Next-Generation Sustainable Composites with Flax Fibre and Biobased Vitrimer Epoxy Polymer Matrix
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
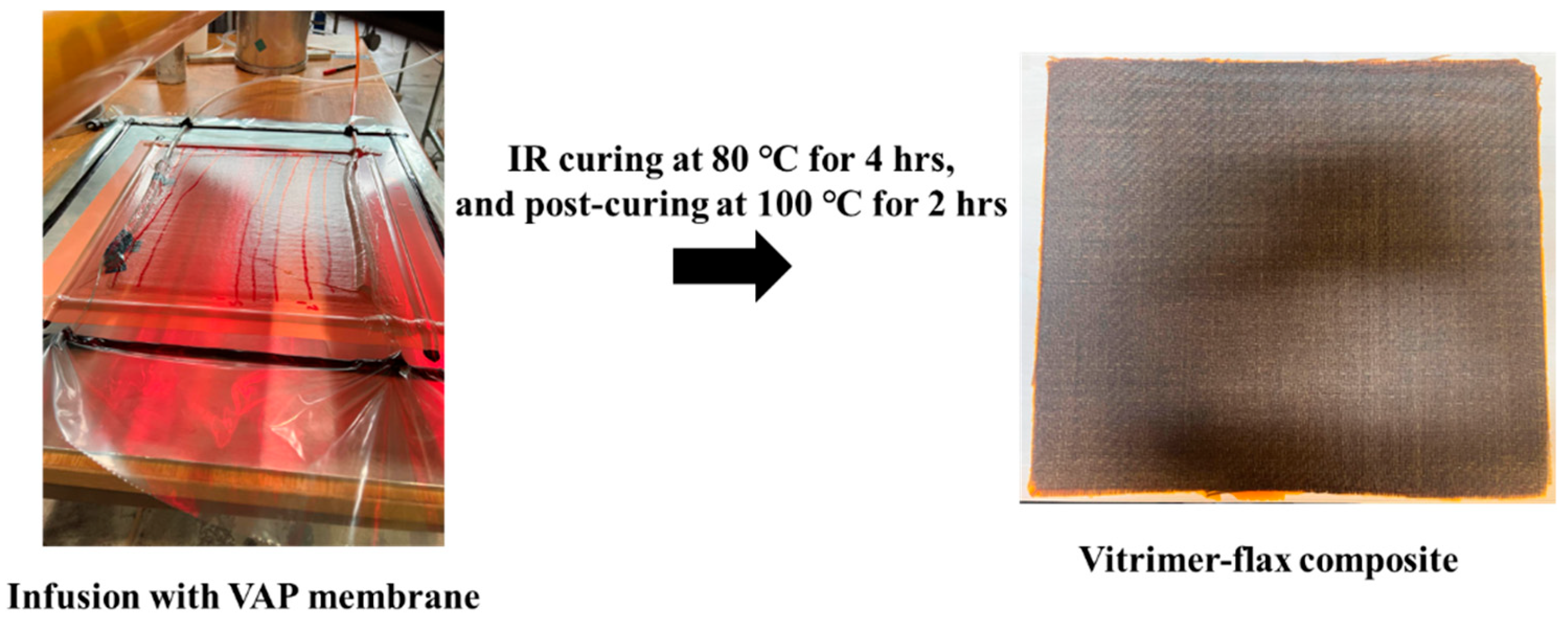
2.2. Preparation of Vitrimer Epoxy Resin (VER) and Vitrimer Epoxy Flax Fibre-Reinforced Composites (VER-FFRC)
2.3. Characterisation
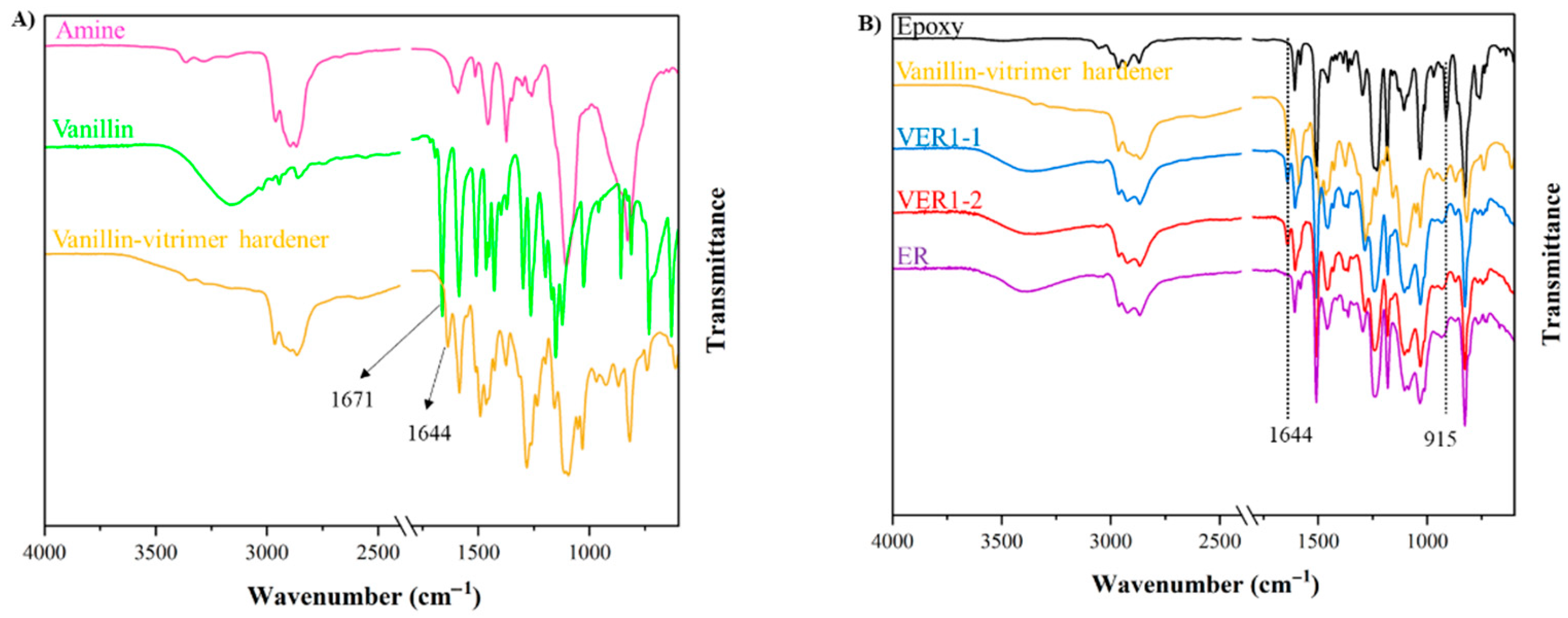
2.3.1. Chemical Characterisation
2.3.2. Rheological Characterisation
2.3.3. Morphological Characterisation
2.3.4. Thermomechanical Characterisation
2.3.5. Mechanical Characterisation
2.3.6. Solvent Resistance
2.3.7. Chemical Recyclability
3. Results and Discussion
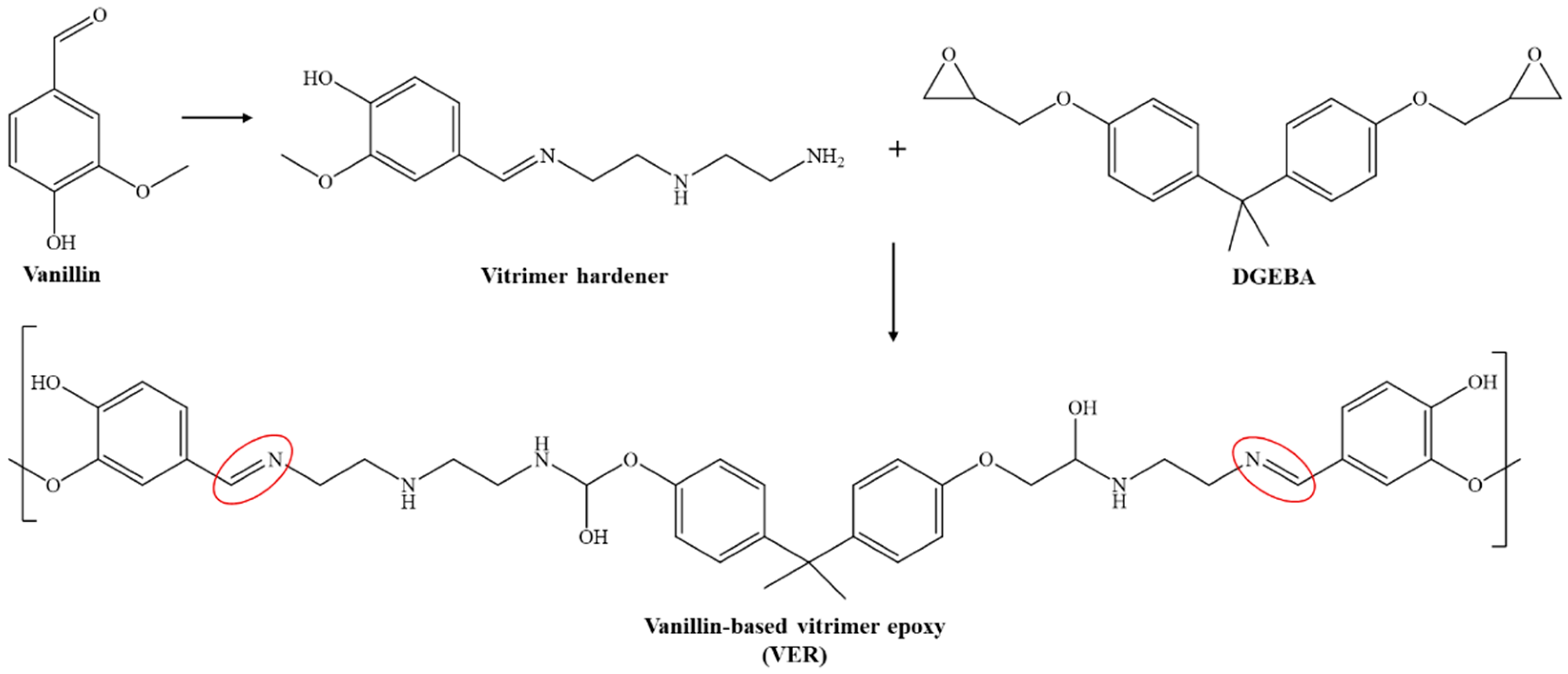
3.1. Formation and Structural Polymerisation of Vanillin-Based Vitrimer Hardener (V-Hardener) and Vitrimer Epoxy Resin (VER)
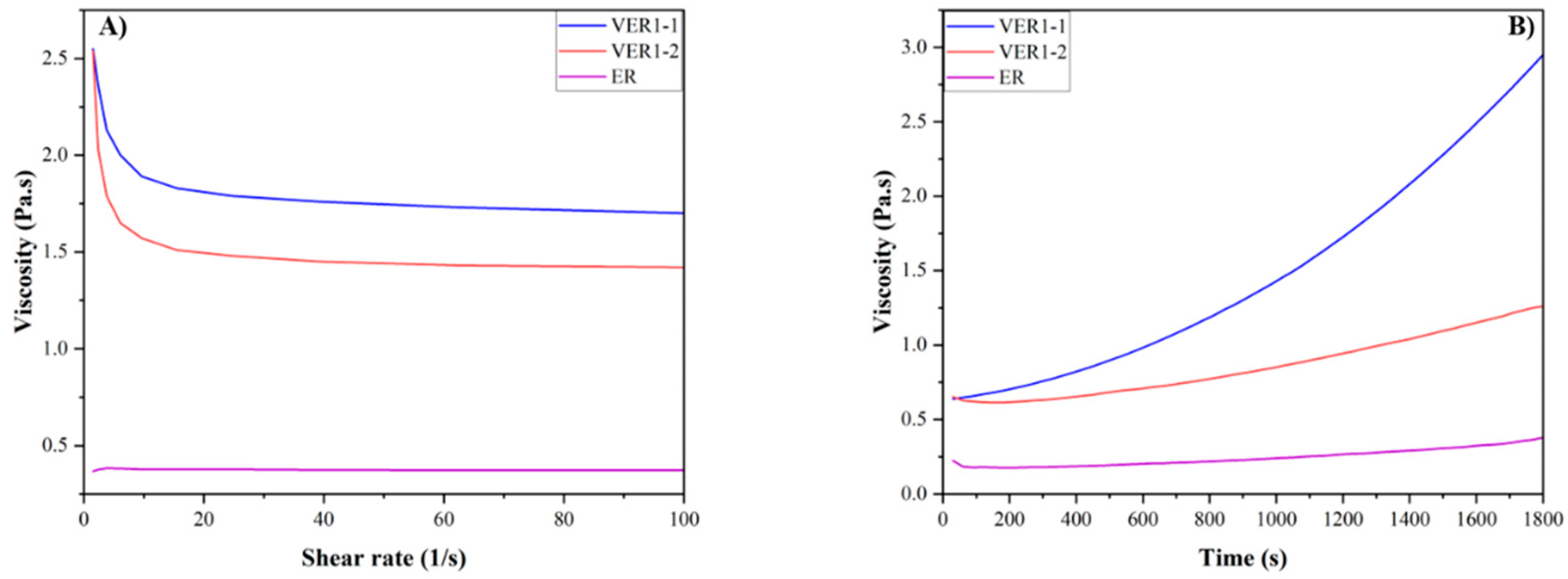
3.2. Viscosity of the Vitrimer Epoxy Resin
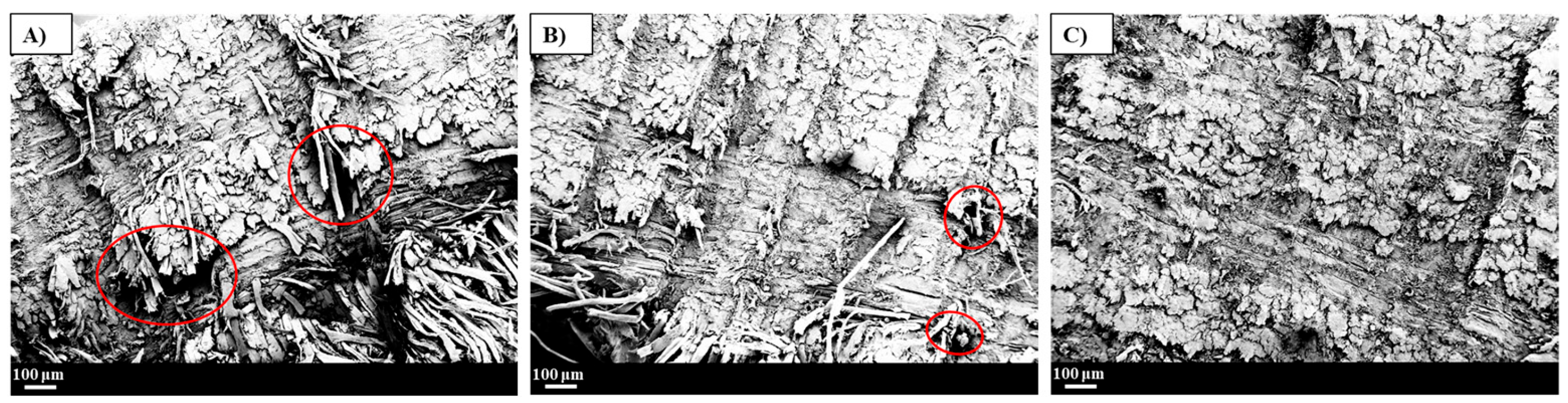
3.3. Fracture Morphology of the Vitrimer Flax Fibre-Reinforced Composites
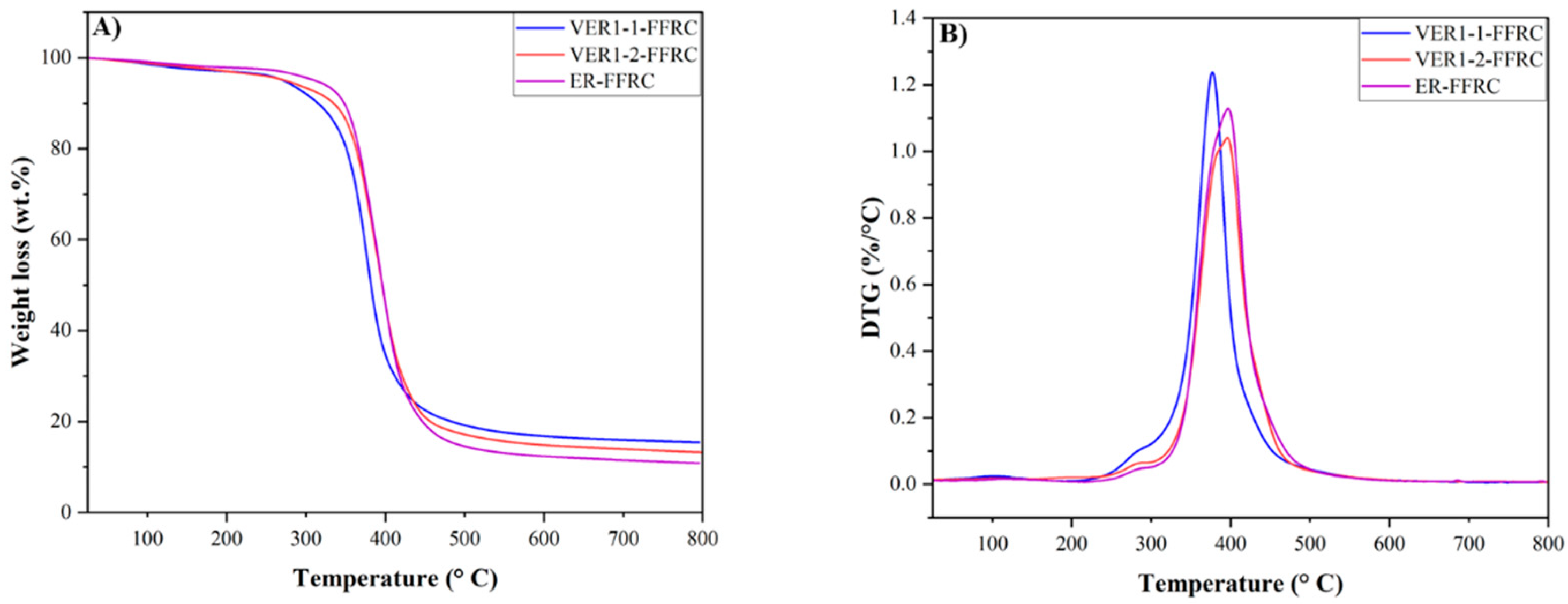
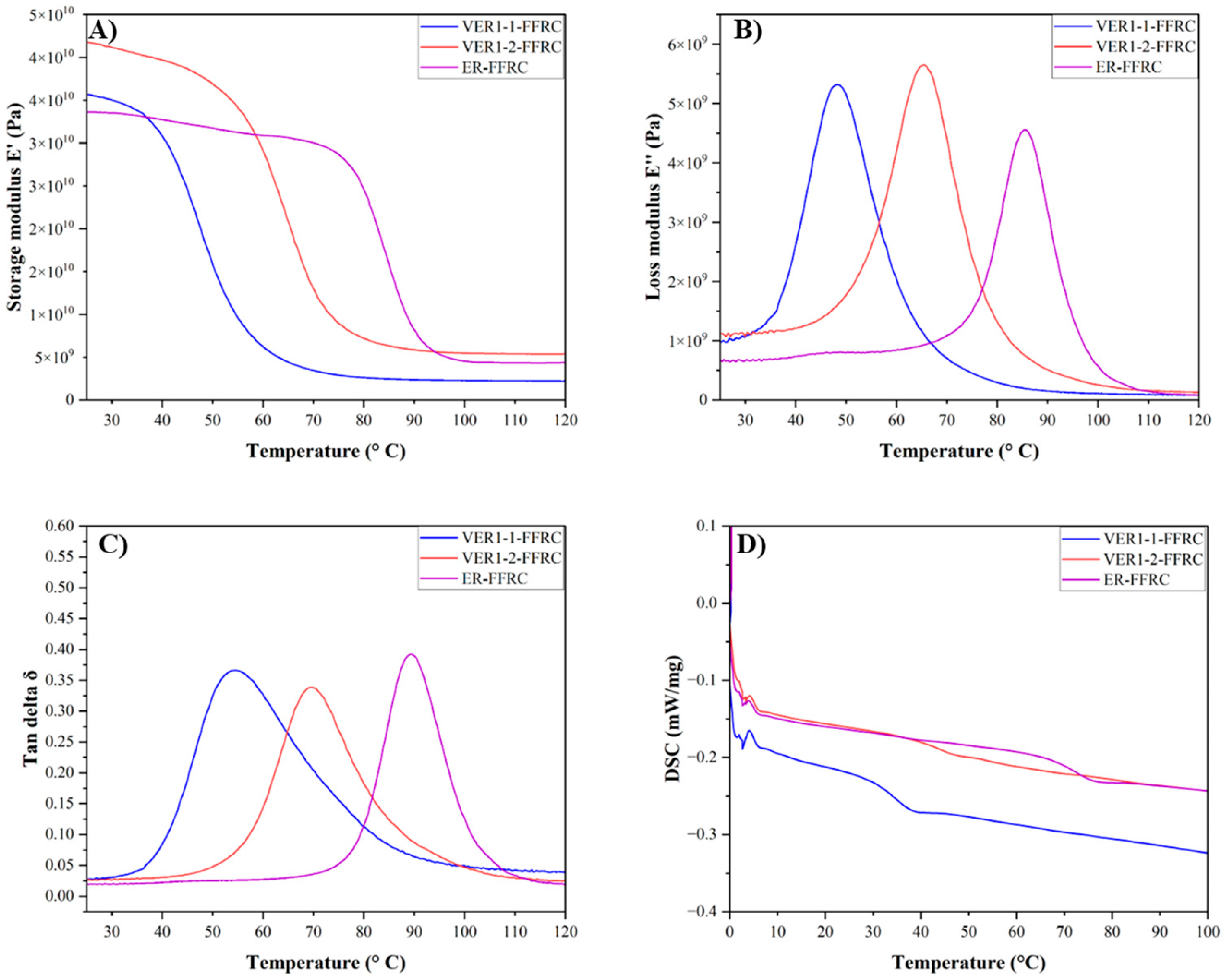
3.4. Thermomechanical Characteristics (TGA, DSC, and DMA)
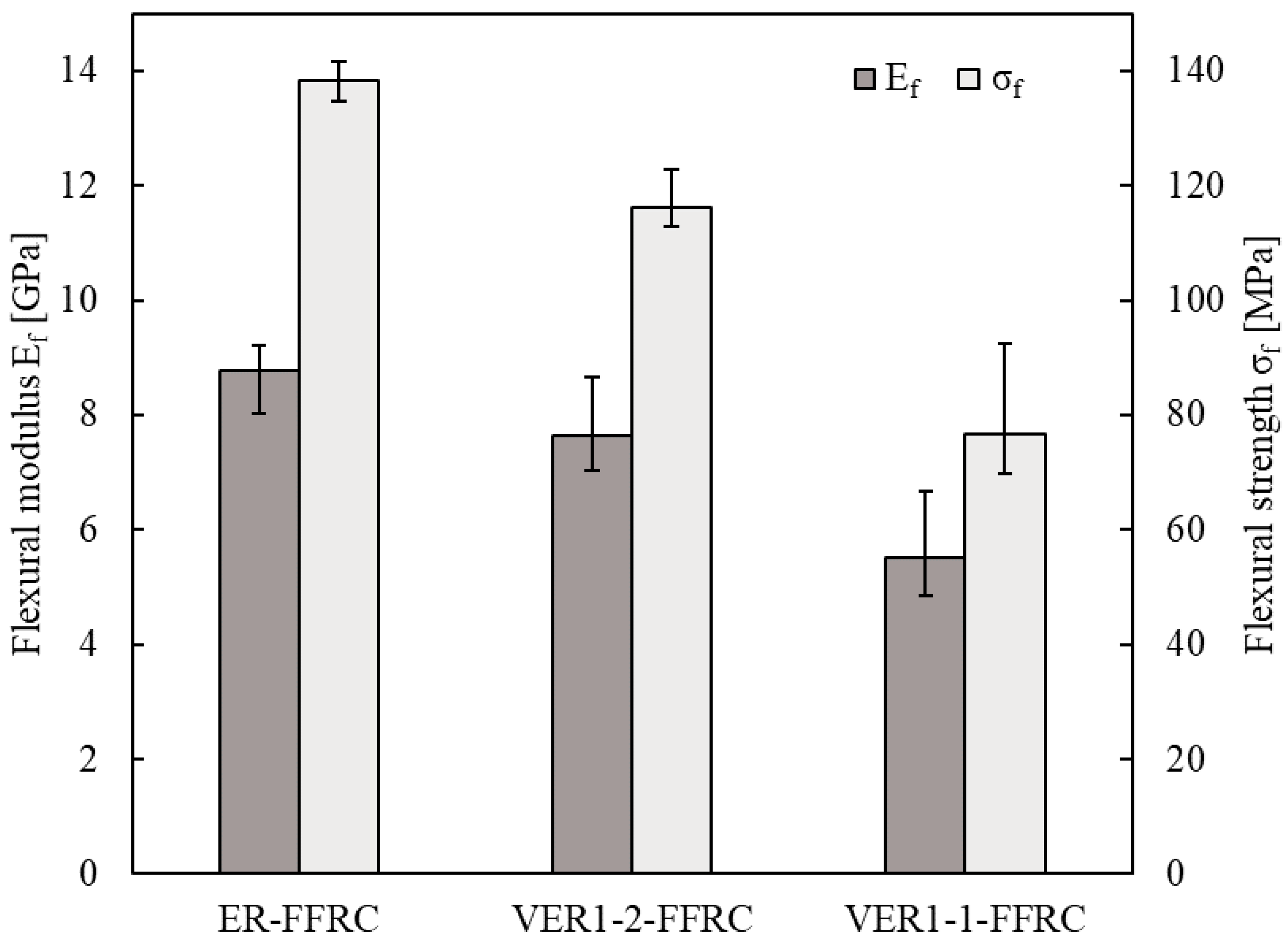
3.5. Mechanical Characteristics (Flexural 4-Point Bending Test)
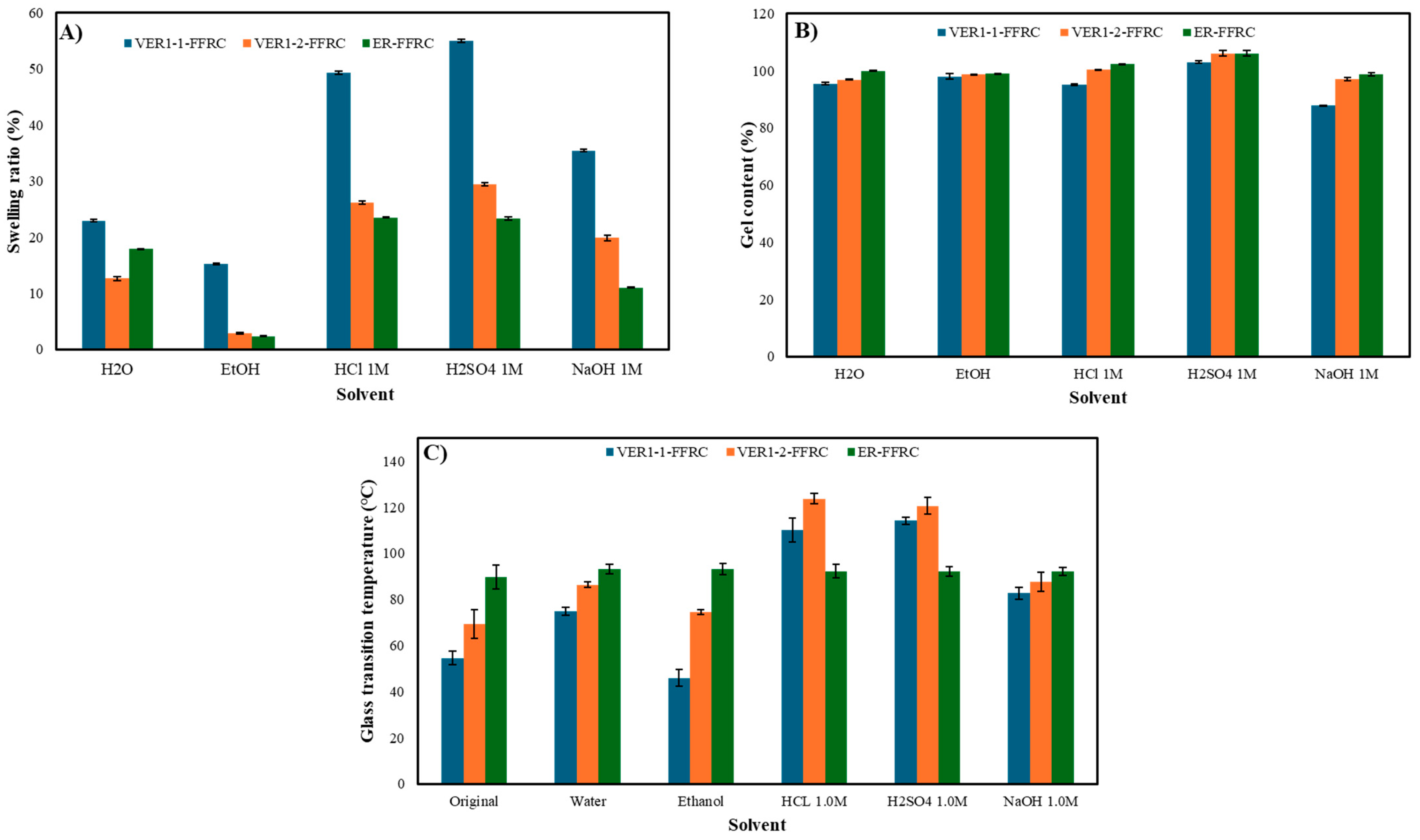
3.6. Solvent Resistance Test
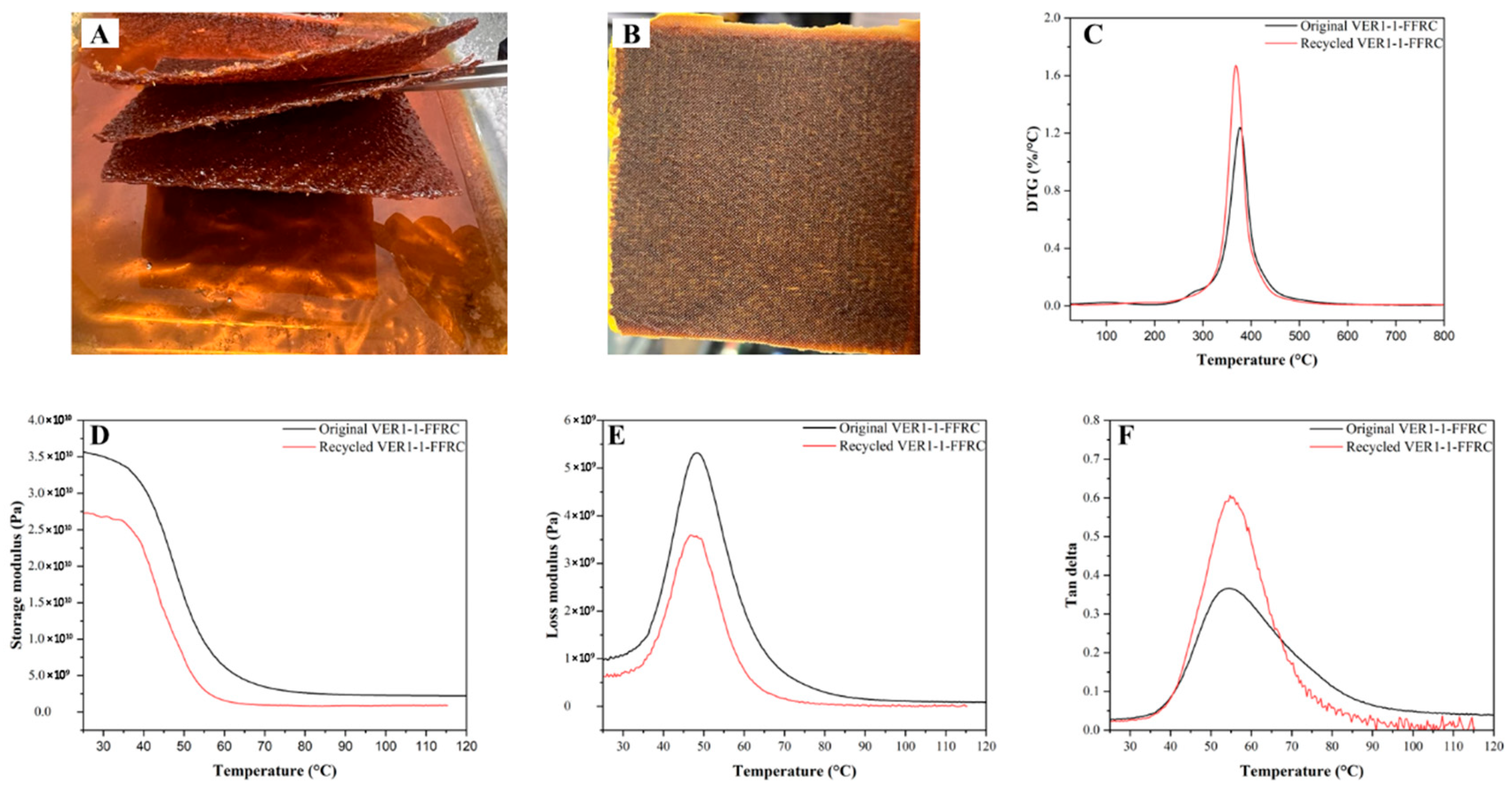
3.7. Chemical Recyclability in Aradur Hardener
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dong, K.; Tang, S.; Zhao, D.; Pang, Y.; Zhao, C. Vanillin-derived bio-based epoxy resins containing dual dynamic Schiff base and disulfide bonds with reprocessability and degradability. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2024, 230, 111077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.; Gangil, B.; Ranakoti, L.; Verma, J. 4—Study of physical, thermal, and mechanical properties of thermosetting polymer composites. In Dynamic Mechanical and Creep-Recovery Behavior of Polymer-Based Composites; Verma, A., Jain, N., Rangappa, S.M., Siengchin, S., Matykiewicz, D., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024; pp. 33–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangil, B.; Kumar, S.; Tejyan, S.; Ranakoti, L.; Verma, S. 2—Introduction to thermosetting polymer composites: Applications, advantages, and drawbacks. In Dynamic Mechanical and Creep-Recovery Behavior of Polymer-Based Composites; Verma, A., Jain, N., Rangappa, S.M., Siengchin, S., Matykiewicz, D., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024; pp. 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Hu, H.; Lin, Z.; Cao, C.; Liu, H.; Li, X.; Yao, H. A novel method of reclaiming high-value carbon fiber from waste epoxy composite via molten salt thermal treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 496, 153792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.M.; Shah, A.H.; Wang, S.; Mehmood, S.; Wang, J.; Liu, W.; Xu, X. A comprehensive review on epoxy biocomposites based on natural fibers and bio-fillers: Challenges, recent developments and applications. Adv. Fiber Mater. 2022, 4, 683–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteserin, C.; Blanco, M.; Uranga, N.; Sanchez, J.; Laza, J.M.; Vilas, J.L.; Aranzabe, E. Sustainable biobased epoxy thermosets with covalent dynamic imine bonds for green composite development. Polymer 2023, 285, 126339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Xue, C.; Chen, X.; Wu, H.; Sui, L.; Li, X. Comparative analysis of natural fiber reinforced polymer and carbon fiber reinforced polymer in strengthening of reinforced concrete beams. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 263, 121572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Dai, S.; Zhang, H.; Bi, L.; Jiang, J.; Chen, Y. Reprocessable, Self-Adhesive, and Recyclable Carbon Fiber-Reinforced Composites Using a Catalyst-Free Self-Healing Bio-Based Vitrimer Matrix. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 16281–16290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.; Radjef, R.; Nikzad, M.; Bjekovic, R.; Fox, B. A vanillin-based vitrimer matrix for recyclable and sustainable carbon fibre-reinforced composites. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 483, 144289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Shen, M.; Fu, F.; Li, Q.; Liu, H.; Song, Z. High strength, self-healing and hydrophobic fully bio-based polybenzoxazine reinforced pine oleoresin-based vitrimer and its application in carbon fiber reinforced polymers. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 484, 149585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Hong, Y.; Jeong, J.; Oh, D.; Goh, M. Robust Biobased Vitrimers and Its Application to Closed-Loop Recyclable Carbon Fiber-Reinforced Composites. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 14112–14123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Dai, S.; Xu, S.; Wang, J.; Bi, L.; Jiang, J.; Chen, Y. Hyperbranched polyester catalyzed self-healing bio-based vitrimer for closed-loop recyclable carbon fiber-reinforced polymers. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2022, 228, 109676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.T.; Nisha, S.S.; Radjef, R.; Nikzad, M.; Bjekovic, R.; Fox, B. Recyclable and Biobased Vitrimers for Carbon Fibre-Reinforced Composites—A Review. Polymers 2024, 16, 1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debsharma, T.; Engelen, S.; De Baere, I.; Van Paepegem, W.; Du Prez, F. Resorcinol-Derived Vitrimers and Their Flax Fiber-Reinforced Composites Based on Fast Siloxane Exchange. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2023, 44, 2300020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fei, M.; Liu, W.; Shao, L.; Cao, Y.; Bliss, B.J.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, J. Hemp fiber reinforced dual dynamic network vitrimer biocomposites with direct incorporation of amino silane. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 480, 148091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, P.; Nutt, S. Flax–reinforced vitrimer epoxy composites produced via RTM. J. Compos. Sci. 2024, 8, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohewal, S.S.; Yu, Z.; Kearney, L.T.; Toomey, M.D.; Ghossein, H.K.; Naskar, A.K. Flax fiber-reinforced fatty acid vitrimer biocomposite with enhanced chemical recyclability. MRS Commun. 2024, 14, 534–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Yang, W.; Qi, W.; Chen, Z.; Lin, J.; Bian, X.; He, S. Cost-efficient and recyclable epoxy vitrimer composite with low initial viscosity based on exchangeable disulfide crosslinks. Polym. Test. 2022, 113, 107670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obadia, M.M.; Jourdain, A.; Cassagnau, P.; Montarnal, D.; Drockenmuller, E. Tuning the viscosity profile of ionic vitrimers incorporating 1, 2, 3-triazolium cross-links. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1703258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Formon, G.J.; Storch, S.; Delplanque, A.Y.G.; Bresson, B.; Van Zee, N.J.; Nicolaÿ, R. Overcoming the tradeoff between processability and mechanical performance of elastomeric vitrimers. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2306065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schenk, V.; Labastie, K.; Destarac, M.; Olivier, P.; Guerre, M. Vitrimer composites: Current status and future challenges. Mater. Adv. 2022, 3, 8012–8029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DIN EN ISO 14125; Fibre-Reinforced Plastic Composites—Determination of Flexural Properties. Deutsches Institut für Normung e.V.: Berlin, Germany, 2011.
- Rashid, M.A.; Zhu, S.; Jiang, Q.; Wei, Y.; Liu, W. Developing easy processable, recyclable, and self-healable biobased epoxy resin through dynamic covalent imine bonds. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2022, 5, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, X.; Cui, X.; Qin, J.; Shi, M.; Wang, D.; Liang, L.; Yang, C. Imine-Containing Epoxy Vitrimer Cured by Active Ester: Properties and Theoretical Analysis. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2023, 5, 10042–10052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Wang, D. Comparing Surface and Bulk Curing Processes of an Epoxy Vitrimer. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 15479–15486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soman, B.; Evans, C.M. Effect of precise linker length, bond density, and broad temperature window on the rheological properties of ethylene vitrimers. Soft Matter 2021, 17, 3569–3577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taplan, C.; Guerre, M.; Winne, J.M.; Du Prez, F.E. Fast processing of highly crosslinked, low-viscosity vitrimers. Mater. Horiz. 2020, 7, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klosterman, D.; Browning, C.; Hakim, I.; Lach, K. Investigation of various techniques for controlled void formation in fiberglass/epoxy composites. J. Compos. Mater. 2021, 55, 489–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, K.; McIlhagger, A.; Harkin-Jones, E.; McGarrigle, C.; Dixon, D.; Shar, M.A.; McMillan, A.; Archer, E. Characterization of continuous carbon fibre reinforced 3D printed polymer composites with varying fibre volume fractions. Compos. Struct. 2022, 282, 115033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Hao, C.; Zhang, S.; Yang, X.; Wang, L.; Han, J.; Li, Y.; Xin, J.; Zhang, J. A Self-Healable High Glass Transition Temperature Bioepoxy Material Based on Vitrimer Chemistry. Macromolecules 2018, 51, 5577–5585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memon, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, Q.; Liu, W. An imine-containing epoxy vitrimer with versatile recyclability and its application in fully recyclable carbon fiber reinforced composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2020, 199, 108314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memon, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhu, C. Correlating the thermomechanical properties of a novel bio-based epoxy vitrimer with its crosslink density. Mater. Today Commun. 2021, 29, 102814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamani, P.; Zabihi, O.; Ahmadi, M.; Mahmoodi, R.; Kannangara, T.; Joseph, P.; Naebe, M. Biobased Carbon Fiber Composites with Enhanced Flame Retardancy: A Cradle-to-Cradle Approach. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 10, 1059–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamani, P.; Zabihi, O.; Ahmadi, M.; Mahmoodi, R.; Naebe, M. The Quest for Sustainable Composites: Developing High-Performance, Flame-Retardant, and Recyclable Carbon Fiber-Reinforced Epoxy Vitrimer Composites. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2024, 6, 3611–3623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamani, P.; Zabihi, O.; Ahmadi, M.; Zamani, M.R.; Zohuriaan-Mehr, M.J.; Kannangara, T.; Joseph, P.; Naebe, M. Assessing sustainability and green chemistry in synthesis of a Vanillin-based vitrimer at scale: Enabling sustainable manufacturing of recyclable carbon fiber composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2024, 179, 108016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Saed, M.O.; Terentjev, E.M. Rheology of vitrimers. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; de la Cruz, M.O. Effect of molecular structure on the dynamics and viscoelasticity of vitrimers. Polymer 2024, 308, 127371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, K.L.; Lai, J.C.; Rahman, R.A.; Adrus, N.; Al-Saffar, Z.H.; Hassan, A.; Lim, T.H.; Wahit, M.U. A review on recent approaches to sustainable bio-based epoxy vitrimer from epoxidized vegetable oils. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 189, 115857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javanshour, F.; Prapavesis, A.; Pärnänen, T.; Orell, O.; Lessa Belone, M.C.; Layek, R.K.; Kanerva, M.; Kallio, P.; Van Vuure, A.W.; Sarlin, E. Modulating impact resistance of flax epoxy composites with thermoplastic interfacial toughening. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2021, 150, 106628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, K.; Ahmad, F.; Dawood, M.S.I.S.; Islam, M.S.; Ali, S.; Raza, A.; Shahed, C.A. Mechanical property enhancement of graphene-kenaf-epoxy multiphase composites for automotive applications. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2024, 177, 107916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, F.; Zhao, R.; Li, C.; Xi, Z.; Wang, Q.; Xie, H. Influence of the epoxy/acid stoichiometry on the cure behavior and mechanical properties of epoxy vitrimers. Molecules 2022, 27, 6335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, P.-X.; Li, Y.-D.; Hu, Z.; Zeng, J.-B. Fire-resistant and high-performance epoxy vitrimers for fully recyclable carbon fiber-reinforced composites. Mater. Today Chem. 2024, 36, 101965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbard, A.M.; Ren, Y.; Sarvestani, A.; Konkolewicz, D.; Picu, C.R.; Roy, A.K.; Varshney, V.; Nepal, D. Recyclability of Vitrimer materials: Impact of catalyst and processing conditions. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 29125–29134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, H.-I.; Hu, J.-Y.; Shiu, J.-W.; Rwei, S.-P.; Chen, C.-W. Sustainability and repeatedly recycled epoxy-based vitrimer electromagnetic shielding composite material. Polym. Test. 2023, 127, 108200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Samples | Vanillin (grams) | Aradur® 3487 Hardener (grams) | v-Hardener (grams) | Araldite® LY 1564 Epoxy (grams) | Curing Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| v-hardener | 10 | 20 | - | - | |
| VER1-1 | - | - | 10 | 10 |
|
| VER1-2 | - | - | 10 | 20 | |
| VER1-1-FFRC | - | - | 100 | 100 | |
| VER1-2-FFRC | - | - | 75 | 150 | |
| ER-FFRC (reference) * | - | 34 | - | 100 | |
| Fibre volume fraction for all flax composite samples is 30% | |||||
| Sample | Td5% (℃) | Tdeg (℃) | Char Residue at 800 °C (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| VER1-1-FFRC | 271.6 | 377.0 | 15.42 |
| VER1-2-FFRC | 274.5 | 395.9 | 12.44 |
| ER-FFRC Reference | 311.7 | 396.7 | 10.82 |
| Sample | Tga (°C) | Tgb (°C) | (MPa) | υe (mol·m−3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VER1-1-FFRC | 54.1 | 34.4 | 2872.9 | 321.3 |
| VER1-2-FFRC | 68.8 | 42.7 | 4034.1 | 433.5 |
| ER-FFRC Reference | 83.4 | 71.2 | 4298.2 | 440.1 |
| Sample ID | Tg (°C) | υe (mol·m−3) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| VER1-1-FFRC | Original | 54.1 ± 2.07 | 319.5 ± 2.47 |
| Water | 73.0 ± 2.14 | 233.2 ± 25.3 | |
| Ethanol | 47.7 ± 6.12 | 221.0 ± 1.41 | |
| HCl 1.0 M | 109.6 ± 1.82 | 580.2 ± 3.75 | |
| H2SO4 1.0 M | 109.7 ± 4.80 | 616.7 ± 39.6 | |
| NaOH 1.0 M | 77.4 ± 6.43 | 215.1 ± 34.3 | |
| VER1-2-FFRC | Original | 68.8 ± 1.89 | 434.7 ± 1.68 |
| Water | 83.6 ± 2.79 | 369.6 ± 12.6 | |
| Ethanol | 71.9 ± 3.30 | 359.7 ± 4.78 | |
| HCl 1.0 M | 115.2 ± 11.7 | 433.9 ± 35.8 | |
| H2SO4 1.0 M | 111.4 ± 12.6 | 401.3 ± 34.1 | |
| NaOH 1.0 M | 84.8 ± 5.17 | 463.0 ± 9.14 | |
| ER-FFRC | Original | 83.4 ± 7.11 | 442.9 ± 3.87 |
| Water | 87.2 ± 7.80 | 383.4 ± 17.6 | |
| Ethanol | 86.7 ± 8.85 | 456.8 ± 8.93 | |
| HCl 1.0 M | 87.7 ± 6.70 | 485.6 ± 37.5 | |
| H2SO4 1.0 M | 87.8 ± 7.37 | 420.6 ± 11.6 | |
| NaOH 1.0 M | 87.9 ± 6.08 | 376.3 ± 15.5 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tran, H.T.T.; Baur, J.; Radjef, R.; Nikzad, M.; Bjekovic, R.; Carosella, S.; Middendorf, P.; Fox, B. Next-Generation Sustainable Composites with Flax Fibre and Biobased Vitrimer Epoxy Polymer Matrix. Polymers 2025, 17, 1891. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17141891
Tran HTT, Baur J, Radjef R, Nikzad M, Bjekovic R, Carosella S, Middendorf P, Fox B. Next-Generation Sustainable Composites with Flax Fibre and Biobased Vitrimer Epoxy Polymer Matrix. Polymers. 2025; 17(14):1891. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17141891
Chicago/Turabian StyleTran, Hoang Thanh Tuyen, Johannes Baur, Racim Radjef, Mostafa Nikzad, Robert Bjekovic, Stefan Carosella, Peter Middendorf, and Bronwyn Fox. 2025. "Next-Generation Sustainable Composites with Flax Fibre and Biobased Vitrimer Epoxy Polymer Matrix" Polymers 17, no. 14: 1891. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17141891
APA StyleTran, H. T. T., Baur, J., Radjef, R., Nikzad, M., Bjekovic, R., Carosella, S., Middendorf, P., & Fox, B. (2025). Next-Generation Sustainable Composites with Flax Fibre and Biobased Vitrimer Epoxy Polymer Matrix. Polymers, 17(14), 1891. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17141891







