Conductive Hydrogel Motion Sensor with Low-Temperature Stability for Winter Sports and Sensing Rescue
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Design
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Gelatin-SDS-NaCl-C18-PAAm-PA Hydrogels
2.3. Measurements of Mechanical Properties
2.4. Measurements of Electrical Properties
2.5. Differential Scanning Calorimetry Analysis
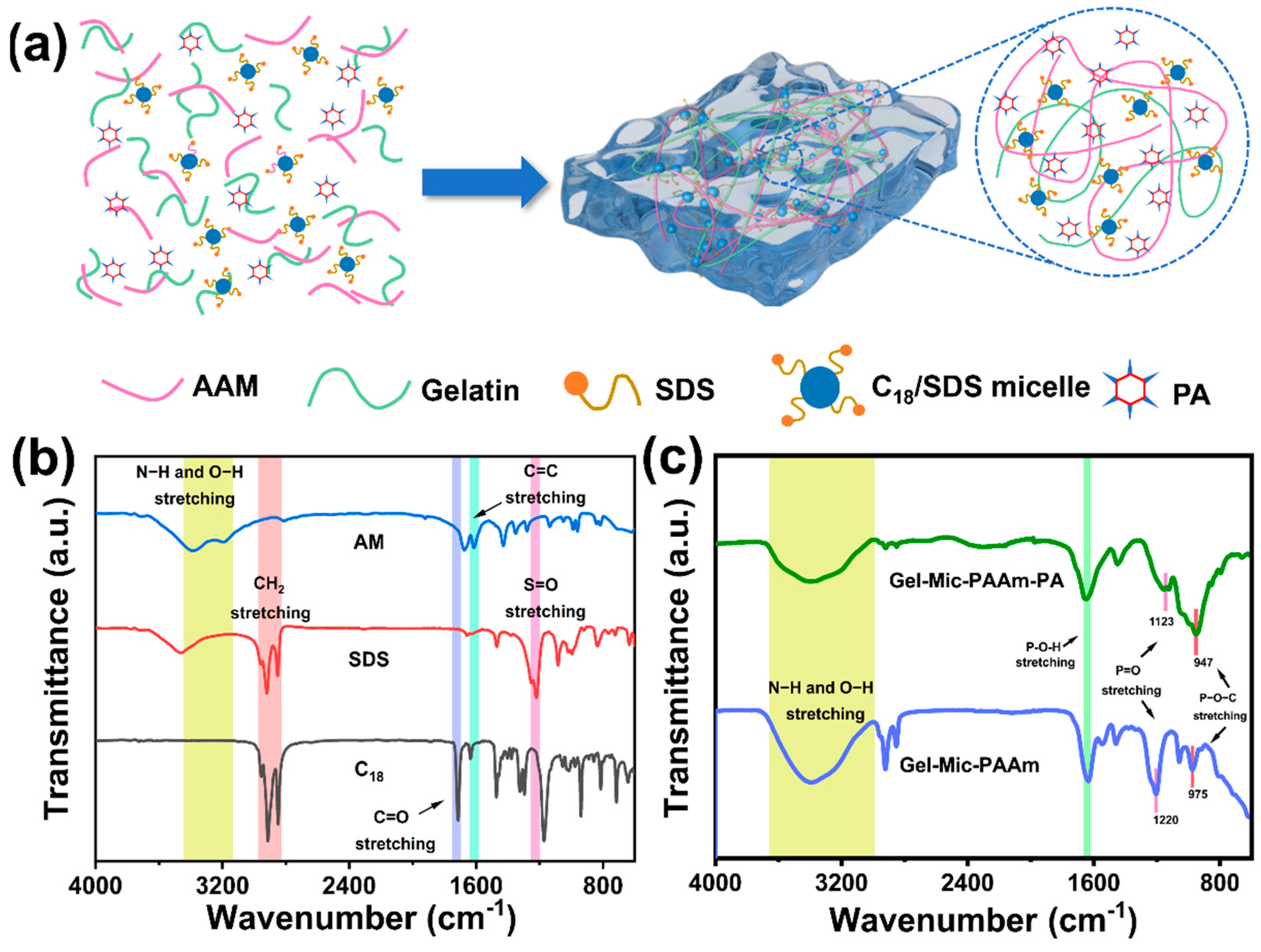
2.6. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy Measurements
2.7. Drying-Resistance Capabilities
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preparation of Gel-Mic-PAAm-PA Hydrogel
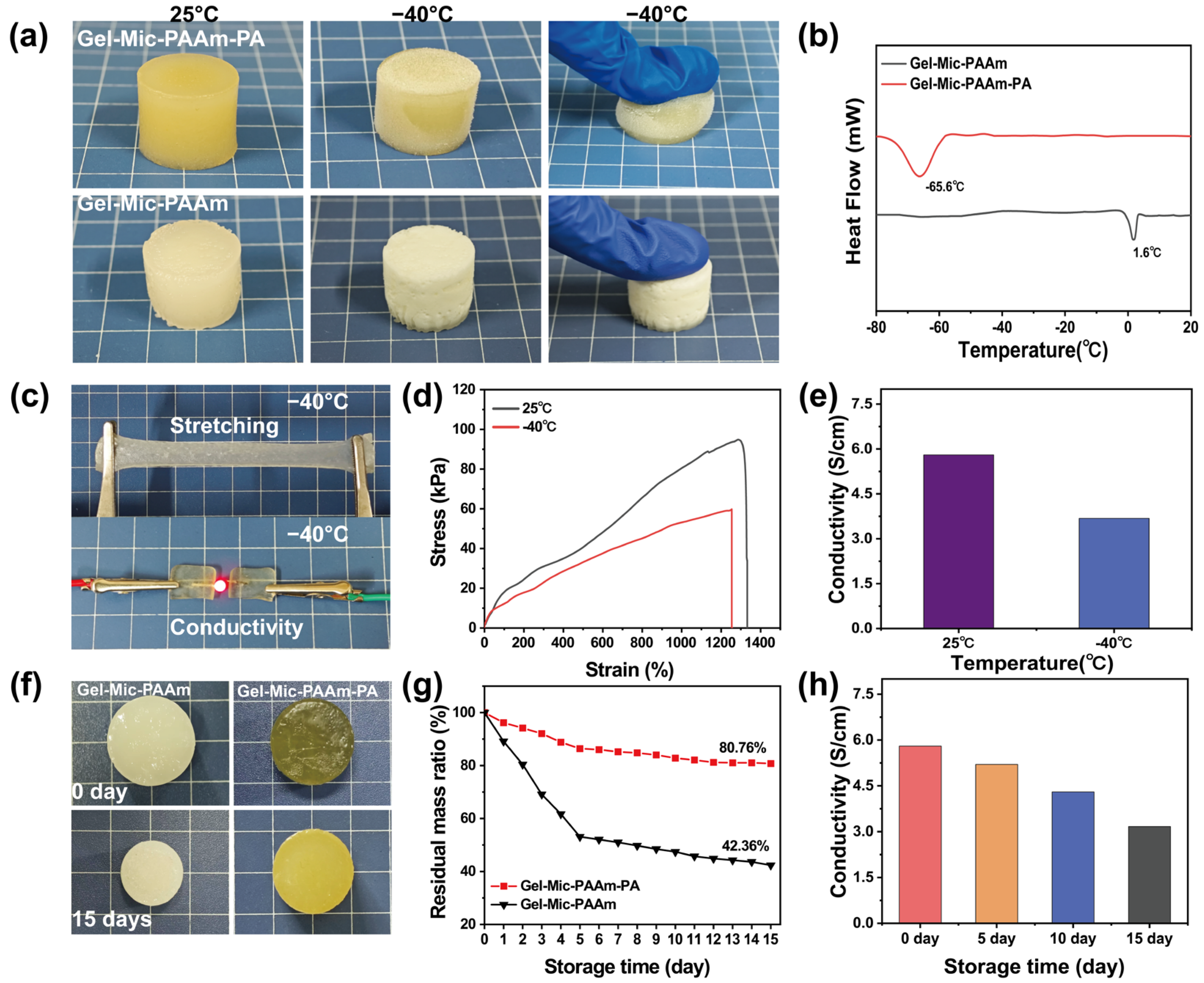
3.2. Mechanical Properties of the Hydrogel
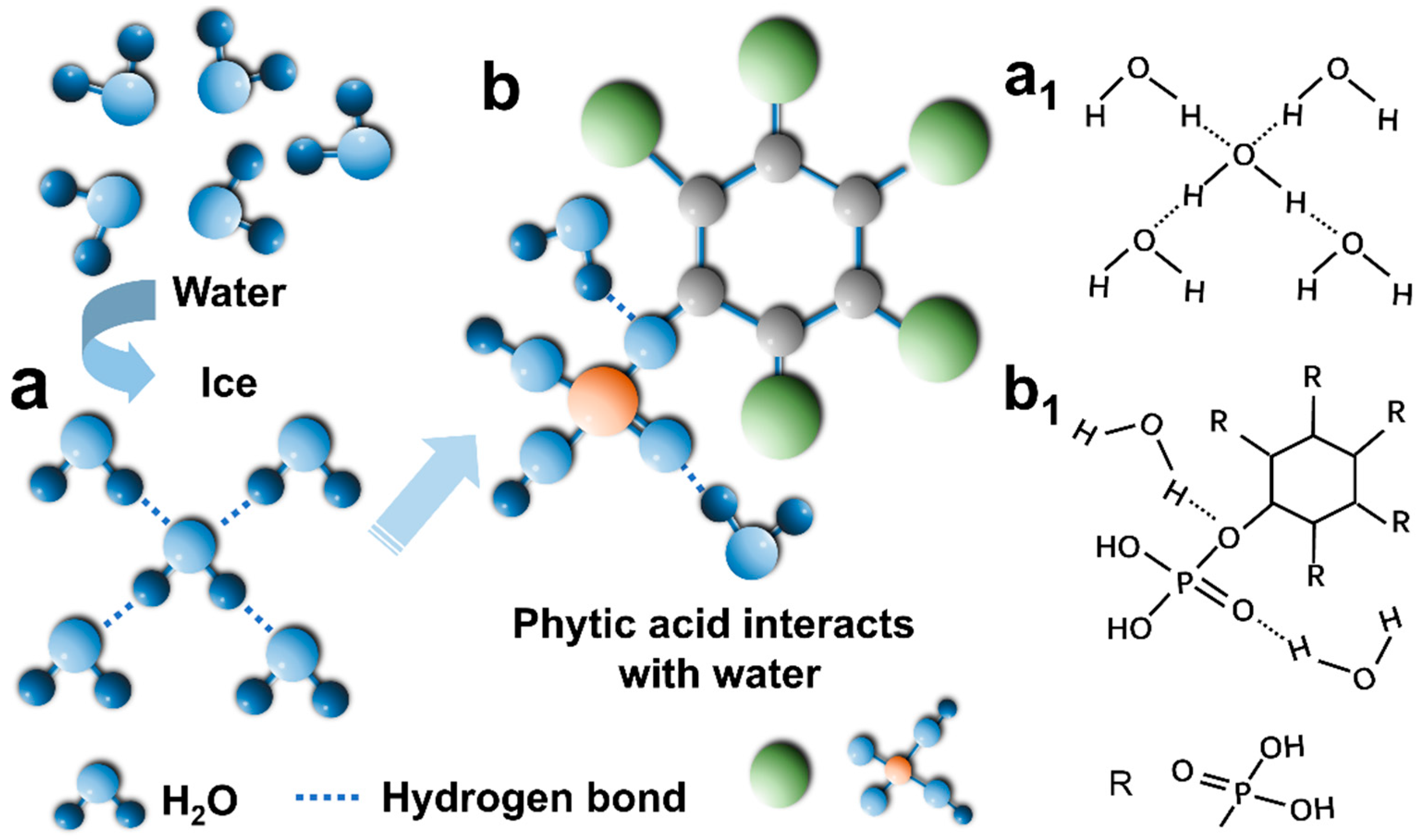
3.3. Anti-Freezing and Anti-Drying Performance Test
| Anti-Freezing Agents | Conductive Components | Conductivity at 25 °C (S·cm−1) | Low-Temperature Conductivity (S·cm−1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phytic acid | Phytic acid | 5.8 | 3.68 (−40 °C) | This work |
| Glycerol/LiCl | LiCl | 5.249 | 3.649 (−40 °C) | [44] |
| CNFs | Propylene carbonate | 4.2 | 1.8 (−40 °C) | [45] |
| Glycerol | ANI | 6.69 | 1.71 (−40 °C) | [46] |
| Ethylene glycol | AMIM-CL | 0.48 | 0.45 (−20 °C) | [47] |
| LiCl | LiCl | 8.99 | 2.58 (−20 °C) | [48] |
| DMSO | CMC-Na | 2.1 | 1.7 (−40 °C) | [49] |
| Glycerol | a LMNPs | 1.2 | 0.55 (−20 °C) | [50] |
| a VBIMBr | a VBIMBr | 1.303 | 0.849 (−20 °C) | [51] |
| KOH | KOH | 10.5 | 1.81 (−20 °C) | [52] |
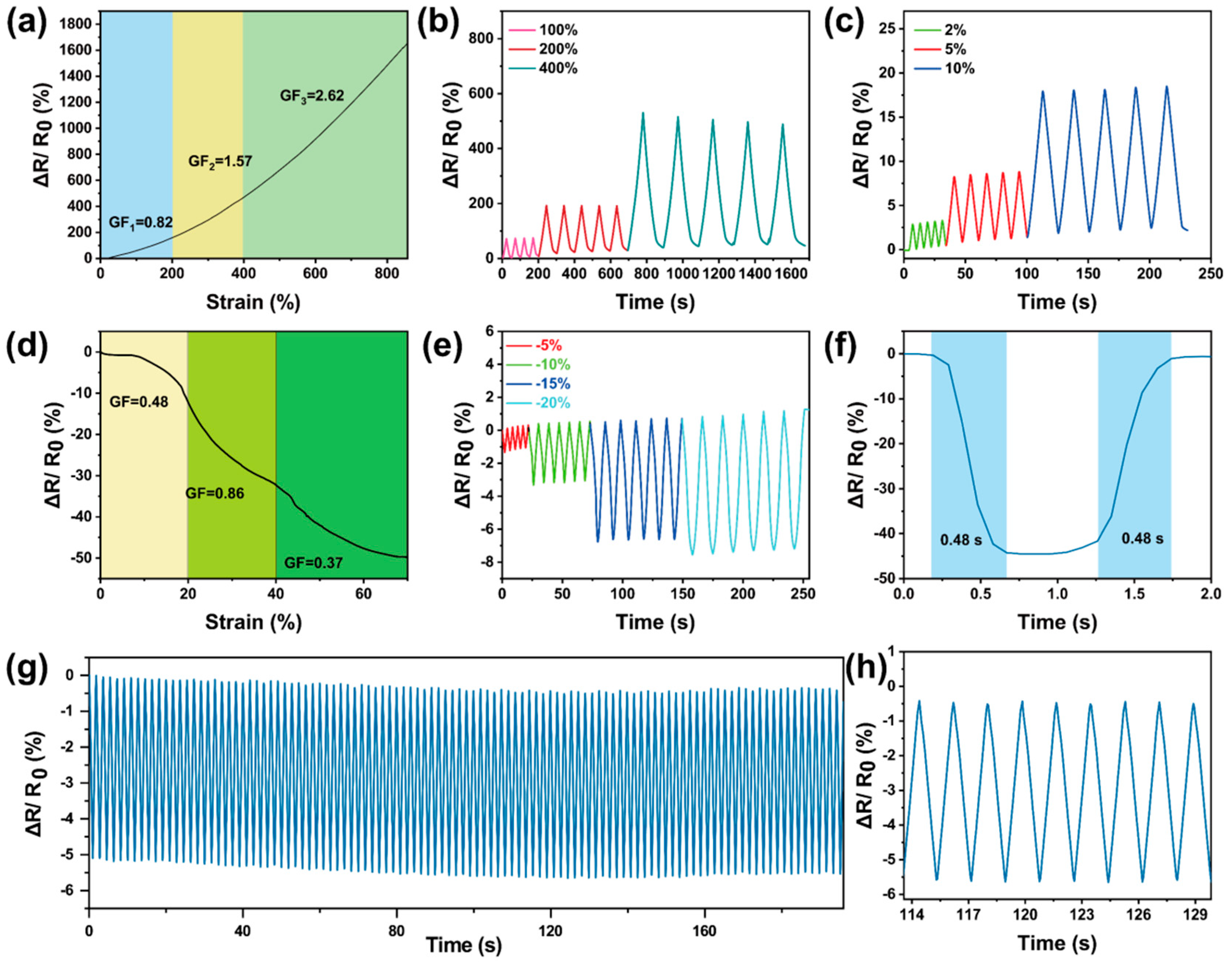
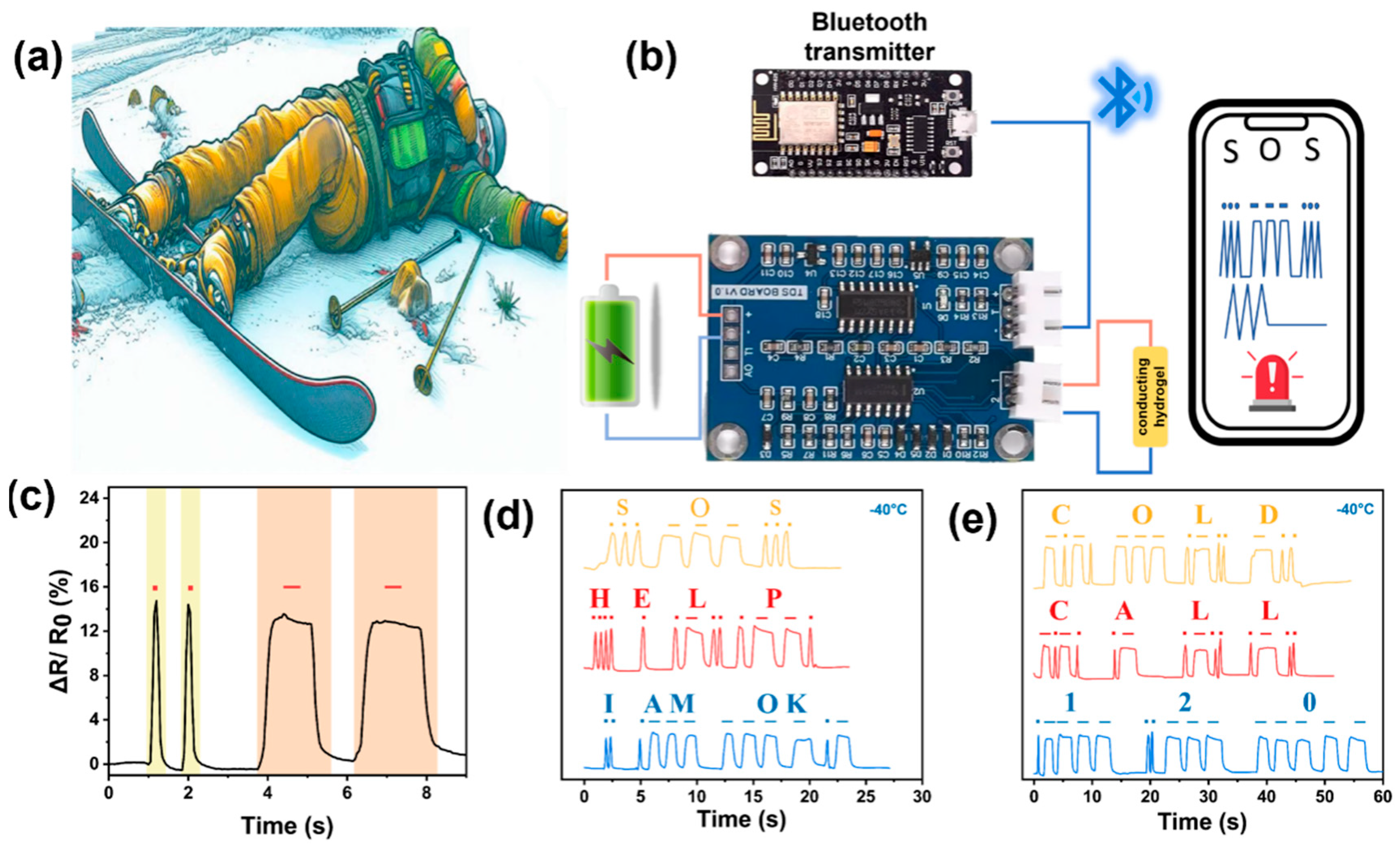
3.4. Motion Sensing of Gel-Mic-PAAm-PA Hydrogel
3.5. Gel-Mic-PAAm-PA Hydrogel for Wearable Sensing Devices
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, M.K.; Zhang, Y.F.; Lian, L.S.Y.; Liu, K.; Lu, M.; Chen, Y.B.; Zhang, L.Q.; Zhang, X.C.; Wan, P.B. Flexible Accelerated-Wound-Healing Antibacterial MXene-Based Epidermic Sensor for Intelligent Wearable Human-Machine Interaction. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2208141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.T.; Lin, C.M.; Deng, P.W.; Cao, L.N.Y.; Wang, W.G.; Li, W.J.; Lin, H.Z.; Yang, Y.; Wang, H.; Ye, M.D.; et al. Self-powered wearable human-computer interaction system based on kapok cellulose nanofibers. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 488, 151059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, C.C. Embedded-machine learning and soft, flexible sensors for wearable devices—viewing from an AI engineer. Mater. Today Phys. 2024, 42, 101376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.C.; Zhang, H.N.; Fang, L.; Wang, Z.X.; He, W.; Shi, S.W.; Zhang, R.Y.; Cheng, J.; Wang, P.H. A self-powered flexible piezoelectric sensor patch for deep learning-assisted motion identification and rehabilitation training system. Nano Energy 2024, 123, 109427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Caño, R.; Saha, T.; Moonla, C.; de la Paz, E.; Wang, J.S. Ketone bodies detection: Wearable and mobile sensors for personalized medicine and nutrition. Trac-Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 159, 116938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatnagar, P.; Zaferani, S.H.; Rafiefard, N.; Baraeinejad, B.; Vazifeh, A.R.; Mohammadpour, R.; Ghomashchi, R.; Dillersberger, H.; Tham, D.; Vashaee, D. Advancing personalized healthcare and entertainment: Progress in energy harvesting materials and techniques of self-powered wearable devices. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2023, 139, 101184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, J.H.; Lim, J.H.; Lee, J.M.; Chung, B.G. Electro-Responsive Conductive Blended Hydrogel Patch. Polymers 2023, 15, 2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, D.; Xu, B.A. Advanced Interfacial Design for Electronic Skins with Customizable Functionalities and Wearability. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2306793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, S.S.; Shi, Q.F.; Hong, J.L.; Zhu, D.; Lin, Y.C.; Li, Y.H.; Lei, W.; Lee, C.K.; Wu, J. Water-Modulated Biomimetic Hyper- Attribute-Gel Electronic Skin for Robotics and Skin-Attachable Wearables. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 1355–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.Y.; Yao, D.J.; Wang, H.; Ding, Q.L.; Luo, Y.B.; Ding, H.J.; Yu, J.H.; Zhang, H.; Tao, K.; Zhang, S.; et al. A Breathable, Stretchable, and Self-Calibrated Multimodal Electronic Skin Based on Hydrogel Microstructures for Wireless Wearables. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2316339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Y.M.; Huang, J.Y.; Li, S.H.; Wang, X.Q.; Liu, L.X.; Wang, M.Y.; Chen, Z.; Li, X.; Lai, Y.K. Flexible MXene-Based Hydrogel Enables Wearable Human-Computer Interaction for Intelligent Underwater Communication and Sensing Rescue. ACS Appl. Mater. 2021, 13, 4740–4749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, G.; Ju, J.; Lu, H.; Shi, X.M.; Wang, X.; Wang, W.; Xia, Q.Y.; Zhou, G.D.; Sun, W.; Li, C.M.; et al. A Weavable and Scalable Cotton-Yarn-Based Battery Activated by Human Sweat for Textile Electronics. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2103822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, M.L.; Yi, C.H.; Han, Y.K.; Wang, L.; Li, X.; Xu, G.L.; He, K.; Li, N.C.; Hou, Y.X.; Wang, Z.G.; et al. Hierarchical Network Enabled Flexible Textile Pressure Sensor with Ultrabroad Response Range and High-Temperature Resistance. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2105738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.G.; Chao, M.Y.; Wan, P.B.; Zhang, L.Q. A wearable breathable pressure sensor from metal-organic framework derived nanocomposites for highly sensitive broad-range healthcare monitoring. Nano Energy 2020, 70, 104560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.C.Y.; Sheng, Z.; Huang, J.L.; Liu, W.Y.; Ding, H.Y.; Peng, J.F.; Zhong, B.W.; Sun, Y.H.; Ouyang, X.P.; Cheng, H.Y.; et al. Moisture-resistant MXene-sodium alginate sponges with sustained superhydrophobicity for monitoring human activities. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 432, 134370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, L.W.; Zhao, J.Y.; Aono, K.; Li, W.L.; Wen, Z.C.; Pizzella, S.; Wang, Y.; Chakrabartty, S.; Wang, C. Stretchable Sponge Electrodes for Long-Term and Motion-Artifact-Tolerant Recording of High-Quality Electrophysiologic Signals. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 11792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.Y.; Xu, T.; Cai, C.Y.; Liu, K.; Liu, W.; Zhang, M.; Du, H.S.; Si, C.L.; Zhang, K. Multifunctional Superelastic, Superhydrophilic, and Ultralight Nanocellulose-Based Composite Carbon Aerogels for Compressive Supercapacitor and Strain Sensor. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2113082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.G.; Zhang, J.Z.; Qin, S.; Wang, Z.Y.; Usman, K.A.S.; Hegh, D.; Liu, J.Q.; Lei, W.W.; Razal, J.M. Superelastic Ti3C2TxMXene-Based Hybrid Aerogels for Compression-Resilient Devices. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 5000–5010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suo, J.; Liu, Y.F.; Wu, C.; Chen, M.; Huang, Q.Y.; Liu, Y.M.; Yao, K.M.; Chen, Y.B.; Pan, Q.Q.; Chang, X.Y.; et al. Wide-Bandwidth Nanocomposite-Sensor Integrated Smart Mask for Tracking Multiphase Respiratory Activities. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2203565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Liu, Y.; Qu, X.C.; Shi, B.J.; Zheng, Q.; Lin, X.B.; Chao, S.Y.; Wang, C.Y.; Zhou, J.; Sun, Y.; et al. Ultra-Stretchable and Fast Self-Healing Ionic Hydrogel in Cryogenic Environments for Artificial Nerve Fiber. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2105416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.D.; Du, C.F.; Liao, L.L.; Zhang, H.J.; Zhou, H.Q.; Zhou, W.C.; Ren, T.N.; Sun, Z.C.; Lu, Y.F.; Nie, Z.T.; et al. Approaching intrinsic dynamics of MXenes hybrid hydrogel for 3D printed multimodal intelligent devices with ultrahigh superelasticity and temperature sensitivity. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.X.; Cheng, Y.; Cao, C.Y.; Mao, J.J.; Li, L.Q.; Huang, J.Y.; Gao, S.W.; Dong, X.L.; Chen, Z.; Lai, Y.K. A semi-interpenetrating network ionic hydrogel for strain sensing with high sensitivity, large strain range, and stable cycle performance. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 385, 123912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z.; Li, X.Y.; Zhang, R.Z.; Zhang, L.B. Stimuli-Responsive Hydrogels for Antibacterial Applications. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2024, 13, 202400513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raza, M.A.; Gull, N.; Lee, S.W.; Seralathan, K.K.; Park, S.H. Development of stimuli-responsive chitosan based hydrogels with anticancer efficacy, enhanced antibacterial characteristics, and applications for controlled release of benzocaine. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2022, 109, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.R.; Xu, T.L.; Zhang, X.J. Multifunctional conductive hydrogel-based flexible wearable sensors. Trac-Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 134, 116130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.Y.; Liu, J.; Shen, X.D.; Li, H. Advances in the Preparation of Tough Conductive Hydrogels for Flexible Sensors. Polymers 2023, 15, 4001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmani, P.; Shojaei, A. A review on the features, performance and potential applications of hydrogel-based wearable strain/pressure sensors. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 298, 102553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.Q.; Liu, Y.Z.; Wang, S.Q.; Fu, X.M.; Zhao, T.C.; Chen, X.; Shao, Z.Z. Physically Cross-Linked Silk Fibroin-Based Tough Hydrogel Electrolyte with Exceptional Water Retention and Freezing Tolerance. ACS Appl. Mater. 2020, 12, 25353–25362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, Y.K.; Handschuh-Wang, S.; Zhang, J.W.; Lu, W.; Zhou, X.C.; Chen, T. Biomimetic anti-freezing polymeric hydrogels: Keeping soft-wet materials active in cold environments. Mater. Horiz. 2021, 8, 351–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Q.; Cao, L.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, H.; Li, J.; Wei, Y. Zwitterionic Hydrogel with High Transparency, Ultrastretchability, and Remarkable Freezing Resistance for Wearable Strain Sensors. Biomacromolecules 2021, 22, 1220–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.Z.; Wang, W.Q.; Gu, K.; Yao, J.R.; Shao, Z.Z.; Chen, X. Poly(vinyl alcohol) Hydrogels with Integrated Toughness, Conductivity, and Freezing Tolerance Based on Ionic Liquid/Water Binary Solvent Systems. Acs Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 29008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.D.; Guan, Y.J.; Liu, M.J.; Kang, X.C.; Tian, Y.; Deng, W.C.; Yu, P.; Ning, C.Y.; Zhou, L.; Fu, R.M.; et al. Tough, Antifreezing, and Piezoelectric Organohydrogel as a Flexible Wearable Sensor for Human-Machine Interaction. ACS Nano 2024, 18, 3720–3732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, H.J.; Huang, Q.Q.; Lu, M.J.; Fu, J.X.; Liang, Z.; Zhang, T.; Wang, D.; Li, C.P. Anti-Freezing Nanocomposite Organohydrogels with High Strength and Toughness. Polymers 2022, 14, 3721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Y.; Liu, R.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Xiao, H.; Yuan, G. Concentrated hydrogel electrolyte for integrated supercapacitor with high capacitance at subzero temperature. Sci. China Chem. 2021, 64, 852–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Xiang, L.; Ou, H.; Li, F.; Zhang, Y.; Qian, Y.; Hao, L.; Diao, J.; Zhang, M.; Zhu, P.; et al. Multifunctional organohydrogels enabling sensitive strain sensing and self-powered triboelectricity. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2005135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Xia, H.; Chen, P.Y.; She, W.; Zhang, H.N.; Ma, J.; Ruan, Q.S.; Zhang, W.; Sun, Z.M. Thermochromic Hydrogels with Dynamic Solar Modulation and Regulatable Critical Response Temperature for Energy-Saving Smart Windows. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2109597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.W.; Zhang, Z.T.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.C.; Li, Z.J.; Wang, M. Shape memory polyacrylamide/gelatin hydrogel with controllable mechanical and drug release properties potential for wound dressing application. Polymer 2021, 226, 123786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Y.M.; Zang, X.R.; Chen, J.J.; Zhu, T.X.; Yang, Y.; Huang, J.Y.; Cai, W.L.; Lai, Y.K. Environmental Stability Stretchable Organic Hydrogel Humidity Sensor for Respiratory Monitoring with Ultrahigh Sensitivity. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2301127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, T.; Zhu, J.X.; Xu, S.; Jia, L.; Ma, Y.L. Highly stretchable, self-healing and conductive silk fibroin-based double network gels via a sonication-induced and self-emulsifying green procedure. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 11574–11582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.J.; Zhang, X.N.; Song, Y.H.; Zhao, Y.P.; Chen, L.; Su, F.M.; Li, L.B.; Wu, Z.L.; Zheng, Q. Ultrastiff and Tough Supramolecular Hydrogels with a Dense and Robust Hydrogen Bond Network. Chem. Mater. 2019, 31, 1430–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, J.L.; Le, D.D.; Wang, Q.L.; Xin, Q.; Hu, E.M.; Lei, Z.W.; Wang, H.Q.; Wang, H.Q. Polyvinyl alcohol/phytic acid/phosphorylated chitosan hydrogel electrode highly efficient electroadsorption of low concentration uranium from uranium tailings leachate. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 254, 128008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Q.C.; Cheng, W.; Wang, X.R.; Pan, L.J.; Xu, B.X.; Xu, H.X. A Self-Healable, Highly Stretchable, and Solution Processable Conductive Polymer Composite for Ultrasensitive Strain and Pressure Sensing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1705551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diouf-Lewis, A.; Commereuc, S.; Verney, V. Toward greener polyolefins: Antioxidant effect of phytic acid from cereal waste. Eur. Polym. J. 2017, 96, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, X.Y.; Zhu, K.; Chen, H.; Ye, S.; Cui, P.; Dou, L.Y.; Ma, J.; Zhao, C.; He, J.; Feng, P. Recyclable, anti-freezing and anti-drying silk fibroin-based hydrogels for ultrasensitive strain sensors and all-hydrogel-state super-capacitors. Mater. Today Chem. 2023, 32, 101624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.Z.; Pi, W.J.; Hu, X.X.; He, X.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, J.Q.; Yang, S.R. Heat- and freeze-tolerant organohydrogel with enhanced ionic conductivity over a wide temperature range for highly mechanoresponsive smart paint. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 608, 2158–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.H.; Han, X.D.; Ye, S.F.; Cui, P.X.; Dou, L.Y.; Ma, W.B.; Tao, X.Y.; Wei, X.Y.; Heng, S.J. Flexible all-in-one supercapacitors enabled by self-healing and anti-freezing polymer hydrogel electrolyte. Energy Storage 2022, 53, 105096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.Y.; Hou, M.H.; Wang, L.F.; Zhang, X.P.; Liu, L.F. Anti-bacterial, anti-freezing starch/ionic liquid/PVA ion-conductive hydrogel with high performance for multi-stimulation sensitive responsive sensors. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 477, 147065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.H.; Yu, L.; Wang, S.S.; Zhang, L.; Chen, L.; Xu, X.; Song, Z.Q.; Liu, H.; Chen, C.J. Strong, tough, ionic conductive, and freezing-tolerant all-natural hydrogel enabled by cellulose-bentonite coordination interactions. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.Q.; Li, Z.; Zuo, M.; Zeng, X.H.; Tang, X.; Sun, Y.; Lin, L. Stretchable, freezing-tolerant conductive hydrogel for wearable electronics reinforced by cellulose nanocrystals toward multiple hydrogen bonding. Carbohyd. Polym. 2022, 280, 119018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.Q.; Tan, C.Y.; He, Y.Q.; Luo, B.H.; Liu, M.X. Chitin nanocrystals stabilized liquid metal for highly stretchable and anti-freeze hydrogels as flexible strain sensor. Carbohyd. Polym. 2024, 328, 121728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, T.D.; Pan, J.J.; Wang, N.; Xia, Z.P.; Zhang, Q.S.; Fan, J.; Tao, L.; Shou, W.; Gao, Y. Cold-resistant, highly stretchable ionic conductive hydrogels for intelligent motion recognition in winter sports. Mater. Horiz. 2024, 11, 1234–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, N.; Lu, F.; Yu, Y.; Su, L.; Gao, X.P.; Zheng, L.Q. Alkaline Double-Network Hydrogels with High Conductivities, Superior Mechanical Performances, and Antifreezing Properties for Solid-State Zinc-Air Batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. 2020, 12, 11778–11788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Z.H.; Sun, X.; Zhang, H.T.; Yu, Q.Y.; Wang, X.Y.; He, S.S.; Yao, F.L.; Li, J.J. A transparent, ultrastretchable and fully recyclable gelatin organohydrogel based electronic sensor with broad operating temperature. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 4447–4456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.Y.; Lin, Z.F.; Sun, Z.T.; Zhu, Z.H.; Lin, W.; Xu, Y.T.; Peng, Z.C.; Sun, Z.L.; Wang, Z.Y. Road Narrow-Inspired Strain Concentration to Wide-Range-Tunable Gauge Factor of Ionic Hydrogel Strain Sensor. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, 2303338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, W.; Ming, Y.; Yang, L.; Ni, Y.; Chen, Y.; Xu, W.; Li, L.; Zheng, C.; Lin, W. Conductive Hydrogel Motion Sensor with Low-Temperature Stability for Winter Sports and Sensing Rescue. Polymers 2025, 17, 1365. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17101365
Li W, Ming Y, Yang L, Ni Y, Chen Y, Xu W, Li L, Zheng C, Lin W. Conductive Hydrogel Motion Sensor with Low-Temperature Stability for Winter Sports and Sensing Rescue. Polymers. 2025; 17(10):1365. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17101365
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Wei, Yang Ming, Libing Yang, Yimeng Ni, Yu Chen, Weidong Xu, Lefei Li, Chan Zheng, and Wanyang Lin. 2025. "Conductive Hydrogel Motion Sensor with Low-Temperature Stability for Winter Sports and Sensing Rescue" Polymers 17, no. 10: 1365. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17101365
APA StyleLi, W., Ming, Y., Yang, L., Ni, Y., Chen, Y., Xu, W., Li, L., Zheng, C., & Lin, W. (2025). Conductive Hydrogel Motion Sensor with Low-Temperature Stability for Winter Sports and Sensing Rescue. Polymers, 17(10), 1365. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17101365






