Medicago Sativa Stems—A Multi-Output Integrated Biorefinery Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
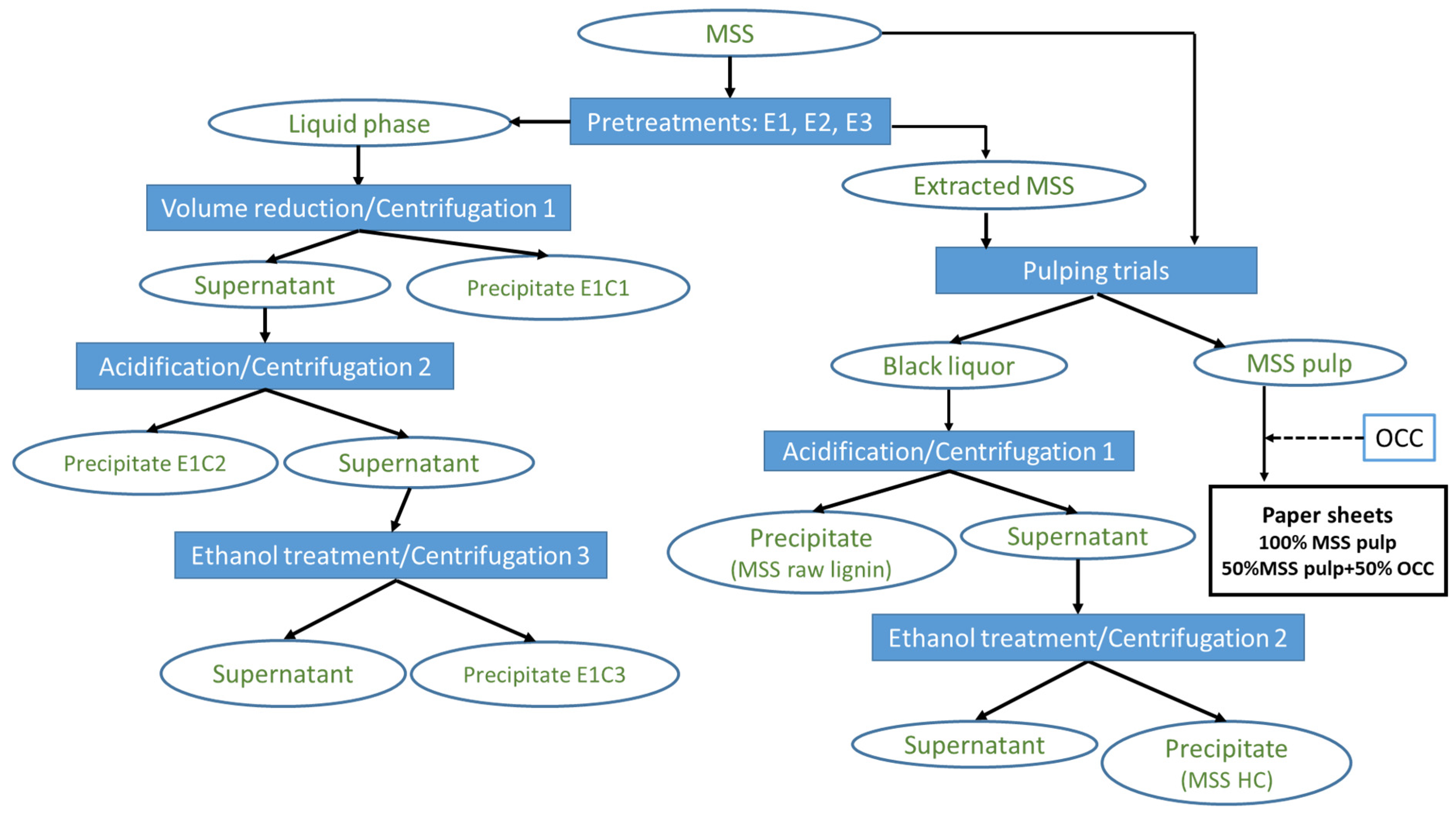
2.2. Experimental Approach
2.2.1. Pretreatments
2.2.2. SMSS Processing via Alkaline Treatment (Soda Pulping)
2.2.3. LMSS Processing and Component Separation
2.2.4. BL Processing and Component Separation
2.2.5. Solid Sample Processing
2.3. Chemical Characterization: Methods and Assessments
2.4. Equipment
2.4.1. The Reactor
2.4.2. Pulp Processing Gear
2.4.3. HPLC
2.4.4. FTIR
2.4.5. Solid Separation
3. Results
3.1. Chemical Characterization of Raw MS
3.2. Chemical Characterization of the Solid Phase Resulting After Pretreatments (SMSS)
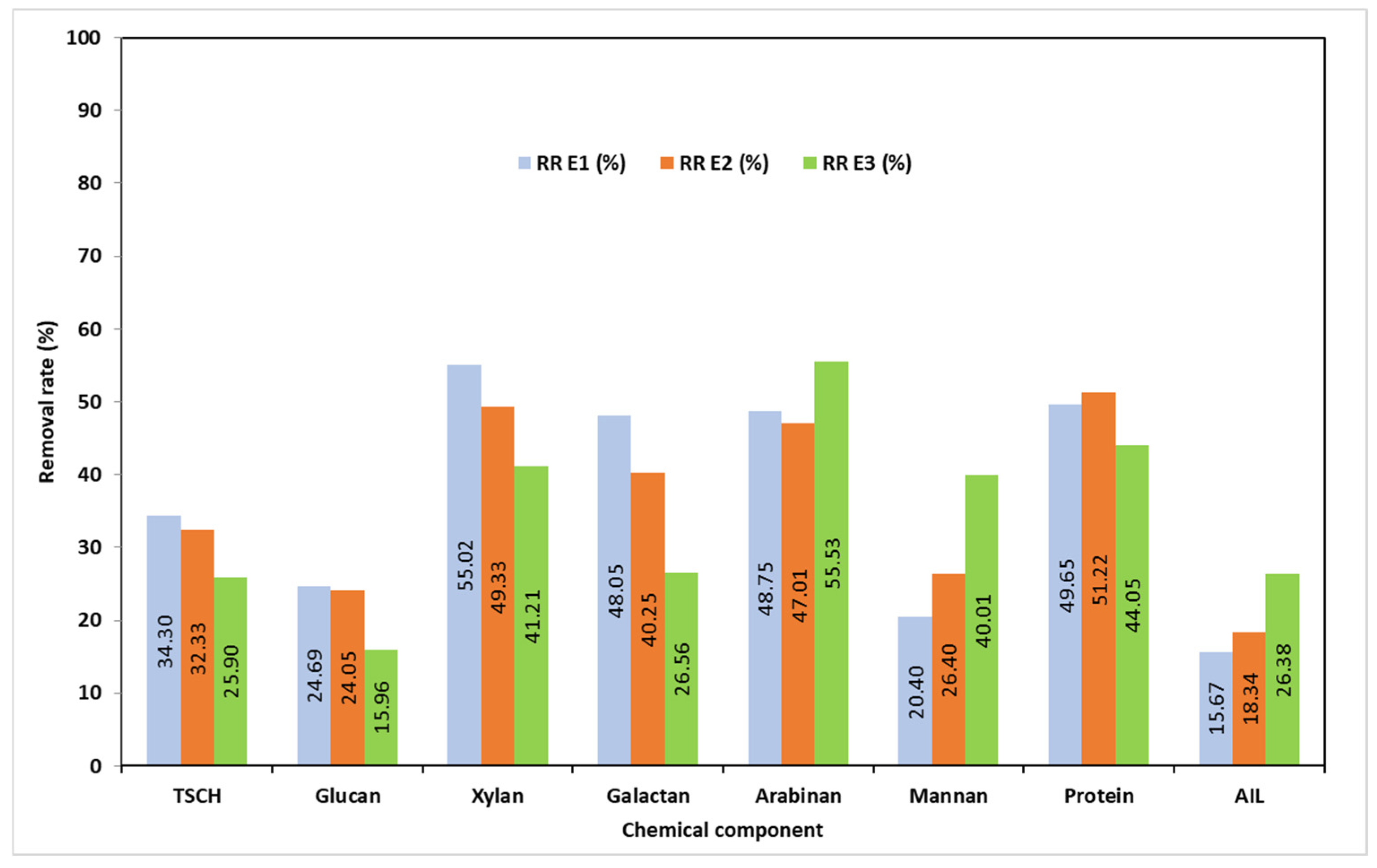
3.3. Chemical Characterization of the Liquid Phase Resulting After Pretreatments (LMSS)
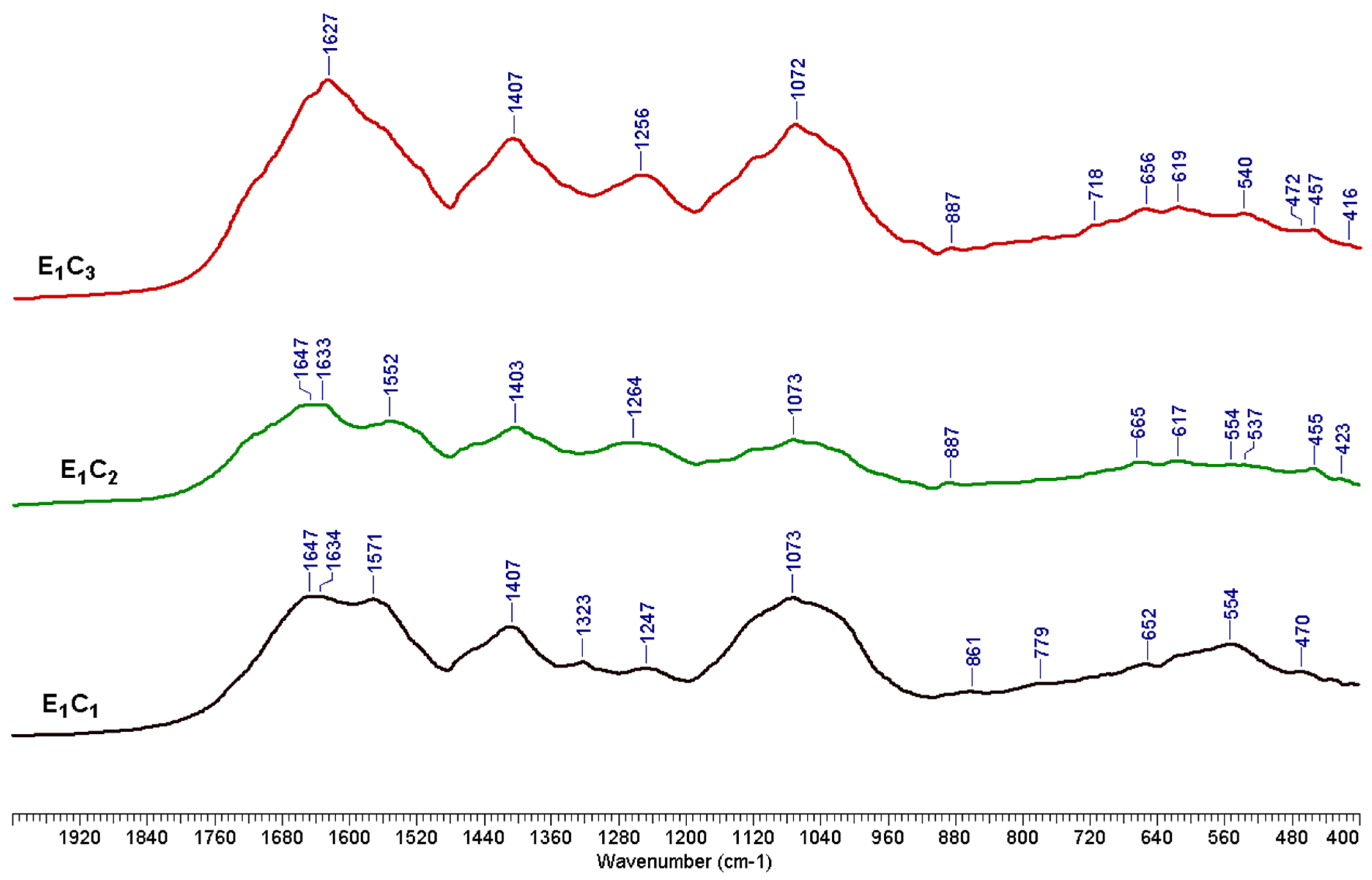
3.4. Chemical Characterizations of the Solids Obtained by Sequential Fractionation of E1 LMSS
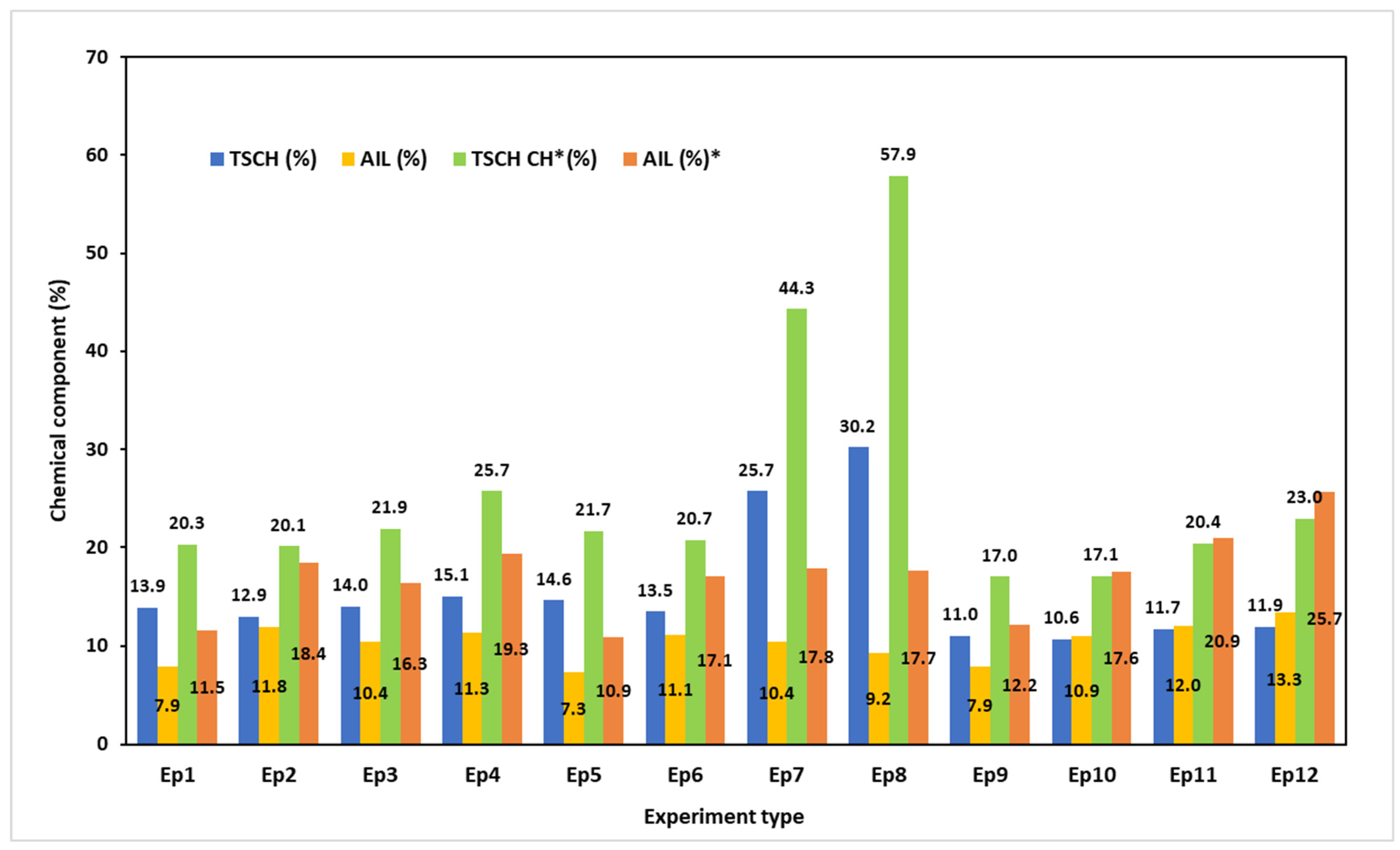
3.5. Chemical Characterizations of the MS Pulp Obtained After Pulping Trials
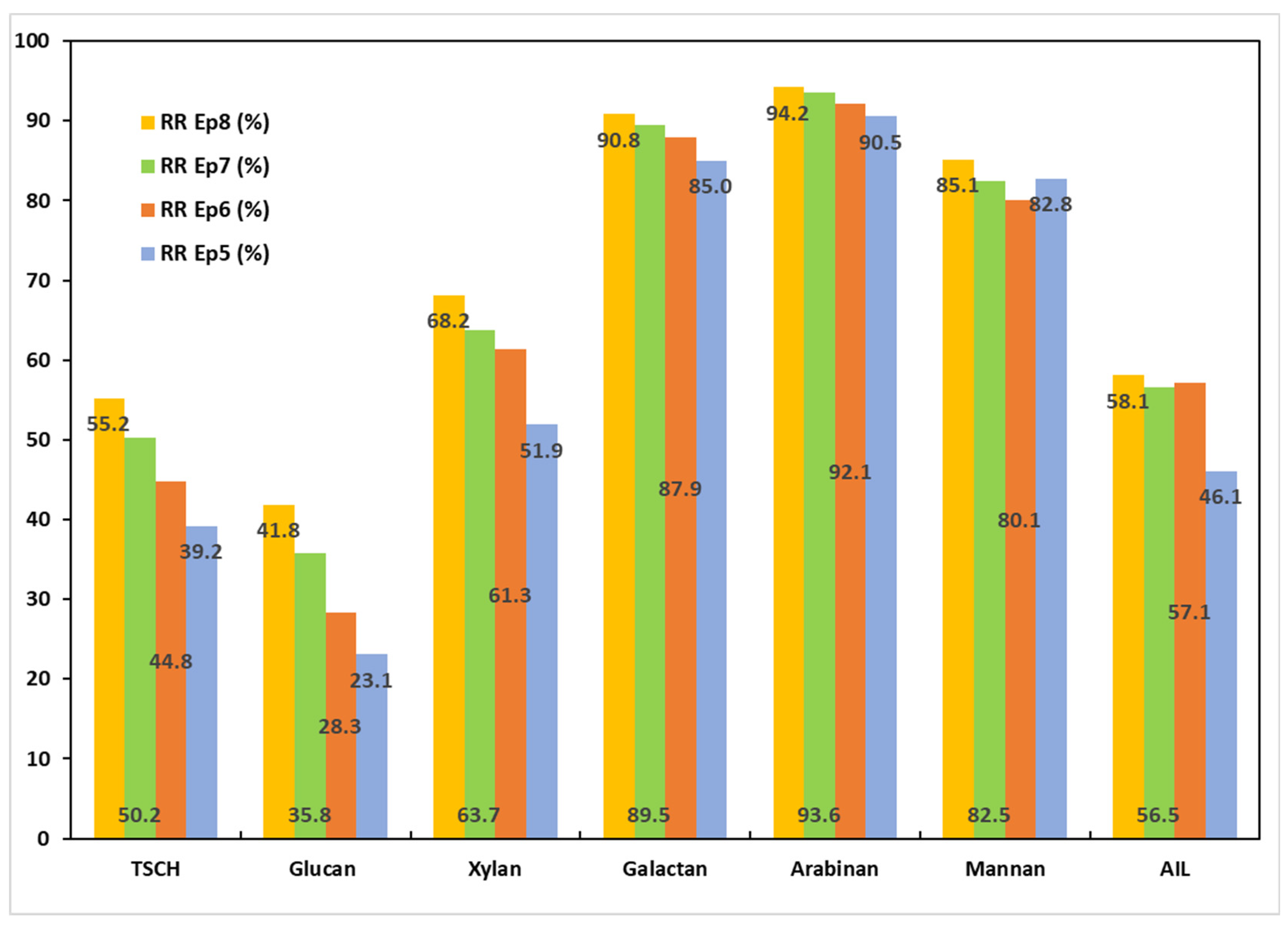
3.5.1. Chemical Characterizations of the Solids Obtained After PT1
3.5.2. Chemical Characterizations of the Solids Obtained After PT2
3.5.3. Chemical Characterizations of the Solids Obtained After PT3
3.6. Chemical Characterizations of the BLs Obtained After Pulping Trials
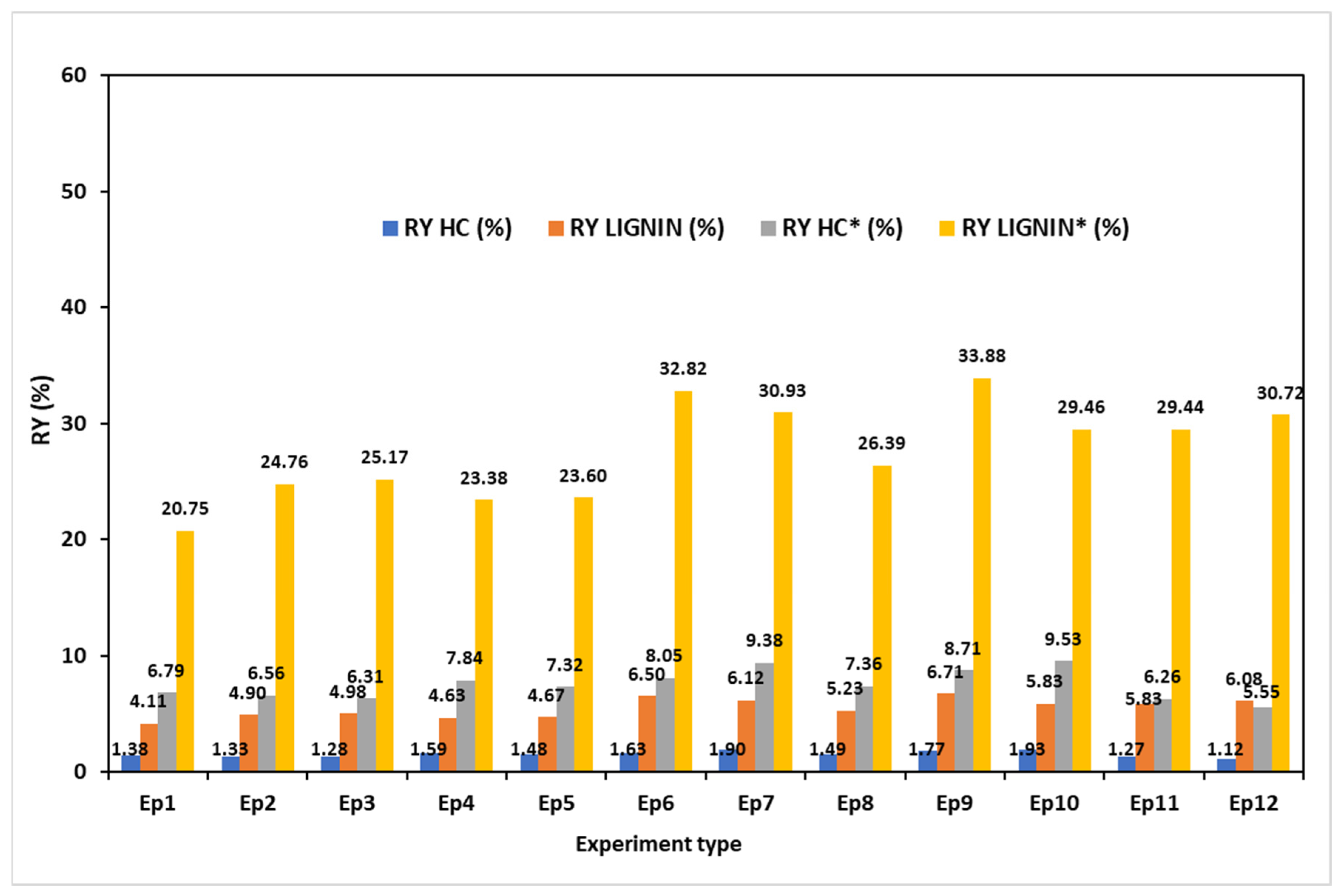
3.7. Characterization of the Recovered Hemicelluloses
3.8. Characterization of the Recovered Lignin
3.9. Hemicellulose and Lignin Recovery Yields
3.10. The Papermaking Potential of the MSS Isolated Fibers
3.10.1. Pure MSS Fibers
3.10.2. Blend of 50% MSS–50% OCC
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Russelle, M.P. Alfalfa: After an 8000-year journey, the “Queen of Forages” stands poised to enjoy renewed popularity. Am. Sci. 2001, 89, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Li, X.; Liu, X.; Wang, N.; An, Q.; Ye, X.M.; Zhao, Z.T.; Zhao, M.; Han, Y.; Ouyang, K.H. Investigation of chemical composition, antioxidant activity, and the effects of alfalfa flavonoids on growth performance. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 8569237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Huangfu, W.; Yang, X.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, X.; Wang, C.; Shi, Y.; Cui, Y. “King of the forage”—Alfalfa supplementation improves growth, reproductive performance, health condition and meat quality of pigs. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 1025942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asgharipour, M.R.; Mousavinik, S.M.; Enayat, F.F. Evaluation of energy input and greenhouse gases emissions from alfalfa production in the Sistan region, Iran. Energy Rep. 2016, 2, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, K.B.; Rusch, H.L.; Heuschele, D.J. Alfalfa Stem Cell Wall Digestibility: Current Knowledge and Future Research Directions. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radović, J.; Sokolović, D.; Marković, J. Alfalfa-most important perennial forage legume in animal husbandry. Biotechnol. Anim. Husb. 2009, 25, 465–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robin, N. Alfalfa & Forage Dynamics in the Current Agricultural Landscape; Agricultural Outlook Forum; USDA: Washington, DC, USA, 2023.
- Latif, A.; Sun, Y.; Noman, A. Herbaceous Alfalfa plant as a multipurpose crop and predominant forage specie in Pakistan. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2023, 7, 1126151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ominski, P.D.; Entz, M.H.; Kenkel, N. Weed suppression by Medicago sativa in subsequent cereal crops: A comparative survey. Weed Sci. 1999, 47, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valkova, M.; Maneva, S.; Dimitrova, T.; Vladimirov, V.; Milanova, S. Suppressive Capacity of Medicago sativa and Dactylis glomerata on the Growth and Development of Ambrosia artemisiifolia. Herbologia 2009, 10, 19–27. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; He, C.; Meng, P.; Sun, S.; Gao, J.; Zhang, J.; Cai, J. Effects of Different Moisture Conditions on Biological Nitrogen Fixation Capacity and Nutritive Value of Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) Seedlings. J. Soil. Sci. Plant Nutr. 2024, 24, 8235–8247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; He, C.; Meng, P.; Wang, J.; Gao, J.; Xue, P. Effects of Intercropping Mowing Frequency on Biological Nitrogen Fixation Capacity Nutritive Value Yield in Alfalfa (Medicago sativa, L. cv. Vernal). Plants 2025, 14, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Pan, C. Overland runoff erosion dynamics on steep slopes with forages under field simulated rainfall and inflow. Hydrol. Process. 2020, 34, 1794–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; Chen, K.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, C.; Lu, C.; Wang, H.; Wu, F. The contribution rate of stem-leaf and root of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) to sediment and runoff reduction. Land Degrad. Dev. 2023, 34, 3991–4005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bora, K.S.; Sharma, A. Phytochemical and pharmacological potential of Medicago sativa: A review. Pharm. Biol. 2011, 49, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafińska, K.; Pomastowski, P.; Wrona, O.; Górecki, R.; Buszewski, B. Medicago sativa as a source of secondary metabolites for agriculture and pharmaceutical industry. Phytochem. Lett. 2017, 20, 520–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haedo, J.P.; Martínez, L.C.; Graffigna, S.; Marrero, H.J.; Torretta, J.P. Managed and wild bees contribute to alfalfa (Medicago sativa) pollination. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2022, 324, 107711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagler, J.R.; Mueller, S.; Teuber, L.R.; Machtley, S.A.; Van Deynze, A. Foraging range of honey bees, Apis mellifera, in alfalfa seed production fields. J. Insect Sci. 2011, 11, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, A.L.; Sheaffer, C.C.; Tautges, N.E.; Putnam, D.H.; Hunter, M.C. Alfalfa, Wildlife, and the Environment, 2nd ed.; National Alfalfa and Forage Alliance: Kennewick, WA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Beiyuan, J.; Hu, W.; Zhang, Z.; Duan, C.; Cui, Q.; Zhu, X.; He, H.; Huang, X.; Fang, L. Phytoremediation of potentially toxic elements (PTEs) contaminated soils using alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.): A comprehensive review. Chemosphere 2022, 293, 133577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, C.-d.; Chen, T.; Yang, J.-Y. Remediation of vanadium contaminated soil by alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) combined with vanadium-resistant bacterial strain. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 20, 101090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaweł, E.; Grzelak, M.; Janyszek, M. Lucerne (Medicago sativa L.) in the human diet—Case reports and short reports. J. Herb. Med. 2017, 10, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mielmann, A. The utilisation of lucerne (Medicago sativa): A review. Br. Food J. 2013, 115, 590–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mielmann, A.; Bothma, C.; Hugo, A.; Hugo, C.J. A comparative study of the chemical composition of lucerne (Medicago sativa L.) and spinach beet (Beta vulgaris var. cicla L.). S. Afr. J. Bot. 2017, 108, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Authority, E.F.S. Scientific Opinion of the Panel on Dietetic Products Nutrition and Allergies on a request from the European Commission on the safety of ‘Alfalfa protein concentrate’ as food. EFSA J. 2009, 997, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Decision, E.C. Commission Decission of 13 October 2009 authorising the placing on the market of a leaf extract from Lucerne (Medicago sativa) as novel food or novel food ingredient under Regulation (EC) No 258/97 of the European Parliament and of the Council. Off. J. Eur. Communities 2009, 294, 12–13. [Google Scholar]
- Francis, H.; Debs, E.; Koubaa, M.; Alrayess, Z.; Maroun, R.G.; Louka, N. Sprouts Use as Functional Foods. Optimization of Germination of Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.), Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.), and Radish (Raphanus sativus L.) Seeds Based on Their Nutritional Content Evolution. Foods 2022, 11, 1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghaderi-Ghahfarokhi, M.; Shakarami, M.; Zarei, M. Alfalfa sprout flour: A promising ingredient to improve probiotic survival and antioxidant activity in mint-flavored stirred yogurt. Appl. Food Res. 2024, 4, 100555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortune Business Insights. Alfalfa Market Size, Share & Industry Analysis, by Animal Type (Cattle, Horse, and Others), by Feed Type (Hay, Cubes, and Pellets) and Regional Forecast, 2025–2032. 2025. Available online: https://www.fortunebusinessinsights.com/alfalfa-pellets-market-103597 (accessed on 8 March 2025).
- Hadidi, M.; Orellana Palacios, J.C.; McClements, D.J.; Mahfouzi, M.; Moreno, A. Alfalfa as a sustainable source of plant-based food proteins. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 135, 202–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, M.; Andersen, C.A.; Jensen, P.R.; Hobley, T.J. Scale-Up of Alfalfa (Medicago sativa) Protein Recovery Using Screw Presses. Foods 2022, 11, 3229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.H.; Yoo, C.G.; Lamsal, B.P. Front-end recovery of protein from lignocellulosic biomass and its effects on chemical pretreatment and enzymatic saccharification. Bioprocess. Biosyst. Eng. 2013, 36, 687–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferullo, J.-M.; Vézina, L.-P.; Castonguay, Y.; Allard, G.; Nadeau, P.; Willemot, C.; Laberge, S. Post-Harvest Alteration of In Vitro Translatable mRNA Population in Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). Crop Sci. 1996, 36, 1011–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGechan, M.B. A review of losses arising during conservation of grass forage: Part 1, field losses. J. Agric. Eng. Res. 1989, 44, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGechan, M.B. A review of losses arising during conservation of grass forage: Part 2, storage losses. J. Agric. Eng. Res. 1990, 45, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotz, C.; Abrams, S. Losses and quality changes during alfalfa hay harvest and storage. Trans. ASAE 1988, 31, 350–0355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotz, C.A. Postharvest changes in alfalfa quality. In Proceedings of the 35th California Alfalfa & Forage Symposium, Visalia, CA, USA, 12–14 December 2005; UCC Cooperative Extension, Agronomy Research and Extension Center: Reedley, CA, USA, 2005; pp. 53–262. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, N.P.; OelkeI, E.A. Generating Electricity from Alfalfa Biomass. In Proceedings of the 26th California Alfalfa Symposium and 26th National Alfalfa Symposium, San Diego, CA, USA, 9–10 December 1996; pp. 81–93. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, S.; Harris, R.; Kan, E. Effect of Alfalfa-Derived Biochar on Anaerobic Digestion of Dairy Manure. Agronomy 2022, 12, 911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuhli, V.; Zohorović, M.; Zenunović, A.; Bršadinac, J.; Hasić, A.; Halilović, S.; Andrejaš, F.; Selimbašić, V.; Bihorac, E.; Kucalović, E. Use Alfalfa Grown On Contaminated Land as an Energy Crop For Biogas Production. Am. J. Eng. Res. 2021, 10, 201–205. [Google Scholar]
- Saruul, P.; Srienc, F.; Somers, D.A.; Samac, D.A. Production of a Biodegradable Plastic Polymer, Poly-β-Hydroxybutyrate, in Transgenic Alfalfa. Crop Sci. 2002, 42, 919–927. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Xi, X.; Wu, Z.; Lei, H.; Lei, L.; Tian, M. An Eco-Friendly Wood Adhesive from Alfalfa Leaf Protein. J. Renew. Mater. 2020, 8, 1429–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, X.; Guo, G.; Huo, W.; Li, Q.; Xu, Q.; Chen, L. Ensiling pretreatment fortified with laccase and microbial inoculants enhances biomass preservation and bioethanol production of alfalfa stems. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 857, 159442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-García, S.; Moreira, M.T.; Feijoo, G. Environmental performance of lignocellulosic bioethanol production from Alfalfa stems. Biofuels Bioprod. Biorefin. 2010, 4, 118–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dale, B.E. Biomass refining: Protein and ethanol from alfalfa. Ind. Eng. Chem. Prod. Res. Dev. 1983, 22, 466–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rock, K.P.; Thelemann, R.T.; Jung, H.-J.G.; Tschirner, U.W.; Sheaffer, C.C.; Johnson, G.A. Variation due to Growth Environment in Alfalfa Yield, Cellulosic Ethanol Traits, and Paper Pulp Characteristics. BioEnergy Res. 2009, 2, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momzyakova, K.S.; Deberdeev, T.R.; Valishina, Z.T.; Deberdeev, R.Y.; Ibragimov, A.V.; Alexandrov, A.V. Research of Physical and Chemical Properties of Powder Cellulose from Various Type of Raw Materials. Mater. Sci. Forum 2020, 992, 791–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, J.; Tschirner, U. Fiber length and pulping characteristics of switchgrass, alfalfa stems, hybrid poplar and willow biomasses. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momzyakova, K.S.; Pulyaeva, M.A.; Kazakov, Y.V.; Deberdeev, T.R.; Kanarskii, A.V.; Aleksandrov, A.A.; Deberdeev, R.Y. Evaluation of the Paper-Making Properties of Cellulose Extracted from Oat and Alfalfa Straw. Polym. Sci. Ser. D 2022, 15, 431–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokina, I.; Plaksenkova, I.; Jankovskis, L.; Jermaļonoka, M.; Galek, R. New Insights on Biosynthesis of Nanoparticles Using Plants Emphasizing the Use of Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). J. Nanotechnol. 2024, 2024, 9721166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Li, Z.; Zhang, C.-Y.; Li, M.; Lee, Y.; Zhang, G.-G. Extract Methods, Molecular Characteristics, and Bioactivities of Polysaccharide from Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). Nutrients 2019, 11, 1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puițel, A.C.; Bălușescu, G.; Balan, C.D.; Nechita, M.T. The Potential Valorization of Corn Stalks by Alkaline Sequential Fractionation to Obtain Papermaking Fibers, Hemicelluloses, and Lignin—A Comprehensive Mass Balance Approach. Polymers 2024, 16, 1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puițel, A.C.; Suditu, G.D.; Drăgoi, E.N.; Danu, M.; Ailiesei, G.-L.; Balan, C.D.; Chicet, D.-L.; Nechita, M.T. Optimization of Alkaline Extraction of Xylan-Based Hemicelluloses from Wheat Straws: Effects of Microwave, Ultrasound, and Freeze–Thaw Cycles. Polymers 2023, 15, 1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 5269-2:2004, I; Pulps—Preparation of Laboratory Sheets for Physical Testing Part 2: Rapid-Köthen Method. 3rd ed. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004.
- ISO 1924:2008; Paper and Board: Determination of Tensile Properties. Part 2: Constant Rate of Elongation Method (20 mm/min). International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008.
- ISO 2758:2014; Paper—Determination of Bursting Strength. 4th ed. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014.
- Sluiter, A.; Hames, B.; Ruiz, R.; Scarlata, C.; Sluiter, J.; Templeton, D.; Crocker, D. Determination of structural carbohydrates and lignin in biomass. Lab. Anal. Proced. 2008, 1617, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 5983-2:2009 I; Animal Feeding Stuffs—Determination of Nitrogen Content and Calculation of Crude Protein Content Part 2: Block Digestion and Steam Distillation Method. 2nd ed. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009.
- TAPPI T280 pm-99; Acetone Extractives of Wood and Pulp. TAPPI: Peachtree Corners, GA, USA, 1999; Volume 3.
- TAPPI T 207 om-88; Water solubility of Wood and Pulp. TAPPI: Peachtree Corners, GA, USA, 2008; Volume 3.
- TAPPI T 211 om-02; Ash in Wood, Pulp, Paper and Paperboard: Combustion at 525 C. TAPPI: Peachtree Corners, GA, USA, 2002; Volume 5.
- Sluiter, A.; Hames, B.; Ruiz, R.; Scarlata, C.; Sluiter, J.; Templeton, D. Determination of Sugars, Byproducts, and Degradation Products in Liquid Fraction Process Samples; NREL/TP-510-42623; Laboratory Analytical Procedure (LAP): Golden, CO, USA, 2006; Volume 11, pp. 65–71.
- Sluiter, A.; Hames, B.; Ruiz, R.; Scarlata, C.; Sluiter, J.; Templeton, D. Determination of Ash in Biomass Laboratory Analytical Procedure; NREL/TP-510-42622; NREL: Golden, CO, USA, 2005; Volume 19.
- Serna-Loaiza, S.; Adamcyk, J.; Beisl, S.; Miltner, M.; Friedl, A. Sequential pretreatment of wheat straw: Liquid hot water followed by organosolv for the production of hemicellulosic sugars, lignin, and a cellulose-enriched pulp. Waste Biomass Valorization 2022, 13, 4771–4784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Hansen, M.; Jensen, P.R.; Hobley, T.J. Development of a sugar platform and fermentation media from residues from alfalfa biorefining. Ind. Crops Prod. 2024, 209, 117927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dien, B.S.; Miller, D.J.; Hector, R.E.; Dixon, R.A.; Chen, F.; McCaslin, M.; Reisen, P.; Sarath, G.; Cotta, M.A. Enhancing alfalfa conversion efficiencies for sugar recovery and ethanol production by altering lignin composition. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 6479–6486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warnke, A.H.; Ruhland, C.T. The effects of harvest regime, irrigation, and salinity on stem lignocellulose concentrations in alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 176, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamb, J.F.S.; Jung, H.-J.G.; Sheaffer, C.C.; Samac, D.A. Alfalfa Leaf Protein and Stem Cell Wall Polysaccharide Yields under Hay and Biomass Management Systems. Crop Sci. 2007, 47, 1407–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hojilla-Evangelista, M.P.; Selling, G.W.; Hatfield, R.; Digman, M. Extraction, composition, and functional properties of dried alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) leaf protein. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 97, 882–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horvat, D.; Viljevac Vuletić, M.; Andrić, L.; Baličević, R.; Kovačević Babić, M.; Tucak, M. Characterization of Forage Quality, Phenolic Profiles, and Antioxidant Activity in Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). Plants 2022, 11, 2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serna-Loaiza, S.; Dias, M.; Daza-Serna, L.; De Carvalho, C.C.C.R.; Friedl, A. Integral Analysis of Liquid-Hot-Water Pretreatment of Wheat Straw: Evaluation of the Production of Sugars, Degradation Products, and Lignin. Sustainability 2022, 14, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serna-Loaiza, S.; Zikeli, F.; Adamcyk, J.; Friedl, A. Towards a wheat straw biorefinery: Combination of Organosolv and Liquid Hot Water for the improved production of sugars from hemicellulose and lignin hydrolysis. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2021, 14, 100667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Li, Z.; Dai, S.; Tian, G.; Wang, Z. Production of hemicelluloses sugars, cellulose pulp, and lignosulfonate surfactant using corn stalk by prehydrolysis and alkaline sulfite cooking. Ind. Crops Prod. 2023, 192, 115880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Dong, H.; Yu, W.; Gao, Y.; Mao, G.; An, Y.; Xie, H.; Song, A.; Zhang, Z. Enhanced enzymatic sugar production from corn stover by combination of water extraction and glycerol-assisted instant catapult steam explosion. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2024, 11, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grdadolnik, J.; Maréchal, Y. Bovine serum albumin observed by infrared spectrometry, I.I. Hydration mechanisms and interaction configurations of embedded H2O molecules. Biopolymers 2001, 62, 54–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Yang, S.; Kong, J.; Dong, A.; Yu, S. Obtaining information about protein secondary structures in aqueous solution using Fourier transform IR spectroscopy. Nat. Protoc. 2015, 10, 382–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrade, J.; Pereira, C.G.; de Almeida Junior, J.C.; Viana, C.C.R.; de Oliveira Neves, L.N.; da Silva, P.H.F.; Bell, M.J.V.; dos Anjos, V.D.C. FTIR-ATR determination of protein content to evaluate whey protein concentrate adulteration. LWT 2019, 99, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Lei, T.; Ma, Y.; Su, H.; Xuan, C. Influence and prediction of chemical composition of alfalfa on the quality and specific energy consumption of alfalfa briquettes. Ind. Crops Prod. 2024, 222, 119891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth, A. Infrared spectroscopy of proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Bioenerg. 2007, 1767, 1073–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandt, C. Identification and classification of proteins by FTIR microspectroscopy. A proof of concept. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Gen. Subj. 2024, 1868, 130688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Niu, Y.; Dai, B.; Yu, L. A Novel Alkaline Hemicellulosic Heteroxylan Isolated from Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) Stem and Its Thermal and Anti-inflammatory Properties. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 2970–2978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Westman, G.; Theliander, H. The molecular properties and carbohydrate content of lignins precipitated from black liquor. Holzforschung 2015, 69, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maitz, S.; Wernsperger, L.; Kienberger, M. Isolation of Carboxylic Acids and NaOH from Kraft Black Liquor with a Membrane-Based Process Sequence. Membranes 2023, 13, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Sharma, M.; Esperança, A.; Moreira, M.J.; Gando-Ferreira, L.M. Green recovery and optimization of hemicellulose extraction from black liquor using acetic acid and cyclopentyl methyl ether. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 116282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, B.T.; Brelid, H.; Theliander, H. Carbohydrate content of black liquor and precipitated lignin at different ionic strengths in flow-through kraft cooking. Holzforschung 2018, 72, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjostrom, E. The behavior of wood polysaccharides during alkaline pulping processes. Tappi J. 1997, 60, 151–154. [Google Scholar]
- Ciftci, D.; Flores, R.A.; Saldaña, M.D.A. Cellulose Fiber Isolation and Characterization from Sweet Blue Lupin Hull and Canola Straw. J. Polym. Environ. 2018, 26, 2773–2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.; Zu, M.; Wu, R.; Xiao, C.; Kang, J.; Fan, Y. Study on the mechanism of lignin and lignin-carbohydrate complex hydrolysis under alkaline conditions by density functional theory. Biomass Bioenergy 2024, 185, 107233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morya, R.; Kumar, M.; Tyagi, I.; Kumar Pandey, A.; Park, J.; Raj, T.; Sirohi, R.; Kumar, V.; Kim, S.-H. Recent advances in black liquor valorization. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 350, 126916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Huang, H.; He, T.; Sun, J.; Chen, K.; Yue, F. Highly selective extraction of lignin and hemicellulose with retained original structure from sugarcane bagasse via low-temperature soaking and acidic precipitation. Ind. Crops Prod. 2024, 209, 118015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, T.; Wang, L. Thermal treatment of poplar hemicelluloses at 180 to 220 C under nitrogen atmosphere. BioResources 2017, 12, 1128–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, J.M.; Bauer, S.; Sorek, H.; Sreekumar, S.; Wang, K.; Toste, F.D. Studies on the vanadium-catalyzed nonoxidative depolymerization of Miscanthus giganteus-derived lignin. ACS Catal. 2013, 3, 1369–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horikawa, Y.; Hirano, S.; Mihashi, A.; Kobayashi, Y.; Zhai, S.; Sugiyama, J. Prediction of Lignin Contents from Infrared Spectroscopy: Chemical Digestion and Lignin/Biomass Ratios of Cryptomeria japonica. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2019, 188, 1066–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymanska-Chargot, M.; Chylinska, M.; Kruk, B.; Zdunek, A. Combining FT-IR spectroscopy and multivariate analysis for qualitative and quantitative analysis of the cell wall composition changes during apples development. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 115, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kędzierska-Matysek, M.; Matwijczuk, A.; Florek, M.; Barłowska, J.; Wolanciuk, A.; Matwijczuk, A.; Chruściel, E.; Walkowiak, R.; Karcz, D.; Gładyszewska, B. Application of FTIR Spectroscopy for Analysis of the Quality of Honey. BIO Web Conf. 2018, 10, 02008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottah, V.E.; Ezugwu, A.L.; Ezike, T.C.; Chilaka, F.C. Comparative analysis of alkaline-extracted hemicelluloses from Beech, African rose and Agba woods using FTIR and HPLC. Heliyon 2022, 8, e09714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, B.C. An IR spectral interpretation potpourri: Carbohydrates and alkynes. Spectroscopy 2017, 32, 18–24. [Google Scholar]
- Fahey, L.M.; Nieuwoudt, M.K.; Harris, P.J. Predicting the cell-wall compositions of Pinus radiata (radiata pine) wood using ATR and transmission FTIR spectroscopies. Cellulose 2017, 24, 5275–5293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Renard, C.M.G.C.; Bureau, S.; Le Bourvellec, C. Revisiting the contribution of ATR-FTIR spectroscopy to characterize plant cell wall polysaccharides. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 262, 117935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauraj; Kumar, A.; Kumar, B.; Kulshreshtha, A.; Negi, Y.S. Redox-sensitive nanoparticles based on xylan-lipoic acid conjugate for tumor targeted drug delivery of niclosamide in cancer therapy. Carbohydr. Res. 2021, 499, 108222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadányi, R.; Zinovyev, G.; Majerčiak, M.; Štosel, M.; Jablonský, M.; Ház, A. Optimizing Hardwood Lignin Precipitation from Kraft Black Liquor: A Study of Temperature and pH Effects. Forests 2024, 15, 1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, P.S.B.D.; Erdocia, X.; Gatto, D.A.; Labidi, J. Characterisation of Kraft lignin separated by gradient acid precipitation. Ind. Crops Prod. 2014, 55, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sewring, T.; Julie, D.; Lynn, S.; Helen, S.; Tuve, M.; and Theliander, H. Acid Precipitation of Kraft Lignin from Aqueous Solutions: The Influence of pH, Temperature, and Xylan. J. Wood Chem. Technol. 2019, 39, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Theliander, H. Precipitation of lignin from softwood black liquor: An investigation of the equilibrium and molecular properties of lignin. BioResources 2015, 10, 1696–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiller, P.S.; Min, B.C.; Ahn, H.K.; Carrejo, E.; Sanders, J.; Rios, D.C.; Park, S. Techno-economic analysis of novel lignin extraction from black liquor. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 366, 132757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauwaert, J.; Stals, I.; Lancefield, C.S.; Deschaumes, W.; Depuydt, D.; Vanlerberghe, B.; Devlamynck, T.; Bruijnincx, P.C.A.; Verberckmoes, A. Pilot scale recovery of lignin from black liquor and advanced characterization of the final product. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 221, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minu, K.; Jiby, K.K.; Kishore, V.V.N. Isolation and purification of lignin and silica from the black liquor generated during the production of bioethanol from rice straw. Biomass Bioenergy 2012, 39, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, N.H.; Pham, H.H.; Le, T.M.; Lauwaert, J.; Diels, L.; Verberckmoes, A.; Do, N.H.N.; Tran, V.T.; Le, P.K. The novel method to reduce the silica content in lignin recovered from black liquor originating from rice straw. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domínguez-Robles, J.; Sánchez, R.; Díaz-Carrasco, P.; Espinosa, E.; García-Domínguez, M.T.; Rodríguez, A. Isolation and characterization of lignins from wheat straw: Application as binder in lithium batteries. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 104, 909–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadiku, N.A.; Yusuph, A.F. Characterisation of lignins isolated from Bamboo organosolv and kraft black liquor. Maderas. Cienc. Tecnol. 2023, 25, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruwoldt, J.; Syverud, K.; Tanase-Opedal, M. Purification of soda lignin. Sustain. Chem. Environ. 2024, 6, 100102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, H.; Guo, Z.; Xu, F. High Purity and Low Molecular Weight Lignin Nano-Particles Extracted from Acid-Assisted MIBK Pretreatment. Polymers 2020, 12, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popescu, C.; Vasile, C.; Popescu, M.; Singurel, G.; Popa, V.; Munteanu, B. Analytical methods for lignin characterization, I.I. Spectroscopic studies. Cell. Chem. Technol. 2006, 40, 597. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; McDonald, A.G. Fractionation and characterization of industrial lignins. Ind. Crops Prod. 2014, 62, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Xing, D.; Lia, J. FTIR Studies of the Changes in Wood Chemistry from Wood Forming Tissue under Inclined Treatment. Energy Procedia 2012, 16, 758–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collier, W.; Kalasinsky, V.F.; Schultz, T.P. Infrared study of lignin: Assignment of methoxyl CH bending and stretching bands. Holzforschung 1997, 51, 167–168. [Google Scholar]
- Sammons, R.J.; Harper, D.P.; Labbé, N.; Bozell, J.J.; Elder, T.; Rials, T.G. Characterization of organosolv lignins using thermal and FT-IR spectroscopic analysis. BioResources 2013, 8, 2752–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, S.C.; McDonald, A.G. Chemical and thermal characterization of three industrial lignins and their corresponding lignin esters. BioResources 2010, 5, 990–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyanto, S.; Intan, A.P.; Rianto, B.; Kusworo, T.D.; Pramudono, B.; Untoro, E.; Ratu, P. The effect of acid concentration (H2SO4) on the yield and functional group during lignin isolation of biomass waste pulp and paper industry. Reaktor 2019, 19, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.-J.; Xiao, L.-P.; Deng, J.; Sun, R.-C. Isolation and Structural Characterization of Lignin Polymer from Dendrocalamus sinicus. BioEnergy Res. 2013, 6, 1212–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negrão, D.R.; Sain, M.; Leão, A.L.; Sameni, J.; Jeng, R.; Jesus, J.P.F.D.; Monteiro, R.T.R. Fragmentation of lignin from organosolv black liquor by white rot fungi. BioResources 2015, 10, 1553–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, T.; Kait, C.F.; Murugesan, T. A “Fourier transformed infrared” compound study of lignin recovered from a formic acid process. Procedia Eng. 2016, 148, 1312–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Tran, M.H.; Lee, E.Y. Hydroxymethylation of technical lignins obtained from different pretreatments for preparation of high-performance rigid polyurethane foam. Eur. J. Wood Wood Prod. 2022, 80, 1225–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teramura, H.; Sasaki, K.; Oshima, T.; Kawaguchi, H.; Ogino, C.; Sazuka, T.; Kondo, A. Effective usage of sorghum bagasse: Optimization of organosolv pretreatment using 25% 1-butanol and subsequent nanofiltration membrane separation. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 252, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johakimu, J.K.; Jerome, A.; Sithole, B.B.; Prabashni, L. Fractionation of organic substances from the South African Eucalyptus grandis biomass by a combination of hot water and mild alkaline treatments. Wood Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 365–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dafchahi, M.N.; Acharya, B. Green extraction of xylan hemicellulose from wheat straw. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2024, 14, 21229–21243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Liu, H.; Hui, L.; Wang, H.; Liu, H. Characterization of liquefied products from corn stalk and its biomass components by polyhydric alcohols with phosphoric acid. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 215, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Gu, X.; Shi, Y. A review on lignin antioxidants: Their sources, isolations, antioxidant activities and various applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 210, 716–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimah, A.; Hani, I.K.; Laksana, R.P.B.; Ismayati, M.; Solihat, N.N.; Sari, F.P.; Budiman, I.; Ghozali, M.; Farobie, O.; Nawawi, D.S.; et al. Extraction of lignin from sugarcane trash and its potency as biosurfactant. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2023, 24, 101630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, S.; Ma, Q.; Zhang, S.; Shen, C.; Li, J.; Zhao, H.; Guo, D.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, H. Evaluation of oxy-organosolv pretreatment on lignin extraction from wheat straw. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 229, 861–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismaeilimoghadam, S.; Mahdavi, S.; Pourhashemi, M.; Shahraki, A.; Jonoobi, M. Mono Ethanol Amine (MEA) Pulping of Wheat Straw: An Environmentally Friendly Suggestion for the Fluff Pulp Production. J. Renew. Mater. 2024, 12, 1771–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urdaneta, F.; Kumar, R.; Marquez, R.; Vera, R.E.; Franco, J.; Urdaneta, I.; Saloni, D.; Venditti, R.A.; Pawlak, J.J.; Jameel, H.; et al. Evaluating chemi-mechanical pulping processes of agricultural residues: High-yield pulps from wheat straw for fiber-based bioproducts. Ind. Crops Prod. 2024, 221, 119379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Xue, Z.; Liang, F.; Miao, B.; Wang, T.; Huang, D.; Yuan, H.; Jiang, Y. Enhancement of the wheat straw pretreatment in pulping: The microbial intelligent response. Ind. Crops Prod. 2025, 223, 120109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahan, M.S.; Rahman, M.M. Effect of pre-hydrolysis on the soda-anthraquinone pulping of corn stalks and Saccharum spontaneum (kash). Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 88, 583–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Roy, A.; Nayeem, J.; Popy, R.S.; Ferdous, T.; Jahan, M.S. Tissue paper from corn stalk pulp in biorefinery concept. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2024, 14, 24623–24630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, G.; Shen, K. Wheat Straw Pulping for Paper and Paperboard. In Global Wheat Production; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018; p. 223. [Google Scholar]
- Salehi, K.; Kordsachia, O.; Saake, B. The potential of wheat straw high yield MEA pulp for enhancing strength properties of recycled paper. BioResources 2017, 12, 8255–8271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balea, A.; Merayo, N.; Seara, M.; Fuente, E.; Blanco, A.; Negro, C. Effect of NFC from organosolv corn stalk pulp on retention and drainage during papermaking. Cell. Chem. Technol. 2016, 50, 377–383. [Google Scholar]
- Mayank, G.; Amit, K.; Surendra, P. Wheat straw pulp as reinforcing aid for recycled softwood pulp. IPPTA J. 2008, 20, 113–117. [Google Scholar]
- Serrano, I.; Afailal, Z.; Sánchez-Paniagua, N.; González, P.; Bautista, A.; Gil-Lalaguna, N.; Gonzalo, A.; Arauzo, J.; Crespo, C.; Sánchez, J.L. Production of derivatives from wheat straw as reinforcement material for paper produced from secondary fibers. Cellulose 2024, 31, 2541–2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagel, S.; Schütt, F. Reinforcement Fiber Production from Wheat Straw for Wastepaper-Based Packaging Using Steam Refining with Sodium Carbonate. Clean. Technol. 2024, 6, 322–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Pretreatments (10:1 Liquid-to-Solid Ratio, 90 min, 75 °C) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Experiment Codes | Experimental Environments | Inputs | Output Codes | |
| Solids | Liquids | |||
| E1 | water | 300 g o.d. MSS | E1C1 | E1C1S1 |
| E1C2 | E1C2S2 | |||
| E1C3 | E1C3S3 | |||
| E2 | pH 12 buffer solution | - | ||
| E3 | NaOH solution (8 g/L) | - | ||
| Pulping experiments (10:1 liquid-to-solid ratio) | ||||
| Experiment codes | Experimental parameters | Inputs (200 g o.d.) | Output codes (pulps and BLs) | |
| PT1 | 15% NaOH, 30 min, 145 °C | Raw MSS | EP1 | |
| MSS from E1 | EP2 | |||
| MSS from E2 | EP3 | |||
| MSS from E3 | EP4 | |||
| PT2 | 20% NaOH, 30 min, 145 °C | Raw MSS | EP5 | |
| MSS from E1 | EP6 | |||
| MSS from E2 | EP7 | |||
| MSS from E3 | EP8 | |||
| PT3 | 20% NaOH, 60 min, 160 °C | Raw MSS | EP9 | |
| MSS from E1 | EP10 | |||
| MSS from E2 | EP11 | |||
| MSS from E3 | EP12 | |||
| Sample | Structural Carbohydrates (%) | Other Components (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glucan | Xylan | Galactan | Arabinan | Mannan | Protein | AIL * | |
| MS | 30.89 | 8.17 | 1.88 | 2.87 | 3.30 | 12.75 | 20.11 |
| MSS | 32.90 | 12.48 | 2.26 | 3.64 | 1.89 | 8.54 | 19.80 |
| MSL | 10.96 | 3.75 | 2.41 | 4.01 | 0.57 | 24.11 | 18.85 |
| MS OD | 16.37 | 5.88 | 3.05 | 3.40 | 1.01 | 22.03 | 14.58 |
| Pretreatment | Solid Yield, (%) | Structural Carbohydrates (%) | Other Components (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glucan | Xylan | Galactan | Arabinan | Mannan | Protein | AIL | ||
| E1 | 75.84 | 32.67 | 7.40 | 1.55 | 2.46 | 1.98 | 5.67 | 22.36 |
| E2 | 73.08 | 34.19 | 8.65 | 1.85 | 2.64 | 1.90 | 5.70 | 22.47 |
| E3 | 71.63 | 38.60 | 10.24 | 2.32 | 2.26 | 1.58 | 6.67 | 20.67 |
| Pretreatment | Structural Carbohydrates (g/L) | Other Components (g/L) | % Protein | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glucan | Xylan | Galactan | Arabinan | Mannan | AIL | IM | OM | SM | OM | |
| E1 | 0.46 | 1.49 | 0.19 | 0.30 | 0.21 | 0.84 | 3.71 | 12.48 | 19.72 | 25.58 |
| E2 | 0.50 | 2.01 | 0.67 | 0.78 | 0.08 | 1.81 | 11.51 | 22.74 | 15.33 | 18.57 |
| E3 | 1.86 | 2.22 | 0.47 | 0.76 | 0.11 | 2.63 | 13.17 | 24.39 | 12.33 | 23.61 |
| Solid Fraction | Structural Carbohydrates (%) | Other Components (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glucan | Xylan | Galactan | Arabinan | Mannan | Protein | AIL | |
| E1C1 | 3.27 | 4.02 | 1.03 | 1.65 | 0.97 | 30.29 | 17.94 |
| E2C2 | 2.34 | 3.95 | 1.36 | 1.91 | 0.99 | 43.69 | 15.78 |
| E3C3 | 2.94 | 4.17 | 3.56 | 4.75 | 1.53 | 29.44 | 14.74 |
| Experiment | Solid Yield, (%) | Structural Carbohydrates (%) | AIL (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glucan | Xylan | Galactan | Arabinan | Mannan | |||
| EP1 | 49.9 | 49.80 | 11.96 | 0.87 | 0.80 | 0.72 | 22.10 |
| EP2 | 59.74 | 52.57 | 11.59 | 0.88 | 0.82 | 0.81 | 22.03 |
| EP3 | 59.32 | 51.56 | 11.20 | 0.72 | 0.70 | 0.87 | 21.99 |
| EP4 | 55.47 | 54.21 | 11.27 | 0.65 | 0.65 | 0.82 | 20.47 |
| Experiment | Solid Yield, (%) | Structural Carbohydrates (%) | AIL (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glucan | Xylan | Galactan | Arabinan | Mannan | |||
| EP5 | 47.13 | 53.70 | 12.74 | 0.72 | 0.73 | 0.69 | 22.64 |
| EP6 | 53.9 | 57.70 | 11.81 | 0.67 | 0.70 | 0.92 | 20.79 |
| EP7 | 53.22 | 54.34 | 11.65 | 0.61 | 0.60 | 0.85 | 22.13 |
| EP8 | 54.6 | 48.94 | 10.16 | 0.53 | 0.54 | 0.72 | 21.21 |
| Experiment | Solid Yield, (%) | Structural Carbohydrates (%) | AIL (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glucan | Xylan | Galactan | Arabinan | Mannan | |||
| EP9 | 38.43 | 46.58 | 10.17 | 0.43 | 0.57 | 0.54 | 21.11 |
| EP10 | 51.15 | 47.55 | 9.24 | 0.34 | 0.52 | 0.37 | 20.52 |
| EP11 | 48.45 | 48.42 | 9.77 | 0.35 | 0.44 | 0.47 | 18.86 |
| EP12 | 47.41 | 52.31 | 10.15 | 0.38 | 0.46 | 0.79 | 16.91 |
| Pulp Sample | OCC | EP9 | EP9+OCC | EP10 | EP10+OCC | EP11 | EP11+OCC | EP12 | EP12+OCC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | |||||||||
| Drainage resistance (°SR) | 33 | 52 | 43 | 55 | 45.0 | 51 | 45 | 46 | 45 |
| Tensile index (N·m/g) | 28.26 | 38.25 | 32.50 | 47.34 | 34.81 | 44.85 | 39.31 | 45.41 | 37.86 |
| Burst index (kPa∙m2/g) | 0.90 | 0.70 | 1.06 | 0.90 | 1.14 | 1.22 | 1.34 | 1.42 | 1.54 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Puițel, A.C.; Bârjoveanu, G.; Balan, C.D.; Nechita, M.T. Medicago Sativa Stems—A Multi-Output Integrated Biorefinery Approach. Polymers 2025, 17, 1709. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17121709
Puițel AC, Bârjoveanu G, Balan CD, Nechita MT. Medicago Sativa Stems—A Multi-Output Integrated Biorefinery Approach. Polymers. 2025; 17(12):1709. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17121709
Chicago/Turabian StylePuițel, Adrian Cătălin, George Bârjoveanu, Cătălin Dumitrel Balan, and Mircea Teodor Nechita. 2025. "Medicago Sativa Stems—A Multi-Output Integrated Biorefinery Approach" Polymers 17, no. 12: 1709. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17121709
APA StylePuițel, A. C., Bârjoveanu, G., Balan, C. D., & Nechita, M. T. (2025). Medicago Sativa Stems—A Multi-Output Integrated Biorefinery Approach. Polymers, 17(12), 1709. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17121709









