A Review on the Recent Advancements of Polymer-Modified Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery Under Stimuli-Trigger
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles (MSNs)
2.1. Synthesis and Structural Characteristics
2.2. Challenges of MSN in Biological Applications
3. Polymer Modification of MSNs
3.1. Purpose of Polymer Functionalization
3.2. Types of Polymers Used for the Modification of MSNs
3.3. Functionalization Strategies for the Modifications of MSNs
| Method | Advantages | Limitations | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Covalent Grafting | - Strong, stable attachment - Good control over surface chemistry - Long circulation stability | - May block pores, reducing drug loading - Requires multi-step reactions and harsh conditions - Difficult to reverse | [32] |
| Electrostatic Adsorption | - Simple and mild process - Reversible binding - Suitable for sensitive biomolecules | - Weak interaction, prone to desorption - Sensitive to pH and ionic strength - Lower long-term stability | [34] |
| Physical Entrapment | - Easy to perform - No chemical modification required - Minimal reaction steps | - Poor control over release and coating - Risk of premature polymer leaching - Weak interaction with the MSN surface | [31] |
| Grafting-To | - Pre-synthesized polymers with defined properties - Good for functional polymer integration | - Low grafting density due to steric hindrance - Limited surface coverage and uniformity | [38] |
| Grafting-From | - High grafting density - Precise control over chain length and density - Uniform coating | - Complex synthesis - Requires initiators and controlled polymerization - Potential toxicity from residual catalysts | [36] |
3.4. Characterization of Polymer Functionalized MSNs
4. Advantages of Drug Delivery
Classification of Stimuli
5. Recent Advancements in Polymer-Modified MSNs for Controlled Drug Delivery
Classification of Various Stimuli-Triggered Drug Delivery from the PM-MSNs
- (i)
- pH-responsive systems
- (ii)
- Redox-responsive systems

- (iii)
- Enzyme-responsive systems
- (iv)
- Light-triggered systems
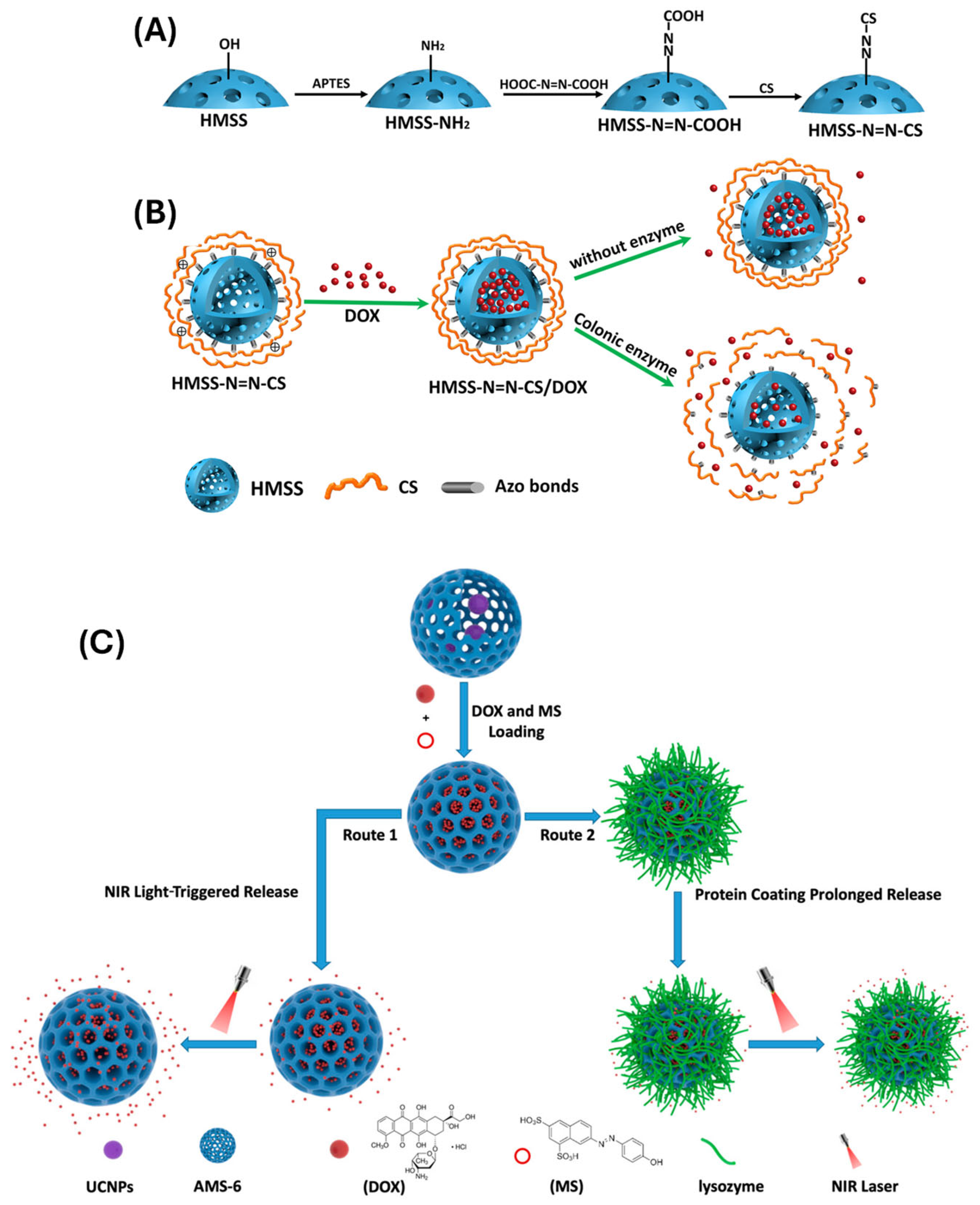
- (v)
- Thermo-responsive systems
- (vi)
- Ultrasound-responsive systems
- (vii)
- Dual and multi-stimuli responsive systems

6. Biological Considerations and Applications
6.1. Cellular Uptake and Intracellular Trafficking
6.2. Targeting Strategies
6.3. In Vitro and In Vivo Performance
7. Challenges and Future Perspectives
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carvalho, G.C.; Sábio, R.M.; de Cássia Ribeiro, T.; Monteiro, A.S.; Pereira, D.V.; Ribeiro, S.J.L.; Chorilli, M. Highlights in Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as a Multifunctional Controlled Drug Delivery Nanoplatform for Infectious Diseases Treatment. Pharm. Res. 2020, 37, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chircov, C.; Spoiala, A.; Paun, C.; Craciun, L.; Ficai, D.; Ficai, A.; Andronescu, E.; Turculet, S.C. Mesoporous Silica Platforms with Potential Applications in Release and Adsorption of Active Agents. Molecules 2020, 25, 3814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zid, L.; Zelenak, V.; Almasi, M.; Zelenakova, A.; Szucsova, J.; Bednarcik, J.; Sulekova, M.; Hudak, A.; Vahovska, L. Mesoporous Silica as a Drug Delivery System for Naproxen: Influence of Surface Functionalization. Molecules 2020, 25, 4722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, T.T.; Elyafi, A.K.E.; Mohammed, A.R.; Al-Khattawi, A. Delivery of Poorly Soluble Drugs via Mesoporous Silica: Impact of Drug Overloading on Release and Thermal Profiles. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorthy, M.S.; Thirupathi, K.; Krishnan, S.; Guganathan, L.; Dave, S.; Phan, T.T.V.; Kim, S.-C. Preparation of Magnetic Iron Oxide Incorporated Mesoporous Silica Hybrid Composites for pH and Temperature-Sensitive Drug Delivery. Magnetochemistry 2023, 9, 81. [Google Scholar]
- Mi, P. Stimuli-responsive nanocarriers for drug delivery, tumor imaging, therapy and theranostics. Theranostics 2020, 10, 4557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoj, D.; Rajendran, S.; Naushad, M.; Moorthy, M.S.; Gracia, F.; Moscoso, M.S.; Gracia-Pinilla, M.A. Mesoporogen free synthesis of CuO/TiO2 heterojunction for ultra-trace detection of catechol in water samples. Env. Res. 2023, 216, 114428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seljak, K.B.; Kocbek, P.; Gašperlin, M. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles as delivery carriers: An overview of drug loading techniques. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 59, 101906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorthy, M.S.; Kim, S.H.; Huh, P.; Jung, Y.S.; Kim, S.C. Dramatic reduction of toxicity of Poly(hexamethylene guanidine) disinfectant by charge neutralization. Environ. Res. 2023, 231, 116172. [Google Scholar]
- Maleki, A.; Kettiger, H.; Schoubben, A.; Rosenholm, J.M.; Ambrogi, V.; Hamidi, M. Mesoporous silica materials: From physico-chemical properties to enhanced dissolution of poorly water-soluble drugs. J. Control. Release 2017, 262, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, C.; Gao, Y.; Jiang, T.; Wang, S. The synthesis and application involving regulation of the insoluble drug release from mesoporous silica nanotubes. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 330, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirupathi, K.; Raorane, C.J.; Ramkumar, V.; Ulagesan, S.; Moorthy, M.S.; Raj, V.; Krishnakumar, G.S.; Phan, T.T.V.; Kim, S.-C. Update on chitosan-based hydrogels: Preparation, characterization, and its antimicrobial and antibiofilm applications. Gels 2022, 9, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirupathi, K.; Phan, T.T.V.; Moorthy, M.S.; Ramkumar, V.; Kim, S.-C. pH and thermoresponsive PNIPAm-co-polyacrylamide hydrogel for dual stimuli-responsive controlled drug delivery. Polymers 2022, 15, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohan, A.; Moorthy, M.S.; Phan, T.T.V.; Kim, S.C. pNIPAm-based pH and thermoresponsive copolymer hydrogel for hydrophobic and hydrophilic drug delivery. Gels. 2024, 10, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramkumar, V.; Raorane, C.J.; Chiristy, H.J.; Anandhi, S.; Moorthy, M.S.; Kim, S.C. Hydrogen-bonded keto-enol mechanized chalcone material for optical and antibiofilm applications. J. Mol. Struct. 2023, 1292, 136109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, A.; Suresh, R.; Ashwini, M.; Periyasami, G.; Guganathan, L.; Lin, M.-C.; Kumarasamy, K.; Kim, S.-C.; Moorthy, M.S. Alginate functionalized magnetic-silica composites for pH-responsive drug delivery and magnetic hyperthermia applications. Mater. Lett. 2024, 361, 136088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manivasagan, P.; Hoang, G.; Moorthy, M.S.; Mondal, S.; Doan, V.H.M.; Kim, H.; Phan, T.T.V.; Nguyen, T.P.; Oh, J. Chitosan/fucoidan multilayer coating of gold nanorods as highly efficient near-infrared photothermalagents for cancer therapy. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 2011, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, S.; Hoang, G.; Manivasagan, P.; Moorthy, M.S.; Kim, H.; Phan, T.T.V.; Oh, J. Comparative characterization of biogenic and chemical synthesized hydroxyapatite biomaterials for potential biomedical application. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2019, 228, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djayanti, K.; Maharjan, P.; Cho, K.H.; Jeong, S.; Kim, M.S.; Shin, M.C.; Min, K.A. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as a Potential Nanoplatform: Therapeutic Applications and Considerations. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, S.; Hoang, G.; Manivasagan, P.; Moorthy, M.S.; Phan, T.T.V.; Kim, H.; Nguyen, T.P.; Oh, J. Rapid microwave-assisted synthesis of gold loaded hydroxyapatite collagen nano-biomaterials for drug delivery and tissue engineering applications. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 2977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnanasekaran, L.; Priya, A.K.; Ghfar, A.A.; Sekar, K.; Moorthy, M.S.; Arthi, M.; Soto-Moscoso, M. The influence of heterostructured TiO2/ZnO nanomaterials for the removal of azo dye pollutant. Chemosphere 2022, 308, 136162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatesan, R.; Moorthy, M.S.; Alagumalai, K.; Haldhar, R.; Raorane, C.J.; Raj, V.; Kim, S.-C. Novel approach in biodegradation of synthetic thermoplastic polymers: An overview. Polymers 2022, 14, 4271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, B.; Moorthy, M.S.; Manivasagan, P.; Xu, L.; Song, K.; Lee, K.D.; Kwak, M.; Oh, J.; Jin, J. Fucoidan-coated CuS nanoparticles for chemo-and photothermal therapy against cancer. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 12649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manivasagan, P.; Bharathiraja, S.; Moorthy, M.S.; Mondal, S.; Seo, H.; Lee, K.D.; Oh, J. Marine natural pigments as potential sources for therapeutic applications. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2018, 38, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnanasekaran, L.; Moorthy, M.S.; Naushad, M.; Alothman, Z.A.; Soto-Moscoso, M.; Show, P.L.; Khoo, K.S. Photocatalytic removal of food colorant using NiO/CuO heterojunction nanomaterials. Food Toxicol. 2022, 167, 113277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharathiraja, S.; Manivasagan, P.; Moorthy, M.S.; Bui, N.Q.; Jang, B.; Phan, T.T.V.; Jung, W.-K.; Kim, Y.-M.; Lee, K.D.; Oh, J. Photo-based PDT/PTT dual model killing and imaging of cancer cells using phycocyanin-polypyrrole nanoparticles. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 123, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moorthy, M.S.; Thirupathi, K.; Thirumalai, D.; Aldawood, S.; Kim, S.-C. Surface grafted silica adsorbent for efficient removal of Hg2+ ions from contaminated water. Environ. Res. 2022, 212, 113211. [Google Scholar]
- Mondal, S.; Hoang, G.; Manivasagan, P.; Moorthy, M.S.; Nguyen, T.P.; Phan, T.T.V.; Kim, M.H.; Nam, S.Y.; Oh, J. Nanohydroxyapatite bioactive glass composite scaffold with enhanced mechanical and biological performance for tissue engineering application. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 15735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asrafali, S.P.; Periyasamy, T.; Haldhar, R.; Moorthy, M.S.; Kim, S.-C. Fabrication of SiO2-reinforced polybenzoxazine composites and their thermal and dielectric properties. J. Polym. Res. 2022, 29, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manivasagan, P.; Bharathiraja, S.; Moorthy, M.S.; Mondal, S.; Nguyen, T.P.; Kim, H.; Phan, T.T.V.; Lee, K.D.; Oh, J. Biocompatible Chitosan Oligosaccharide Modified Gold nanorods as Highly Effective Photothermal Agents for Ablation of Breast Cancer Cells. Polymers 2018, 10, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorthy, M.S.; Thirupathi, K.; Periyasamy, T.; Thirumalai, D.; Ramkumar, V.; Asrafali, S.P.; Kim, S.-C. Synthesis of bifunctional groups-integrated mesoporous silica hybrid adsorbent for simultaneous removal of Hg2+ and Cu2+ ions from aqueous solution. Surf. Interfaces 2022, 29, 101808. [Google Scholar]
- Bharathiraja, S.; Bui, N.Q.; Manivasagan, P.; Moorthy, M.S.; Mondal, S.; Seo, H.; Nguyen, T.P.; Phan, T.T.V.; Kim, H.; Lee, K.D.; et al. Multimodel tumor-homing chitosan oligosaccharide-coated biocompatible palladium nanoparticles for photo-based imaging and therapy. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Periyasamy, T.; Asrafali, S.P.; Haldhar, R.; Moorthy, M.S.; Vanaraj, R.; Raorane, C.J.; Kim, S.-C. Modified cotton sponge with bio-based polybenzoxazine for plasticizer absorption and oil–water separation. ACS. Appl. Polym. Mater. 2022, 4, 950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, T.T.V.; Bui, N.Q.; Cho, S.-W.; Bharathiraja, S.; Manivasagan, P.; Moorthy, M.S.; Mondal, S.; Kim, C.-S.; Oh, J. Photoacoustic Imaging-Guided Photothermal Therapy with Tumor-Targeting HA-FeOOH@PPy Nanorods. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, A.; Jung, K.; Li, A.; Liu, J.; Boyer, C. Recent advances in stimuli-responsive polymer systems for remotely controlled drug release. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2019, 99, 101164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Mondal, S.; Jang, B.; Manivasagan, P.; Moorthy, M.S.; Oh, J. Biomimitic synthesis of metal-hydroxyapatite (Au-HAp, Ag-HAp, Au-Ag-HAp): Structural analysis, spectroscopic characterization and biomedical application. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 20490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorthy, M.S.; Bharathiraja, S.; Manivasagan, P.; Oh, J. Synthesis of surface capped mesoporous silica nanoparticles for pH-stimuli responsive drug delivery applications. MedChemCommun 2017, 8, 1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulagesan, S.; Moorthy, M.S.; Phan, T.T.V.; Alagumalai, K.; Thirupathi, K.; Kim, S.C.; Nam, T.J.; Choi, Y.H. Mesoporous silica (SBA-15) with enriched amidoxime functionalities for pH-controlled anticancer drug delivery. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2022, 146, 110132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guganathan, L.; Rajeevgandhi, C.; Sathiyamurthy, K.; Thirupathi, K.; Moorthy, M.S.; Chinnasamy, E.; Raorane, C.J.; Raj, V.; Kim, S.C.; Anand, P. Magnetic Application of Gadolinium Orthoferrite Nanoparticles Synthesized by Sol–Gel Auto-Combustion Method. Gels 2022, 8, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vamsi, E.B.; Devatha, C.P. Green synthesis of mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MSNs) and its application on degradation of triclosan. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2024, 10, 100818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorthy, M.S.; Thirumalai, D.; Thirupathi, K.; Kim, S.C. Synthesis of dithiol-modified mesoporous silica adsorbent for selective adsorption of mercury ions from wastewater. Appl. Nanosci. 2023, 13, 6015. [Google Scholar]
- Melendez-Ortiz, H.I.; Puente-Urbina, B.; Leon, G.C.; Mata-Padilla, J.; Garcia-Uriostegui, L. Synthesis of spherical SBA-15 mesoporous silica. Influence of reaction conditions on the structural order and stability. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 7564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, N. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles: Synthesis, classification, drug loading, pharmacokinetics, biocompatibility, and application in drug delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2019, 16, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Zhang, H.; Cao, C.; Zhang, J.; Li, F.; Huang, Q. Quaternized Chitosan-Capped Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as Nanocarriers for Controlled Pesticide Release. Nanomaterials 2016, 6, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandomierski, M.; Chojnacka, M.; Dlugosz, M.; Pokora, M.; Zwolinska, J.; Majchrzycki, L.; Voelkel, A. Mesoporous Silica Modified with Polydopamine and Zinc Ions as a Potential Carrier in the Controlled Release of Mercaptopurine. Materials 2023, 16, 4358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popova, M.; Trendafilova, I.; Zgureva, D.; Kalvachev, Y.; Boycheva, S.; Tuser, N.N.; Szegedi, A. Polymer-coated mesoporous silica nanoparticles for controlled release of the prodrug sulfasalazine. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2018, 44, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saputra, O.A.; Lestari, W.A.; Kurniansyah, V.; Lestari, W.W.; Sugiura, T.; Mukti, R.R.; Martien, R.; Wibowo, F.R. Organically surface engineered mesoporous silica nanoparticles control the release of quercetin by pH stimuli. Sci Rep. 2020, 12, 20661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azali, N.S.; Kamarudin, N.H.N.; Jaafar, J.A.; Timmiati, S.H.; Sajab, M.S. Modification of mesoporous silica nanoparticles with pH responsive polymer poly (2-vinylpyrrolidone) for the release of 5-Florouracil. Mater. Proc. 2020, 31, A12. [Google Scholar]
- Moorthy, M.S.; Vanaraj, R.; Thirupathi, K.; Ulagesan, S.; Nam, T.J.; Phan, T.T.V.; Kim, S.C. L-lysine-modified pNIPAm-co-GMA copolymer hydrogel for pH-and temperature-responsive drug delivery and fluorescence imaging applications. Gels 2023, 9, 363. [Google Scholar]
- Stephen, S.; Gorain, B.; Choudhury, H.; Chatterjee, B. Exploring the role of mesoporous silica nanoparticle in the development of novel drug delivery systems. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2022, 12, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Wang, B.; Chen, J.; He, J.; Qiu, X. Facile Synthesis of Three Types of Mesoporous Silica Microspheres as Drug Delivery Carriers and their Sustained-Release Properties. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2023, 20, 1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Li, M.; Liu, T.; Liu, J.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xu, S.; Liu, H. A dual-functional HER2 aptamer-conjugated, pH-activated mesoporous silica nanocarrier-based drug delivery system provides in vitro synergistic cytotoxicity in HER2-positive breast cancer cells. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 4029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Liu, S.; Cheng, J.; Yuan, S.; Yang, Y.; Fang, T.; Cao, K.; Wei, K.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Y. Charge-Selective Delivery of Proteins Using Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Fused with Lipid Bilayers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 3645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, R.; Wang, J.; Chen, Z. Aptamers as Smart Ligands for Targeted Drug Delivery in Cancer Therapy. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Li, S.; Shi, R.; Liu, H. Multifunctional mesoporous silica nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esfahani, K.M.M.; Alavi, S.E.; Cabot, P.J.; Islam, N.; Izake, E.L. Application of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles in Cancer Therapy and Delivery of Repurposed Anthelmintics for Cancer Therapy. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, F.; Chen, W.; Wei, K. Erianin-Loaded Photo-Responsive Dendrimer Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles: Exploration of a Psoriasis Treatment Method. Molecules 2022, 27, 6328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, M.; Wang, T.; Feng, R.; Zeng, P.; Chen, Z. Establishment of ultrasound-responsive SonoBacteriaBot for targeted drug delivery and controlled release. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1144963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moodley, T.; Singh, M. Current Stimuli-Responsive Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Cancer Therapy. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Kang, J.H.; Jang, J.; Lee, E.J.; Kim, J.H.; Byun, J.; Shin, U.S. Dual stimuli-responsive mesoporous silica nanoparticles for efficient loading and smart delivery of doxorubicin to cancer with RGD-integrin targeting. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 188, 106525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumder, J.; Minko, T. Multifunctional and stimuli-responsive nanocarriers for targeted therapeutic delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2021, 18, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Q.; Cui, J.; Shi, A.; Wu, J. Environmental stimulus-responsive mesoporous silica nanoparticles as anticancer drug delivery platforms. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2024, 234, 113758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rani, R.; Malik, P.; Dhania, S.; Mukherjee, T.K. Recent Advances in Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticle-Mediated Drug Delivery for Breast Cancer Treatment. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Citoglu, S.; Duran, H. Recent advances in porous nanomaterials-based drug delivery systems for osteoarthritis. Nanoselect 2024, 5, 230099. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, R.; Wang, W.; Wen, Y.; Zhang, X. Recent Advance on Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles-Based Controlled Release System: Intelligent Switches Open up New Horizon. Nanomaterials 2015, 5, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senapati, S.; Mahanta, A.K.; Kumar, S.; Maiti, P. Controlled drug delivery vehicles for cancer treatment and their performance. Sig. Transduct. Target. Ther. 2018, 3, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safaran, N.; Javadi, S.; Pourmadadi, M.; Ghaemi, A.; Yazdian, F.; Rashedi, H.; Rahdar, A.; Aboudzadeh, M.A. Advances in polymeric and non-polymeric nanocarriers for the magnified delivery of levofloxacin against bacterial infection. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2024, 26, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salve, R.; Kumar, P.; Ngamcherdtrakul, W.; Gajbhiye, V.; Yantasee, W. Stimuli-responsive mesoporous silica nanoparticles: A custom-tailored next generation approach in cargo delivery. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 124, 112084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramezanian, S.; Moghaddas, J.; Roghani-Mamaqani, H.; Rezamand, A. Dual pH- and temperature-responsive poly(dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate)-coated mesoporous silica nanoparticles as a smart drug delivery system. Sci Rep. 2023, 13, 20194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, M.D. Layer-by-layer hyaluronic acid/chitosan polyelectrolyte coated mesoporous silica nanoparticles as pH-responsive nanocontainers for optical bleaching of cellulose fabrics. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 146, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watermann, A.; Brieger, J. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles as drug delivery vehicles in cancer. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Hua, M.; Liu, H.; Li, J. How to design nanoporous silica nanoparticles in regulating drug delivery: Surface modification and porous control. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2021, 263, 114835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, M.; Cui, L.; Zhang, L. Enhanced Efficacy against Drug-Resistant Tumors Enabled by Redox-Responsive Mesoporous-Silica-Nanoparticle-Supported Lipid Bilayers as Targeted Delivery Vehicles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashique, S.; Sandhu, N.K.; Chawla, V.; Chawla, P.A. Targeted Drug Delivery: Trends and Perspectives. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2021, 18, 1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, D.; Ma, Y.; Xu, X.; Xie, J.; Ju, S. Stimuli-Responsive Polymeric Nanoplatforms for Cancer Therapy. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 707319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iranshahy, M.; Hanafi-Bojd, H.Y.; Aghili, S.; Irashahi, M.; Nabavi, S.M.; Saberi, S.; Filosa, R.; Neshad, I.F.; Hasanpour, M. Curcumin-loaded mesoporous silica nanoparticles for drug delivery: Synthesis, biological assays and therapeutic potential—A review. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 22250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.; Wu, H.; Yin, Z.Z.; Gao, J.; Wu, D.; Qin, Y.; Kong, Y. Disulfide-cleavage- and pH-triggered drug delivery based on a vesicle structured amphiphilic self-assembly. Mater. Sci. Eng. C-Mater. Biol. Appl. 2020, 107, 110366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naz, S.; Wang, M.; Han, Y.; Hu, Y.; Teng, L.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, J. Enzyme-responsive mesoporous silica nanoparticles for tumor cells and mitochondria multistage-targeted drug delivery. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.-L.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Q.-L.; Yang, Y.-W. Enzyme-responsive supramolecular nanovalves crafted by mesoporous silica nanoparticles and choline-sulfonatocalix 4 arene 2 pseudorotaxanes for controlled cargo release. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 9033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Niu, Y.; Li, S.; Lv, M.; Liu, J.; Zhang, L.; Cui, L.; Qu, L. TPGS and Doca dual-modified mesoporous silica nanoparticle-supported lipid bilayers enhance the efficient delivery and in vivo absorption of Coenzyme Q10. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2023, 81, 104243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, D.; Han, C.; Liu, C.; Ma, X.; Qian, J.; Zhou, J.; Li, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, W. Chitosan-capped enzyme-responsive hollow mesoporous silica nanoplatforms for colon-specific drug delivery. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.S.; Moorthy, M.S.; Ha, C.-S. Periodic mesoporous organosilicas for advanced applications. NPG Asia Mater. 2014, 6, e96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.; Kulanthaivel, S.; Mondal, A.; Mishra, S.; Banerjee, B.; Bhaumik, A.; Banerjee, I.; Giri, S. Mesoporous silica nanoparticle based enzyme responsive system for colon specific drug delivery through guar gum capping. Colloids. Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 150, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, N.; Zhao, Q.; Wan, L.; Wang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Wang, P.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, T.; Wang, S. Hybrid lipid-capped mesoporous silica for stimuli-responsive drug release and overcoming multidrug resistance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 3342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, B.; Luo, Z.; Ding, X.; Li, J.; Dai, L.; Zhou, J.; Zhao, X.; Ye, J.; Cai, K. Enzyme responsive mesoporous silica nanoparticles for targeted tumor therapy in vitro and in vivo. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 3614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Shang, H.; Lai, S.; Di, Y.; Sun, X.; Qiao, N.; Han, L.; Zhao, Z.; Lu, Y. Preparation and evaluation of controllable drug delivery system: A light responsive nanosphere based on β-cyclodextrin/mesoporous silica. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2023, 62, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Wang, H.; Wang, H.; Han, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Liu, X.; Feng, B.; Zhang, H. Light-responsive dual-functional biodegradable mesoporous silica nanoparticles with drug delivery and lubrication enhancement for the treatment of osteoarthritis. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 6394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, S.; Zheng, J.; Lv, P.; Zhang, D.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liao, R. Controlled Drug Release from Cyclodextrin-Gated Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Based on Switchable Host-Guest Interactions. Bioconjug. Chem. 2018, 29, 2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Du, Z.; Bao, G.; Fang, G.; Cappadona, M.; McClements, L.; Tuch, B.E.; Lu, H.; Xu, X. Smart Drug-Delivery System of Upconversion Nanoparticles Coated with Mesoporous Silica for Controlled Release. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, L.; Tan, X.; Sun, T.; Sun, Y.; Luo, J.; Zhang, H. Lubrication and drug release behaviors of mesoporous silica nanoparticles grafted with sulfobetaine-based zwitterionic polymer. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2020, 112, 110886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Yang, J.; Sun, Y.; He, M.; Liang, J.; Luo, J.; Cui, W.; Deng, L.; Xu, X.; Wang, B.; et al. Thermo-Sensitive Dual-Functional Nanospheres with Enhanced Lubrication and Drug Delivery for the Treatment of Osteoarthritis. Chemistry 2020, 26, 10564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajebi, S.; Abdollahi, A.; Roghani-Mamaqani, H.; Salami-Kalajahi, M. Temperature-Responsive Poly(N-Isopropylacrylamide) Nanogels: The Role of Hollow Cavities and Different Shell Cross-Linking Densities on Doxorubicin Loading and Release. Langmuir 2020, 36, 2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thirupathi, K.; Moorthy, M.S.; Radhakrishnan, S.; Ulagesan, S.; Nam, T.J.; Phan, T.T.V.; Kim, S.C. Thermosensitive Polymer-Modified Mesoporous Silica for pH and Temperature-Responsive Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, P.; Li, G.; Ma, S.; Zhou, H.; Chen, X. Multi-Responsive Nanocarriers Based on β-CD-PNIPAM Star Polymer Coated MSN-SS-Fc Composite Particles. Polymers 2019, 11, 1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Moreno, P.; de Vicente, J.; Nardecchia, S.; Marchal, J.A.; Boulaiz, H. Thermo-Sensitive Nanomaterials: Recent Advance in Synthesis and Biomedical Applications. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanzalaco, S.; Armelin, E. Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) and Copolymers: A Review on Recent Progresses in Biomedical Applications. Gels 2017, 3, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, B.; Zhao, Q.; Ye, X. Ultrasound and Magnetic Responsive Drug Delivery Systems for Cardiovascular Application. J. Cardiovasc. Pharm. 2020, 76, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzano, M.; Vallet-Regi, M. Ultrasound responsive Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Xia, H. Ultrasound Reversible Response Nanocarrier Based on Sodium Alginate Modified Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles. Sec. Polym. Chem. 2019, 7, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, V.A.; Vo, V.G.; Shim, K.; Lee, S.W.; An, S.S.A. Multimodal Mesoporous Silica Nanocarriers for Dual Stimuli-Responsive Drug Release and Excellent Photothermal Ablation of Cancer Cells. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 7667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, R.; Liu, Z.; Bai, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, X. Multiple-Responsive Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Highly Accurate Drugs Delivery to Tumor Cells. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 4306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Yuan, P.; Liu, Z.; Bai, Y.; Zhou, Y. Dual responsive hydrogels based on functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles as an injectable platform for tumor therapy and tissue regeneration. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 5968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Carmona, M.; Lozano, D.; Colilla, M.; Vallet-Regí, M. Lectin-conjugated pH-responsive mesoporous silica nanoparticles for targeted bone cancer treatment. Acta Biomater. 2018, 65, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, T.T.V.; Moorthy, M.S. Preparation of Dual pH-and Temperature-Sensitive Nanogels for Curcumin Delivery. Mater. Proc. 2023, 14, 71. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, J.; Ling, J.; Zhang, X.; Ouyang, X.; Omer, A.M.; Yang, G. pH/glutathione dual-responsive copper sulfide-coated organic mesoporous silica for synergistic chemo-photothermal therapy. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2024, 657, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, R.H.; Liu, Z.N.; Bai, Y.K.; Zhou, Y.S.; Chen, X. Effective Control of Enzyme Activity Based on a Subtle Nanoreactor: A Promising Strategy for Biomedical Applications in the Future. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2018, 1, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, W.; Sun, C.; Jiang, T.; Gao, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, S. Polydopamine-coated mesoporous silica nanoparticles for multi-responsive drug delivery and combined chemo-photothermal therapy. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 105, 110103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moorthy, M.S.; Bharathiraja, S.; Manivasagan, P.; Mondal, S.; Kim, H.; Lee, K.D.; Oh, J. Fucoidan-coated core-shell magnetic mesoporous silica nanoparticles for chemotherapy and magnetic hyperthermia-based thermal therapy applications. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 15334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharathiraja, S.; Moorthy, M.S.; Manivasagan, P.; Seo, H.; Lee, K.D.; Oh, J. Chlorin e6 conjugated silica nanoparticles for targeted and effective photodynamic therapy. Photodiagnosis Phototodyn. Ther. 2017, 19, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, Y.; Moorthy, M.S.; Manivasagan, P.; Bharathiraja, S.; Oh, J. Magnetic hyperthermia and pH-responsive effective drug delivery to the sub-cellular level of human breast cancer cells by modified CoFe2O4 nanoparticle. Biochimia 2017, 113, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharathiraja, S.; Manivasagan, P.; Moorthy, M.S.; Bui, N.Q.; Lee, K.D.; Oh, J. Chlorin e6 conjugated copper sulfide nanoparticles for photodynamic combined photothermal therapy. Photodiag. Photodyn. Ther. 2017, 19, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manivasagan, P.; Bharathiraja, S.; Moorthy, M.S.; Oh, Y.; Song, K.; Seo, H.; Oh, J. Anti-EGFR antibody conjugation of fucoidan-coated gold nanorods as novel photothermal ablation agents for cancer therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interface 2017, 9, 14633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, Y.; Je, J.-Y.; Moorthy, M.S.; Seo, H.; Cho, W.H. pH and NIR-light-responsive magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for mitochondria-mediated apoptotic cell death induced by chemo-photothermal therapy. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 531, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovtareva, S.; Kusepova, L.; Tazhkenova, G.; Mashan, T.; Bazarbaeva, K.; Kopishev, E. Surface Modification of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Application in Targeted Delivery Systems of Antitumour Drugs. Polymers 2024, 16, 1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Yuan, X.; Lin, W.; Cai, C.; Zhang, L. pH-responsive controlled release of mesoporous silica nanoparticles capped with Schiff base copolymer gatekeepers: Experiment and molecular dynamics simulation. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 176, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, T.T.V.; Bui, N.Q.; Moorthy, M.S.; Lee, K.D.; Oh, J. Synthesis and in vitro performance of polypyrrole-coated iron-platinum nanoparticles for photothermal therapy and photoacoustic imaging. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, K.; Zhou, D.; Wu, L.; Li, J.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, S.; He, R.; Xiao, L.; Zoya, I.; Yu, L.; et al. Gold-Nanoparticle-Based Multistage Drug Delivery System for Antitumor Therapy. Drug Deliv. 2022, 29, 3186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, S.; Manivasagan, P.; Bharathiraja, S.; Moorthy, M.S.; Nguyen, V.T.; Kim, H.; Nam, S.Y.; Lee, K.D.; Oh, J. Hydroxyapatite coated iron oxide nanoparticles: A promising nanomaterials for magnetic hyperthermia cancer treatment. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, T.T.V.; Bharathiraja, S.; Nguyen, V.T.; Moorthy, M.S.; Manivasagan, P.; Oh, J. Polypyrrole-methylene blue nanoparticles as a single multifunctional nanoplatform for near-infrared photo-induced therapy and photoacoustic imaging. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 35027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manivasagan, P.; Bui, N.Q.; Bharathiraja, S.; Moorthy, M.S.; Oh, Y.; Song, K.; Seo, H.; Yoon, M.; Oh, J. Multifunctional biocompatible chitosan-polypyrrole nanocomposites as novel reagents for photoacuastic imaging- guided photothermal ablation of cancer. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Cheng, K.; Chen, K.; Xu, C.; Ma, P.; Dang, G.; Yang, Y.; Lei, Q.; Huang, H.; Yu, Y.; et al. Nanoparticle-Based Medicines in Clinical Cancer Therapy. Nano Today 2022, 45, 101512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorthy, M.S.; Kim, H.-B.; Bae, J.-H.; Kim, S.-H.; Ha, C.-S. Design of core-shell magnetic mesoporous silica hybrids for pH and UV light stimuli- responsive cargo release. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 29106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorthy, M.S.; Oh, Y.; Bharathiraja, S.; Manivasagan, P.; Rajarathinam, T.; Jang, B.; Phan, T.T.V.; Jang, H.; Oh, J. Synthesis of amine-polyglycidol functionalized Fe3O4@SiO2 nanocomposites for magnetic hyperthermia, pH-responsive drug delivery, and bioimaging applications. RSC. Adv. 2016, 6, 110444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shair Mohammad, I.; Chaurasiya, B.; Yang, X.; Lin, C.; Rong, H.; He, W. Homotype-Targeted Biogenic Nanoparticles to Kill Multidrug-Resistant Cancer Cells. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorthy, M.S.; Park, J.-H.; Bae, J.-H.; Kim, S.-H.; Ha, C.-S. Mesoporous organosilica hybrids with a tunable amphoteric framework for controlled drug delivery. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 6487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorthy, M.S.; Song, H.-J.; Bae, J.-H.; Kim, S.-H.; Ha, C.-S. Red fluorescent hybrid mesoporous organo-silicas for simultaneous cell imaging and anticancer drug delivery. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 43342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorthy, M.S.; Kim, M.-J.; Bae, J.-H.; Park, S.S.; Saravanan, N.; Kim, S.-H.; Ha, C.-S. Multifunctional Periodic Mesoporous Organosilicas for Biomolecule Recognition Biomedical Applications in Cancer Therapy, and Metal Adsorption. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 17, 3028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorthy, M.S.; Seo, D.-J.; Song, H.-J.; Park, S.S.; Ha, C.-S. Magnetic mesoporous silica hybrid nanoparticles for highly selective boron adsorption. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 12485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

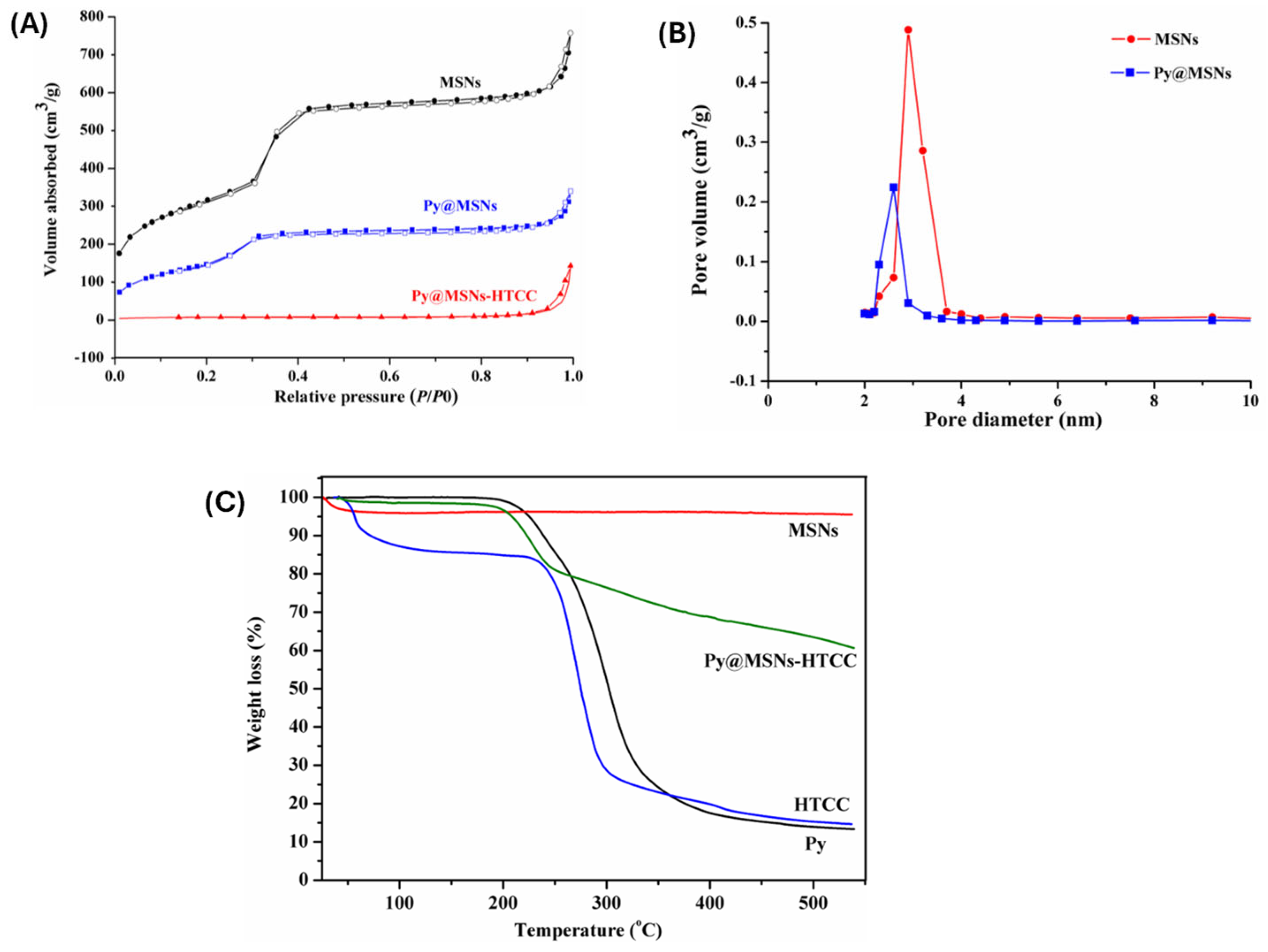
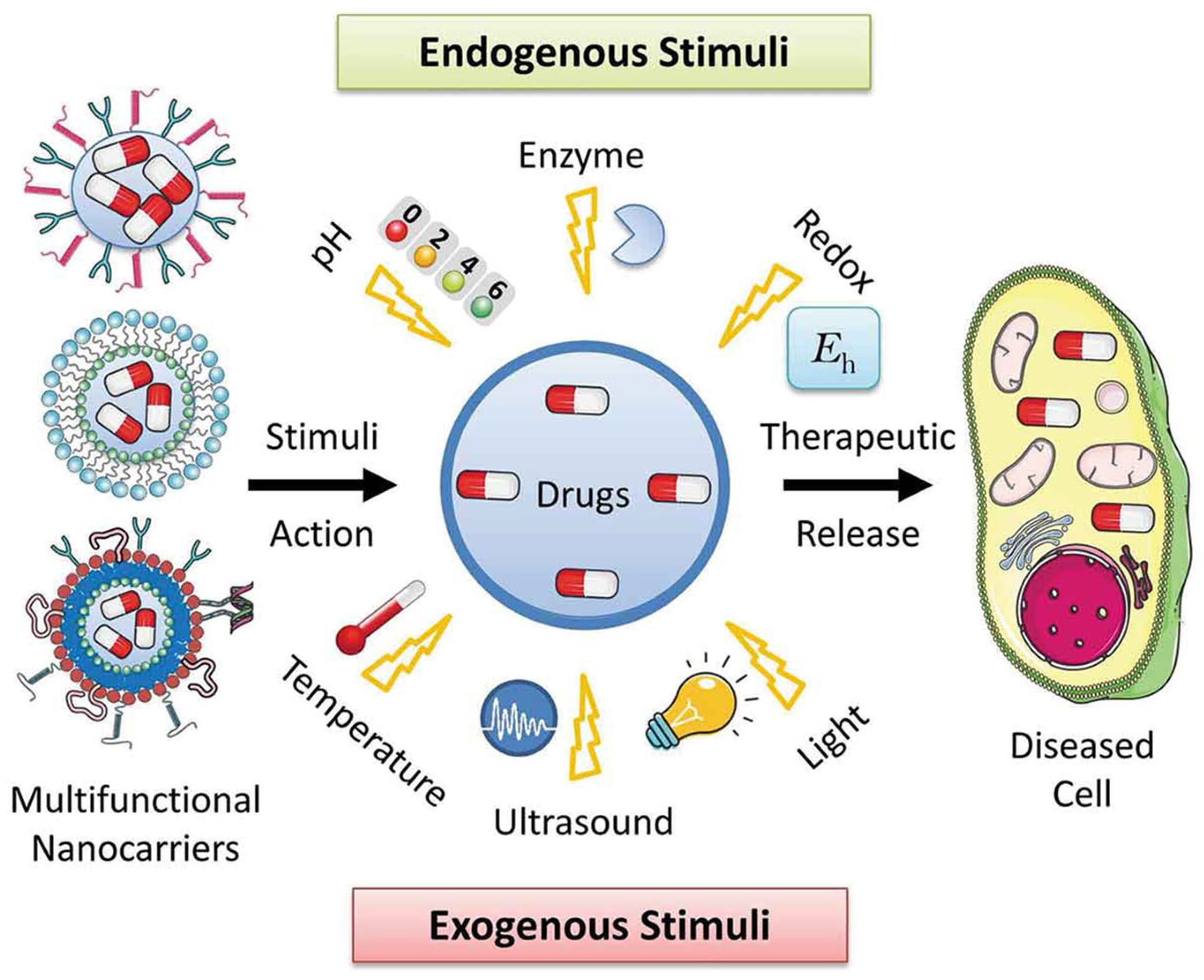
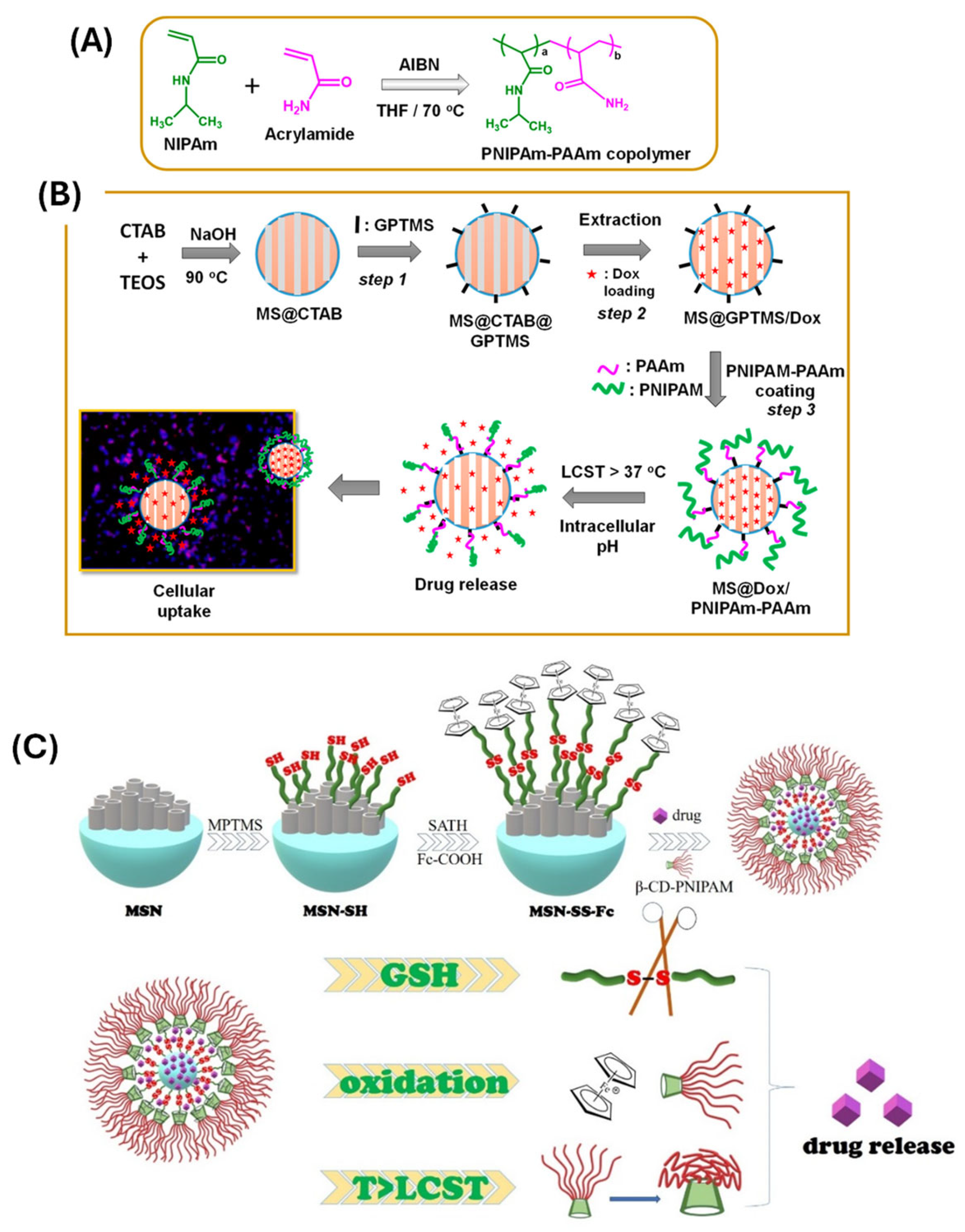

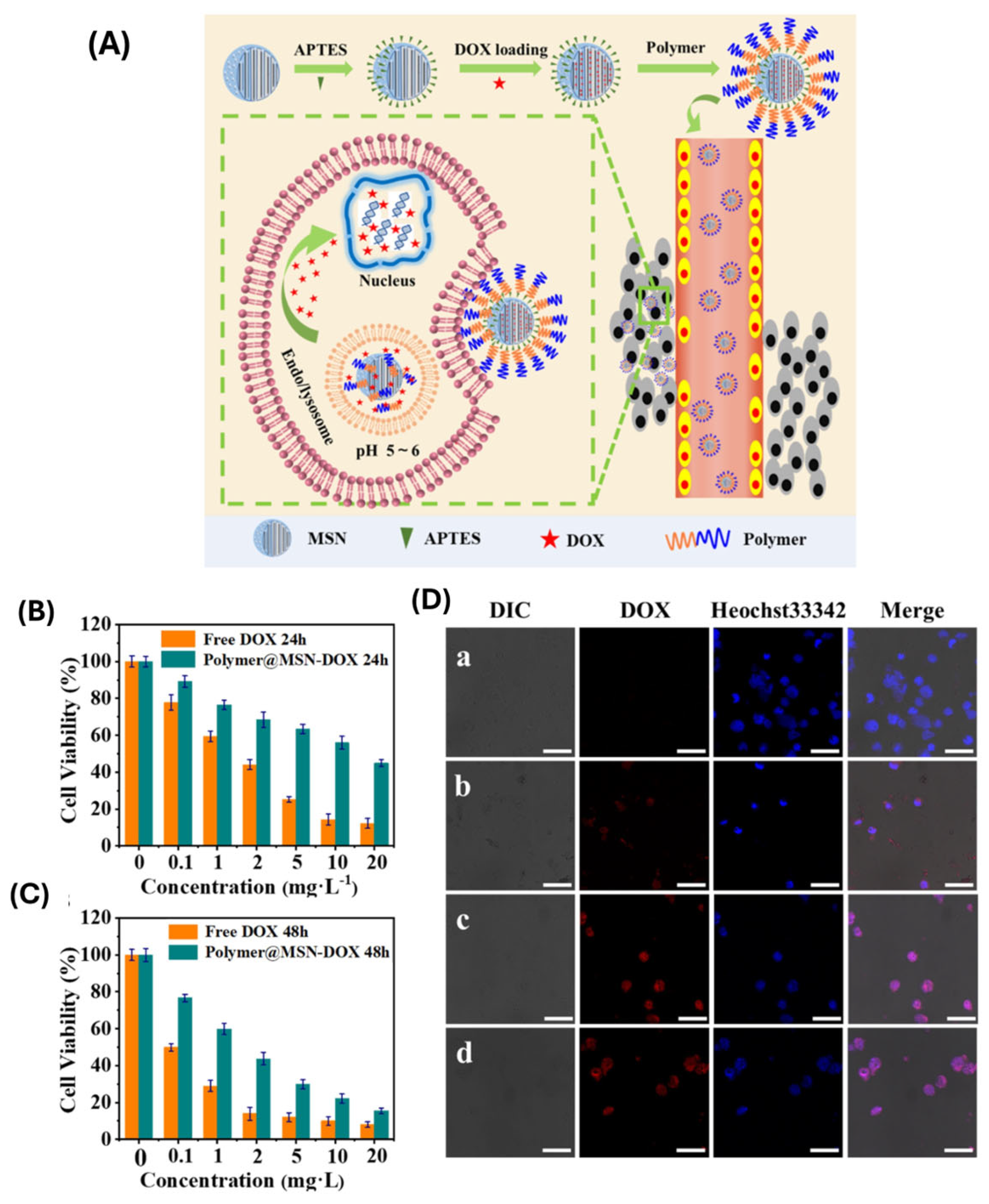
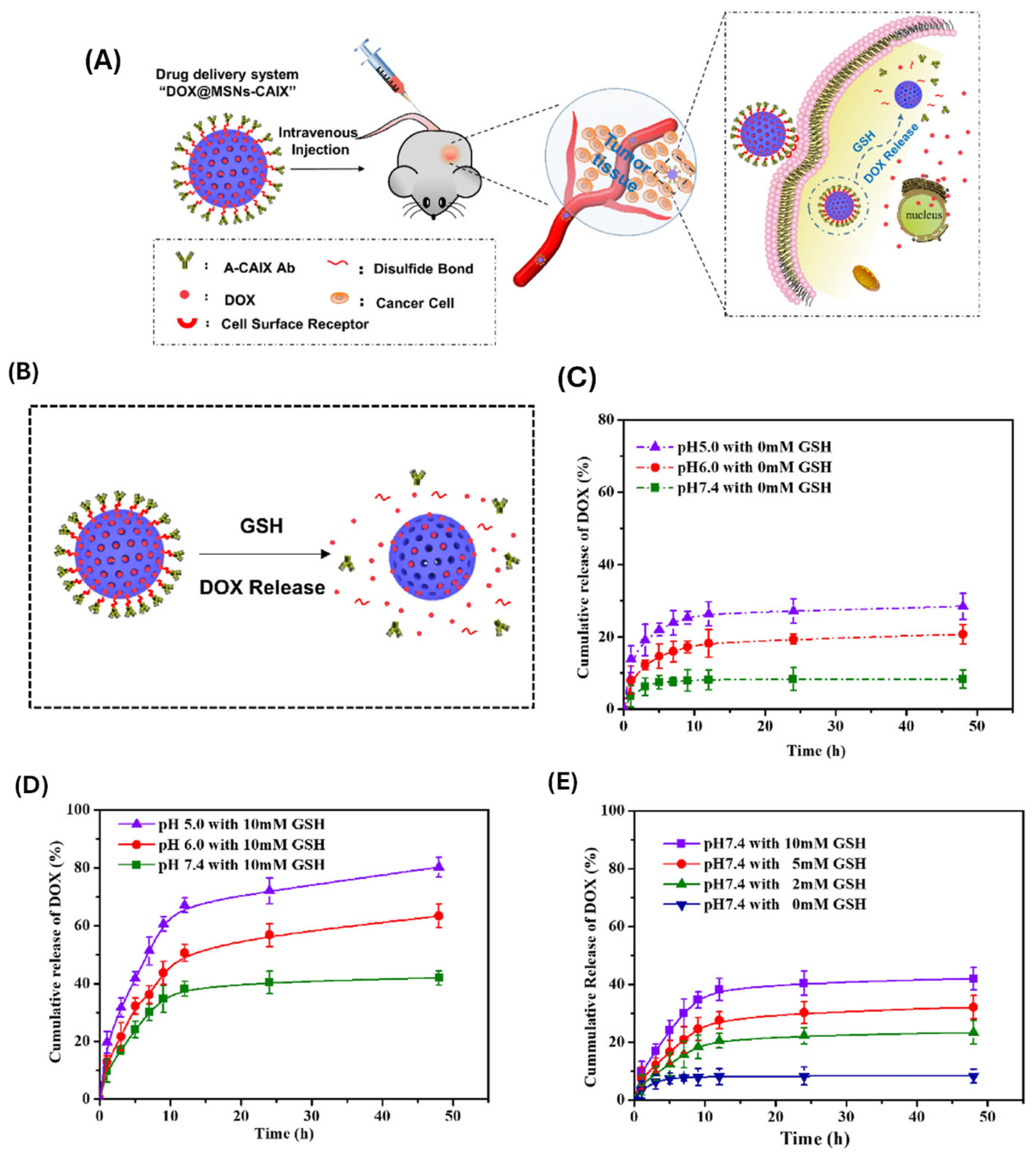

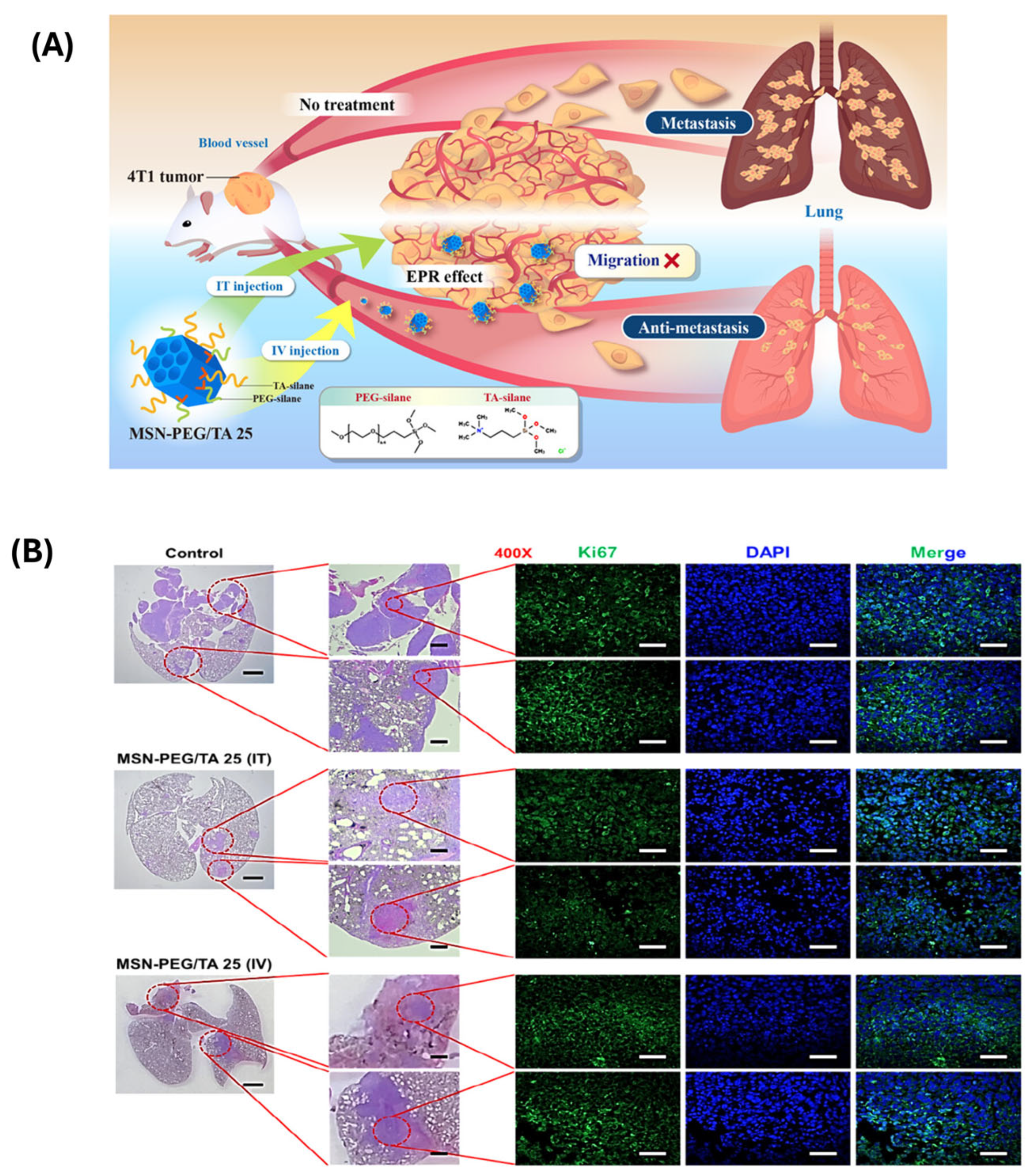
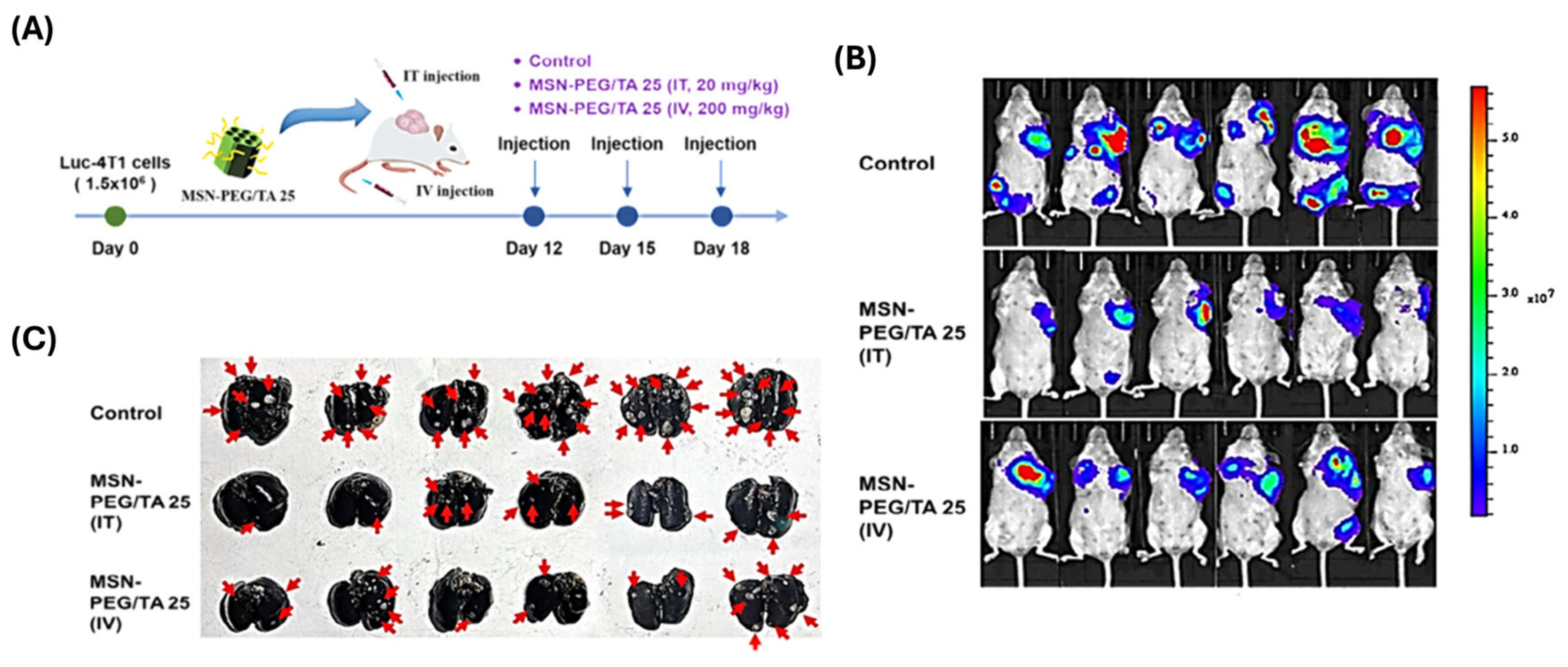
| Polymer Type | Hydrodynamic Size Range (nm) | Zeta Potential | Colloidal Stability | Biocompatibility | Stimuli-Responsiveness | Degradability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PEG (Polyethylene Glycol) | 100–150 | Neutral to slightly negative | High | Excellent | None | Non-biodegradable (but inert) |
| Chitosan | 120–180 | Positive | Moderate to High | Good | pH-responsive | Biodegradable |
| PNIPAM (Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)) | 130–200 | Slightly negative | High | Good | Thermo-responsive (~32 °C) | Limited |
| PAA (Polyacrylic Acid) | 110–160 | Strongly negative | Moderate | Fair | pH-responsive | Non-biodegradable |
| PLA (Polylactic Acid) | 100–170 | Slightly negative | Moderate | Excellent | Slow hydrolysis | Biodegradable |
| PCL (Polycaprolactone) | 120–180 | Slightly negative | Moderate | Excellent | None | Biodegradable |
| Dextran | 100–160 | Neutral | High | Excellent | Enzyme-responsive | Biodegradable |
| Trial Identifier | Formulation | Application | Phase | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT01266096 | ^124I-cRGDY-PEG-C′ dots | PET imaging of melanoma and brain tumors | I | Active, not recruiting |
| NCT02106598 | cRGDY-PEG-Cy5.5-C′ dots | Fluorescence imaging of head and neck melanoma | II | Recruiting |
| NCT03465618 | ^89Zr-DFO-cRGDY-PEG-Cy5-C’ dots | PET-CT imaging of malignant brain tumors | I | Active, not recruiting |
| NCT04167969 | ^64Cu-NOTA-PSMA-PEG-Cy5.5-C′ dots | PET/MRI-guided surgery for prostate cancer | I | Recruiting |
| NCT01270139 | Silica-gold nanoparticles (NANOM-FIM) | Photothermal therapy for atherosclerosis | - | Completed |
| NCT00848042 | AuroShells (silica-gold nanoshells) | Photothermal ablation of head and neck cancer | - | Completed |
| NCT04240639 | AuroShells (silica-gold nanoshells) | MRI/US-guided photothermal ablation of prostate cancer | - | Active, not recruiting |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Santhamoorthy, M.; Asaithambi, P.; Ramkumar, V.; Elangovan, N.; Perumal, I.; Kim, S.C. A Review on the Recent Advancements of Polymer-Modified Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery Under Stimuli-Trigger. Polymers 2025, 17, 1640. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17121640
Santhamoorthy M, Asaithambi P, Ramkumar V, Elangovan N, Perumal I, Kim SC. A Review on the Recent Advancements of Polymer-Modified Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery Under Stimuli-Trigger. Polymers. 2025; 17(12):1640. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17121640
Chicago/Turabian StyleSanthamoorthy, Madhappan, Perumal Asaithambi, Vanaraj Ramkumar, Natarajan Elangovan, Ilaiyaraja Perumal, and Seong Cheol Kim. 2025. "A Review on the Recent Advancements of Polymer-Modified Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery Under Stimuli-Trigger" Polymers 17, no. 12: 1640. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17121640
APA StyleSanthamoorthy, M., Asaithambi, P., Ramkumar, V., Elangovan, N., Perumal, I., & Kim, S. C. (2025). A Review on the Recent Advancements of Polymer-Modified Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery Under Stimuli-Trigger. Polymers, 17(12), 1640. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17121640








