Balsam-Pear-Skin-Like-Structure Polyvinylidene Fluoride/Ethylene–Vinyl Alcohol Fibrous Membrane for Highly Efficient Oil/Water Separation Through One-Step Electrospinning
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Fabrication of PVDF/EVOH NFM
2.3. Characterization
2.4. Measurements
3. Results
3.1. Construction of Balsam-Pear-Skin-like-Structure PVDF/EVOH NFM
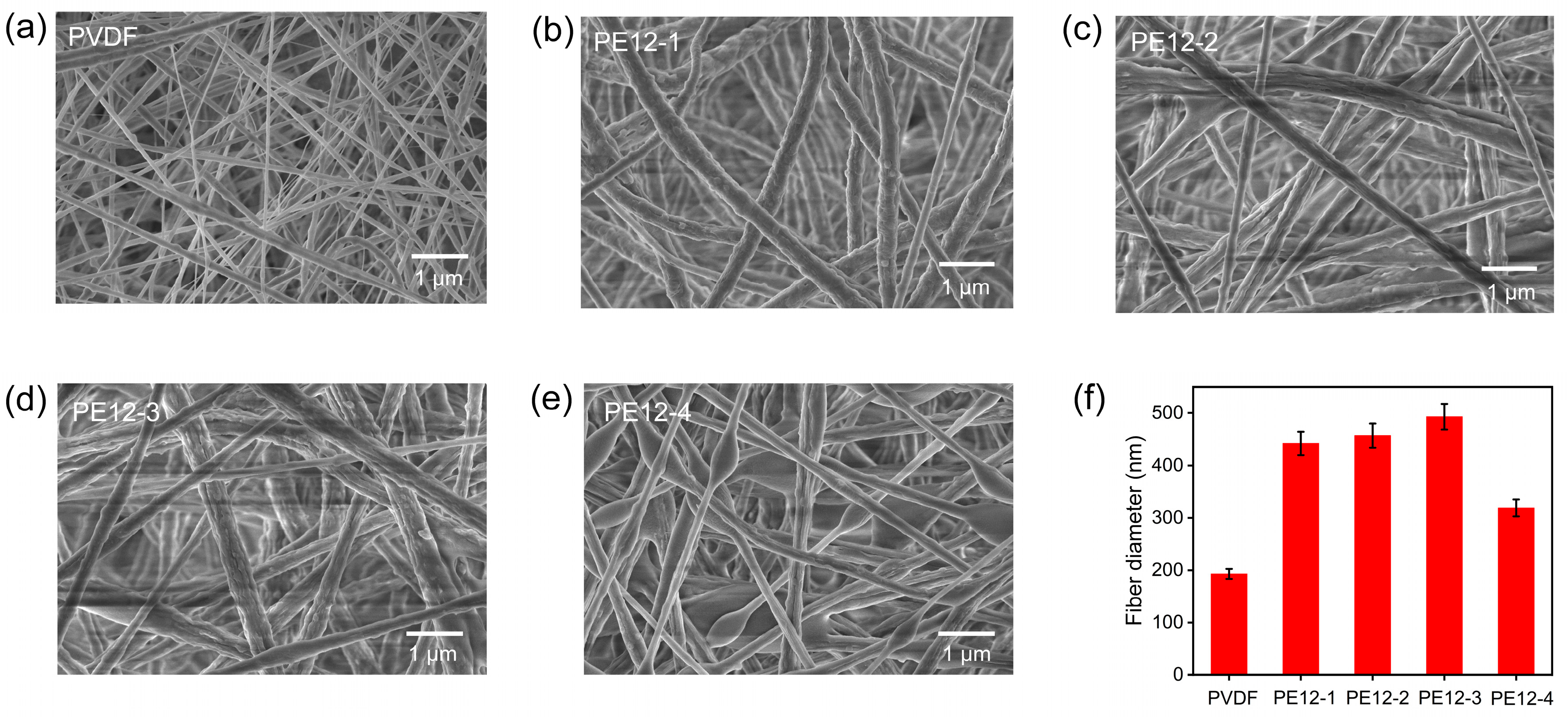
3.2. Morphology and Microstructure of PVDF/EVOH NFM
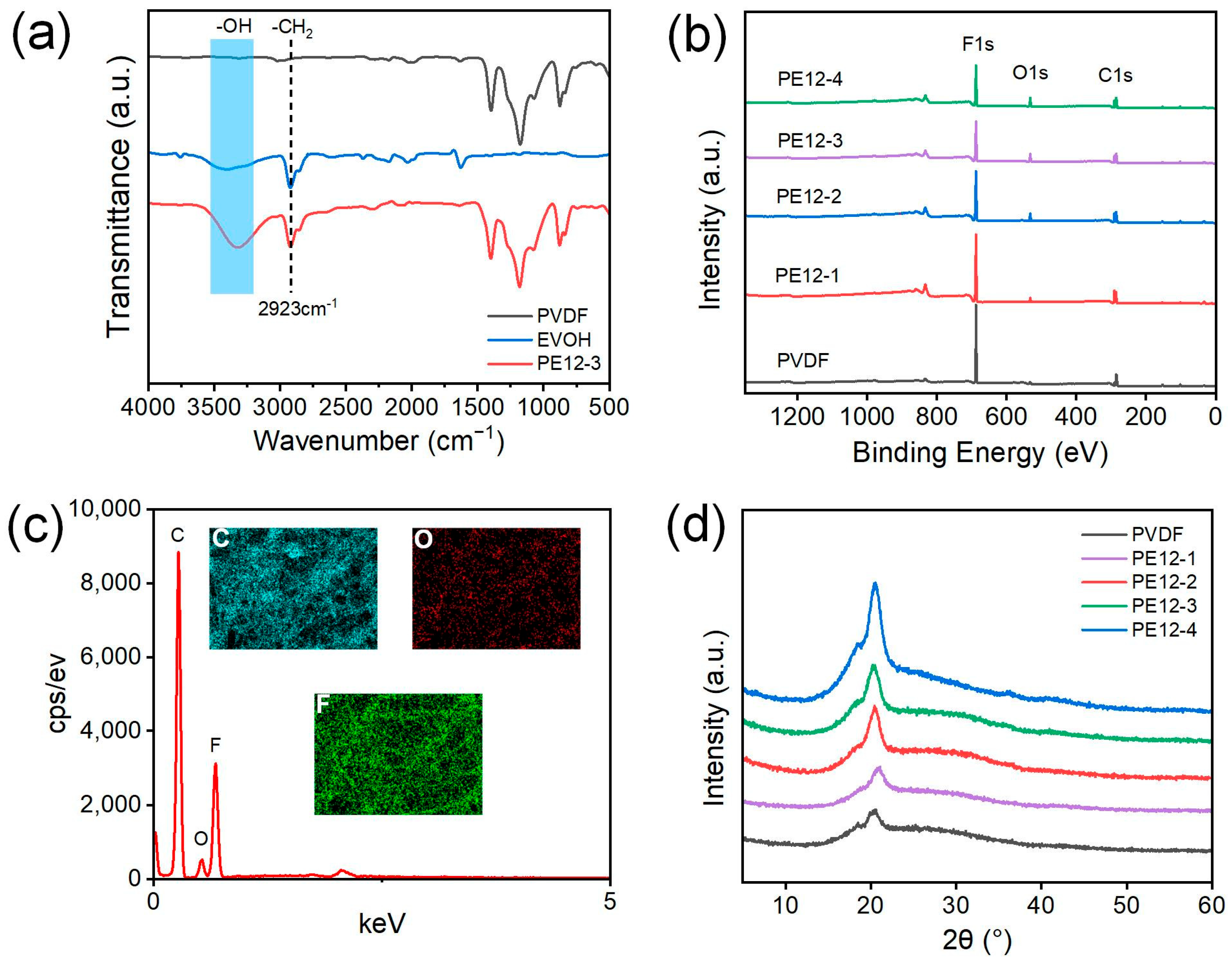
3.3. Surface Chemical and Physical Properties of PVDF/EVOH NFMs
3.4. Porous Structure of PVDF/EVOH NFMs
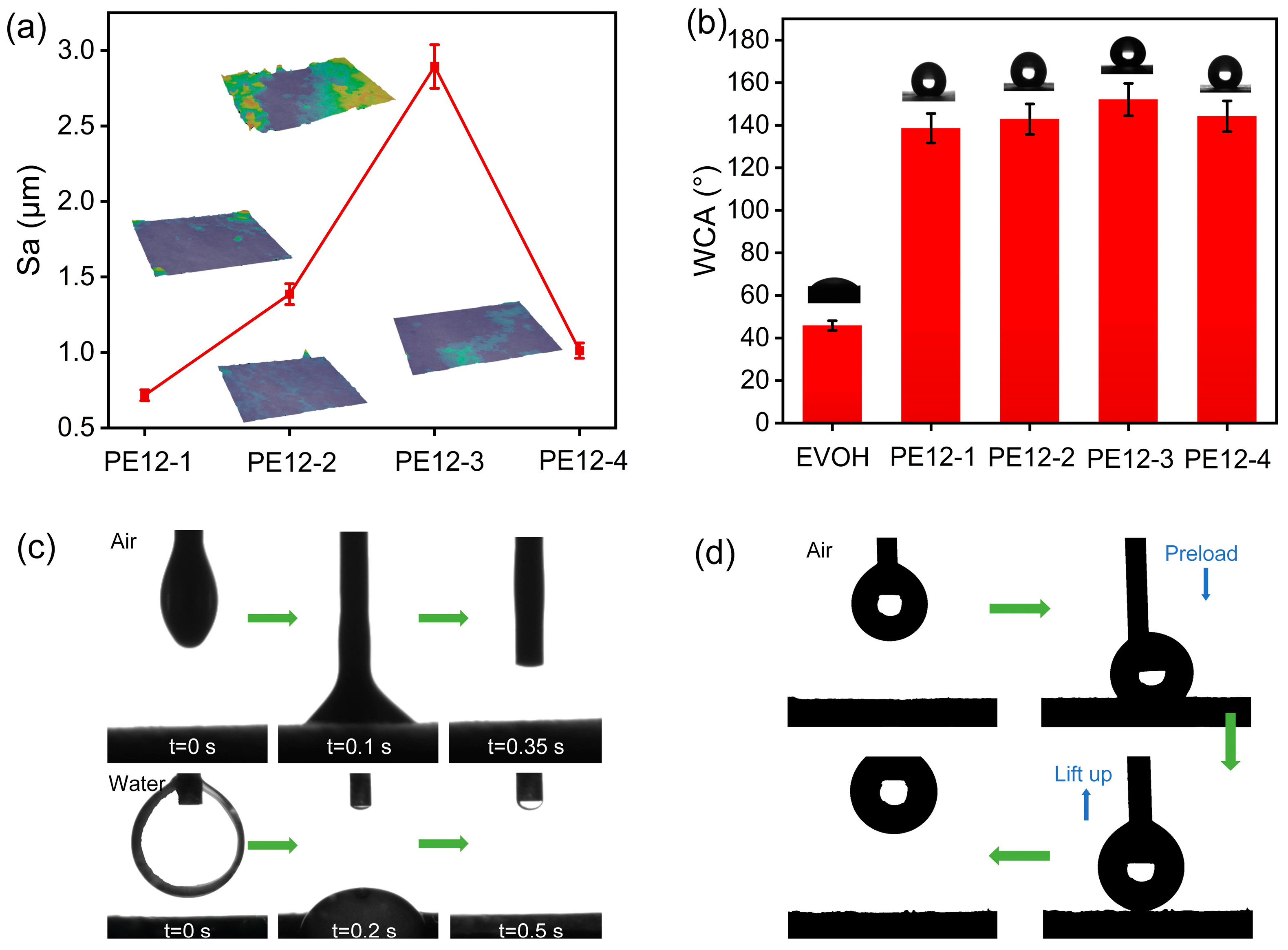
3.5. Surface Wettability of PVDF/EVOH NFMs
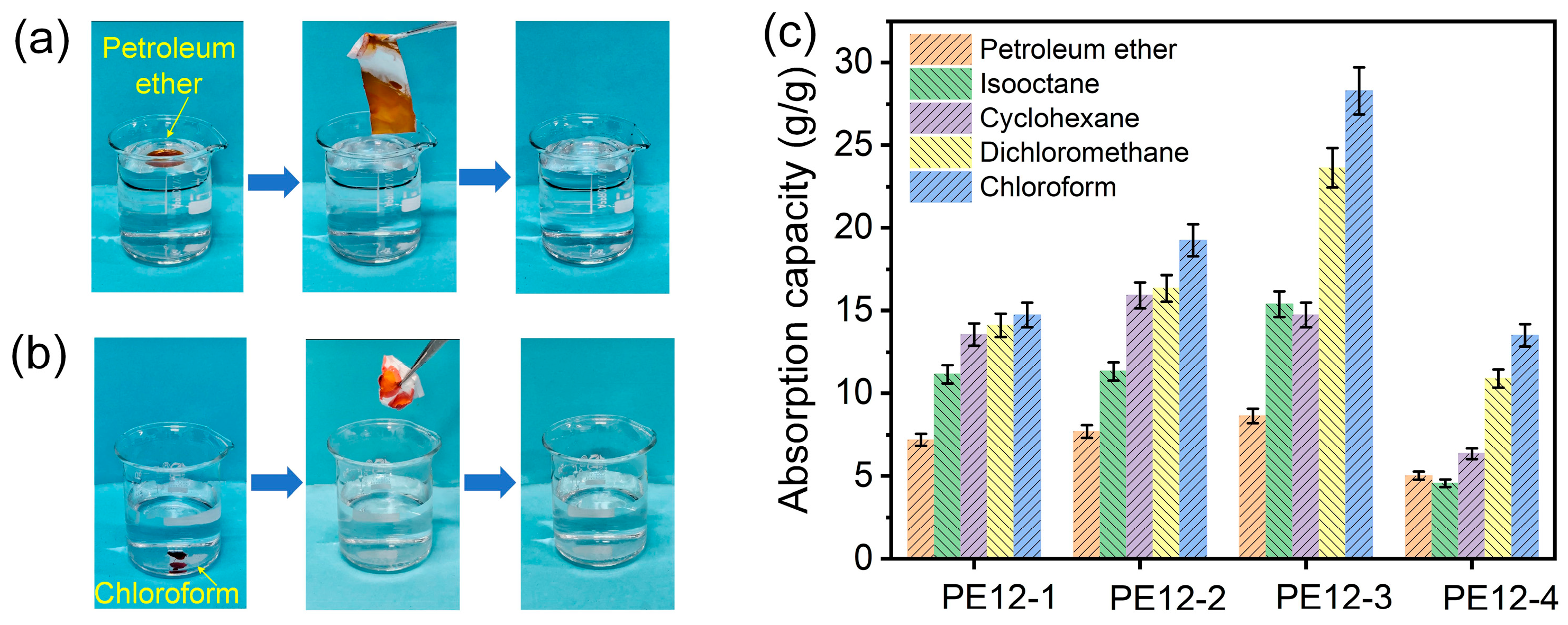
3.6. Oil Absorption Capability of PVDF/EVOH NFMs
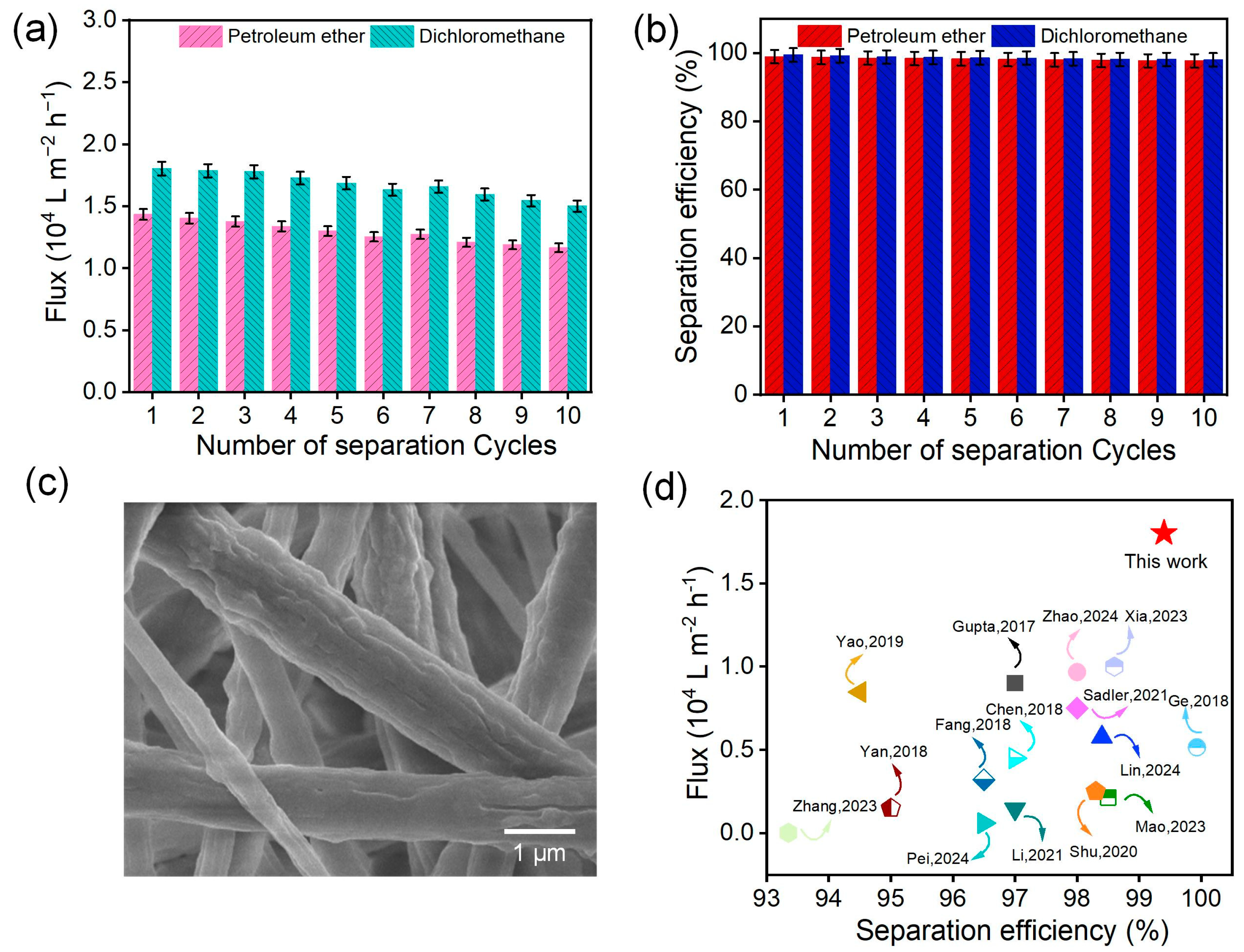
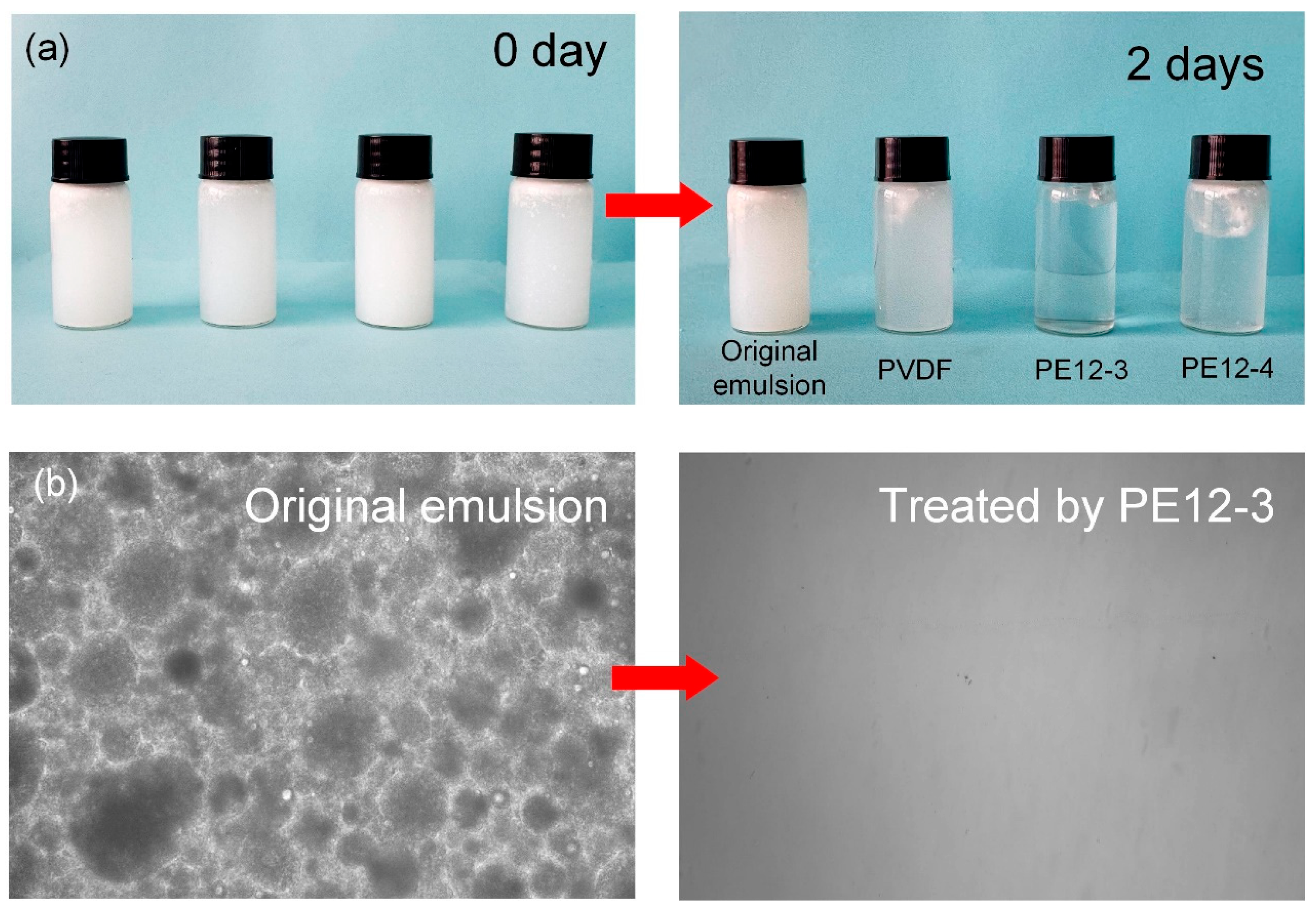
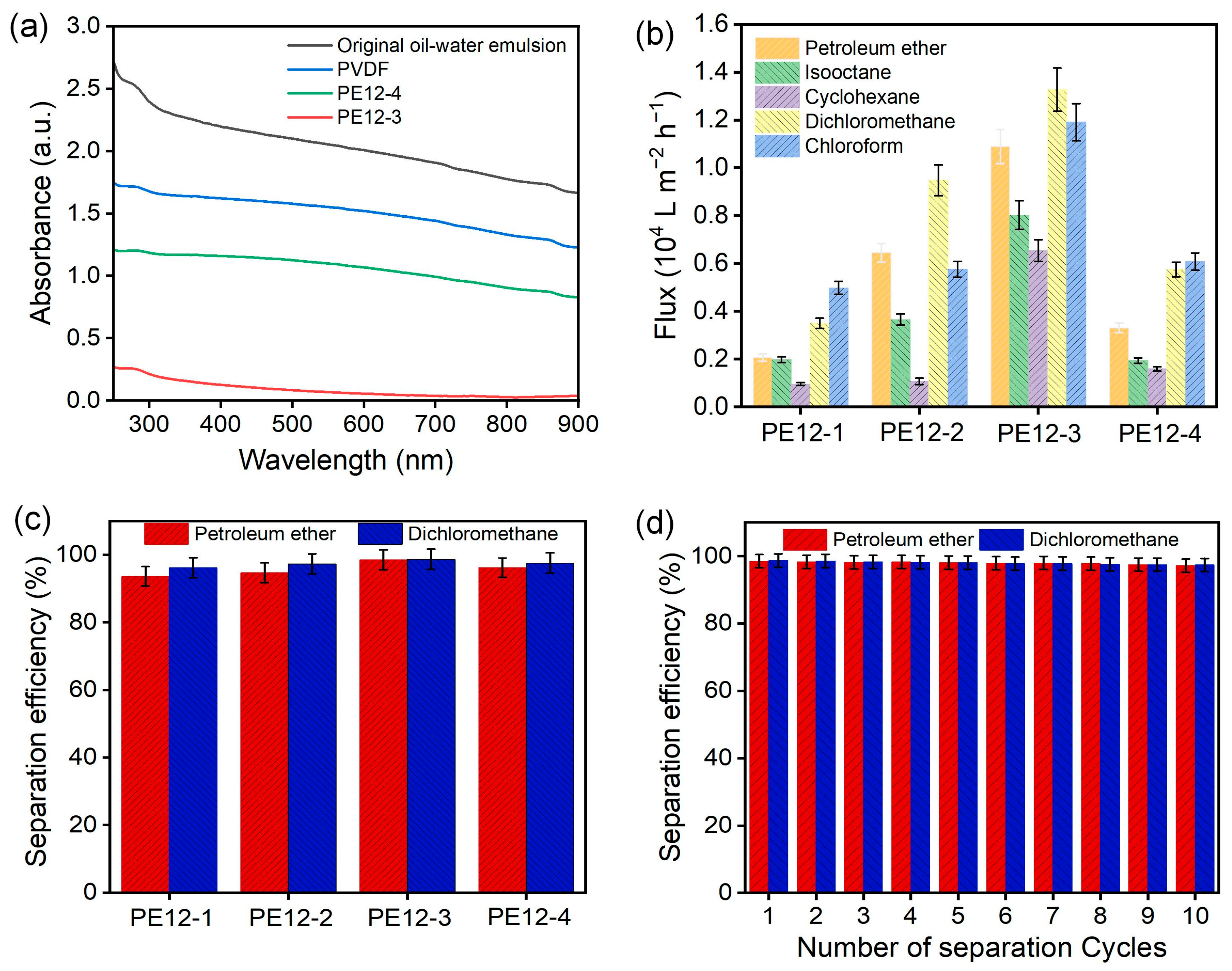
3.7. Oil/Water Separation of PVDF/EVOH NFMs
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NFM | Nanofibrous membrane |
| WVIPS | Water vapor-induced phase separation |
| PE | PVDF/EVOH |
| EVOH | Ethylene–vinyl alcohol |
| PVDF | Polyvinylidene fluoride |
| DMAc | N,N-dimethylacetamide |
| FTIR | Fourier transform infrared spectra |
| XPS | X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy |
| EDS | Energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy |
| XRD | X-ray diffraction |
| WVT | Water vapor transmission |
| WCA | Water contact angle |
References
- Li, J.; Xu, C.; Tian, H.; Zha, F.; Qi, W.; Wang, Q. Blend-electrospun poly (vinylidene fluoride)/stearic acid membranes for efficient separation of water-in-oil emulsions. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 538, 494–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, W.; Yuan, C.; Jia, L.; Liu, Y.; Huang, A.; Cui, Y. Two-dimensional fluorinated covalent organic frameworks with tunable hydrophobicity for ultrafast oil–water separation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202113348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Han, N.; Tan, L.; Qian, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, M.; Li, W.; Cui, Z.; Zhang, X. Bioinspired superwettable covalent organic framework nanofibrous composite membrane with a spindle-knotted structure for highly efficient oil/water emulsion separation. Langmuir 2019, 35, 16545–16554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Huo, L.; Jin, Y.; Yuan, S.; Zhao, R.; Zhao, J.; Li, Z.; Li, Y. Fluorine-free superhydrophobic PET fabric with high oil flux for oil–water separation. Prog. Org. Coat. 2022, 163, 106671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, L.; Si, Y.; Yu, J.; Ding, B. Electrospun nanofibrous membranes: An effective arsenal for the purification of emulsified oily wastewater. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2002192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Tang, N.; Jia, C.; Zhang, Y. A superwetting rough structured nanofibrous membrane with enhancing anti-fouling performance for oil–water separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 359, 130800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthwal, S.; Lim, S.-H. A durable, fluorine-free, and repairable superhydrophobic aluminum surface with hierarchical micro/nanostructures and its application for continuous oil-water separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 618, 118716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; Zong, D.; Jin, Q.; Yu, J.; Ding, B. Biomimetic and superwettable nanofibrous skins for highly efficient separation of oil-in-water emulsions. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1705051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Song, X.; Chen, J.; Chen, Y.; Yu, W.; Liu, Y. A novel polyurethane-polydimethylsiloxane/polylactic acid electrospinning fiber membrane for oil/water separation. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2023, 668, 131445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kota, A.K.; Kwon, G.; Choi, W.; Mabry, J.M.; Tuteja, A. Hygro-responsive membranes for effective oil–water separation. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.; Pan, J.; Gai, W.; Pan, X.; Chen, H.; Li, J.; Huang, L. Fabrication and characterization of PVDF-CTFE/SiO2 electrospun nanofibrous membranes with micro and nano-rough structures for efficient oil-water separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 311, 123228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Zhao, J.; Oderinde, O.; Han, J.; Liu, Z.; Gao, B.; Xiong, R.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, S.; Huang, C. Durable superhydrophobic and superoleophilic electrospun nanofibrous membrane for oil-water emulsion separation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 532, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, Y.; Cao, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Li, W. Electrospun PVDF-SiO2 nanofibrous membranes with enhanced surface roughness for oil-water coalescence separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 269, 118726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Wei, Z.; Gu, J.; Wu, Z.; Zhao, Y. Rational design of Janus nanofibrous membranes with novel under-oil superhydrophilic/superhydrophobic asymmetric wettability for water-in-diesel emulsion separation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 606, 1563–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Li, Y.; Sheng, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, L.; Yu, J.; Ding, B. Environmentally friendly and breathable fluorinated polyurethane fibrous membranes exhibiting robust waterproof performance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 29302–29310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, L.; Yu, J.; Ding, B. Human skin-like, robust waterproof, and highly breathable fibrous membranes with short perfluorobutyl chains for eco-friendly protective textiles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 30887–30894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Cao, L.; Yin, X.; Si, Y.; Yu, J.; Ding, B. Semi-interpenetrating polymer network biomimetic structure enables superelastic and thermostable nanofibrous aerogels for cascade filtration of PM2.5. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1910426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, N.; Li, Y.; Ge, J.; Si, Y.; Yu, J.; Yin, X.; Ding, B. Ultrathin cellulose voronoi-nanonet membranes enable high-flux and energy-saving water purification. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 31852–31862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Gong, X.; Wang, S.; Tian, Y.; Yin, X.; Wang, X.; Yu, J.; Zhang, S.; Ding, B. Two-dimensional nanofibrous networks by superspreading-based phase inversion for high-efficiency separation. Nano Lett. 2023, 23, 10579–10586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Liu, K.; Xi, Y.; Li, Z. One-step electrospinning PCL/ph-LPSQ nanofibrous membrane with excellent self-cleaning and oil-water separation performance. Polymer 2022, 249, 124858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Bai, T.; Yue, Y.; Cheng, W.; Bai, L.; Wang, D.; Lu, J.; Cao, M.; Shi, S.Q.; Huan, S. Nanostructured superior oil-adsorbent nanofiber composites using one-step electrospinning of polyvinylidene fluoride/nanocellulose. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2022, 224, 109490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahreen, L.; Chase, G.G. Effects of electrospinning solution properties on formation of beads in TiO2 fibers with PdO particles. J. Eng. Fibers Fabr. 2015, 10, 155892501501000308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Li, Z.; Hong, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Qiu, S.; Wang, C.; Wei, Y. Influence of solvents on the formation of ultrathin uniform poly (vinyl pyrrolidone) nanofibers with electrospinning. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2004, 42, 3721–3726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.; Park, Y.S.; Choi, G.H.; Park, H.J.; Ahn, C.-H.; Hwang, S.S.; Lee, A.S. Alkaline-Stable, In Situ Menshutkin Coat and Curable Ammonium Network: Ion-Solvating Membranes for Anion Exchange Membrane Water Electrolyzers. Int. J. Energy Res. 2023, 2023, 7416537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherpinski, A.; Biswas, A.; Lagaron, J.M.; Dufresne, A.; Kim, S.; Buttrum, M.; Espinosa, E.; Cheng, H. Preparation and evaluation of oxygen scavenging nanocomposite films incorporating cellulose nanocrystals and Pd nanoparticles in poly (ethylene-co-vinyl alcohol). Cellulose 2019, 26, 7237–7251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.-M.; Xiao, T.-J.; Zhang, Z.-M.; Tanioka, A. Effect of interfacial tension on the formation of the gradient morphology in polymer blends. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1998, 206, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, K.; Hu, X.; Dai, C.; Yi, T. Crystal structures of electrospun PVDF membranes and its separator application for rechargeable lithium metal cells. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2006, 131, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Tang, X.; Li, W.; Liu, H.; Zhang, J.; Wang, H.; Li, J. EVOH in situ fibrillation and its effect of strengthening, toughening and hydrophilic modification on PVDF hollow fiber microfiltration membrane via TIPS process. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 5971–5987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulhussein, A.T.; Kannarpady, G.K.; Biris, A.S. One-step synthesis of a steel-polymer wool for oil-water separation and absorption. NPJ Clean Water 2019, 2, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; McLaughlin, E.; Pfeffer, R.; Lin, Y. Adsorption of oils from pure liquid and oil–water emulsion on hydrophobic silica aerogels. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 99, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Liang, Y.N.; Tang, X.-Z.; Shen, W.; Hu, X. Additive-free poly (vinylidene fluoride) aerogel for oil/water separation and rapid oil absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 308, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Ma, H. Solvent-free green preparation of reusable EG-PVDF foam for efficient oil-water separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 253, 117506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorneanu, P.P.; Cojocaru, C.; Olaru, N.; Samoila, P.; Airinei, A.; Sacarescu, L. Electrospun PVDF fibers and a novel PVDF/CoFe2O4 fibrous composite as nanostructured sorbent materials for oil spill cleanup. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 424, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Zhao, G.; Zhang, L.; Wang, G.; Chai, J. Ultralight and hydrophobic PVDF/PMMA open-cell foams with outstanding heat-insulation and oil-adsorption performances fabricated by CO2 molten foaming. J. CO2 Util. 2022, 63, 102108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Yang, F.; Guo, Z. Superwetting surfaces for filtration separation of high-viscosity raw petroleum/water mixtures. J. Mater. Chem. A 2022, 10, 14273–14292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Huang, C.; Liu, L.Y.; Yao, L.; Ning, B.; Yang, L. Separation efficiency prediction of non-Newtonian oil-water swirl-vane separators in offshore platform based on GA-BP neural network. Ocean Eng. 2024, 296, 116984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.K.; Dunderdale, G.J.; England, M.W.; Hozumi, A. Oil/water separation techniques: A review of recent progresses and future directions. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 16025–16058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Chen, F.; Chao, J.; Zhang, D.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, D. Femtosecond laser engineered eggshell membrane for durable oil/water separation under harsh conditions. J. Membr. Sci. 2023, 668, 121242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Lu, X.; Xin, Z.; Zhang, H.; Li, X. A durable bio-based polybenzoxazine/SiO2 modified fabric with superhydrophobicity and superoleophilicity for oil/water separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 229, 115792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Fu, J.; Yin, F.; Li, C.; Xu, Y.; Peng, G. Dopamine triggered the polymerization and co-deposition of HEMA on PVDF membranes to prepare oil-water separation membranes. Surf. Interfaces 2024, 54, 105267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Guo, Z. A facile method to mussel-inspired superhydrophobic thiol-textiles@ polydopamine for oil/water separation. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 554, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, T.; Qian, Q.; Hou, Z.; Liu, Y.; Lu, M. Preparation of smart and reversible wettability cellulose fabrics for oil/water separation using a facile and economical method. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 200, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Chen, W.; Wu, W.; Pan, Z.; Liang, Z.; Gan, J. Facile fabrication of superhydrophilic/underwater superoleophobic polyvinyl acetate/sodium silicate composite coating for the effective water/oil separation and the study on the anti-fouling property, durability and separation mechanism. Prog. Org. Coat. 2021, 150, 105979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Zhang, R.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, X.; Lan, J.; Wu, Y.; Wang, L.; Lu, H. Intelligent Devices Harnessing Underwater Superoleophobic and Underoil Superhydrophobic Quartz Sands for the Separation of Diverse Stratified and Emulsified Water–Oil Mixtures. Langmuir 2024, 40, 10792–10803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, X.; Wang, Y.; Gao, Z.; Xing, W.; Zhang, X.; Li, L.; Tong, A.; Huang, L.; Kipper, M.J.; Tang, J. Acid, Alkali, and Abrasion-Resistant Nanofibrous Membranes Composed of ZIF-8 Metal–Organic Framework and Carbon Nanotubes for Oil–Water Separation. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2023, 6, 22363–22372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Y.; Wu, X.; Lv, Y.; Liang, N.; Lv, S.; Guo, J.; Jia, D. A direct electrospinning strategy prepared series of coal-derived nanofibers for efficient oil-water separation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2024, 645, 158815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadler, E.; Crick, C.R. Suction or gravity-fed oil-water separation using PDMS-coated glass filters. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2021, 29, e00321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, D.; Xi, P.; Cheng, B.; Wang, Y.; Yang, L.; Wang, X.; Yan, X. One-step electrospinning cellulose nanofibers with superhydrophilicity and superoleophobicity underwater for high-efficiency oil-water separation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 162, 1536–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Li, P.; Zhou, W.; Wang, Z.; Fan, X.; Chen, M.; Fang, Y.; Liu, H. Shrimp shell-inspired antifouling chitin nanofibrous membrane for efficient oil/water emulsion separation with in situ removal of heavy metal ions. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 7, 2064–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Deng, C.; Hou, X.; Li, T.; Lu, Y.; Liu, F. Preparation and Characterization of a Janus Membrane with an “Integrated” Structure and Adjustable Hydrophilic Layer Thickness. Membranes 2023, 13, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, Q.; Mo, J.; Han, S.; Liu, X.; Qu, B.; Xie, J.; Wang, X.; Zhao, J. Balsam-Pear-Skin-Like-Structure Polyvinylidene Fluoride/Ethylene–Vinyl Alcohol Fibrous Membrane for Highly Efficient Oil/Water Separation Through One-Step Electrospinning. Polymers 2025, 17, 1389. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17101389
Jiang Q, Mo J, Han S, Liu X, Qu B, Xie J, Wang X, Zhao J. Balsam-Pear-Skin-Like-Structure Polyvinylidene Fluoride/Ethylene–Vinyl Alcohol Fibrous Membrane for Highly Efficient Oil/Water Separation Through One-Step Electrospinning. Polymers. 2025; 17(10):1389. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17101389
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Qijiao, Jinpeng Mo, Shaobo Han, Xi Liu, Baoliu Qu, Juan Xie, Xianfeng Wang, and Jing Zhao. 2025. "Balsam-Pear-Skin-Like-Structure Polyvinylidene Fluoride/Ethylene–Vinyl Alcohol Fibrous Membrane for Highly Efficient Oil/Water Separation Through One-Step Electrospinning" Polymers 17, no. 10: 1389. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17101389
APA StyleJiang, Q., Mo, J., Han, S., Liu, X., Qu, B., Xie, J., Wang, X., & Zhao, J. (2025). Balsam-Pear-Skin-Like-Structure Polyvinylidene Fluoride/Ethylene–Vinyl Alcohol Fibrous Membrane for Highly Efficient Oil/Water Separation Through One-Step Electrospinning. Polymers, 17(10), 1389. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17101389






