Self-Powered Triboelectric Ethanol Sensor Based on CuO-Doped Electrospun PVDF Fiber with Enhanced Sensing Performance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
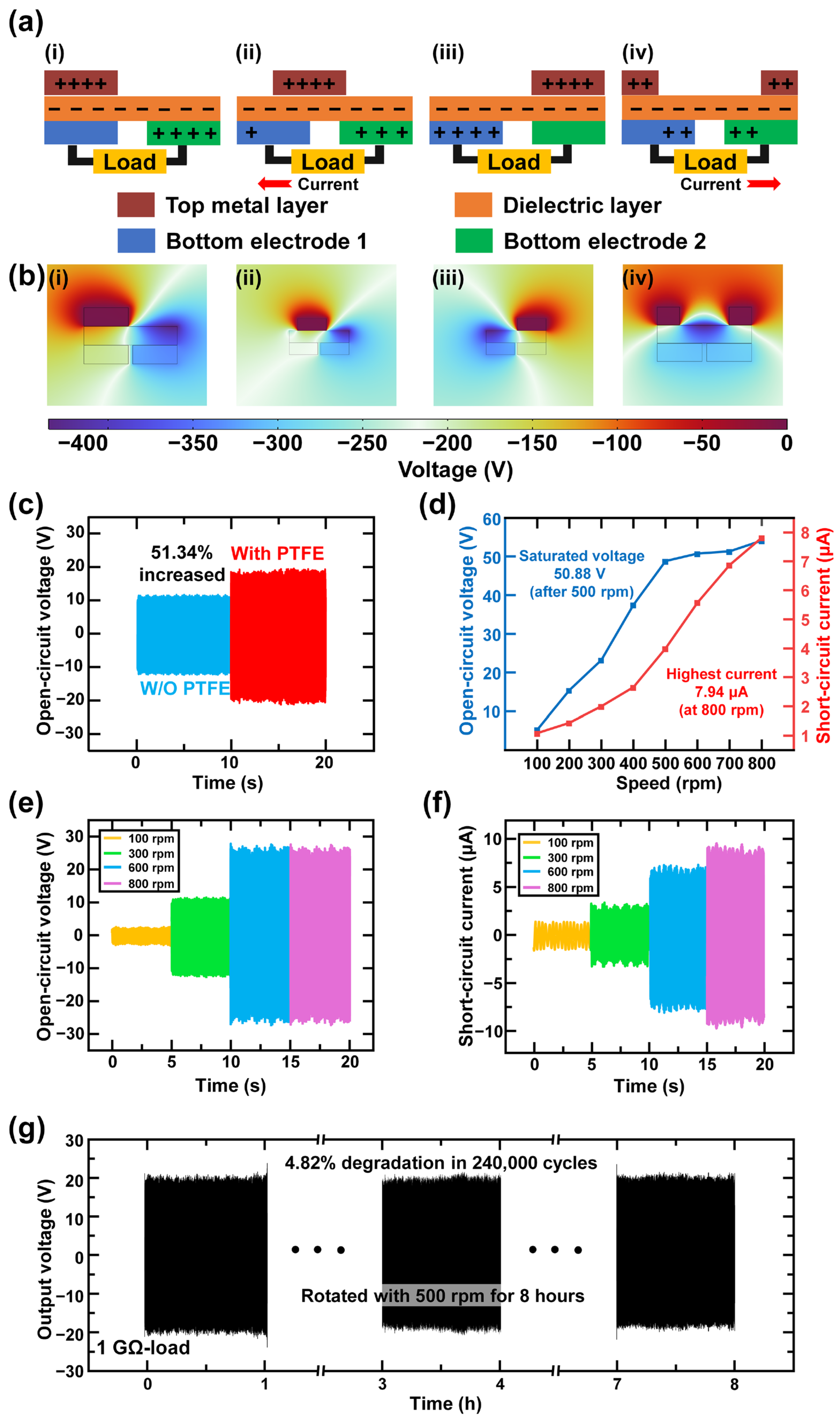
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kalimuldina, G.; Turdakyn, N.; Abay, I.; Medeubayev, A.; Nurpeissova, A.; Adair, D.; Bakenov, Z. A Review of Piezoelectric PVDF Film by Electrospinning and Its Applications. Sensors 2020, 20, 5214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, C.J.; Chase, G.G.; Yarin, A.L.; Reneker, D.H. Effects of Parameters on Nanofiber Diameter Determined from Electrospinning Model. Polymer 2007, 48, 6913–6922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, F.E.; Lalia, B.S.; Hashaikeh, R. A Review on Electrospinning for Membrane Fabrication: Challenges and Applications. Desalination 2015, 356, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.-M.; Zhang, Y.-Z.; Kotaki, M.; Ramakrishna, S. A Review on Polymer Nanofibers by Electrospinning and Their Applications in Nanocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2003, 63, 2223–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Wang, X.; Shen, Y.; Dong, K.; Shen, L.; Alzalab, A.A.A. Research Progress, Models and Simulation of Electrospinning Technology: A Review. J. Mater. Sci. 2022, 57, 58–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, S.; Chen, Z.; Shen, T.; Wang, Y.; Yin, R.; Liu, H.; Liu, C.; Shen, C. Ultrasensitive Electrospinning Fibrous Strain Sensor with Synergistic Conductive Network for Human Motion Monitoring and Human-Computer Interaction. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2025, 213, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Qiu, C.; Jia, P.; An, F.; Zhou, L.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, D. Polyaniline/ZnO Heterostructure-Based Ammonia Sensor Self-Powered by Electrospinning of PTFE-PVDF/MXene Piezo-Tribo Hybrid Nanogenerator. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 496, 154226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, C.; Shi, S.; Si, Y.; Fei, B.; Huang, H.; Hu, J. Recent Progress of Wearable Piezoelectric Pressure Sensors Based on Nanofibers, Yarns, and Their Fabrics via Electrospinning. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2023, 8, 2201161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, N.; Fan, G.; Yu, J.; Gao, J.; Sun, G.; Ding, B. Electreted Polyetherimide–Silica Fibrous Membranes for Enhanced Filtration of Fine Particles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 439, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.-P.; Zhang, Q.-J.; Li, C.-X.; Guo, C.-Y.; Zhong, L.-B.; Zheng, Z.-H.; Zhang, J.-Y.; Shao, Z.-D.; Zheng, Y.-M. Environmentally Durable and Washable Tanghulu-like Amphiphobic Fluorinated PVA/SiO2 Electrospun Nanofibrous Membrane for Efficient and Reusable Oil Aerosol Filtration. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 360, 130887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Zhou, X.; Wang, B.; Dai, F.; Liu, J. Modified PVDF/PMMA/SiO2 Composite Nanofibrous Membrane in Airborne Filtration: Transparency, Mechanical Properties and Filtration Performance. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 114109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Chen, W.; Wang, P.; Dou, X. Silicalite-1/PDMS Hybrid Membranes on Porous PVDF Supports: Preparation, Structure and Pervaporation Separation of Dichlorobenzene Isomers. Polymers 2022, 14, 1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, T.; Zhang, S.; Jiang, L.; Xia, J.; Xie, J.; Chen, K.; Bao, L.; Lei, J.; Wang, J. Room-Temperature, Energy Storage Textile with Multicore-Sheath Structure Obtained via in-Situ Coaxial Electrospinning. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 436, 135226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.; Zeng, Z.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Sun, D.; Cui, C. Versatile Electrospinning Technology on Solid-State Electrolytes for Energy Storage: A Brief Review. J. Energy Storage 2024, 86, 111285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Luo, H.; Chen, H.; Li, M.; Wan, Y.; Peng, B.; Li, X.; Zhang, D. Gradient Structured All-Organic Dielectrics by Electrospinning for Enhanced Energy Storage Performance. J. Mater. Chem. A 2024, 12, 12501–12514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amrutha, B.; Prasad, G.; Sathiyanathan, P.; Reza, M.S.; Kim, H.; Pathak, M.; Prabu, A.A. Fabrication of CuO-NP-Doped PVDF Composites Based Electrospun Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Wearable and Biomedical Applications. Polymers 2023, 15, 2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, X.; Wu, Z.; Yu, X.; Wang, M.; Zang, D.; Long, Y.; Guo, N.; Weng, L.; Liu, Y.; Gao, J. Preparation and Properties of Triboelectric Nanogenerator Based on PVDF-TrFE/PMMA Electrospun Film. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2025, 8, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, H.-Y.; Jing, X.; Zheng, Q.; Fang, L.; Huang, H.-X.; Turng, L.-S.; Gong, S. High-Performance Flexible Triboelectric Nanogenerator Based on Porous Aerogels and Electrospun Nanofibers for Energy Harvesting and Sensitive Self-Powered Sensing. Nano Energy 2018, 48, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, R.; Tangestaninejad, S.; Marandi, A.; Moghadam, M.; Mohammadpoor-Baltork, I.; Kardanpour, R.; Abdolvand, H. Innovative Cross-Linked Electrospun PVA/MOF Nanocomposites for Removal of Cefixime Antibiotic. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rwei, S.-P.; Huang, C.-C. Electrospinning PVA Solution-Rheology and Morphology Analyses. Fibers Polym. 2012, 13, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koosha, M.; Mirzadeh, H. Electrospinning, Mechanical Properties, and Cell Behavior Study of Chitosan/ PVA Nanofibers. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2015, 103, 3081–3093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, R.; Xiao, Y.; Luo, H.; Qiao, X.; Hou, J. One-Step Electrospinning PMMA-SPO with Hierarchical Architectures as a Multi-Functional Transparent Screen Window. New J. Chem. 2022, 46, 16675–16683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piperno, S.; Lozzi, L.; Rastelli, R.; Passacantando, M.; Santucci, S. PMMA Nanofibers Production by Electrospinning. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2006, 252, 5583–5586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtari, F.; Samadi, A.; Rashed, A.O.; Li, X.; Razal, J.M.; Kong, L.; Varley, R.J.; Zhao, S. Recent Progress in Electrospun Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF)-Based Nanofibers for Sustainable Energy and Environmental Applications. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2025, 148, 101376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesan, H.M.; Arun, A.P. High-Performance Triboelectric Nanogenerators Based on Ag-Doped ZnO Loaded Electrospun PVDF Nanofiber Mats for Energy Harvesting and Healthcare Monitoring. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 3347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, F.; Long, S.; Huang, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, R.; Shi, J.; Zou, Y.; Zou, X. Fast Response and Stable Dyed Cellulose Nanofibrous Films for Shrimp Spoilage Detection. Food Chem. 2025, 474, 143260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.-L.; Yu, S.-H. Nanoparticles Meet Electrospinning: Recent Advances and Future Prospects. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 4423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Ding, Y.; Jiang, S.; Chen, L.; Liao, X.; Hou, H. Polyimide/BaTiO3/MWCNTs Three-Phase Nanocomposites Fabricated by Electrospinning with Enhanced Dielectric Properties. Mater. Lett. 2014, 135, 158–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Ma, Z.; Pang, X.; Ahmad, M.; Zhao, Y.; Su, N.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, H.; Subhan, F.; et al. Electrospinning Prepared Nickel-Based Carbon Fibers with Enhanced Adsorption Capacity for Adsorption Desulfurization of Fuels. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 478, 147254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, S.; Wang, Z.L. Theoretical Systems of Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2015, 14, 161–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Wu, C.; Li, X.; Yao, Y.; Lan, L.; Zhao, F.; Ye, Z.; Ying, Y.; Ping, J. All-Electrospun Flexible Triboelectric Nanogenerator Based on Metallic MXene Nanosheets. Nano Energy 2019, 59, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, S.-B.; Park, S.-J.; Kim, W.-G.; Tcho, I.-W.; Jin, I.-K.; Han, J.-K.; Kim, D.; Choi, Y.-K. Self-Powered Wearable Keyboard with Fabric Based Triboelectric Nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2018, 53, 596–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Shin, H.J.; Lee, H.; Jeong, C.K.; Park, H.; Hwang, G.; Lee, H.; Joe, D.J.; Han, J.H.; Lee, S.H.; et al. In Vivo Self-Powered Wireless Transmission Using Biocompatible Flexible Energy Harvesters. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1700341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, O.; Wang, X.; Hou, M.; Zheng, M.; Hao, D.; Bai, Z.; Zou, X.; Cui, B.; Liu, C.; Liu, X. Smart Nanoengineered Electronic-Scaffolds Based on Triboelectric Nanogenerators as Tissue Batteries for Integrated Cartilage Therapy. Nano Energy 2023, 107, 108158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, B.; Qin, X.; Zhu, Q.; Wang, H.; Wen, Z.; Sun, X.; He, Y.; Lee, S.-T. Triboelectric Current Stimulation Alleviates in Vitro Cell Migration and in Vivo Tumor Metastasis. Nano Energy 2022, 100, 107471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatta, T.; Faruk, O.; Islam, M.R.; Kim, H.S.; Rana, S.S.; Pradhan, G.B.; Deo, A.; Kwon, D.-S.; Yoo, I.; Park, J.Y. Polymeric Multilayered Planar Spring-Based Hybrid Nanogenerator Integrated with a Self-Powered Vibration Sensor for Automotive Vehicles IoT Applications. Nano Energy 2024, 127, 109793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Gui, Y.; Wang, Y.; Cao, L.; He, G.; Tang, C. CuO/TiO2 /MXene-Based Sensor and SMS-TENG Array Integrated Inspection Robots for Self-Powered Ethanol Detection and Alarm at Room Temperature. ACS Sens. 2024, 9, 1188–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Park, J.G.; Kim, K.N.; Thokchom, A.K.; Bae, J.; Baik, J.M.; Kim, T. Transparent-Flexible-Multimodal Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Mechanical Energy Harvesting and Self-Powered Sensor Applications. Nano Energy 2018, 48, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Yin, J.; Fang, Y.; Xiao, X.; Zou, Y.; Wang, S.; Chen, J. Deep Learning Assisted Ternary Electrification Layered Triboelectric Membrane Sensor for Self-Powered Home Security. Nano Energy 2023, 113, 108524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, P.; Fu, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, C.; Li, X. Triboelectric Active Pressure Sensor with Ultrabroad Linearity Range by Femtosecond Laser Shaping Based on Electrons Dynamics Control. Nano Energy 2023, 113, 108592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.-Y.; Long, Y.; Huang, Z.; Zi, Y.; Tao, L.-Q.; Li, C.-H.; Sun, H.; Li, J. Laser-Induced Graphene (LIG)-Based Pressure Sensor and Triboelectric Nanogenerator towards High-Performance Self-Powered Measurement-Control Combined System. Nano Energy 2022, 96, 107099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, T.; Bing, Z.; Wu, Y.; Chen, W.; Zhou, Z.; Fang, F.; Liang, S.; Guo, R.; Tu, S.; Pan, G.; et al. A Multi-Dimensional Tactile Perception System Based on Triboelectric Sensors: Towards Intelligent Sorting without Seeing. Nano Energy 2024, 123, 109398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.; Mo, J.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, N.; Wu, Z.; Wang, S.; Nie, S. Integration of a Porous Wood-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerator and Gas Sensor for Real-Time Wireless Food-Quality Assessment. Nano Energy 2021, 83, 105833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-J.; Lee, J.-H. Highly Sensitive and Selective Gas Sensors Using P-Type Oxide Semiconductors: Overview. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 192, 607–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Yu, H.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, M. High-Power Triboelectric Nanogenerator Prepared from Electrospun Mats with Spongy Parenchyma-like Structure. Nano Energy 2017, 34, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.; Wang, X.; Yi, Z.; Yang, B.; Wang, X.; Chen, X.; Liu, J.; Yang, C. Flexible Single-Electrode Triboelectric Nanogenerator and Body Moving Sensor Based on Porous Na2CO3/Polydimethylsiloxane Film. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 3652–3659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Jin, Z.; Yang, W.; Liu, S. Construction of Flower-like Hierarchical Ni-Doped SnO2 Nanosheets and Their Gas Sensing Properties for Ethanol. New J. Chem. 2023, 47, 15283–15290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Du, Z.; Wu, H.-C.; Gao, F.; Jiang, L.; Hou, H.; Chen, S.; Li, W.; Hu, F.; Yang, W.; et al. High-Temperature Resistant Ethanol Sensing Enhanced by ZnO Nanoparticles/SiC Nanowire Heterojunctions. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2024, 645, 158828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umar, A.; Ibrahim, A.A.; Algadi, H.; Nakate, U.T.; Choudhury, S.P.; Alsuwian, T.; Albargi, H.; Alsaiari, M.A.; Baskoutas, S. Selective Ethanol Gas Sensing Performance of Flower-Shaped CuO Composed of Thin Nanoplates. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2021, 32, 18565–18579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subha, P.P.; Jayaraj, M.K. Enhanced Room Temperature Gas Sensing Properties of Low Temperature Solution Processed ZnO/CuO Heterojunction. BMC Chem. 2019, 13, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shooshtari, M.; Salehi, A.; Vollebregt, S. Effect of Humidity on Gas Sensing Performance of Carbon Nanotube Gas Sensors Operated at Room Temperature. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 5763–5770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shooshtari, M.; Salehi, A.; Vollebregt, S. Effect of Temperature and Humidity on the Sensing Performance of TiO2 Nanowire-Based Ethanol Vapor Sensors. Nanotechnology 2021, 32, 325501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amann, A.; Costello, B.D.L.; Miekisch, W.; Schubert, J.; Buszewski, B.; Pleil, J.; Ratcliffe, N.; Risby, T. The Human Volatilome: Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) in Exhaled Breath, Skin Emanations, Urine, Feces and Saliva. J. Breath Res. 2014, 8, 034001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litra, D.; Chiriac, M.; Ababii, N.; Lupan, O. Acetone Sensors Based on Al-Coated and Ni-Doped Copper Oxide Nanocrystalline Thin Films. Sensors 2024, 24, 6550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madvar, H.R.; Kordrostami, Z.; Mirzaei, A. Sensitivity Enhancement of Resistive Ethanol Gas Sensor by Optimized Sputtered-Assisted CuO Decoration of ZnO Nanorods. Sensors 2022, 23, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Lv, X.; Wang, T.; Pei, W.; Yang, Y.; Li, F.; Yin, D.; Yu, H.; Dong, X. CuO-Based Gas Sensor Decorated by Polyoxometalates Electron Acceptors: From Constructing Heterostructure to Improved Sensitivity and Fast Response for Ethanol Detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2024, 415, 136016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, H.; Tanioka, A. Functionality in Electrospun Nanofibrous Membranes Based on Fiber’s Size, Surface Area, and Molecular Orientation. Membranes 2011, 1, 249–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Li, H.; Zhao, L.; Lu, J.; Pan, C.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z. Triboelectric Nanogenerator Enhanced Schottky Nanowire Sensor for Highly Sensitive Ethanol Detection. Nano Lett. 2020, 20, 4968–4974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Wang, F.; Ding, Y.; Lei, R.; Shi, Y.; Tao, X.; Li, S.; Yang, Y.; Chen, X. Self-Powered Room-Temperature Ethanol Sensor Based on Brush-Shaped Triboelectric Nanogenerator. Research 2021, 2021, 8564780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Gui, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yang, J. A Self-Powered β-Ni(OH)2/MXene Based Ethanol Sensor Driven by an Enhanced Triboelectric Nanogenerator Based on β-Ni(OH)2@PVDF at Room Temperature. Nano Energy 2023, 107, 108132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Chun, J.; Kim, J.W.; Choi, W.J.; Baik, J.M. Self-Powered, Room-Temperature Electronic Nose Based on Triboelectrification and Heterogeneous Catalytic Reaction. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 7049–7055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, M.; Zhang, R.; Jia, X.; Gao, X.; Gao, W.; Cheng, L.; Qin, Y. A Polymer Based Self-Powered Ethanol Gas Sensor to Eliminate the Interference of Ultraviolet Light. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2021, 332, 113173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupan, O.; Postica, V.; Cretu, V.; Wolff, N.; Duppel, V.; Kienle, L.; Adelung, R. Single and Networked CuO Nanowires for Highly Sensitive P-Type Semiconductor Gas Sensor Applications. Phys. Status Solidi RRL 2016, 10, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Xuan, X.; Jiang, D.; Li, H.; Li, C.; Li, M. Wireless Antenna Sensor with CuO@Cu-Vertical Graphene and Cysteine-PDMS Composite for Ethanol Gas Detection. Anal. Chim. Acta 2024, 1319, 342969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aamir, L. Novel P-Type Ag-WO3 Nano-Composite for Low-Cost Electronics, Photocatalysis, and Sensing: Synthesis, Characterization, and Application. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 864, 158108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Shi, X.; Chen, K.; Yang, X.; Chen, J. Titanium-Doped P-Type WO3 Thin Films for Liquefied Petroleum Gas Detection. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.-Q.; Hu, M.; Wei, X.-Y. A Study of Transition from N- to p-Type Based on Hexagonal WO3 Nanorods Sensor. Chin. Phys. B 2014, 23, 040704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, N. Nickel Oxide Nanostructures for Gas Sensing: Recent Advances, Challenges, and Future Perspectives. ACS Sens. 2025, 10, 1641–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majhi, S.M.; Naik, G.K.; Lee, H.-J.; Song, H.-G.; Lee, C.-R.; Lee, I.-H.; Yu, Y.-T. Au@NiO Core-Shell Nanoparticles as a p-Type Gas Sensor: Novel Synthesis, Characterization, and Their Gas Sensing Properties with Sensing Mechanism. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 268, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakate, U.T.; Ahmad, R.; Patil, P.; Wang, Y.; Bhat, K.S.; Mahmoudi, T.; Yu, Y.T.; Suh, E.; Hahn, Y.-B. Improved Selectivity and Low Concentration Hydrogen Gas Sensor Application of Pd Sensitized Heterojunction N-ZnO/p-NiO Nanostructures. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 797, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Ruan, S.; Han, J.; Yin, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, C.; Adimi, S.; Wen, S.; Xu, Y. Oxygen Vacancies Dominated CuO@ZnFe2O4 Yolk-Shell Microspheres for Robust and Selective Detection of Xylene. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 295, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mnethu, O.; Nkosi, S.S.; Kortidis, I.; Motaung, D.E.; Kroon, R.E.; Swart, H.C.; Ntsasa, N.G.; Tshilongo, J.; Moyo, T. Ultra-Sensitive and Selective p-Xylene Gas Sensor at Low Operating Temperature Utilizing Zn Doped CuO Nanoplatelets: Insignificant Vestiges of Oxygen Vacancies. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 576, 364–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciftyurek, E.; Li, Z.; Schierbaum, K. Adsorbed Oxygen Ions and Oxygen Vacancies: Their Concentration and Distribution in Metal Oxide Chemical Sensors and Influencing Role in Sensitivity and Sensing Mechanisms. Sensors 2022, 23, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emiroglu, S.; Bârsan, N.; Weimar, U.; Hoffmann, V. In Situ Diffuse Reflectance Infrared Spectroscopy Study of CO Adsorption on SnO2. Thin Solid Film. 2001, 391, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthik, K.; Victor Jaya, N.; Kanagaraj, M.; Arumugam, S. Temperature-Dependent Magnetic Anomalies of CuO Nanoparticles. Solid State Commun. 2011, 151, 564–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.; Kim, I.; Park, J.; Kim, D. A Waterwheel Hybrid Generator with Disk Triboelectric Nanogenerator and Electromagnetic Generator as a Power Source for an Electrocoagulation System. Nano Energy 2022, 95, 107048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, C.; Wang, Z.; Cai, M.; Cheng, S.; Wang, Z.; Zhai, C.; Cui, J.; Zheng, Y.; Xue, C. Enhancing Output Performance of Triboelectric Nanogenerator by Increasing Charge Storage Capacity of Electrodes. Nano Res. 2025, 18, 94907039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Sensing Material | Device Type | Response Time | Limit of Detection | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZnO nanowire/Ag | Separated | 20 s (5 ppm) | 5 ppm | [25] |
| WO3 nanorods | Separated | 5 s (100 ppm) | 5 ppm | [59] |
| β-Ni(OH)2/MXene | Separated | 15 s (100 ppm) | 5 ppm | [60] |
| ZnO/PTFE layer | Integrated | 240 s (2%) | 10 ppm | [61] |
| Polyimide nanowire | Integrated | 28 s (10,000 ppm) | 500 ppm | [62] |
| CuO@ES-PVDF | Integrated | 6 s (1000 ppm) | 10 ppm | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, Q.; Cho, H.; Kim, I.; Lee, J.; Kim, D. Self-Powered Triboelectric Ethanol Sensor Based on CuO-Doped Electrospun PVDF Fiber with Enhanced Sensing Performance. Polymers 2025, 17, 1400. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17101400
He Q, Cho H, Kim I, Lee J, Kim D. Self-Powered Triboelectric Ethanol Sensor Based on CuO-Doped Electrospun PVDF Fiber with Enhanced Sensing Performance. Polymers. 2025; 17(10):1400. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17101400
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Quanyu, Hyunwoo Cho, Inkyum Kim, Jonghwan Lee, and Daewon Kim. 2025. "Self-Powered Triboelectric Ethanol Sensor Based on CuO-Doped Electrospun PVDF Fiber with Enhanced Sensing Performance" Polymers 17, no. 10: 1400. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17101400
APA StyleHe, Q., Cho, H., Kim, I., Lee, J., & Kim, D. (2025). Self-Powered Triboelectric Ethanol Sensor Based on CuO-Doped Electrospun PVDF Fiber with Enhanced Sensing Performance. Polymers, 17(10), 1400. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17101400








