3D Printing Continuous Fiber Reinforced Polymers: A Review of Material Selection, Process, and Mechanics-Function Integration for Targeted Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material Selection
2.1. Selection of Fibers
2.2. Matrix Materials
2.2.1. Properties of Matrix Materials at Room Temperature
2.2.2. Mechanical Performance Under High-Temperature Conditions of Matrix Materials
2.2.3. Compatibility of Matrix Materials with 3D Printing Processes
2.3. Interfacial Treatment
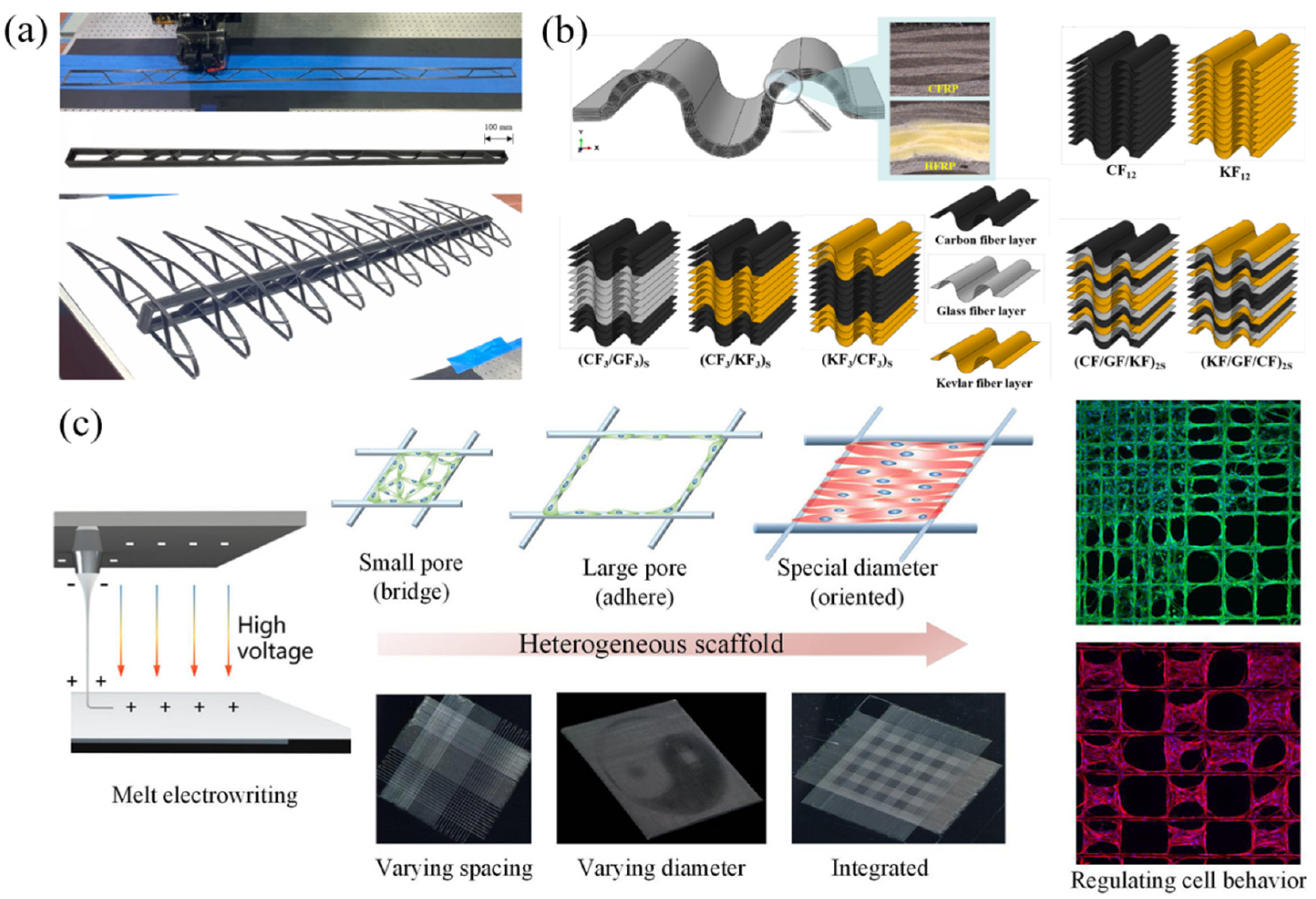
2.4. Challenges in Material Selection
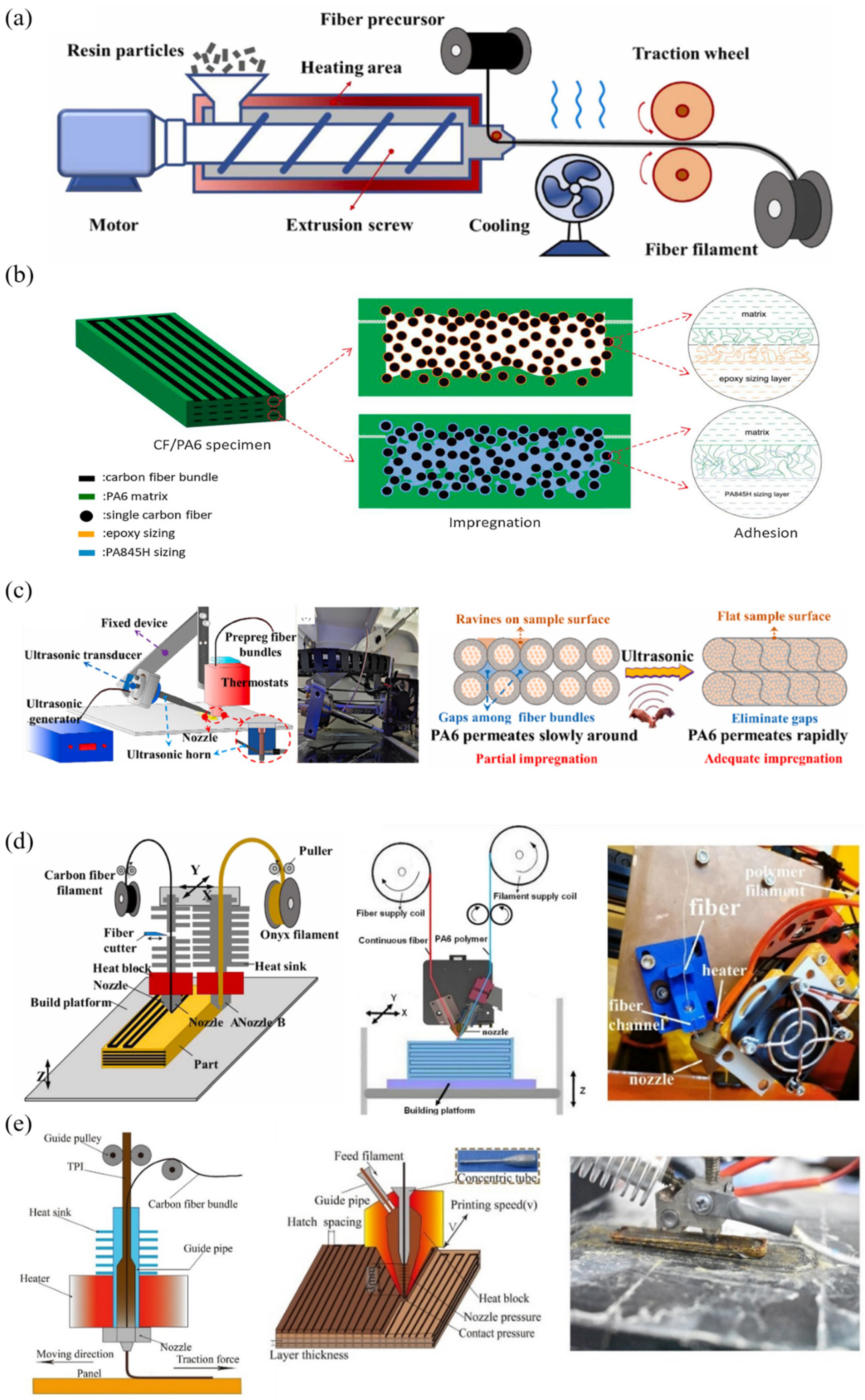
3. Manufacturing Technologies and Processes
3.1. FDM/FFF Techology
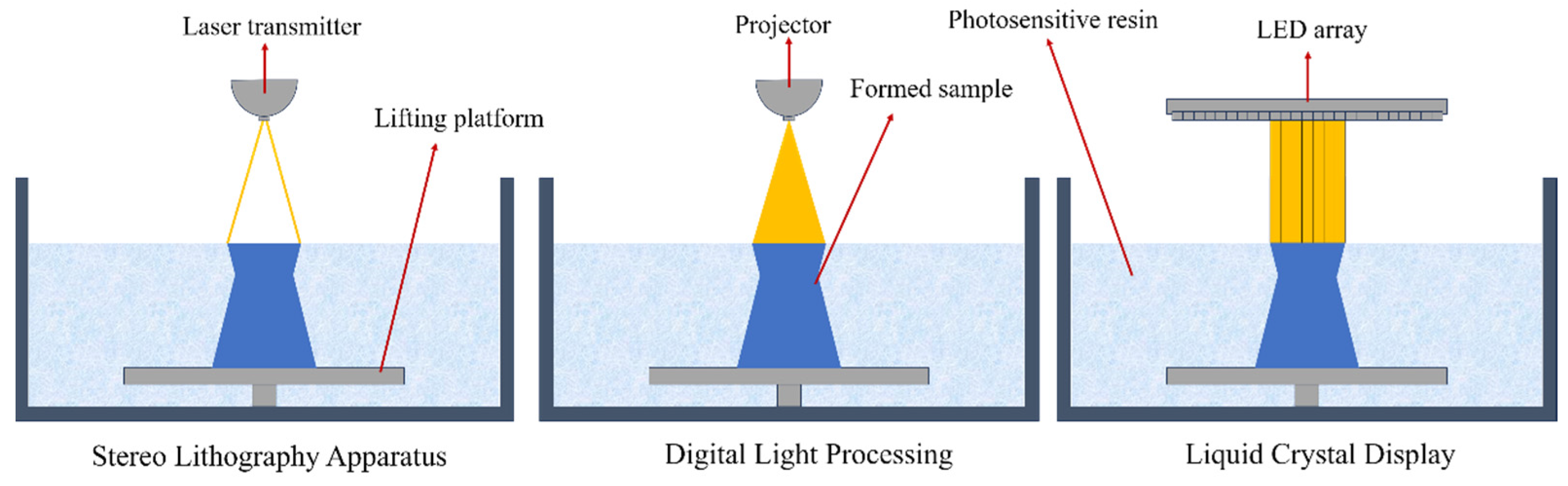
3.2. Photopolymerization Methods
| Technology Classification | Core Method | Characteristics | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| FDM Technology | |||
| Pre-impregnated filament method | Uses pre-impregnated fiber filaments | High tensile strength and stiffness, but prone to fiber breakage/misalignment | [10,11,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63,64] |
| In situ impregnation method | Independent fiber feeding with simultaneous matrix deposition | High-precision fiber alignment, but complex process control | [12,57,65,66,67,68,69,70,71] |
| FDM Technology Variants | |||
| Ultrasonic-assisted printing | Ultrasonic-enhanced fiber wetting | Improved interfacial bonding, but requires complex equipment | [66,72] |
| Microwave-assisted printing | Microwave rapid heating and curing | Faster printing speed, requires specialized equipment | [67,73] |
| Sinusoidal path extrusion | Path optimization for interlayer bonding | Enhanced interlayer performance, but complex algorithms required | [74,75] |
| Robotic arm technology | Multi-axis deposition for complex surfaces | High precision for complex structures, but costly | [76,77] |
| Photopolymerization Methods | |||
| SLA/DLP | UV curing of liquid resin | High precision, but challenging for continuous fiber alignment | [49,51,78,79,80,81] |
| Two-stage UV curing | Stepwise curing for fiber fixation | High fiber alignment precision, but multiple process steps | [73,82] |
| Resin bath fiber feeding | Robotic fiber positioning in liquid resin | Excellent mechanical properties, but difficult to process | [79,81] |
3.3. Critical Process Parameters
4. Mechanical Properties
5. Functionality
5.1. Electrical Properties
5.2. Thermal Properties
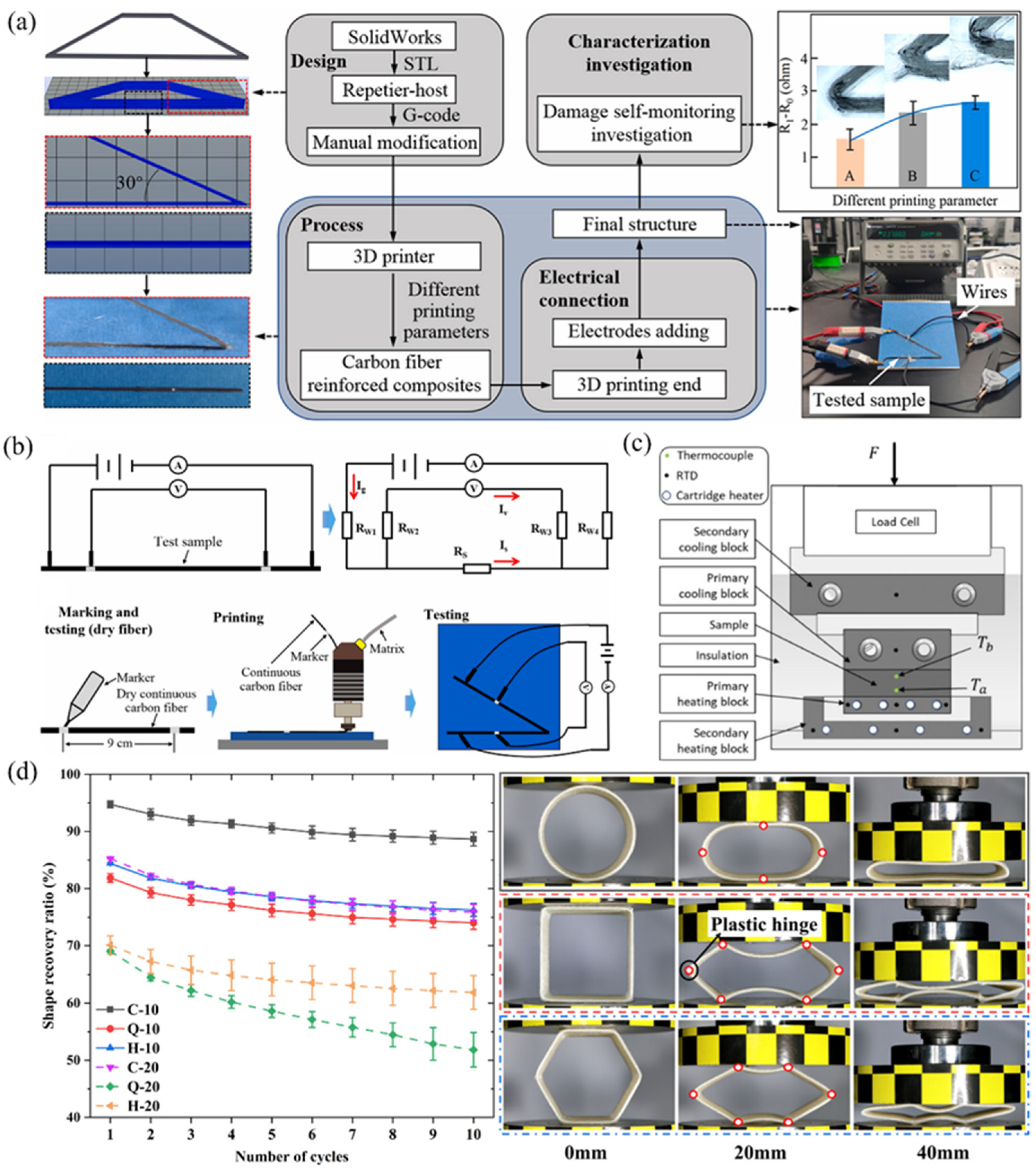
5.3. Intelligent Functionality: Self-Sensing, Self-Monitoring, and Shape Memory/Recovery Behaviors
6. Application Fields
6.1. Aerospace Applications
6.2. Applications in Automotive Industry
6.3. Biomedical Applications
6.4. Civil Engineering Application
6.5. Other Applications
7. Challenges and Future Potential
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kabir, S.M.F.; Mathur, K.; Seyam, A.-F.M. A critical review on 3D printed continuous fiber-reinforced composites: History, mechanism, materials and properties. Compos. Struct. 2020, 232, 111476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Huang, T.; Jiang, Q.; He, L.; Bismarck, A.; Hu, Q. Recent progress of 3D printed continuous fiber reinforced polymer composites based on fused deposition modeling: A review. J. Mater. Sci. 2021, 56, 12999–13022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickson, A.N.; Abourayana, H.M.; Dowling, D.P. 3D Printing of Fibre-Reinforced Thermoplastic Composites Using Fused Filament Fabrication—A Review. Polymers 2020, 12, 2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuo, P.; Li, S.; Ashcroft, I.A.; Jones, A.I. Material extrusion additive manufacturing of continuous fibre reinforced polymer matrix composites: A review and outlook. Compos. Part B-Eng. 2021, 224, 109143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, P.; Peng, Y.; Li, S.; Rao, Y.; Le Duigou, A.; Wang, K.; Ahzi, S. 3D printed continuous fiber reinforced composite lightweight structures: A review and outlook. Compos. Part B-Eng. 2022, 250, 110450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Hou, Z.; Tian, X.; Zhu, W.; Wang, C.; Luo, M.; Malakhov, A.V.; Polilov, A.N.; Zhi, D.; Ding, H.; et al. 3D printing of curvilinear fiber reinforced variable stiffness composite structures: A review. Compos. Part B-Eng. 2024, 291, 112039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soutis, C. Fibre reinforced composites in aircraft construction. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 2005, 41, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, H.; Chen, H.; Fang, D. Preparation and characterization of 3D printed continuous carbon fiber reinforced thermosetting composites. Polym. Test. 2018, 65, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsayed, Y.; Elkholy, A.; Melenka, G.; Kempers, R. Proceedings of The Canadian Society for Mechanical Engineering International Congress. In Proceedings of the Canadian Society for Mechanical Engineering International Congress, Toronto, ON, Canada, 27–30 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T.; Tian, X.; Zhang, M.; Abliz, D.; Li, D.; Ziegmann, G. Interfacial performance and fracture patterns of 3D printed continuous carbon fiber with sizing reinforced PA6 composites. Compos. Part A-Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2018, 114, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Tian, X.; Shang, J.; Zhu, W.; Li, D.; Qin, Y. Impregnation and interlayer bonding behaviours of 3D-printed continuous carbon-fiber-reinforced poly-ether-ether-ketone composites. Compos. Part A-Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2019, 121, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Ding, Y.C.; Lei, Z.P.; Welch, S.; Zhang, W.; Dunn, M.; Yu, K. 3D printing of continuous fiber-reinforced thermoset composites. Addit. Manuf. 2021, 40, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Y.; Zou, B.; Ding, S.; Wang, X.; Liu, J.; Li, L. Preparation of pre-impregnated continuous carbon fiber reinforced nylon6 filaments and the mechanical properties of 3D printed composites. Mater. Today Commun. 2023, 35, 106163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Kang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J. An investigation of preparation of continuous carbon fiber reinforced PLA prepreg filament. Compos. Commun. 2023, 39, 101530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, Q.; Li, D.; Zhang, Z.; Fu, L.; Zhu, W. High-content continuous carbon fiber reinforced multifunctional prepreg filaments suitable for direct 3D-printing. Compos. Commun. 2023, 44, 101726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popan, A.; Popan, I.A.; Cosma, C.; Ceclan, V.; Balc, N. Experimental Study on 3D Printed Parts Made of Continuous Fiberglass Reinforced Polymer. ACTA Tech. Napoc. Ser.-Appl. Math. Mech. Eng. 2021, 64, 81–86. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, L.; Chen, K.; Xue, P.; Cui, Y.; Jia, M. Impregnation modeling and preparation optimization of continuous glass fiber reinforced polylactic acid filament for 3D printing. Polym. Compos. 2021, 42, 5731–5742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Yu, L.; Chen, K.; Xue, P.; Jia, M.; Hua, Z. Amelioration of interfacial properties for CGF/PA6 composites fabricated by ultrasound-assisted FDM 3D printing. Compos. Commun. 2023, 39, 101551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wei, X.; Mao, J.; Zhao, M.; Liu, G. Experimental analysis of 3D printed continuous carbon/glass hybrid fiber reinforced PLA composites: Revealing synergistic mechanical properties and failure mechanisms. Polym. Compos. 2024, 45, 10888–10897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rijckaert, S.; Daelemans, L.; Cardon, L.; Boone, M.; Van Paepegem, W.; De Clerck, K. Continuous Fiber-Reinforced Aramid/PETG 3D-Printed Composites with High Fiber Loading through Fused Filament Fabrication. Polymers 2022, 14, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, O.; Yasar, A.; Karacor, B. Properties of basalt/aramid fiber reinforced hybrid composites compared to carbon fiber composites. Polym. Compos. 2023, 44, 3509–3521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Fu, K.; Li, Y. Efficient plant fibre yarn pre-treatment for 3D printed continuous flax fibre/poly(lactic) acid composites. Compos. Part B-Eng. 2021, 227, 109389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, R.; Lin, H.; Cheng, P.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, K.; Peng, Y.; Wu, Y.; Ahzi, S. Investigation on dynamic strength of 3D-printed continuous ramie fiber reinforced biocomposites at various strain rates using machine learning methods. Polym. Compos. 2022, 43, 5235–5249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, P.; Wang, K.; Chen, X.; Le Duigou, A.; Peng, Y.; Wen, W. Compressive property and shape memory effect of 3D printed continuous ramie fiber reinforced biocomposite corrugated structures. Smart Mater. Struct. 2022, 31, 124003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Li, P.; Zhang, J.; Wang, S.; Shi, S.Q.; Kong, F. A review of fused filament fabrication of continuous natural fiber reinforced thermoplastic composites: Techniques and materials. Polym. Compos. 2023, 44, 8200–8222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Fu, K.; Yang, Z.; Li, Y. Design and fabrication of high-performance 3D printed continuous flax fibre/PLA composites. J. Manuf. Process. 2023, 99, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touchard, F.; Marchand, D.; Chocinski-Arnault, L.; Fournier, T.; Magro, C. 3D printing of continuous cellulose fibre composites: Microstructural and mechanical characterisation. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2023, 29, 1879–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Bi, Z.; Fu, K.; Li, Y. Investigation of recovery behavior on 3D-printed continuous plant fiber-reinforced composites. Addit. Manuf. 2024, 88, 104254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, S.; Soete, J.; Lomov, S.V.; Gorbatikh, L.; Zeng, C. Bamboo-inspired 3D printed continuous fiber-reinforced vascular composites. Compos. Commun. 2024, 53, 102219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Zou, B. Improvement of Heat Treatment Process on Mechanical Properties of FDM 3D-Printed Short- and Continuous-Fiber-Reinforced PEEK Composites. Coatings 2022, 12, 827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miri, S.; Kalman, J.; Canart, J.-P.; Spangler, J.; Fayazbakhsh, K. Tensile and thermal properties of low-melt poly aryl ether ketone reinforced with continuous carbon fiber manufactured by robotic 3D printing. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 122, 1041–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qayyum, J.A.; Li, A.; Wu, J.; Lyu, Y.; Koutsos, V.; Zhang, H.; Radacsi, N.; Yang, D. On the printability and inter-layer adhesion in 3D printing of continuous carbon fibre reinforced PEEK composite using tape and filament. Compos. Part A-Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2024, 190, 108654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Zheng, J.; Chen, Y.; Fan, C.; Song, W.; Shan, Z. Melt-impregnation and sizing optimization for the fabrication of high-performance 3D printed continuous carbon fiber-reinforced polyetheretherketone filaments. In Polymer Composites; John Wiley Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Han, S.N.M.F.; Taha, M.M.; Mansor, M.R.; Rahman, M.A.A. Investigation of tensile and flexural properties of kenaf fiber-reinforced acrylonitrile butadiene styrene composites fabricated by fused deposition modeling. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2022, 69, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Bao, C.; Lu, W.; Liu, R.; Ma, H.; Li, S.; Sun, K. Fabrication of a continuous carbon fiber-reinforced phenolic resin composites via in situ-curing 3D printing technology. Compos. Commun. 2023, 38, 101497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiatiporntipthak, K.; Thajai, N.; Kanthiya, T.; Rachtanapun, P.; Leksawasdi, N.; Phimolsiripol, Y.; Rohindra, D.; Ruksiriwanich, W.; Sommano, S.R.; Jantanasakulwong, K. Reaction Mechanism and Mechanical Property Improvement of Poly(Lactic Acid) Reactive Blending with Epoxy Resin. Polymers 2021, 13, 2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.X.; Lee, D.; Lee, G.H.; Kim, S.M.; Ben, G.; Lee, W.I.; Choi, S.W. Effect of Temperature on the Mechanical Properties and Polymerization Kinetics of Polyamide-6 Composites. Polymers 2020, 12, 1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalakrishnan, T.; Venkatesan, R.; Chandrasekaran, M.; Deepa, S.; Kim, S.-C. Advances in implant for surface modification to enhance the interfacial bonding of shape memory alloy wires in composite resins. Prog. Org. Coat. 2024, 188, 108242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, H.; Li, Q.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, N.; Wang, C. Mechanical and Thermal Properties of 3D-Printed Continuous Bamboo Fiber-Reinforced PE Composites. Materials 2025, 18, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.; Myung, J.H.; Yoon, J.; Yu, W.-R. Three-dimensional printing of continuous carbon fiber-reinforced polymer composites via in-situ pin-assisted melt impregnation. Addit. Manuf. 2022, 55, 102860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Huang, Y.; Cheng, P.; Xiong, Y.; Le Duigou, A.; Peng, Y.; Rao, Y.; Ahzi, S. Novel application of dual-nozzle 3D printer for enhanced in-situ impregnation 3D printing of dry continuous fiber reinforced composites. Compos. Part A-Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2024, 183, 108231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terekhina, S.; Egorov, S.; Tarasova, T.; Skornyakov, I.; Guillaumat, L.; Hattali, M.L. In-nozzle impregnation of continuous textile flax fiber/polyamide 6 composite during FFF process. Compos. Part A-Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2022, 153, 106725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, W.L.; Lin, G.Q.; Wu, W.Z.; Geng, P.; Hu, X.; Gao, Z.W.; Zhao, J. Separated 3D printing of continuous carbon fiber reinforced thermoplastic polyimide. Compos. Part A-Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2019, 121, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Tian, X.; Li, D. Interfacial Transcrystallization and Mechanical Performance of 3D-Printed Fully Recyclable Continuous Fiber Self-Reinforced Composites. Polymers 2021, 13, 3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Wang, K.; Zhu, W.; Peng, Y.; Ahzi, S.; Chinesta, F. Investigation on the mechanical properties of 3D printed hybrid continuous fiber-filled composite considering influence of interfaces. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 123, 3147–3158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.; Liu, P.; Tian, X.; Zhu, W.; Wang, C.; He, J.; Lan, H.; Li, D. Hybrid effect of 3D-printed coaxial continuous hybrid fibre-reinforced composites. Thin-Walled Struct. 2023, 188, 110820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Tian, X.; Yin, L.; Li, D. 3D Printing of Continuous Fiber Reinforced Low Melting Point Alloy Matrix Composites: Mechanical Properties and Microstructures. Materials 2020, 13, 3463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Tian, X.; Cao, H.; Liu, T.; Zia, A.A.; Li, D. 3D printing of fully recyclable continuous fiber self-reinforced composites utilizing supercooled polymer melts. Compos. Part A-Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2023, 169, 107513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sano, Y.; Matsuzaki, R.; Ueda, M.; Todoroki, A.; Hirano, Y. 3D printing of discontinuous and continuous fibre composites using stereolithography. Addit. Manuf. 2018, 24, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuzaki, R.; Nakamura, T.; Sugiyama, K.; Ueda, M.; Todoroki, A.; Hirano, Y.; Yamagata, Y. Effects of Set Curvature and Fiber Bundle Size on the Printed Radius of Curvature by a Continuous Carbon Fiber Composite 3D Printer. Addit. Manuf. 2018, 24, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blok, L.G.; Longana, M.L.; Yu, H.; Woods, B.K.S. An investigation into 3D printing of fibre reinforced thermoplastic composites. Addit. Manuf. 2018, 22, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Rudolph, N.; Woytowitz, P. Reliable Optimized Structures with High Performance Continuous Fiber Thermoplastic Composites from Additive Manufacturing (AM). In Proceedings of the Sampe Conference Proceedings, Charlotte, NC, USA, 20–23 May 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Z.; Tian, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, D. 3D printed continuous fibre reinforced composite corrugated structure. Compos. Struct. 2018, 184, 1005–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araya-Calvo, M.; Lopez-Gomez, I.; Chamberlain-Simon, N.; Luis Leon-Salazar, J.; Guillen-Giron, T.; Sebastian Corrales-Cordero, J.; Sanchez-Brenes, O. Evaluation of compressive and flexural properties of continuous fiber fabrication additive manufacturing technology. Addit. Manuf. 2018, 22, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, H.; Ali, Z.; Ali, I.; Cheng, L. Tailoring strength and modulus by 3D printing different continuous fibers and filled structures into composites. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2019, 2, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuba, D.; Matsuzaki, R.; Ochi, S.; Ogihara, S. 3D printing of composite materials using ultralow-melt-viscosity polymer and continuous carbon fiber. Compos. Part C Open Access 2022, 8, 100250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, H.; Yan, Y.; Feng, L.; Dassios, K.G.; Zhang, H.; Cheng, L. First printing of continuous fibers into ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2019, 102, 3244–3255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhoundi, B.; Behravesh, A.H.; Saed, A.B. Improving mechanical properties of continuous fiber-reinforced thermoplastic composites produced by FDM 3D printer. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2019, 38, 99–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loke, G.; Yuan, R.; Rein, M.; Khudiyev, T.; Jain, Y.; Joannopoulos, J.; Fink, Y. Structured multimaterial filaments for 3D printing of optoelectronics. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, J.; Li, Y.; Li, L. Ultrasound-assisted 3D printing of continuous fiber-reinforced thermoplastic (FRTP) composites. Addit. Manuf. 2019, 30, 100926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, P.; Wang, K.; Le Duigou, A.; Liu, J.; Liu, Z.; Peng, Y.; Ahzi, S. A novel dual-nozzle 3D printing method for continuous fiber reinforced composite cellular structures. Compos. Commun. 2022, 37, 101448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Zhang, H.; Wu, J.; Chen, J.; Yang, D. Improved fibre placement in filament-based 3D printing of continuous carbon fibre reinforced thermoplastic composites. Compos. Part A-Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2023, 168, 107454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, K.; Ghosh, T.K. 3D Printing of Textiles: Potential Roadmap to Printing with Fibers. Adv. Mater. 2019, 32, 1902086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, Y.; Zhang, S.; Han, W.; Wang, B.; Duan, Y.; Xiao, H. Investigation on process parameters of 3D printed continuous carbon fiber-reinforced thermosetting epoxy composites. Addit. Manuf. 2020, 33, 101184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Liu, X.; Zhao, W.; Wang, G.; Liu, B. An overview of research on FDM 3D printing process of continuous fiber reinforced composites. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1213, 52037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velu, R.; Raspall, F.; Singamneni, S. 3D printing technologies and composite materials for structural applications. In Green Composites for Automotive Applications; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridgeshire, UK, 2019; pp. 171–196. [Google Scholar]
- Li, N.; Link, G.; Jelonnek, J. 3D microwave printing temperature control of continuous carbon fiber reinforced composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2020, 187, 107939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Ladani, R.B.; Brandt, M.; Li, Y.; Mouritz, A.P. Carbon fibre damage during 3D printing of polymer matrix laminates using the FDM process. Mater. Des. 2021, 205, 109679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, B.; Shang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Cuadros, A.P.; Qu, J.; Sun, B.; Gu, B.; Chou, T.-W.; Fu, K.K. Dynamic Capillary-Driven Additive Manufacturing of Continuous Carbon Fiber Composite. Matter 2020, 2, 1594–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Long, Y.; Yang, Z.; Fu, K.; Li, Y. An investigation into printing pressure of 3D printed continuous carbon fiber reinforced composites. Compos. Part A-Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2022, 162, 107162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Kang, Y.; Ma, C.; Wang, Y. Research on a Fiber Corner Compensation Algorithm in a 3D Printing Layer of Continuous Fiber-Reinforced Composite Materials. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 6687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, K.; Liu, L.; Huang, X.; Xiao, X. 3D printing of continuous fiber reinforced diamond cellular structural composites and tensile properties. Compos. Struct. 2020, 250, 112610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Link, G.; Jelonnek, J. Rapid 3D microwave printing of continuous carbon fiber reinforced plastics. CIRP Ann.-Manuf. Technol. 2020, 69, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, J.; Tian, X.; Luo, M.; Zhu, W.; Li, D.; Qin, Y.; Shan, Z. Controllable inter-line bonding performance and fracture patterns of continuous fiber reinforced composites by sinusoidal-path 3D printing. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2020, 192, 108096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Kong, D.; Liu, J. Research on Heating Zone Length of Continuous Fiber Reinforced Composites 3D Printing Nozzle. Chemistryselect 2021, 6, 11293–11298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, A.M.; Dunn, M.L.; Yu, K. Robotic 3D Printing of Continuous Fiber Reinforced Thermoset Composites. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2024, 9, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhoundi, B.; Jahanshahi, A.S.; Abbassloo, A. G-code generation for deposition of continuous glass fibers on curved surfaces using material extrusion-based 3D printing. Eng. Res. Express 2024, 6, 15401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiyama, K.; Matsuzaki, R.; Malakhov, A.V.; Polilov, A.N.; Ueda, M.; Todoroki, A.; Hirano, Y. 3D printing of optimized composites with variable fiber volume fraction and stiffness using continuous fiber. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2020, 186, 107905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, C.; Han, B.; Hou, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Tian, X.; Lu, T.J. 3D printed continuous fiber reinforced composite auxetic honeycomb structures. Compos. Part B-Eng. 2020, 187, 107858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.; Tian, X.; Zheng, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhe, L.; Li, D.; Malakhov, A.V.; Polilov, A.N. A constitutive model for 3D printed continuous fiber reinforced composite structures with variable fiber content. Compos. Part B-Eng. 2020, 189, 107893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.A.; Islam, M.Z.; Gibbon, L.; Ulven, C.A.; La Scala, J.J. 3D printing of continuous carbon fiber reinforced thermoset composites using UV curable resin. Polym. Compos. 2021, 42, 5859–5868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Abdullah, A.M.; Ding, Y.; Chung, C.; Dunn, M.L.; Yu, K. 3D Printing of continuous fiber composites using two-stage UV curable resin. Mater. Horiz. 2023, 10, 5508–5520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azarov, A.V.; Kolesnikov, V.A.; Khaziev, A.R. Development of equipment for composite 3D printing of structural elements for aerospace applications. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 934, 012049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Lu, L.; Liu, J. Path-driven shell lattices designed for continuous fiber composite 3D printing. Addit. Manuf. 2023, 78, 103838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, H.; Cheng, Y.; Ye, W.; Zhang, D.; Li, J.; Miao, Z.; Rudykh, S. Effect of Process Parameters on Tensile Mechanical Properties of 3D Printing Continuous Carbon Fiber-Reinforced PLA Composites. Materials 2020, 13, 3850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, K.; Luces, J.V.S.; Shirasu, K.; Hoshikawa, Y.; Okabe, T.; Hirata, Y. A novel single-stroke path planning algorithm for 3D printers using continuous carbon fiber reinforced thermoplastics. Addit. Manuf. 2022, 55, 102816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Granland, K.; Chen, C.; Tang, Y. Exploring optimal adaptive process parameters for curved infill paths of additive manufactured carbon fibre reinforced polymers. Compos. Commun. 2023, 39, 101549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, Z.; Liu, C.; Li, J.; Qin, X.; Yu, J. Fiber bundle deposition model and variable speed printing strategy for in-situ impregnation 3D printing of continuous fiber reinforced thermoplastic composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2024, 255, 110723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Link, G.; Wang, T.; Ramopoulos, V.; Neumaier, D.; Hofele, J.; Walter, M.; Jelonnek, J. Path-designed 3D printing for topological optimized continuous carbon fibre reinforced composite structures. Compos. Part B-Eng. 2020, 182, 107612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Zou, B.; Zhang, P.; Liu, Q.; Zhuang, Y.; Feng, Z.; Wang, F.; Wang, X. Layer thickness and path width setting in 3D printing of pre-impregnated continuous carbon, glass fibers and their hybrid composites. Addit. Manuf. 2024, 83, 104054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Wang, Y.; Lou, R.; Yao, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, H. A new method of preparing lattice structures of continuous carbon fiber-reinforced thermoplastics. Compos. Struct. 2023, 329, 117781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Wang, H.; Fu, K.; Ye, L. 3D printed continuous CF/PA6 composites: Effect of microscopic voids on mechanical performance. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2020, 191, 108077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Mouritz, A.P.; Ladani, R.B.; Li, Y.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, H. 3D printing of curved continuous fibre filaments using fused deposition modelling. Mater. Des. 2025, 252, 113762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Li, N.; Link, G.; Jelonnek, J.; Fleischer, J.; Dittus, J.; Kupzik, D. Load-dependent path planning method for 3D printing of continuous fiber reinforced plastics. Compos. Part A-Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2021, 140, 106181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Yixuan, H.; Bowen, L.; Peng, J. Microscopic Analysis of Continuous Fiber 3D Printing with Oblique Axis for Process Optimization. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2023, 25, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Wang, F.; Guan, S.; Fu, R.; Wang, H.; Lei, Y. A new path planning strategy driven by geometric features and tensile properties for 3D printing of continuous fiber reinforced thermoplastic composites. Compos. Part B-Eng. 2024, 288, 111885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wein, F.; Mirbach, J.; Angre, A.; Greifenstein, J.; Huebner, D. Multi-layer continuous carbon fiber pattern optimization and a spline based path planning interpretation. J. Manuf. Process. 2025, 135, 375–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, S.M.F.; Mathur, K.; Seyam, A.-F.M. The Road to Improved Fiber-Reinforced 3D Printing Technology. Technologies 2020, 8, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadizadeh, M.; Fidan, I. Tensile Performance of 3D-Printed Continuous Fiber-Reinforced Nylon Composites. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2021, 5, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, R.G.; Pavez, G.M. Flexural characteristics of additively manufactured continuous fiber-reinforced honeycomb sandwich structures. Compos. Part C Open Access 2025, 16, 100563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarifi, I.M. A performance evaluation study of 3D printed nylon/glass fiber and nylon/carbon fiber composite materials. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 21, 884–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, H.; Flater, P.; Gaskey, B.; Gibbons, S. Failure mechanisms of 3D printed continuous fiber reinforced thermoplastic composites with complex fiber configurations under impact. Prog. Addit. Manuf. 2023, 9, 753–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousapour, M.; Kumar, S.S.; Partanen, J.; Salmi, M. 3D printing of a continuous carbon fiber reinforced bronze-matrix composite using material extrusion. Compos. Part B-Eng. 2024, 289, 111961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gracego, A.X.; Ding, Y.; Dong, G.; Dunn, M.L.; Yu, K. Mechanical Properties and Printable Curvature of Continuous Fiber Composites Fabricated by Embedded 3D Printing. In Advanced Materials Technologies; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Kong, D.; Zhang, Q.; Li, W.; Liu, J. Process parameters and mechanical properties of continuous glass fiber reinforced composites-polylactic acid by fused deposition modeling. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2021, 40, 686–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Y.; Zou, B.; Ding, S.; Wang, P. Shear and Tensile Behaviors of Fiber-Reinforced Resin Matrix Composites Printed by the FDM Technology. Coatings 2022, 12, 1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedulov, B.; Fedorenko, A.; Khaziev, A.; Antonov, F. Optimization of parts manufactured using continuous fiber three-dimensional printing technology. Compos. Part B-Eng. 2021, 227, 109406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.; Tian, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhe, L.; Zheng, Z.; Li, D.; Malakhov, A.V.; Polilov, A.N. Design and 3D printing of continuous fiber reinforced heterogeneous composites. Compos. Struct. 2020, 237, 111945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.A.; Gibbon, L.; Islam, M.Z.; Hall, E.; Ulven, C.A. Adjustment of Mechanical Properties of 3D Printed Continuous Carbon Fiber-Reinforced Thermoset Composites by Print Parameter Adjustments. Polymers 2024, 16, 2996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Essawi, B.; Abdallah, S.; Ali, S.; Mohammed, A.N.A.; Susantyoko, R.A.; Pervaiz, S. Optimization of infill density, fiber angle, carbon fiber layer position in 3D printed continuous carbon-fiber reinforced nylon composite. Results Eng. 2024, 21, 101926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Sun, S.; Chi, S.; Hu, C.; Ling, C.; Fu, H.; Han, Z. Effect of process parameters on forming quality and flexural strength of continuous fiber reinforced cement-based 3D printed composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 438, 137241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghnatios, C.; Fayazbakhsh, K. Warping estimation of continuous fiber-reinforced composites made by robotic 3D printing. Addit. Manuf. 2022, 55, 102796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, L.M.; Aranda, M.T.; Munoz-Reja, M.; Coelho, C.A.C.P.; Tavara, L. Ageing effect on the low-velocity impact response of 3D printed continuous fibre reinforced composites. Compos. Part B-Eng. 2023, 267, 111031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuncius, T.; Rimasauskas, M.; Rimasauskiene, R. Interlayer Adhesion Analysis of 3D-Printed Continuous Carbon Fibre-Reinforced Composites. Polymers 2021, 13, 1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Shan, Z.; Chen, K.; Wang, S.; Zou, A.; Sun, Q. Bending properties and failure behavior of 3D printed fiber reinforced resin T-beam. Polym. Compos. 2022, 43, 4556–4568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Wang, H.; Wang, G.; Fu, R.; Guan, S.; Zhou, J. Effects of internal configurations and its processing quality on compressive performance for 3D printed continuous fiber reinforced composites honeycomb sandwich. Thin-Walled Struct. 2024, 202, 112046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ipekci, A.; Ekici, B. Experimental and statistical analysis of robotic 3D printing process parameters for continuous fiber reinforced composites. J. Compos. Mater. 2021, 55, 2645–2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, M.; Thakur, D.; Chandel, S.; Salunkhe, S. Experimental investigations on thermal, flame retardant, and impact properties of additively manufactured continuous FRPC. Polym. Compos. 2022, 43, 2941–2951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, Z.; Wang, H.; He, Q.; Kim, D.-E.; Chang, L. Friction and wear behaviour of additively manufactured continuous carbon fibre reinforced PA6 composites. Compos. Part B-Eng. 2021, 226, 109332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Um, H.-J.; Lee, J.-S.; Shin, J.-H.; Kim, H.-S. 3D printed continuous carbon fiber reinforced thermoplastic composite sandwich structure with corrugated core for high stiffness/load capability. Compos. Struct. 2022, 291, 115590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zhang, Q.; Cao, H.; Yuan, Y. Effect of fibre arrangements on tensile properties of 3D printed continuous fibre-reinforced thermoplastic composites. Plast. Rubber Compos. 2021, 51, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Li, B.; Wo, W.; Hu, X.; Chang, M.; Jin, P. Topology Design of 3D Printing Continuous Fiber-Reinforced Structure Considering Strength and Non-Equidistant Fiber. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2023, 26, 2301340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Fu, K.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y. Topology optimization of 3D-printed continuous fiber-reinforced composites considering manufacturability. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2022, 230, 109727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Liu, W.; Sun, L. Mechanical characterization of 3D printed continuous carbon fiber reinforced thermoplastic composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2022, 227, 109618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, A.; Wu, J.; Sun, B.; Wang, C.; Yang, D. Effectiveness of fibre placement in 3D printed open-hole composites under uniaxial tension. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2022, 220, 109269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, S.; Zhang, K.; Wu, J.; Li, A.; Liu, J.; Yang, D. 3D printing of continuous carbon fibre reinforced polymer composites with optimised structural topology and fibre orientation. Compos. Struct. 2023, 313, 116914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, S.; Wang, F.; Wang, H.; Wang, G.; Lei, Y.; Fu, R.; Jia, Z. Enhancing planar compression performance of 3D printed continuous carbon fiber reinforced honeycomb sandwich structures using interleaved core paths. J. Manuf. Process. 2024, 120, 940–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, P.; Wang, K.; Peng, Y.; Ahzi, S. Effects of cellular crossing paths on mechanical properties of 3D printed continuous fiber reinforced biocomposite honeycomb structures. Compos. Part A-Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2023, 178, 107972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ye, L. Path-Dependent Progressive Failure Analysis for 3D-Printed Continuous Carbon Fibre Reinforced Composites. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2024, 37, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, Z.; Cao, J.; Pagani, A.; Zhang, C. Fracture toughness determination and mechanism for mode-I interlaminar failure of 3D-printed carbon-Kevlar composites. Compos. Commun. 2023, 39, 101532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Luo, J.; Luo, Q.; Li, Q.; Sun, G. Experimental study on interface failure behavior of 3D printed continuous fiber reinforced composites. Addit. Manuf. 2022, 59, 103077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, K.; Tiwari, V. Mode-I interlaminar fracture behavior of additively manufactured continuous carbon and Kevlar reinforced composites. In Mechanics of Advanced Materials and Structures; Taylor Francis Group: Abingdon, UK, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Wang, K.; Zhu, W.; Peng, Y.; Ahzi, S.; Chinesta, F. Contributions of interfaces on the mechanical behavior of 3D printed continuous fiber reinforced composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 340, 127842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Xia, L.; Wu, Y.; Le, T.X.; Zuo, W.; Liu, S.; Zhao, L. Extended phase field modeling of interface debonding and bulk cracking in realistic 3D printed fiber reinforced composites. Compos. Struct. 2024, 345, 118396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.-J.; Jeon, M.-S.; Lee, J.-R. Evaluation of manufacturing defects in 3D printed carbon fiber reinforced cylindrical composite structure based on laser ultrasonic testing. NDT E Int. 2023, 135, 102802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zheng, W.; Feng, X.; Wang, Y.; Ji, Q.; Ma, K.; Wu, F.; Xue, Y.; Guo, W.; Lu, B. Wet twisting treatment, process parameter optimisation and mechanical failure mechanisms of 3D printed carbon fibre reinforced composites. Compos. Commun. 2025, 55, 102308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, W.; Cheng, Y.; Dou, H.; Zhang, D.; Yang, F.; Li, Z.; Cai, W. Low-velocity impact response and compression behaviour after the impact of 3D-printed CCFR self-sensing honeycomb structures. Compos. Part B-Eng. 2023, 266, 110992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, H.; Ye, W.; Zhang, D.; Cheng, Y.; Wu, C. Comparative study on in-plane compression properties of 3D printed continuous carbon fiber reinforced composite honeycomb and aluminum alloy honeycomb. Thin-Walled Struct. 2022, 176, 109335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vattathurvalappil, S.H.; Najam, T.; Aves, M.; Baluch, A.H.; Ali, U.; Nazir, A. Effect of fiber steering and drilling in notched continuous fiber 3D-printed composites. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2025, 31, 883–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.Y.; Yu, S.; Kim, H.; Cha, E.; Shin, G.S.; Bin Eo, S.; Moon, S.Y.; Lee, M.W.; Kucher, M.; Boehm, R.; et al. Process-structure-property study of 3D-printed continuous fiber reinforced composites. Compos. Part A-Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2024, 188, 136366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.Z.; Rahman, M.A.; Gibbon, L.; Hall, E.; Ulven, C.A.; La Scala, J.J. Mechanical Characterization and Production of Various Shapes Using Continuous Carbon Fiber-Reinforced Thermoset Resin-Based 3D Printing. Polymers 2024, 16, 1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, C.; Fu, Y.-T.; Xia, D.; Xu, P.-H.; Xiang, C.-T.; Wu, J.; Li, J.-Y.; Li, Y.-Q.; Li, F.; et al. Mechanical characterization of 3D printed multiscale carbon nanofiller/continuous fiber reinforced polymer hybrid composites. In Polymer Composites; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Shi, J.; Liu, Z. Bending performance enhancement by nanoparticles for FFF 3D printed nylon and nylon/Kevlar composites. J. Compos. Mater. 2021, 55, 1017–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wu, J.; Robert, C.; Bradaigh, C.M.O.; Yang, D. 3D printing and epoxy-infusion treatment of curved continuous carbon fibre reinforced dual-polymer composites. Compos. Part B-Eng. 2022, 234, 109687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.A.; Hall, E.; Gibbon, L.; Islam, M.Z.; Ulven, C.A.; La Scala, J.J. A Mechanical Performance Study of Dual Cured Thermoset Resin Systems 3D-Printed with Continuous Carbon Fiber Reinforcement. Polymers 2023, 15, 1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toth, C.; Virag, A.D.; Vas, L.M.; Kovacs, N.K. Prediction and analysis of flexural stiffness for 3D-printed continuous fiber-reinforced composites with different matrix fill ratios and layer orders. Polym. Test. 2024, 135, 108459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikiema, D.; Balland, P.; Sergent, A. Study of 3D-printed onyx parts reinforced with continuous glass fibers: Focus on mechanical characterization, analytical prediction and numerical simulation. J. Compos. Mater. 2024, 58, 1717–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giarmas, E.; Tsongas, K.; Tzimtzimis, E.K.; Korlos, A.; Tzetzis, D. Mechanical and FEA-Assisted Characterization of 3D Printed Continuous Glass Fiber Reinforced Nylon Cellular Structures. J. Compos. Sci. 2021, 5, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saniei, S.M.; Hadizadeh, M.; Mashroteh, H.; Azizi Tafti, R. Investigating the mechanical properties of 3D fused deposition modeling composites reinforced with continuous fibers: Effects of fiber number and negative Poisson structure. J. Ind. Text. 2024, 54, 15280837241253875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Zhu, W.; Li, S.; Peng, Y.; Ahzi, S. Investigations of quasi-static indentation properties of 3D printed polyamide/continuous Kevlar/continuous carbon fiber composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2022, 139, e52758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Li, S.; Wu, Y.; Rao, Y.; Peng, Y. Simultaneous reinforcement of both rigidity and energy absorption of polyamide-based composites with hybrid continuous fibers by 3D printing. Compos. Struct. 2021, 267, 113854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Zou, B.; Zhang, P.; Liu, Q.; Feng, Z.; Quan, T.; Wang, F.; Li, L.; Liu, J. Layout design and mechanical behavior of 3D printed intralayer hybrid continuous carbon/glass fiber composites. J. Manuf. Process. 2024, 115, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Hou, Z.; Tian, X.; Zhu, W.; Wang, C.; He, J.; Li, D. Evaluation and prediction of tensile properties of 3D-printed continuous carbon/Kevlar fiber-filled composites by coaxial hybrid process. Polym. Compos. 2024, 45, 6278–6286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, J.; Yang, N.; Yu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, H.; Wu, W.; Ma, G. Experiment and Simulation Study on the Crashworthiness of Markforged 3D-Printed Carbon/Kevlar Hybrid Continuous Fiber Composite Honeycomb Structures. Materials 2025, 18, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, L.; Li, Z.; Sun, Q.; Jiang, H. Experimental study on hydrothermal aging of 3D-printed hybrid composite trapezoidal structures with continuous carbon-fiber and short carbon-fiber. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2025, 171, 109351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Dong, Y. Multiscale coupling analysis of energy absorption in 3D printed continuous fiber reinforced thermoplastic orthogonal fabric composites. Addit. Manuf. 2024, 84, 104084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Li, J.; Qian, X.; Rudykh, S. 3D printed recoverable honeycomb composites reinforced by continuous carbon fibers. Compos. Struct. 2021, 268, 113974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Yao, X. Multi-scale analysis for 3D printed continuous fiber reinforced thermoplastic composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2021, 216, 109065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galos, J.; Hu, Y.; Ravindran, A.R.; Ladani, R.B.; Mouritz, A.P. Electrical properties of 3D printed continuous carbon fibre composites made using the FDM process. Compos. Part A-Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2021, 151, 106661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, P.; Ye, Z.; Huang, Y.; Wang, D.; Peng, Y.; Wang, K.; Ahzi, S. Electrical resistance-based self-monitoring of manufacturing damage in 3D printed continuous carbon fiber reinforced composites. Compos. Commun. 2023, 43, 101749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, W.; Dou, H.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, D. Self-sensing properties of 3D printed continuous carbon fiber-reinforced PLA/TPU honeycomb structures during cyclic compression. Mater. Lett. 2022, 317, 132077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olcun, S.; Ibrahim, Y.; Isaacs, C.; Karam, M.; Elkholy, A.; Kempers, R. Thermal conductivity of 3D-printed continuous pitch carbon fiber composites. Addit. Manuf. Lett. 2022, 4, 100106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olcun, S.; Elkholy, A.; Kempers, R. High thermal conductivity continuous pitch carbon fiber 3D printed using a 6-axis robot arm. Prog. Addit. Manuf. 2024, 9, 2189–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talha, M.; Khurram, A.; Munir, A.; Nadeem, H. Thermo-mechanical analysis of 3D-printed continuous glass fiber reinforced onyx thermoplastic composites. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2025, 31, 1082–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, C.; Yao, X.; Liu, C.; Lan, L.; Fu, J. Self-monitoring continuous carbon fiber reinforced thermoplastic based on dual-material three-dimensional printing integration process. Carbon 2018, 140, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Cai, R.; Cheng, P.; Wang, J.; Rao, Y.; Peng, Y.; Wang, K.; Ahzi, S.; Yao, S. Shape recovery and energy absorption properties of 3D printed continuous ramie fiber reinforced thin-walled biocomposite structures. Polym. Compos. 2024, 45, 10976–10988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Kergariou, C.; Kim, B.C.; Perriman, A.; Le Duigou, A.; Guessasma, S.; Scarpa, F. Design of 3D and 4D printed continuous fibre composites via an evolutionary algorithm and voxel-based Finite Elements: Application to natural fibre hygromorphs. Addit. Manuf. 2022, 59, 103144. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Tian, X.; Li, W.; He, S.; Zhao, P.; Hu, H.; Jia, Q.; Luo, M. 3D printing of topologically optimized wing spar with continuous carbon fiber reinforced composites. Compos. Part B-Eng. 2024, 272, 111166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukia, I.; Esnaola, A.; Erice, B.; Aurrekoetxea, J. Impact behaviour of bio-inspired sandwich panels integrally manufactured from 3D printed continuous carbon fibre reinforced polyamide. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2024, 250, 110515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Liu, C.; Liang, Y.; Lin, Z.; Han, Z.; Ren, L. Integration 3D printing of bionic continuous carbon fiber reinforced resin composite. Mater. Res. Express 2021, 8, 95602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhao, Q.; Lin, Z.; Han, Z.; Ren, L. Bionic Design and 3D Printing of Continuous Carbon Fiber-Reinforced Polylactic Acid Composite with Barbicel Structure of Eagle-Owl Feather. Materials 2021, 14, 3618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Yang, Y.; Jiang, H.; Ren, Y. On lateral crashworthiness and failure mechanisms of multi-fibers hybrid composite corrugated structures with carbon, glass, Kevlar. Thin-Walled Struct. 2024, 198, 111689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.; He, J.; Tian, X.; Zhu, W.; Wang, C.; Liu, P.; Lan, H.; Li, D. Performance and failure modes of continuous fibre-reinforced energy absorption tubes by cylindrical layered 3D printing. Virtual Phys. Prototyp. 2024, 19, e2367122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, S.-W.; Mei, H.; Zhang, M.-G.; Zhou, S.-X.; Yan, Y.-K.; Cheng, L.-F.; Zhang, L.-T.; Lu, J. 3D printing assemble technology toward advanced photocatalysis. Mater. Today Nano 2023, 24, 100385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Ming, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, F.; Lou, J.; Zhu, Y.; Duan, Y.; Wang, B.; Xiao, H. Fabrication of a novel continuous fiber 3D printed thermoset all-composite honeycomb sandwich structure with polymethacrylimide foam reinforcement. Compos. Commun. 2023, 45, 101794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashvand, K.; Eder, M.A.; Sarhadi, A. In-situ and adhesive repair of continuous fiber composites using 3D printing. Addit. Manuf. 2024, 80, 103975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Gao, Q.; Wang, P.; Shao, L.; Yuan, H.; Fu, J.; Chen, W.; He, Y. Structure-induced cell growth by 3D printing of heterogeneous scaffolds with ultrafine fibers. Mater. Des. 2019, 181, 108092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, H.; Ye, W.; Zhang, D.; Cheng, Y.; Huang, K.; Yang, F.; Rudykh, S. Research on drop-weight impact of continuous carbon fiber reinforced 3D printed honeycomb structure. Mater. Today Commun. 2021, 29, 102869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Xu, X.; Lin, Z.; Liang, Y. Continuous 3D Printing of Biomimetic Beetle Mandible Structure with Long Bundles of Aramid Fiber Composites. Biomimetics 2023, 8, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Liu, Q.; Chen, B.; Zhang, S.; Ferrara, L.; Li, W. Effect of raw materials on the performance of 3D printing geopolymer: A review. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 84, 108501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.-J.; Yan, Z.-T.; Jiang, Y.-Y.; Li, P.-L. 3D printing of FRP grid and bar reinforcement for reinforced concrete plates: Development and effectiveness. Compos. Struct. 2024, 335, 117946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, T.H.; Zeng, J.J.; Hu, X.W.; Chen, J.D.; Wu, P.P.; Liu, H.T.; Zhuge, Y. Flexural fatigue behavior of FRP-reinforced UHPC tubular beams. Eng. Struct. 2025, 330, 119848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.J.; Sun, H.Q.; Deng, R.B.; Yan, Z.T.; Zhuge, Y. Bond performance between FRP bars and 3D-printed high-performance concrete. Structures 2025, 73, 108377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Zeng, J.-J.; Zhuge, Y.; Liao, J.-J.; Zhou, J.-K.; Ma, G. Compressive behavior of FRP-confined 3D printed ultra-high performance concrete cylinders. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 83, 108304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.J.; Feng, S.Z.; Zhao, B.; Wu, F.Y.; Zhuge, Y.; Wang, H. Recyclable thermoplastic FRP bars for reinforced concrete structures: Current status and future opportunities. Compos. Struct. 2024, 348, 118438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Xiong, Y.; Zhou, L. Additive manufacturing of continuous fiber reinforced polymer composites: Design opportunities and novel applications. Compos. Commun. 2021, 27, 100907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Property | Carbon Fiber | Glass Fiber | Aramid Fiber | Natural Fiber | Hybrid Fiber |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristics | High strength-to-weight ratio, High modulus, Corrosion resistance | Good mechanical properties, Low cost, High toughness | High strength, High modulus, Heat resistance | Sustainability, Biodegradability, Low density | Performance optimization, Cost-performance balance |
| Density (g/cm3) | 1.8 | 2.5 | 1.44 | ||
| Tensile strength (Mpa) | 3500–7000 | 2000–4000 | 2800–4100 | ||
| Modulus (GPa) | 230–600 | 70–90 | 60–130 | ||
| References | [8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15] | [16,17,18,19] | [20,21] | [22,23,24,25,26,27,28] | [19,21] |
| Matrix Material | Type | Characteristics | Application Fields | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PLA | Thermoplastic | Biodegradability, Low cost, Easy processing; Lower mechanical properties and thermal stability (softens at 50–60 °C) | Beginner projects, Biomedical applications | [14,22,26] |
| PA6 | Excellent mechanical properties, High-temperature stability | Aerospace, Automotive industry | [10,13] | |
| PEEK | High continuous service temperature (250 °C), Outstanding chemical stability, High mechanical performance | Aerospace, Automotive industry, Extreme environments | [11,30,31,32,33] | |
| ABS | Good impact resistance, excellent electrical insulation properties, superior chemical stability | Electrical Engineering, Functional Prototyping | [34] | |
| Epoxy resin | Thermosetting | High insulation properties, Excellent mechanical performance, High moisture resistance; Complex curing process, Relatively low flame resistance | Aerospace, Automotive industry, Electronics and electrical engineering | [8] |
| Phenolic resin | High temperature resistance, Excellent chemical stability, Short curing time; High water absorption, Low toughness | Fire-resistant materials, Acid and alkali-resistant chemical equipment | [35] |
| Parameter | Effects | Optimization Methods | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Printing speed | Affects fiber placement accuracy and matrix distribution; High speed may increase porosity | Adjust speed to balance precision and efficiency | [17,68,83,84] |
| Nozzle temperature | Excessive temperature may degrade matrix; Insufficient temperature leads to poor impregnation | Adaptive temperature control based on material properties | [85,86,87,88] |
| Fiber feed rate | Mismatch with extrusion rate causes fiber accumulation or matrix deficiency | Synchronize feed and extrusion rates to maintain consistent fiber volume fraction | [89,90,91] |
| Path planning | Determines fiber orientation and part anisotropy | Load-dependent path planning or geometry-driven path optimization | [92,93,94,95,96,97] |
| Influencing Factor | Affected Mechanical Properties | Optimization Strategies | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fiber type | Tensile strength, Compressive strength, Flexural modulus, Impact toughness | Select carbon fibers (high strength), glass fibers (cost-effective), or aramid fibers (toughness) | [99,100,101,102,103] |
| Fiber volume fraction | Tensile strength, Compressive strength, Flexural modulus, Interlaminar bonding strength | Maintain 40–50% volume fraction to balance performance and porosity | [54,104,105,106,107,108] |
| Printing parameters | Tensile strength, Compressive strength, Flexural modulus, Impact toughness, Interlaminar bonding strength | Adjust nozzle temperature (avoid degradation), optimize printing speed (balance efficiency/quality), modify layer thickness (enhance interlayer bonding) | [85,105,109,110,111,112,113,114,115,116,117] |
| Fiber orientation | Tensile strength, Compressive strength, Flexural modulus, Impact toughness, Interlaminar bonding strength | Align fibers along load direction, topology-optimized paths, hybrid fiber layouts | [118,119,120,121,122,123,124,125,126,127,128,129] |
| Interfacial issues | Shear strength, Tensile strength, Flexural strength | Modification of interlayer stacking sequence, Adjustment of fiber orientation, Application of composite fiber interfaces | [130,131,132,133,134,135,136] |
| Fiber pretreatment | Tensile strength, Interfacial adhesion, Overall reliability | Surface coating, chemical modification | [137,138,139,140,141,142,143,144,145] |
| Structural design | Tensile strength, Flexural modulus, Impact toughness, Energy absorption efficiency | Topology optimization, honeycomb structures, multi-scale optimization | [146,147,148,149] |
| Hybrid fiber systems and advanced processes | Tensile strength, Compressive strength, Flexural modulus, Impact toughness | Carbon/glass or carbon/aramid fiber hybrids, multi-axial alignment | [150,151,152,153,154,155,156,157,158] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, H.; Zhu, S.; Chen, L.; Wang, L.; Zhang, H.; Wang, P.; Sun, K.; Wang, H.; Liu, C. 3D Printing Continuous Fiber Reinforced Polymers: A Review of Material Selection, Process, and Mechanics-Function Integration for Targeted Applications. Polymers 2025, 17, 1601. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17121601
Zheng H, Zhu S, Chen L, Wang L, Zhang H, Wang P, Sun K, Wang H, Liu C. 3D Printing Continuous Fiber Reinforced Polymers: A Review of Material Selection, Process, and Mechanics-Function Integration for Targeted Applications. Polymers. 2025; 17(12):1601. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17121601
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Haoyuan, Shaowei Zhu, Liming Chen, Lianchao Wang, Hanbo Zhang, Peixu Wang, Kefan Sun, Haorui Wang, and Chengtao Liu. 2025. "3D Printing Continuous Fiber Reinforced Polymers: A Review of Material Selection, Process, and Mechanics-Function Integration for Targeted Applications" Polymers 17, no. 12: 1601. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17121601
APA StyleZheng, H., Zhu, S., Chen, L., Wang, L., Zhang, H., Wang, P., Sun, K., Wang, H., & Liu, C. (2025). 3D Printing Continuous Fiber Reinforced Polymers: A Review of Material Selection, Process, and Mechanics-Function Integration for Targeted Applications. Polymers, 17(12), 1601. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17121601