional Cellulose-Based Materials: Classification, Properties, and Applications. Adv. Fiber Mater. 2024, 6, 1343–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, D.A.; Tripathi, L.; Fricker, A.T.R.; Asare, E.; Orlando, I.; Raghavendran, V.; Roy, I. Bacterial Cellulose: A Smart Biomaterial with Diverse Applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. R. Rep. 2021, 145, 100623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.; Lan, X.; Chen, S.; Zhong, X.; Li, W. Physical Character, Total Polyphenols, Anthocyanin Profile and Antioxidant Activity of Red Cabbage as Affected by Five Processing Methods. Food Res. Int. 2023, 169, 112929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, M.K.; Zahra, N.; Saeed, A.; Babar, L.; Malik, M.; Shehbaz, M.; Raza, M.H. Isolation and Quantification of Anthocyanins from Red Cabbage (Brassica oleracea L.) and Its Potential Uses as Antioxidant in Natural Food. Actapharm 2024, 62, 907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, S.; Omara, T.; Kahwa, I.; Khan, U.M. Anticancer Potential of Delphinidin and Its Derivatives: Therapeutic and Mechanistic Insights. Med. Chem. Res. 2024, 33, 1769–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, Z.L.; Mohammed, R.K. The Study of the Antibacterial Effect of Anthocyanin Pigment Extracted From Red Cabbage (Brassica oleracea Var. Capitata f. Rubra) and Red Radish Peels (Raphanus sativus. Var. Sativus). IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2024, 1371, 052089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, M.-C.; Chen, C.-C.; Tseng, T.-H.; Chang, Y.-C.; Lin, Y.-J.; Tsai, I.-N.; Wang, C.-C.; Wang, C.-J. Hibiscus Anthocyanins Extracts Induce Apoptosis by Activating AMP-Activated Protein Kinase in Human Colorectal Cancer Cells. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, M.G.; Hanafy, N.A.N.; Ali, R.A.; El-Monem, D.D.A.; El-Shafiey, S.H.; El-Magd, M.A. Unveiling the Therapeutic Potential of Anthocyanin/Cisplatin-Loaded Chitosan Nanoparticles against Breast and Liver Cancers. Cancer Nano 2024, 15, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Song, G.; Zhao, C.; Qi, W.; Wang, Y. Interactions between Anthocyanins and Gut Microbiota in Promoting Healthy Aging. J. Future Foods 2025, 5, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.X.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.; He, C.; Li, F.P. The Extract of Huanglian, a Medicinal Herb, Induces Cell Growth Arrest and Apoptosis by Upregulation of Interferon-β and TNF-α in Human Breast Cancer Cells. Carcinogenesis 2005, 26, 1934–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.-S.; Stoner, G.D. Anthocyanins and Their Role in Cancer Prevention. Cancer Lett. 2008, 269, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hafidh, R.R.; Abdulamir, A.S.; Abu Bakar, F.; Jalilian, F.A.; Jahanshiri, F.; Abas, F.; Sekawi, Z. Novel Anticancer Activity and Anticancer Mechanisms of Brassica oleracea L. Var. Capitata f. Rubra. Eur. J. Integr. Med. 2013, 5, 450–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Arruda Nascimento, E.; De Lima Coutinho, L.; Da Silva, C.J.; De Lima, V.L.A.G.; Dos Santos Aguiar, J. In Vitro Anticancer Properties of Anthocyanins: A Systematic Review. Biochim. Et. Biophys. Acta BBA-Rev. Cancer 2022, 1877, 188748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Gao, M.; Lu, H.; Chen, Q.; Lian, X. Anthocyanins Prevent the Development and Progression of Urethane-Induced Lung Cancer by Regulating Energy Metabolism in Mice. Food Nutr. Res. 2024, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rugină, D.; Hanganu, D.; Diaconeasa, Z.; Tăbăran, F.; Coman, C.; Leopold, L.; Bunea, A.; Pintea, A. Antiproliferative and Apoptotic Potential of Cyanidin-Based Anthocyanins on Melanoma Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faur, C.-A.; Zăhan, M.; Bunea, C.I.; Hârșan, E.; Bora, F.-D.; Bunea, A. Antiproliferative and Biochemical Evaluation of Rose Extracts: Impact on Tumor and Normal Skin Cells. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1477243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poommarapan, K.; Tancharoen, S.; Leenutaphong, P.; Srichan, R.; Nararatwanchai, T.; Rummaneethorn, P. Apoptotic Effects of Oryza sativa L. Extract in Human Melanoma Cell. J. Dep. Med. Ser. 2024, 49, 77–86. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, E.; Yu, H.; Kim, E.; Hwang, J.; Yoo, J.; Choi, J.; Jeong, H.-S.; Jang, S. The Therapeutic Effects of Blueberry-Treated Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles in Ischemic Stroke. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, S.; Peixoto, F.; Da Silveria, T.F.F.; Barros, L.; Gaivão, I. Antigenotoxic and Cosmetic Potential of Elderberry (Sambucus nigra) Extract: Protection against Oxidative DNA Damage. Food Funct. 2024, 15, 10795–10810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; He, L.; Sun, J.; Ye, H.; Yin, C.; Zhang, W.; Han, H.; Jin, W. Exploring the Potential of Anthocyanins for Repairing Photoaged Skin: A Comprehensive Review. Foods 2024, 13, 3506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Păcularu-Burada, B.; Cîrîc, A.-I.; Begea, M. Anti-Aging Effects of Flavonoids from Plant Extracts. Foods 2024, 13, 2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Melnyk, H.; Havryliuk, O.; Zaets, I.; Sergeyeva, T.; Zubova, G.; Korovina, V.; Scherbyna, M.; Savinska, L.; Khirunenko, L.; Amler, E.; et al. Red Cabbage Anthocyanin-Loaded Bacterial Cellulose Hydrogel for Colorimetric Detection of Microbial Contamination and Skin Healing Applications. Polymers 2025, 17, 2116. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17152116
Melnyk H, Havryliuk O, Zaets I, Sergeyeva T, Zubova G, Korovina V, Scherbyna M, Savinska L, Khirunenko L, Amler E, et al. Red Cabbage Anthocyanin-Loaded Bacterial Cellulose Hydrogel for Colorimetric Detection of Microbial Contamination and Skin Healing Applications. Polymers. 2025; 17(15):2116. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17152116
Chicago/Turabian StyleMelnyk, Hanna, Olesia Havryliuk, Iryna Zaets, Tetyana Sergeyeva, Ganna Zubova, Valeriia Korovina, Maria Scherbyna, Lilia Savinska, Lyudmila Khirunenko, Evzen Amler, and et al. 2025. "Red Cabbage Anthocyanin-Loaded Bacterial Cellulose Hydrogel for Colorimetric Detection of Microbial Contamination and Skin Healing Applications" Polymers 17, no. 15: 2116. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17152116
APA StyleMelnyk, H., Havryliuk, O., Zaets, I., Sergeyeva, T., Zubova, G., Korovina, V., Scherbyna, M., Savinska, L., Khirunenko, L., Amler, E., Bardosova, M., Gorbach, O., Rogalsky, S., & Kozyrovska, N. (2025). Red Cabbage Anthocyanin-Loaded Bacterial Cellulose Hydrogel for Colorimetric Detection of Microbial Contamination and Skin Healing Applications. Polymers, 17(15), 2116. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17152116







