Dynamic Ester-Linked Vitrimers for Reprocessable and Recyclable Solid Electrolytes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiments
2.1. Preparation of Ester-Linked Vitrimer Electrolytes
2.2. Reprocessing of Ester-Linked Vitrimer Electrolytes
2.3. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
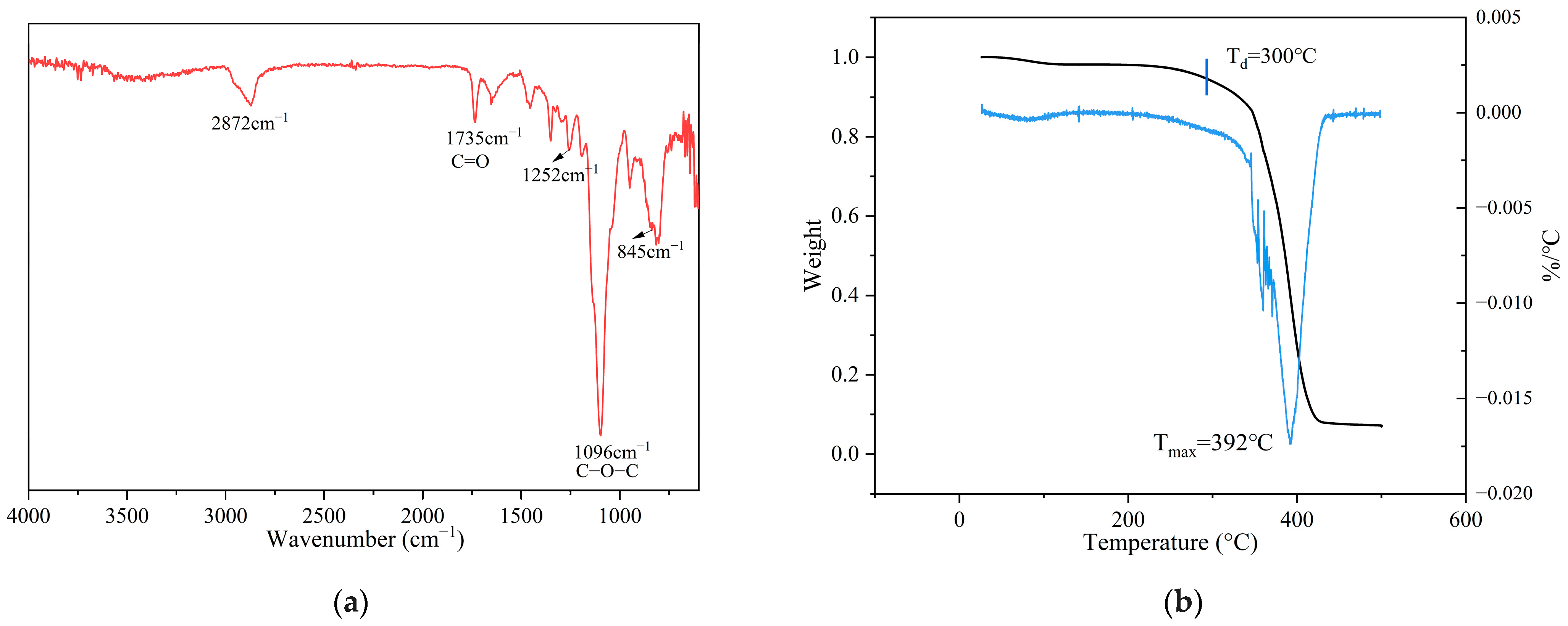
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of Ester-Linked Vitrimer Electrolytes
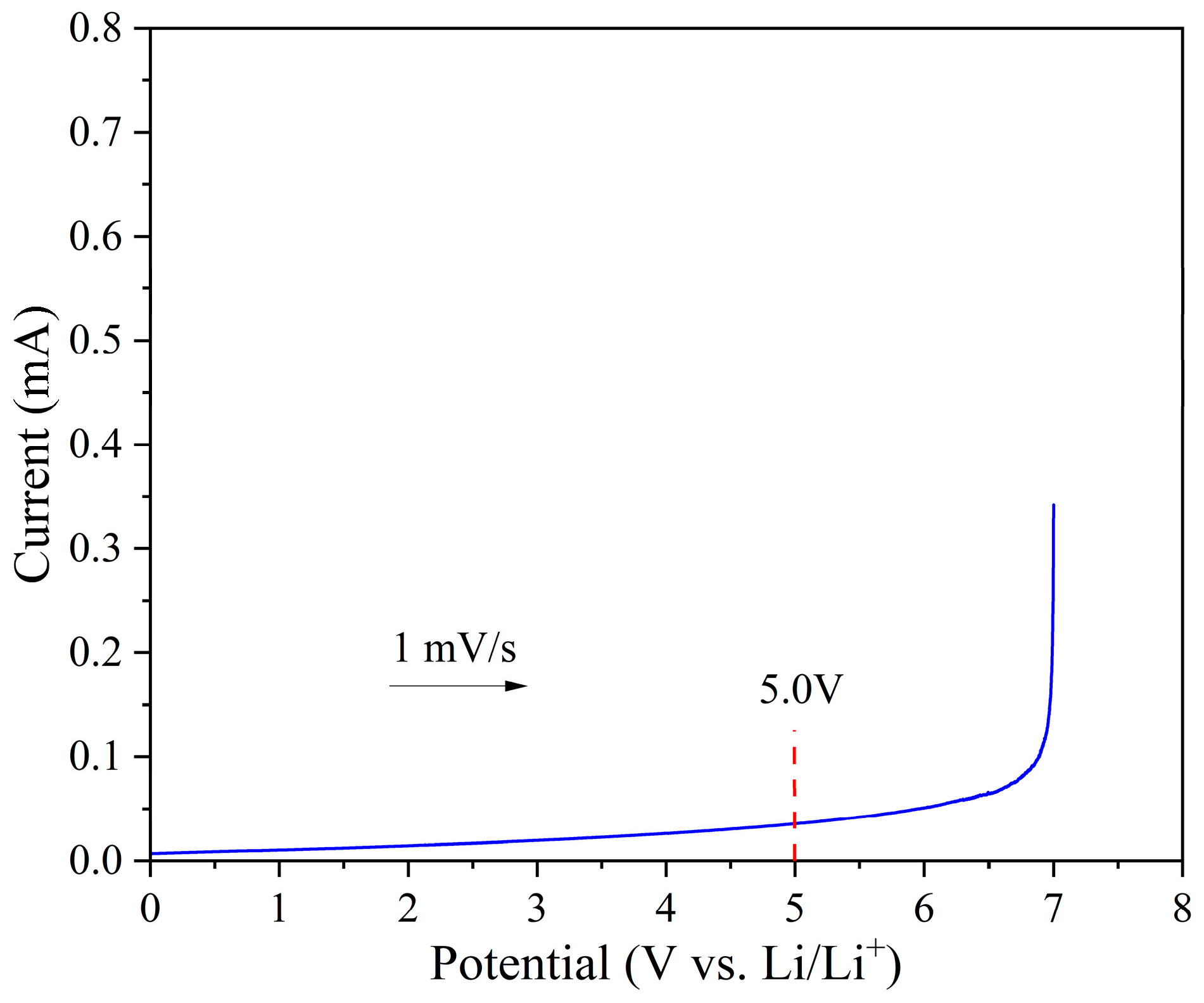
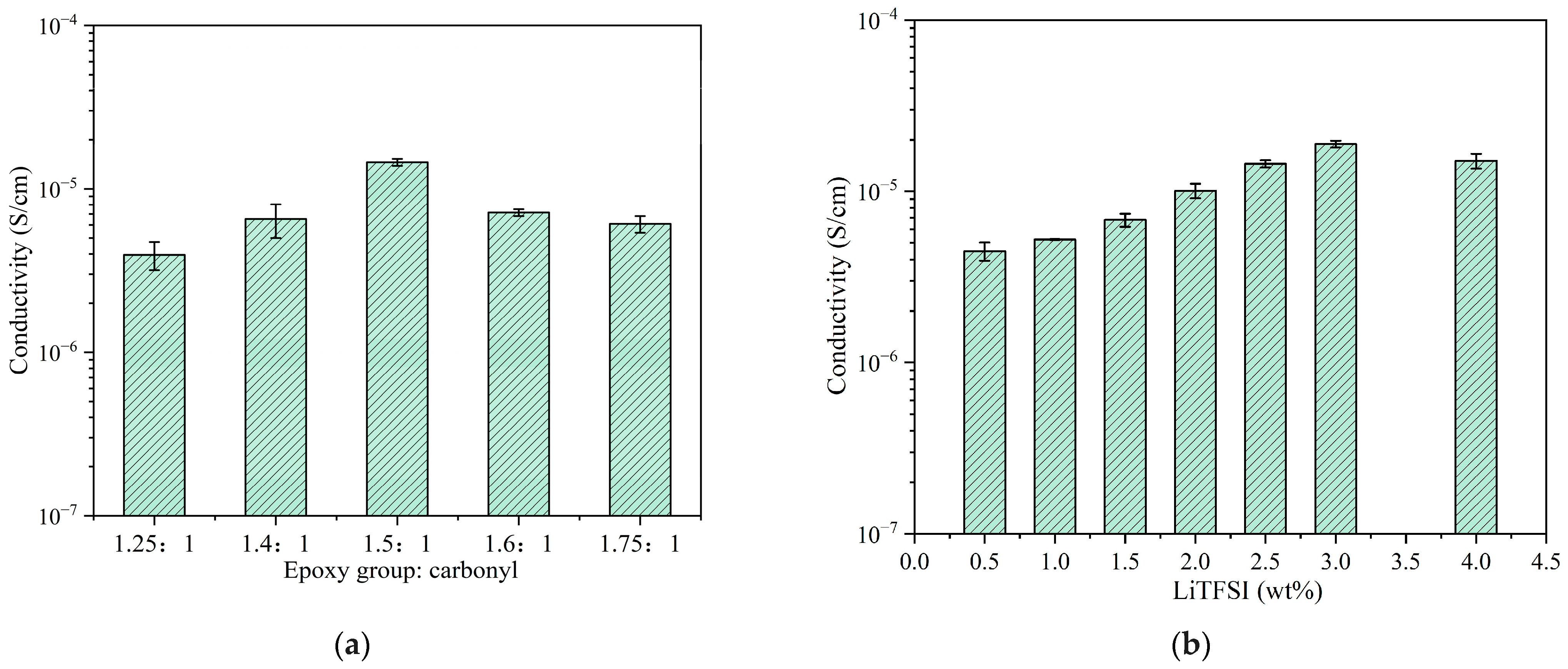
3.2. Electrochemical Performance of the Ester-Linked Vitrimer Electrolytes
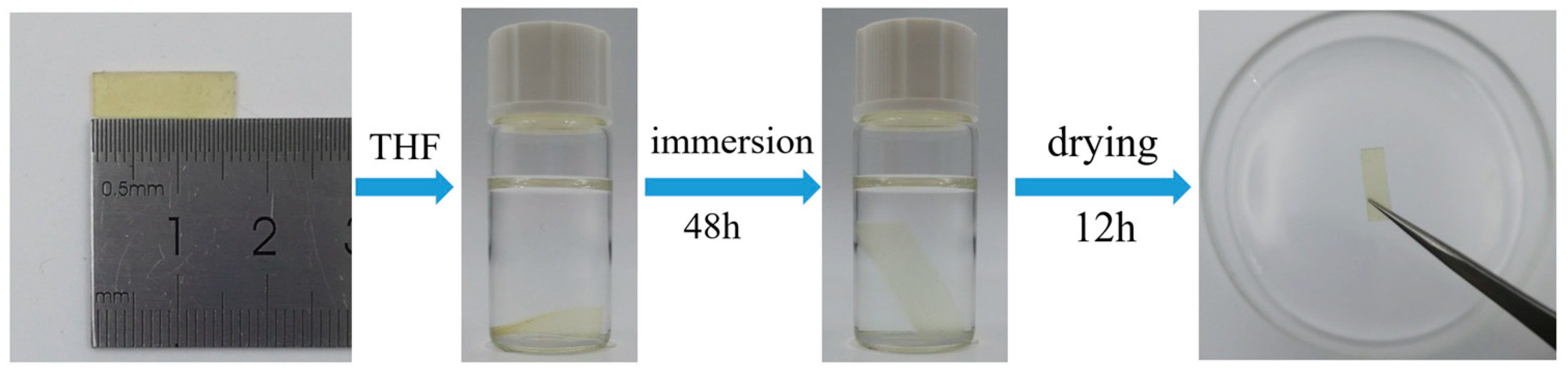
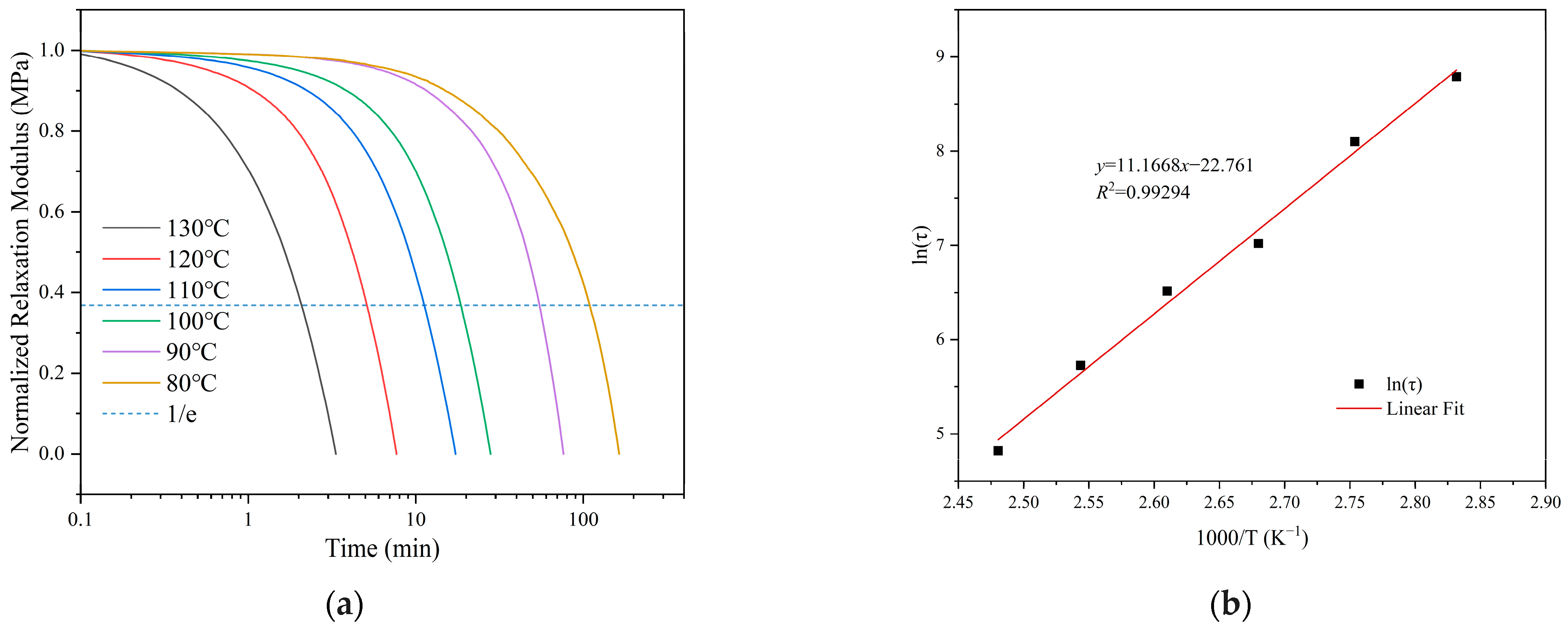
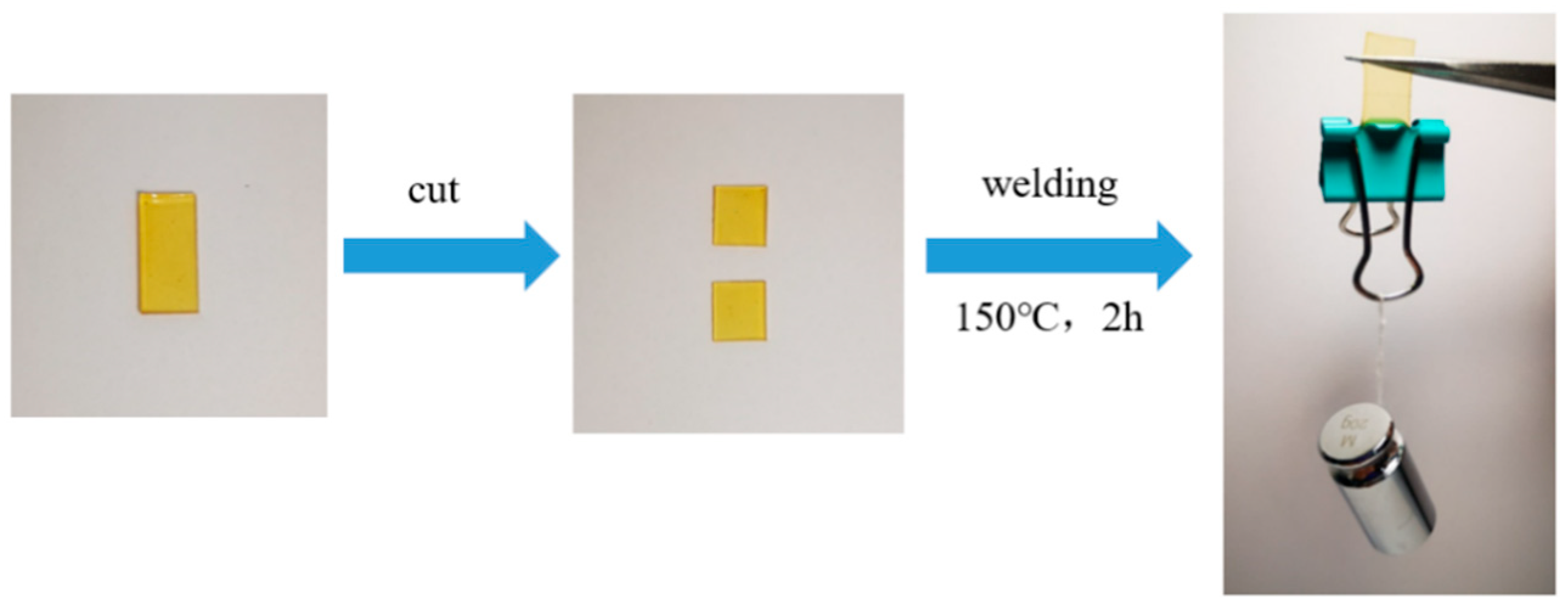
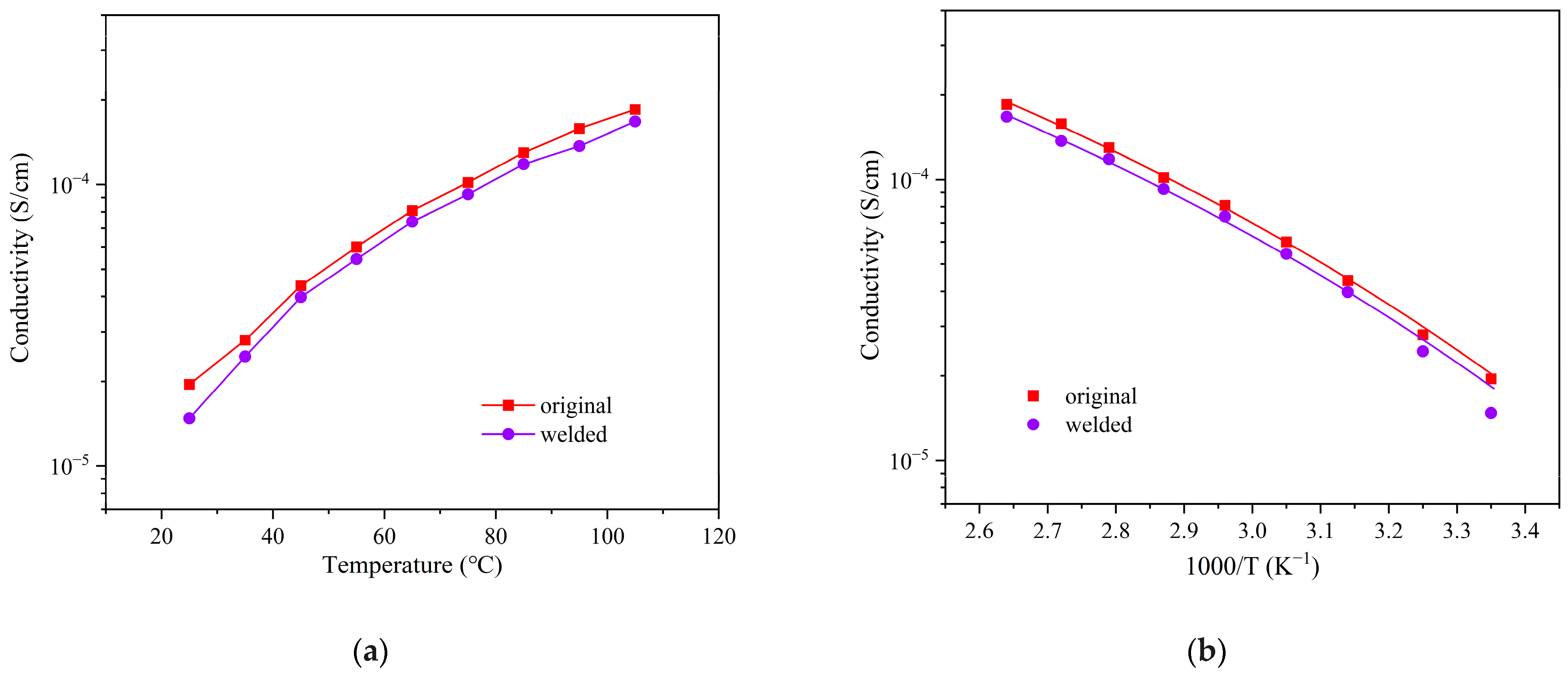
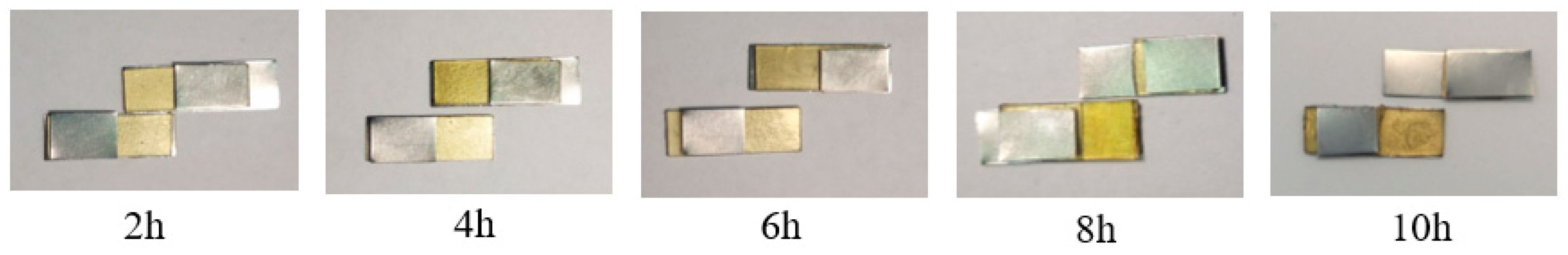
3.3. Recyclability and Reprocessability of the Ester-Linked Vitrimer Electrolytes
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guo, Z.; Zhao, H.; Xiao, Y.; Liang, S.; Zhang, X.; Wang, N.; Yang, J.; Huang, X. Recent Progress of Thin Solid-State Electrolytes and Applications for Solid-State Lithium Pouch Cells. Mater. Today Energy 2025, 48, 101801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asha Shalini, V.J.; Johnsi, M.; Azhagulakshmi, M.; Dhivya, S.; Balasubramanian, N. A Review on Solid-State Electrolytes for Li-S Batteries: Encompassing Background to Recent Advancements. Mater. Res. Bull. 2025, 184, 113249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, B.; Wei, Z.; Yao, S.; Zhao, S.; Gao, Z.; Savilov, S.; Chen, G.; Shen, Z.X.; Du, F. Challenges and Prospectives of Sodium-Containing Solid-State Electrolyte Materials for Rechargeable Metal Batteries. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2025, 163, 100949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, S.; Bashir, T.; Hayat, A.; Abd-Rabboh, H.S.M.; Shen, L.; Orooji, Y.; Lin, H. Recent Progress and Fundamentals of Solid-State Electrolytes for All Solid-State Rechargeable Batteries: Mechanisms, Challenges, and Applications. J. Energy Storage 2024, 92, 112110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Shanmukaraj, D.; Tkacheva, A.; Armand, M.; Wang, G. Polymer Electrolytes for Lithium-Based Batteries: Advances and Prospects. Chem 2019, 5, 2326–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Kim, J.; Kim, J.; Kim, M.; Song, T.; Paik, U. Sustainable and Cost-Effective Electrode Manufacturing for Advanced Lithium Batteries: The Roll-to-Roll Dry Coating Process. Chem. Sci. 2025, 16, 6598–6619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Yang, Q.; Kong, D.; Li, Y.; He, Y.; Zhang, N.; Hu, H. Effect of Thermal Pre-compressing on Ionic Conductivity and Mechanical Properties of PEO -based Solid-state Electrolytes. J Appl. Polym. Sci 2024, 141, e56156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, L.; Ma, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, J.; Dong, S.; Liu, Z.; Cui, G.; Chen, L. All Solid-State Polymer Electrolytes for High-Performance Lithium Ion Batteries. Energy Storage Mater. 2016, 5, 139–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, J.; Liao, S.; Shi, L.; Su, B.; Xu, F.; Guo, Z.; Li, H.; Wei, F. Solid-State Polymer Electrolytes in Lithium Batteries: Latest Progress and Perspective. Polym. Chem. 2024, 15, 473–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wang, T.; Sun, L.; Song, T.; Yan, H.; Li, C.; Mu, D.; Zheng, J.; Dai, Y. Stable Cycling of All-Solid-State Lithium Metal Batteries Enabled by Salt Engineering of PEO-Based Polymer Electrolytes. Energy Env. Mater. 2024, 7, e12580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Li, J.; Li, J.; An, C. Review—Interfaces: Key Issue to Be Solved for All Solid-State Lithium Battery Technologies. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167, 070541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, F.; Wu, L.; Lin, W.; Zhang, Y.; Kang, Q.; Zhang, F.; Shen, Y.; Gao, Q.; Huang, Z.; Huang, Y. Progress and Perspectives on Molecular Design of Crosslinked Polymer Electrolytes for Solid-State Lithium Batteries. Rev. Mater. Res. 2025, 1, 100013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Fu, Q.; Li, Z.; Chen, S.; Wu, J.; Wei, L.; Guo, X. Ultraviolet-Cured Semi-Interpenetrating Network Polymer Electrolytes for High-Performance Quasi-Solid-State Lithium Metal Batteries. Chem. A Eur. J 2021, 27, 7773–7780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, F.; Huang, Y.; Wu, L.; Zhou, S.; Kang, Q.; Lin, W.; Liao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, K.; Shen, Y.; et al. Multisite Crosslinked Poly(Ether-urethane)-Based Polymer Electrolytes for High-Voltage Solid-State Lithium Metal Batteries. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2409269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Zhang, Y.-H.; Shi, F.-N.; Zhang, L.-N. UV-Derived Double Crosslinked PEO-Based Solid Polymer Electrolyte for Room Temperature. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 629, 492–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, W.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, L.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, N.; Liu, Y.; Yan, P.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; et al. An H2O-Initiated Crosslinking Strategy for Ultrafine-Nanoclusters-Reinforced High-Toughness Polymer-In-Plasticizer Solid Electrolyte. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2304712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, W.; Li, F.; Liu, T.; Gong, S.; Gao, Q.; Li, J.; Fang, Z. Recyclable, Self-Healing Solid Polymer Electrolytes by Soy Protein-Based Dynamic Network. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2103623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.; Deng, K.; Xu, Z.; Xiao, M.; Meng, Y. Highly Conductive Self-Healing Polymer Electrolytes Based on Synergetic Dynamic Bonds for Highly Safe Lithium Metal Batteries. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 442, 136083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Park, S.; Kim, S.; Kim, S.-K. Vitrimer with Dynamic Imine Bonds as a Solid-State Electrolyte for Lithium Metal Batteries. Mater. Today Energy 2024, 45, 101690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, B.B.; Evans, C.M. Catalyst-Free Dynamic Networks for Recyclable, Self-Healing Solid Polymer Electrolytes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 18932–18937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yu, Z.; Huang, Z.; Lai, J.-C.; Tok, J.B.-H.; Cui, Y.; Bao, Z. Reprocessable and Recyclable Polymer Network Electrolytes via Incorporation of Dynamic Covalent Bonds. Chem. Mater. 2022, 34, 2393–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, S.; Wang, H.; Hang, G.; Zhang, T.; Li, L.; Zheng, S. Poly(Thiourethane-Co-Ethylene Oxide) Networks Crosslinked with Disulfide Bonds: Reinforcement with POSS and Use for Recyclable Solid Polymer Electrolytes. Polymer 2023, 284, 126318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barabanova, A.I.; Lokshin, B.V.; Kharitonova, E.P.; Afanasyev, E.S.; Askadskii, A.A.; Philippova, O.E. Curing Cycloaliphatic Epoxy Resin with 4-Methylhexahydrophthalic Anhydride: Catalyzed vs. Uncatalyzed Reaction. Polymer 2019, 178, 121590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capelot, M.; Unterlass, M.M.; Tournilhac, F.; Leibler, L. Catalytic Control of the Vitrimer Glass Transition. ACS Macro Lett. 2012, 1, 789–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Kong, D.; He, Y.; Hu, H. A Coupled Electrochemical-Mechanical Model for All-Solid-State Lithium Batteries with Pre-Stretched Solid Polymer Electrolytes. J. Energy Storage 2025, 110, 115302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.; Yang, Q.; He, Y.; Zhang, L.; Hu, H. Finite Elastic-Viscoplastic Deformation Behaviour of PEO-Based Solid Polymer Electrolyte: Experimental Investigation and Constitutive Modelling. Mech. Mater. 2023, 185, 104773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, C.; Nan, W.; Peng, S.; Liu, J.; Yan, S. Polyether-Based Composite Solid-State Electrolyte to Realize Stable High-Rate Cycling for High-Voltage Lithium Metal Batteries at Room Temperature. Mater. Today Chem. 2024, 40, 102219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, L.; Du, X.; Guo, L.; Tan, X.; Tong, Y.; Zhou, D.; Liu, C.; Qin, Y.; Zeng, G. Self-Healing Polymer Electrolytes with Nitrogen-boron Coordinated Boroxine for All-Solid-State Lithium Metal Batteries. J. Energy Storage 2023, 74, 109485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Tong, Y.; Wang, T.; Zhang, A.; Xu, Q. Self-Healing and Recyclable Polyurethane-Based Solid-State Polymer Electrolyte via Diels-Alder Dynamic Network. J. Mol. Struct. 2025, 1321, 139793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Luo, C.; Lu, H.; Yu, K. Primary Recycling of Anhydride-cured Engineering Epoxy Using Alcohol Solvent. Polym. Eng. Sci 2019, 59, E111–E119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimbo, M.; Ochi, M.; Iesako, H. Mechanical Relaxation Mechanism of Epoxide Resins Cured with Acid Anhydrides. J. Polym. Sci. Polym. Phys. Ed. 1984, 22, 1461–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Qi, X.; Tanaka, M.; Kawakami, H. Gel Polymer Electrolyte Membranes Consisted of Solvate Ionic Liquid and Crosslinked Network Polymers Bearing Different Main Chains: Fabrication and Lithium Battery Application. Electrochim. Acta 2025, 514, 145661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, M.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Niu, B.; Tian, L.; Long, D. Dynamically Reversible Cross-Linked Polymer Electrolytes with Highly Ionic Conductivity for Dendrite-Free Lithium Metal Batteries. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 496, 153830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zuo, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Gan, H.; Li, S.; Yu, L.; Zhou, B.; Xue, Z. Covalently Cross-Linked Polymer Stabilized Electrolytes with Self-Healing Performance via Boronic Ester Bonds. Polym. Chem. 2020, 11, 5893–5902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.D.; Roh, S.; Nguyen, M.T.N.; Nam, Y.; Kim, D.-J.; Lim, B.; Yoon, Y.S.; Lee, J.S. Synthesis of a Copolymer with a Dynamic Disulfide Network and Its Application to a Lithium-Ion Capacitor Polymer Electrolyte. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 497, 154430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whba, R.; Su’ait, M.S.; TianKhoon, L.; Ibrahim, S.; Mohamed, N.S.; Ahmad, A. In-Situ UV Cured Acrylonitrile Grafted Epoxidized Natural Rubber (ACN-g-ENR)—LiTFSI Solid Polymer Electrolytes for Lithium-Ion Rechargeable Batteries. React. Funct. Polym. 2021, 164, 104938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, L.; Tan, X.; Du, X.; Xue, X.; Tong, Y.; Zhou, D.; Ling, Y.; Xie, Y.; Zhao, J. Self-Healing Polymer Electrolytes with Dynamic-Covalent Borate for Solid-State Lithium Metal Batteries. Eur. Polym. J. 2023, 195, 112191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, Y.H.; Li, S.; Zuo, C.; Zhang, Y.; Gan, H.; Li, S.; Yu, L.; He, D.; Xie, X.; Xue, Z. Self-Healing Solid Polymer Electrolyte Facilitated by a Dynamic Cross-Linked Polymer Matrix for Lithium-Ion Batteries. Macromolecules 2020, 53, 1024–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Wang, X.; Xu, Z.; Guan, T.; Mo, D.; Deng, K. Rapid Self-Healing, Highly Conductive and near-Single-Ion Conducting Gel Polymer Electrolytes Based on Dynamic Boronic Ester Bonds for High-Safety Lithium Metal Batteries. J. Energy Storage 2024, 75, 109712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Zhu, S.; Jiang, Z.; Tang, X.; Tian, T.; Hu, Z.; Du, P.; Wang, Y.; Tang, H. Dual In-Situ Curing Gel Polymer Electrolyte for Solid-State Lithium Battery. Mater. Today Commun. 2025, 45, 112414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Youcef, H.; Garcia-Calvo, O.; Lago, N.; Devaraj, S.; Armand, M. Cross-Linked Solid Polymer Electrolyte for All-Solid-State Rechargeable Lithium Batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 220, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Sherlock, D.; West, R.; West, R.; Amine, K.; Lyons, L.J. Cross-Linked Network Polymer Electrolytes Based on a Polysiloxane Backbone with Oligo(Oxyethylene) Side Chains: Synthesis and Conductivity. Macromolecules 2003, 36, 9176–9180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boaretto, N.; Joost, C.; Seyfried, M.; Vezzù, K.; Di Noto, V. Conductivity and Properties of Polysiloxane-Polyether Cluster-LiTFSI Networks as Hybrid Polymer Electrolytes. J. Power Sources 2016, 325, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mindemark, J.; Lacey, M.J.; Bowden, T.; Brandell, D. Beyond PEO—Alternative Host Materials for Li+-Conducting Solid Polymer Electrolytes. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2018, 81, 114–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin Rusayyis, M.A.; Torkelson, J.M. Reprocessable Covalent Adaptable Networks with Excellent Elevated-Temperature Creep Resistance: Facilitation by Dynamic, Dissociative Bis(Hindered Amino) Disulfide Bonds. Polym. Chem. 2021, 12, 2760–2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, L.; Rowan, S.J. Trapping Dynamic Disulfide Bonds in the Hard Segments of Thermoplastic Polyurethane Elastomers. Macro Chem. Phys. 2017, 218, 1600320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| LiTFSI (wt%) | A (S/cm) | T0 (K) | Ea (kJ/mol) | Tg (K) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5% | 8.76 × 10−3 | 174 | 7.98 | 224 |
| 1.0% | 6.76 × 10−3 | 172 | 7.49 | 222 |
| 1.5% | 6.12 × 10−3 | 171 | 6.97 | 221 |
| 2.0% | 6.48 × 10−3 | 170 | 6.79 | 220 |
| 2.5% | 5.80 × 10−3 | 170 | 6.38 | 220 |
| 3.0% | 6.91 × 10−3 | 169 | 6.27 | 219 |
| 4.0% | 7.97 × 10−3 | 168 | 6.86 | 218 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, X.; Zhang, H.; Hu, H. Dynamic Ester-Linked Vitrimers for Reprocessable and Recyclable Solid Electrolytes. Polymers 2025, 17, 1991. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17141991
Shi X, Zhang H, Hu H. Dynamic Ester-Linked Vitrimers for Reprocessable and Recyclable Solid Electrolytes. Polymers. 2025; 17(14):1991. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17141991
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Xiaojuan, Hui Zhang, and Hongjiu Hu. 2025. "Dynamic Ester-Linked Vitrimers for Reprocessable and Recyclable Solid Electrolytes" Polymers 17, no. 14: 1991. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17141991
APA StyleShi, X., Zhang, H., & Hu, H. (2025). Dynamic Ester-Linked Vitrimers for Reprocessable and Recyclable Solid Electrolytes. Polymers, 17(14), 1991. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17141991








