The Production of High-Permeable and Macrovoid-Free Polysulfone Hollow Fiber Membranes and Their Utilization in CO2 Capture Applications via the Membrane-Assisted Gas Absorption Technique
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
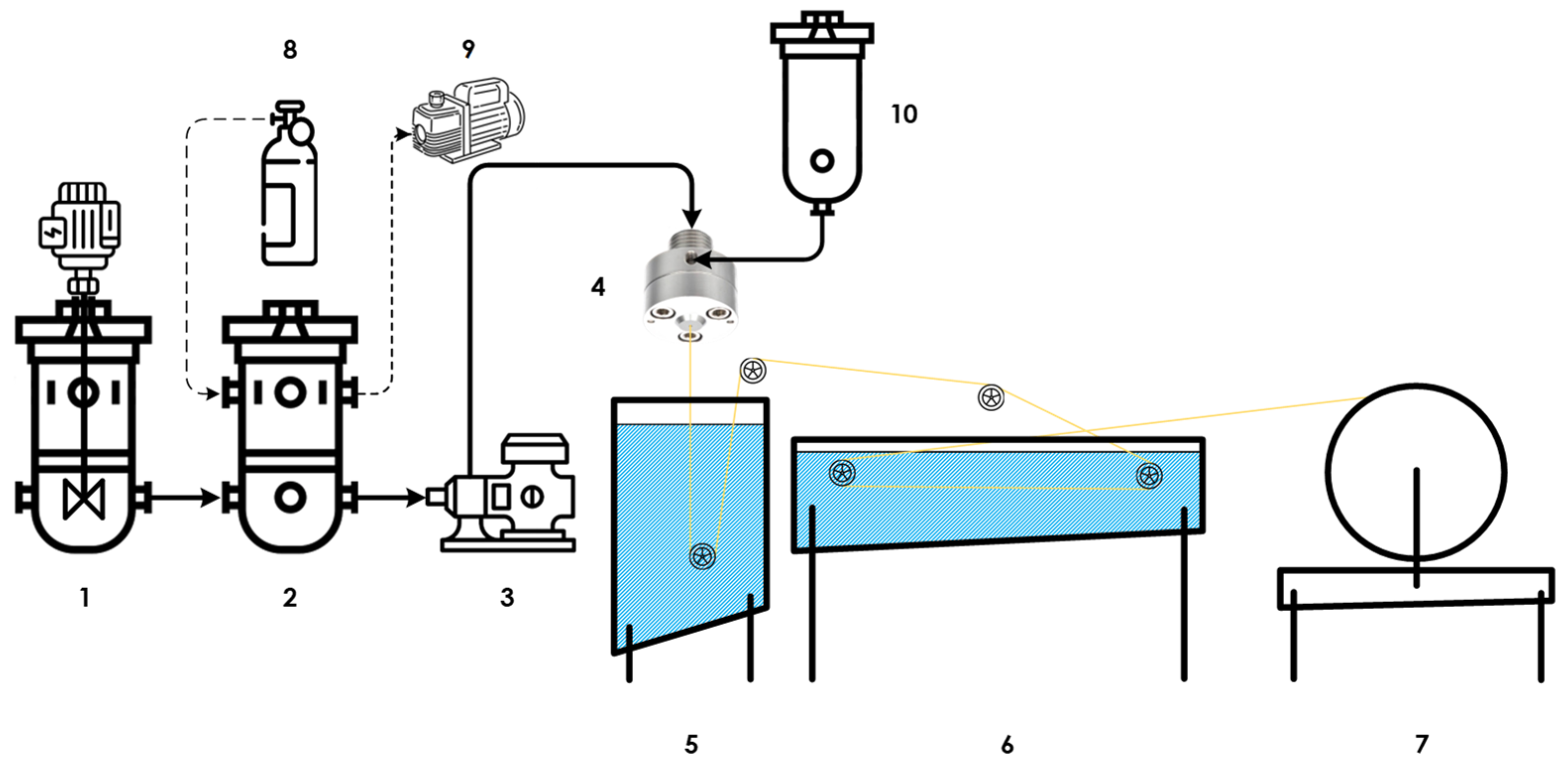
2.2. Asymmetric Hollow Fiber Spinning
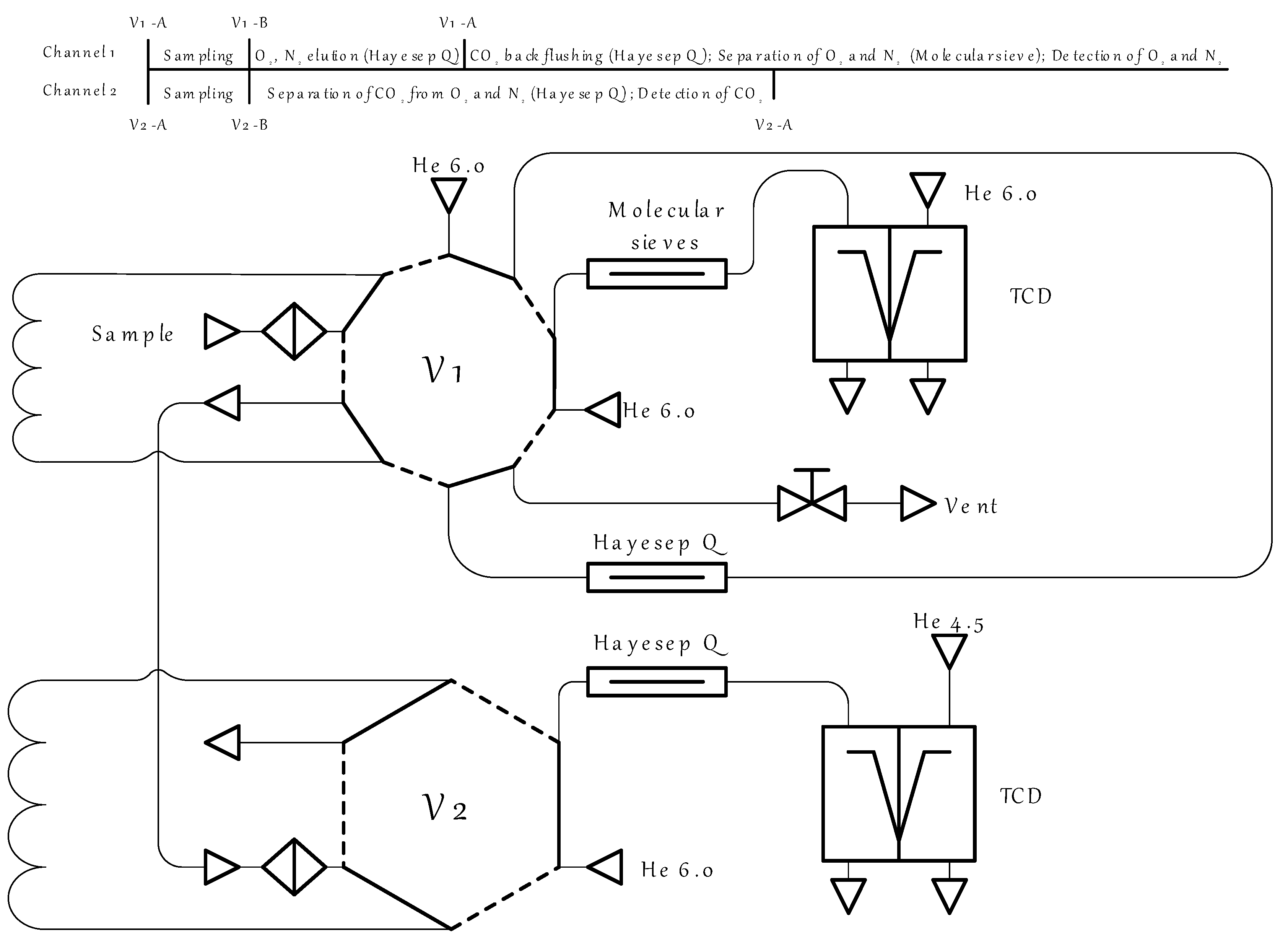
2.3. Hollow Fibers’ Characterization
2.4. Absorbent Synthesis
2.5. Absorbent Characterization
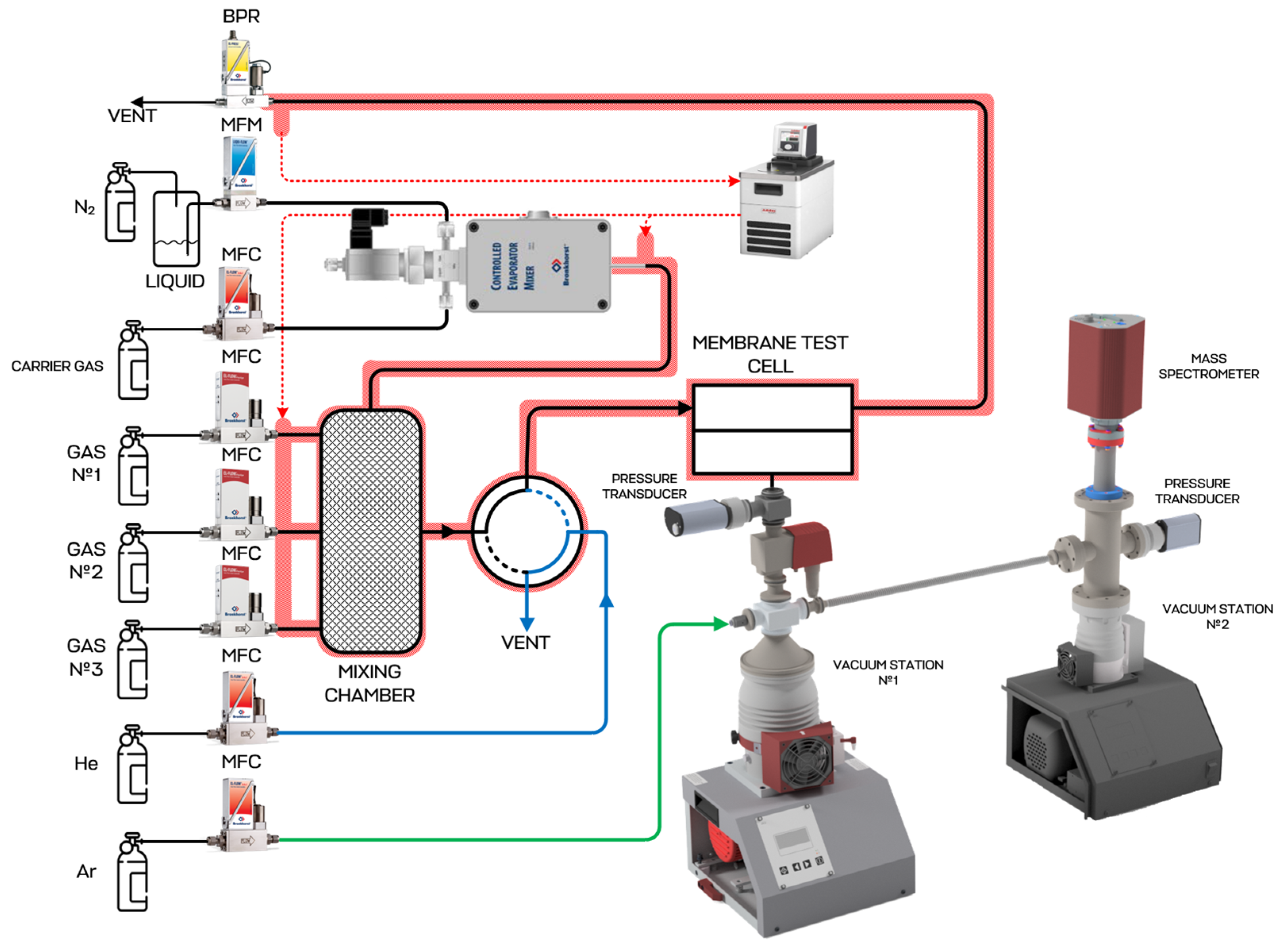
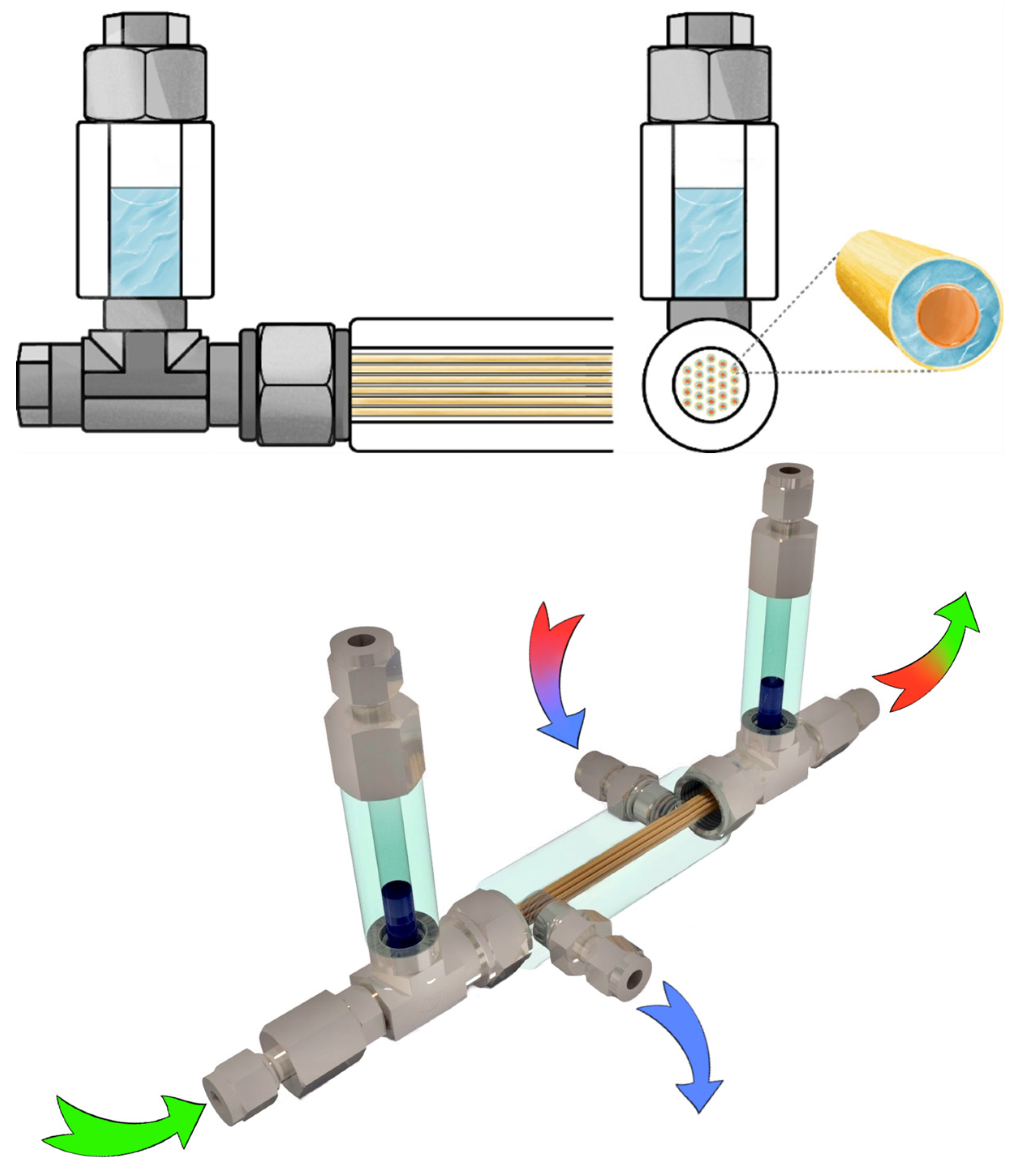
2.6. Membrane-Assisted Gas Absorption Cell Design
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Hollow Fiber Membranes’ Mass Transfer Properties
3.2. Absorbent Properties
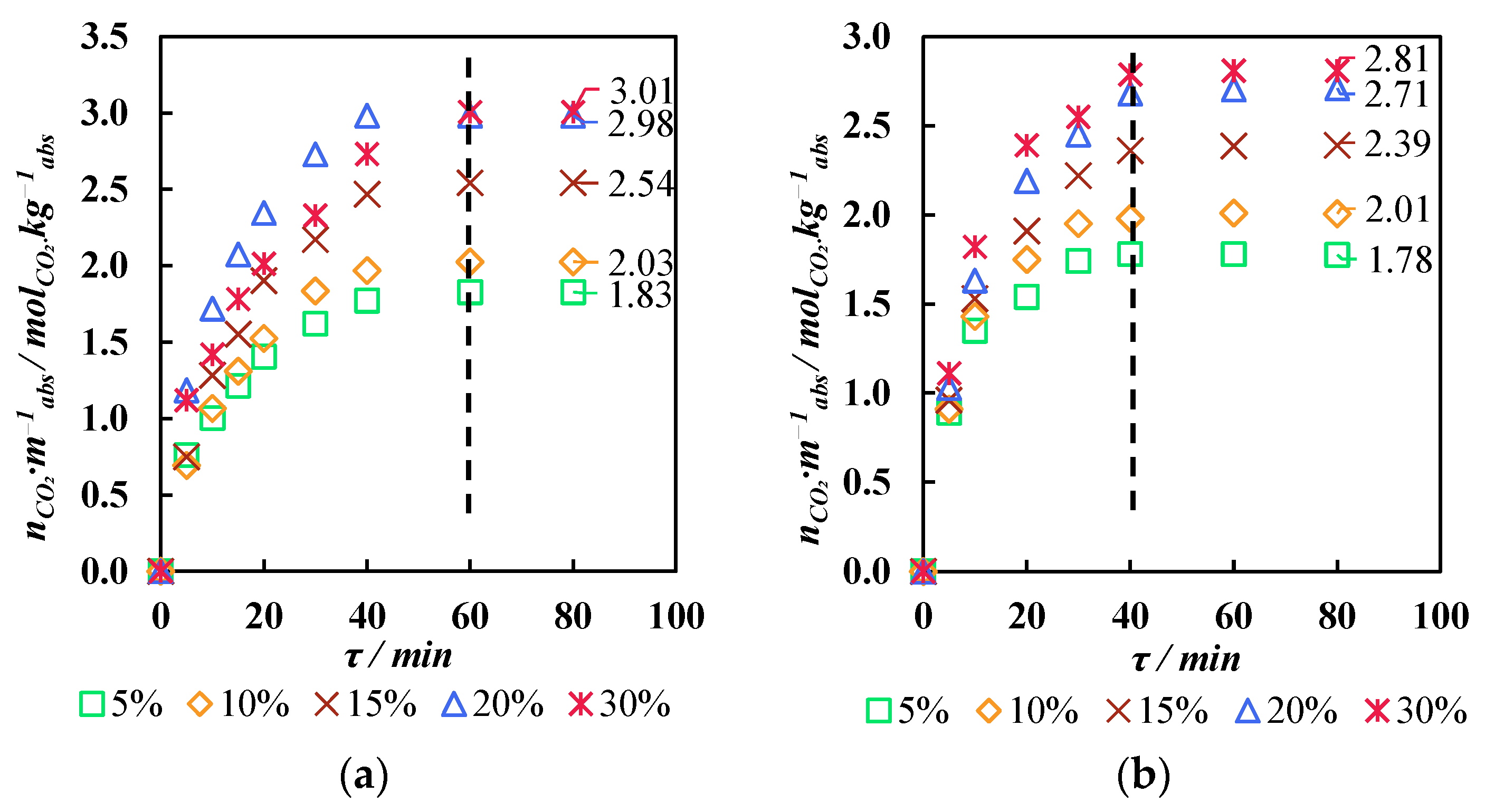
3.3. Membrane-Assisted Gas Absorption Performance
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mendonça, A.K.d.S.; de Andrade Conradi Barni, G.; Moro, M.F.; Bornia, A.C.; Kupek, E.; Fernandes, L. Hierarchical Modeling of the 50 Largest Economies to Verify the Impact of GDP, Population and Renewable Energy Generation in CO2 Emissions. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2020, 22, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.H.; Tan, C.S. A Review: CO2 Utilization. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2014, 14, 480–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, T.; Yamada, K. Economic Evaluation toward Zero CO2 Emission Power Generation System after 2050 in Japan. Energy Procedia 2017, 142, 2761–2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, L.; Qu, G.; Cheng, M.; Ren, Y.; Lu, P.; Zhang, T.; Wang, Y.; Wu, F. Advanced Materials for CO2 Capture and Storage: A Comprehensive Review of Current Progress and Future Prospects. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 115881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Xiaoying, L.; Mehmood, S.; Khan, M.A.; Oláh, J. Assessing the Impact of FDI, CO2 Emissions, Economic Growth, and Income Inequality on Renewable Energy Consumption in Asia. Energy Strategy Rev. 2025, 58, 101653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- This Is How Rising CO2 Levels Will Impact Climate Change|World Economic Forum. Available online: https://www.weforum.org/stories/2020/07/climate-change-increased-carbon-dioxide-emissions-scientists/ (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- Smithson, P.A. IPCC, 2001: Climate Change 2001: The Scientific Basis. Contribution of Working Group 1 to the Third Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2002; Volume 22, p. 1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, S.; Wu, Z.; Yang, Z.; Yang, L.; Sun, Z. Two-Stage Multi-Objective Optimal Scheduling Strategy for the Virtual Power Plant Considering Flexible CCS and Virtual Hybrid Energy Storage Mode. J. Energy Storage 2024, 103, 114323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Net Zero by 2050—Analysis—IEA. Available online: https://www.iea.org/reports/net-zero-by-2050 (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- Yu, C.H.; Huang, C.H.; Tan, C.S. A Review of CO2 Capture by Absorption and Adsorption. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2012, 12, 745–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soo, X.Y.D.; Lee, J.J.C.; Wu, W.Y.; Tao, L.; Wang, C.; Zhu, Q.; Bu, J. Advancements in CO2 Capture by Absorption and Adsorption: A Comprehensive Review. J. CO2 Util. 2024, 81, 102727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, M.; Song, L.; Liao, H.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Deng, X.; Feng, W. A Review on Development of Post-Combustion CO2 Capture Technologies: Performance of Carbon-Based, Zeolites and MOFs Adsorbents. Fuel 2024, 371, 132103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sifat, N.S.; Haseli, Y. A Critical Review of CO2 Capture Technologies and Prospects for Clean Power Generation. Energies 2019, 12, 4143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madejski, P.; Chmiel, K.; Subramanian, N.; Kuś, T. Methods and Techniques for CO2 Capture: Review of Potential Solutions and Applications in Modern Energy Technologies. Energies 2022, 15, 887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalmykov, D.O.; Shirokikh, S.A.; Tsoy, A.V.; Legkov, S.A.; Yushkin, A.A.; Anokhina, T.S.; Bazhenov, S.D. Oxygen Removal with Composite Membrane Contactors to Prevent Amine Solvent Degradation in Post-Combustion CO2 Capture: A Comprehensive Parametric Study. J. Memb. Sci. 2025, 717, 123611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Ho, W.S.W. Recent Advances in Polymeric Membranes for CO2 Capture. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2018, 26, 2238–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Zhang, M.; Guan, K.; Zhao, J.; Liu, G.; Jin, W. High-Performance CO2 Capture through Polymer-Based Ultrathin Membranes. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1900735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkotsis, P.; Peleka, E.; Zouboulis, A. Membrane-Based Technologies for Post-Combustion CO2 Capture from Flue Gases: Recent Progress in Commonly Employed Membrane Materials. Membranes 2023, 13, 898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramezani, R.; Di Felice, L.; Gallucci, F. A Review on Hollow Fiber Membrane Contactors for Carbon Capture: Recent Advances and Future Challenges. Processes 2022, 10, 2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atlaskin, A.A.; Kryuchkov, S.S.; Stepakova, A.N.; Moiseenko, I.S.; Tsivkovsky, N.S.; Smorodin, K.A.; Petukhov, A.N.; Atlaskina, M.E.; Vorotyntsev, I.V. Experimental Determination of the Gas Transport Characteristics of Polysulfone and Poly(Phenylene Oxide) Hollow Fiber Membranes in Relation to Noble Gases. Membr. Membr. Technol. 2023, 5, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grushevenko, E.A.; Sokolov, S.; Kholodkov, D.N.; Arzumanyan, V.V.; Kuznetsov, N.Y.; Nikul’shin, P.V.; Bazhenov, S.D.; Volkov, A.V.; Borisov, I.L.; Maksimov, A.L. Novel Polyethylene Glycol Methyl Ether Substituted Polysiloxane Membrane Materials with High CO2 Permeability and Selectivity. React. Funct. Polym. 2025, 206, 106102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anselmi, H.; Mirgaux, O.; Bounaceur, R.; Patisson, F. Simulation of Post-Combustion CO2 Capture, a Comparison among Absorption, Adsorption and Membranes. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2019, 42, 797–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfister, M.; Belaissaoui, B.; Favre, E. Membrane Gas Separation Processes from Wet Postcombustion Flue Gases for Carbon Capture and Use: A Critical Reassessment. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 591–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorotyntsev, V.M.; Drozdov, P.N.; Vorotyntsev, I.V.; Murav’Ev, D.V. Fine Gas Purification to Remove Slightly Penetrating Impurities Using a Membrane Module with a Feed Reservoir. Dokl. Chem. 2006, 411, 243–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trubyanov, M.M.; Kirillov, S.Y.; Vorotyntsev, A.V.; Sazanova, T.S.; Atlaskin, A.A.; Petukhov, A.N.; Kirillov, Y.P.; Vorotyntsev, I.V. Dynamic Behavior of Unsteady-State Membrane Gas Separation: Modelling of a Closed-Mode Operation for a Membrane Module. J. Memb. Sci. 2019, 587, 117173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorotyntsev, I.V.; Drozdov, P.N.; Shablikin, D.N.; Gamajunova, T.V. Ammonia Separation and Purification by Absorbing Pervaporation. Desalination 2006, 200, 379–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorotyntsev, V.M.; Mochalov, G.M.; Matveev, A.K.; Malyshev, A.V.; Vorotyntsev, I.V. Determination of Trace Impurities of H2, O2, Ar, N2, CO, CO2, and Hydrocarbons in High-Purity Monosilane by Gas Chromatography. J. Anal. Chem. 2003, 58, 156–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Li, Q.; Guo, B.; Sheng, M.; Wang, D.; Mao, S.; Ye, N.; Qiao, Z.; Kang, G.; Cao, Y.; et al. Industrial-Scale Spiral-Wound Facilitated Transport Membrane Modules for Post-Combustion CO2 Capture: Development, Investigation and Optimization. J. Memb. Sci. 2023, 670, 121368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, D. Design and Optimization of Hybrid Membrane–Solvent-Processes for Post-Combustion CO2 Capture. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2022, 36, 100768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.X.; Chang, F.L.; Kang, D.Y.; Chen, C.L. Hybrid Membrane Process for Post-Combustion CO2 Capture from Coal-Fired Power Plant. J. Memb. Sci. 2020, 603, 118001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Riensche, E.; Weber, M.; Stolten, D. Cascaded Membrane Processes for Post-Combustion CO2 Capture. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2012, 35, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadirkhan, F.; Sean, G.P.; Ismail, A.F.; Wan Mustapa, W.N.F.; Halim, M.H.M.; Kian, S.W.; Yean, Y.S. CO2 Plasticization Resistance Membrane for Natural Gas Sweetening Process: Defining Optimum Operating Conditions for Stable Operation. Polymers 2022, 14, 4537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontos, G.; Tsioptsias, C.; Tsivintzelis, I. Cellulose Acetate–Ionic Liquid Blends as Potential Polymers for Efficient CO2 Separation Membranes. Polymers 2024, 16, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atlaskin, A.A.; Kryuchkov, S.S.; Yanbikov, N.R.; Smorodin, K.A.; Petukhov, A.N.; Trubyanov, M.M.; Vorotyntsev, V.M.; Vorotyntsev, I.V. Comprehensive Experimental Study of Acid Gases Removal Process by Membrane-Assisted Gas Absorption Using Imidazolium Ionic Liquids Solutions Absorbent. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 239, 116578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petukhov, A.N.; Atlaskin, A.A.; Kryuchkov, S.S.; Smorodin, K.A.; Zarubin, D.M.; Petukhova, A.N.; Atlaskina, M.E.; Nyuchev, A.V.; Vorotyntsev, A.V.; Trubyanov, M.M.; et al. A Highly-Efficient Hybrid Technique—Membrane-Assisted Gas Absorption for Ammonia Recovery after the Haber-Bosch Process. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 421, 127726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petukhov, A.N.; Atlaskin, A.A.; Smorodin, K.A.; Kryuchkov, S.S.; Zarubin, D.M.; Atlaskina, M.E.; Petukhova, A.N.; Stepakova, A.N.; Golovacheva, A.A.; Markov, A.N.; et al. An Efficient Technique for Ammonia Capture in the Haber–Bosch Process Loop—Membrane-Assisted Gas Absorption. Polymers 2022, 14, 2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijesh, A.M.; Isloor, A.M. Review on Polymeric Membrane Materials for Gas Separations Which Are Stated above the Robeson’s Trade-off Upper Bound. In Current Trends and Future Developments on (Bio-)Membranes: Modern Approaches in Membrane Technology for Gas Separation and Water Treatment; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024; pp. 3–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dibrov, G.; Ivanov, M.; Semyashkin, M.; Sudin, V.; Fateev, N.; Kagramanov, G. Elaboration of High Permeable Macrovoid Free Polysulfone Hollow Fiber Membranes for Air Separation. Fibers 2019, 7, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aroon, M.A.; Ismail, A.F.; Montazer-Rahmati, M.M.; Matsuura, T. Morphology and Permeation Properties of Polysulfone Membranes for Gas Separation: Effects of Non-Solvent Additives and Co-Solvent. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2010, 72, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, M.V.; Storozhuk, I.P.; Dibrov, G.A.; Semyashkin, M.P.; Pavlukovich, N.G.; Kagramanov, G.G. Fabrication of Hollow Fiber Membrane from Polyarylate–Polyarylate Block Copolymer for Air Separation. Pet. Chem. 2018, 58, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kryuchkov, S.; Smorodin, K.; Stepakova, A.; Atlaskin, A.; Tsivkovsky, N.; Atlaskina, M.; Tolmacheva, M.; Kazarina, O.; Petukhov, A.; Vorotyntsev, A.; et al. Membrane Air Separation Process Simulation: Insight in Modelling Approach Based on Ideal and Mixed Permeance Values. Int. J. Technol. 2024, 15, 1218–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atlaskina, M.E.; Kazarina, O.V.; Petukhov, A.N.; Atlaskin, A.A.; Tsivkovsky, N.S.; Tiuleanu, P.; Malysheva, Y.B.; Lin, H.; Zhong, G.-J.; Lukoyanov, A.N.; et al. Amino Acid-Based Ionic Liquid as a Promising CO2 Sorption Increasing Agent by Aqueous MDEA Solution. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 395, 123635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trubyanov, M.M.; Mochalov, G.M.; Vorotyntsev, I.V.; Vorotyntsev, A.V.; Suvorov, S.S.; Smirnov, K.Y.; Vorotyntsev, V.M. An Improved Back-Flush-to-Vent Gas Chromatographic Method for Determination of Trace Permanent Gases and Carbon Dioxide in Ultra-High Purity Ammonia. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1447, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkel, T.C.; Gupta, R.P.; Turk, B.S.; Freeman, B.D. Mixed-Gas Permeation of Syngas Components in Poly(Dimethylsiloxane) and Poly(1-Trimethylsilyl-1-Propyne) at Elevated Temperatures. J. Memb. Sci. 2001, 191, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Teo, W.K.; Li, K. Preparation and Characterization of High-Flux Polysulfone Hollow Fibre Gas Separation Membranes. J. Memb. Sci. 2002, 204, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagase, Y.; Naruse, A.; Matsui, K. Chemical Modification of Polysulphone: 2. Gas and Liquid Permeability of Polysulphone/Polydimethylsiloxane Graft Copolymer Membranes. Polymer 1990, 31, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aitken, C.L.; Koros, W.J.; Paul, D.R. Effect of Structural Symmetry on Gas Transport Properties of Polysulfones. Macromolecules 1992, 25, 3424–3434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolders, C.A.; Reuvers, A.J.; Boom, R.M.; Wienk, I.M. Microstructures in Phase-Inversion Membranes. Part 1. Formation of Macrovoids. J. Memb. Sci. 1992, 73, 259–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKelvey, S.A.; Koros, W.J. Phase Separation, Vitrification, and the Manifestation of Macrovoids in Polymeric Asymmetric Membranes. J. Memb. Sci. 1996, 112, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesting, R.E.; Fritzsche, A.K.; Murphy, M.K.; Cruse, C.A.; Handermann, A.C.; Malon, R.F.; Moore, M.D. The Second-Generation Polysulfone Gas-Separation Membrane. I. The Use of Lewis Acid: Base Complexes as Transient Templates to Increase Free Volume. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1990, 40, 1557–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, D.; He, X. Preparation and Characterization of Polyvinylalcohol/Polysulfone Composite Membranes for Enhanced CO2/N2 Separation. Polymers 2022, 15, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahadori, A. Natural Gas Processing: Technology and Engineering Design; Gulf Professional Publishing: Houston, TX, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Laribi, S.; Dubois, L.; De Weireld, G.; Thomas, D. Study of the Post-Combustion CO2 Capture Process by Absorption-Regeneration Using Amine Solvents Applied to Cement Plant Flue Gases with High CO2 Contents. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2019, 90, 102799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkel, T.C.; Lin, H.; Wei, X.; Baker, R. Power Plant Post-Combustion Carbon Dioxide Capture: An Opportunity for Membranes. J. Memb. Sci. 2010, 359, 126–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atlaskin, A.A.; Petukhov, A.N.; Stepakova, A.N.; Tsivkovsky, N.S.; Kryuchkov, S.S.; Smorodin, K.A.; Moiseenko, I.S.; Atlaskina, M.E.; Suvorov, S.S.; Stepanova, E.A.; et al. Membrane Cascade Type of “Continuous Membrane Column” for Power Plant Post-Combustion Carbon Dioxide Capture Part 1: Simulation of the Binary Gas Mixture Separation. Membranes 2023, 13, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| № | Air Gap, cm | Q, GPU | α | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N2 | O2 | CO2 | CO2/N2 | O2/N2 | ||
| 1 | 10 | 316.49 | 411.44 | 1171.01 | 3.7 | 1.30 |
| 2 | 15 | 214.66 | 364.93 | 1030.37 | 4.8 | 1.70 |
| 3 | 20 | 123.9 | 284.96 | 805.35 | 6.5 | 2.3 |
| 4 | 25 | 34.84 | 108.00 | 463.37 | 13.3 | 3.10 |
| 5 | 30 | 3.88 | 20.96 | 75.27 | 19.4 | 5.40 |
| № | Air Gap, cm | Q, GPU | α | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N2 | O2 | CO2 | H2O | CO2/N2 | O2/N2 | H2O/CO2 | ||
| 1 | 10 | 317.27 | 349.00 | 1046.99 | 2512.78 | 3.3 | 1.10 | 2.4 |
| 2 | 15 | 214.48 | 311.00 | 900.82 | 2882.62 | 4.2 | 1.45 | 3.2 |
| 3 | 20 | 122.54 | 257.34 | 747.49 | 4036.45 | 6.1 | 2.1 | 5.4 |
| 4 | 25 | 34.85 | 107.00 | 442.6 | 3300.00 | 12.7 | 3.07 | 7.5 |
| 5 | 30 | 3.73 | 19.40 | 70.12 | 715.22 | 18.8 | 5.20 | 10.2 |
| Dope Composition | Q, GPU | α | Ref. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O2 | CO2 | O2/N2 | CO2/N2 | ||
| PSF/DMF/THF/IPA | 20.96 | 75.27 | 5.4 | 19.4 | Present study |
| PSF/DMA/THF/EtOH * | 25.6 | - | 6 | - | [38] |
| PSF/NMP/THF/EtOH/PEG | 17.6 | - | - | [39] | |
| PSF/NMP/H2O/EtOH * | 23.2 | 119.1 | 6.4 | 33 | [45] |
| PSF/NMP/PA | 20 | 4.4 | [50] | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Țiuleanu, P.; Atlaskin, A.A.; Smorodin, K.A.; Kryuchkov, S.S.; Atlaskina, M.E.; Petukhov, A.N.; Vorotyntsev, A.V.; Tsivkovskiy, N.S.; Sysoev, A.A.; Vorotyntsev, I.V. The Production of High-Permeable and Macrovoid-Free Polysulfone Hollow Fiber Membranes and Their Utilization in CO2 Capture Applications via the Membrane-Assisted Gas Absorption Technique. Polymers 2025, 17, 1407. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17101407
Țiuleanu P, Atlaskin AA, Smorodin KA, Kryuchkov SS, Atlaskina ME, Petukhov AN, Vorotyntsev AV, Tsivkovskiy NS, Sysoev AA, Vorotyntsev IV. The Production of High-Permeable and Macrovoid-Free Polysulfone Hollow Fiber Membranes and Their Utilization in CO2 Capture Applications via the Membrane-Assisted Gas Absorption Technique. Polymers. 2025; 17(10):1407. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17101407
Chicago/Turabian StyleȚiuleanu, Pavel, Artem A. Atlaskin, Kirill A. Smorodin, Sergey S. Kryuchkov, Maria E. Atlaskina, Anton N. Petukhov, Andrey V. Vorotyntsev, Nikita S. Tsivkovskiy, Alexander A. Sysoev, and Ilya V. Vorotyntsev. 2025. "The Production of High-Permeable and Macrovoid-Free Polysulfone Hollow Fiber Membranes and Their Utilization in CO2 Capture Applications via the Membrane-Assisted Gas Absorption Technique" Polymers 17, no. 10: 1407. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17101407
APA StyleȚiuleanu, P., Atlaskin, A. A., Smorodin, K. A., Kryuchkov, S. S., Atlaskina, M. E., Petukhov, A. N., Vorotyntsev, A. V., Tsivkovskiy, N. S., Sysoev, A. A., & Vorotyntsev, I. V. (2025). The Production of High-Permeable and Macrovoid-Free Polysulfone Hollow Fiber Membranes and Their Utilization in CO2 Capture Applications via the Membrane-Assisted Gas Absorption Technique. Polymers, 17(10), 1407. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17101407








