Electrospun Polybenzimidazole Membranes: Fabrication and Fine-Tuning Through Physical and Statistical Approaches
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Electrospinning of PBI and Design of Experiments
2.2. Sample Characterization
2.2.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) Evaluation: Morphological Characterization and Fiber Analysis
2.2.2. Porosity and Air Permeability
2.2.3. X-Ray Diffraction
2.2.4. Attenuated Total Reflectance Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (ATR-FTIR)
2.2.5. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
2.2.6. Mechanical Tests
2.3. Calendering
3. Results
3.1. Electrospinning Process: Morphological Study
3.1.1. Effects of Voltage and Collector Distance
3.1.2. Effects of Viscosity and Interactions with the Other Parameters
3.2. Fiber Diameter Distribution, Porosity and Air Permeability
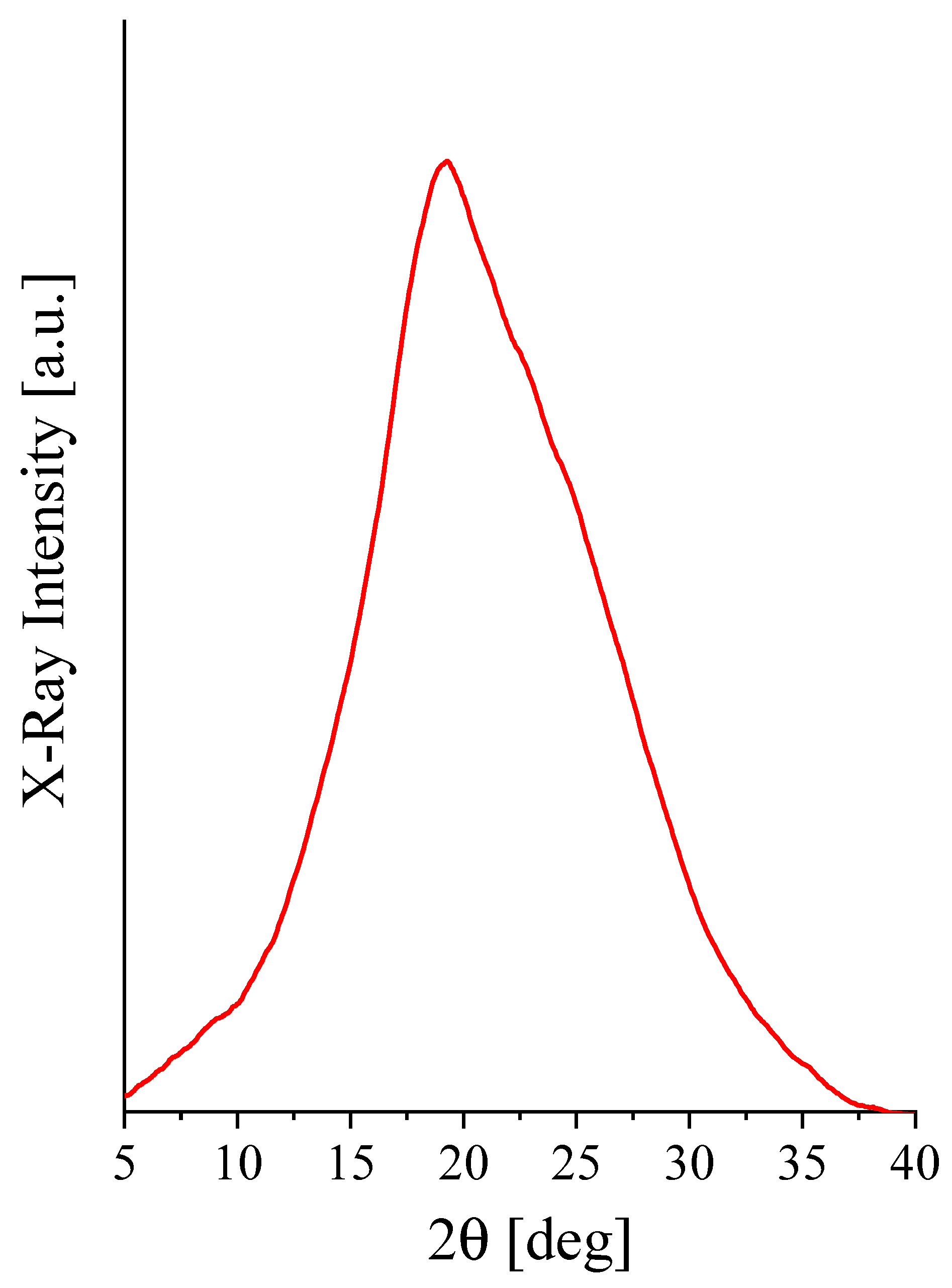
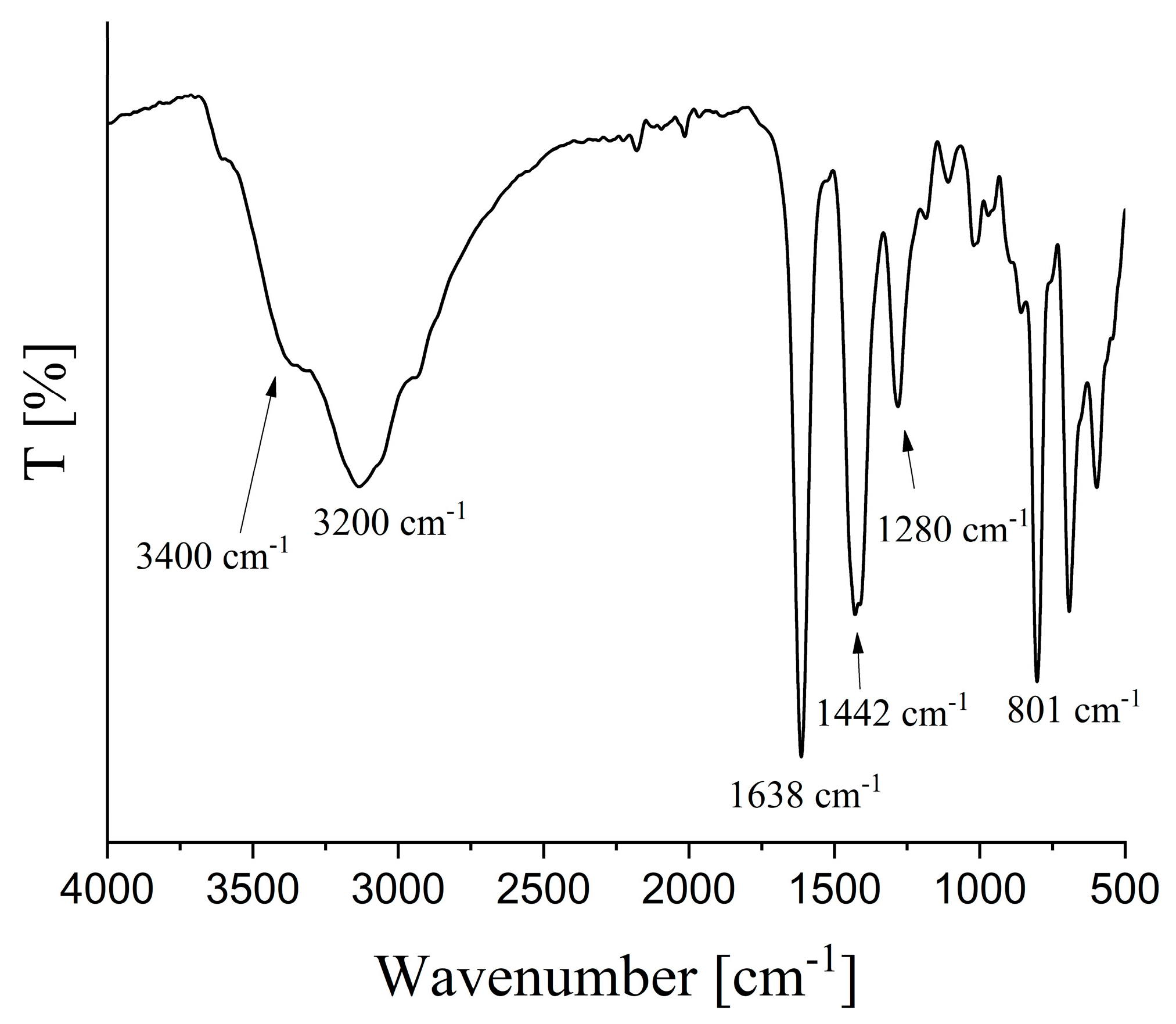
3.3. Structural Characterization: WAXD, TGA and ATR-FTIR
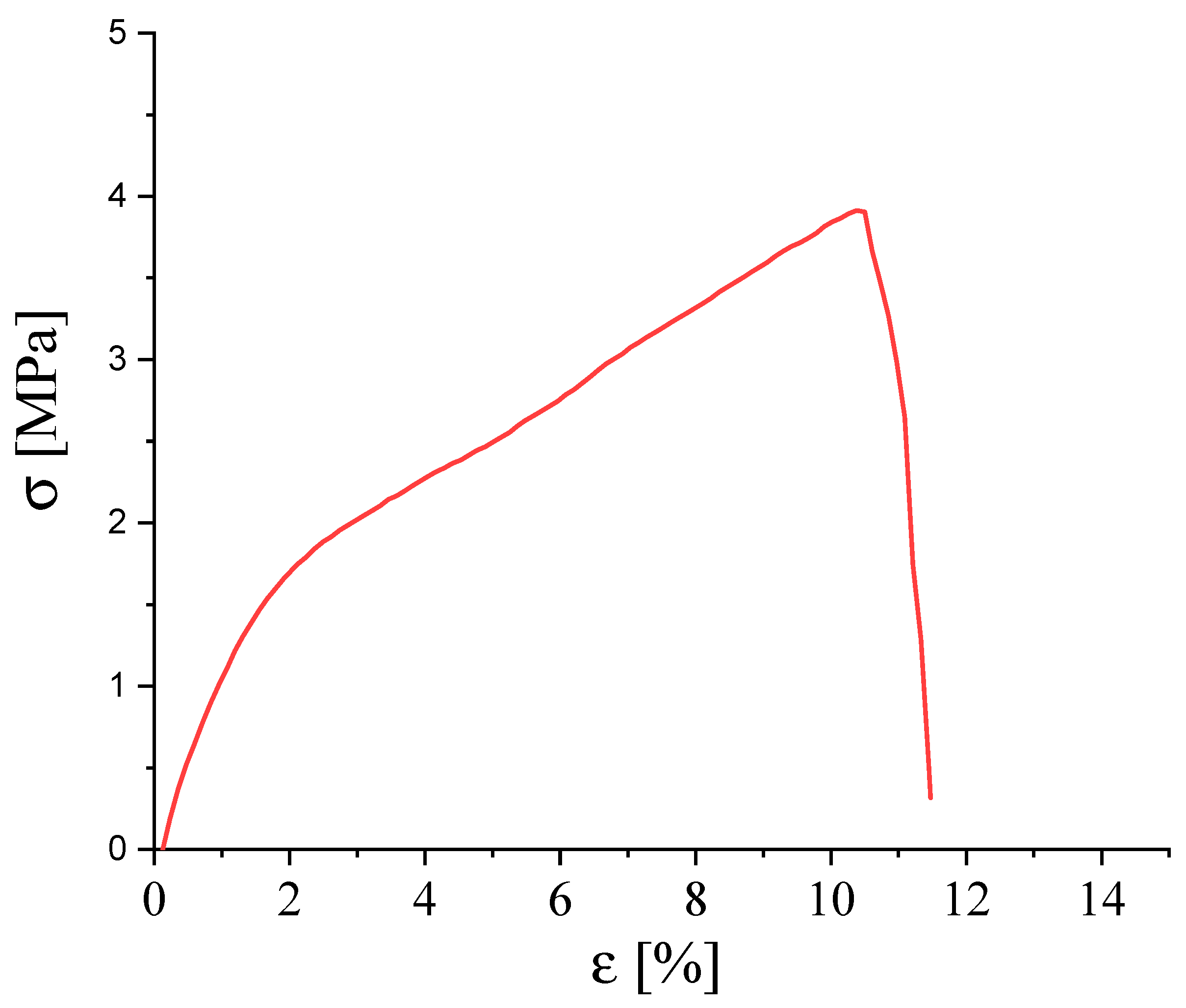
3.4. Mechanical Test
3.5. PBI-Based Electrospun Fine-Tuning
3.5.1. ANOVA Model for Yi
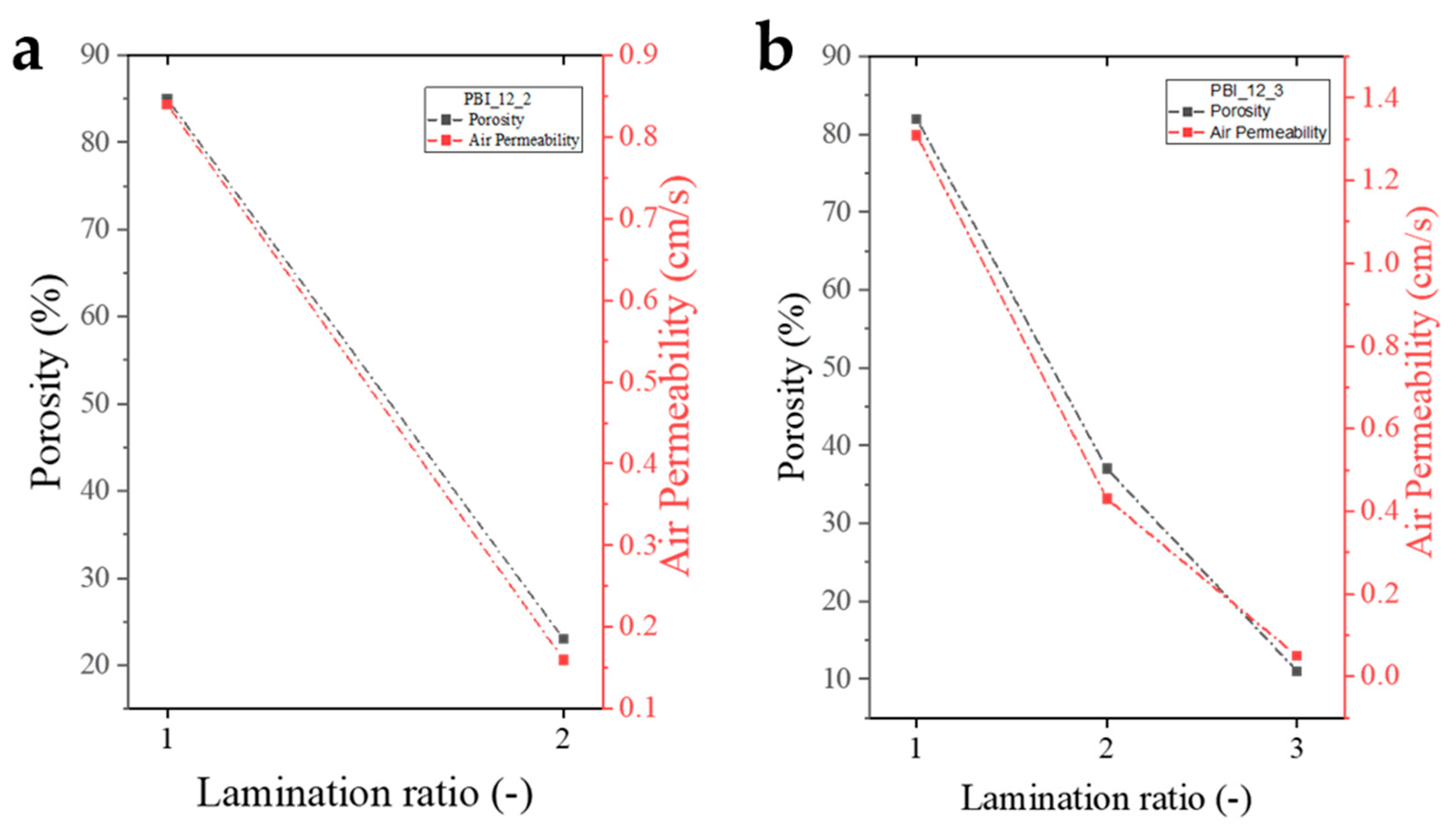
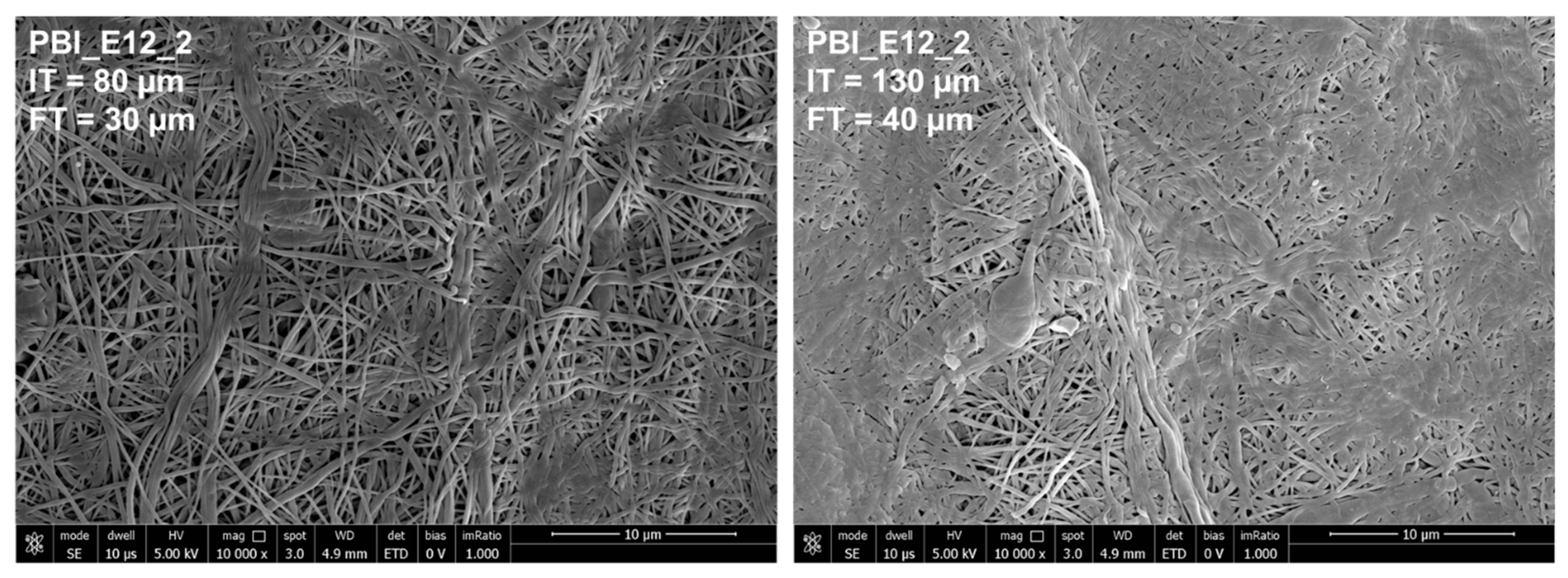
3.5.2. Calendering Process
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chung, T.-S. A Critical Review of Polybenzimidazoles. Polym. Revs. 1997, 37, 277–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, H.; Marvel, C.S. Polybenzimidazoles, new thermally stable polymers. J. Polym. Sci. 1961, 50, 511–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuse, E.W. Aromatic polybenzimidazoles. Syntheses, properties, and applications. In Synthesis and Degradation Rheology and Extrusion; Advances in Polymer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1982; Volume 47, pp. 1–42. ISBN 978-3-540-11774-2. [Google Scholar]
- Gieselman, M.B.; Reynolds, J.R. Water-soluble polybenzimidazole-based polyelectrolytes. Macromolecules 1992, 25, 4832–4834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Sannigrahi, A.; Maity, S.; Jana, T. Role of Solvent Protic Character on the Aggregation Behavior of Polybenzimidazole in Solution. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 3122–3132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Shi, Z.; Xu, H.; Fang, J.; Ma, X.; Yin, J. Preparation, Characterization, and Properties of Novel Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxane−Polybenzimidazole Nanocomposites by Friedel−Crafts Reaction. Macromolecules 2010, 43, 6731–6738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namazi, H.; Ahmadi, H. Improving the proton conductivity and water uptake of polybenzimidazole-based proton exchange nanocomposite membranes with TiO2 and SiO2 nanoparticles chemically modified surfaces. J. Power Sources 2011, 196, 2573–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singha, S.; Jana, T. Structure and Properties of Polybenzimidazole/Silica Nanocomposite Electrolyte Membrane: Influence of Organic/Inorganic Interface. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 21286–21296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joseph, R.M.; Merrick, M.M.; Liu, R.; Fraser, A.C.; Moon, J.D.; Choudhury, S.R.; Lesko, J.; Freeman, B.D.; Riffle, J.S. Synthesis and characterization of polybenzimidazole membranes for gas separation with improved gas permeability: A grafting and blending approach. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 564, 587–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Singh, R.P.; Dudeck, K.W.; Berchtold, K.A.; Benicewicz, B.C. Influence of polybenzimidazole main chain structure on H2/CO2 separation at elevated temperatures. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 461, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Tang, Y.; Song, C.; Zhang, J. Polybenzimidazole-membrane-based PEM fuel cell in the temperature range of 120–200 °C. J. Power Sources 2007, 172, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Song, K.; Hao, C.; Liang, W.; Li, X.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.; Song, Y. Fabrication of S-PBI cation exchange membrane with excellent anti-fouling property for enhanced performance in electrodialysis. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2023, 661, 130910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akther, N.; Daer, S.; Wei, Q.; Janajreh, I.; Hasan, S.W. Synthesis of polybenzimidazole (PBI) forward osmosis (FO) membrane and computational fluid dynamics (CFD) modeling of concentration gradient across membrane surface. Desalination 2019, 452, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, K.A.; More, K.L.; Andrew Payzant, E.; Meisner, R.A.; Sumpter, B.G.; Benicewicz, B.C. A comparative study of phosphoric acid-doped m-PBI membranes. J. Polym. Sci. B Polym. Phys. 2014, 52, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, W.; Aili, D.; Cleemann, L.N.; Li, Q. Crosslinking of Electrospun Polybenzimidazole Fibers and Mats. SSRN 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Lee, C.N.; Teoh, S.H. Nanofibrous modification on ultra-thin poly(e-caprolactone) membrane via electrospinning. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2007, 27, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Aili, D.; Zhang, W.; Azizi, K.; Cleemann, L.N.; Li, Q. Reinforced Polybenzimidazole Membranes by Crosslinked Fiber Mats for High Temperature Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells. Electrochim. Acta 2025, 529, 146260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosal, K.; Chandra, A.; Praveen, G.; Snigdha, S.; Roy, S.; Agatemor, C.; Thomas, S.; Provaznik, I. Electrospinning over Solvent Casting: Tuning of Mechanical Properties of Membranes. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rnjak-Kovacina, J.; Weiss, A.S. Increasing the Pore Size of Electrospun Scaffolds. Tissue Eng. Part B Rev. 2011, 17, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didenko, A.; Vaganov, G.; Nesterova, A.; Kamalov, A.; Lavrentiev, V.; Popova, E.; Kraft, V.; Anokhina, T.; Borisov, I.; Abalov, I.; et al. Porous nonwoven calendered fabrics (membranes) based on electrospun prepolymers of modified polyimides. Polym. Eng. Sci 2025, 65, 1665–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judd, C.M.; McClelland, G.H.; Ryan, C.S. Data Analysis: A Model Comparison Approach To Regression, ANOVA, and Beyond, 3rd ed.; Taylor and Francis: London, UK, 2017; ISBN 978-1-138-81982-5. [Google Scholar]
- Carotenuto, F.; Fiaschini, N.; Di Nardo, P.; Rinaldi, A. Towards a Material-by-Design Approach to Electrospun Scaffolds for Tissue Engineering Based on Statistical Design of Experiments (DOE). Materials 2023, 16, 1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhfeld, W.F. Experimental Design: Efficiency, Coding, and Choice Designs. In Marketing Research Methods in SAS: Experimental Design, Choice, Conjoint, and Graphical Techniques; SAS Institute Inc.: Cary, NC, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez Marquez, A.; Gareis, I.E.; Dias, F.J.; Gerhard, C.; Lezcano, M.F. Methods to Characterize Electrospun Scaffold Morphology: A Critical Review. Polymers 2022, 14, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ASTM D638-14; Standard Test Method for Tensile Properties of Plastics. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2022.
- Okutan, N.; Terzi, P.; Altay, F. Affecting parameters on electrospinning process and characterization of electrospun gelatin nanofibers. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 39, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valizadeh, A.; Mussa Farkhani, S. Electrospinning and electrospun nanofibres. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2014, 8, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keirouz, A.; Chung, M.; Kwon, J.; Fortunato, G.; Radacsi, N. 2D and 3D electrospinning technologies for the fabrication of nanofibrous scaffolds for skin tissue engineering: A review. WIREs Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2020, 12, e1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, M.; Quan, Z.; Qin, X.; Yu, J.; Li, Y. Impacts of viscosity on bending behavior of the electrospun jet: Simulation model and experiment. Polymer 2024, 311, 127529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, C. Extension rate and bending behavior of electrospinning jet: The role of solution conductivity. Polymer 2021, 222, 123672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, T.U.; Gorga, R.E.; Krause, W.E. Mechanical Properties of Electrospun Fibers—A Critical Review. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2021, 23, 2100153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Jensen, J.O.; Savinell, R.F.; Bjerrum, N.J. High temperature proton exchange membranes based on polybenzimidazoles for fuel cells. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2009, 34, 449–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleha, W.F.G.; Ramesh, R.; Nalajala, N.; Ladewig, B.P.; Neergat, M. Dielectric relaxations in phosphoric acid-doped poly(2,5-benzimidazole) and its composite membranes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatfield, D.A.; Einhorn, I.N. Stepwise thermal degradation of a polybenzimidazole foam. J. Polym. Sci. Polym. Chem. Ed. 1981, 19, 601–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Zhang, H.; Scanlon, E.; Ramanathan, L.S.; Choe, E.-W.; Rogers, D.; Apple, T.; Benicewicz, B.C. High-Temperature Polybenzimidazole Fuel Cell Membranes via a Sol−Gel Process. Chem. Mater. 2005, 17, 5328–5333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zholobko, O.; Wu, X.; Zhou, Z.; Aulich, T.; Thakare, J.; Hurley, J. A comparative experimental study of the hygroscopic and mechanical behaviors of electrospun nanofiber membranes and solution-cast films of polybenzimidazole. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 137, 49639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, H.M.S.; Bhowmik, S.; Benedictus, R. Performance evaluation of polybenzimidazole coating for aerospace application. Prog. Org. Coat. 2017, 105, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asensio, J.A.; Sánchez, E.M.; Gómez-Romero, P. Proton-conducting membranes based on benzimidazole polymers for high-temperature PEM fuel cells. A chemical quest. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 3210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
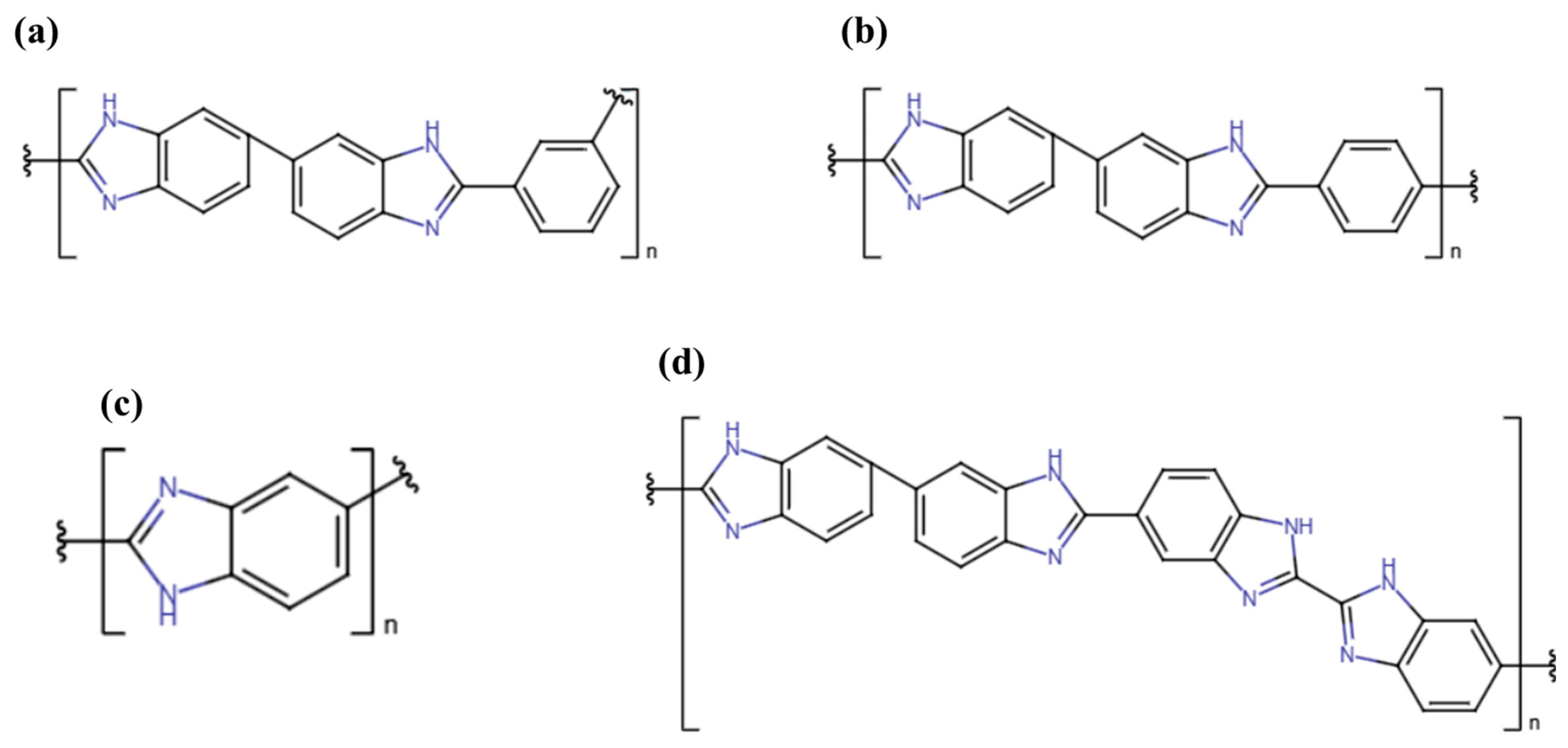
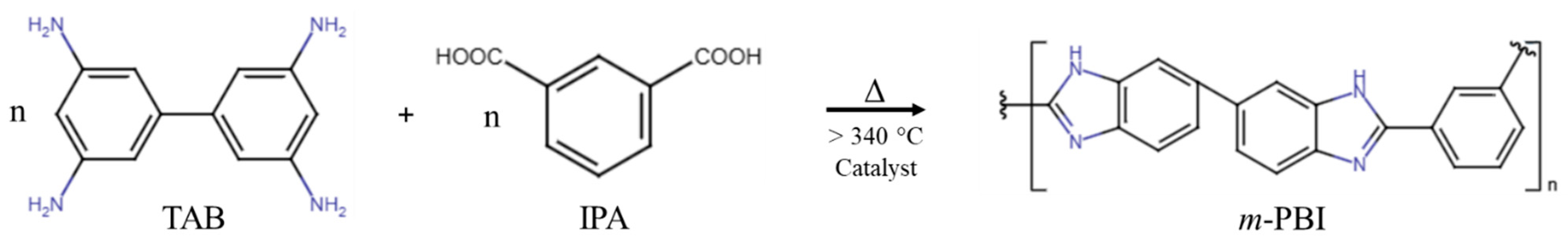
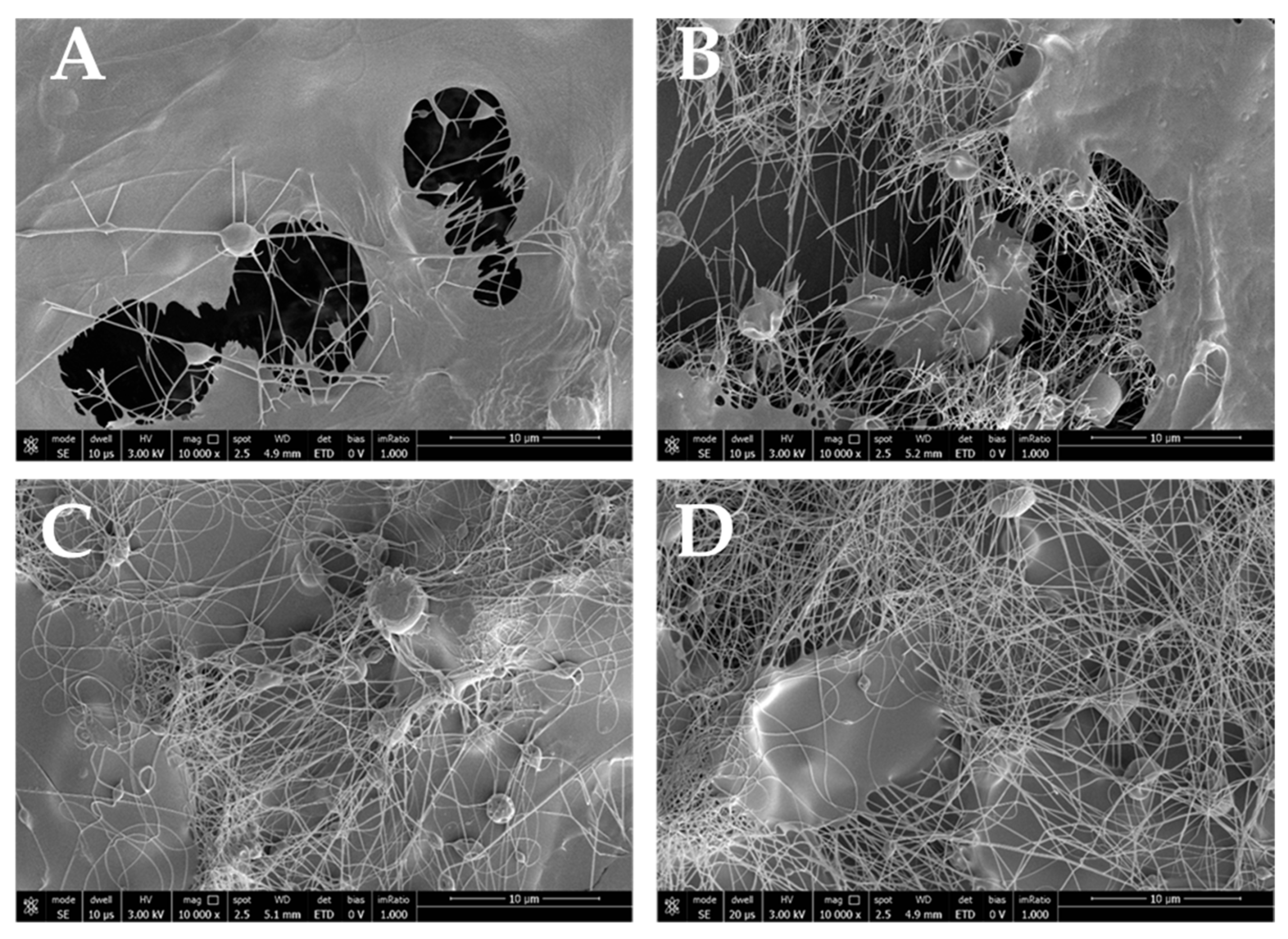

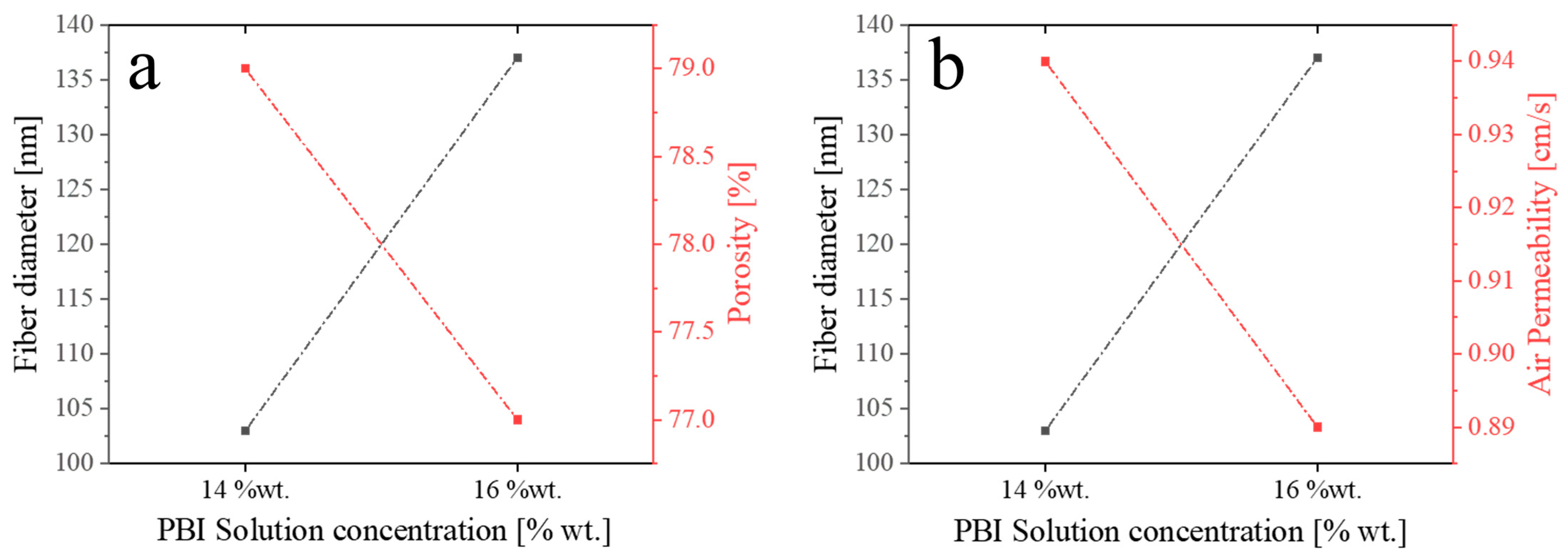


| Sample | Temperature [°C] | Relative Humidity [%] | V Ejector [kV] | V Collector [kV] | Needle–Collector Distance [mm] | Flow Rate [mL/h] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PBI_15_A | 25 | 40 | 20 | −20 | 125 | 5 |
| PBI_15_B | 35 | 25 | 20 | −20 | 125 | 0.4 |
| PBI_15_C | 40 | 25 | 20 | −20 | 125 | 1 |
| PBI_15_D | 45 | 20 | 20 | −20 | 125 | 1 |
| Sample | Flow Rate [mL/h] | V Ejector [kV] | Height [mm] | Concentration [%wt.] | Temperature [°C] | Humidity [%] | V Collector [kV] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PBI_E01 | 1 | 17 | 135 | 14 | 45 | 20 | −20 |
| PBI_E02 | 2 | 17 | 135 | 14 | 45 | 20 | −20 |
| PBI_E03 | 1 | 20 | 135 | 14 | 45 | 20 | −20 |
| PBI_E04 | 2 | 20 | 135 | 14 | 45 | 20 | −20 |
| PBI_E05 | 1 | 17 | 115 | 14 | 45 | 20 | −20 |
| PBI_E06 | 2 | 17 | 115 | 14 | 45 | 20 | −20 |
| PBI_E07 | 1 | 20 | 115 | 14 | 45 | 20 | −20 |
| PBI_E08 | 2 | 20 | 115 | 14 | 45 | 20 | −20 |
| PBI_E09 | 1 | 17 | 135 | 16 | 45 | 20 | −20 |
| PBI_E10 | 2 | 17 | 135 | 16 | 45 | 20 | −20 |
| PBI_E11 | 1 | 20 | 135 | 16 | 45 | 20 | −20 |
| PBI_E12 | 2 | 20 | 135 | 16 | 45 | 20 | −20 |
| PBI_E13 | 1 | 17 | 115 | 16 | 45 | 20 | −20 |
| PBI_E14 | 2 | 17 | 115 | 16 | 45 | 20 | −20 |
| PBI_E15 | 1 | 20 | 115 | 16 | 45 | 20 | −20 |
| PBI_E16 | 2 | 20 | 115 | 16 | 45 | 20 | −20 |
| PBI_E17 | 1.5 | 18.5 | 125 | 15 | 45 | 20 | −20 |
| Parameter | Label | Unit | Low Level (−1) | High Level (+1) | Average Level (0) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flow rate | X1 | mL/h | 1 | 2 | 1.5 |
| Ejector voltage | X2 | kV | 17 | 20 | 18.5 |
| Needle–collector distance | X3 | mm | 115 | 135 | 125 |
| PBI-solution concentration | X4 | %wt. | 14 | 16 | 15 |
| Parameter | Label | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Mean Fibre Diameter (FD) | Y1 | nm |
| FD Dev. St. | Y2 | nm |
| Air Permeability | Y3 | cm/s |
| Porosity | Y4 | % |
| Beads | Y5 | % |
| PBI Solution Concentration [%wt.] | Mean Fiber Diameter [nm] | Air Permeability [cm/s] | Porosity [%] |
|---|---|---|---|
| 14 | 103 ± 25 | 0.9 ± 0.5 | 79 ± 5 |
| 16 | 137 ± 30 | 0.9 ± 0.4 | 77 ± 8 |
| Sample | Young’s Module [GPa] | Tensile Strength [MPa] | Elongation at Break [%] |
|---|---|---|---|
| PBI Cast Film | 5.9 ± 1 [36] | 120 ± 16 MPa [36] | 10 ± 2 [32] |
| PBI_E12 | 0.1 ± 0.02 | 4 ± 0.3 MPa | 10 ± 2 |
| Sample | X1 * [-] | X2 * [-] | X3 * [-] | X4 * [-] | Y1 [nm] | Y2 [nm] | Y3 [cm/s] | Y4 [%] | Y5 [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PBI_E01 | −1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | 132 | 30 | 1.20 | 76 | 1.06 |
| PBI_E02 | 1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | 125 | 33 | 1.52 | 75 | 1.07 |
| PBI_E03 | −1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | 100 | 25 | 0.75 | 83 | 22.2 |
| PBI_E04 | 1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | 102 | 25 | 0.91 | 82 | 6.56 |
| PBI_E05 | −1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | 105 | 28 | 0.84 | 82 | 46.7 |
| PBI_E06 | 1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | 89 | 22 | 1.11 | 83 | 6.79 |
| PBI_E07 | −1 | 1 | −1 | −1 | 83 | 20 | 0.52 | 72 | 52.2 |
| PBI_E08 | 1 | 1 | −1 | −1 | 89 | 20 | 0.68 | 76 | 8.23 |
| PBI_E09 | −1 | −1 | 1 | 1 | 133 | 33 | 0.95 | 74 | 0 |
| PBI_E10 | 1 | −1 | 1 | 1 | 116 | 27 | 1.27 | 84 | 49.3 |
| PBI_E11 | −1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 174 | 28 | 0.91 | 85 | 0 |
| PBI_E12 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 156 | 26 | 0.79 | 85 | 0 |
| PBI_E13 | −1 | −1 | −1 | 1 | 143 | 35 | 1.16 | 70 | 14.6 |
| PBI_E14 | 1 | −1 | −1 | 1 | 132 | 29 | 0.89 | 77 | 1.89 |
| PBI_E15 | −1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | 114 | 28 | 0.59 | 76 | 13.7 |
| PBI_E16 | 1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | 130 | 40 | 0.55 | 68 | 3.99 |
| PBI_E17 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 139 | 41 | 0.59 | 79 | 9.81 |
| Output Variable | Model Equation | R2 | R2adj |
|---|---|---|---|
| Y1 | Y1 = 120.2 + 9.47 X3 + 16.9 X4 + 5.01 X2X3 + 7.90 X2X4 + 9.04 X2X3X4 | 0.918 | 0.8687 |
| Y2 | Y2 = 28.11 − 1.440 X2 + 2.653 X4 + 1.492 X1X2 − 0.759 X2X3 + 1.317 X2X4 − 2.661 X3X4 − 1.442 X1X2X3 + 1.257 X1X2X4 − 1.472 X1X3X4 | 0.983 | 0.936 |
| Y3 | Y3 = 0.9149 − 0.2031 X2 + 0.1231 X3 − 0.0644 X1X4 | 0.833 | 0.778 |
| Y4 | Y4 = 78.11 + 0.831 X1 + 2.436 X3 − 0.692 X4 − 1.434 X1X2 + 2.957 X2X3 + 0.767 X2X4 + 2.255 X3X4 − 1.824 X1X2X4 + 1.035 X1X3X4 − 0.886 X2X3X4 | 0.978 | 0.943 |
| Y5 | Y5 = 14.01 − 4.54 X1 − 4.24 X3 − 3.83 X4 − 4.13 X1X2 + 8.75 X1X3 + 7.9 X1X4 + 6.13 X3X4 − 3.99 X1X2X3 − 4.39 X2X3X4 | 0.954 | 0.876 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De Gregorio, E.; Roviello, G.; Naticchioni, V.; Cigolotti, V.; Pozio, A.; Hein, L.A.; De Luca, C.; Ferone, C.; Rinaldi, A.; Tarallo, O. Electrospun Polybenzimidazole Membranes: Fabrication and Fine-Tuning Through Physical and Statistical Approaches. Polymers 2025, 17, 1594. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17121594
De Gregorio E, Roviello G, Naticchioni V, Cigolotti V, Pozio A, Hein LA, De Luca C, Ferone C, Rinaldi A, Tarallo O. Electrospun Polybenzimidazole Membranes: Fabrication and Fine-Tuning Through Physical and Statistical Approaches. Polymers. 2025; 17(12):1594. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17121594
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe Gregorio, Emmanuel, Giuseppina Roviello, Valentina Naticchioni, Viviana Cigolotti, Alfonso Pozio, Luis Alexander Hein, Carlo De Luca, Claudio Ferone, Antonio Rinaldi, and Oreste Tarallo. 2025. "Electrospun Polybenzimidazole Membranes: Fabrication and Fine-Tuning Through Physical and Statistical Approaches" Polymers 17, no. 12: 1594. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17121594
APA StyleDe Gregorio, E., Roviello, G., Naticchioni, V., Cigolotti, V., Pozio, A., Hein, L. A., De Luca, C., Ferone, C., Rinaldi, A., & Tarallo, O. (2025). Electrospun Polybenzimidazole Membranes: Fabrication and Fine-Tuning Through Physical and Statistical Approaches. Polymers, 17(12), 1594. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17121594















