Relation Between Injection Molding Conditions, Fiber Length, and Mechanical Properties of Highly Reinforced Long Fiber Polypropylene: Part II Long-Term Creep Performance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Processing
2.3. Specimen Preparation
2.4. Fiber Analysis
2.5. Micro Computed Tomography (MicroCT)
2.6. Dynamic Mechanical Analysis (DMA)
2.7. Creep Tests
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Fiber Length Analysis
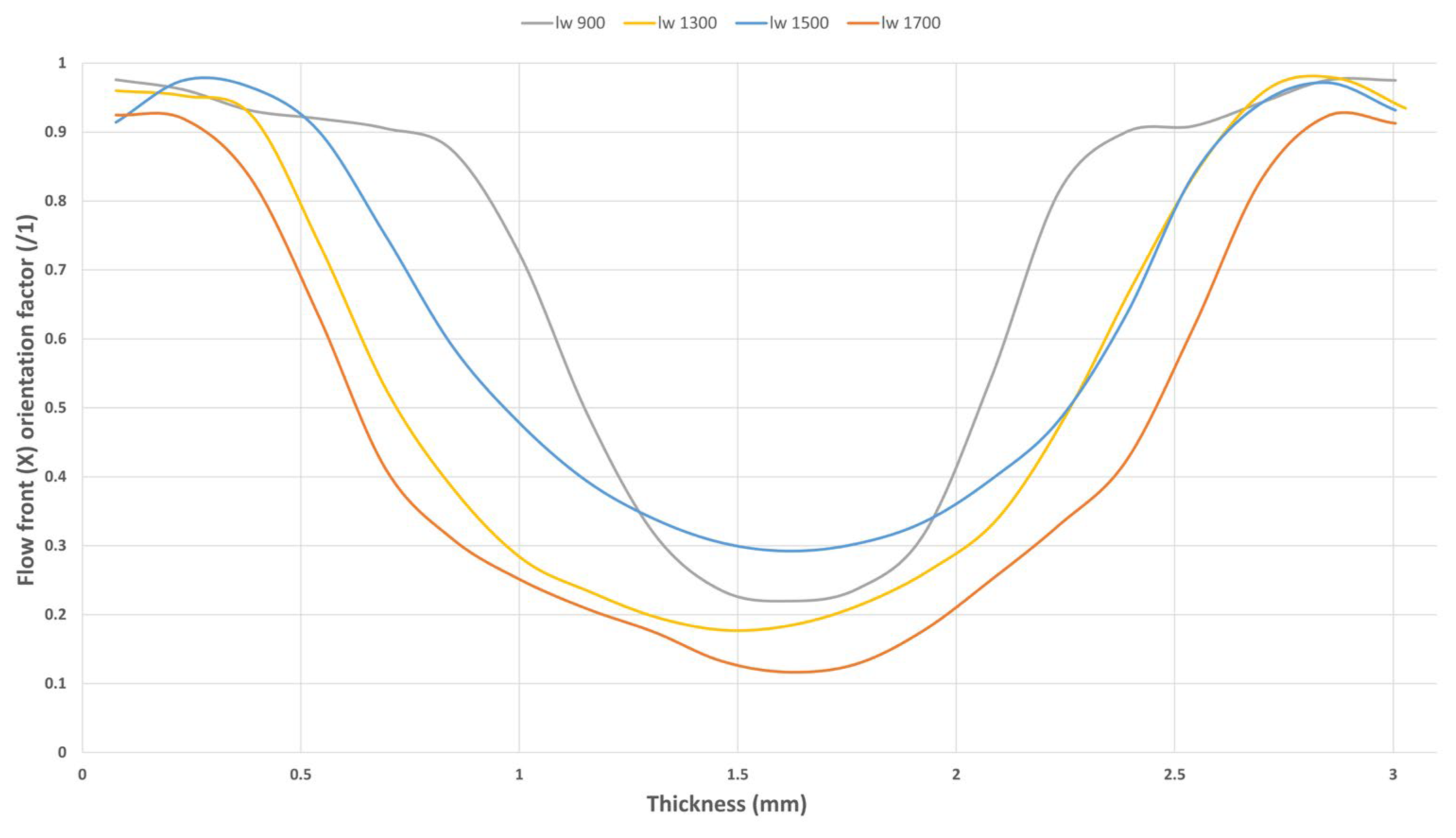
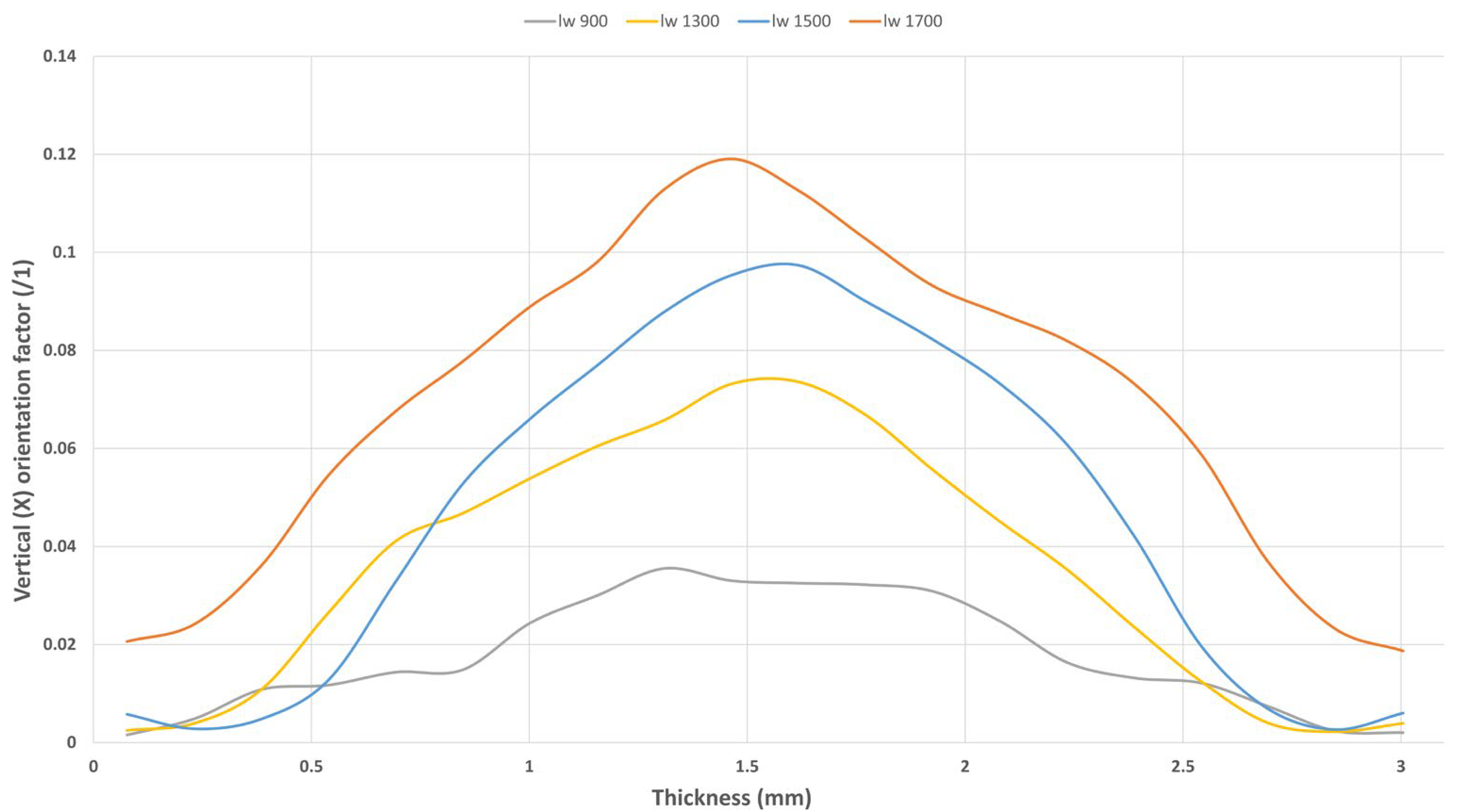
3.2. Fiber Orientation Analysis
3.2.1. Fiber Entanglement
3.2.2. Skin/Core Relationship
3.3. Dynamic Mechanical Analysis (DMA)
3.3.1. Storage Modulus (E’)
3.3.2. Loss Modulus (E’’)
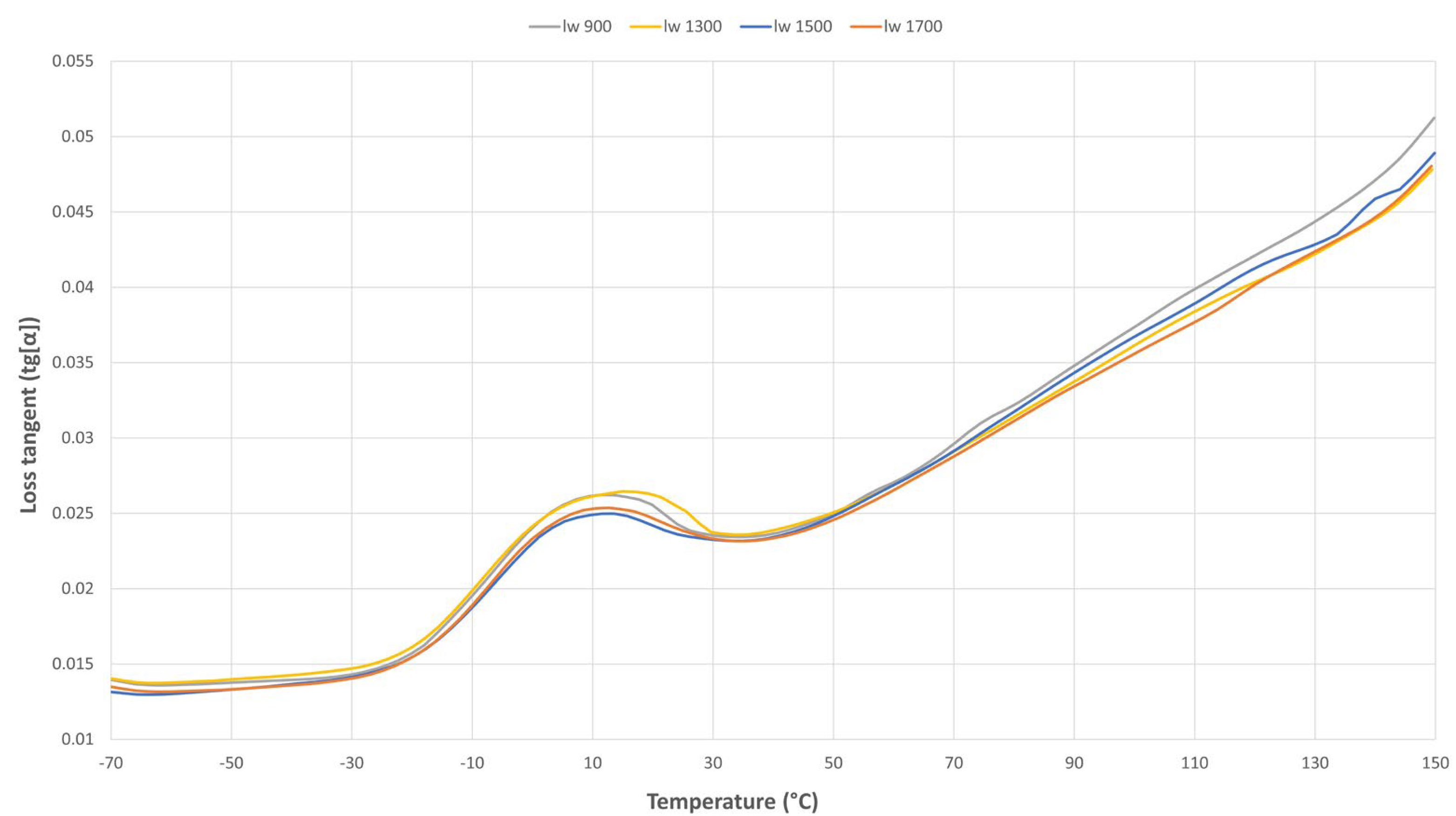
3.3.3. Loss Tangent (Tg[α])
3.4. Creep Tests
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hossain, M.T.; Shahíd, M.A.; Mahmud, N.; Habib, A.; Rana, M.M.; Khan, S.A.; Hossain, M.D. Research and application of polypropylene: A review. Discover. Nano. 2024, 19, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Ji, Q.; Guo, Z.; Li, C.; Guo, R.; Tian, J.; Zhang, Z.; He, T.; Xian, G. Design, preparation, and mechanical properties of glass fiber reinforced thermoplastic self-anchor plate cable exposed in alkaline solution environment. Polym. Compos. 2024, 45, 11687–11700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, H.; Ahmad, Z.; Mazlan, S.A.; Faizal, M.A.J.; Siebert, G.; Petru, M.; Koloor, S.S.R. Lightweight glass fiber-reinforced polymer composite for automotive bumper applications: A Review. Polymers 2023, 15, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ning, H.; Hassen, A.A.; Chawla, K.; Selim, M.; Pillay, S. A review of long fibre-reinforced thermoplastic or long fibre thermoplastic (LFT) composites. Int. Mater. Rev. 2020, 65, 164–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quijano-Solis, C.; Yan, N. Characterization of biofiber breakage in composite processing using a capillary rheometer. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2014, 33, 1463–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajmadi, M.; Fatemi, A. A fatigue damage model for life prediction of injection-molded short glass fiber-reinforced thermoplastic composites. Polymers 2021, 13, 2250. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Jin, F.; Hou, Z. Influence of polymer matrices on the tensile and impact properties of long fiber-reinforced thermoplastic composites. Polymers 2023, 15, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, A.; Chawla, K.K.; Vaidya, U.K.; Chawla, N.; Koopman, M. Characterization of fatigue behavior of long fiber reinforced thermoplastic (LFT) composites. Mater. Charact. 2009, 60, 537–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Jin, F. Design of short fiber reinforced thermoplastic composites: A review. Polym. Compos. 2022, 43, 4835–4847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhang, J.; He, J. A gradient structure formed in injection-molded polycarbonate in situ hybrid composites and its corresponding performances. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2004, 94, 625–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokes, V.K.; Inzinna, L.P.; Liang, E.W. A phenomenological study of the mechanical properties of long-fiber filled injection-molded thermoplastic composites. Polym. Compos. 2000, 21, 696–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, R.; Rzepka, B. Fiber orientation mechanism for injection molding of long fibre composites. Int. Polym. Proc. 1991, 6, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafranche, E.; Krawczak, P.; Ciolczyk, J.P.; Maugey, J. Injection moulding of long glass fibre reinforced polyamide 6-6: Guidelines to improve flexural properties. Express Polym. Lett. 2007, 1, 456–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafranche, E.; Krawczak, P.; Ciolczyk, J.P.; Maugey, J. Injection moulding of long glass fiber reinforced polyamide 66: Processing conditions/microstructure/flexural properties relationship. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2005, 24, 114–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodhe, M.; Ebel, A.; Wolff-Fabris, F.; Altstädt, V. Influence of processing parameters on the fiber length and impact properties of injection molded long glass fiber reinforced polypropylene. Int. Polym. Proc. 2011, 26, 293–303. [Google Scholar]
- Badiola, J.H.; Pineda, D.; Lekube, B. Relation between injection molding conditions, fiber length and mechanical properties for highly reinforced long fiber polypropylene. Polym. Compos. 2023, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, D.; Giovanela, M.; Gonella, L.B.; Crespo, J.S. Influence of injection molding on the flexural strength and surface quality of long glass fiber-reinforced polyamide 6.6 composites. Mater. Des. 2015, 85, 695–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu-Khan, T.; Denault, J.; Habib, P.; Low, A. The effects of injection molding on the mechanical behavior of long-fiber reinforced PBT/PET blends. Compos. Sci. Technol. 1991, 40, 423–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Tian, J.; Li, C.; Wang, J.; Xian, G. Experimental and numerical analysis of a new thermoplastic pultrusion technology of CF/PA6 rod using prepreg tapes. Polym. Compos. 2025, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tienamnn, J.; Mola, J.; Land, P.; Krumpholz, T.; Krupp, U. Quasi static and fatigue properties of long carbon fiber reinforced polyamide. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2022, 31, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; He, M.; Qin, S.; Yu, J.; Guo, J.; Xu, G. Study on dynamic mechanical, thermal and mechanical properties of long glass fiber reinforced thermoplastic polyurethane/polyoxymethylene composties. Polym. Compos. 2016, 39, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Zhang, D.; Guo, J.; Qin, S.; Ming, X. Mechanical, thermal and dynamic mechanical properties of long glass fiber-reinforced thermoplastic Polyurethane/polyoxymethylene composites. Polym. Compos. 2014, 35, 2067–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Zhang, D.; Guo, J.; Wu, B. Dynamic mechanical properties, thermal, mechanical properties and morphology of long glass fiber-reinforced thermoplastic polyurethane/acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene composites. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2014, 29, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortazavian, S.; Fatemi, A. Fatigue behavior and modeling of short fiber reinforced polymer composites: A literature review. Int. J. Fatigue 2015, 70, 297–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, Z.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Z.; Zhu, P. Fatigue failure mechanism analysis and life prediction of short fiber reinforced polymer composites under tension-tension loading. Int. J. Fatigue 2022, 160, 106880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Liu, S.; Pan, Y.; Miu, X.; Liu, J. Durability of glass fiber-reinforced polymer bars in water and simulated concrete pore solution. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 299, 123995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Deng, C.L.; Zhao, J.; Wang, J.S.; Cheng, L.; Wang, Y.Z. An efficiently halogen-free flame-retardant long-glass-fiber-reinforced polypropylene composites. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2011, 96, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rerzai, F.; Yunus, R.; Ibrahim, N.A. Effect of fiber length on thermomechanical properties of short carbon fiber reinforced polypropylene composites. Mater. Des. 2009, 30, 260–263. [Google Scholar]
- Nayak, S.K.; Mohanty, S.; Samal, S.K. Influence of short bamboo/glass fiber on the thermal, dynamic mechanical and rheological properties of polypropylene hybrid composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. A Struct. 2009, 523, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meneghetti, G.; Ricotta, M.; Luchetta, G.; Carmignato, S. An hysteresis energy-based synthesis of fully reversed axial fatigue behavior of different polypropylene composites. Compos. B Eng. 2014, 65, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eftekhari, M.; Fatemi, A. Creep-fatigue interaction and thermos-mechanical fatigue behaviors of thermoplastics and their composites. Int. J. Fatigue. 2016, 91, 136–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, T.; Somiya, S. Analysis of creep behavior in thermoplastics based on visco-elastic theory. Mech. Time-Depend. Mater. 2011, 15, 293–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirinbayan, M.; Rezaei-khamseh, M.; Nikooharf, M.H.; Tcharkhtchi, A.; Fitoussi, J. Multi-scale analysis of mechanical properties and damage behavior of polypropylene composites (GF50-PP) plate at room and cryogenic temperatures. Compos. Struct. 2021, 278, 114713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Wang, X.; Wu, D. Preparation, microstructures, and properties of long-glass-fiber-reinforced thermoplastic composites based on polycarbonate/poly(butyleneterephtalate) alloys. J. Reinf. Plast. Compu. 2015, 34, 1804–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevali, V.S.; Janowski, G.M. Flexural creep of long fiber-reinforced thermoplastic composites: Effect of processing-dependent fiber variables on creep response. Compos. Part. A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2010, 41, 1253–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasappa, P.; Lee-Sulivan, P.; Xiao, X.; Foss, P.H. Tensile creep of a long-fiber glass mat thermoplastic composite. I. Short-term tests. Polym. Compos. 2009, 30, 1204–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alwekar, S.; Ogle, R.; Kim, S.; Vaidya, U. Manufacturing and characterization of continuous fiber-reinforced thermoplastic tape overmolded long fiber thermoplastic. Compos. Part. B-Eng. 2021, 207, 108597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; He, M.; Quin, S.; Yu, J. Effect of fiber length and dispersion on properties of long glass fiber reinforced thermoplastic composites based on poly(butylene terephthalate). RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 15439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.; Li, J.; Zhang, F.; Wang, C.; Guo, S. Effect of multistage tensile extrusion induced fiber orientation on fracture characteristics of high density polyethylene/short glass fiber composites. Comp. Sci. Technol. 2014, 100, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartus, S.D.; Vaidya, U.K. Performance of long fiber reinforced thermoplastics subjected to transverse intermediate velocity blunt object impact. Compos. Struct. 2005, 67, 263–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomason, J.L. The influence of fibre length, diameter and concentration on the modulus of glass fibre reinforced polyamide 6,6. Compos. Part. A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2008, 39, 1732–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.-Y.; Lauke, B.; Mai, Y.-W. Science and Engineering of Short Fibre-Reinforced Polymer Composites; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Thomasson, J.L.; Vlug, M.A.; Schipper, G.; Krikort, H.L. Influence of fibre length and concentration on the properties of glass fibre-reinforced polypropylene: Part 3. Strength and strain failure. Compos. Part. A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 1996, 27, 1075–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 8256: 2023; Plásticos Determinación de la Resistencia al Impacto-Tracción. Asociación Española de Normalización: Madrid, Spain, 2024.
- ISO 179-1:2023; Plásticos Determinación de las Propiedades al Impacto Charpy Parte 1: Ensayo de Impacto no Instrumentado. Asociación Española de Normalizacion: Madrid, Spain, 2024.






| Glass Fiber Content (%) | Tensile Modulus (MPa) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Elongation at Break (%) | Heat Deflection Temperature (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 | 10.500 | 115 | 1.9 | 158 |
| Limits | Vf [m/s] | Pback [bar] |
|---|---|---|
| Min | 0.15 | 20 |
| Max | 0.4 | 50 |
| ID | Pback [bar] | Vf [m/s] | ln [μm] | lw [μm] | FLR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 20 | 0.15 | 826 | 1480 | 1.79 |
| 4 | 20 | 0.4 | 903 | 1676 | 1.85 |
| 6 | 50 | 0.15 | 482 | 870 | 1.8 |
| 8 | 50 | 0.4 | 686 | 1265 | 1.84 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Badiola, J.H.; Astobitza, U.; Iturrondobeitia, M.; Burgoa, A.; Ibarretxe, J.; Arriaga, A. Relation Between Injection Molding Conditions, Fiber Length, and Mechanical Properties of Highly Reinforced Long Fiber Polypropylene: Part II Long-Term Creep Performance. Polymers 2025, 17, 1630. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17121630
Badiola JH, Astobitza U, Iturrondobeitia M, Burgoa A, Ibarretxe J, Arriaga A. Relation Between Injection Molding Conditions, Fiber Length, and Mechanical Properties of Highly Reinforced Long Fiber Polypropylene: Part II Long-Term Creep Performance. Polymers. 2025; 17(12):1630. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17121630
Chicago/Turabian StyleBadiola, Jon Haitz, U. Astobitza, M. Iturrondobeitia, A. Burgoa, J. Ibarretxe, and A. Arriaga. 2025. "Relation Between Injection Molding Conditions, Fiber Length, and Mechanical Properties of Highly Reinforced Long Fiber Polypropylene: Part II Long-Term Creep Performance" Polymers 17, no. 12: 1630. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17121630
APA StyleBadiola, J. H., Astobitza, U., Iturrondobeitia, M., Burgoa, A., Ibarretxe, J., & Arriaga, A. (2025). Relation Between Injection Molding Conditions, Fiber Length, and Mechanical Properties of Highly Reinforced Long Fiber Polypropylene: Part II Long-Term Creep Performance. Polymers, 17(12), 1630. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17121630







