Development of Glass Fibers Laminates Toughened with Core–Shell Rubber Particles for Applications in Cold Environments
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
- Atlac® 580: This is a commercial high-grade bisphenol A vinyl ester urethane resin, provided by AOC resins (Collierville, TN, USA). This resin is used for highly demanding applications since it combines exceptional chemical and heat resistance [density (23 °C): 1.07 g/cm3; viscosity: 400–500 mPa∙s].
- Butanox® M-50: This is a medium-reactive methyl ethyl ketone peroxide (MEKP), provided by Nouryon (Amsterdam, The Netherlands), used to cure unsaturated polyester resins [density (20 °C): 1.18 g/cm3; viscosity (20 °C): 24 mPa∙s].
- KANE ACE™ MX-010 (K): This is a liquid impact modifier provided by Kaneka (Tokyo, Japan) suitable tailored for improving the toughness of thermoset resins through the dispersion of Kaneka’s novel core–shell rubber (CSR) [viscosity (25 °C): 6000 cPs]. The dispersed core–shell rubber is polybutadiene rubber, and the product contains 40 wt.% of CSR.
- HEXFORCE®: This is a twill glass fiber fabric purchased from Mike Compositi (Milan, Italy). It is used a reinforcement to produce laminated composites. The fabric is woven in twill 2/2 [grammage: 220 g/m2; thickness: 1.2 mm].
- Roving 600 111A plain weave glass fiber, produced by Owens Corning (Toledo, OH, USA), is a fabric with a much higher grammage (280 g/m2) with respect to HEXFORCE fabric, and the weaving is plain. It is made from Advantex® Glass (Owens Corning, Toledo, OH, USA), a boron-free corrosion resistant E-CR glass fiber.
- M113 chopped strand mat glass fiber produced by Owens Corning (Toledo, OH, USA) is a nonwoven fabric produced using Advantex® glass fibers that combines the mechanical properties of traditional E-glass with the corrosion resistance of E-CR glass. This mat is made with low-size strands of glass roving held together by a styrene-soluble powder binder. The mat grammage is 300 g/m2.
2.2. Resin Manufacturing and Characterization
2.3. Resin Rheological Evaluation
2.4. Glass Fiber Laminated Composite Manufacturing and Characterization Methods
3. Results and Discussion
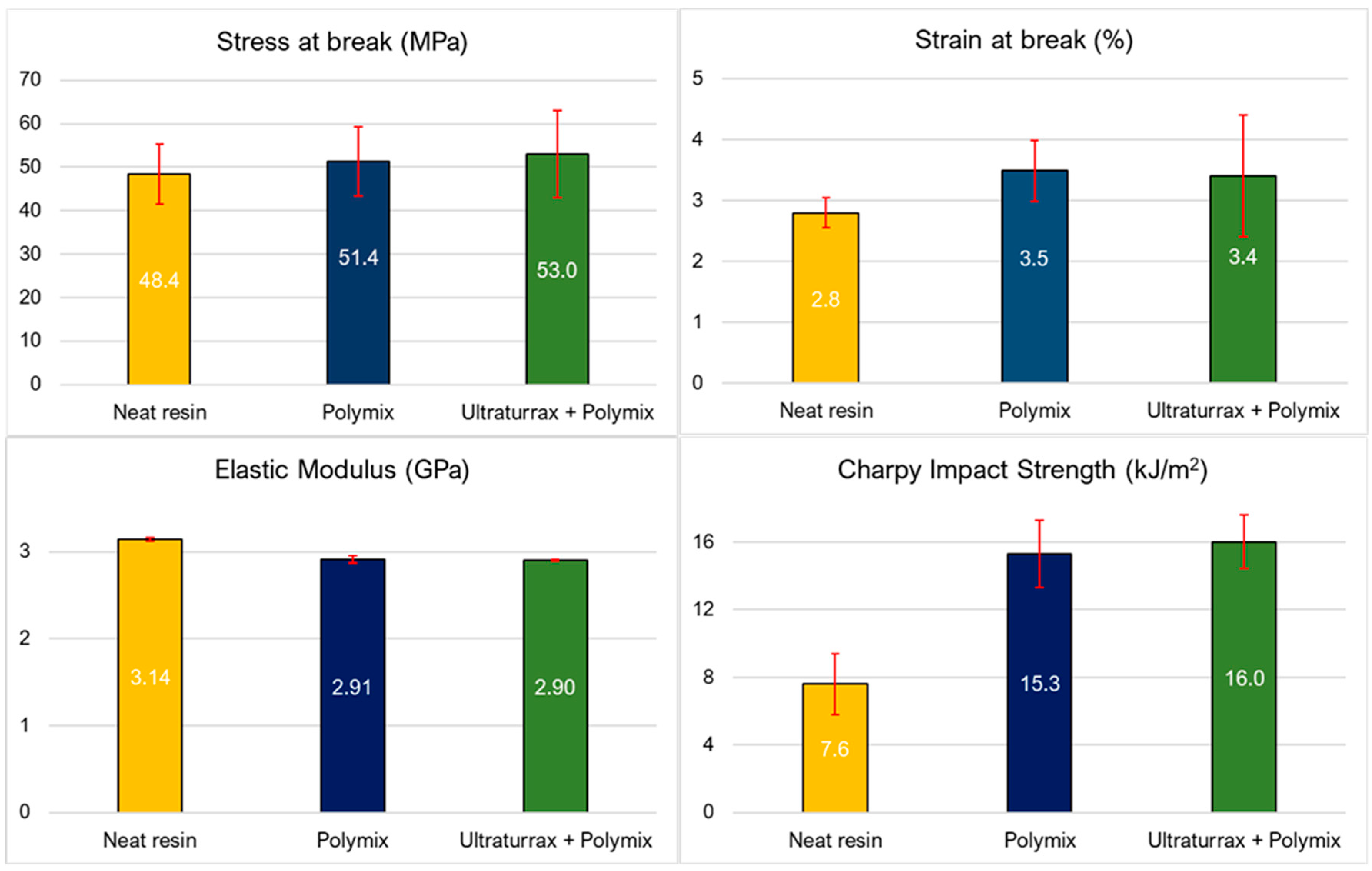
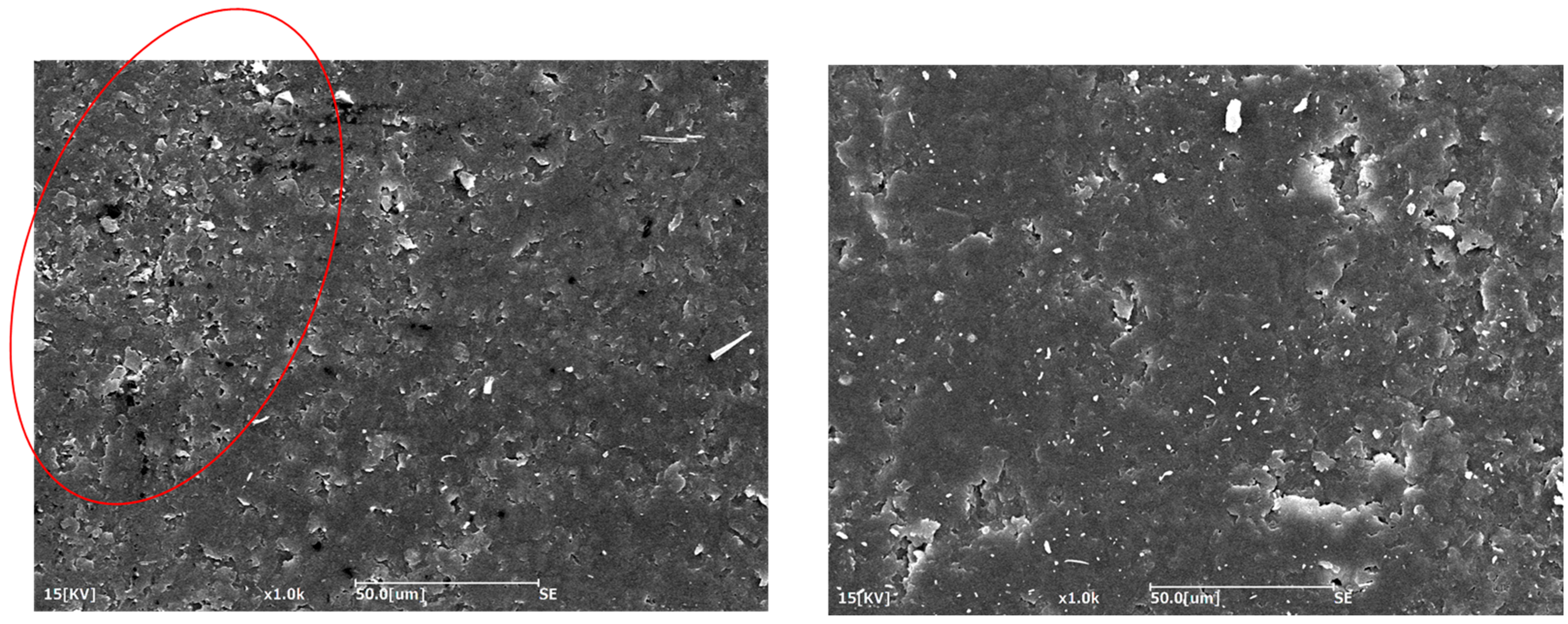
3.1. Resin Results Adopting Different Mixing Procedures
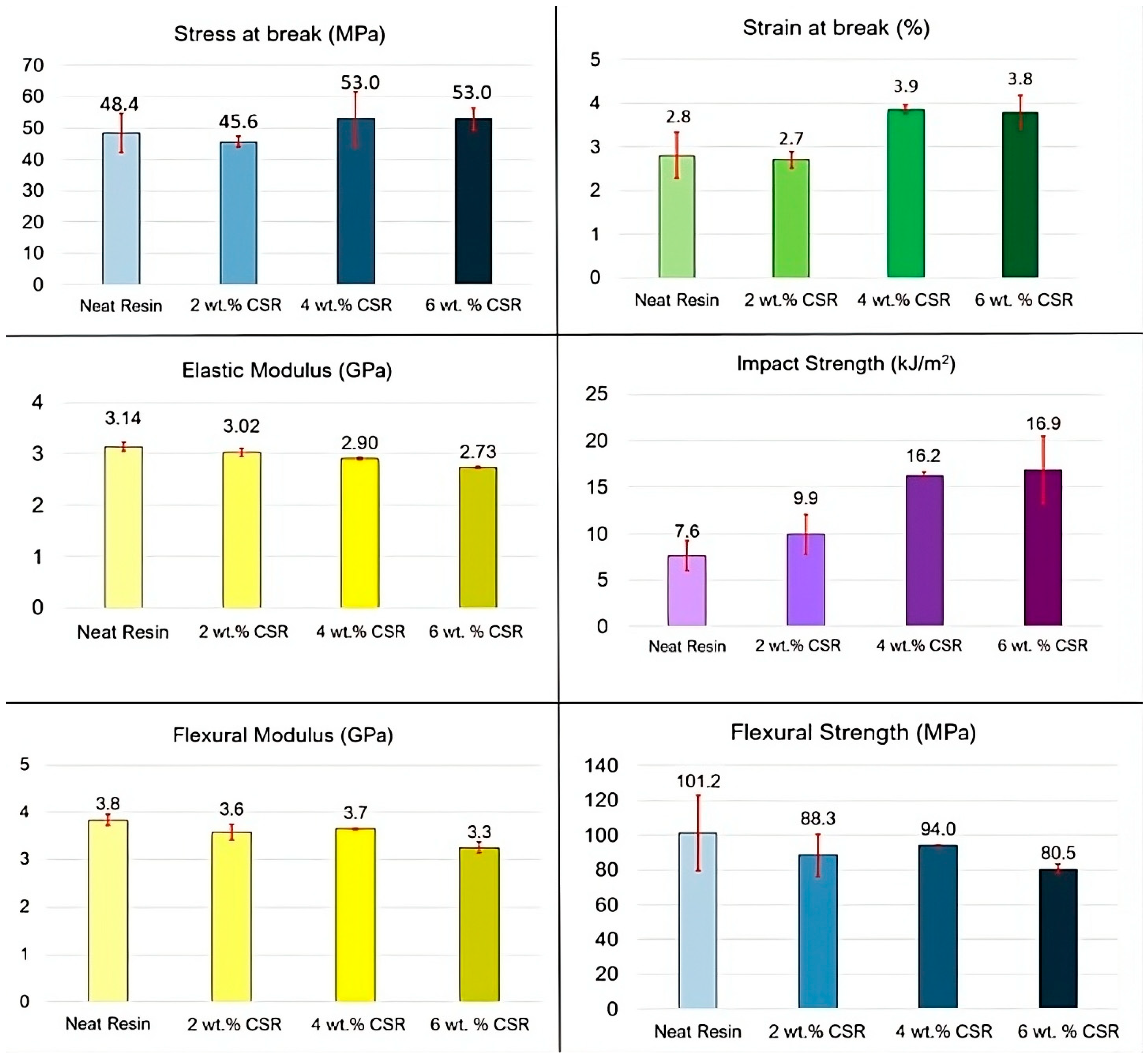
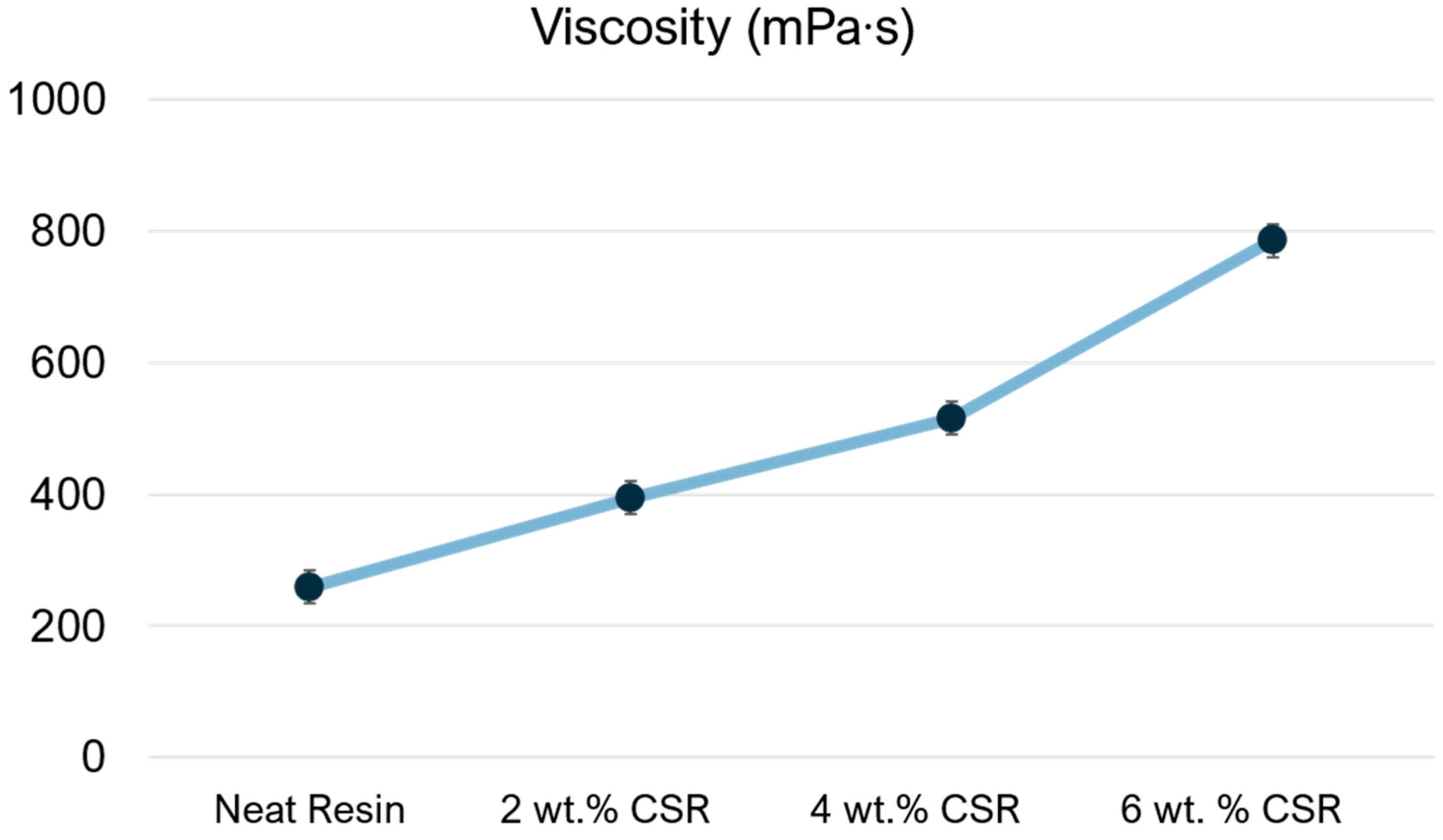
3.2. Resin Results with Different Liquid Toughener Amounts
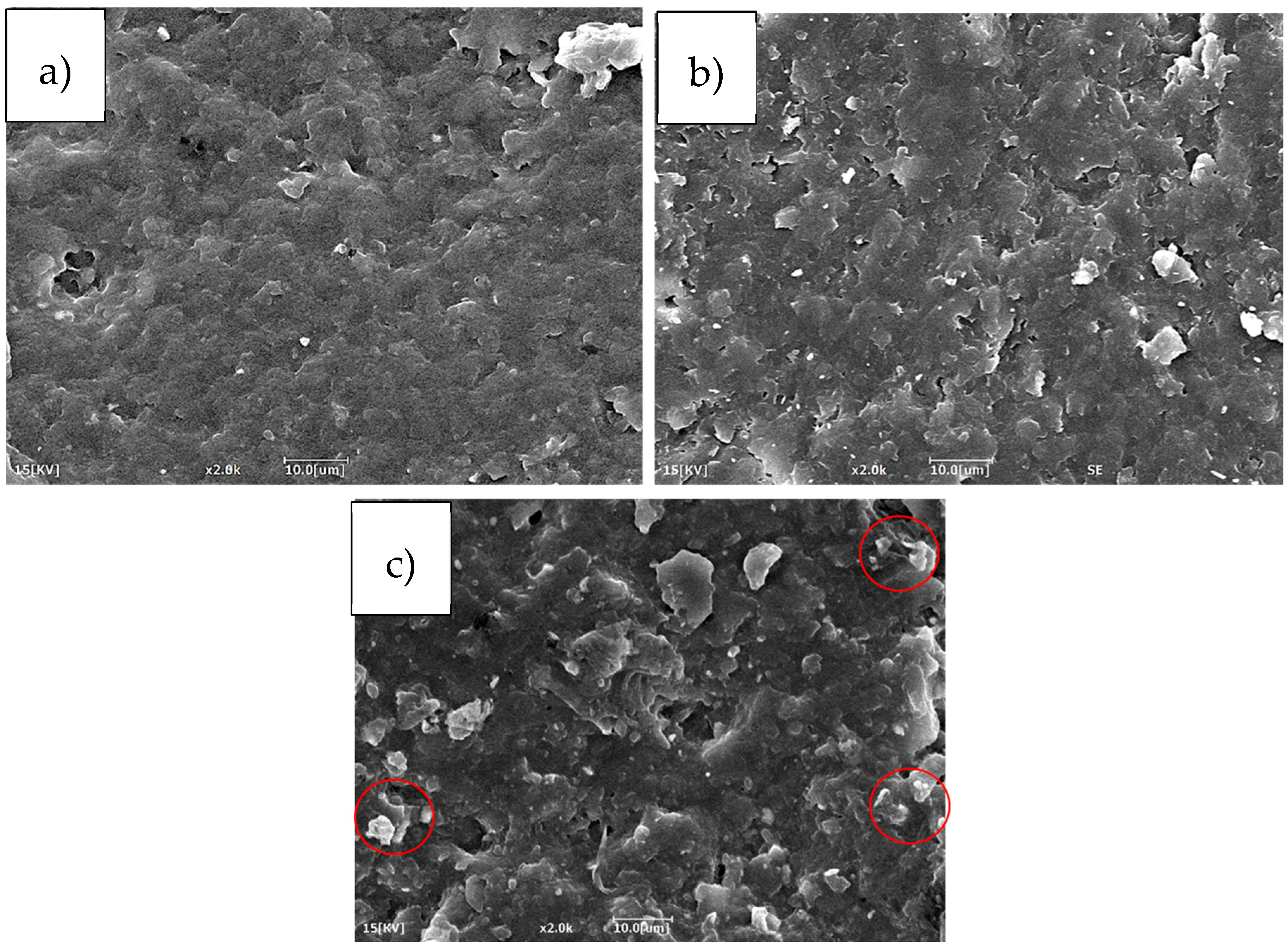
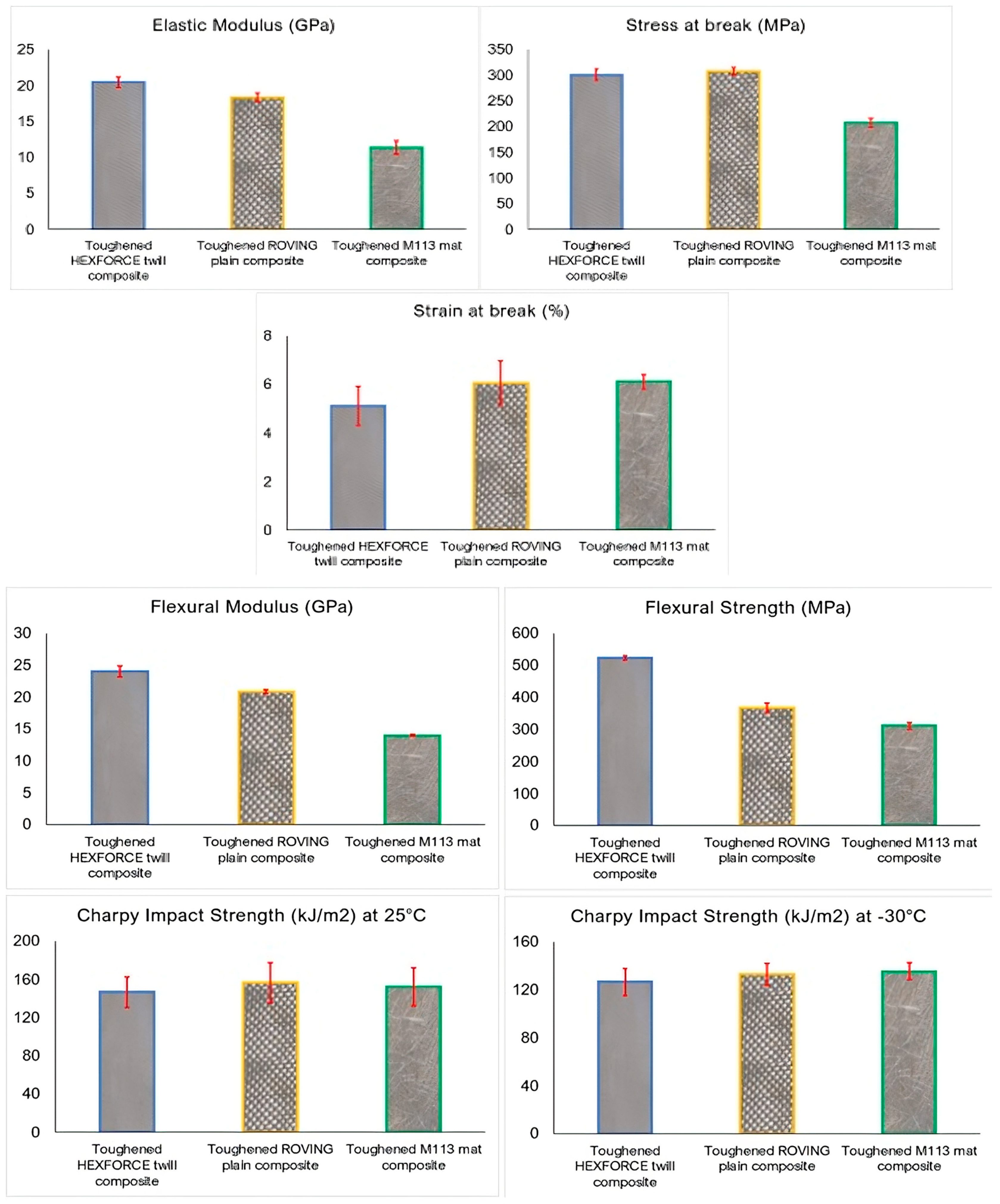
3.3. Glass Fiber Laminated Composite Results with Toughened and Untoughened Resin
3.4. Effect of Architecture, Grammage, Orientation and Type of Glass Fiber Reinforcement
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Phiri, R.; Mavinkere Rangappa, S.; Siengchin, S.; Oladijo, O.P.; Ozbakkaloglu, T. Advances in Lightweight Composite Structures and Manufacturing Technologies: A Comprehensive Review. Heliyon 2024, 10, e39661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beaumont, P.W.R. The Structural Integrity of Composite Materials and Long-Life Implementation of Composite Structures. Appl. Compos. Mater. 2020, 27, 449–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simões, S. High-Performance Advanced Composites in Multifunctional Material Design: State of the Art, Challenges, and Future Directions. Materials 2024, 17, 5997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkins, T. The Importance of Toughness in Manufacturing. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2018, 261, 280–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamzat, A.K.; Murad, M.S.; Adediran, I.A.; Asmatulu, E.; Asmatulu, R. Fiber-Reinforced Composites for Aerospace, Energy, and Marine Applications: An Insight into Failure Mechanisms under Chemical, Thermal, Oxidative, and Mechanical Load Conditions. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2025, 8, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Lei, Z.; Taynton, P.; Huang, S.; Zhang, W. Malleable and Recyclable Thermosets: The Next Generation of Plastics. Matter 2019, 1, 1456–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucknall, C.B.; Heather, P.S.; Lazzeri, A. Rubber Toughening of Plastics. J. Mater. Sci. 2000, 24, 2255–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salins, S.S.; Shetty, S.; Sachidananda, H.K. Investigating Energy Absorption and Crack Propagation in Natural Rubber–Epoxy Composites: Design, Fabrication, and Fracture Analysis. In Polymer Bulletin; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, I.; Collyer, A.A. Rubber Toughening Mechanisms in Polymeric Materials. In Rubber Toughened Engineering Plastics; Collyer, A.A., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1994; pp. 29–56. [Google Scholar]
- Awaja, F.; Zhang, S.; Tripathi, M.; Nikiforov, A.; Pugno, N. Cracks, Microcracks and Fracture in Polymer Structures: Formation, Detection, Autonomic Repair. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2016, 83, 536–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmerman, J.F.; Tillman, M.S.; Hayes, B.S.; Seferis, J.C. Matrix and Fiber Influences on the Cryogenic Microcracking of Carbon Fiber/Epoxy Composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2002, 33, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arends, C.B. Polymer Toughening; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1996; ISBN 9781003067399. [Google Scholar]
- Bagheri, R.; Pearson, R.A. Role of Particle Cavitation in Rubber-Toughened Epoxies: 1. Microvoid Toughening. Polymer 1996, 37, 4529–4538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, J.R.; Tracey, D.M. On the Ductile Enlargement of Voids in Triaxial Stress Fields∗. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 1969, 17, 201–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, M.L.; Frontini, P.M.; Williams, R.J.J. Analysis of the Damage Zone around the Crack Tip for Two Rubber-Modified Epoxy Matrices Exhibiting Different Toughenability. Polymer 2003, 44, 1537–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, H.R.; Schneider, J.A.; Murphy, T.L. Experimental Studies of the Deformation Mechanisms of Core-Shell Rubber-Modified Diglycidyl Ether of Bisphenol-A Epoxy at Cryogenic Temperatures. J. Compos. Mater. 2014, 48, 1279–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sue, H.-J. Craze-like Damage in a Core-Shell Rubber-Modified Epoxy System. J. Mater. Sci. 1992, 27, 3098–3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, R.; Ma, X.; Cai, L.; Zhang, Z.; Fang, Y.; Wang, J. Low Viscosity and Low Temperature Curing Reactive POSS/Epoxy Hybrid Resin with Enhanced Toughness and Comprehensive Thermal Performance. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 7263–7275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaskova-Kuzmina, T.; Stankevics, L.; Tarasovs, S.; Sevcenko, J.; Špaček, V.; Sarakovskis, A.; Zolotarjovs, A.; Shmits, K.; Aniskevich, A. Effect of Core–Shell Rubber Nanoparticles on the Mechanical Properties of Epoxy and Epoxy-Based CFRP. Materials 2022, 15, 7502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, P.K.; Iqbal, N.; Kumar, D.; Rajagopal, C. Polysiloxane-Based Core-Shell Microspheres for Toughening of Epoxy Resins. J. Polym. Res. 2014, 21, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naguib, M.; Grassini, S.; Sangermano, M. Core/Shell PBA/PMMA-PGMA Nanoparticles to Enhance the Impact Resistance of UV-Cured Epoxy Systems. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2013, 298, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, D.; Ivankovic, A. Effect of Core–Shell Rubber (CSR) Nano-Particles on Mechanical Properties and Fracture Toughness of an Epoxy Polymer. Polymer 2015, 66, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semitekolos, D.; Terzopoulou, S.; Charitidis, C. Enhancing Carbon Fiber-Reinforced Polymers’ Performance and Reparability Through Core–Shell Rubber Modification and Patch Repair Techniques. Polymers 2025, 17, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shree, S.; Tate, J.S.; Deshpande, A. Mechanical Characterization of Core Shell Rubber Particles Modified Vinyl Ester and Glass Fiber Reinforced Composites. In Proceedings of the SAMPE—Society for the Advancement of Material and Process Engineering, Charlotte, NC, USA, 20–23 May 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Gardner, N.; Gupta, S.; Shukla, A.; Nolet, S. Dynamic Response of Nano-Scale Core-Shell Rubber Toughened Sandwich Composites. Strain 2014, 50, 501–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, X.; Lin, T.; Jiang, Q.; Zeng, Y.; Liu, W. Toughening of Vinyl Ester Resins and Carbon Fiber-Reinforced Composites Using Core-Shell Rubber Particles with Varied Surface Functionalization. Compos. Commun. 2025, 53, 102204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Xiao, Z. Fabrication of Vinyl Ester-Modified Phenolic Resin Composite Coatings for the Protection of Combustible Cartridge Cases. ACS Omega 2025, 10, 13807–13815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubino, F.; Nisticò, A.; Tucci, F.; Carlone, P. Marine Application of Fiber Reinforced Composites: A Review. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garay, A.C.; Paese, L.T.; Souza, J.A.; Amico, S.C. Studies on Thermal and Viscoelastic Properties of Vinyl Ester Resin and Its Composites with Glass Fiber. Matéria 2015, 20, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afshar, A.; Alkhader, M.; Korach, C.S.; Chiang, F.-P. Effect of Long-Term Exposure to Marine Environments on the Flexural Properties of Carbon Fiber Vinylester Composites. Compos. Struct. 2015, 126, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, H.; Yang, R.; Zhang, W. Synthesis of a Novel Vinyl Ester Resin and Its Glass Fiber Composite with Good Flame Retardant and Mechanical Properties. Mater. Today Chem. 2025, 43, 102434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baley, C.; Davies, P.; Troalen, W.; Chamley, A.; Dinham-Price, I.; Marchandise, A.; Keryvin, V. Sustainable Polymer Composite Marine Structures: Developments and Challenges. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2024, 145, 101307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.K.; Schmalbach, K.M.; Kinaci, E.; Stanzione, J.F.; Palmese, G.R. Recent Advances in Plant-Based Vinyl Ester Resins and Reactive Diluents. Eur. Polym. J. 2018, 98, 199–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Białkowska, A.; Bakar, M.; Kucharczyk, W.; Zarzyka, I. Hybrid Epoxy Nanocomposites: Improvement in Mechanical Properties and Toughening Mechanisms—A Review. Polymers 2023, 15, 1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awang Ngah, S.; Taylor, A.C. Toughening Performance of Glass Fibre Composites with Core–Shell Rubber and Silica Nanoparticle Modified Matrices. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2016, 80, 292–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouhi, E.; Bahrami, K.; Poorabdollah, M. Remarkable Enhancement of Physical-mechanical Properties in Unsaturated Polyester Resin Composites Using SiO2@CTBN Hybrid Particles. Polym. Compos. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dal Pont, B.; Aliotta, L.; Tognarelli, E.; Gigante, V.; Lazzeri, A. Toughened Vinyl Ester Resin Reinforced with Natural Flax Fabrics. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 10459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 527; Plastics, Determination of Tensile Properties. Part 2: Test Conditions for Moulding and Extrusion Plastics. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012.
- ISO 179-1; Plastics–Determination of Charpy Impact Properties—Part 1: Non-Instrumented Impact Test. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2000.
- Moore, D.; Pavan, A.; Williams, J.G. Fracture Mechanics Testing Methods for Polymers, Adhesives, and Composites; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2001; Volume 375. [Google Scholar]
- Sorrentino, L.; Turchetta, S.; Parodo, G.; Papa, R.; Toto, E.; Santonicola, M.G.; Laurenzi, S. RIFT Process Analysis for the Production of Green Composites in Flax Fibers and Bio-Based Epoxy Resin. Materials 2022, 15, 8173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chohan, J.S.; Boparai, K.S.; Singh, R.; Hashmi, M.S.J. Manufacturing Techniques and Applications of Polymer Matrix Composites: A Brief Review. Adv. Mater. Process. Technol. 2022, 8, 884–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, R.; Marouf, B.T.; Pearson, R.A. Rubber-Toughened Epoxies: A Critical Review. J. Macromol. Sci.® Part C Polym. Rev. 2009, 49, 201–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, R.; Tan, L. Advances in Toughening Modification Methods for Epoxy Resins: A Comprehensive Review. Polymers 2025, 17, 1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wu, Q.; Zhu, H.; Lin, Q.; Wang, C. Impact Resistance Enhancement by Adding Core-Shell Particle to Epoxy Resin Modified with Hyperbranched Polymer. Polymers 2017, 9, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, J. PMMA/MMA Binary Liquid Resins and Composites: Molecular Weight, Initiator Selection, Mechanical Properties and Pot Life. Polym. Compos. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, D.; Ivankovic, A. The Curing Behaviour and Thermo-Mechanical Properties of Core-Shell Rubber-Modified Epoxy Nanocomposites. Polym. Polym. Compos. 2019, 27, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinette, E.J. Toughening Vinyl Ester Matrix Composites by Tailoring Nanoscale and Mesoscale Interfaces; Drexel University: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Carolan, D.; Ivankovic, A.; Kinloch, A.J.; Sprenger, S.; Taylor, A.C. Toughened Carbon Fibre-Reinforced Polymer Composites with Nanoparticle-Modified Epoxy Matrices. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 52, 1767–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islami, D.P.; Muzaqih, A.F.; Adiputra, R.; Prabowo, A.R.; Firdaus, N.; Ehlers, S.; Braun, M.; Jurkovič, M.; Smaradhana, D.F.; Carvalho, H. Structural Design Parameters of Laminated Composites for Marine Applications: Milestone Study and Extended Review on Current Technology and Engineering. Results Eng. 2024, 24, 103195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Zhang, H.; Yang, D. Bearing Performance and Progressive Failure Analysis of Bolted Joint in 3D Printed Pseudo-Woven CFRP Composite with Fibre Steering. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2025, 188, 108526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreozzi, M.; Bianchi, I.; Gentili, S.; Mancia, T.; Simoncini, M. Effect of Fabric Areal Weight on the Mechanical Properties of Composite Laminates in Carbon-Fiber-Reinforced Polymers. J. Compos. Sci. 2023, 7, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benhamadouche, L.; Moussaoui, N.; Benkhelif, A.; Jawaid, M.; Rokbi, M.; Osmani, H.; Fouad, H.; Singh, B. Resistance to Crack Propagation of a Composite with Recycled Jute Fabric—Polypropylene. Compos. Struct. 2025, 356, 118884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çava, K.; İpek, H.; Uşun, A.; Aslan, M. Examine the Mechanical Properties of Woven Glass Fiber Fabric Reinforced Composite Plate Manufactured with Vat-photopolymerization. Polym. Compos. 2024, 45, 17105–17120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şimşir, E. Study of Impact Behavior of Glass-Fiber-Reinforced Aluminum Composite Sandwich Panels at Constant Energy Levels. Coatings 2025, 15, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putic, S.; Stamenovic, M.; Bajceta, B.; Stajcic, P.; Bosnjak, S. The Influence of High and Low Temperatures on the Impact Properties of Glass-Epoxy Composites. J. Serbian Chem. Soc. 2007, 72, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Fabric Typology | Number of Plies | Grammage (g/m2) | Laminate Thickness (mm) | Glass Fibers Density (g/cm3) | Volume Fiber Fraction |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HEXFORCE® Twill | 9 | 220 | 2.5 | 2.5 | 0.3 |
| Roving 600 111A Plain Weave | 7 | 280 | 2.5 | 2.5 | 0.3 |
| M113 Chopped Strand Mat | 6 | 300 | 2.5 | 2.5 | 0.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gigante, V.; Dal Pont, B.; Montanelli, C.; Aliotta, L.; Lazzeri, A. Development of Glass Fibers Laminates Toughened with Core–Shell Rubber Particles for Applications in Cold Environments. Polymers 2025, 17, 1641. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17121641
Gigante V, Dal Pont B, Montanelli C, Aliotta L, Lazzeri A. Development of Glass Fibers Laminates Toughened with Core–Shell Rubber Particles for Applications in Cold Environments. Polymers. 2025; 17(12):1641. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17121641
Chicago/Turabian StyleGigante, Vito, Bianca Dal Pont, Chiara Montanelli, Laura Aliotta, and Andrea Lazzeri. 2025. "Development of Glass Fibers Laminates Toughened with Core–Shell Rubber Particles for Applications in Cold Environments" Polymers 17, no. 12: 1641. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17121641
APA StyleGigante, V., Dal Pont, B., Montanelli, C., Aliotta, L., & Lazzeri, A. (2025). Development of Glass Fibers Laminates Toughened with Core–Shell Rubber Particles for Applications in Cold Environments. Polymers, 17(12), 1641. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17121641









